Modeling and Analysis of Interorganizational Knowledge Transfer Considering Reputation Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Interorganizational Knowledge Transfer
2.2. Role of Reputation Mechanisms
2.3. Evolutionary Game Theory in ION
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Mathematical Model
3.2. Evolutionary Model
3.3. Network Model
4. Methodology
4.1. Reputation Mechanisms
4.2. Learning Dynamics Based on Reputation Mechanisms
5. Results and Discussion
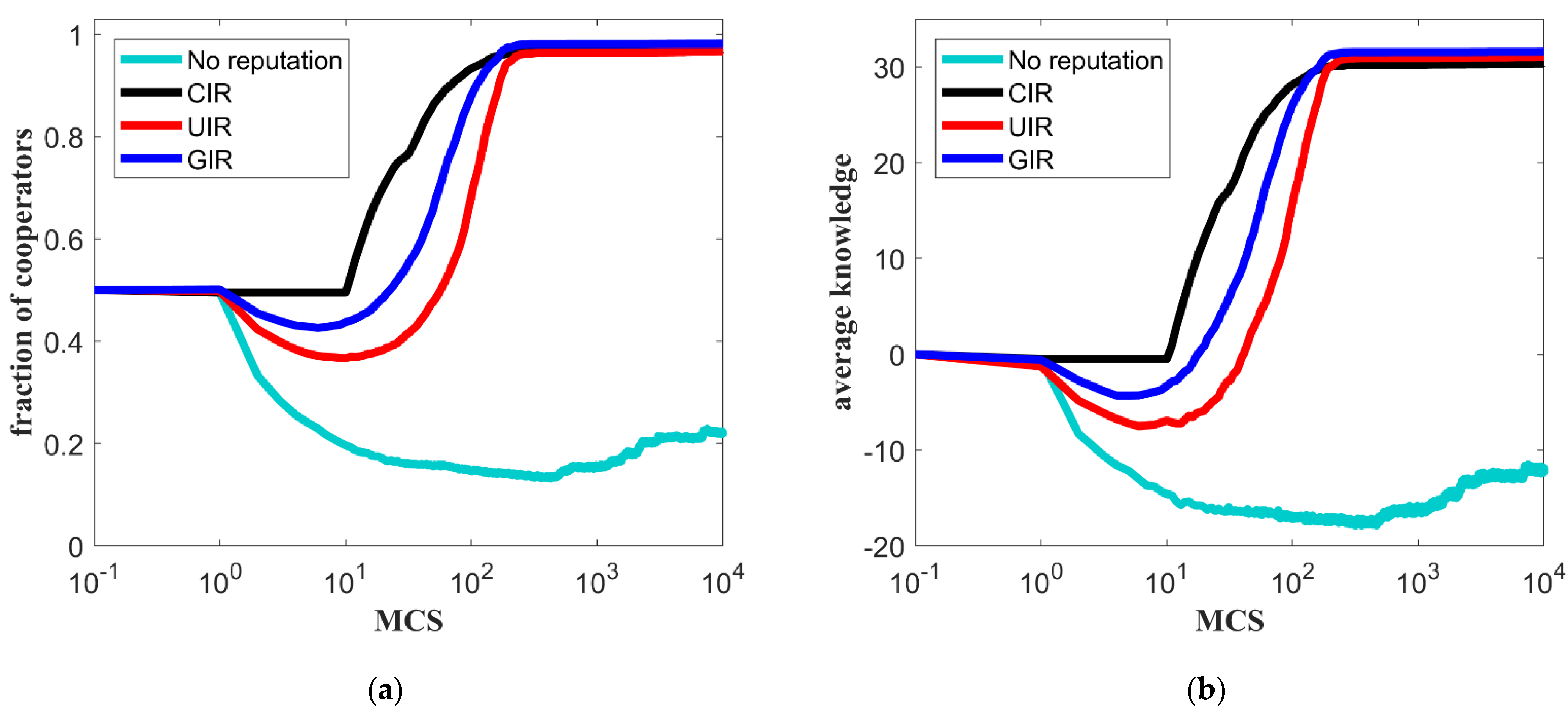
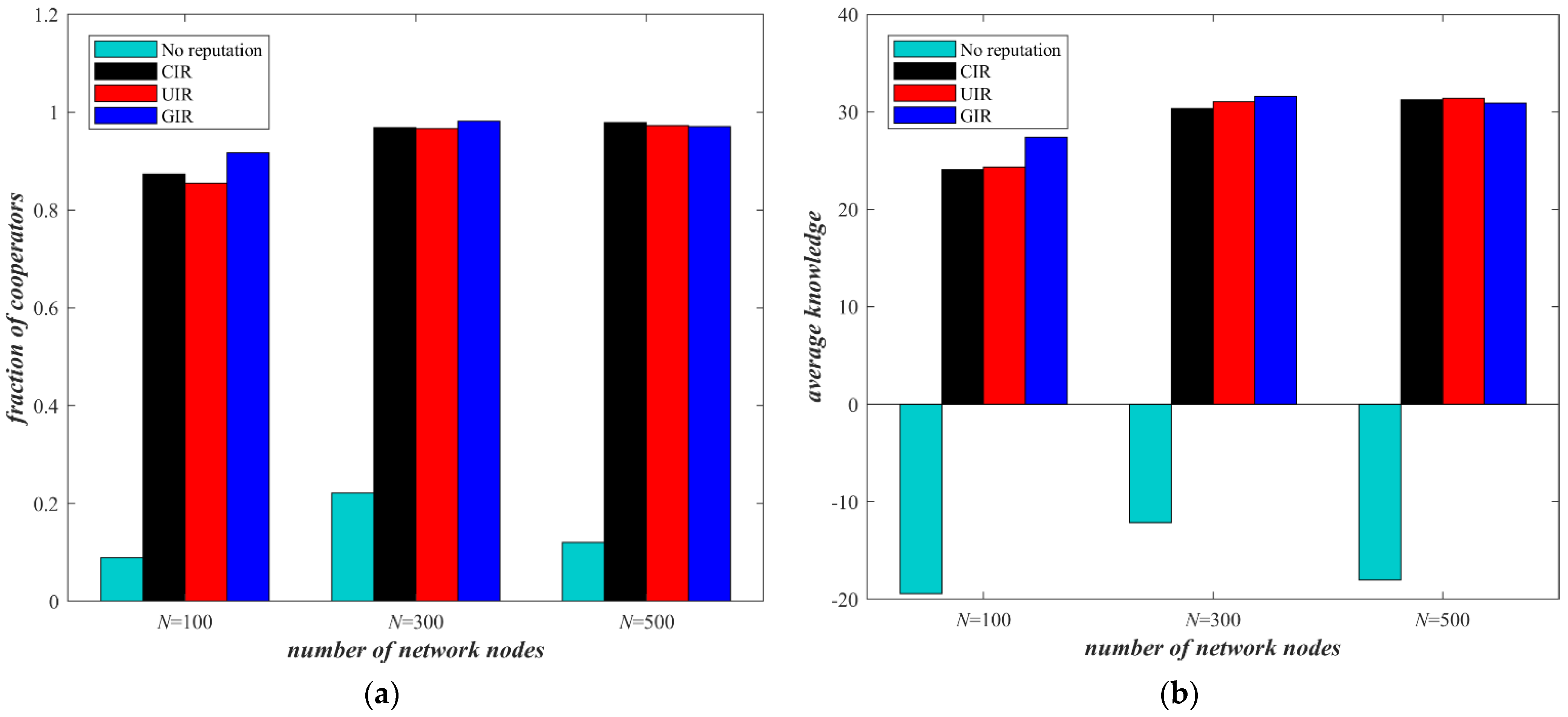
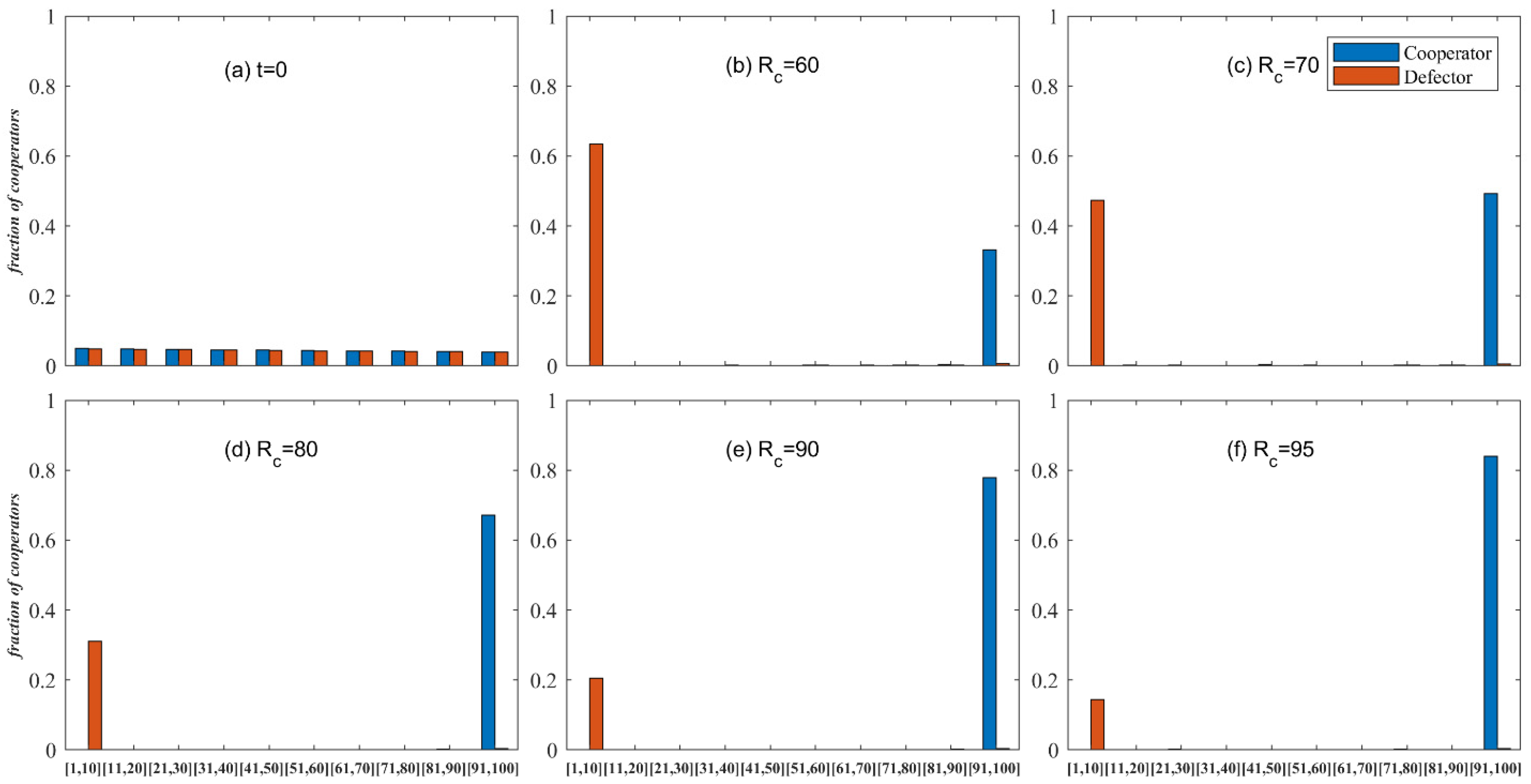
5.1. The Influence of Initial Reputation Distribution on Knowledge Transfer
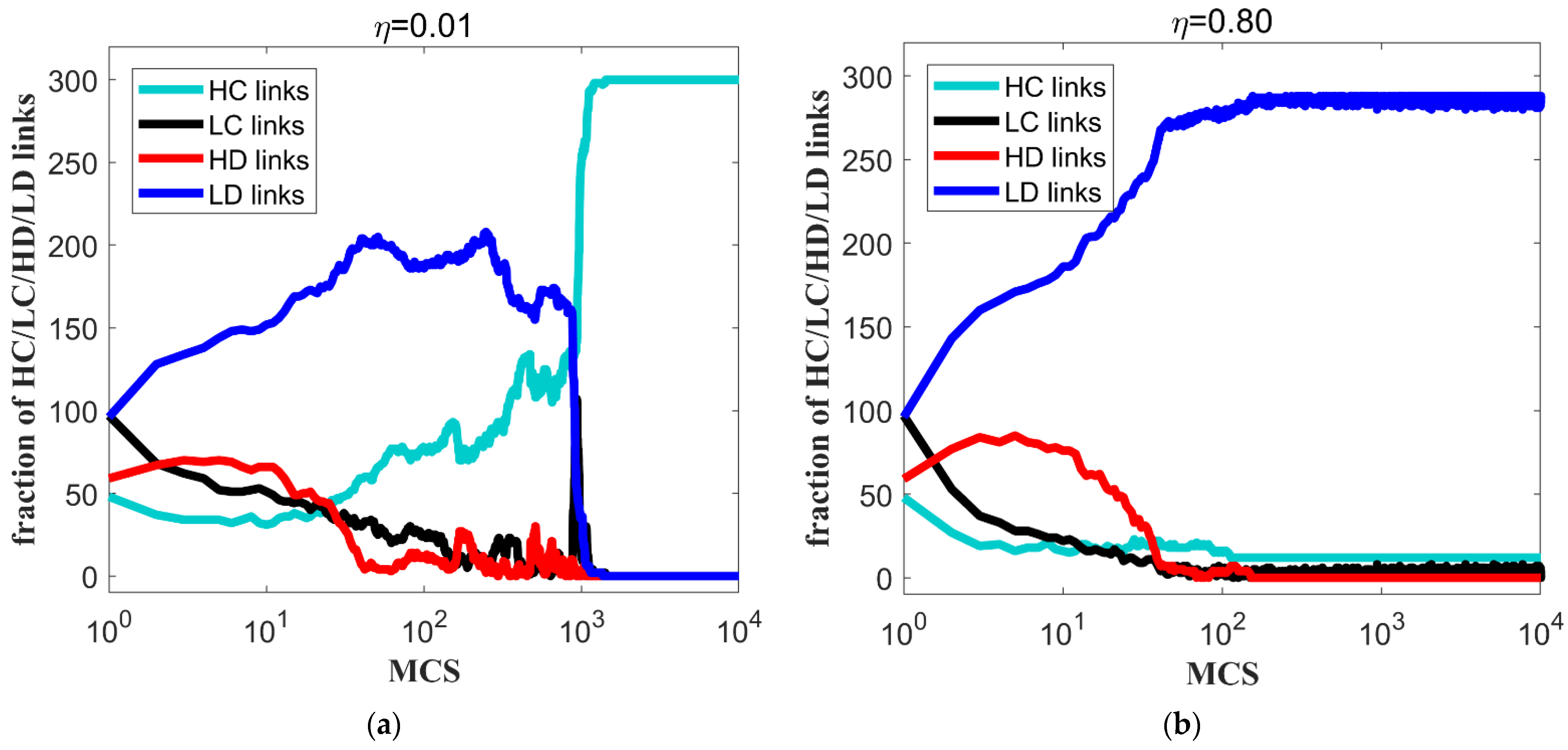
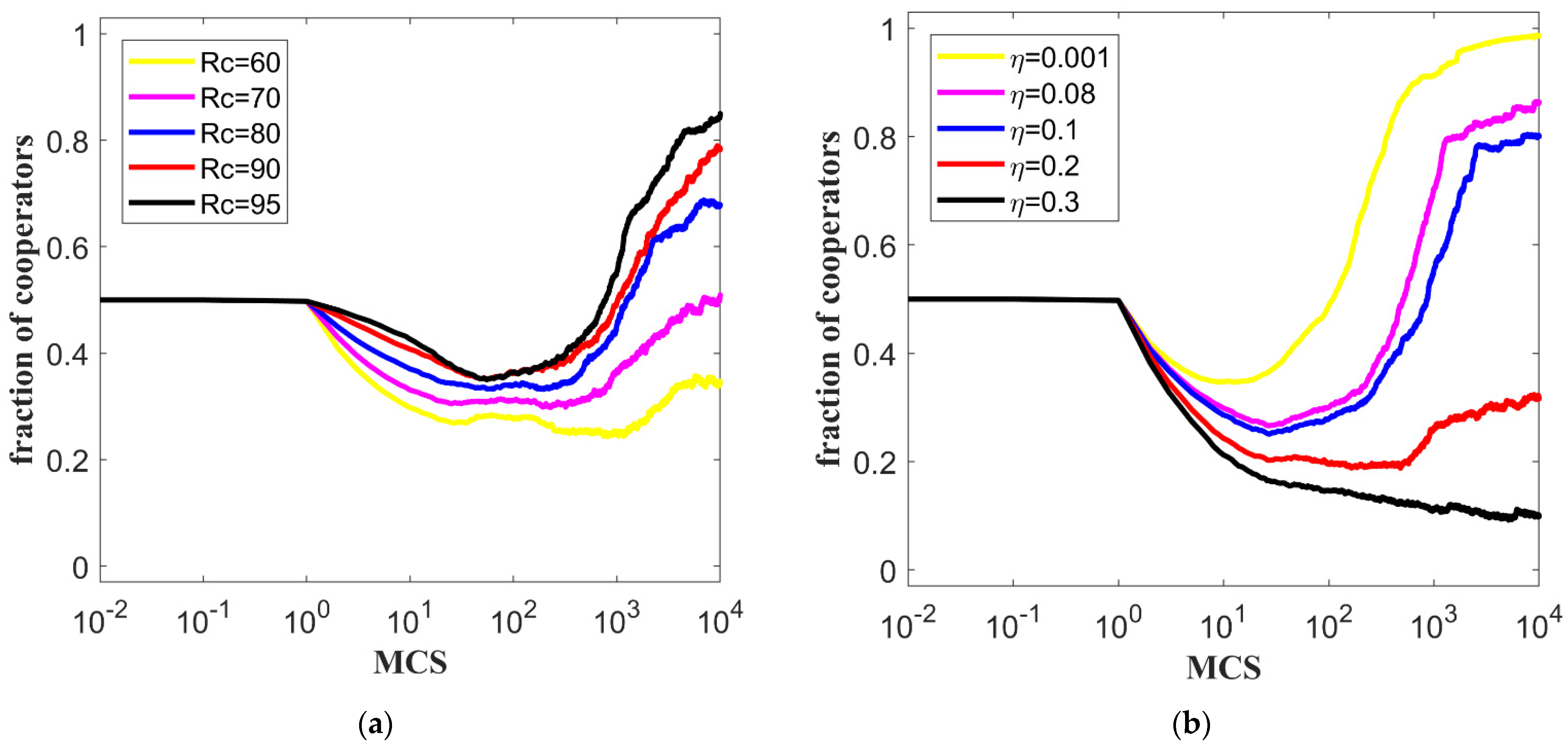
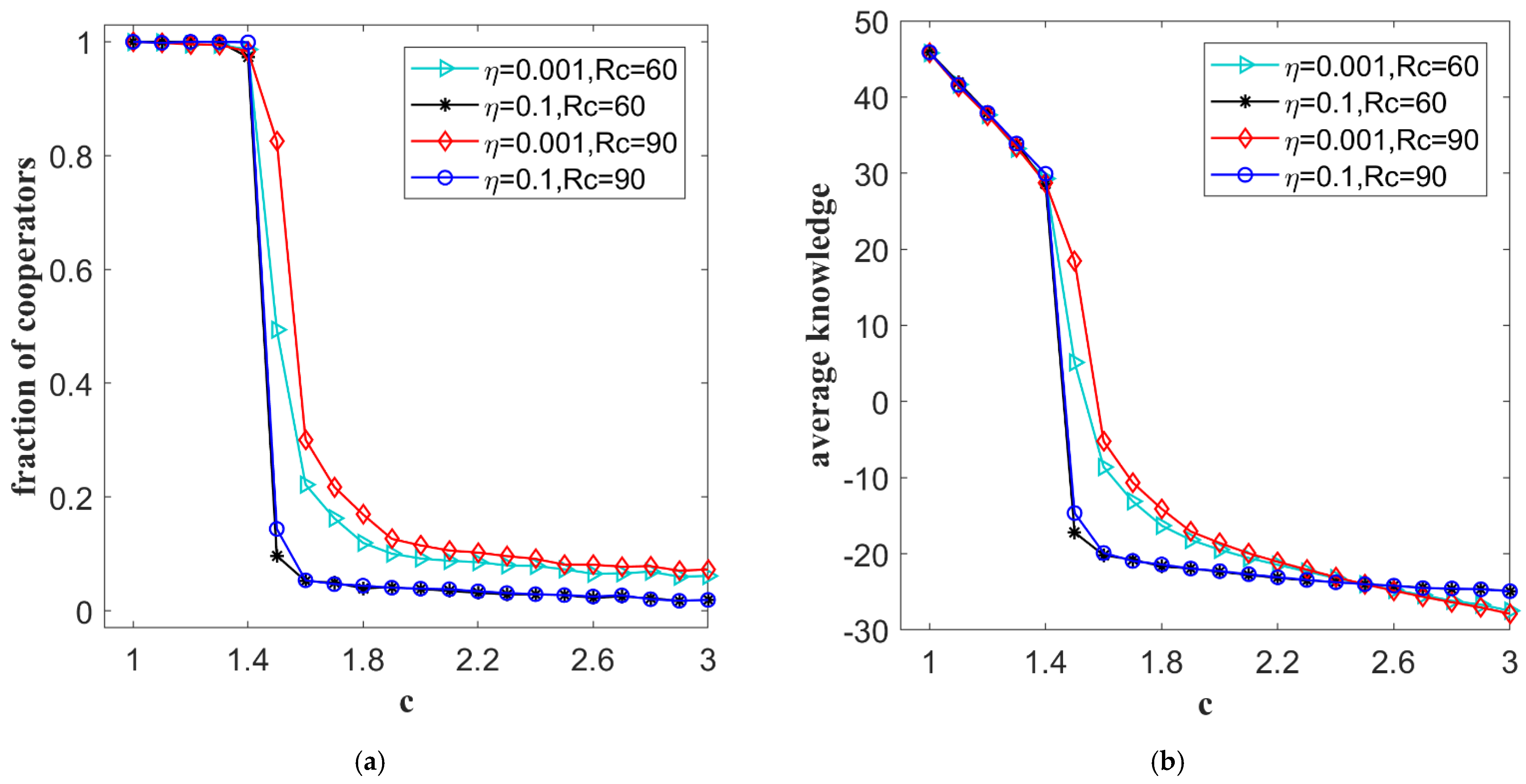
5.2. The Influence of Reputation Threshold and Multiplicative Factor on Knowledge Transfer
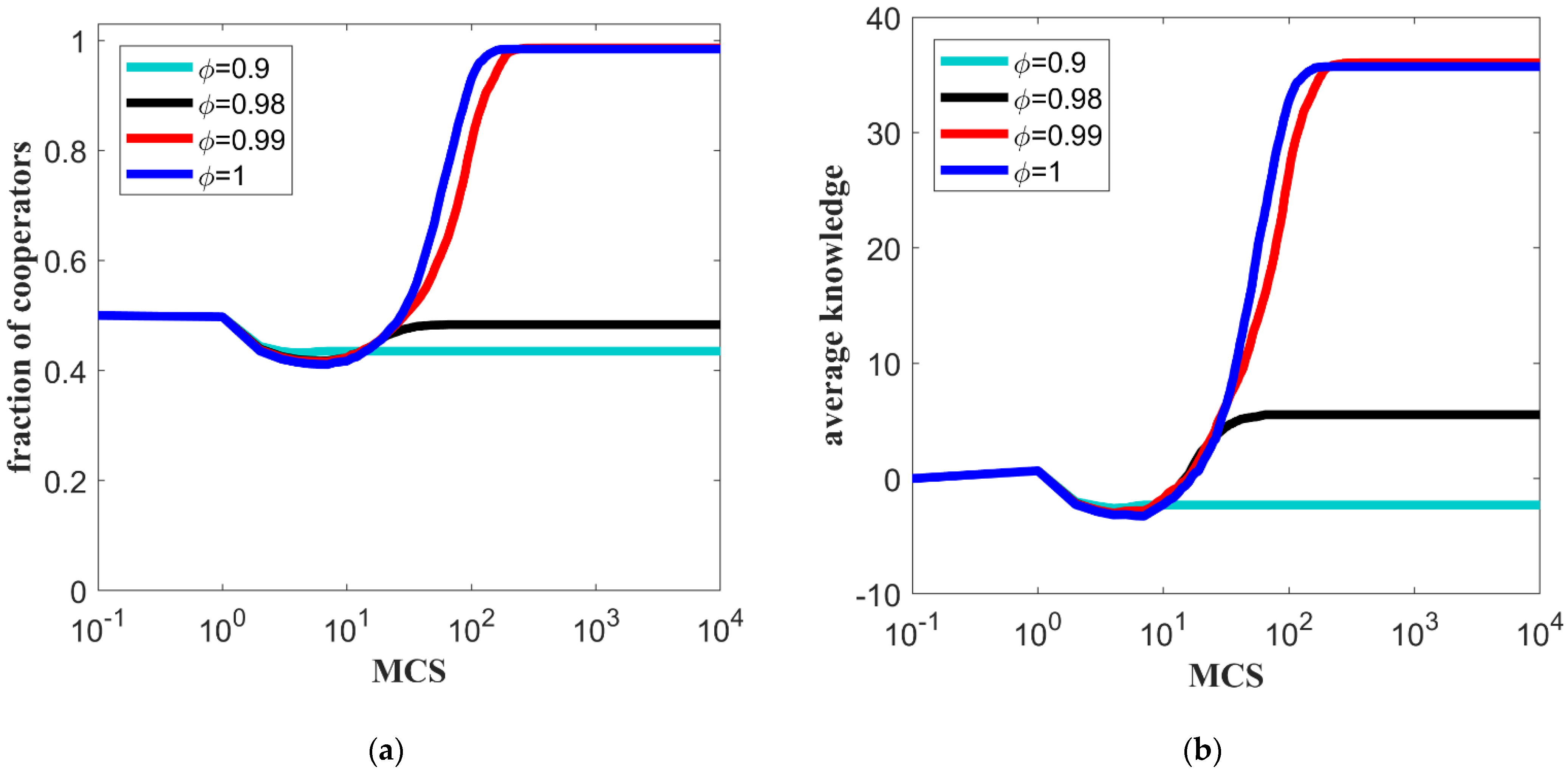
5.3. The Influence of Decaying Rate of Reputation on Knowledge Transfer
6. Conclusions and Implications
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| number of existing nodes connected to a new node at each time step | |
| number of nodes in an original ION | |
| ultimately ION with and | |
| knowledge transfer absorption efficiency of knowledge agent i | |
| comprehension and application ability of knowledge agent i | |
| length of the stock knowledge time window of knowledge agent i | |
| the depreciation rate of stock knowledge of knowledge agent i | |
| own stock knowledge of agent i in an ION | |
| amount of knowledge transferred from agent i to agent j | |
| amount of knowledge transferred from agent j to agent i | |
| collaboration level between agents | |
| knowledge complementarity of agent i | |
| the trust level of agent i to agent j | |
| knowledge transfer cost coefficient of agent i | |
| collaboration cost coefficient of agent i | |
| reward coefficient obtained when agent i selects knowledge transfer | |
| penalties for opportunism, or free-riding, or non-transfer | |
| revenue function of knowledge transfer of agent i in ION | |
| profit matrix of evolutionary game | |
| the payoff if agent i and agent j both select the transfer strategy at time t | |
| the payoff if agent i and agent j select the (transfer, non-transfer) strategy at time t | |
| the payoff if agent i and agent j select the (non-transfer, transfer) strategy at time t | |
| the payoff if agent i and agent j both select the non-transfer strategy at time t | |
| knowledge absorption capacity function of agent i | |
| the strategy of agent i | |
| 1 if agent i transfers knowledge at time t, otherwise being 0 | |
| accumulated payoffs of agent i at time t in ION | |
| decaying rate of a reputation effect | |
| reputation value of agent i at time t | |
| high reputation standard value | |
| the multiplicative factor of high reputation | |
| improved coevolutionary rule | |
| the proportion of agents choosing knowledge transfer at time t in ION | |
| average knowledge transfer of agents at time t in ION |
References
- Marchiori, D.; Franco, M. Knowledge transfer in the context of inter-organizational networks: Foundations and intellectual structures. J. Innov. Knowl. 2020, 5, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stjerne, I.S.; Söderlund, J.; Minbaeva, D. Crossing times: Temporal boundary-spanning practices in interorganizational projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2019, 37, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, P.J.; Glaister, K.W.; Klijn, E.; Tan, H. Knowledge Accession and Knowledge Acquisition in Strategic Alliances: The Impact of Supplementary and Complementary Dimensions. Br. J. Manag. 2009, 20, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Understanding cooperative behavior of agents with heterogeneous perceptions in dynamic networks. Physica A 2018, 509, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autant-Bernard, C.; Fadairo, M.; Massard, N. Knowledge diffusion and innovation policies within the European regions: Challenges based on recent empirical evidence. Res. Policy 2013, 42, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, S.-C.; Yang, C.-W.; Hsu, W.-Y. Inter-organizational knowledge transfer: The perspective of knowledge governance. J. Knowl. Manag. 2013, 17, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T. Cooperation by design: Structure and cooperation in interorganizational networks. J. Bus. Res. 2005, 58, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Z.; Zhu, X.Y.; Guan, J. Evolution of knowledge transfer network of R&D team in manufacturing enterprises based on evolutionary game theory. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2018, 33, 145–156. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, M.A. Five rules for the evolution of cooperation. Science 2006, 314, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, J.S.; Li, Y. The institutional antecedent to firms’ interorganizational network portfolios: Evidence from China. Public Relat. Rev. 2019, 45, 101776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sáez, P.; Cruz-González, J.; Navas-López, J.E.; del Mar Perona-Alfageme, M. Organizational integration mechanisms and knowledge transfer effectiveness in MNCs: The moderating role of cross-national distance. J. Int. Manag. 2021, 27, 100872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X. Knowledge transfer efficiency measurement with application for open innovation networks. Int. J. Technol. Manag. 2019, 81, 118–142. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, R.M. Toward a knowledge-based theory of the firm. Strateg. Manag. J. 1996, 17, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, K.Z. Governing interfirm knowledge transfer in the Chinese market: The interplay of formal and informal mechanisms. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2013, 42, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, G.E.; Greiner, B.; Ockenfels, A. Engineering trust: Reciprocity in the production of reputation information. Manag. Sci. 2013, 59, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kreps, D.M.; Wilson, R. Reputation and imperfect information. J. Econ. Theory 1982, 27, 253–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimpel-Leal, K.; Lettice, F. Generative Mechanisms for Scientific Knowledge Transfer in the Food Industry. Sustainability 2021, 13, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, D.G.; Arbesman, S.; Christakis, N.A. Dynamic social networks promote cooperation in experiments with humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19193–19198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, L.H.; Liu, T. Knowledge transfer in buyer-supplier relationships: The role of transactional and relational governance mechanisms. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 78, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.; Makarius, E.E.; Stevens, C.E. A reputation transfer perspective on the internationalization of emerging market firms. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 123, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, J. Risk, uncertainty and governance in megaprojects: A critical discussion of alternative explanations. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2012, 30, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtinen, J.; Peltokorpi, A.; Artto, K. Megaprojects as organizational platforms and technology platforms for value creation. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2019, 37, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klessova, S.; Thomas, C.; Engell, S. Structuring inter-organizational R&D projects: Towards a better understanding of the project architecture as an interplay between activity coordination and knowledge integration. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2020, 38, 291–306. [Google Scholar]
- Gnyawali, D.R.; Park, B.-J. Co-opetition between giants: Collaboration with competitors for technological innovation. Res. Policy 2011, 40, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wang, L.; Zeng, S. Inter-organizational knowledge acquisition and firms’ radical innovation: A moderated mediation analysis. J. Bus. Res. 2018, 90, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudambi, R.; Piscitello, L.; Rabbiosi, L. Reverse Knowledge Transfer in MNEs: Subsidiary Innovativeness and Entry Modes. Long Range Plan. 2014, 47, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, C. Evolutionary Game Simulation of Knowledge Transfer in Industry-University-Research Cooperative Innovation Network under Different Network Scales. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Y. Knowledge diffusion simulation of knowledge networks: Based on complex network evolutionary algorithms. Cluster Comput. 2019, 22, 15255–15265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Bai, Q.; Sindakis, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, T. Vulnerability of multinational corporation knowledge network facing resource loss. Manag. Decis. 2019, 59, 84–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geneste, L.; Galvin, P. Trust and knowledge acquisition by small and medium-sized firms in weak client–firm exchange relationships. Int. Small Bus. J. 2015, 33, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenyan, J.; Büyüközkan, G.; Feyzioğlu, O. Modeling collaboration formation with a game theory approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 2073–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Raahemi, B.; Benyoucef, M. Knowledge sharing in dynamic virtual enterprises: A socio-technological perspective. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2011, 24, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, K.Y.J.; Robins, J.A. Finding Knowledge: The Role of Reputation in Knowledge-Transfer to Chinese Companies. Long Range Plan. 2014, 47, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balboni, B.; Marchi, G.; Vignola, M. Knowledge transfer in the context of buyer-supplier relationship: An analysis of a supplier’s customer portfolio. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 80, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabher, G. Temporary Architectures of Learning: Knowledge Governance in Project Ecologies. Organ. Stud. 2004, 25, 1491–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkpen, A.C. Knowledge transfer and international joint ventures: The case of NUMMI and General Motors. Strateg. Manag. J. 2008, 29, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbig, P.; Milewicz, J.; Golden, J. A model of reputation building and destruction. J. Bus. Res. 1994, 31, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, G.E.; Ockenfels, A.; Ebeling, F. Information value and externalities in reputation building. Int. J. Ind. Organ. 2011, 29, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Wang, L.; Sun, S.W.; Wang, J.; Xia, C.-Y. Evolution of cooperation in the spatial public goods game with adaptive reputation assortment. Phys. Lett. A 2016, 380, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y. Cross-over effects of corporate reputation and store image: Role of knowledge and involvement. Manag. Decis. 2019, 57, 3096–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havakhor, T.; Soror, A.A.; Sabherwal, R. Diffusion of knowledge in social media networks: Effects of reputation mechanisms and distribution of knowledge roles. Inf. Syst. J. 2018, 28, 104–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallo, E.; Yan, C. The effects of reputational and social knowledge on cooperation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3647–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quan, J.; Tang, C.; Wang, X. Reputation-based discount effect in imitation on the evolution of cooperation in spatial public goods games. Physica A 2021, 563, 125488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, T.; Tran, L.; Krumme, C.; Rand, D.G. The value of reputation. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 2791–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barabási, A.L.; Albert, R.; Jeong, H. Mean-field theory for scale-free random networks. Physica A 1999, 272, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.-B. Information fusion based on reputation and payoff promotes cooperation in spatial public goods game. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 368, 124805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Liu, S.; Bai, Y. Reputation-based co-evolutionary model promotes cooperation in prisoner’s dilemma game. Phys. Lett. A 2020, 384, 126233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xue, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Q.; Luo, X. Major Knowledge Diffusion Paths of Megaproject Management: A Citation-Based Analysis. Proj. Manag. J. 2020, 51, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.-G.; Yi, S.-P. Modeling and analysis knowledge transmission process in complex networks by considering internalization mechanism. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 143, 110593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Chen, W.; Lang, Y.F. Knowledge dynamic growth in the innovation network of industrial cluster: Based on process perspective. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2015, 30, 431–441. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Zhang, Q. Time scales of knowledge transfer with learning and forgetting. Physica A 2019, 525, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.G.; Wang, Y.T.; Chen, T.Q. The intertemporal evolution model of enterprise R&D cooperative network. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2019, 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sakakibara, M. Knowledge sharing in cooperative research and development. Manag. Decis. Econ. 2003, 24, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joseph, K.; Thevaranjan, A. Monitoring and incentives in sales organizations: An agency-theoretic perspective. Mark. Sci. 1998, 17, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, M.; Li, N. Scale-free network provides an optimal pattern for knowledge transfer. Physica A 2010, 389, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P. Individual choice and reputation distribution of cooperative behaviors among heterogeneous groups. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2015, 77, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Hauert, C.; Nowak, M.A.; Wang, L. Reputation-based partner choice promotes cooperation in social networks. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 78, 026117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cong, R.; Wu, B.; Qiu, Y.Y.; Wang, L. Evolution of cooperation driven by reputation-based migration. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35776. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Chu, C.; Shen, C.; Shi, L. Reputation-based coevolution of link weights promotes cooperation in spatial prisoner’s dilemma game. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2018, 109, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, G.; Yu, L.; Shi, B.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z. Rigorous or tolerant: The effect of different reputation attitudes in complex networks. Futur. Gener. Comp. Syst. 2018, 83, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, T. Dynamic Evolution of Knowledge Sharing Behavior among Enterprises in the Cluster Innovation Network Based on Evolutionary Game Theory. Sustainability 2019, 12, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Knowledge Transfer j | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| C | D | ||
| knowledge transfer i | C | ||
| D | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Guo, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, D. Modeling and Analysis of Interorganizational Knowledge Transfer Considering Reputation Mechanisms. Sustainability 2021, 13, 14020. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132414020
Huang X, Guo P, Wang X, Wang D. Modeling and Analysis of Interorganizational Knowledge Transfer Considering Reputation Mechanisms. Sustainability. 2021; 13(24):14020. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132414020
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xiaoxia, Peng Guo, Xiaonan Wang, and Ding Wang. 2021. "Modeling and Analysis of Interorganizational Knowledge Transfer Considering Reputation Mechanisms" Sustainability 13, no. 24: 14020. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132414020
APA StyleHuang, X., Guo, P., Wang, X., & Wang, D. (2021). Modeling and Analysis of Interorganizational Knowledge Transfer Considering Reputation Mechanisms. Sustainability, 13(24), 14020. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132414020






