A Cost-Efficient-Based Cooperative Allocation of Mining Devices and Renewable Resources Enhancing Blockchain Architecture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Blockchain-Based Energy Management
1.2. Energy Consumption of Miners
1.3. Allocation-Based Energy Management
- Modelling and precisely formulating the blockchain structure based on the energy consumption of the miners during the process of data transactions;
- Suggesting the modified reconfiguration of mining devices using an IPS based effective corporative allocation algorithm to improve the energy management of the blockchain technology;
- Developing a stochastic effect based on unscented transform method to precisely model the energy management of smart grid in the presence of blockchain tech.
2. Security Achievement under Blockchain Technology
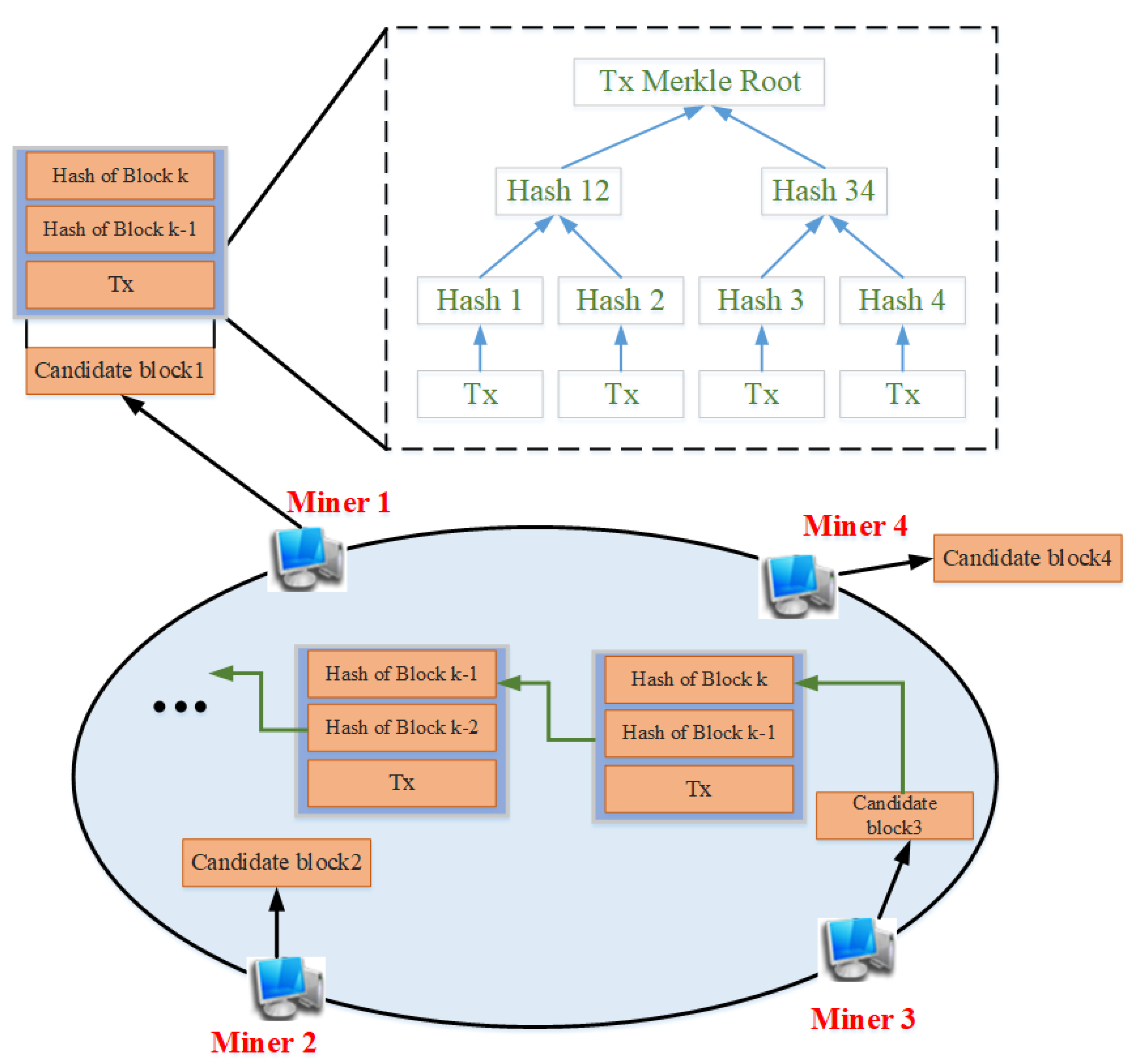
2.1. Blockchain Structure
2.1.1. Decentralized Network
2.1.2. Consensus Protocol and Algorithm
2.1.3. Cryptographic Process
3. Utility Function Formulation of Mining Devices
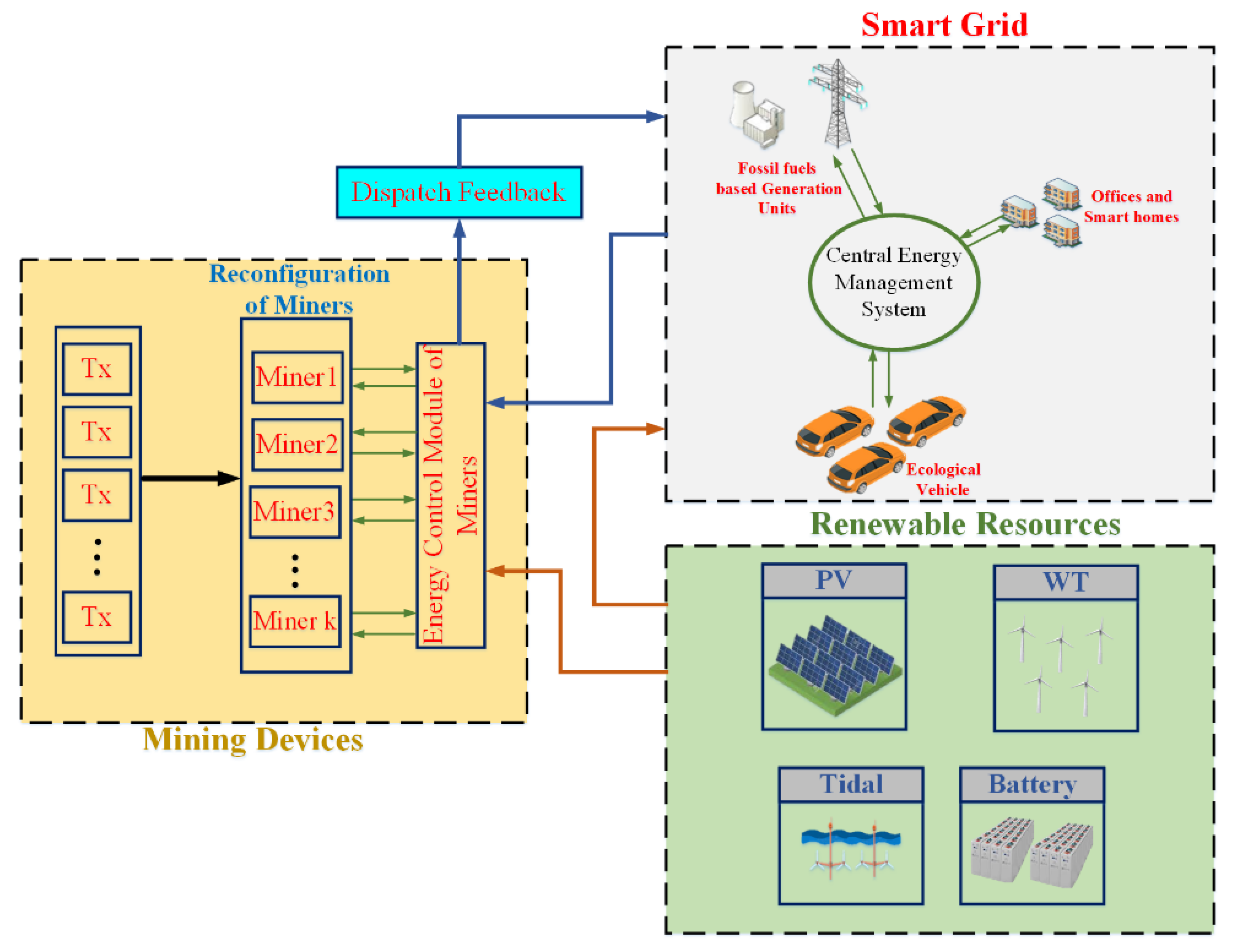
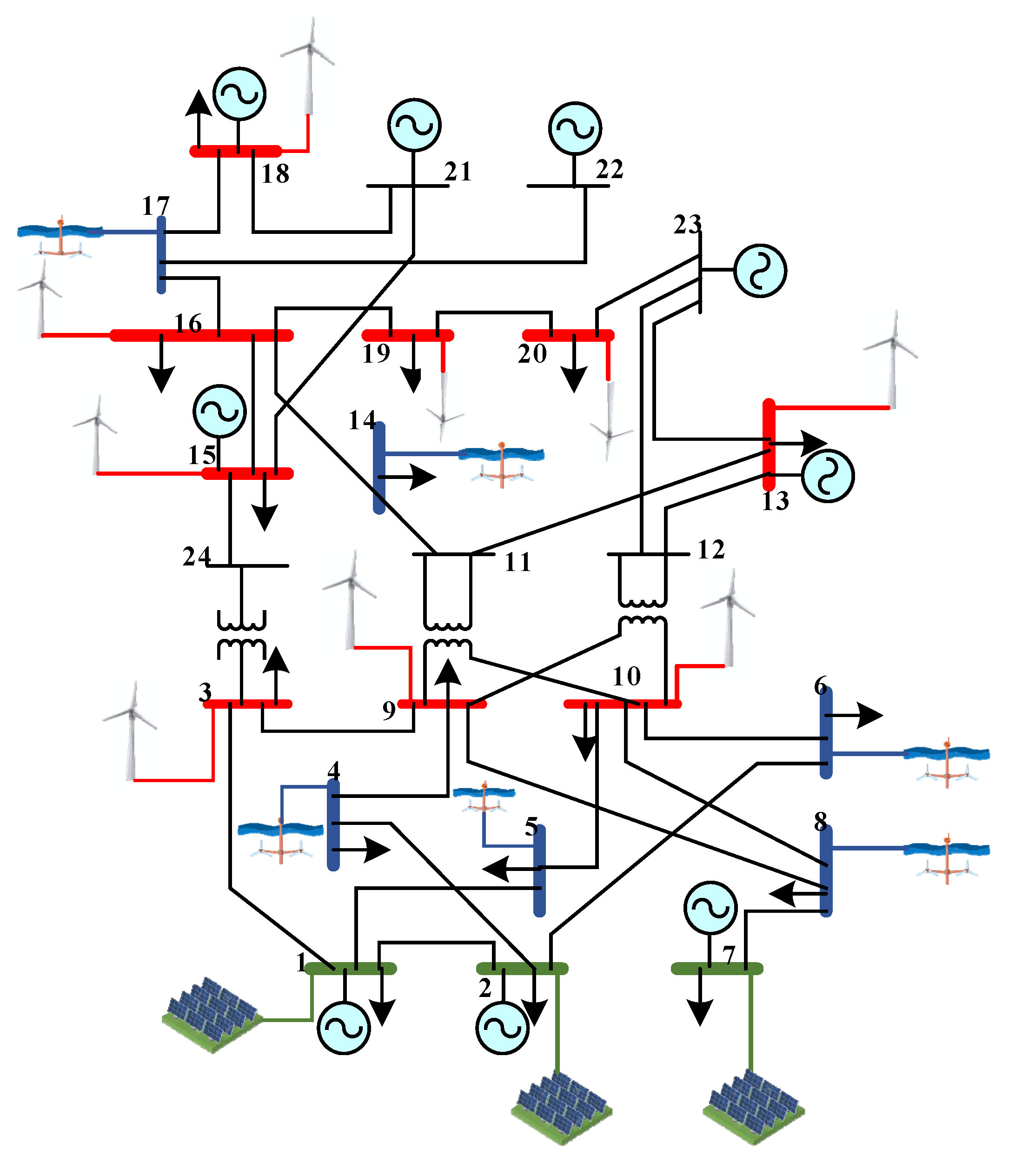
4. Smart Grid Energy Management Considering the Miner Technology
4.1. The Basic Formulation of the Smart Grid
4.2. The Intelligent Priority Selection Algorithm Framework
5. Stochastic Quantization Model
6. Simulation Results
- Mode I: assessing the blockchain technology under various hash rates;
- Mode II: analyzing the IPS based simultaneous allocation of mining devises and DGRs;
- Mode III: checking the effect of uncertainty on the energy cost of miners;
- Each mode is expressed and discussed in detail in the subsequent parts.
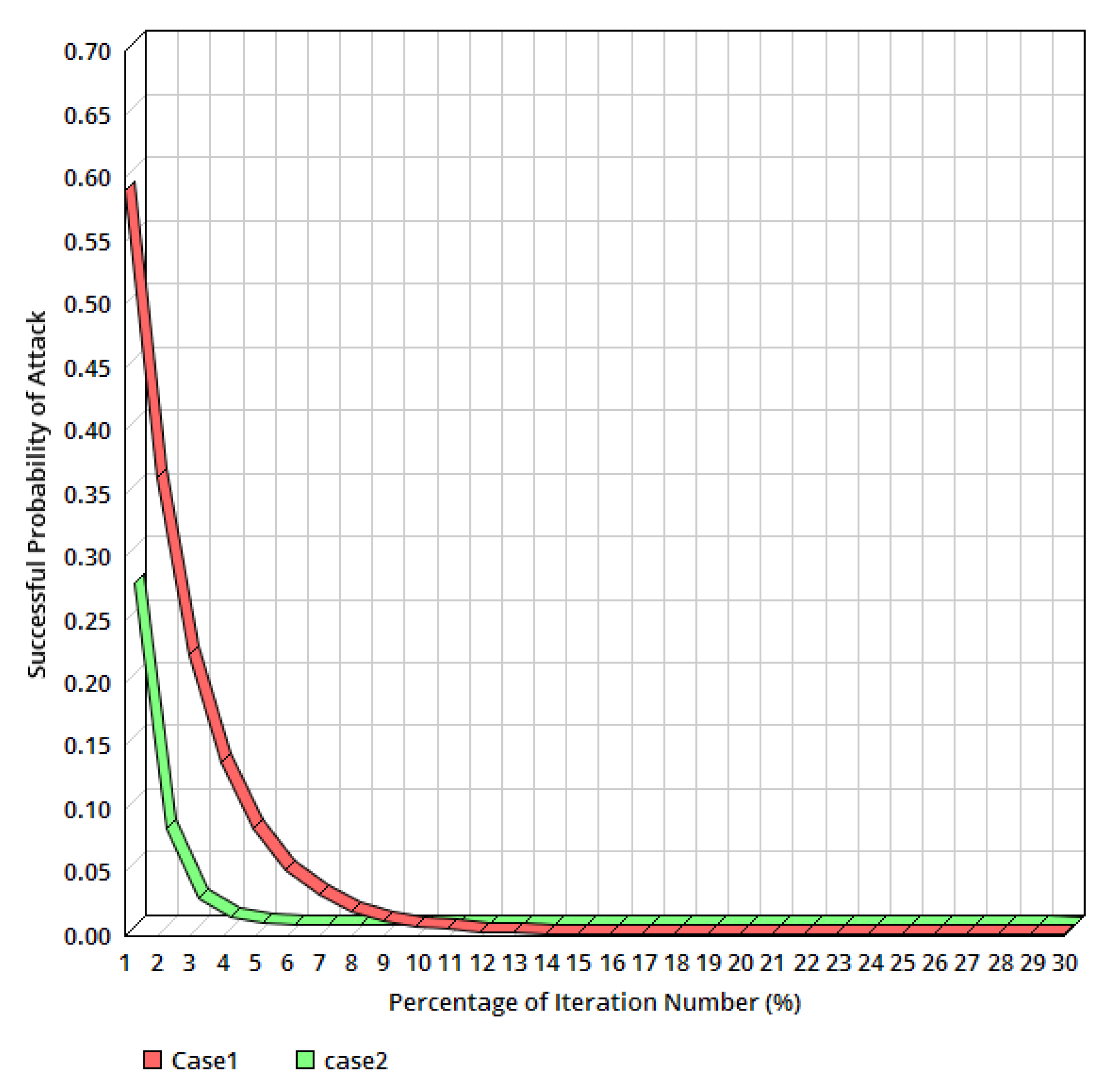
6.1. Assessing the Blockchain Technology under Various Hash Rates
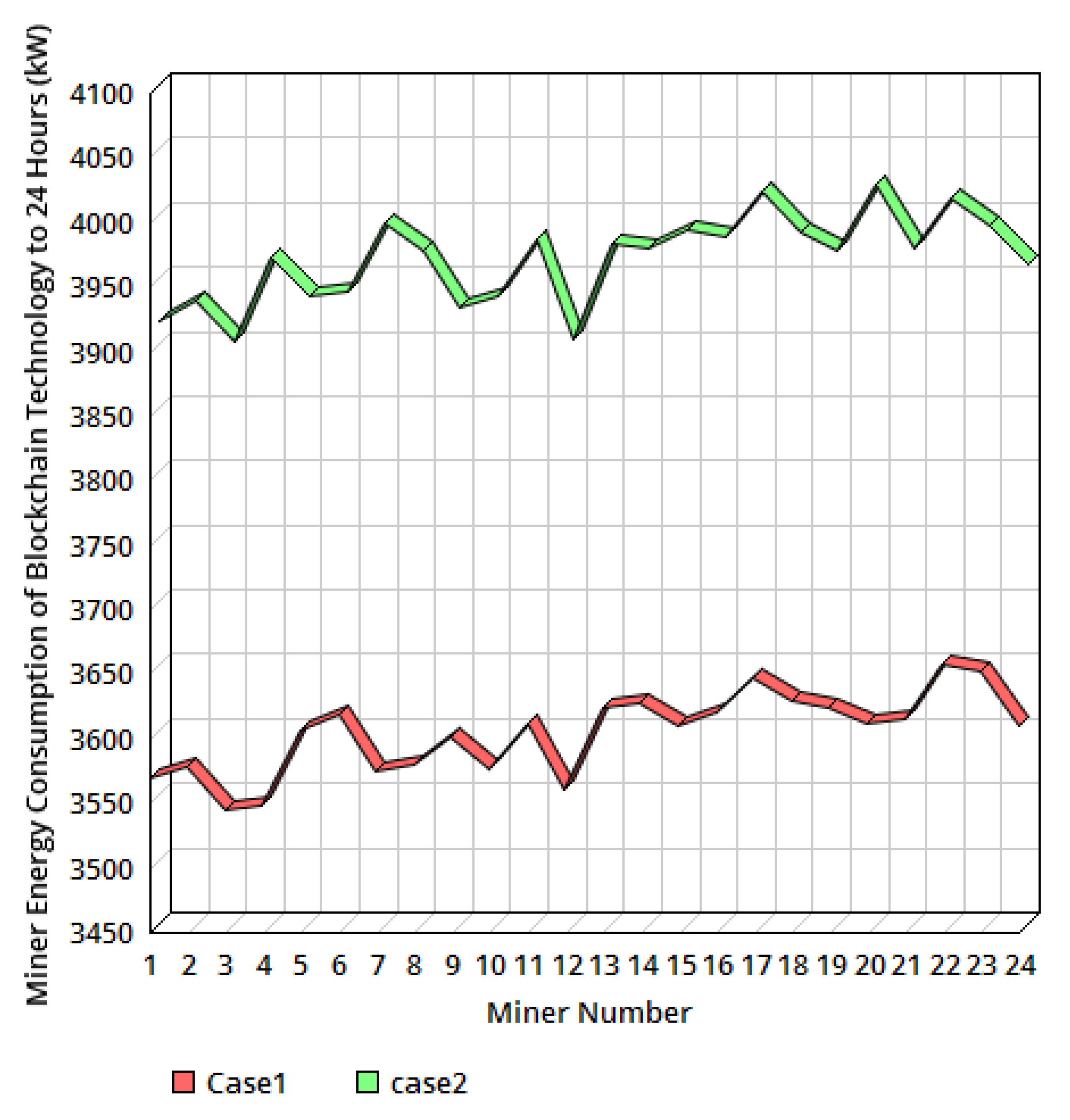
6.2. Analyzing the IPS Based Simultaneous Allocation of Mining Devices and DGRs
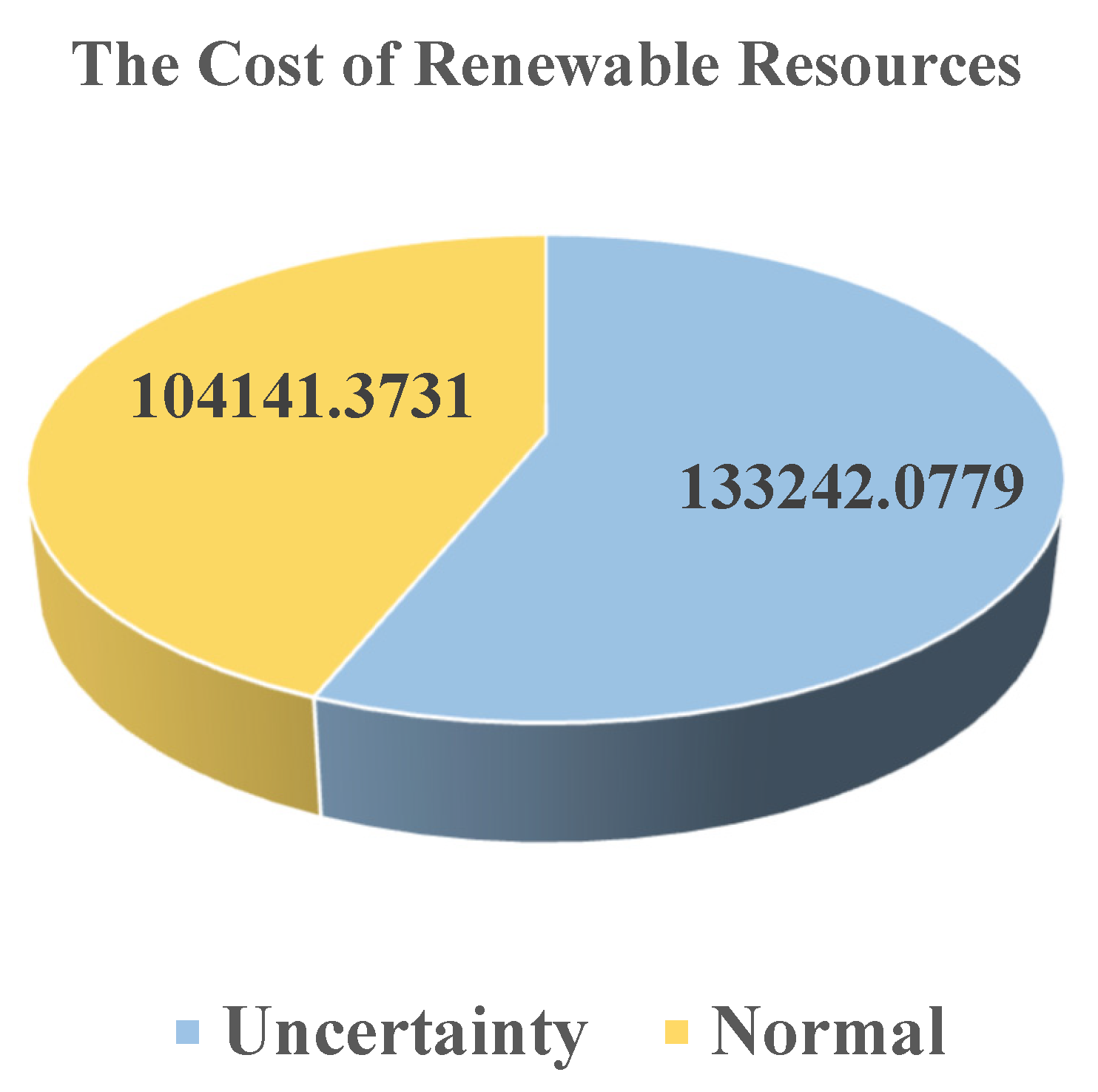
6.3. Checking the Effect of Uncertainty on the Energy Cost of Miners
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Sets/Indices | |
| Set/index of line | |
| Set/index of generator | |
| Set/index of time where = {1…24}. | |
| Set/index of number of bus | |
| Constants | |
| Solar radiation | |
| Power loss related to PV | |
| Wind speed | |
| The cut-in and rated tidal current speeds | |
| The consumed energy | |
| V, f | Voltage and frequency |
| S | Constant value |
| T | Tax rate related to security |
| W | Computational power |
| Direct irradiation | |
| Sea water density | |
| Swept area of the turbine blades | |
| Wind density | |
| Area of rotor blades | |
| Shut up and shut down of the generator. | |
| Capacity of the PVs | |
| Electrical demands of the smart grid | |
| Maximum and minimum value of the storage system energy | |
| The demand of the microgrid | |
| Limits of generation active power | |
| Limits of generation reactive power | |
| Limits of reserve | |
| Generation price of the generator. | |
| Prices of the WT, tidal, PV, and storage system, respectively | |
| ,,, | Maximum and minimum of the transaction power of the line |
| Value of the average and variance | |
| Weight of the mean value | |
| Covariance matrix | |
| P | Number of uncertain parameters |
| Variables | |
| Power output of the storage, WT, tidal and PV, respectively | |
| The generation reactive power of the generators and the line reactive power flow | |
| Sorted matrix of the best values of the objective function | |
| Objective function of the elements of matrix | |
| Best solution of the matrix | |
| Matrix of | |
| , | Binary variables of charging and discharging modes of EH energy storage |
| Matrix of control variables | |
| The generation active power of the generators and the line active power flow | |
| Ch/Dis powers of storage | |
| Binary variables of the generator | |
| Voltage and angle of the bus | |
| Energy of the storage system | |
| Costs of the smart grid | |
References
- Mohamed, M.A.; Hajjiah, A.; Alnowibet, K.A.; Alrasheedi, A.F.; Awwad, E.M.; Muyeen, S.M. A secured advanced management architecture in peer-to-peer energy trading for multi-microgrid in the stochastic environment. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Sun, H.; Chen, R.; Guo, Q. Research on nodal energy price of combined heat and power system for Energy Internet. Power Syst. Technol. 2016, 40, 3375–3382. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, M.; Dampage, U.; Das, B.K.; Nasif, O.; Borowski, P.F.; Mohamed, M.A. Investigating the Impact of Economic Uncertainty on Optimal Sizing of Grid-Independent Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems. Processes 2021, 9, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Yan, W.; Ren, Z.; Wang, Q.; Mohamed, M.A. A robust dispatch model for integrated electricity and heat networks considering price-based integrated demand response. Energy 2022, 239, 121875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Tao, J.; Elsayed, S.K.; Elattar, E.E.; Almalaq, A.; Mohamed, M.A. Stochastic multi-carrier energy management in the smart islands using reinforcement learning and unscented transform. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 130, 106988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Ren, Z.; Yan, W.; Wang, Q.; Mohamed, M.A. A Wind Power Accommodation Capability Assessment Method for Multi-Energy Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Jin, T.; Su, W. Multi-agent energy management of smart islands using primal-dual method of multipliers. Energy 2020, 208, 118306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, N.; Chi, Y. A Nove l Electricity Transaction Mode of Microgrids Based on Blockchain and Continuous Double Auction. Energies 2017, 10, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mengelkamp, E.; Gärttner, J.; Rock, K.; Kessler, S.; Orsini, L.; Weinhardt, C. Designing microgrid energy markets: A case study: The Brooklyn Microgrid. Appl. Energy 2018, 210, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Hajjiah, A.; Jermsittiparsert, K.; Al-Sumaiti, A.S.; Elsayed, S.K.; Ghoneim, S.S.; Mohamed, M.A. A secured social-economic framework based on PEM-blockchain for optimal scheduling of reconfigurable interconnected microgrids. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 40797–40810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Taha, A.F.; Wang, J.; Kvaternik, K.; Hahn, A. Energy Crowdsourcing and Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading in Blockchain-Enabled Smart Grids. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 49, 1612–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Kang, J.; Yu, R.; Ye, D.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, Y. Consortium blockchain for secure energy trading in industrial internet of things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 14, 3690–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, H. Exploring Blockchain for the Coordination of Distributed Energy Resources. In Proceedings of the 2021 55th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS), Baltimore, MD, USA, 14–26 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Eyal, I.; Emin, G.S. Majority is not enough: Bitcoin mining is vulnerable. In International Conference on Financial Cryptography and Data Security; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- UTBC. Available online: http://utbc.net/ (accessed on 5 February 2021).
- PPCoin. Available online: https://peercoin.net/ (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Bentov, I.; Lee, C.; Mizrahi, A.; Rosenfeld, M. Proof of activity: Extending bitcoin’s proof of work via proof of stake [extended abstract] y. ACM SIGMETRICS Perform. Eval. Rev. 2014, 42, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosh, D.; Shetty, S.; Foytik, P.; Kamhoua, C.; Njilla, L. CloudPoS: A proof-of-stake consensus design for blockchain integrated cloud. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 11th International Conference on Cloud Computing (CLOUD), San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–7 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, T.; Yuan, Y.; Ahmed, Z.; Moniz, K.; Cao, G.; Wang, C. Proof of contribution: A modification of proof of work to increase mining efficiency. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 42nd Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Tokyo, Japan, 23–27 July 2018; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kanchev, H.; Lu, D.; Colas, F.; Lazarov, V.; Francois, B. Energy Management and Operational Planning of a Microgrid with a PV-Based Active Generator for Smart Grid Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 4583–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palma-Behnke, R.; Benavides, C.; Lanas, F.; Severino, B.; Reyes-Chamorro, L.; Llanos, J.; Saez, D. A Microgrid Energy Management System Based on the Rolling Horizon Strategy. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, L.; Alnowibet, K.A.; Alrasheedi, A.F.; Moazzen, F.; Awwad, E.M.; Mohamed, M.A. A stochastic machine learning based approach for observability enhancement of automated smart grids. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 72, 103071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghussain, L.; Ahmad, A.D.; Abubaker, A.M.; Mohamed, M.A. An integrated photovoltaic/wind/biomass and hybrid energy storage systems towards 100% renewable energy microgrids in university campuses. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 46, 101273. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Abdullah, H.M.; El-Meligy, M.A.; Sharaf, M.; Soliman, A.T.; Hajjiah, A. A novel fuzzy cloud stochastic framework for energy management of renewable microgrids based on maximum deployment of electric vehicles. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 129, 106845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Jermsittiparsert, K.; Alrashood, S.T.; Rezaei, M.; Al-Ghussain, L.; Mohamed, M.A. An advanced machine learning based energy management of renewable microgrids considering hybrid electric vehicles’ charging demand. Energies 2021, 14, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gözel, T.; Hocaoglu, M.H. An analytical method for the sizing and siting of distributed generators in radial systems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2009, 79, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabha, D.R.; Jayabarathi, T. Optimal placement and sizing of multiple distributed generating units in distribution networks by invasive weed optimization algorithm. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2016, 7, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalesi, N.; Rezaei, N.; Haghifam, M.-R. DG allocation with application of dynamic programming for loss reduction and reliability improvement. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2011, 33, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yue, H.; Yu, K. Perturbed stochastic fractal search for solar PV parameter estimation. Energy 2019, 189, 116247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, T.; Tyagi, B.; Kumar, V. Dynamic state estimation of generators using spherical simplex unscented transform-based unbiased minimum variance filter. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2020, 14, 2997–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, B.; Si, Y.; Yang, Y.; Mohamed, M.A. A two-stage optimal scheduling method for active distribution networks considering uncertainty risk. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 4633–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalonen, H. The uncertainty of innovation: A systematic review of the literature. J. Manag. Res. 2012, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamoto, S. Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system. Decentralized Bus. Rev. 2008, 13, 21260. [Google Scholar]
- Shetty, S.S.; Kamhoua, C.A.; Njilla, L.L. (Eds.) Blockchain for Distributed Systems Security; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Awwad, E.M.; El-Sherbeeny, A.M.; Nasr, E.A.; Ali, Z.M. Optimal scheduling of reconfigurable grids considering dynamic line rating constraint. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2020, 14, 1862–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.; Aghaei, J.; Chabok, H.; Roustaei, M.; Niknam, T.; Kavousi-Fard, A.; Shafie-Khah, M.; Catalao, J.P.S. Synergies between Transportation Systems, Energy Hub and the Grid in Smart Cities. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.; Aghaei, J.; Letafat, A.; Rajabdorri, M.; Niknam, T.; Shafie-Khah, M.; Catalão, J.P. Security-Constrained Unit Commitment Problem with Transmission Switching Reliability and Dynamic Thermal Line Rating. IEEE Syst. J. 2019, 13, 3933–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.; Aghaei, J.; Rajabdorri, M.; Shafie-khah, M.; Lotfi, M.; Javadi, S.M.; Catalão, P.J. Multiobjective Congestion Management and Transmission Switching Ensuring System Reliability. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2019 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC/I&CPS Europe), Genoa, Italy, 11–14 June 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Daneshvar, M.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Asadi, S.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A.; Rasouli, M.; Abapour, M.; Gharehpetian, G.B. Chance-constrained models for transactive energy management of interconnected microgrid clusters. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 271, 122177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, J.; Zareipour, H. A Price-Maker/Price-Taker Model for the Operation of Battery Storage Systems in Electricity Markets. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 6912–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidi, M.; Zare, K. Integration of Smart Energy Hubs in Distribution Networks under Uncertainties and Demand Response Concept. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 34, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Almalaq, A.; Abdullah, H.M.; Alnowibet, K.A.; Alrasheedi, A.F.; Zaindin, M.S.A. A Distributed Stochastic Energy Management Framework Based-Fuzzy-PDMM for Smart Grids Considering Wind Park and Energy Storage Systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 46674–46685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, D.; Zhu, C.; Yang, Y.; Abdullah, H.M.; Mohamed, M.A. Stochastic management of hybrid AC/DC microgrids considering electric vehicles charging demands. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1338–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Quynh, N.V.; Abdullah, H.M.; Almalaq, A.; Do, T.D.; Abdelkader, S.M.; Mohamed, M.A. Optimal Scheduling and Management of a Smart City Within the Safe Framework. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 161847–161861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Sarkar, D. BFO-based firefly algorithm for multi-objective optimal allocation of generation by integrating renewable energy sources. Int. J. Grid Util. Comput. 2021, 12, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Dong, J.S.; Sadiq, A.S.; Faris, H. Genetic Algorithm: Theory, Literature Review, and Application in Image Reconstruction. Nov. Bioinspired Actuator Des. Robot. 2020, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwar, N.; Meena, N.; Yang, J.; Parashar, S. Modified Bacterial Foraging Optimization and Application. In Swarm Intelligence Algorithms; Informa UK Limited: London, UK, 2020; pp. 29–41. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, T.; Mohamed, M.A.; Wang, Q. A Novel Three-Step Classification Approach Based on Time-Dependent Spectral Features for Complex Power Quality Disturbances. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Eltamaly, A.M.; Alolah, A. Swarm intelligence-based optimization of grid-dependent hybrid renewable energy systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jin, T.; Mohamed, M.A. A Fast and Robust Fault Section Location Method for Power Distribution Systems Considering Multisource Information. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

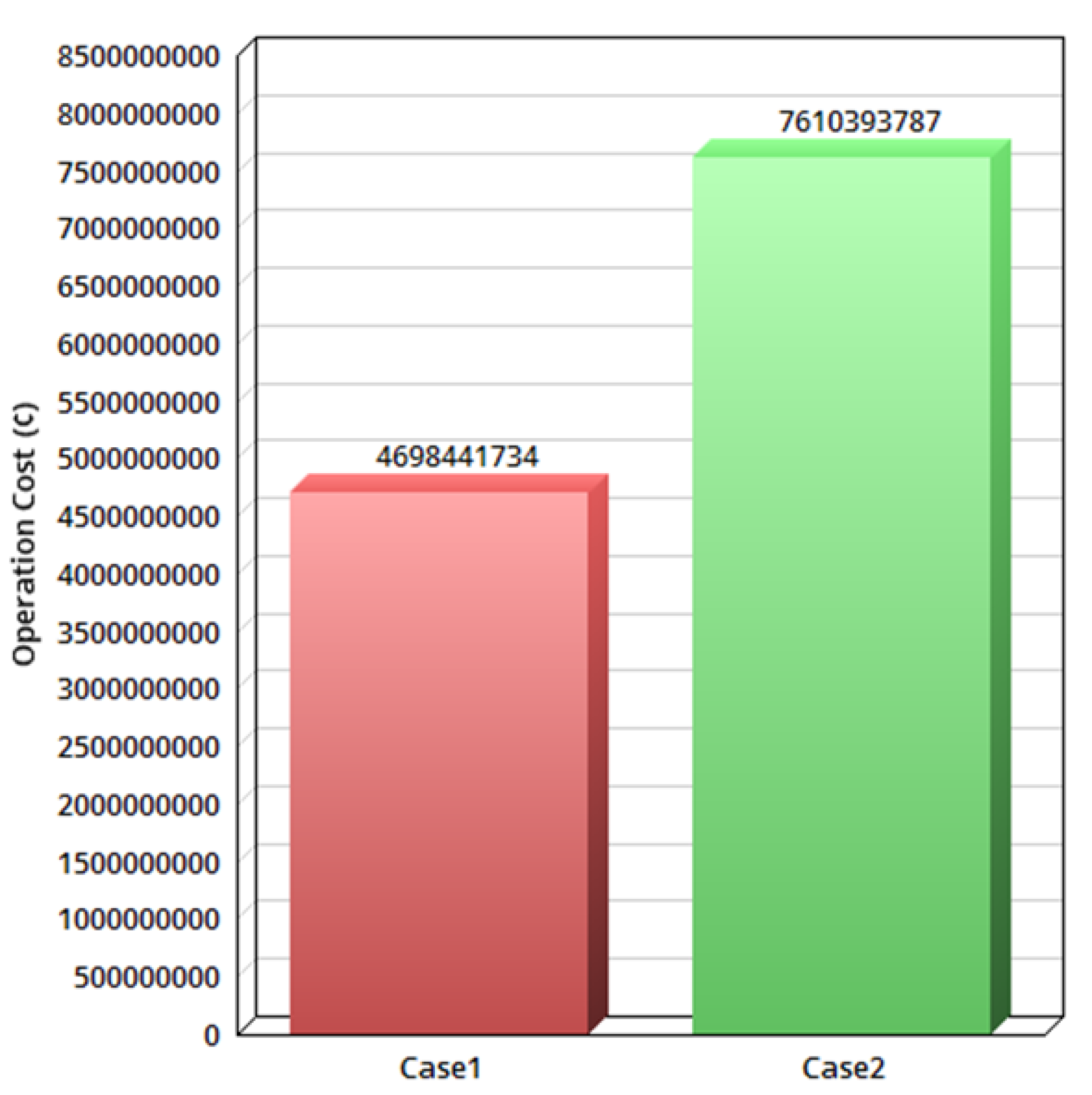
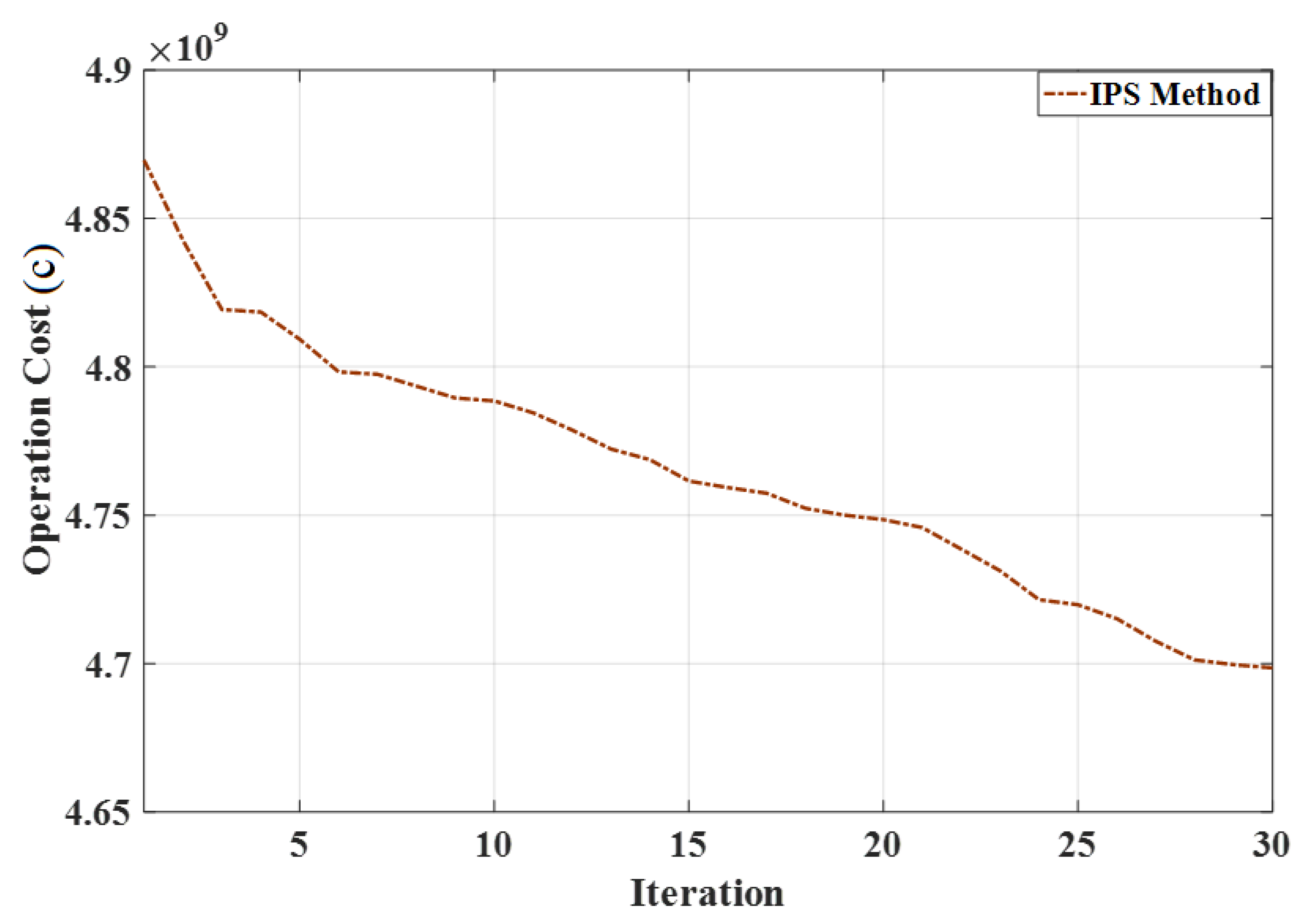
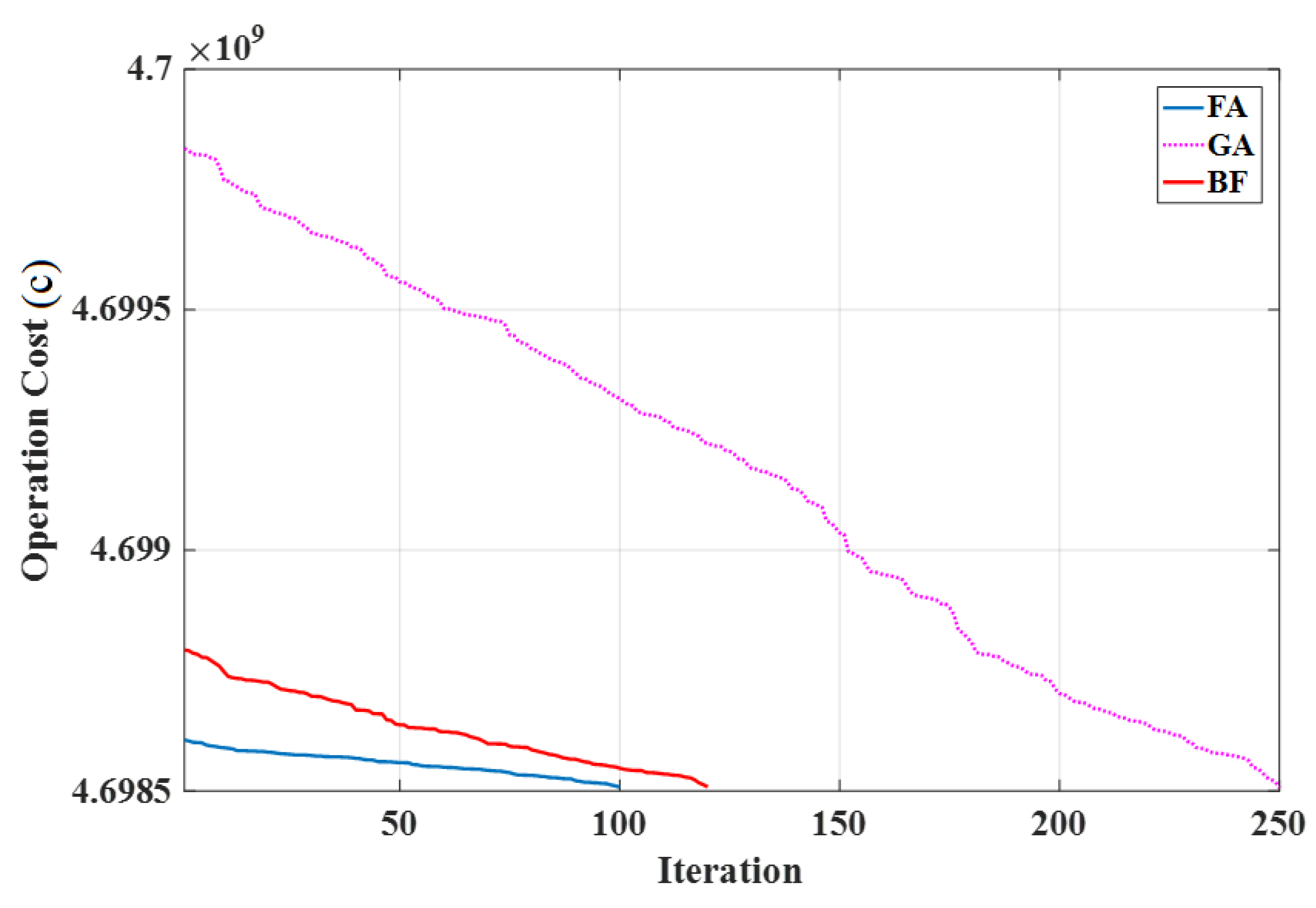
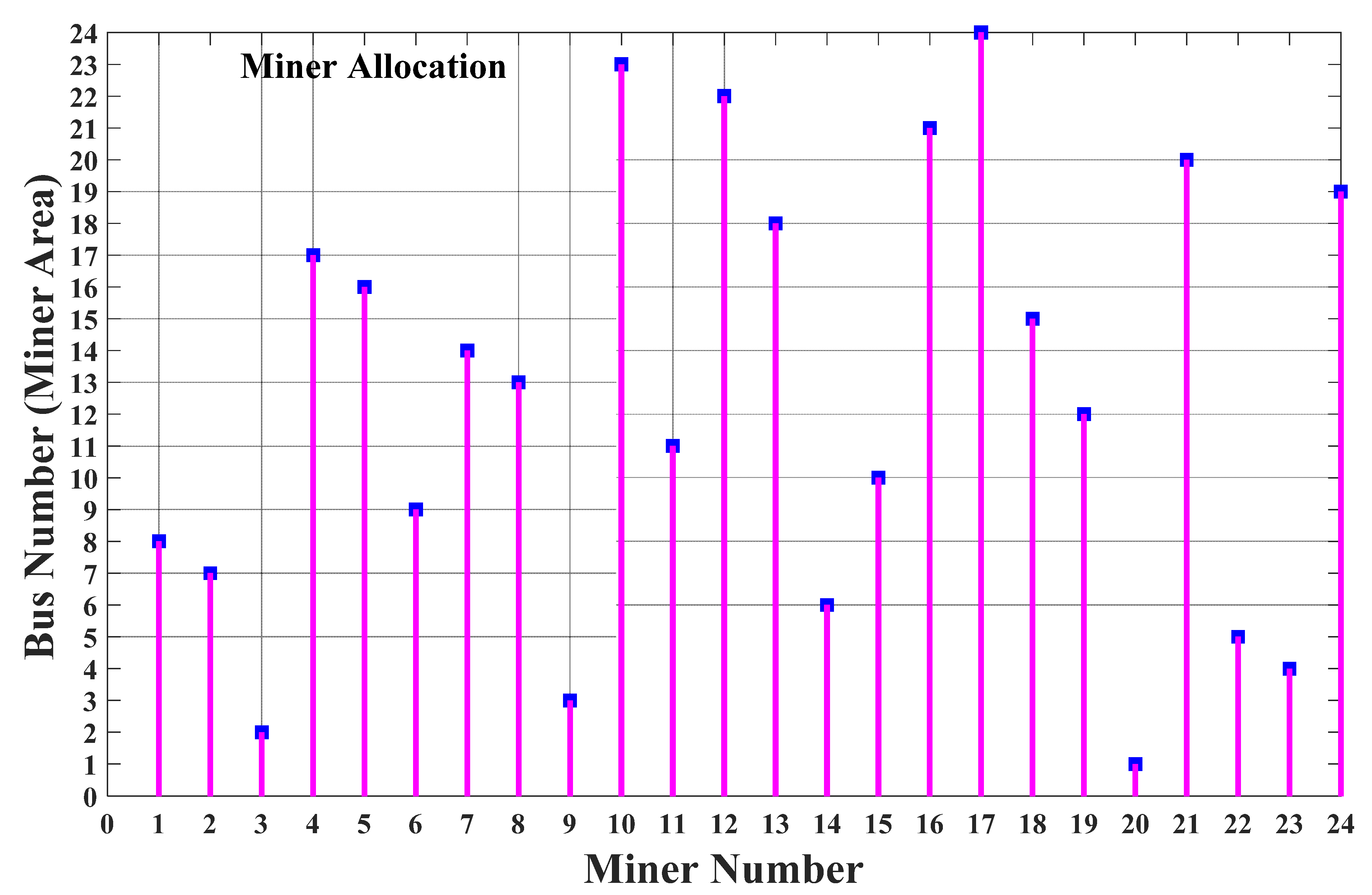
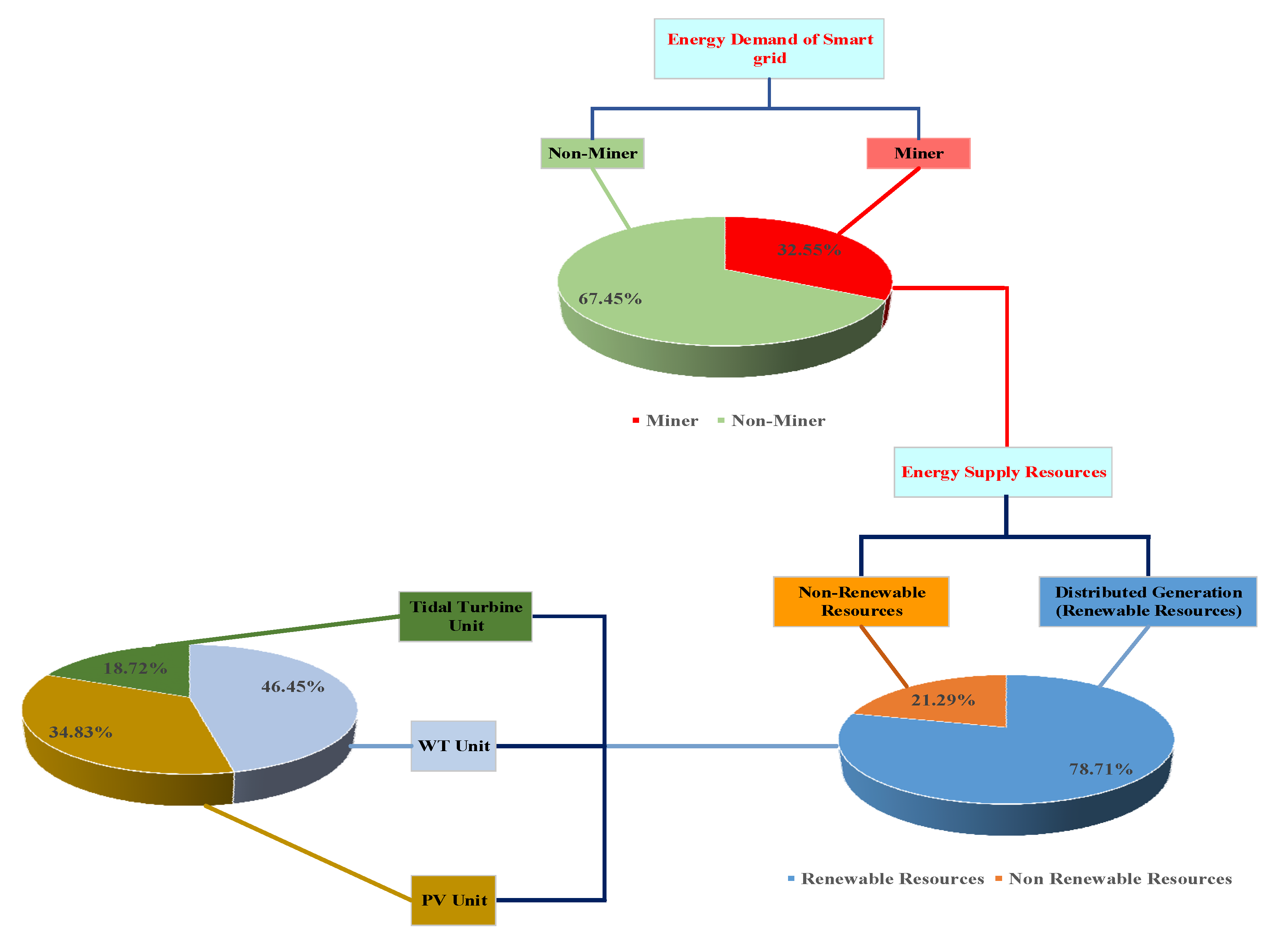
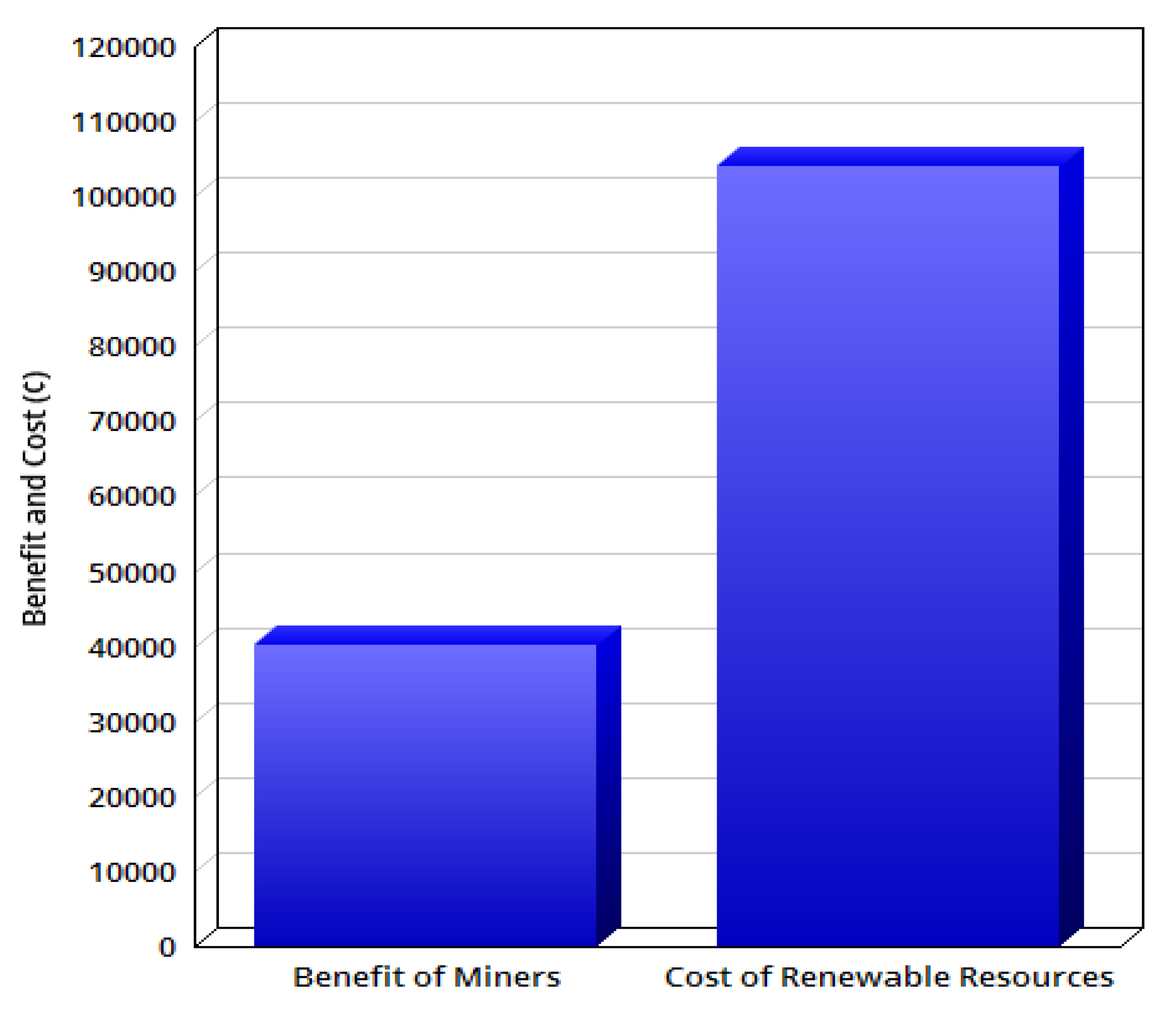
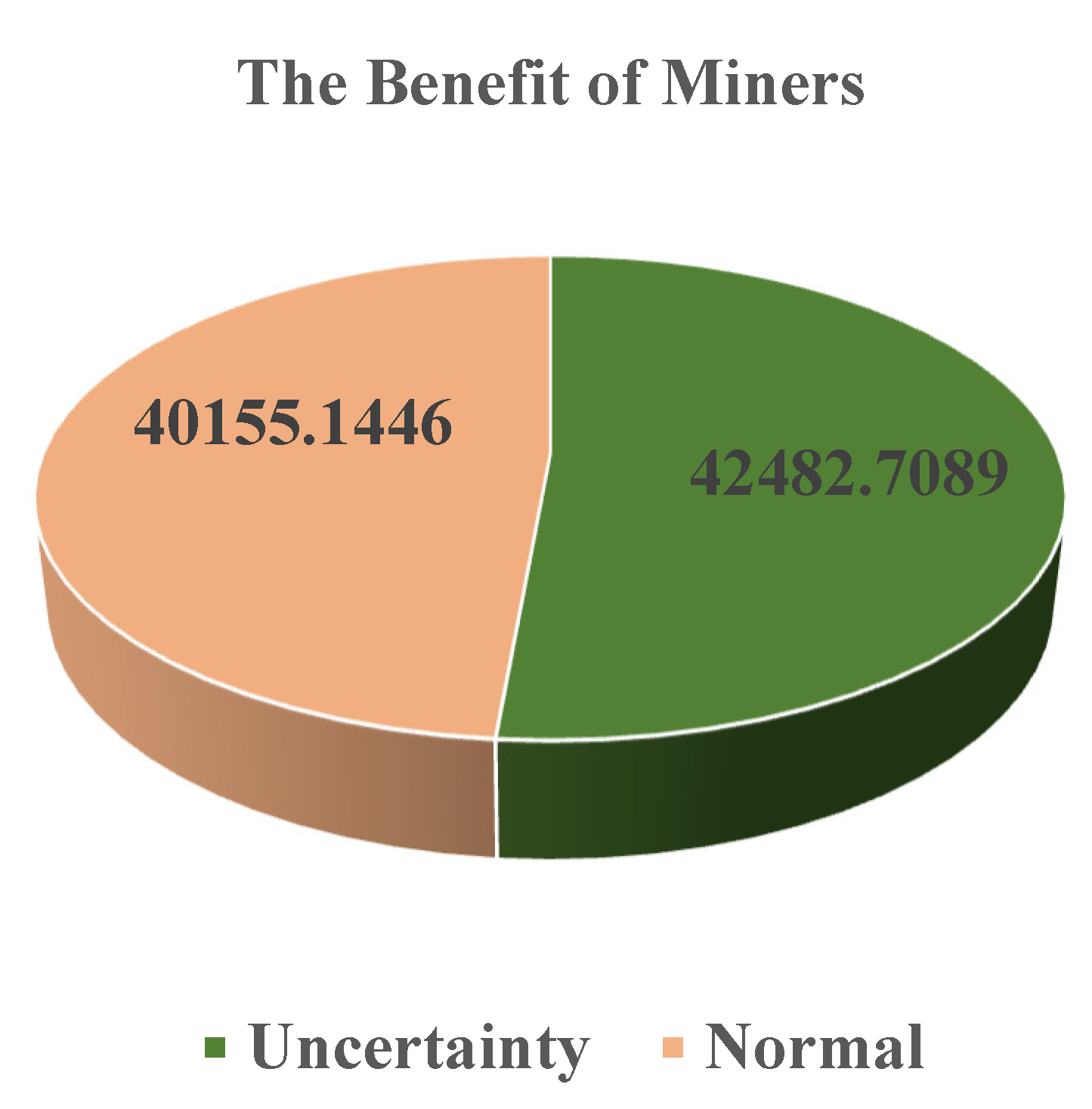
| Different Cases | Cost of Smart Grid (¢) | Total Cost (¢) |
|---|---|---|
| The modified framework | 4,698,441,734 | 4,698,505,720 |
| The basic structure | 6,921,944,531 | 6,921,904,376 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed, M.A.; Mirjalili, S.; Dampage, U.; Salmen, S.H.; Obaid, S.A.; Annuk, A. A Cost-Efficient-Based Cooperative Allocation of Mining Devices and Renewable Resources Enhancing Blockchain Architecture. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10382. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810382
Mohamed MA, Mirjalili S, Dampage U, Salmen SH, Obaid SA, Annuk A. A Cost-Efficient-Based Cooperative Allocation of Mining Devices and Renewable Resources Enhancing Blockchain Architecture. Sustainability. 2021; 13(18):10382. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810382
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed, Mohamed A., Seyedali Mirjalili, Udaya Dampage, Saleh H. Salmen, Sami Al Obaid, and Andres Annuk. 2021. "A Cost-Efficient-Based Cooperative Allocation of Mining Devices and Renewable Resources Enhancing Blockchain Architecture" Sustainability 13, no. 18: 10382. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810382
APA StyleMohamed, M. A., Mirjalili, S., Dampage, U., Salmen, S. H., Obaid, S. A., & Annuk, A. (2021). A Cost-Efficient-Based Cooperative Allocation of Mining Devices and Renewable Resources Enhancing Blockchain Architecture. Sustainability, 13(18), 10382. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810382









