Numerical Investigation for Riverbank Filtration Sustainability Considering Climatic Changes in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions; Case Study of RBF Site at Embaba, Nile Delta, Egypt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.1.1. Geomorphology, Land Use, and Metrological Conditions
2.1.2. Geology Setting
2.1.3. Hydrogeological Systems
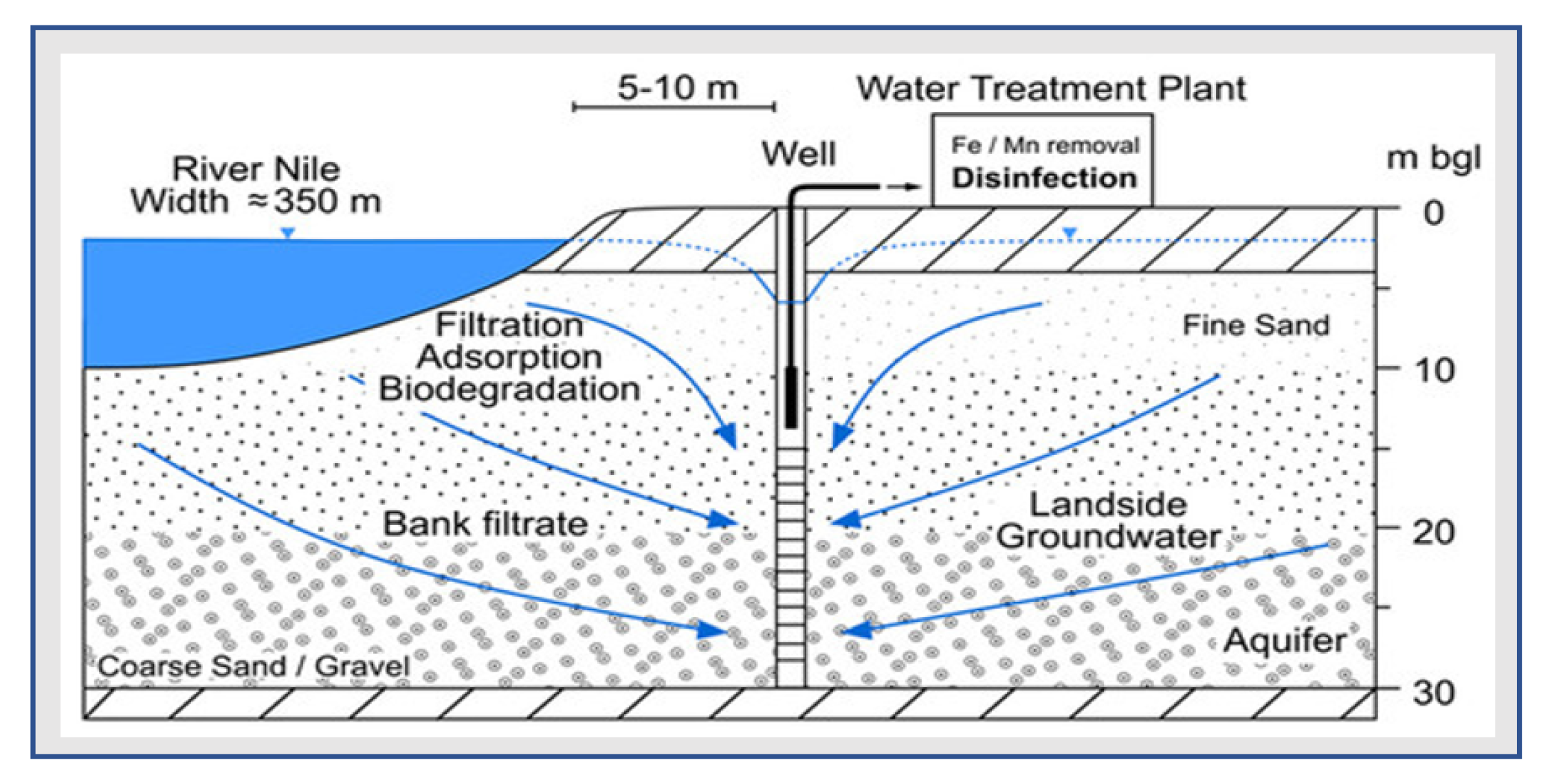
2.2. Embaba River Bank Filtration Site
2.3. Contaminant Transport Model
2.3.1. Design and Setup of Model
2.3.2. Boundary Conditions and Hydraulic Parameters
2.4. Model Calibration
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Impact of River Boundary Stages on RBF Portion
3.2. Impact of Aquifer Recharge Reduction on RBF Portion
3.3. Effect of General Head Reduction on RBF Portion
3.4. Combined Effects of River Stage, General Head and Groundwater Recharge on RBF Portion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Terink, W.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Droogers, P. Climate change projections of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration for the Middle East and Northern Africa until 2050. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 3055–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droogers, P.; Immerzeel, W.; Terink, W.; Hoogeveen, J.; Bierkens, M.; Van Beek, L.; Debele, B. Water resources trends in Middle East and North Africa towards 2050. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3101–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khaled, A.; Abdel, A. Water Conflicts and Conflict Management Mechanisms in the Middle East and North Africa Region; Centre for Environment and Development for the Arab Region and Europe (CEDARE): Cairo Governorate, Egypt, 2006. Available online: http://water.cedare.int/cedare.int/files15/File2862.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Abd-Elaty, I.; Zelenakova, M.; Straface, S.; Vranayová, Z.; Abu-hashim, M. Integrated Modelling for Groundwater Contamination from Polluted Streams Using New Protection Process Techniques. Water 2019, 11, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bates, B.; Kundzewicz, Z.; Wu, S. Climate Change and Water; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Secretariat: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- Abd-Elaty, I.; Eldeeb, H.; Vranayova, Z.; Zelenakova, M. Stability of Irrigation Canal Slopes Considering the Sea Level Rise and Dynamic Changes: Case Study El-Salam Canal, Egypt. Water 2019, 11, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd Ellah, R.G. Water resources in Egypt and their challenges, Lake Nasser case study. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2020, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhafez, A.A.; Metwalley, S.M.; Abbas, H. Irrigation: Water Resources, Types and Common Problems in Egypt. In Technological and Modern Irrigation Environment in Egypt; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 15–34. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elaty, I.; Pugliese, L.; Mesaros, P.; El Shinawi, A. Simulation-Based Solutions Reducing Soil and Groundwater Contamination from Fertilizers in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions: Case Study the Eastern Nile Delta, Egypt. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucksthuhl, S.; Ward, C. Water Scarcity, Climate Change and Conflict in the Middle East: Securing Livelihoods, Building Peace; Bloomsbury Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sprenger, C.; Lorenzen, G.; Hülshoff, I.; Grützmacher, G.; Ronghang, M.; Pekdeger, A. Vulnerability of bank filtration systems to climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.; Ray, C. A Combined RBF and ASR System for Providing Drinking Water in Water Scarce Areas; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 29–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Hui, L.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zeng, R. Effectiveness of riverbank filtration for removal of nitrogen from heavily polluted rivers: A case study of Kuihe River, Xuzhou, Jiangsu, China. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, P. Risk Assessment for Chemical Spills in the River Rhine; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Pholkern, K.; Srisuk, K.; Grischek, T.; Soares, M.; Schäfer, S.; Archwichai, L.; Saraphirom, P.; Pavelic, P.; Wirojanagud, W. Riverbed clogging experiments at potential river bank filtration sites along the Ping River, Chiang Mai, Thailand. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 7699–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, F.; Shamrukh, M. Riverbank Filtration: Developing Countries Choice for Water Supply Treatment, Egypt Case. In Proceedings of the 1st International Water Association IWA Malaysia Young Water Professionals Conference (IWAYWP2010), Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia, 16–19 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wahaab, R.A.; Salah, A.; Grischek, T. Water Quality Changes during the Initial Operating Phase of Riverbank Filtration Sites in Upper Egypt. Water 2019, 11, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, M.W.; Schuetz, J.W. An introduction to ground-water modeling using virtual reality modeling language (VRML). J. Geosci. Educ. 2003, 51, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, D. An overview assessment of the effectiveness and global popularity of some methods used in measuring riverbank filtration. J. Hydrol. 2017, 550, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paufler, S.; Grischek, T.; Bartak, R.; Ghodeif, K.; Wahaab, R.; Boernick, H. Riverbank filtration in Cairo, Egypt: Part II—detailed investigation of a new riverbank filtration site with a focus on manganese. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenheinz, D.; Grischek, T. Behavior of dissolved organic carbon during bank filtration under extreme climate conditions. In Riverbank Filtration for Water Security in Desert Countries; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 51–67. [Google Scholar]
- Capmas. Egypt Census 2020. Egyptian Central Agency for Public Mobilization and Statistics: Cairo, Egypt. Available online: https://www.capmas.gov.eg/Pages/populationClock.aspx (accessed on 2 January 2021).
- El-Arabi, N.; Fekri, A.; Zaghloul, E.; Elbeih, S.; Laake, A. Assessment of Groundwater Movement at Giza Pyramids Plateau Using GIS Techniques. J. Appl. Sci. Res 2013, 9, 4711–4722. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, S.H. Investigation of rainfall–runoff modeling for Egypt by using remote sensing and GIS integration. Catena 2014, 120, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodeif, K.; Paufler, S.; Grischek, T.; Wahaab, R.; Souaya, E.; Bakr, M.; Abogabal, A. Riverbank filtration in Cairo, Egypt—part I: Installation of a new riverbank filtration site and first monitoring results. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, R. The Geology of Egypt; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, J. Contribution to the Geography of Egypt; Government Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Sabry, A. Chapter 2 Geological Settings Nile Delta; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- RIGW. Hydrogeological Map of Egypt; National Water Research Center: Fountain Valley, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- RIGW. Monitoring of Groundwater Microbiological Activities in the Nile Delta Aquifer; National Water Research Center: Fountain Valley, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sherif, M. Assessment, modeling and management of seawater intrusion in the Nile delta aquifer. In Tecnología De La Intrusión De Agua De Mar En Acuíferos Costeros: Países Mediterráneos© Igme; Instituto Geológico y Minero de España: Madrid, Spain, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Leaven, M. Hydrogeological Study of the Nile Delta and Adjacent Desert Areas, Egypt, with Emphasis on Hydrochemistry and Isotope Hydrology; Free University of Amsterdam: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Sefelnasr, A.; Sherif, M. Impacts of seawater rise on seawater intrusion in the Nile Delta aquifer, Egypt. Groundwater 2014, 52, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helalia, A.M. The relation between soil infiltration and effective porosity in different soils. Agric. Water Manag. 1993, 24, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, E.-S.E. Land and Groundwater Resources in the Egypt’s Nile Valley, Delta, and Its Fringes. In Groundwater in the Nile Delta; Negm, A.M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 45–103. [Google Scholar]
- HCWW. Internal Report; Holding Company for Water and Wastewater: Cairo Governorate, Egypt, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ghodeif, K.; Grischek, T.; Bartak, R.; Wahaab, R.; Herlitzius, J. Potential of river bank filtration (RBF) in Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javandel, I.; Doughty, C.; Tsang, C.-F. Groundwater Transport: Handbook of Mathematical Models; Lawrence Berkeley Lab.: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- SWS. User’s Manual; SWS: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2010; Volume N2L 5J2. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elaty, I.; Abd-elhamid, H.; Fahmy, M.; Abd-Elaal, G. Study of Impact of some changes on groundwater system in Nile delta aquifer. Egypt. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2014, 17, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Agha, D.E.; Closas, A.; Molle, F. Survey of groundwater use in the central part of the Nile Delta. In Water and Salt Management in the Nile Delta: Report; IWMI: Gujarat, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- El-Atfy, H. Integrated National Water Resources Plan in Egypt; Ministry of Water Resources and Irrigation Alexandria Governorate: Governorate, Egypt, 2007.
- Morsy, W. Environmental Management to Groundwater Resources for Nile Delta Region. Ph.D. Thesis, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elaty, I.; Sallam, G.A.; Straface, S.; Scozzari, A. Effects of climate change on the design of subsurface drainage systems in coastal aquifers in arid/semi-arid regions: Case study of the Nile delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Abd-Elaty, I.; Hussain, M.S. Mitigation of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers using coastal earth fill considering future sea level rise. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 23234–23245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elaziz, S.; Zelenakova, M.; Mesaros, P.; Purcz, P.; Abd-Elhamid, H.F. Anthropogenic Activity Effects on Canals Morphology, Case Study: Nile Delta, Egypt. Water 2020, 12, 3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Zelenakova, M.; Vranayova, Z.; Fathy, I. Evaluating the Impact of Urban Growth on the Design of Storm Water Drainage Systems. Water 2020, 12, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Main Hydraulic Units | Layer # | Hydraulic Conductivity | Storage Coefficient | Specific Yield | Effective Porosity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kh | Kv | S | Ss | n | ||
| m/day | m/day | - | 1/m | % | ||
| Clay cap | 1 | 0.25–5 | 0.025–0.5 | 10−3 | 0.1 | 40 |
| Coarse sand Quaternary | from 2 to 6 | 25–70 | 2.5–7 | 2.5 × 10−3 | 0.2 | 25 |
| Item | Scenario | RBF Efficiency (%) | Travel Time (Day) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Value | |||
| 1 | base | - | 67.42 | 200 |
| 2 | River stage reduction (%) | From 14.68 to 14.70 m | 61.05 | 220 |
| 3 | From 13.21to 13.23 m | 49.2 | 280 | |
| 4 | From 11.15 to 11.17 m | 35.46 | 800 | |
| 5 | From 9.72 to 9.77 m | 32.11 | 875 | |
| 6 | Aquifer recharge reduction [mm/y] | 150 | 66.5 | 200 |
| 7 | 100 | 65.55 | 200 | |
| 8 | 50 | 64.99 | 200 | |
| 9 | 10 | 64.47 | 200 | |
| 10 | General head reduction (m) | From 12.90 to12.92 m | 78.94 | 140 |
| 11 | From 9.67 to 9.69 | 84.48 | 95 | |
| 12 | From 6.45 to 6.47 m | 87.75 | 80 | |
| 13 | From 3.22 to 3.24 m | 89 | 70 | |
| 14 | Combination of river stage and general head reduction (%) with aquifer recharge reduction(mm/y) | 75% with 150 mm/y | 67.80 | 220 |
| 15 | 50% with 100 mm/y | 69.79 | 220 | |
| 16 | 25%with 50 mm/y | 67.24 | 220 | |
| 17 | 12.5% with 10 mm/y | 63.10 | 240 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abd-Elaty, I.; Ghanayem, H.M.; Zeleňáková, M.; Mésároš, P.; Saleh, O.K. Numerical Investigation for Riverbank Filtration Sustainability Considering Climatic Changes in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions; Case Study of RBF Site at Embaba, Nile Delta, Egypt. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13041897
Abd-Elaty I, Ghanayem HM, Zeleňáková M, Mésároš P, Saleh OK. Numerical Investigation for Riverbank Filtration Sustainability Considering Climatic Changes in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions; Case Study of RBF Site at Embaba, Nile Delta, Egypt. Sustainability. 2021; 13(4):1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13041897
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbd-Elaty, Ismail, Hala M. Ghanayem, Martina Zeleňáková, Peter Mésároš, and Osama K. Saleh. 2021. "Numerical Investigation for Riverbank Filtration Sustainability Considering Climatic Changes in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions; Case Study of RBF Site at Embaba, Nile Delta, Egypt" Sustainability 13, no. 4: 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13041897
APA StyleAbd-Elaty, I., Ghanayem, H. M., Zeleňáková, M., Mésároš, P., & Saleh, O. K. (2021). Numerical Investigation for Riverbank Filtration Sustainability Considering Climatic Changes in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions; Case Study of RBF Site at Embaba, Nile Delta, Egypt. Sustainability, 13(4), 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13041897








