Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Construction and Demolition Waste Management in Australia: A Research Agenda
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- What are the limitations of current C&DWM practices?
- What are the benefits and barriers to the adoption of BIM for C&DWM?
- What are the potential solutions to those challenges?
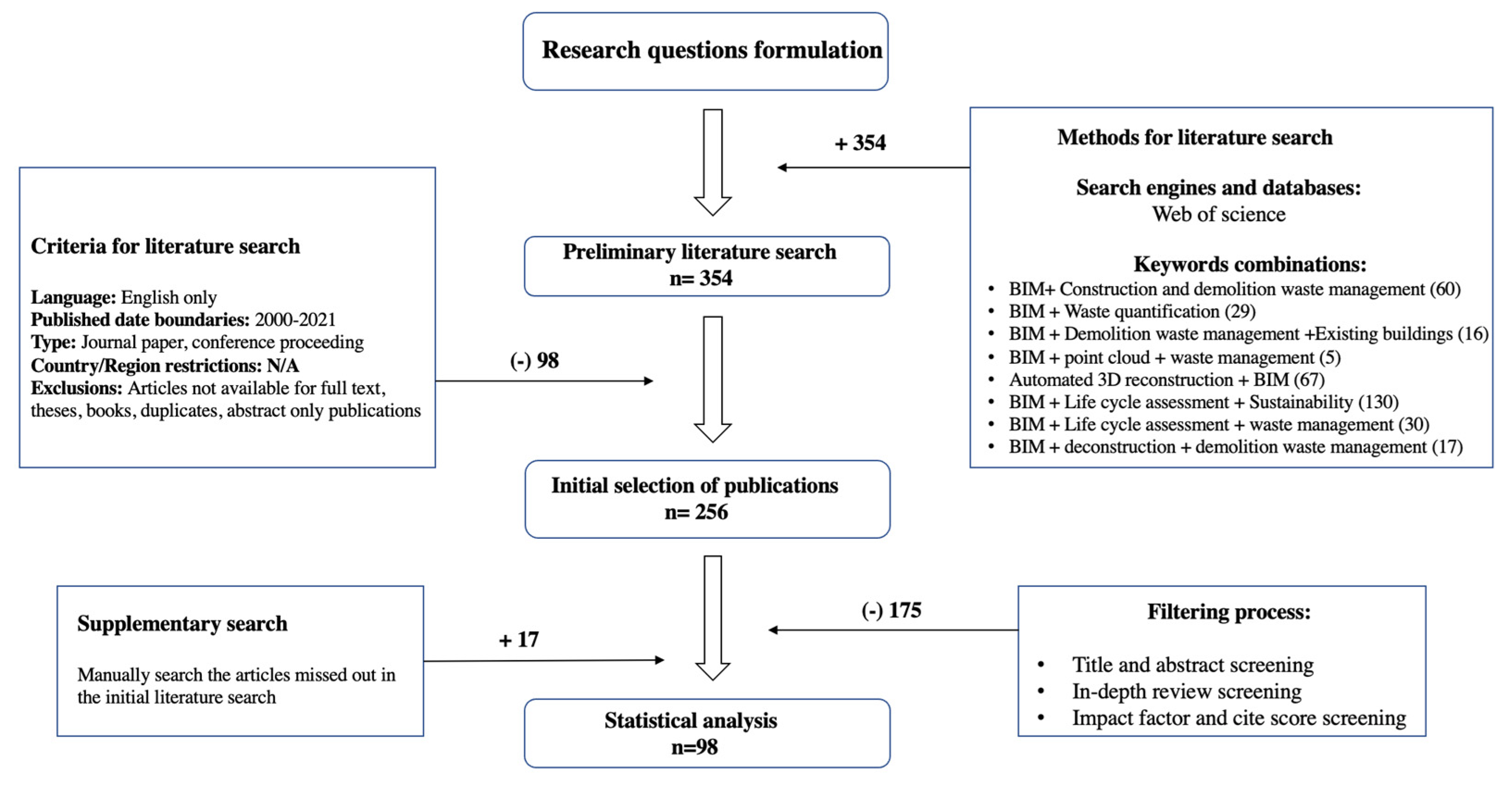
2. Materials and Methods
- What are the limitations of current C&DWM practices?
- What are the benefits and barriers to the adoption of BIM for C&DWM?
- BIM + C&DW management (60)
- BIM + waste quantification (29)
- BIM + DWM + existing buildings (16)
- BIM + point cloud + waste management (5)
- Automated 3D reconstruction + BIM (67)
- BIM + LCA + sustainability (130)
- BIM + LCA + waste management (30)
- BIM + deconstruction + DWM (17)
3. Results
3.1. C&D Waste Management Principles
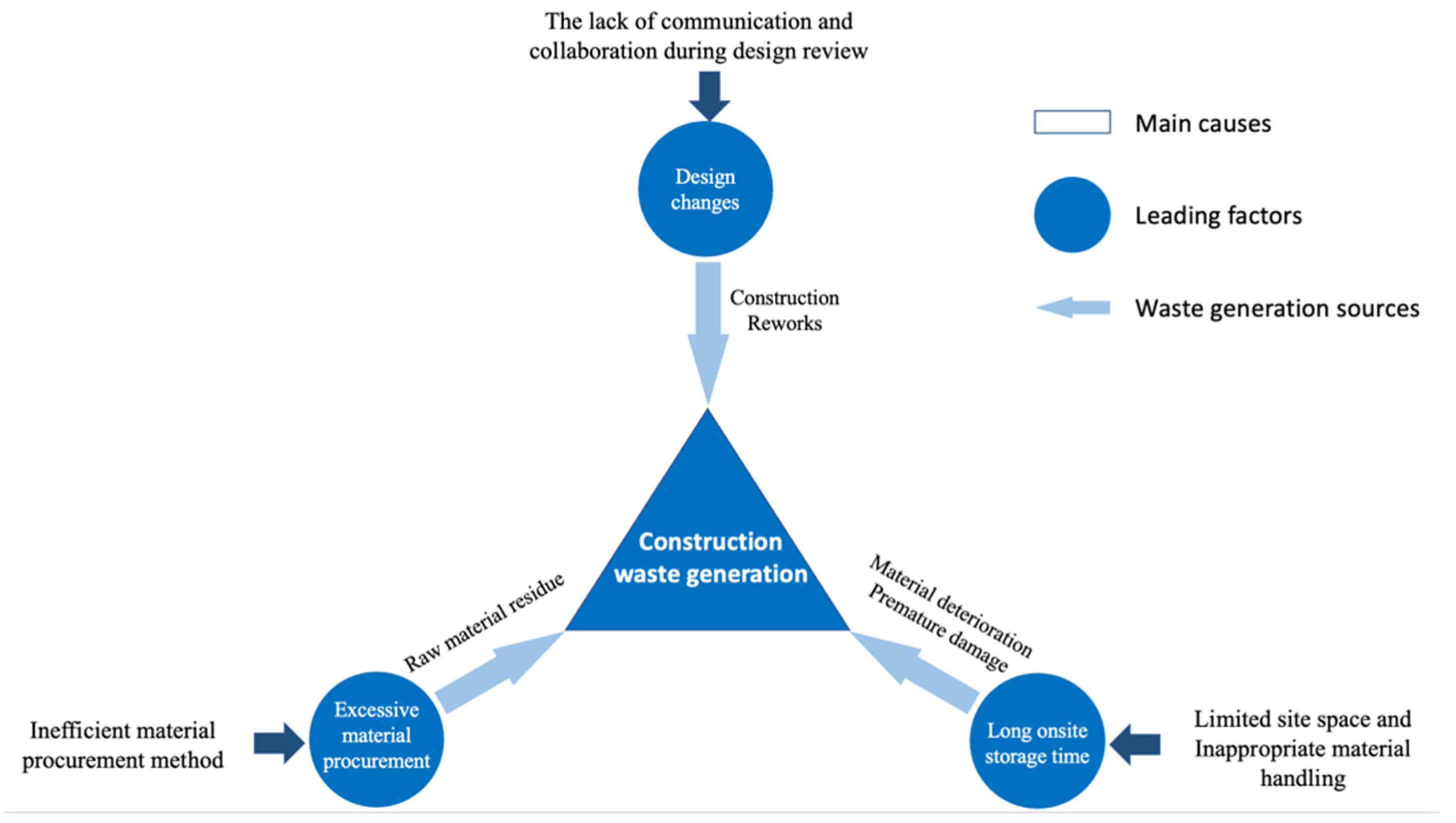
3.2. Barriers to Implementing Effective C&D Waste Management
3.2.1. Technology Barriers
3.2.2. Policy Barriers
3.2.3. Human Barriers
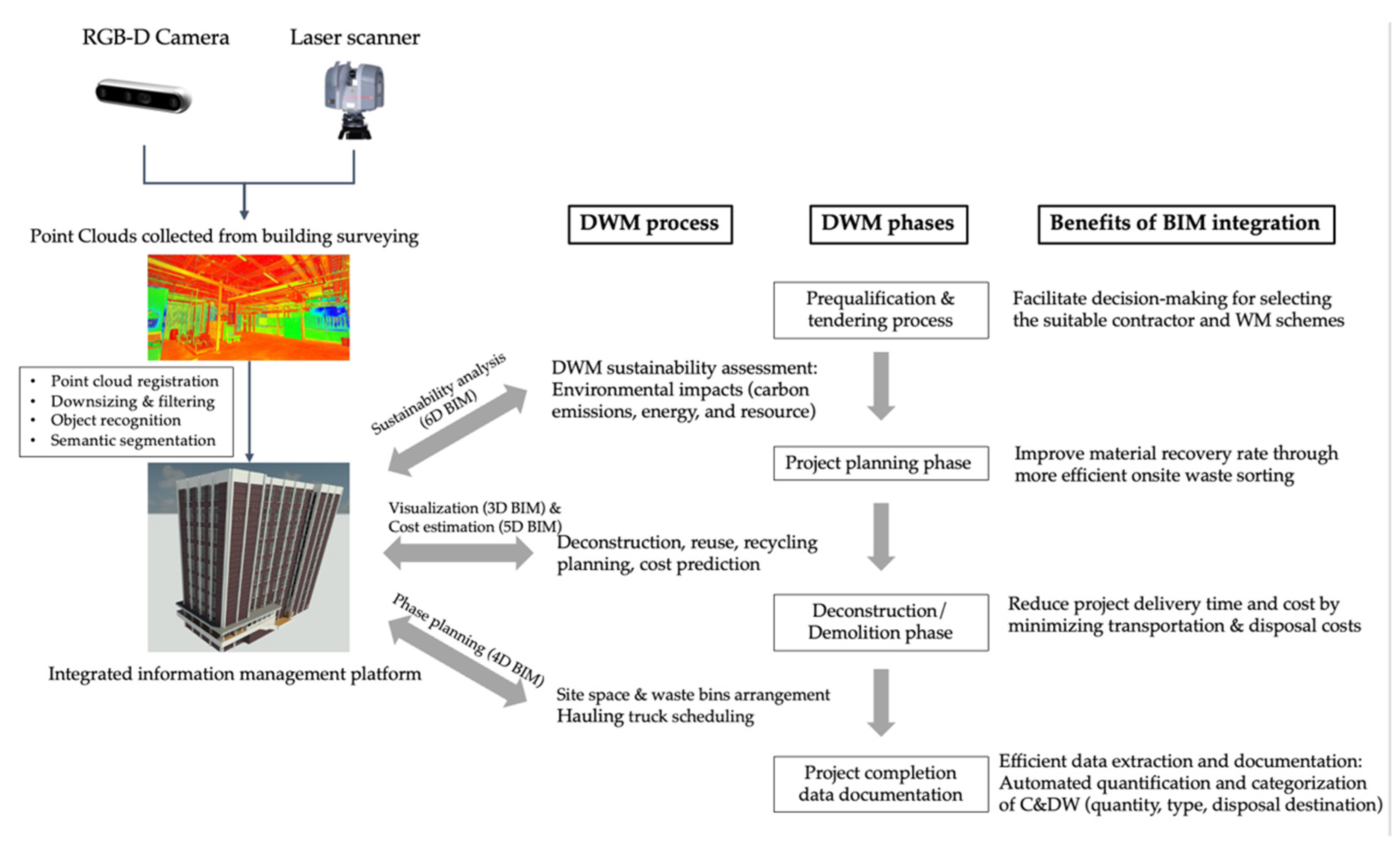
3.3. BIM for C&D Waste Management
3.3.1. BIM-Based 3D Coordination and Material Quantification for Waste Minimization
3.3.2. BIM-Based 4D Planning for Efficient Deconstruction and Onsite Waste Collection and Segregation
3.3.3. BIM-Based Cost Analysis for Enhancing the Cost-Effectiveness of C&DWM
3.3.4. BIM-Based LCA for Appraising the Sustainability Performance of C&DWM
3.3.5. BIM-Based Collaboration for Tackling Managerial and Cultural Barriers
4. Discussion
4.1. Challenges of Adopting BIM in DWM for Existing Buildings
4.1.1. Constructing the BIM Models for Existing Buildings without Up-to-Date Drawings
4.1.2. Engaging BIM-Based DWM with the Deconstruction Planning Process
4.2. Research Agenda
4.2.1. How to Effectively Collect and Integrate Building Data by Using Different Data Capturing Techniques
4.2.2. How to Improve the Efficiency of Converting Collected Data into Semantic BIM Objects
4.2.3. How to Aid Designers to Evaluate the Sustainability of Various DWM Scenarios
5. Conclusions
- The inefficient building data acquisition and integration process due to limitations of individual data-capturing techniques and the incompatibility of different data sources
- The error-prone, time-consuming object recognition and semantic labelling process for converting point clouds into BIMs with adequate LoD for DWM applications
- Existing waste management software and inherent waste analytic functionalities are not compatible with BIM, thus making them detached from the BIM-based design process
- Improving the efficiency and quality of data acquisition by deploying various data-capturing tools
- Realizing an automated conversion from point cloud to BIM by identifying the best combinations of algorithms for object recognition and semantic labelling
- Extending BIM-based sustainability analysis to the DWM domain by developing extended IFC data schema and comprehensive material databases
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, L.Y.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Tam, C.M.; Drew, D. Mapping Approach for Examining Waste Management on Construction Sites. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2004, 130, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeheyis, M.; Hewage, K.; Alam, M.S.; Eskicioglu, C.; Sadiq, R. An Overview of Construction and Demolition Waste Management in Canada: A Lifecycle Analysis Approach to Sustainability. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2013, 15, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, P.; Ripa, M.; Ulgiati, S. Exploring Environmental and Economic Costs and Benefits of a Circular Economy Approach to the Construction and Demolition Sector. A Literature Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 618–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickin, J.; Randell, P. Australian National Waste Report 2020. In Australian Government: Department of the Environment and Energy 2020; Blue Environment: Docklands, VIC, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Duan, H.; Zillante, G.; Zuo, J.; Yuan, H. Combining Life Cycle Assessment and Building Information Modelling to Account for Carbon Emission of Building Demolition Waste: A Case Study. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 3154–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.Y. Comparing the Implementation of Concrete Recycling in the Australian and Japanese Construction Industries. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Leeftink, R.B.; Rotter, V.S. Evaluation of the Economic Feasibility for the Recycling of Construction and Demolition Waste in China—The Case of Chongqing. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, L.B.; Waldmann, D. Development of a Bim-Based Web Tool as a Material and Component Bank for a Sustainable Construction Industry. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poon, C.S.; Yu, A.T.W.; Ng, L.H. On-Site Sorting of Construction and Demolition Waste in Hong Kong. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2001, 32, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, K.M.; Townsend, T.G. Estimating Construction and Demolition Debris Generation Using a Materials Flow Analysis Approach. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2247–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, J.; Cheng, J.C.P. Identifying Potential Opportunities of Building Information Modeling for Construction and Demolition Waste Management and Minimization. Autom. Constr. 2017, 79, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faniran, O.O.; Caban, G. Minimizing Waste on Construction Project Sites. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 1998, 5, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.P.; Shen, L.Y.; Hao, J.J.L.; Lu, W.S. A Model for Cost–Benefit Analysis of Construction and Demolition Waste Management Throughout the Waste Chain. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, H.; Kang, X.; Lu, W. Critical Success Factors for On-Site Sorting of Construction Waste: A China Study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, S.O.; Oyedele, L.O.; Bilal, M.; Akinade, O.O.; Alaka, H.A.; Owolabi, H.A.; Kadiri, K.O. Waste Effectiveness of the Construction Industry: Understanding the Impediments and Requisites for Improvements. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 102, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmani, M. Construction Waste Minimization in the UK: Current Pressures for Change and Approaches. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 40, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaillon, L.; Poon, C.S.; Chiang, Y.H. Quantifying the Waste Reduction Potential of Using Prefabrication in Building Construction in Hong Kong. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, V.W.Y.; Tam, C.M.; Zeng, S.X.; Ng, W.C.Y. Towards Adoption of Prefabrication in Construction. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 3642–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Su, Y.; Si, H.; Chen, J. Managerial Areas of Construction and Demolition Waste: A Scientometric Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.; Yuan, H. Exploring Critical Success Factors for Waste Management in Construction Projects of China. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2010, 55, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gálvez-Martos, J.L.; Styles, D.; Schoenberger, H.; Zeschmar-Lahl, B. Construction and Demolition Waste Best Management Practice in Europe. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akinade, O.; Oyedele, L.; Oyedele, A.; Davila Delgado, J.M.; Bilal, M.; Akanbi, L.; Ajayi, A.; Owolabi, H. Design for Deconstruction Using a Circular Economy Approach: Barriers and Strategies for Improvement. Prod. Plan. Control. 2019, 31, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovea, M.D.; Powell, J.C. Developments in Life Cycle Assessment Applied to Evaluate the Environmental Performance of Construction and Demolition Wastes. Waste Manag. 2016, 50, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, X.; Lenihan, H.; O’Regan, B. A Model for Assessing the Economic Viability of Construction and Demolition Waste Recycling - The Case of Ireland. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2006, 46, 302–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Duan, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, X. Quantification of Carbon Emission of Construction Waste by Using Streamlined LCA: A Case Study of Shenzhen, China. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2015, 17, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Tucker, R. Overcoming Barriers to the Reuse of Construction Waste Material in Australia: A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2017, 17, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.; Kabirifar, K.; Frimpong, B.E.; Shariati, M.; Mirmozaffari, M.; Boskabadi, A. Improving construction and demolition waste collection service in an urban area using a simheuristic approach: A case study in Sydney. Aust. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtarian, S.; Maqsood, T.; Wong, P.S.P.; Yang, R.J.; Khalfan, M. Review of waste strategy documents in Australia: Analysis of strategies for construction and demolition waste. Int. J. Environ. Technol. Manag. 2020, 23, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seror, N.; Portnov, B.A. Identifying Areas Under Potential Risk of Illegal Construction and Demolition Waste Dumping Using GIS Tools. Waste Manag. 2018, 75, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Duan, H.; Ouyang, L.; Huang, W.; Zuo, J. An Innovative Approach to Managing Demolition Waste via GIS (Geographic Information System): A Case Study in Shenzhen City, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakchan, A.; Faust, K.M.; Leite, F. Seven-Dimensional Automated Construction Waste Quantification and Management Framework: Integration with Project and Site Planning. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udawatta, N.; Zuo, J.; Chiveralls, K.; Zillante, G. Attitudinal and Behavioural Approaches to Improving Waste Management on Construction Projects in Australia: Benefits and Limitations. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2015, 15, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtarian, S.; Maqsood, T.; Wong, P.S.P.; Khalfan, M.; Yang, R.J. Market development for construction and demolition waste stream in Australia. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. Innov. 2020, 3, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtarian, S.; Caldera, S.; Maqsood, T.; Ryley, T.; Khalfan, M. An investigation into challenges and opportunities in the Australian construction and demolition waste management system. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Webber, R.; Kalutara, P.; Browne, W.; Pienaar, J. Construction and Demolition Waste Management in Australia: A Mini-Review. Waste Manag. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zuo, J.; Yuan, H.; Zillante, G.; Wang, J. Cross-Regional Mobility of Construction and Demolition Waste in Australia: An Exploratory Study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 156, 104710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.S.; Yu, A.T.W.; See, S.C.; Cheung, E. Minimizing Demolition Wastes in Hong Kong Public Housing Projects. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2004, 22, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udawatta, N.; Zuo, J.; Chiveralls, K.; Zillante, G. Improving Waste Management in Construction Projects: An Australian Study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 101, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udawatta, N.; Zuo, J.; Chiveralls, K.; Zillante, G. From Green Buildings to Living Buildings? Rating Schemes and Waste Management Practices in Australian Educational Buildings. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2021, 28, 1278–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udawatta, N.; Zuo, J.; Chiveralls, K.; Yuan, H.; George, Z.; Elmualim, A. Major Factors Impeding the Implementation of Waste Management in Australian Construction Projects. J. Green Build. 2018, 13, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinade, O.O.; Oyedele, L.O.; Ajayi, S.O.; Bilal, M.; Alaka, H.A.; Owolabi, H.A.; Arawomo, O.O. Designing Out Construction Waste Using BIM Technology: Stakeholders’ Expectations for Industry Deployment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, Q. Encouraging the Environmentally Sound Management of C&D Waste in China: An Integrative Review and Research Agenda. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.T.W.; Poon, C.S.; Wong, A.; Yip, R.; Jaillon, L. Impact of Construction Waste Disposal Charging Scheme on Work Practices at Construction Sites in Hong Kong. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poon, C.S.; Yu, A.T.W.; Wong, A.; Yip, R. Quantifying the Impact of Construction Waste Charging Scheme on Construction Waste Management in Hong Kong. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2013, 139, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinade, O.O.; Oyedele, L.O.; Munir, K.; Bilal, M.; Ajayi, S.O.; Owolabi, H.A.; Alaka, H.A.; Bello, S.A. Evaluation Criteria for Construction Waste Management Tools: Towards a Holistic BIM Framework. Int. J. Sustain. Build. Technol. Urban. Dev. 2016, 7, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newaz, M.T.; Davis, P.; Sher, W.; Simon, L. Factors Affecting Construction Waste Management Streams in Australia. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinade, O.O.; Oyedele, L.O.; Bilal, M.; Ajayi, S.O.; Owolabi, H.A.; Alaka, H.A.; Bello, S.A. Waste Minimisation Through Deconstruction: A BIM Based Deconstructability Assessment Score (BIM-DAS). Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2015, 105, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Yuan, H. A Framework for Understanding Waste Management Studies in Construction. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Won, J.; Cheng, J.C.P.; Lee, G. Quantification of Construction Waste Prevented by BIM-Based Design Validation: Case Studies in South Korea. Waste Manag. 2016, 49, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Hong, W.H.; Park, J.W.; Cha, G.W. An Estimation Framework for Building Information Modeling (BIM)-Based Demolition Waste by Type. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiyu, S.A.; Oyedele, L.O.; Akinade, O.; Owolabi, H.; Akanbi, L.; Gbadamosi, A. BIM Competencies for Delivering Waste-Efficient Building Projects in a Circular Economy. DIBE 2020, 4, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, B.C.; Leite, F.; Faust, K.M. 4D-BIM to Enhance Construction Waste Reuse and Recycle Planning: Case Studies on Concrete and Drywall Waste Streams. Waste Manag. 2020, 116, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.C.P.; Ma, L.Y.H. A BIM-Based System for Demolition and Renovation Waste Estimation and Planning. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1539–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, B.; Bulbul, T.; Pearce, A.; Thabet, W. Potential Application of BIM in Cost-Benefit Analysis of Demolition Waste Management. Constr. Res. Congr. 2014, 2014, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbarnezhad, A.; Ong, K.C.G.; Chandra, L.R. Economic and Environmental Assessment of Deconstruction Strategies Using Building Information Modeling. Autom. Constr. 2014, 37, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoghi, M.; Kim, S. Dynamic Modeling for Life Cycle Cost Analysis of BIM-Based Construction Waste Management. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanghelini, G.M.; Cherubini, E.; Soares, S.R. How Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) Is Aiding Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) in Results Interpretation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaei, F.; Zoghi, M.; Khoshand, A. Life Cycle Environmental Impact Assessment to Manage and Optimize Construction Waste Using Building Information Modeling (BIM). Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2019, 21, 784–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soust-Verdaguer, B.; Llatas, C.; García-Martínez, A. Critical Review of Bim-Based LCA Method to Buildings. Energy Build. 2017, 136, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C. Calculation of a Building’s Life Cycle Carbon Emissions Based on Ecotect and Building Information Modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.S.; Cho, K. BIM Application to Select Appropriate Design Alternative with Consideration of LCA and LCCA. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 281640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kehily, D.; Underwood, J. Embedding Life Cycle Costing in 5D BIM. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2017, 22, 145–167. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Tae, S.; Roh, S.; Kim, T. Green Template for Life Cycle Assessment of Buildings Based on Building Information Modeling: Focus on Embodied Environmental Impact. Sustainability 2015, 7, 16498–16512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jalaei, F.; Jrade, A. Integrating Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Energy Analysis Tools with Green Building Certification System to Conceptually Design Sustainable Buildings. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2014, 19, 494–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, M.; Wojtasiewicz, M.; Martínez-Rocamora, A.; Solís-Guzmán, J.; Alba-Rodríguez, M.D.; Bim, L.C.A. Integration for the Environmental Impact Assessment of the Urbanization Process. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eadie, R.; Browne, M.; Odeyinka, H.; McKeown, C.; McNiff, S. BIM Implementation Throughout the UK Construction Project Lifecycle: An Analysis. Autom. Constr. 2013, 36, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.; Lee, G. The Status of BIM Adoption on Six Continents. Int. J.; Civil, Struct. Constr. Archit. Eng. 2015, 9, 406–410. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.P.; Ma, T.; Sigh, A.B.; Zhang, C.; Hui, K.M. (2018-16) Investigation of Readiness for 4D and 5D BIM Adoption in the Australian Construction Industry. Manag. Rev. 2018, 11, 43–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, T.; Xiao, J. Estimation of Building-Related Construction and Demolition Waste in Shanghai. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2327–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Osmani, M.; Demian, P.; Baldwin, A. A BIM-Aided Construction Waste Minimisation Framework. Autom. Constr. 2015, 59, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.; Webster, C.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X. Computational Building Information Modelling for Construction Waste Management: Moving from Rhetoric to Reality. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rašković, M.; Ragossnig, A.M.; Kondracki, K.; Ragossnig-Angst, M. Clean Construction and Demolition Waste Material Cycles Through Optimised Pre-Demolition Waste Audit Documentation: A Review on Building Material Assessment Tools. Waste Manag. Res. 2020, 38, 923–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Cho, Y.K.; Kim, C. Automatic BIM Component Extraction from Point Clouds of Existing Buildings for Sustainability Applications. Autom. Constr. 2015, 56, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, H.; Dai, F.; Lourakis, M. Automated as-Built 3D Reconstruction of Civil Infrastructure Using Computer Vision: Achievements, Opportunities, and Challenges. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2015, 29, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Lee, S. Image-Based Technologies for Constructing As-Is Building Information Models for Existing Buildings. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2017, 31, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatla, A.; Choe, S.Y.; Fierro, O.; Leite, F. Evaluation of Accuracy of as-Built 3D Modeling from Photos Taken by Handheld Digital Cameras. Autom. Constr. 2012, 28, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Adan, A.; Akinci, B.; Huber, D. Automatic Creation of Semantically Rich 3D Building Models from Laser Scanner Data. Autom. Constr. 2013, 31, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, X.J.; Livesey, P.; Wang, J.; Huang, S.; He, X.; Zhang, C. Deconstruction Waste Management Through 3-d Reconstruction and Bim: A Case Study. Vis. Eng. 2017, 5, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, J.; Hong, S.; Jeong, S.; Kim, S.; Cho, H.; Hong, S.; Heo, J. Productive Modeling for Development of as-Built BIM of Existing Indoor Structures. Autom. Constr. 2014, 42, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Jung, J.; Kim, S.; Cho, H.; Lee, J.; Heo, J. Semi-Automated Approach to Indoor Mapping for 3D as-Built Building Information Modeling. Comput. Environ. Urban. Syst. 2015, 51, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, R.; Luu, T.H.; Mueller-Roemer, J.S.; Sevilmis, N.; Schultmann, F. Deconstruction Project Planning of Existing Buildings Based on Automated Acquisition and Reconstruction of Building Information. Autom. Constr. 2018, 91, 226–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Li, J.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Yang, M.; Chen, D. A BIM-LCA Approach for Estimating the Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Large-Scale Public Buildings: A Case Study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Shi, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, S. A BIM-Based Construction and Demolition Waste Information Management System for Greenhouse Gas Quantification and Reduction. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Vilariño, L.; Lagüela, S.; Armesto, J.; Arias, P. Semantic As-Built 3D Models Including Shades for the Evaluation of Solar Influence on Buildings. Sol. Energy 2013, 92, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keeffe, S.; Bosché, F. The Need for Convergence of BIM and 3D Imaging in the Open World. CITA BIM Gather. 2015, 1, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.A.; Yeoh, J.K.W. BIM for Existing Buildings: Potential Opportunities and Barriers. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.K.W.; Ge, J.; He, S.X. Digitisation in Facilities Management: A Literature Review and Future Research Directions. Autom. Constr. 2018, 92, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.K.W.; Zhou, J. Enhancing Environmental Sustainability over Building Life Cycles Through Green BIM: A Review. Autom. Constr. 2015, 57, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanbi, L.A.; Oyedele, L.O.; Akinade, O.O.; Ajayi, A.O.; Davila Delgado, M.; Bilal, M.; Bello, S.A. Salvaging Building Materials in a Circular Economy: A BIM-Based Whole-Life Performance Estimator. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2018, 129, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barki, H.; Fadli, F.; Shaat, A.; Boguslawski, P.; Mahdjoubi, L. BIM Models Generation from 2D CAD Drawings and 3D Scans: An Analysis of Challenges and Opportunities for AEC Practitioners. Build. Inf. Model. (BIM) Des. Constr. Oper. 2015, 1, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz-Vilariño, L.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.; Lagüela, S.; Armesto, J.; Khoshelham, K. Door Recognition in Cluttered Building Interiors Using Imagery and LiDAR Data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial. Inf. Sci. ISPRS Arch. 2014, 40, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Eybpoosh, M.; Akinci, B. Developing as-Built Building Information Model Using Construction Process History Captured by a Laser Scanner and a Camera. In Proceedings of the Construction Research Congress Construction Challenges in a Flat World, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 21–23 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Patraucean, V.; Armeni, I.; Nahangi, M.; Yeung, J.; Brilakis, I.; Haas, C. State of Research in Automatic As-Built Modelling. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction and Mining: Connected to the Future, Oulu, Finland, 15–18 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Volk, R.; Stengel, J.; Schultmann, F. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Existing Buildings– Literature Review and Future Needs. Autom. Constr. 2014, 38, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Huang, S.; Zhao, L.; Ge, J.; He, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X. High Quality 3D Reconstruction of Indoor Environments Using RGB-D Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, ICIEA 2017, Siem Reap, Cambodia, 18–20 June 2017; pp. 1739–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; Costa, A.A.; Silvestre, J.D.; Pyl, L. Integration of LCA and LCC Analysis Within a BIM-Based Environment. Autom. Constr. 2019, 103, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; Costa, A.A.; Silvestre, J.D.; Pyl, L. Informetric Analysis and Review of Literature on the Role of BIM in Sustainable Construction. Autom. Constr. 2019, 103, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.P.; Alecrim, I.; Bragança, L.; Mateus, R. Integrating BIM-Based LCA and Building Sustainability Assessment. Sustainability 2020, 12, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, D.; Kalantari, M.; Rajabifard, A. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Construction and Demolition Waste Management in Australia: A Research Agenda. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12983. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132312983
Han D, Kalantari M, Rajabifard A. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Construction and Demolition Waste Management in Australia: A Research Agenda. Sustainability. 2021; 13(23):12983. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132312983
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Dongchen, Mohsen Kalantari, and Abbas Rajabifard. 2021. "Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Construction and Demolition Waste Management in Australia: A Research Agenda" Sustainability 13, no. 23: 12983. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132312983
APA StyleHan, D., Kalantari, M., & Rajabifard, A. (2021). Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Construction and Demolition Waste Management in Australia: A Research Agenda. Sustainability, 13(23), 12983. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132312983







