Urban Planning and European Innovation Policy: Achieving Sustainability, Social Inclusion, and Economic Growth?
Abstract
1. Introduction
“The salesmen, before I had announced the policy, were spurred by the great sales to think that even greater sales might be had if only we had more models. It is strange how, just as soon as an article becomes successful, somebody starts to think that it would be more successful if only it were different. There is a tendency to keep monkeying with styles and to spoil a good thing by changing it.”—Henry Ford [1]
2. Historical and Scientific Background of Innovation in the EU
3. Methods
- to uncover what the term “innovation” means in EU policy and how it relates to the goals of sustainability, economic growth, and social inclusion;
- how innovation is used in identifying and supporting initiatives and research throughout the EU;
- what a critical eye on the implementation of local policies driven by the European innovation logic can reveal.
- sustainability,
- social inclusion,
- economic growth,
- and which of the following mechanisms were used for achieving those objectives, if any:
- efficiency,
- digitalization and “smart” technologies,
- behavioural change.
4. Analysis
- “A European Green Deal: Europe aims to be the first climate-neutral continent by becoming a modern, resource-efficient economy
- A Europe fit for the digital age: The EU’s digital strategy will empower people with a new generation of technologies
- An economy that works for people: The EU must create a more attractive investment environment, and growth that creates quality jobs, especially for young people and small businesses
- A stronger Europe in the world: The EU will strengthen its voice in the world by championing multilateralism and a rules-based global order
- Promoting our European way of life: Europe must protect the rule of law if it is to stand up for justice and the EU’s core values
- A new push for European democracy: We need to give Europeans a bigger say and protect our democracy from external interference such as disinformation and online hate messages.”
4.1. A European Innovation-Based Lexicon
4.1.1. Concepts
Innovation
Innovation Policy
The Innovation Principle
The Innovation Union
4.1.2. Entities
The European Innovation Council (EIC)
European Innovation Partnerships (EIPs)
- stepping up research and development efforts;
- coordinating investments in demonstration and pilots;
- anticipating and fast-tracking any necessary regulation and standards;
- mobilising ‘demand’ in particular through better coordinated public procurement to ensure that any breakthroughs are quickly brought to market.
Innovation Communities
- “innovative products and services to be developed in every area imaginable, including climate change, healthy living and active ageing
- new companies to be started
- a new generation of entrepreneurs to be trained” [75].
4.1.3. Operationalizations
Innovation Deals
Innovation Procurement Guidance
Innovation Scoreboards
Innovation-Friendly Regulatory Framework
“The Commission Better Regulation procedures and its rolling REFIT programme provide a framework for this work, allowing it to enhance innovation-based opportunities for sustainable growth, jobs and competitiveness. A favourable regulatory framework would also enhance the impact of Horizon 2020 financing instruments, which support initiatives to tackle societal challenges and ensure industrial development, innovation and competitiveness in Europe.”
‘Jobs, growth and investment will only return to Europe if we create the right regulatory environment and promote a climate of entrepreneurship and job creation. We must not stifle innovation and competitiveness with too prescriptive and too detailed regulations […] “red tape” both at European and at national level that could be swiftly removed as part of my Jobs, Growth and Investment Package’”[7]
Tool #21. Research and Innovation
The Innovation Radar
Missions
“The ability of innovation to spur economic growth has long been recognised. Less recognised is the fact that innovation has not only a rate but also a direction. By harnessing the directionality of innovation, we also harness the power of research and innovation to achieve wider social and policy aims as well as economic goals. Therefore, we can have innovation-led growth that is also more sustainable and equitable. Finding ways to steer economic growth, and the European policy agenda, is difficult but necessary. Missions are a powerful tool to do this. They can provide the means to focus our research, innovation and investments on solving critical problems, while also spurring growth, jobs and resulting in positive spillovers across many sectors.”
“Partly inspired by the Apollo 11 mission to put a man on the moon, European research and innovation missions aim to deliver solutions to some of the greatest challenges facing our world. They are an integral part of the Horizon Europe framework programme beginning in 2021. Each mission is a mandate to solve a pressing challenge in society within a certain timeframe and budget.”
“The introduction of a Climate City Mission is a radical new way of achieving climate neutrality—and of doing so faster, by 2030. The Mission aims to promote system innovation across the value chain of city investment, targeting multiple sectors such as governance, transport, energy, construction and recycling, with support from powerful digital technologies. As such, it requires a change in regulations, approaches and instruments combined with the willingness to go beyond existing schemes and habits.”
4.1.4. Discussion of the Lexicon
4.2. Urban Planning Innovations Supported by the EU
4.3. Two Local-Level Urban Planning Illustrations: Local-Level Drawbacks of Planning Based on EU Innovation Policies
4.3.1. Mobility for the Elderly in the Netherlands
“We have started some innovation ateliers. That sometimes delivers really nice projects. Something that we are confronted with there, though, for example, is that you get self-employed people that are simply looking for a project. Do you then find that ok? Or do you say, yes, well, we precisely want to stimulate local inhabitants that simply have a good idea for their neighbourhood and who aren’t really in it for the money? We’ve had quite a few discussions about that.”(Interview local official, 2018, author translation from Dutch)
- initiatives being encouraged to focus on displaying signs of innovativeness, rather than seeking to demonstrate their added value in more concrete terms relevant to their context;
- initiatives being vulnerable to wilful interpretations of policy makers and funders, who can decide to focus on the elements that do, or those that do not, highlight their level of innovation– something that is easy to do because of the vagueness of the innovation concept;
- the open interpretability of what can be funded on the basis of innovativeness leaves local government struggling to set ad hoc priorities that are not co-determined democratically, which can be seen as difficult for some, and as an (undemocratic) opportunity to push for personal agendas for others.
4.3.2. A “Repair Café” in Leipzig, Germany
5. Discussion
5.1. Thinking about the Future: From Innovation as a Narrowing Policy Device to Real Policy Diversity
5.2. Thinking about the Present: From Broad Terminologies and Social Acceleration to Resonant Engagement
5.3. Thinking about the Past: From Willed Amnesia to Historical Awareness
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Table of Scientific Publications on Innovation in Key Planning Journals Between 2015 and 2020
| Author(s) | Title | Year | Key Message | Stance towards Innovation * | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environment and Planning D: Society and Space (only one publication fit the criteria) | |||||
| A. S. Rai | The affect of Jugaad: Frugal innovation and postcolonial practice in India’s mobile phone ecology. | 2015 | Linking geographical, temporal, and economic relationships between affect and innovation | neutral | [126] |
| Planning Theory (three publications fit the criteria) | |||||
| A. Agger and E. Sørensen | Managing collaborative innovation in public bureaucracies. | 2016 | Tasks and tensions emerging during collaborative innovation management | neutral | [22] |
| F. Bragaglia | Social innovation as a ‘magic concept’ for policy-makers and its implications for urban governance. | 2020 | Discusses the appeal of social innovation discourses and logics, but also their drawbacks | positive–critical | [10] |
| E. Skrimizea | Scale: The Universal Laws of Growth, Innovation, Sustainability, and the Pace of Life in Organisms, Cities, Economies, and Companies. [book review] | 2020 | Praising book review, highlighting the book author’s critical view on the value of technological innovation, but as a minor point | neutral–critical | [127] |
| Environment and Planning A (sixteen publications fit the criteria) | |||||
| R. H. W. Boyer | Grassroots Innovation for Urban Sustainability: Comparing the Diffusion Pathways of Three Ecovillage Projects | 2015 | Unequal diffusion opportunities for grassroots innovations and niche regime change initiatives | positive–neutral | [128] |
| C. C. Wang | Geography of Knowledge Sourcing, Search Breadth and Depth Patters, and Innovative Performance: A Firm Heterogeneity Perspective | 2015 | How knowledge sourcing affects innovation dynamics | positive–neutral | [129] |
| A. Davies and J. Fitchett | In the Family Way: Bringing a Mother-Daughter (Matrilineal) Perspective to Retain Innovation and Consumer Culture | 2015 | How storytelling between mothers and daughters affects consumption (and retail innovation) | positive–neutral | [130] |
| R. Shearmur and D. Doloreux | Central places or networks? Paradigms, metaphors, and spatial configurations of innovation-related service use | 2015 | The importance of central places for innovation services | positive–neutral | [131] |
| T. Wainwright | Circulating financial innovation: new knowledge and securitization in Europe | 2015 | Critical review of the role of securitization in Europe after the global financial crisis of 2008 | neutral–critical | [132] |
| C. Corradini and L. De Propris | Technological diversification and new innovators in European regions: evidence from patent data | 2015 | Exploration of the transformative potential of diversity and technological innovation through innovation | positive–neutral | [133] |
| A. Smith, T. Hargreaves, S. Hieschler, M. Martiskainen, and G. Seyfang | Making the most of community energies: Three perspectives on grassroots innovation | 2015 | How to realize the full transformative potential of grassroots innovations | positive | [134] |
| I. Liefner and S. Jessberger | The use of the analytical hierarchy process as a method of comparing innovation across regions: The examples of the equipment manufacturing industries of Shanghai and Xiamen, China. | 2016 | How innovation can be measured and compared across regions | neutral–positive | [135] |
| T. Wainwright and G. Manville | Financialization and the third sector: Innovation in social housing bond markets | 2016 | Critical review of impact of innovation through financialization in housing bond markets in the UK | neutral–critical | [136] |
| V. Brinks, O. Ibert, F. C. Müller, and S. Schmidt | From ignorance to innovation: Serendipity and purposeful mobility in creative processes—The cases of biotechnology, legal services and board games | 2018 | Reconceptualizing creativity in terms of ignorance and therefore reassessing the process of knowledge acquisition | neutral–positive | [137] |
| S. J. Herstad, M.C.W. Solheim, and M. Engen | Learning through urban labour pools: Collected worker experiences and innovation in services. | 2019 | How firms collect innovation potential through worker variety | positive–neutral | [138] |
| L. Fang | Agglomeration and innovation: Selection or true effect? | 2019 | Quantitative analysis of the relationship between agglomeration and innovation that eliminates the “selection effect” | positive–neutral | [139] |
| J. Wang and Y. Tan | Social factory as prosaic state space: Redefining labour in China’s mass innovation/mass entrepreneurship campaign | 2019 | Critical review the impact of China’s mass innovation/mass entrepreneurship campaign | neutral–critical | [140] |
| J.-M. Lehmann and P. Smets | An innovative resilience approach: Financial self-help groups in contemporary financial landscapes in the Netherlands | 2019 | Financial self-help as innovative resilience | positive | [141] |
| C. Lorne | The limits to openness: Co-working, design and social innovation in the neoliberal city. | 2020 | Critique of discourse of “openness”—in innovation, social innovation, entrepreneurship, and more. The critique is connected much more to the “openness” than innovation. | neutral–critical | [54] |
| C. Corradini | The geography of innovation as reflected by social media. | 2020 | How to measure and analyse innovation with the help of social media | neutral–positive | [142] |
| Journal of the American Planning Association (two publications fit the criteria, both book reviews) | |||||
| T. C. Cornille | Innovation in Public Transport Finance: Property Value Capture, by Shishir Mathur: (2014). Farnham, Surry, UK: Ashgate. 212 pages $109.95 (hardcover). | 2015 | Commending review of the book, saying that it makes constructive and clarifying use of the concept of innovation | positive–neutral | [143] |
| L. Lindsey | Leading the Inclusive City: Place-Based Innovation for a Bounded Planet, by Robin Hambleton: (2015). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press. 416 pages. $44.95 (paperback). | 2016 | Critical review of the book about place-based innovation and inclusion as not sufficiently inspirational, but both the book and the review highlight innovation as positive | positive | [144] |
| Journal of Planning Literature (two publications fit the criteria) | |||||
| L. Fang | Do Clusters Encourage Innovation? A Meta-analysis. | 2015 | How innovation can be encouraged and measured through particular spatial configurations (i.e., clusters). | positive | [145] |
| A. Hagen and U. Higdem | Calculate, Communicate and Innovate: Do We Need “Innovate” as a Third Position? | 2019 | Literature review on the use of the concept of “innovation” in planning theory from 1945 to 2019. | neutral–positive | [21] |
Appendix B. Table of Innovation-Based Urban Planning Project Search Results
| Project Acronym, Title | Description and End Date |
|---|---|
| MAKING-CITY: Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | “MAKING-CITY is a large-scale demonstration project aiming at the development of new integrated strategies to address the urban energy system transformation towards low carbon cities, with the positive energy district (PED) approach as the core of the urban energy transition pathway. The project will be intensively focused on achieving evidences about the actual potential of the PED concept, as foundation of a high efficient and sustainable route to progress beyond the current urban transformation roadmaps.” (emphasis added) End date: 30 November 2023 Promotion of: Sustainability Through: Efficiency |
| SmartEnCity | “SmartEnCity’s main Objective is to develop a highly adaptable and replicable systemic approach towards urban transformation into sustainable, smart and resource-efficient urban environments in Europe through the integrated planning and implementation of measures aimed at improving energy efficiency in main consuming sectors in cities, while increasing their supply of renewable energy, and demonstrate its benefits.” (emphasis added) End date: 31 July 2021 Promotion of: Sustainability, Social Inclusion, Economic Growth Through: Efficiency, Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies |
| Ruggedised: Rotterdam, Umea and Glasgow: Generating Exemplar Districts in Sustainable Energy Deployment | “The RUGGEDISED project will create urban spaces powered by secure, affordable and clean energy, smart electro-mobility, smart tools and services. The overall aims are: 1. Improving the quality of life of the citizens, by offering the citizens a clean, safe, attractive, inclusive and affordable living environment. 2. Reducing the environmental impacts of activities, by achieving a significant reduction of CO2 emissions, a major increase in the investment and usage of RES and an increase in the deployment of electric vehicles. 3. Creating a stimulating environment for sustainable economic development, by generating more sustainable jobs, stimulating community involvement in smart solutions and to boost start-up and existing companies to exploit the opportunities of the green digital economy and Internet of Things.” (emphasis added) End date: 31 October 2021 Promotion of: Sustainability, Social Inclusion, Economic Growth Through: Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies |
| Water4Cities: Holistic Surface Water and Groundwater Management for Sustainable Cities | “The Water4Cities project will rely on sensor technologies, data and visual analytics to enable localization, visualization and analysis of urban water (both surface water and groundwater) at a holistic urban setting providing services to multiple water stakeholders. More specifically, the Water4Cities project aims to develop the necessary models and associated platform that will enable water providers and relevant stakeholders to (a) monitor in real-time the urban water resources; (b) support their decisions for optimal urban water management causing minimal environmental impact and (c) involve policy makers, corporations and the public to provide the support for sound and balanced decision-making. Beyond the scientific results, Water4Cities will target the exchange of knowledge among project partners.” End date: 28 February 2021 Promotion of: Sustainability, Social Inclusion Through: Efficiency, Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies |
| Sharing Cities | “Sharing Cities has four key objectives. (1) To achieve scale in the European smart cities market by proving that properly designed smart city solutions, based around common needs, can be integrated in complex urban environments. […] (2) Adopt a digital first approach which proves the extent to which ICT integration can improve and connect up existing infrastructure, as well as the design and running of new city infrastructure. […] (3) Accelerate the market to understand, develop and trial business, investment and governance models, essential for the true aggregation and replication (through collaboration) of smart city solutions in cities of different sizes and maturities. […] (4) Share and collaborate for society: to respond to increasing demand for participation; to enhance mechanisms for citizens’ engagement; to improve local governments capacity for policy making and service delivery through collaboration and co-design; resulting in outcomes that are better for citizens, businesses and visitors.” (emphasis added) End date: 31 December 2020 Promotion of: Sustainability, Social Inclusion/Participation, Economic Growth Through: Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies, Behavioural Change |
| MiRTLE: Next generation, high performance, long range, standoff, concealed threat detection system to protect European citizens and critical infrastructure | “Acts of terrorism aim to instil fear into Europe’s citizens. Since 2000, approximately 163,000 people have died from global terrorism. […] Radio Physics Solutions Ltd. has developed MiRTLE (Millimetre-wave Radar Threat Level Evaluation), the world’s first, high performance, long range (up to 50 m), low cost, standoff “concealed threat” detection system for the protection of citizens and critical infrastructure. MiRTLE is capable of screening large groups of people automatically and autonomously, without operator intervention, in real-time. Our highly innovative system detects PBIEDs, guns (including 3D printed) and knives up to a range of 50 m in real-time, with targets in motion, all without privacy concerns. The overall objective of this project is to successfully refine, scale-up and demonstrate our superior technology to our customer base. We are planning to capture an 8% market share of the improvised explosive devices (IED) and weapon detection market, which will in turn generate cumulative revenues of €161m, cumulative EBITDA of €43m by 2025 and create 302 high skilled jobs in Europe.” (emphasis added) End date: 31 July 2020 Promotion of: Economic Growth Through: Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies |
| CIVITAS ECCENTRIC: Innovative solutions for sustainable mobility of people in suburban city districts and emission free freight logistics in urban centres. | “The cities of Madrid, Stockholm, Munich, Turku and Ruse have formed the CIVITAS ECCENTRIC consortium to tackle the challenges of mobility in suburban districts and clean, silent and CO2 free city logistics. […] ECCENTRIC will demonstrate and test the potential and replicability of integrated and inclusive urban planning approaches, innovative policies and emerging technologies to reach sustainable urban mobility objectives. The solutions will be implemented in 5 living laboratory areas in the outskirts that face high population growth and an increasing pressure on the existing transport networks. […] To reach CO2 free city logistics by 2030, ECCENTRIC will test clean vehicles and fuels, formulate new regulations and services and develop consolidation solutions in close partnerships with the private sector” (emphasis added) End date: 31 August 2020 Promotion of: Sustainability, Social Inclusion Through: Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies (relatively little, exceptional) |
| PORTIS: PORT-Cities: Integrating Sustainability | “Thanks to the Civitas Initiative, the partner cities expect to prove that more efficient and sustainable mobility is conducive to the establishment of vital and multi-modal hubs for urban, regional, national and International movements of passengers and goods. To do this, they establish integrated living laboratories clustering local measures according to four major aspects of sustainable urban mobility: 1. Governance: to increase port-city collaborative planning and participation, leading to enhanced forms of SUMPs. 2. People: to foster less car-dependent mobility styles, leading to modal shift in favour of collective and more active transport. 3. Transport system: to strengthen the efficiency of road traffic management to/from the port and through the city, and foster the use of clean vehicles. 4. Goods: to enhance logistics and freight transport, improving the efficiency and coordination of city, port and regional freight movements.” (emphasis added) End date: 31 August 2020 Promotion of: Sustainability, Social Inclusion Through: Efficiency, Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies, Behavioural Change |
| RISEN: Rail Infrastructure Systems Engineering Network | “Social and economic growth, security and sustainability in Europe are at risk of being compromised due to aging and failing railway infrastructure systems. This partly reflects a recognised skill shortage in railway infrastructure engineering. This project, RISEN, aims to enhance knowledge creation and transfer using both international and intersectoral secondment mechanisms […] This project adds research skill mobility and innovation dimension to existing bilateral collaborations between universities through research exchange, joint research supervision, summer courses, international training and workshops, and joint development of innovative inventions. […] RISEN aims to produce the next generation of engineers and scientists needed to meet the challenge of providing sustainable, smart and resilient railway infrastructure systems critical for maintaining European competitiveness. The emphasis will be placed on the resilience and adaptation of railway and urban transport infrastructures using integrated smart systems.” End date: 31 March 2020 Promotion of: Sustainability, Economic Growth Through: Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies (relatively little, exceptional) |
| PULSE: Participatory Urban Living for Sustainable Environments | “PULSE (Participatory Urban Living for Sustainable Environments) will leverage diverse data sources and big data analytics to transform public health from a reactive to a predictive system, and from a system focused on surveillance to an inclusive and collaborative system supporting health equity. Working within five global cities, PULSE will harvest open city data, and data from health systems, urban and remote sensors, personal devices and social media to enable evidence-driven and timely management of public health events and processes.” End date: 31 October 2019 Promotion of: Sustainability, Social Inclusion Through: Efficiency, Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies |
| smarticipate: smart services for calculated impact assessment in open governance | “SMARTICIPATE is a data-rich citizen dialogue system, transforming public data into new intelligence, and transposing elements of intelligent ICT development to urban governance. The aim is to integrate bottom-up processes in the realm of city planning, using the full potential of citizens by sharing ideas in the co-production of decision making. smarticipate thereby transforms interaction between citizens, businesses and public administrations in the management of cities, providing a must-have tool that improves cities’ performance, leverages government-citizen relationships, reduces burdens on government via co-production of tasks, and saves money through increased efficiency of processes.” (emphasis added) End date: 31 January 2019 Promotion of: Social Inclusion, Economic Growth Through: Efficiency, Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies |
| PROSFET: Promoting Sustainable Freight Transport in Urban Contexts: Policy and Decision-Making Approaches | “Within a context of growing urban population, advances in urban logistics operations and improved local authority planning, especially in the field of the urban freight transport, can alleviate the associated negative environmental and economic impacts occurring in cities. […] The proposed project will be aimed at identifying local authority planning needs with regards to urban/city logistics activities and the necessary pre-requisites for inclusion of stakeholders in the process. Finally, the project will promote the knowledge transfer of methods and models through the conceptual development of a novel decision support tool (thanks to involved software houses).” End date: 31 December 2019 Promotion of: Sustainability, Social Inclusion Through: Efficiency, Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies |
| DECADE: Deploying High Capacity Dense Small Cell Heterogeneous Networks | “The DECADE project adopts the scheme of Research and Innovation Staff Exchange (RISE), with the effect of inter-sectorial efforts and knowledge integration to tackle the challenges [exponential traffic growth] in HetNet [Heterogenous Networks] planning and optimization. The research consists in fundamental capacity analysis, system modeling, algorithm development, and performance engineering for HetNets. In addition, DECADE serves as a solid platform to promote long-term collaboration between academia and industry collaboration in a rapidly evolving area of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) in Europe.” (emphasis added) End date: 31 July 2019 Promotion of: Social Inclusion, Economic Growth Through: Efficiency, Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies |
| I-Media-Cities: Innovative e-environment for Research on Cities and the Media | “At the end of the project, we will deliver a digital content access platform (interoperable and multilingual), made available to a growing community of researchers and creatives Europe-wide to push the boundaries of what we can learn, through AV [Audio-Visual] material on cities, on European history and identity. The legacy of I-Media-Cities will be a new model for research on digital sources (applicable also to other subject areas), plus appropriate exploitation plans to consolidate and expand the platform into the European reference initiative on AV digital content.” End date: 31 March 2019 Promotion of: Social Inclusion, Economic Growth Through: Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies |
| OrganiCity—Co-creating smart cities of the future | “[…] this project seeks to build a strong foundation for future sustainable cities through co-creation by a wide range of stakeholders. […] By focusing on the city as a sociotechnical whole, OrganiCity brings software, hardware and associated human processes flexibly together into a new living city that is replicable, scalable, as well as socially, environmentally and economically sustainable. […] The OrganiCity consortium will create a novel set of tools for civic co-creation, well beyond the state of the art in trans-disciplinary participatory urban interaction design. […] The aim is to grow sustainable digital solutions for future cities that are adjusted to the culture and capacities of each city unlocking amended services and novel markets.” End date: 30 June 2018 Promotion of: Sustainability, Social Inclusion, Economic Growth Through: Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies |
| URBIS: URBan land recycling Information services for Sustainable cities | “The URBIS project aims to develop, implement and validate in real environment innovative information services related to urban vacant land, based on open geospatial data, to support planning of European Large Urban Zone’s (LUZs) in a sustainable way. […] In particular, the so called Fast Track Services (FTS) on Land Monitoring are currently being developed to include new more detailed layers of information focused on urban and forest areas which will be essential for the development of an information service aimed at identifying and characterising vacant and derelict urban sites. The development of such an information service could play a major role in the promotion of recycling existing urban sites thus contributing to the reduction of urban sprawl.” End date: 31 March 2017 Promotion of: Sustainability Through: Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies |
| SmartH2O: an ICT Platform to leverage on Social Computing for the efficient management of Water Consumption | “The SmartH2O project aims at providing water utilities, the municipalities, and citizens, with an ICT enabled platform to design, develop and implement better water demand management policies, which are based on a shared understanding and motivation by the water users, thus leading to a reduction in water consumption, while not compromising the quality of life. SmartH2O builds a bi-directional communication stream between citizens and the water utility: in one direction, user behavioural data are collected through smart meters and an online social participation application (social game); in the other, awareness campaigns and price signals are delivered through the same app to inform the users on how to save water and money.” End date: 31 March 2017 Promotion of: Sustainability, Social Inclusion Through: Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies, Behavioural Change |
| INDICATE: Indicator-based Interactive Decision Support and Information Exchange Platform for Smart Cities | “INDICATE proposes a novel city-wide decision support system which accounts for all major systems and activities relevant to developing energy-efficient cities. […] INDICATE addresses these issues through the development of a decision support tool that is used in all stages of urban development of a city. […] This is achieved through the integration of Dynamic Simulation Modelling, Geographic Information Systems (GIS), 3D Urban CAD Modelling Tools, Sustainable Urban Indicators and algorithms for Demand Side Management and local balancing of energy use into a single software package.” End date: 30 September 2016 Promotion of: Sustainability, Economic Growth Through: Efficiency, Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies |
| MyWay: European Smart Mobility Resource Manager | “[…] MyWay will investigate, develop and validate an integrated platform, the European Smart Mobility Resource Manager, including cloud-based services and facilities to support community supplied information collection and processing. The purpose is to holistically address the efficient and seamless integration and use of complementary, capacity-limited mobility services in the overall urban travel chain, including all transport modes (motorised and non-motorised, EVs, public transport, flexible services such as transport on-demand) and mobility sharing schemes (e.g., car sharing, motorbike sharing and carpooling). […] The approach gives priority to the egocentric vision of the user, finding the right compromise for each single traveller and offering a solution closest to his personal needs and preferences, making the frequent use of it (as an alternative to an ideal but not always practical solution) a main contribution to the sustainability of urban transport.” End date: 29 February 2016 Promotion of: Sustainability Through: Efficiency, Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies, Behavioural Change |
| DIMMER: District Information Modeling and Management for Energy Reduction | “The DIMMER system integrates BIM and district level 3D models with real-time data from sensors and user feedback to analyse and correlate buildings utilization and provide real-time feedback about energy-related behaviors. It allows open access with personal devices and Augmented Reality (A/R) visualization of energy-related information to client applications for energy and cost-analysis, tariff planning and evaluation, failure identification and maintenance, energy information sharing. […] the expected results are a consistent reduction in both energy consume and CO2 emissions by enabling a more efficient energy distribution policies, according to the real characteristics of district buildings and inhabitants as well as a more efficient utilization and maintenance of the energy distribution network, based on social behavior and users attitudes and demand.” End date: 30 September 2016 Promotion of: Sustainability Through: Efficiency, Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies, Behavioural Change |
| MOBINCITY: SMART MOBILITY IN SMART CITY | “MOBINCITY aims at the optimization of FEV autonomy range and the increase in energy efficiency thanks to the development of a complete ICT-based integrated system able to interact between driver, vehicle and transport and energy infrastructures, taking advantage of the information provided from these sources in order to optimise both energy charging and discharging processes (trip planning and routing).” End date: 30 June 2015 Promotion of: Sustainability Through: Efficiency, Digitalization and “Smart” Technologies, Behavioural Change |
References
- Ford, H. My Life and Work; Doubleday, Page & Company: New York, NY, USA, 1922. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Mission-Oriented Research & Innovation in the European Union: A Problem-Solving Approach to Fuel Innovation-Led Growth; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission Identifying Barriers to Innovation. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/research-and-innovation/law-and-regulations/innovation-friendly-legislation/identifying-barriers_en (accessed on 6 October 2020).
- European Commission. This Is European Social Innovation; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Better Regulation Guidelines. Commission Staff Working Document. European Commission. 2017. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/info/files/better-regulation-guidelines.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- European Commission Innovation Principle Makes EU Laws Smarter and Future-Oriented, Experts Say. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/news/innovation-principle-makes-eu-laws-smarter-and-future-oriented-experts-say-2019-nov-25_en (accessed on 8 October 2020).
- European Commission. Better Regulations for Innovation-Driven Investment at EU Level: Commission Staff Working Document; European Commission; Directorate General for Research and Innovation: Brussels, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Moulaert, F.; MacCallum, D.; Mehmood, A.; Hamdouch, A. (Eds.) The International Handbook on Social Innovation: Collective Action, Social Learning and Transdisciplinary Research; Edward Elgar: Cheltenham, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Moulaert, F.; Mehmood, A.; MacCallum, D.; Leubolt, B. Social Innovation as a Trigger for Transformations—The Role of Research; EU Publications Office: Luxemburg, 2017; ISBN 978-92-79-68440-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bragaglia, F. Social Innovation as a ‘Magic Concept’ for Policy-Makers and Its Implications for Urban Governance. Plan. Theory 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fougère, M.; Segercrantz, B.; Seeck, H. A Critical Reading of the European Union’s Social Innovation Policy Discourse: (Re)Legitimizing Neoliberalism. Organization 2017, 24, 819–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fougère, M.; Meriläinen, E. Exposing Three Dark Sides of Social Innovation through Critical Perspectives on Resilience. Ind. Innov. 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, B. Innovation Contested: The Idea of Innovation over the Centuries; Routledge: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Godin, B.; Vinck, D. (Eds.) Critical Studies of Innovation: Alternative Approaches to the Pro-Innovation Bias; Edward Elgar Publishing Limited: Cheltenham, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Grisolia, F.; Ferragina, E. Social Innovation on the Rise: Yet Another Buzzword in Time of Austerity? Salute e Sociéta 2015, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, T. Wider den Innovationsimperativ! Eine Kritik am Konzept der sozialen Innovation aus Postwachstumsperspektive. In Postwachstumsstadt—Konturen einer solidarischen Stadtpolitik; Brokow-Loga, A., Eckardt, F., Eds.; Oekom Verlag: München, Germany, 2020; pp. 120–137. [Google Scholar]
- Lijster, T. The Future of the New: Artistic Innovation in Times of Social Acceleration; Valiz: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sveiby, K.-E.; Gripenberg, P.; Segercrantz, B. (Eds.) Challenging the Innovation Paradigm; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vinsel, L.; Russel, A. The Innovation Delusion. How Our Obsession with the New Has Disrupted the Work That Matters Most; Penguin Random House LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Uyarra, E.; Flanagan, K.; Magro, E.; Zabala-Iturriagagoitia, J.M. Anchoring the Innovation Impacts of Public Procurement to Place: The Role of Conversations. Environ. Plan. C Politics Space 2017, 35, 828–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, A.; Higdem, U. Calculate, Communicate, and Innovate: Do We Need “Innovate” as a Third Position? J. Plan. Lit. 2019, 34, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agger, A.; Sørensen, E. Managing Collaborative Innovation in Public Bureaucracies. Plan. Theory 2018, 17, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, K.; Van Calster, G.; Reins, L. Towards an Innovation Principle: An Industry Trump or Shortening the Odds on Environmental Protection? Lawinnovation Technol. 2018, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, T.; Pellicer-Sifres, V. From Innovations to Exnovations. Conflicts, (De-)Politicization Processes, and Power Relations Are Key in Analysing the Ecological Crisis. Innov. Eur. J. Soc. Sci. Res. 2020, 33, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, B. καıvoτομία: An Old Word for a New World, or the De-Contestation of a Political and Contested Concept. In Challenging the Innovation Paradigm; Sveiby, K.-E., Gripenberg, P., Segercrantz, B., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 37–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.; von Schönfeld, K.C.; Tan, W.; Papa, E. Maladaptive Planning and the Pro-Innovation Bias: Considering the Case of Automated Vehicles. Urban Sci. 2020, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sie, R.L.; Bitter-Rijpkema, M.; Stoyanov, S.; Sloep, P.B. Factors That Influence Cooperation in Networks for Innovation and Learning. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 37, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sol, J.; Beers, P.J.; Wals, A.E.J. Social Learning in Regional Innovation Networks: Trust, Commitment and Reframing as Emergent Properties of Interaction. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 49, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butzin, A.; Rabadjieva, M. Soziale Innovationen in Mobilität Und Verkehr—Was Sind Sie Und Wer Macht Sie? In Forschung Aktuell Institut Arbeit und Technik; Institut Arbeit und Technik (IAT): Gelsenkirchen, Germany, 2018; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Merkel, S. Applying the Concept of Social Innovation to Population-Based Healthcare. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2018, 28, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, T.; Erkut, B.; Thierbach, N. Entrepreneurial Intentions of Business and Economics Students in Germany and Cyprus: A Cross-Cultural Comparison. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diercks, G.; Larsen, H.; Steward, F. Transformative Innovation Policy: Addressing Variety in an Emerging Policy Paradigm. Res. Policy 2019, 48, 880–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, J.; Ilbery, B.; Maye, D.; Carey, J. Grassroots Social Innovations and Food Localisation: An Investigation of the Local Food Programme in England. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, H.J. The (Social) Innovation—Subjective Well-Being Nexus: Subjective Well-Being Impacts as an Additional Assessment Metric of Technological and Social Innovations. Innovation 2017, 31, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of the European Communities (Ed.) Treaty of Maastricht (Treaty on European Union); Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg; UNIPUB [distributor]: Lanham, MD, USA, 1992; ISBN 978-92-824-0959-6. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Treaty of Lisbon; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brundtland Commission Our Common Future. World Commission on Environment and Development; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Etzkowitz, H. Innovation in Innovation: The Triple Helix of University—Industry—Government Relations. Soc. Sci. Inf. 2003, 42, 293–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzkowitz, H.; Leydesdorff, L. The Endless Transition: A “Triple Helix” of University-Industry-Government Relations. Minerva 1989, 36, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Etzkowitz, H.; Leydesdorff, L. Universities and Global Knowledge Economy: A Triple Helix of University-Industry-Government; Continuum: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Marcovich, A.; Shinn, T. From the Triple Helix to a Quadruple Helix? The Case of Dip-Pen Nanolithography. Minerva 2011, 49, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, S.; Senin, A.A.; Umar, A. Organization Culture and Open Innovation: A Quadruple Helix Open Innovation Model Approach. Int. J. Econ. Financial Issues 2015, 5, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Vallance, P.; Tewdwr-Jones, M.; Kempton, L. Building Collaborative Platforms for Urban Innovation: Newcastle City Futures as a Quadruple Helix Intermediary. Eur. Urban Reg. Stud. 2020, 27, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, D.H.; Meadows, D.L.; Randers, J.; Behrens III, W.W. The Limits to Growth. A Report for The Club of Rome’s Project on the Predicament of Mankind; Universe Books: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, T. Prosperity without Growth; Earthscan: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Raworth, K. Doughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century Economist; Penguin Random House UK: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, T. The Techno-Finance Fix: A Critical Analysis of International and Regional Environmental Policy Documents and Their Implications for Planning. Prog. Plan. 2018, 119, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensuade Vincent, B. The Politics of Buzzwords at the Interface of Technoscience, Market and Society: The Case of ‘Public Engagement in Science’. Public Underst. Sci. 2014, 23, 238–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasu, M.; Leitner, K.-H.; Solitander, N.; Verblane, U. Accelerating the Innovation Race: Do We Need Reflexive Brakes? In Challenging the Innovation Praradigm; Sveiby, K.-E., Gripenberg, P., Segercrantz, B., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2012; pp. 87–112. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, H. Available, accessible, attainable. The mindset of growth and the resonance conception of the good life. In The Good Life Beyond Growth. New Perspectives; Rosa, H., Henning, C., Eds.; Routledge: Oxon, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lennon, M. On ‘the Subject’ of Planning’s Public Interest. Plan. Theory 2017, 16, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroobar, R. Don’t Be Evil: The Case Against Big Tech.; Penguin: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zuboff, S. The Age of Surveillance Capitalism: The Fight for a Human Future at the New Frontier of Power; Profile Books: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lorne, C. The Limits to Openness: Co-Working, Design and Social Innovation in the Neoliberal City. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2020, 52, 747–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, N. Can Society Be Commodities All the Way down? Post-Polanyian Reflections on Capitalist Crisis. Econ. Soc. 2014, 43, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Policies. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/policies_en (accessed on 24 October 2020).
- European Union Goals and Values of the EU. European Union. Available online: https://europa.eu/european-union/about-eu/eu-in-brief_en (accessed on 24 October 2020).
- Pfotenhauer, S.M.; Juhl, J.; Aarden, E. Challenging the “Deficit Model” of Innovation: Framing Policy Issues under the Innovation Imperative. Res. Policy 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryman, A. Social Research Methods, 4th ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission 6 Commission Priorities for 2019-24. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/strategy/priorities-2019-2024_en (accessed on 11 October 2020).
- European Commission. Study Supporting the Interim Evaluation of the Innovation Principle: Final Report; European Commission; Publications Office of the European Union, European Union: Luxemburg, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- von der Leyen, U. A Union That Strives for More. My Agenda for Europe. Political Guidelines for the Next European Commission 2019-2024 2019. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/info/files/political-guidelines-next-commission_en_0.pdf (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- European Commission Research & Innovation. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/strategy/research-and-innovation_en (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- eurostat Glossary: Innovation. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Glossary:Innovation (accessed on 6 October 2020).
- Gouardères, F. Innovation Policy 2020. European Parliament. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/factsheets/en/sheet/67/innovation-policy (accessed on 6 October 2020).
- eip-agri What Is Innovation? European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eip/agriculture/en/what-innovation (accessed on 6 October 2020).
- European Ccommission Social Innovation. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/social/main.jsp?catId=1022&langId=en (accessed on 6 October 2020).
- European Commission Ensuring EU Legislation Supports Innovation. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/research-and-innovation/law-and-regulations/innovation-friendly-legislation_en (accessed on 6 October 2020).
- Ziomek, E. The Innovation Principle—Factsheet 2019. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/research-and-innovation/law-and-regulations/innovation-friendly-legislation_en (accessed on 6 October 2020).
- Bayer, A.G.; Basf, S.E.; Curis GmbH; The Dow Chemical Company; Dow Corning Corporation; Dow AgroScience LLS; Henkel AG & Company; IBM Europe; Novartis, A.G.; Royal Philips; et al. The Innovation Principle. “Stimulating Economic Recovery”. Open Letter to José Manuel Barroso. 2013. Available online: https://corporateeurope.org/sites/default/files/corporation_letter_on_innovation_principle.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- Corporate Europe Observatory The “innovation Principle” Trap. Industries behind Risky Products Push for Backdoor to Bypass EU Safety Rules. Corporate Europe Observatory. Available online: https://corporateeurope.org/en/environment/2018/12/innovation-principle-trap (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- Leroux, J. The “Innovation Principle” Is a Regulatory Trojan Horse from the Industry. The Greens/EFA in the European Parliament. Available online: https://www.greens-efa.eu/en/article/news/the-innovation-principle-is-a-regulatory-trojan-horse-from-the-industry/ (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- European Commission The European Innovation Council (EIC). European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/files/european-innovation-council-eic_en (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- European Commission European Innovation Partnerships (EIPs) Definition and Context 2015. Available online: https://s3platform.jrc.ec.europa.eu/documents/20182/117542/S2E_Fiche_EIPs.pdf/ca0e86c7-b344-48e9-b7a4-678f79fc0c76 (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- EIT Knowledge and Innovation Communities: What Is an Innovation Community? European Institute of Innovation and Technology. Available online: https://eit.europa.eu/our-communities/eit-innovation-communities (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- EIT Vision and Mission. European Institute of Innovation and Technology. Available online: https://eit.europa.eu/who-we-are/eit-glance/mission (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- European Commission Commission Notice: Guidance on Innovation Procurement 2018. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/transparency/regdoc/rep/3/2018/EN/C-2018-3051-F1-EN-MAIN-PART-1.PDF (accessed on 8 October 2020).
- European Commission Commission Advises Public Buyers on How to Capitalise Innovation. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/growth/content/commission-advises-public-buyers-how-capitalise-innovation_en (accessed on 8 October 2020).
- European Commission Innovation Procurement. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/policies/public-procurement/support-tools-public-buyers/innovation-procurement_en (accessed on 8 October 2020).
- European Commission European Innovation Scoreboard. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/growth/industry/policy/innovation/scoreboards_en (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- Hollanders, H.; Es-Sadki, N.; Merkelback, I. Khalilova European Innovation Scoreboard 2020. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/docsroom/documents/42981 (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- European Commission Better Regulation: Guidelines and Toolbox. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/law-making-process/planning-and-proposing-law/better-regulation-why-and-how/better-regulation-guidelines-and-toolbox_en (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- European Commission Better Regulation Toolbox. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/law-making-process/planning-and-proposing-law/better-regulation-why-and-how/better-regulation-guidelines-and-toolbox/better-regulation-toolbox_en (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- European Commission Tool #21. Research & Innovation. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/law-making-process/planning-and-proposing-law/better-regulation-why-and-how/better-regulation-guidelines-and-toolbox/better-regulation-toolbox_en (accessed on 6 October 2020).
- European Commission The Innovation Radar. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/digital-single-market/en/innovation-radar (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- European Commission Missions in Horizon Europe. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/horizon-europe/missions-horizon-europe_en (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- European Commission Proposed Mission: 100 Climate-Neutral Cities by 2030–by and for the Citizens. Report of the Mission Board for Climate-Neutral and Smart Cities 2020. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/info/files/research_and_innovation/funding/documents/ec_rtd_mission-board-report-climate-neutral-and-smart-cities.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- Kallis, G. Degrowth; Agenda Publishing Limited: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission Horizon Prize for Social Innovation: Improved Mobility for Older People. Rules of the Contest 2017. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/news/horizon-prize-social-innovation-commission-awards-three-outstanding-projects-2019-sep-24_en (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- European Commission Horizon Prize for Social Innovation: Commission Awards Three Outstanding Projects. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/news/horizon-prize-social-innovation-commission-awards-three-outstanding-projects-2019-sep-24_en (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- Russell, A.; Meyerson, J.; Vinsel, L.; Dapena Fraiz, L. Welcome. The Maintainers. Available online: https://themaintainers.org/ (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- Alcott, B. Jevon’s Paradox. Ecol. Econ. 2005, 54, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figge, F.; Young, W.; Barkmeyer, R. Sufficiency or Efficiency to Achieve Lower Resource Consumption and Emissions? The Role of the Rebound Effect. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 69, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrell, S. Jevon’s Paradox Revisited: The Evidence for Backfire from Improved Energy Efficiency. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 1456–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bina, O.; Inch, A.; Pereira, L. Beyond Techno-Utopia and Its Discontents: On the Role of Utopianism and Speculative Fiction in Shaping Alternatives to the Smart City Imaginary. Futures 2020, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivy, M. Towards a Critique of Cybernetic Urbanism: The Smart City and the Society of Control. Planning Theory 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shove, E. Beyond the ABC: Climate Change Policy and Theories of Social Change. Environ. Plan. A 2010, 42, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shove, E.; Pantzar, M.; Watson, M. The Dynamics of Social Practice: Everday Life and How It Changes; SAGE Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Urban, J.B.; Hargraves, M.; Trochim, W.M. Evolutionary Evaluation: Implications for Evaluators, Researchers, Practitioners, Funders and the Evidence-Based Program Mandate. Eval. Program Plan. 2014, 45, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copenhagenize.com Bicycle Innovation Lab—Denmark’s First Cultural Centre for Bicycle Culture. Available online: http://www.copenhagenize.com/2011/11/bicycle-innovation-lab-cultural-centre.html (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- Copenhagenize.com Innovative Elevated Cycle Track in Copenhagen. Copenhagenize. 2011. Available online: http://www.copenhagenize.com/2011/12/innovative-elevated-cycle-track-in.html (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- Everett, H. “Future Cycling” Conference: Multi-Billion Pound Investments Could Be Made Available for EU Cycling Strategy. Cycling Industry. Available online: https://cyclingindustry.news/future-cycling-conference-eu-strategy/ (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- TransportXtra How Cycling and Walking Innovation Is Boosting Industry and the Economy. Transportxtra. Available online: https://www.transportxtra.com/publications/local-transport-today/news/59516/how-cycling-and-walking-innovation-is-boosting-industry-and-the-economy (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- Graeber, D.; Cerutti, A. Bullshit Jobs; Simon & Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sennett, R. The Corrosion of Character: The Personal Consequences of Work in the New Capitalism; W. W Norton and Co.: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino, G.; Piva, M.; Vivarelli, M. Are Robots Stealing Our Jobs? IZA Discussion Paper. 2017. No. 10540. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2911478 (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Frey, C.; Osborneb, M. The future of employment: How susceptible are jobs to computerisation? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2017, 114, 254–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovits, D. The Meritocracy Trap: How America’s Foundational Myth Feeds Inequality, Dismantles the Middle Class, and Devours the Elite; Penguin Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, H. Economics in a full world. Sci. Am. 2005, 293, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, H. Social Acceleration: Ethical and Political Consequences of a Desynchronized High-Speed Society. Constellations 2003, 10, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, H. Full Speed Burnout? From the Pleasures of the Motorcycle to the Bleakness of the Treadmill: The Dual Face of Social Acceleration. Int. J. Motorcycle Stud. 2010, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, H.; Henning, C. Good life beyond growth. An introduction. In The Good Life Beyond Growth. New Perspectives; Rosa, H., Henning, C., Eds.; Routledge: Oxon, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg, M.; Hylander, J.P. Boundary Dimensions of Social Innovation: Negotiating Conflicts and Compatibilities When Developing a National Agenda. Innov. Eur. J. Soc. Sci. Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, H.; Henning, C. (Eds.) The Good Life Beyond Growth; Routledge: Oxon, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, H. Unverfügbarkeit; Residenz Verlag GmbH: Wien Salzburg, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, H. Resonanz. Eine Soziologie Der Weltbeziehung; Suhrkamp: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Varoufakis, Y. Austerity; Penguin: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sveiby, K.-E. Innovation and the Global Financial Crisis. Systemic Consequences of Incompetence. In Challenging the Innovation Paradigm; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 113–142. [Google Scholar]
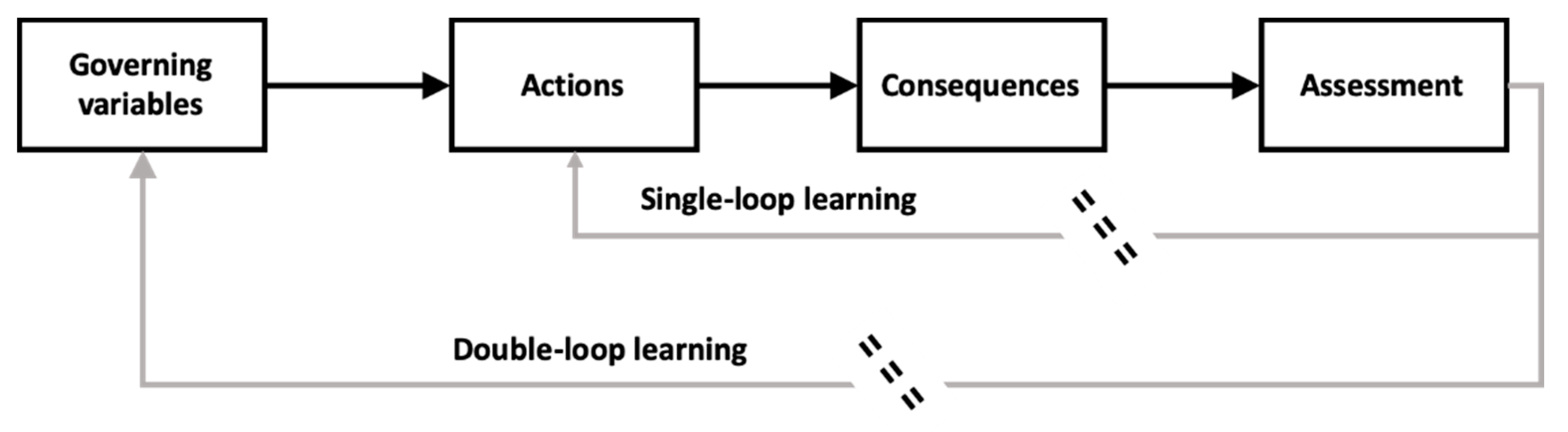
- Argyris, C.; Schön, D. Organizational Learning: A Theory of Action Perspective; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company: Reading, PA, USA, 1978; ISBN 0-201-00174-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, A. The Idea of Justice; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Menand, L. Francis Fukuyama Postpones the End of History. The New Yorker. 2018. Available online: https://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2018/09/03/francis-fukuyama-postpones-the-end-of-history (accessed on 31 October 2020).
- Stanley, T.; Lee, A. It’s Still Not the End of History. The Atlantic. 2014. Available online: https://www.theatlantic.com/politics/archive/2014/09/its-still-not-the-end-of-history-francis-fukuyama/379394/ (accessed on 31 October 2020).
- Brancaccio, E.; Giammetti, R.; Lopreite, M.; Puliga, M. Centralization of Capital and Financial Crisis: A Global Network Analysis of Corporate Control. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2018, 45, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UBS; PwC. Riding the Storm: Market Turbulence Accelerates Diverging Fortunes. UBS Global Wealth Management and PriceWaterhouseCoopers Switzerland. 2020. Available online: https://www.ubs.com/content/dam/static/noindex/wealth-management/ubs-billionaires-report-2020-spread.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Vitali, S.; Glattfelder, J.; Battinson, S. The Network of Global Corporate Control. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, A.S. The Affect of Jugaad: Frugal Innovation and Postcolonial Practice in India’s Mobile Phone Ecology. Environ. Plan. D Soc. Space 2015, 33, 985–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrimizea, E. Scale: The Universal Laws of Growth, Innovation, Sustainability, and the Pace of Life in Organisms, Cities, Economies, and Companies. Plan. Theory 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, R.H.W. Grassroots Innovation for Urban Sustainability: Comparing the Diffusion Pathways of Three Ecovillage Projects. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2015, 47, 320–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C. Geography of Knowledge Sourcing, Search Breadth and Depth Patterns, and Innovative Performance: A Firm Heterogeneity Perspective. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2015, 47, 744–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.; Fitchett, J. In the Family Way: Bringing a Mother-Daughter (Matrilineal) Perspective to Retail Innovation and Consumer Culture. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2015, 47, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearmur, R.; Doloreux, D. Central Places or Networks? Paradigms, Metaphors, and Spatial Configurations of Innovation-Related Service Use. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2015, 47, 1521–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, T. Circulating Financial Innovation: New Knowledge and Securitization in Europe. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2015, 47, 1643–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, C.; De Propris, L. Technological Diversification and New Innovators in European Regions: Evidence from Patent Data. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2015, 47, 2170–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Hargreaves, T.; Hielscher, S.; Martiskainen, M.; Seyfang, G. Making the Most of Community Energies: Three Perspectives on Grassroots Innovation. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2016, 48, 407–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liefner, I.; Jessberger, S. The Use of the Analytical Hierarchy Process as a Method of Comparing Innovation across Regions: The Examples of the Equipment Manufacturing Industries of Shanghai and Xiamen, China. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2016, 48, 1188–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, T.; Manville, G. Financialization and the Third Sector: Innovation in Social Housing Bond Markets. Environ. Plan. A 2017, 49, 819–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinks, V.; Ibert, O.; Müller, F.C.; Schmidt, S. From Ignorance to Innovation: Serendipitous and Purposeful Mobility in Creative Processes—The Cases of Biotechnology, Legal Services and Board Games. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2018, 50, 1742–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herstad, S.J.; Solheim, M.C.; Engen, M. Learning through Urban Labour Pools: Collected Worker Experiences and Innovation in Services. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2019, 51, 1720–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L. Agglomeration and Innovation: Selection or True Effect? Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2020, 52, 423–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tan, Y. Social Factory as Prosaic State Space: Redefining Labour in China’s Mass Innovation/Mass Entrepreneurship Campaign. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2020, 52, 510–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.-M.; Smets, P. An Innovative Resilience Approach: Financial Self-Help Groups in Contemporary Financial Landscapes in the Netherlands. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2020, 52, 898–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, C. The Geography of Innovation as Reflected by Social Media. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2020, 0308518X2096110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornillie, T.C. Innovation in Public Transport Finance: Property Value Capture, by Shishir Mathur: (2014). Farnham, Surrey, UK: Ashgate. 212 Pages. $109.95 (Hardcover). J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2015, 81, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, L. Leading the Inclusive City: Place-Based Innovation for a Bounded Planet, by Robin Hambleton: (2015). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press. 416 Pages. $44.95 (Paperback). J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2016, 82, 60–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L. Do Clusters Encourage Innovation? A Meta-Analysis. J. Plan. Lit. 2015, 30, 239–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
von Schönfeld, K.C.; Ferreira, A. Urban Planning and European Innovation Policy: Achieving Sustainability, Social Inclusion, and Economic Growth? Sustainability 2021, 13, 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031137
von Schönfeld KC, Ferreira A. Urban Planning and European Innovation Policy: Achieving Sustainability, Social Inclusion, and Economic Growth? Sustainability. 2021; 13(3):1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031137
Chicago/Turabian Stylevon Schönfeld, Kim Carlotta, and António Ferreira. 2021. "Urban Planning and European Innovation Policy: Achieving Sustainability, Social Inclusion, and Economic Growth?" Sustainability 13, no. 3: 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031137
APA Stylevon Schönfeld, K. C., & Ferreira, A. (2021). Urban Planning and European Innovation Policy: Achieving Sustainability, Social Inclusion, and Economic Growth? Sustainability, 13(3), 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031137






