1. Introduction
Since the 1980s, financial liberalization and global integration have intensified financial market risks and increased the frequency, severity and scope of financial crises. One of the essential causes of many financial crises is the bursting of real estate market bubbles, such as the Asian financial crisis in 1997 and the global financial crisis in 2008 [
1,
2]. In the case of the 2008 financial crisis, around 2000, the loose monetary policy of the Federal Reserve (FED) boosted the U.S. real estate economy, and financial derivatives, such as subprime loans and securitizations, accumulated the crisis. With the bursting of the real estate bubble, the tsunami of the financial crisis in the United States swept across the world, causing devastating economic, social and political disasters in many countries around the world. Over the next decade, the economic crisis brought by the housing bubble spread to the real economy, with rising unemployment, stagnant economic growth and increased social instability. The global economy is still in a period of recovery.
This shows that the real estate industry is highly correlated with many industries of the macro economy. If the development of the real estate market violates the law of value and produces bubbles, it will bring a huge and long-term negative impact on the development of the whole national economy. Risks and price fluctuations in the real estate market can easily spread to other sectors of the economy and directly affect the stability of the country’s macro economy. Therefore, research on the risk to, the bubbles in and exuberance of the real estate market has important practical significance; indeed, this has been the focus of academic circles in recent years.
Currently, the relevant literature on the risks, bubbles and exuberance of the real estate market is in a period of rapid growth. Scholars in various fields have different research perspectives and diverse research methods, and a relatively unified research paradigm has not been formed. For example, several studies by Philips developed a series of methods based on recursive regression and statistical tests to detect bubbles in real estate and other financial markets [
3,
4,
5]; In addition to mathematical and statistical models, Brunnermeier (2009) [
6] studied the relationship between real estate market risks and financial crises by event sorting and conceptual modeling. Other studies utilized new data sources, such as remote sensing data, to study the supply and risk factors in the real estate market [
7]. Thus, reviewing the important research results from a systematic perspective would summarize and highlight the academic research of the real estate market and provide practical applications for the business community.
In recent years, bibliometrics scholars have adopted quantitative methods to analyze the evolution trend in hotspots by combining the professional knowledge of the research field. Among them, several researchers have carried out bibliometrics analysis on the top literature studies and found the changes in the research hotspots. For example, Pan et al. (2019) [
8] conducted a bibliometric study on the research trends in the field of gray systems. Kocak et al. (2019) [
9] used cluster analysis to summarize the research hotspots in the field of neuroscience. Numerous bibliometric studies have also been published in the fields of economics, finance and real estate [
10,
11,
12].
In this study, a large number of literature studies related to the risks, bubbles and exuberance in the real estate market are quantitatively and systematically analyzed by using the related bibliometrics methods. First of all, this paper describes the statistics of the publications, citations and characteristics of the publishing journals in the related fields. Then, by means of co-citation and co-word analysis, the research hotspots, research trends and evolution process in the related fields are sorted and investigated. In addition, this paper carries out a comparative analysis of the literature on real estate in China and the United States, to provide insight for academic research and policy making regarding the real estate market in China and other emerging countries.
The empirical results of this paper show that the number of publications in this field has shown a fluctuating, rising trend in recent years, while the number of citations shows an exponentially rising trend. From the perspective of research methods, the interdisciplinary studies are still relatively scarce. Important research topics in this fields include bubble tests, risk factors, price dynamics and volatility characteristics of the real estate market. The latest research frontiers include explosive bubbles, momentum, financialization of real estate and immigration. Compared with the United States, studies in China put more emphasizes on real estate policies. Finally, this paper summarizes several promising future research directions, including risk prevention in real estate markets, the dynamic characteristics of bubbles, and simulation of real estate policies.
The remainder of this paper is arranged as following:
Section 2 introduces the bibliometric indicators and the methodology of co-citation and co-word analysis;
Section 3 calculates the bibliometric indicators and other descriptive statistics;
Section 4 focuses on the research area distribution, research hotspots and dynamic evolution of the area of real estate bubbles, risk and exuberance;
Section 5 undertakes a comparative study between the Chinese and US literature, to illustrate the differences in research focuses between emerging economics and developed economics; and
Section 6 concludes the empirical results and puts forward some promising research directions for the future.
6. Conclusions and Discussions
The risk and exuberance of the real estate market are closely related to the macro-economy and several business sectors. In this paper, a bibliometric analysis and systematic review of the related literature in the Web of Science database were conducted, and the high-publishing countries, institutions and scholars in this field were identified. Through a co-citation network and co-word network clustering, the knowledge base, research hotspots and evolution trends in this field were explored. In addition, we also compared the similarities and differences of the real estate studies in China and the United States, enlightening for the relevant studies in developed countries and emerging countries. Based on the above work, we try to provide insights for future research directions in the real estate risk field.
According to the empirical results of this paper, the following main conclusions can be drawn:
- (1)
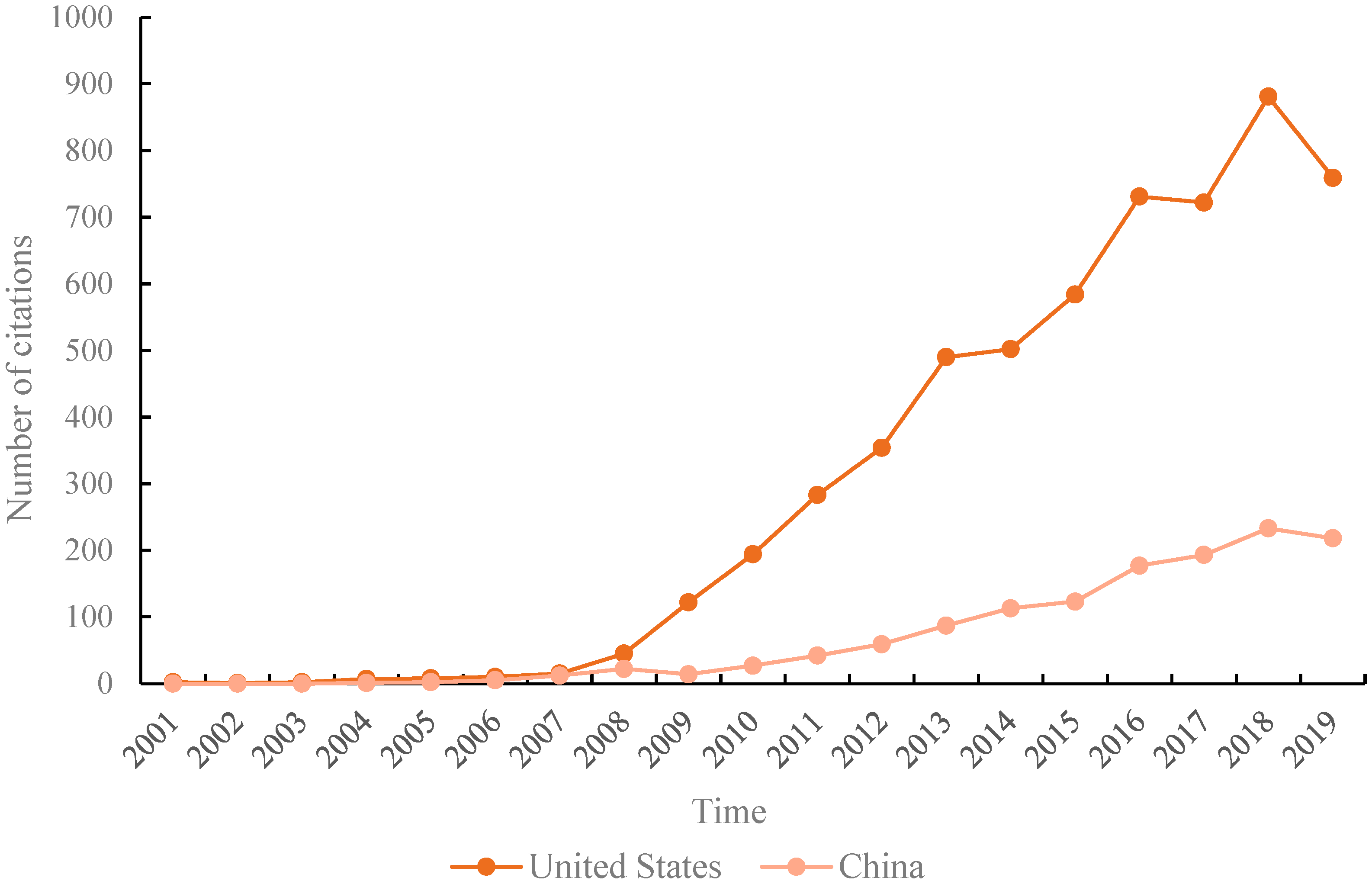
The research in this field have attracted much attention around the world after the 2008 crisis, dominated by scholars from the United States and China.
In 2007, the burst of the real estate bubble led to the subprime mortgage crisis in the United States, which evolved into a global financial crisis. As a result, real estate prices in the United States have fallen sharply, and the national economy has been severely hit. Since then, academia has conducted a lot of research on the causes and effects of the subprime mortgage crisis in the United States, the measurement of real estate market bubbles and the prevention of real estate market risks. Since the reform of China’s housing system in 1998, China’s real estate market has achieved leapfrog development; but, it has also caused problems, such as skyrocketing housing prices, severe market differentiation and over-reliance on real estate for economic development. Scholars are specifically concerned about whether there is a bubble in the Chinese real estate market, how to measure the bubble, the degree of risk in the Chinese real estate market and how to conduct monitoring and early warning. In particular, the current extremely high level of housing prices in China’s metropolis, the excessive proportion of real estate in household asset allocation and the excessive leverage of non-financial companies have led to huge risks for China’s real estate. These topics have always been the focus of scholars’ research.
- (2)
Current studies have commonly employed basic economic theories or econometric methods to detect and quantify real estate bubbles. So far, few studies in this field have adopted interdisciplinary methods and perspectives.
A real estate product is a commodity, but it has the characteristics of both capital goods and durable goods. Scholars mostly analyzed and discussed changes in real estate prices and bubbles from the basic theories related to economics, such as asset price theory and supply–demand relationship theory. The measurement of real estate bubbles and risks mostly use statistical analysis and econometric models and other commonly used methods in economics and management, such as selecting the typical indicators for measurement and judgment, unit root and cointegration tests and other statistical testing methods. Interdisciplinary methods, such as intelligence algorithms or qualitative analysis, are rarely employed.
- (3)
The formation and bursting of real estate bubbles are closely related with real estate risks. Bubble detection provides an effective approach to quantify real estate risks.
The dynamics of real estate price volatility is a direct manifestation of real estate risks. The real estate bubble is caused by the fact that economic entities are affected by speculative factors and expect that real estate prices will continue to rise in the future, and then use leveraged funds to buy and sell real estate in order to make a profit. The real estate bubble generally occurs in the period of economic prosperity and expansion and mainly occurs in highly developed urban areas. Once the real estate bubble bursts, real estate prices will plummet rapidly, a large number of financial institutions will default, triggering economic and financial crises, which will have a longer, broader and deeper impact. Looking back on the world history of the past crises and risk events, they are mostly related to the formation and bursting of the real estate bubble. The emergence of a real estate bubble means the irrational development of the real estate market. Financial institutions issue a large number of real estate loans and hold derivatives related to the real estate market, leading to increasing financial risks. Furthermore, the real estate industry has a strong correlation effect, which is closely related to many industrial sectors. The excessive development of the real estate industry has caused a falsely high demand in related industries, which may lead to overcapacity. This has led to serious problems, such as declining income and sluggish consumption. From the perspective of economic structure, over-reliance on the development of the real estate market has led to a huge influx of funds into the real estate market. It is difficult for the real economy to obtain financial support from financial institutions, causing the economy to become unbalanced. Scholars have found that the real estate bubble is an important risk exposure of systematic risk. Therefore, quantitative detection of real estate bubbles plays a vital role in preventing and resolving economic and financial risks.
- (4)
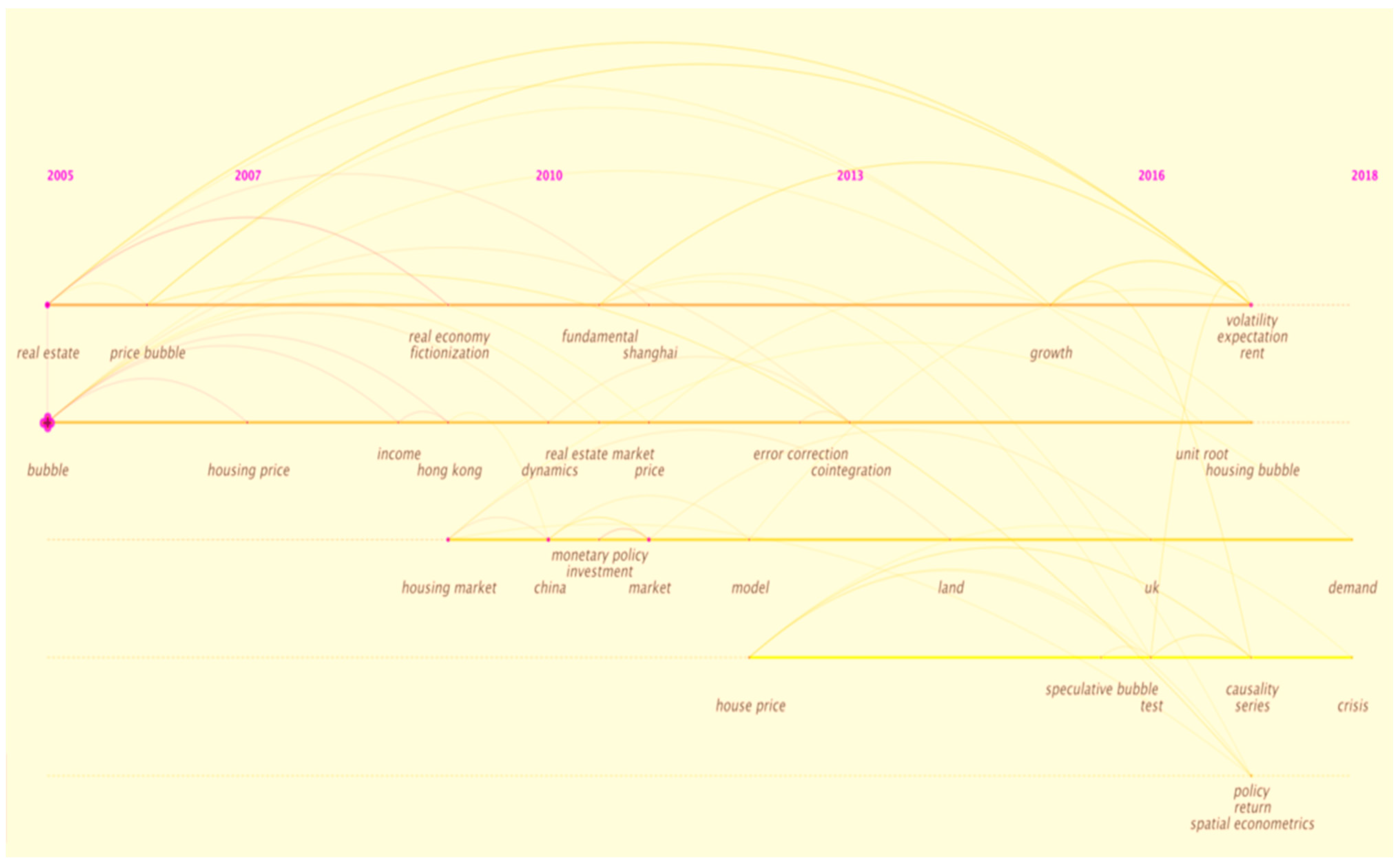
In recent years, explosive bubbles and the financialization of real estate have become frontier hotspots that have gained much popularity.
In recent years, the momentum of global economic growth has been weak, the overall performance of the US economy has been mediocre, economic growth in the euro zone has continued to decline, the Japanese economy has been on the verge of recession and the growth of emerging market economies has continued to diverge. The development of the real economy in various countries is not optimistic. Credit risks and market risks of the corporate sector and financial institutions continue to accumulate, pushing up the vulnerability of the financial system. At the same time, the scale of government deficits and debts has risen sharply, breaking the fiscal conservation policies that many countries have been pursuing, boosting the global debt ratio to continue to rise and increasing financial vulnerabilities. Without the support of fundamentals, real estate prices rose rapidly and the stock market rebounded sharply, pushing up the real estate market bubble and the financial market bubble. Explosive bubbles are caused by factors exogenous to the basic value of assets. These bubbles will continue to expand without converging. Compared with trending bubbles and endogenous bubbles, explosive bubbles may have a greater impact on the market in a short period of time according to recent studies.
Real estate financialization has become a novel risk factor in the real estate market in recent years. The rapid rise and prosperity of the real estate market are inseparable from the support of real estate credit. However, under the rapid expanding of real estate credit, the efficiency of financial resource allocation began to decline and the financial risks have accumulated. In recent years, the phenomenon of corporate financialization has been more serious. The rate of return on investment in the real economy continues to decline and the rate of return on financial investment continues to rise. Macroscopic excess liquidity has flowed into the capital market and the real estate market, causing asset price bubbles and real estate price bubbles, triggering a sharp rise in real estate financial risks. Especially for China, due to the imperfect credit information system, imperfect financing guarantee mechanism and the existence of information asymmetry, the fund transferor has higher requirements for collateral. Because of its immovability, high unit value and long-term appreciation, real estate is especially favored by financial institutions and is an important financing collateral. Rising housing prices and credit expansion will help each other, leading to a natural synergy between real estate and the credit cycle. However, the past real estate-dependent development model has caused problems, such as irrational allocation of social resources and distortion of the economic structure. The development of other industries and the growth of household consumption have changed from a crowd-in effect to a crowd-out effect. Alleviating real estate dependence and promoting the de-financialization of real estate has become an essential choice for healthy and stable economic development. Therefore, these topics have become academic frontiers in the past two years.
- (5)
U.S. scholars pay more attention to topics related to the financial crisis, while Chinese scholars concentrate on topics related to real estate market policies. However, in the real estate risk field, the formation and bursting mechanism of the real estate bubble and the measurement of the real estate bubble are all issues of general global concern.
In 2007, the subprime mortgage crisis triggered by the bursting of the real estate bubble in the United States further led to a global financial crisis. As a result, the U.S. stock market crashed, and the economy fell into a prolonged downturn. Since then, American scholars have done a lot of research on the source, impact and prevention of the financial crisis. Since the beginning of the 20th century, the United States has formed a relatively developed and complete housing financial system. The U.S. housing financial system is highly securitized and market-oriented, which helps to amplify the real estate risks and may become an important tipping point for the financial crisis.
On the other hand, China has not experienced similar events such as the subprime mortgage crisis. China’s housing financial system is very imperfect, financial innovation products related to real estate are rare and the development of asset securitization business is relatively slow. The main link between the real estate market and the financial market is that banks provide credit support for corporate real estate development and for residents to purchase houses. Compared with the US housing market, China’s real estate market involves a special land supply system and local government land financial issues. Moreover, China’s real estate market is affected by the strict control policies of the central government and local governments. The central government has overall control over the tone of real estate market regulation, and local governments have implemented strict purchase restrictions and loan restrictions due to urban policies. In contrast, China’s real estate market has been greatly affected by policy controls. Various regions have implemented policies to restrict purchases and loans strictly due to the city’s policies. Banks and other financial institutions strictly regulate credit policies, guide capital to flow to the real economy, strictly restrict capital inflows into the real estate sector and reduce non-systematic risks. Therefore, Chinese scholars pay more attention to the impact of policies on the real estate market.
Through the above comparison, we find that U.S. scholars tend to analyze the innovation of housing financial products and the real estate risks caused by the development of the housing financial system from the perspective of the financial crisis. Chinese scholars mainly focus on the impact of policy changes on the development of the real estate market. These research issues originated from the specific characteristics of their own country’s real estate market, which may not be significant and contributing to other countries. However, in the real estate risk field, the formation and bursting mechanism of the real estate bubble and the measurement of the real estate bubble are all issues of general global concern.
Based on the above conclusions, this paper attempts to propose several directions worthy of future research in the field of real estate risk: (1) Prevention of real estate market risk. Existing studies have conducted in-depth studies on the risk factors of the real estate market and the driving factors of price fluctuations. However, further studies are needed on how to prevent real estate risks, especially from the perspective of policy making and government decision-making. (2) The real estate market anti-bubble. Most of the existing studies focus on detecting or identifying real estate bubbles, but few of them have discussed how to effectively remove real estate bubbles and restrict market prices to a rational range, which is of more practical significance. (3) Policy planning and simulation of the real estate market. The government’s fiscal policy and monetary policy have an important impact on the formation and bursting of the real estate bubble. For developing countries such as China, the stabilization and rational development of the real estate market are heavily reliant upon effective policies and regulations. How to formulate effective real estate policies, and what impact the implemented policy plans will make, can be further studied by policy simulation tools, providing scientific fundamentals for government decision-making.
There are some limitations to this paper. First, the evolution trends in the number of articles contained in each research topic can be studied in greater detail. In addition, more statistics can be done on the research methods adopted in the literature samples to provide inspiration for future empirical studies. Finally, the papers in the Chinese journal database can be introduced into this research to investigate the academic achievements of Chinese scholars more comprehensively.