Data-Driven Forecasting and Modeling of Runoff Flow to Reduce Flood Risk Using a Novel Hybrid Wavelet-Neural Network Based on Feature Extraction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- − Presenting a hybrid WNN method
- − Using wavelet to increase forecasting accuracy
- − Using feature extraction (energy, standard deviation, and maximum values, etc.)
- − Reducing the computation time using feature extraction
- − Reducing computational complexity by using feature extraction
- − Using all daily, weekly, and monthly data
- − Comparison with other previous methods.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wavelet Neural Network (WNN)
2.2. Wavelet Algorithm
3. Case Study and the Dataset
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Scenario 1
4.2. Scenario 2
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| WNN | Wavelet Neural Network |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| CI | Computational Intelligence |
| GWL | Ground Water Level |
| Qsim | Simulated Streamflow |
| Qobs | Observed Streamflow |
| STD | Standard deviation |
| Max | Maximum |
| Min | Minimum |
| ANFIS | Adaptive Neural Fuzzy Inference System |
| FIS | Fuzzy Inference System |
| WNF | Wavelet Neural Fuzzy |
| R2 | Coefficient of determination |
| WT | Wavelet Transform |
| RBF | Radial Basis Function |
| MSE | Mean Square Error |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| NSE | Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency |
| f(x) | Function |
| R | Coefficient of Correlation |
| φ | Scaling Function |
| ψ | Mother Wavelet |
| α | Scale Parameter |
| β | Translation Parameter |
References
- Mahmoud, K.; Abdel-Nasser, M.; Mustafa, E.; Ali, M.Z. Improved Salp–Swarm Optimizer and Accurate Forecasting Model for Dynamic Economic Dispatch in Sustainable Power Systems. Sustainability 2020, 12, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, K.; Zha, R.; Wu, J.; Lai, K.K. Multivariate EMD-based modeling and forecasting of crude oil price. Sustainability 2016, 8, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Ngo, L.; Madsen, H.; Rosbjerg, D. Simulation and optimisation modelling approach for operation of the Hoa Binh reservoir, Vietnam. J. Hydrol. 2007, 336, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K. Prophecy, reality and uncertainty in distributed hydrological modelling. Adv. Water Resour. 1993, 16, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Singh, V.P.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J. Real-time error correction method combined with combination flood forecasting technique for improving the accuracy of flood forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2015, 521, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.-H.; Huang, C.-J. An electricity price forecasting model by hybrid structured deep neural networks. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tayyab, M.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, X.; Adnan, R. Discharge forecasting by applying artificial neural networks at the Jinsha river basin, China. Eur. Sci. J. 2016, 12, 108–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paraschiv, D.; Tudor, C.; Petrariu, R. The textile industry and sustainable development: A Holt–Winters forecasting investigation for the Eastern European area. Sustainability 2015, 7, 1280–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amiri, A.M.; Nadimi, N.; Yousefian, A. Comparing the efficiency of different computation intelligence techniques in predicting accident frequency. IATSS Res. 2020, 44, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets as a basis for a theory of possibility. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1978, 1, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, M.E.; Taylan, D.; Terzi, O. Adaptive neural-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) approach for modelling hydrological time series. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firat, M.; Turan, M.E.; Yurdusev, M.A. Comparative analysis of fuzzy inference systems for water consumption time series prediction. J. Hydrol. 2009, 374, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernieuwe, H.; Georgieva, O.; De Baets, B.; Pauwels, V.R.N.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; De Troch, F.P. Comparison of data-driven Takagi–Sugeno models of rainfall–discharge dynamics. J. Hydrol. 2005, 302, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrzadeh, H.; Sarukkalige, R.; Jayawardena, A.W. Impact of multi-resolution analysis of artificial intelligence models inputs on multi-step ahead river flow forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2013, 507, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamowski, J.; Sun, K. Development of a coupled wavelet transform and neural network method for flow forecasting of non-perennial rivers in semi-arid watersheds. J. Hydrol. 2010, 390, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-W.; Valdés, J.B. Nonlinear model for drought forecasting based on a conjunction of wavelet transforms and neural networks. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2003, 8, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badrzadeh, H.; Sarukkalige, R.; Jayawardena, A.W. Improving Ann-based short-term and long-term Seasonal River flow forecasting with signal processing techniques. River Res. Appl. 2016, 32, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamowski, J.; Chan, H.F. A wavelet neural network conjunction model for groundwater level forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2011, 407, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, V.; Vafakhah, M.; Shirmohammadi, B.; Behnia, N. A wavelet-ANFIS hybrid model for groundwater level forecasting for different prediction periods. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 1301–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitsazan, M.; Rahmani, G.; Neyamadpour, A. Groundwater level simulation using artificial neural network: A case study from Aghili plain, urban area of Gotvand, south-west Iran. Geopersia 2013, 3, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Husna, N.; Bari, S.H.; Hussain, M.M.; Ur-rahman, M.T.; Rahman, M. Ground water level prediction using artificial neural network. Int. J. Hydrol. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrzadeh, H.; Sarukkalige, R.; Jayawardena, A.W. Hourly runoff forecasting for flood risk management: Application of various computational intelligence models. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.C.; Venkatesh, B.; Krishna, B.; Jain, S.K. Rainfall-runoff modeling using conceptual, data driven, and wavelet based computing approach. J. Hydrol. 2013, 493, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegar, R.; Fijani, E.; Moghaddam, A.A.; Tziritis, E. Forecasting of groundwater level fluctuations using ensemble hybrid multi-wavelet neural network-based models. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourani, V.; Kisi, Ö.; Komasi, M. Two hybrid artificial intelligence approaches for modeling rainfall–runoff process. J. Hydrol. 2011, 402, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Xiang, X.-Y.; Ni, J.-J. Forecast modeling of monthly runoff with adaptive neural fuzzy inference system and wavelet analysis. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thum, G.W.; Tang, S.H.; Ahmad, S.A.; Alrifaey, M. Toward a Highly Accurate Classification of Underwater Cable Images via Deep Convolutional Neural Network. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrifaey, M.; Lim, W.H.; Ang, C.K. A Novel Deep Learning Framework Based RNN-SAE for Fault Detection of Electrical Gas Generator. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 21433–21442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrifaey, M.; Sai Hong, T.; As’arry, A.; Elianddy Supeni, E.; Ang, C.K. Optimization and selection of maintenance policies in an electrical gas turbine generator based on the hybrid reliability-centered maintenance (RCM) model. Processes 2020, 8, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, P.K.D.M.M.; Santos, C.A.G.; da Silva, G.B.L. Analysis of the use of discrete wavelet transforms coupled with ANN for short-term streamflow forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 80, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.M.; Deo, R.C.; Feng, Q.; Ghahramani, A.; Raj, N.; Yin, Z.; Yang, L. Deep learning hybrid model with Boruta-Random forest optimiser algorithm for streamflow forecasting with climate mode indices, rainfall, and periodicity. J. Hydrol. 2021, 599, 126350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Wang, D.; Singh, V.P.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, J. Streamflow and rainfall forecasting by two long short-term memory-based models. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Shu, H.; Kuriqi, A.; Siddiqui, S.; Gagnon, A.S.; Lu, L.; Linh, N.T.T.; Pham, Q.B. Characterization of the 2014 Indus River Flood Using Hydraulic Simulations and Satellite Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.; Vapnik, V. Statistical Learning Theory; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 1, p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Romagnoli, J.A.; Safavi, A.A. Wavelet-based adaptive robust M-estimator for nonlinear system identification. AIChE J. 2000, 46, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.-S.; Lee, T.S.; Kim, H. An application of support vector machines in bankruptcy prediction model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2005, 28, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D. Flood Risk Assessment and Management; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2011; ISBN 1608050475. [Google Scholar]
- Badrzadeh, H.; Sarukkalige, R.; Jayawardena, A.W. Intermittent stream flow forecasting and modelling with hybrid wavelet neuro-fuzzy model. Hydrol. Res. 2018, 49, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Dataset | Mean | Max | Min | STD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily river flow m3/s | Total | 0.88 | 41.29 | 0 | 2.45 |
| Weekly river flow m3/s | Total | 0.84 | 20.44 | 0 | 1.99 |
| Monthly river flow m3/s | Total | 0.87 | 8.96 | 0 | 1.58 |
| Data | MSE | RMSE | NSE | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Mm3) | (m3/s) | |||||||||||||
| All | Train | Test | All | Train | Test | All | Train | Test | All | Train | Test | |||
| Daily | Proposed | Senario 1 | 0.0051 | 0.0055 | 0.0041 | 0.0062 | 0.0065 | 0.0055 | 0.0718 | 0.0747 | 0.0642 | 0.982 | 0.98736 | 0.98648 |
| Senario 2 | 0.0059 | 0.0064 | 0.0048 | 0.0067 | 0.0070 | 0.0060 | 0.0774 | 0.0805 | 0.0697 | 0.999 | 0.99932 | 0.99888 | ||
| Ref [38] | - | - | - | - | 0.017 | 0.020 | - | 0.19 | 0.23 | - | 0.89 | 0.83 | ||
| Weekly | Proposed | Senario 1 | 0.0079 | 0.0100 | 0.0032 | 0.0540 | 0.0605 | 0.0345 | 0.0893 | 0.1000 | 0.0571 | 0.99797 | 0.99766 | 0.99812 |
| Senario 2 | 0.0050 | 0.0061 | 0.0023 | 0.0428 | 0.0475 | 0.0292 | 0.0708 | 0.0785 | 0.0482 | 0.99872 | 0.99844 | 0.99886 | ||
| Ref [38] | - | - | - | - | 0.40 | 0.46 | - | 0.66 | 0.76 | - | 0.87 | 0.68 | ||
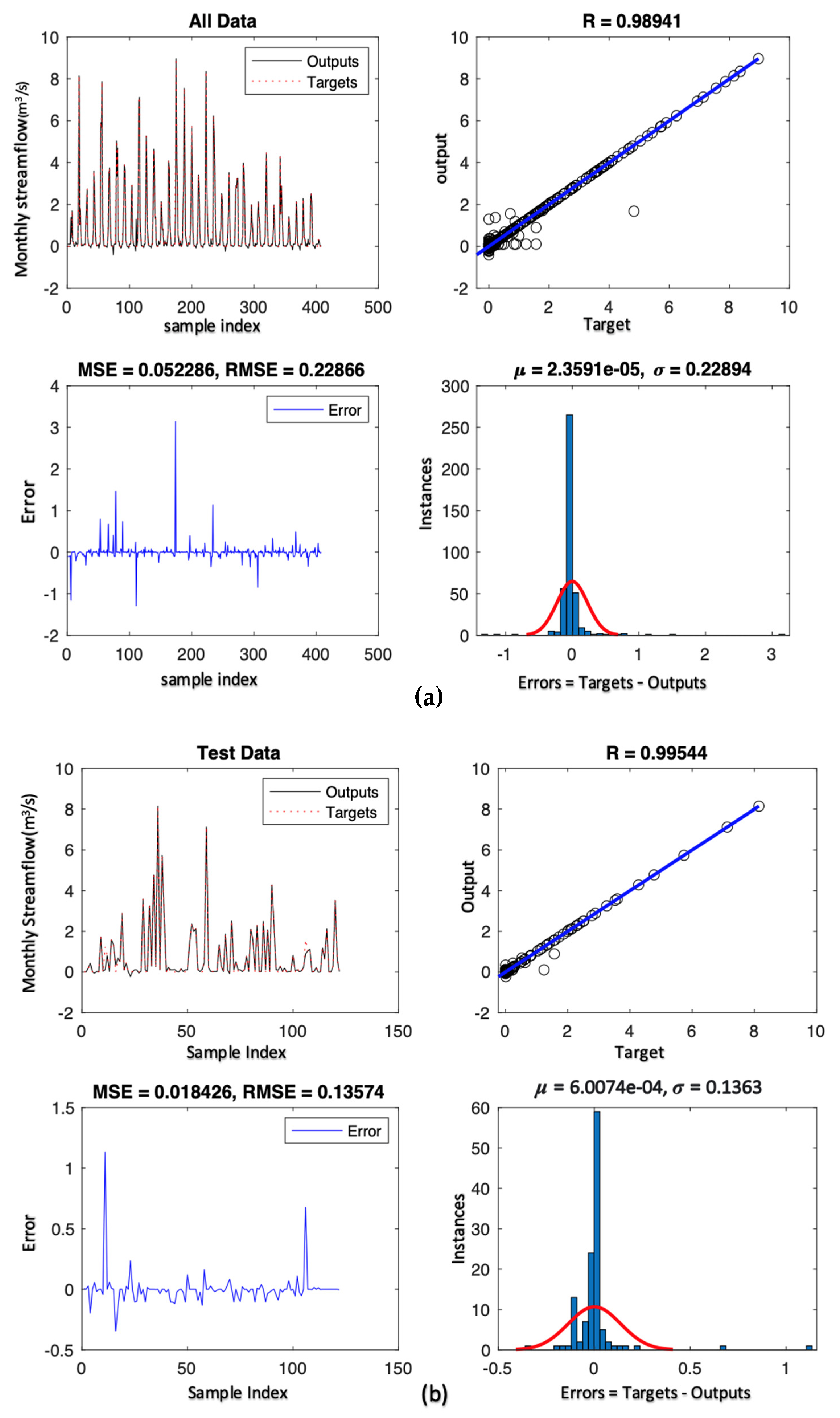
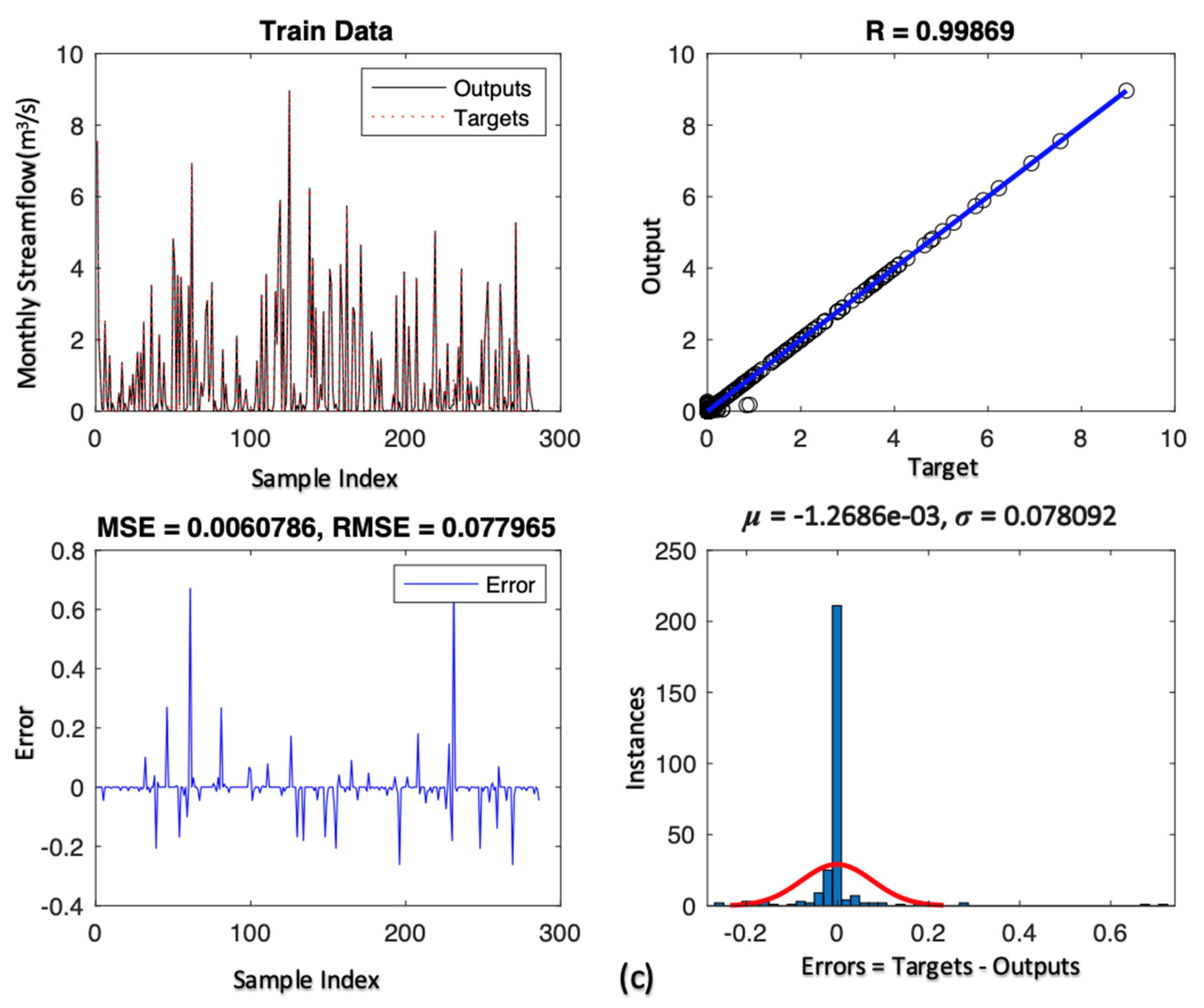
| Monthly | Proposed | Senario 1 | 0.0522 | 0.0667 | 0.0184 | 0.5925 | 0.6695 | 0.3517 | 0.2286 | 0.2583 | 0.1357 | 0.97872 | 0.94999 | 0.99581 |
| Senario 2 | 0.0129 | 0.0060 | 0.0292 | 0.2952 | 0.2019 | 0.4427 | 0.1139 | 0.0779 | 0.1708 | 0.99477 | 0.98552 | 0.99742 | ||
| Ref [38] | - | - | - | - | 1.55 | 1.74 | - | 0.60 | 0.67 | - | 0.84 | 0.59 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malekpour Heydari, S.; Aris, T.N.M.; Yaakob, R.; Hamdan, H. Data-Driven Forecasting and Modeling of Runoff Flow to Reduce Flood Risk Using a Novel Hybrid Wavelet-Neural Network Based on Feature Extraction. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11537. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132011537
Malekpour Heydari S, Aris TNM, Yaakob R, Hamdan H. Data-Driven Forecasting and Modeling of Runoff Flow to Reduce Flood Risk Using a Novel Hybrid Wavelet-Neural Network Based on Feature Extraction. Sustainability. 2021; 13(20):11537. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132011537
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalekpour Heydari, Salimeh, Teh Noranis Mohd Aris, Razali Yaakob, and Hazlina Hamdan. 2021. "Data-Driven Forecasting and Modeling of Runoff Flow to Reduce Flood Risk Using a Novel Hybrid Wavelet-Neural Network Based on Feature Extraction" Sustainability 13, no. 20: 11537. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132011537
APA StyleMalekpour Heydari, S., Aris, T. N. M., Yaakob, R., & Hamdan, H. (2021). Data-Driven Forecasting and Modeling of Runoff Flow to Reduce Flood Risk Using a Novel Hybrid Wavelet-Neural Network Based on Feature Extraction. Sustainability, 13(20), 11537. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132011537





