Objective Sustainability Assessment in the Digital Economy: An Information Entropy Measure of Transparency in Corporate Sustainability Reporting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Transparency in Sustainability Reporting
2.2. Corporate Sustainability Reporting Practices
2.3. Information Entropy as a Measure of Transparency
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Building and Validating a Sustainability Dictionary
3.1.1. Data Collection, Filtering, and Extraction
3.1.2. Quality Evaluation
3.1.3. A Dictionary Probability Space and Information Entropy Measure
- 1.
- qj> 0; i.e., the words in S have a nonzero probability of occurrence in R.
- 2.
- 0 log= 0
- 3.
- p log= ∞
3.2. Interpreting and Applying the Entropy Measure in Practice
4. Results
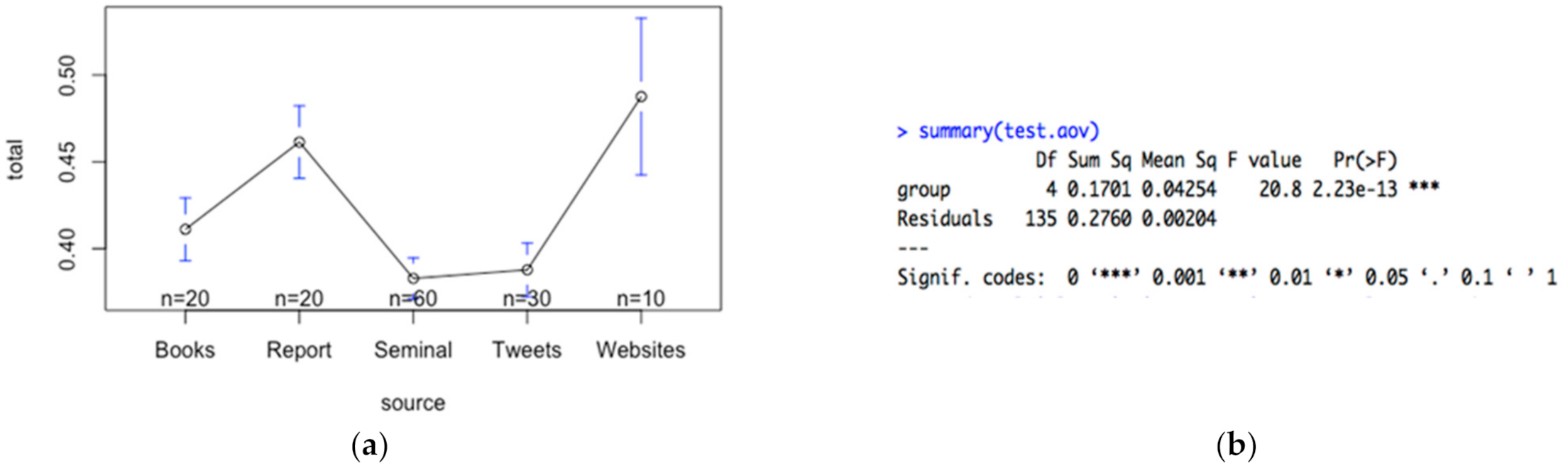
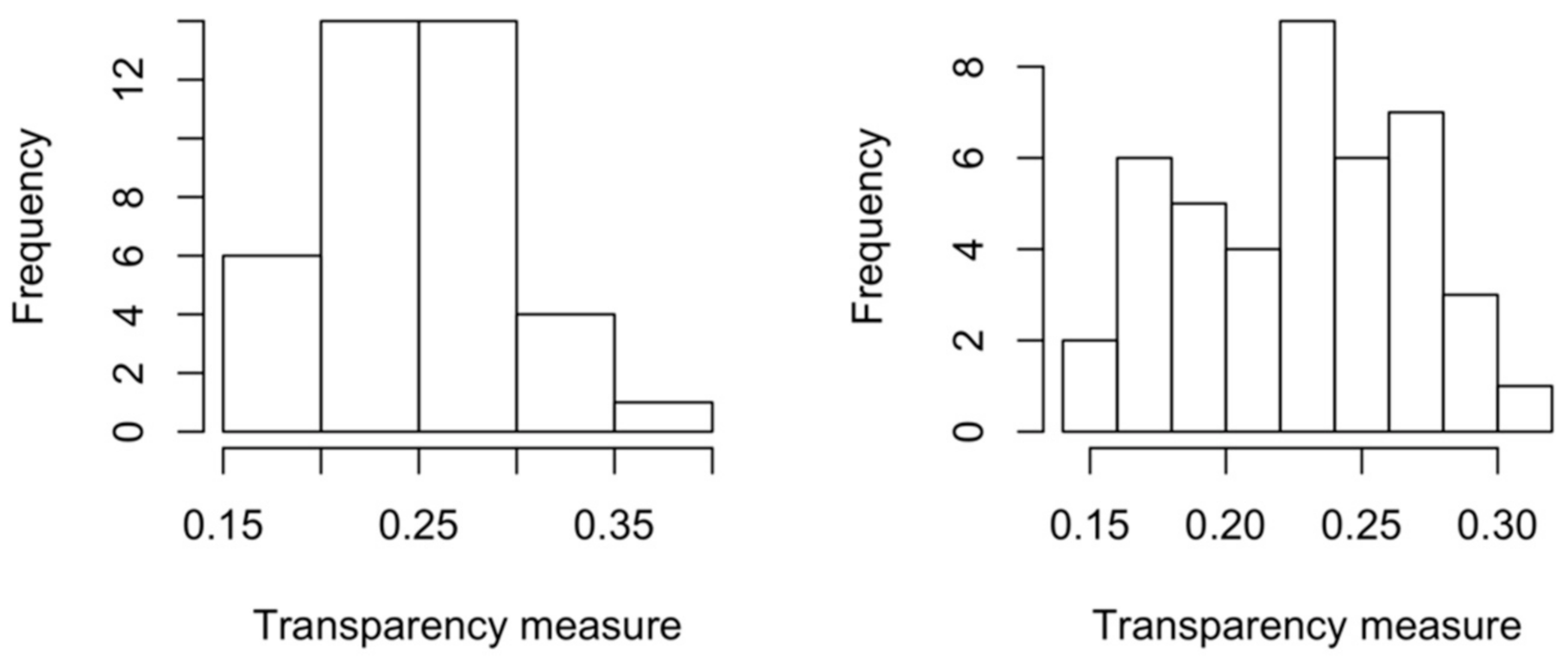
4.1. Entropy-Based Evaluation of the Sustainability Dictionary
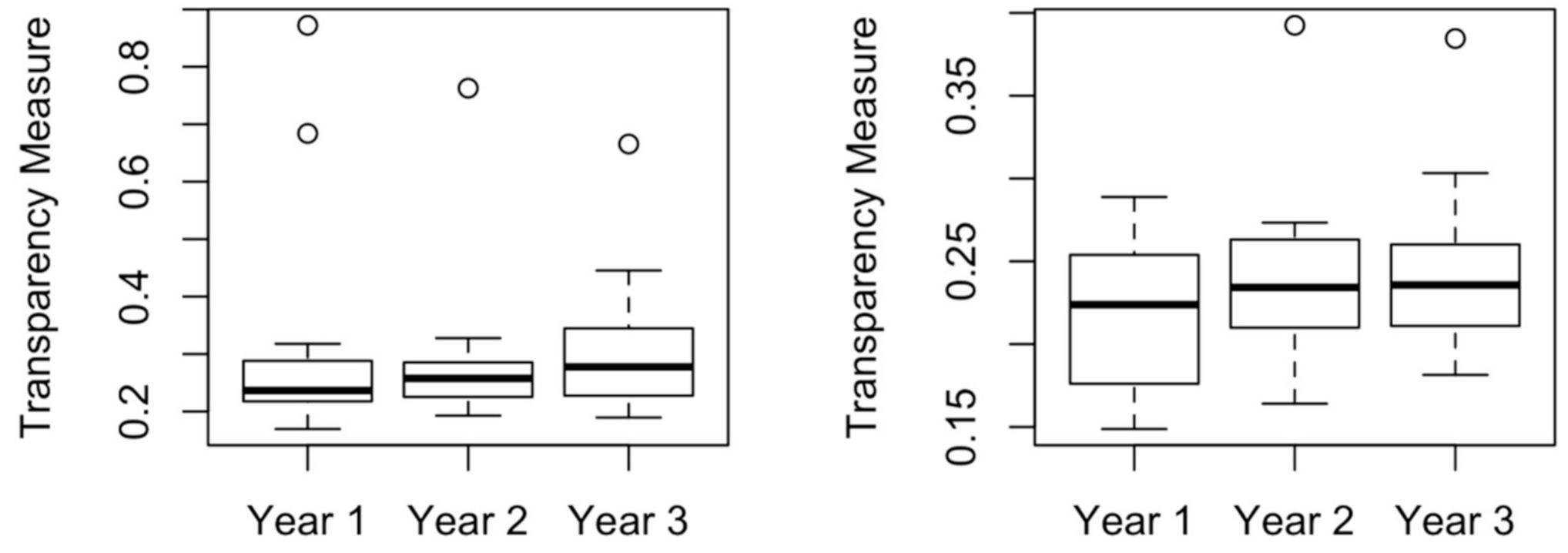
4.2. Applying the Measure of Transparency
4.2.1. Transparency Measures for Selected OPEC and Non-OPEC Firms
4.2.2. Examining the Quality of the Transparency Measure
4.2.3. Comparing OPEC with Non-OPEC
5. Discussion
5.1. Addressing the Subjective Nature of Existing Measures
5.2. Applying the Objective Measure to Compare Producers in the Energy Sector
5.3. Comparison with CSR Rankings
6. Research Contributions
6.1. Theoretical Contributions
6.2. Practical Contributions
7. Conclusions, Limitations, and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Source Set 1: Research Publications on Sustainability | |
| Source | Citation Count |
| Malhotra, A.; Melville, N.P.; Watson, R.T. Spurring impactful research on information systems for environmental sustainability. MIS Q. 2013, 37, 1265–1274. | 259 |
| Martins, C.I.M.; Eding, E.H.; Verdegem, M.C.; Heinsbroek, L.T.; Schneider, O.; Blancheton, J.P.; Verreth, J.A.J. New developments in recirculating aquaculture systems in Europe: A perspective on environmental sustainability. Aquac. Eng. 2010, 43, 83–93. | 694 |
| Mol, A.P.J. Boundless biofuels? Between environmental sustainability and vulnerability. Sociol. Rralis 2007, 47, 297–315. | 238 |
| Chappells, H.; Shove, E. Debating the future of comfort: environmental sustainability, energy consumption and the indoor environment. Build. Res. Inf. 2005, 33, 32–40. | 486 |
| Basiago, A.D. “Economic, social, and environmental sustainability in development theory and urban planning practice.” Environ. 1998, 19, 145–161. | 491 |
| Barbier, E.B.; Markandya, A.; Pearce, D.W. Environmental sustainability and cost-benefit analysis. Environ. Plan. A 1990, 22, 1259–1266. | 272 |
| Morelli, John. Environmental sustainability: A definition for environmental professionals. J. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 1, 2. | 609 |
| Goodland, R.; Daly, H. Environmental sustainability: Universal and non-negotiable. Ecol. Appl. 1996, 6, 1002–1017. | 798 |
| Moldan, B.; Janoušková, S; Hák, T. How to understand and measure environmental sustainability: Indicators and targets. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 17, 4–13. | 882 |
| McBride, A.C; Dale V.H.; Baskaran L.M.; Downing M.E.; Eaton L.M.; Efroymson R.A.; Garten Jr. C.T.; Kline K.L.; Jager H.I.; Mulholland P.J.; Parish E.S. Indicators to support environmental sustainability of bioenergy systems. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1277–1289. | 228 |
| Melville, N.P. Information systems innovation for environmental sustainability. MIS Q. 2010, 34, 1–21. | 1250 |
| Sarkis, J. Manufacturing′s role in corporate environmental sustainability—Concerns for the new millennium. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2001, doi:10.1108/01443570110390390. | 531 |
| Kern, F.; Smith, A. Restructuring energy systems for sustainability? Energy transition policy in the Netherlands. Energy Policy 2009, 36 4093–4103. | 580 |
| Elliot, S. Transdisciplinary perspectives on environmental sustainability: a resource base and framework for IT-enabled business transformation. MIS Q., 2011, 35, 197–236. | 483 |
| Orlitzky, M.; Siegel, D.S.; Waldman D.A. Strategic corporate social responsibility and environmental sustainability. Bus. Soc. 2012, 50, 6–27. | 731 |
| Wognum, P.N.; Bremmers, H.; Trienekens, J.H.; van der Vorst, J.G.; Bloemhof, J.M. Systems for sustainability and transparency of food supply chains–Current status and challenges. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2011, 25, 65–76. | 350 |
| Dangelico, R.M.; Pujari, D. Mainstreaming green product innovation: Why and how companies integrate environmental sustainability. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 95, 471–486. | 925 |
| Kemp, R. Technology and the transition to environmental sustainability: the problem of technological regime shifts. Futures 1994, 26, 1023–1046. | 911 |
| Goodland, R. The concept of environmental sustainability. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1995, 26, 1–24. | 1832 |
| Jenkins, H.; Yakovleva, N. Corporate social responsibility in the mining industry: Exploring trends in social and environmental disclosure. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 271–284. | 1164 |
| Schaltegger, S.; Csutora, M. Carbon accounting for sustainability and management. Status quo and challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 36, 1–16. | 270 |
| Holling, C.S. Understanding the complexity of economic, ecological, and social systems. Ecosyst. 2001, 4, 390–405. | 4556 |
| Ostrom, E.; Burger, J.; Field, C.B.; Norgaard, R.B.; Policansky, D. “Revisiting the commons: local lessons, global challenges.” Sci. 1999, 284, 278–282. | 3420 |
| Sharma, S.; Vredenburg, H. Proactive corporate environmental strategy and the development of competitively valuable organizational capabilities. Strateg. Manag. J. 1998, 19, 729–753. | 3006 |
| Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global change and the ecology of cities. Sci. 2008, 319, 756–760. | 4842 |
| Milne, M.J.; Gray, W. W(h)ither ecology? The triple bottom line, the global reporting initiative, and corporate sustainability reporting. J. Bus. Ethics 2013, 118, 13–29. | 872 |
| Stechemesser, K.; Guenther, E. Carbon accounting: a systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 36, 17–38. | 242 |
| Cheng, B.; Ioannou, I.; Serafeim, G. Corporate social responsibility and access to finance. Strateg. Manag. J. 2014, 35, 1–23. | 1799 |
| Delmas, M.; Blass, V.D. Measuring corporate environmental performance: the trade-offs of sustainability ratings. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2010, 19, 245–260. | 366 |
| Frias-Aceituno, J.V.; Rodriguez-Ariza, L.; Garcia-Sanchez, I.M. The role of the board in the dissemination of integrated corporate social reporting. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2013, 20, 219–233. | 489 |
| Source Set 2: Books on Sustainability | |
| Picon, A. Smart Cities: A Spatialised Intelligence, 1st ed.; Wiley: New Jersey, United States, 2015. | |
| Ioris, A.A.R. Agriculture, Environment and Development: International Perspectives on Water, Land and Politics. Palgrave Macmillan: London, United Kingdom, 2016. | |
| Eric G. Derouane.; Parmon, V.; Lemos, F.; Ribeiro, F.R. Sustainable Strategies for the Upgrading of Natural Gas: Fundamentals, Challenges, and Opportunities. Springer: New York, United States, 2005. | |
| Sayler, G.S.; Sanseverino, J.; Davis, K.L. Biotechnology in the Sustainable Environment. Springer: New York, United States, 1997. | |
| Posselt, G. Towards Energy Transparent Factories. Springer: New York, United States, 2016. | |
| Heinrichs, H.; Martens, P.; Michelsen, G.; Wiek, A. Sustainability Science: An Introduction. Springer: New York, United States, 2016. | |
| Mawhinney, M. Sustainable Development: Understanding the Green Debates. Blackwell Science: New Jersey, United States, 2002. | |
| Dastbaz, M.; Strange, I.; Selkowitz, S. Building Sustainable Futures: Design and the Built Environment. Springer: New York, United States, 2016. | |
| Kaushika, N.D.; Reddy, K.S.; Kaushik, K. Sustainable Energy and the Environment: A Clean Technology Approach. Springer: New York, United States, 2016. | |
| Strange, T.; Bayley, A. Sustainable Development: Linking Economy, Society, Environment. OECD Publications: Paris, France, 2008. | |
| Source Set 3: NGOs | |
| Name | Website |
| CERES | https://www.ceres.org/ (accessed 14 July, 2018) |
| HEIFER | https://www.heifer.org/ (accessed 14 July, 2018) |
| Forum for the Future | https://www.forumforthefuture.org/ (accessed 14 July, 2018) |
| Global Reporting | https://www.globalreporting.org/ (accessed 14 July, 2018) |
| CDP | https://www.cdp.net/en (accessed 14 July, 2018) |
| Natural Capitalism Solutions | https://natcapsolutions.org/ (accessed 14 July, 2018) |
| Rain Forest Action Network | https://www.ran.org/understory/ (accessed 14 July, 2018) |
| Greenpeace | https://www.greenpeace.org (accessed 14 July, 2018) |
| World Wildlife Fund | https://www.worldwildlife.org/ (accessed 14 July, 2018) |
| 350.org | https://350.org/ (accessed 14 July, 2018) |
| Note: Primary source for this data is the suggested list of the top 30 environmental NGOs—https://www.raptim.org/30-environmental-ngos-we-all-should-support (accessed 14 July, 2018) | |
| Source Set 4: Corporate Reports | |
| A selection of available reports in the CSR Hub (https://www.csrhub.com) for the period (2013–2017) from top 20 in Forbes List of the 100 most sustainable companies in the world. | Source: https://www.forbes.com/sites/jeffkauflin/2017/01/17/the-worlds-most-sustainable-companies-2017/?sh=417389604e9d (accessed 14 July, 2018) |
References
- Paris Agreement. Report of the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change 21st Session; United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change: Paris, France, 2015; Article 13; pp. 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bodansky, D. The Paris Climate Change Agreement: A New Hope? Am. J. Int. Law 2016, 110, 288–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tapscott, D.; Ticoll, D. The Naked Corporation: How the Age of Transparency will Revolutionize Business; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlman, T.; Farrington, J. What is Sustainability? Sustainability 2010, 2, 3436–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brundtland Commission (World Commission on Environment and Development). Our Common Future; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Goodland, R. The concept of environmental sustainability. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1995, 26, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghezzo, L. The five dimensions of sustainability. Environ. Polit. 2009, 18, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kassoy, A. No Sustainability without Transparency. Forbes Mag. 2010. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/csr/2010/06/18/no-sustainability-without-transparency/?sh=744daff936f6 (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- Bushman, R.M.; Piotroski, J.D.; Smith, A.J. What determines corporate transparency? J. Account. Res. 2004, 42, 207–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubbink, W.; Graafland, J.; Van Liedekerke, L. CSR, Transparency and the Role of Intermediate Organisations. J. Bus. Ethic. 2008, 82, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, C.C. Trust Diffusion: The Effect of Interpersonal Trust on Structure, Function, and Organizational Transparency. Bus. Soc. 2005, 44, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptein, M.; Van Tulder, R. Effective Stakeholder Dialogues. Bus. Soc. Rev. 2003, 108, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dočekalová, M.P.; Kocmanová, A. Composite indicator for measuring corporate sustainability. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechocki, R. Transparency of Annual Sustainability Reports. Corp. Reput. Rev. 2004, 7, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnackenberg, A. Measuring Transparency: Towards a Greater Understanding of Systemic Transparence and Accountability; Report No. WP-09-02′; Case Western Reserve University: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.A.; Dallas, G.S. Transparency and Disclosure: Overview of Methodology and Study Results—United States. SSRN Electron. J. 2002, 422800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.H.; Saen, R.F. Measuring corporate sustainability management: A data envelopment analysis approach. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012, 140, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figge, F.; Hahn, T.; Schaltegger, S.; Wagner, M. The sustainability balanced scorecard–linking sustainability management to business strategy. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2002, 11, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, A.M.; Issac, B.; Modapothala, J.R. Automatic analysis of corporate sustainability reports and intelligent scoring. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Appl. 2014, 13, 1450006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, M.A.; Blass, V.D. Measuring corporate environmental performance: The trade-offs of sustainability ratings. Bus. Strat. Environ. 2010, 19, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldomiaty, T.I. Measuring Transparency of Corporate Transitional Performance in Egypt: A Quantitative Approach. SSRN Electron. J. 2003, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searcy, C.; Elkhawas, D. Corporate sustainability ratings: An investigation into how corporations use the Dow Jones Sustainability Index. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 35, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, D. The Future of Sustainability Reporting as a Regulatory Mechanism. In Law and the Transition to Business Sustainability; Cahoy, D.R., Colburn, J.E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oncioiu, I.; Petrescu, A.-G.; Bîlcan, F.-R.; Petrescu, M.; Popescu, D.-M.; Anghel, E. Corporate Sustainability Reporting and Financial Performance. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, N.E.; Ohsowski, B. Identifying worldviews on corporate sustainability: A content analysis of corporate sustainability reports. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2018, 27, 128–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Székely, N.; vom Brocke, J. What can we learn from corporate sustainability reporting? Deriving propositions for research and practice from over 9,500 corporate sustainability reports published between 1999 and 2015 using topic modelling technique. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y. Evaluation of Sustainability Information Disclosure Based on Entropy. Entropy 2018, 20, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aureli, S. A comparison of content analysis usage and text mining in CSR corporate disclosure. Int. J. Digit. Acc. Res. 2017, 17, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, S.H.; Kwon, O.K.; Ruan, X.; Chhetri, P.; Lee, P.T.W.; Shahparvari, S. Analyzing sustainability literature in maritime studies with text mining. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasalou, A.; Gill, A.J.; Mazanderani, F.; Papoutsi, C.; Joinson, A. Privacy dictionary: A new resource for the automated content analysis of privacy. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2011, 62, 2095–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Q.; Hine, M.; Ji, S.; Sur, S. Building an Environmental Sustainability Dictionary for the IT Industry. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 50th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, HICSS-50, Honolulu, HI, USA, 4–7 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Entropy, Relative Entropy and Mutual Information. Elem. Inf. Theory 2003, 2, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.H. An intelligent method to forecast transparency of information disclosure of listed companies in Taiwan. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics (ICMLC), Guilin, China, 10–13 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Low, J.K.; Ng, H.T.; Guo, W. A maximum entropy approach to Chinese word segmentation. In Proceedings of the Fourth SIGHAN Workshop on Chinese Language Processing, Jeju Island, Korea, 14–15 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Uchimoto, K.; Sekine, S.; Isahara, H. The unknown word problem: A morphological analysis of Japanese using maximum entropy aided by a dictionary. In Proceedings of the 2001 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 3–4 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnaparkhi, A. A maximum entropy model for part-of-speech tagging. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 17–18 May 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Qian, Y. Information granules and entropy theory in information systems. Sci. China Ser. F Inf. Sci. 2008, 51, 1427–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterji, A.K.; Levine, D.I.; Toffel, M.W. How well do social ratings actually measure corporate social responsibility? J. Econ. Manag. Strategy 2009, 18, 125–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, R. The pareto principle: Its use and abuse. J. Serv. Mark. 1987, 1, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Kullback-Leibler information as a basis for strong inference in ecological studies. Wildl. Res. 2001, 28, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacKay, D.J.C. Information Theory, Inference, and Learning Algorithms, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; Volume 34. [Google Scholar]
- Arthur, H. Concepts in Statistical Mechanics; Gordon and Breach: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Dumitru, V.F.; Jinga, G.; Stănilă, O.G.; Dumitru, M. The impact of the European Directive 2014/95/EU on the energy companies’ disclosures. Proc. Int. Conf. Bus. Excell. 2019, 13, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agudelo, M.A.L.; Johannsdottir, L.; Davidsdottir, B. Drivers that motivate energy companies to be responsible. A systematic literature review of Corporate Social Responsibility in the energy sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 1, 247. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, C.; Tang, S.W.S.; Stubbs, W. On managing hypocrisy: The transparency of sustainability reports. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 114, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Measure | Dimensions | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Complex Performance Indicator (CPI) | 4 factors and 17 KPIs | Dočekalová & Kocmanová (2016) [13] |
| Transparency Scorecard | 8 factors and 3 indicators | Piechocki (2004) [14] |
| Standard & Poor′s T&D score | 3 categories and 98 items | Patel & Dallas (2002) [16] |
| CSR Rating | 12 indicators | https://www.csrhub.com |
| Sustainability Balanced Scorecard (SBSC) | 5 perspectives | Figge et al. (2002) [18] |
| Game theoretical model | 3 criteria | Schnackenberg (2009) [15] |
| Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) | 3 key principles and five areas | Lee & Saen (2012) [17] |
| Intelligent Scoring Method | GRI 3.0 environmental subclass and related 30 performance indicators | Shahi et al. (2014) [19] |
| Corpus Data | Count |
|---|---|
| Number of source sets | 5 |
| Number of sustainability rich documents across all sources | 140 |
| Total corpus size (words) | 5,425,178 |
| Potentially relevant count of single words | 5636 |
| OPEC Companies | Non-OPEC Companies |
|---|---|
| Saudi Aramco | Sinopec |
| Kuwait Petroleum Corporation | Rosneft |
| PDVSA | PetroChina |
| National Iran Oil Company | Exxon Mobil |
| Sabic | Royal Dutch Shell |
| Ras Gas | BP |
| QP | Total SA |
| ADNOC | Lukoil |
| Sonangol | Eni |
| Arabian Gulf Oil Company | Gazprom |
| Nigerian National Petroleum Company | Valero Energy |
| Aiteo | Petrobras |
| Emirates National Oil Company | Chevron Corporation |
| Qatar Gas | PEMEX |
| Kuwait Energy | Petronas |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zakaria, M.; Aoun, C.; Liginlal, D. Objective Sustainability Assessment in the Digital Economy: An Information Entropy Measure of Transparency in Corporate Sustainability Reporting. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031054
Zakaria M, Aoun C, Liginlal D. Objective Sustainability Assessment in the Digital Economy: An Information Entropy Measure of Transparency in Corporate Sustainability Reporting. Sustainability. 2021; 13(3):1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031054
Chicago/Turabian StyleZakaria, Mohammed, Chadi Aoun, and Divakaran Liginlal. 2021. "Objective Sustainability Assessment in the Digital Economy: An Information Entropy Measure of Transparency in Corporate Sustainability Reporting" Sustainability 13, no. 3: 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031054
APA StyleZakaria, M., Aoun, C., & Liginlal, D. (2021). Objective Sustainability Assessment in the Digital Economy: An Information Entropy Measure of Transparency in Corporate Sustainability Reporting. Sustainability, 13(3), 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031054







