Environmental Issues as Drivers for Food Choice: Study from a Multinational Framework
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- I avoid foods with genetically modified organisms;
- I buy fresh vegetables to cook myself more often than frozen;
- I choose the foods I eat because it fits the season;
- It is important to me that the food I eat is prepared/packed in an environmentally friendly way;
- When I cook, I have in mind the quantities to avoid food waste;
- It is important to me that the food I eat comes from my own country;
- I prefer to eat food that has been produced in a way that animals’ rights have been respected;
- I choose foods that have been produced in countries that do not violate Human’s rights;
- I avoid going to restaurants that do not have a recovery policy of food surplus;
- I prefer to buy foods that comply with policies of minimal usage of packaging.
- value ∈ [1.0,3.0]—food choices not influenced by sustainability issues;
- value ∈ [3.0,5.0]—food choices influenced by sustainability issues.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sample Characterization
3.2. Food Choices Related with Environmental and Sustainability Issues
3.3. Influence of Sociodemographic Variables on Sustainable Food Choices
3.4. Tree Classification Analysis
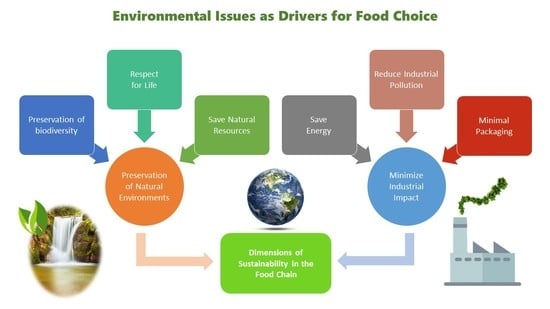
3.5. Dimensions of Sustainability in the Food Chain
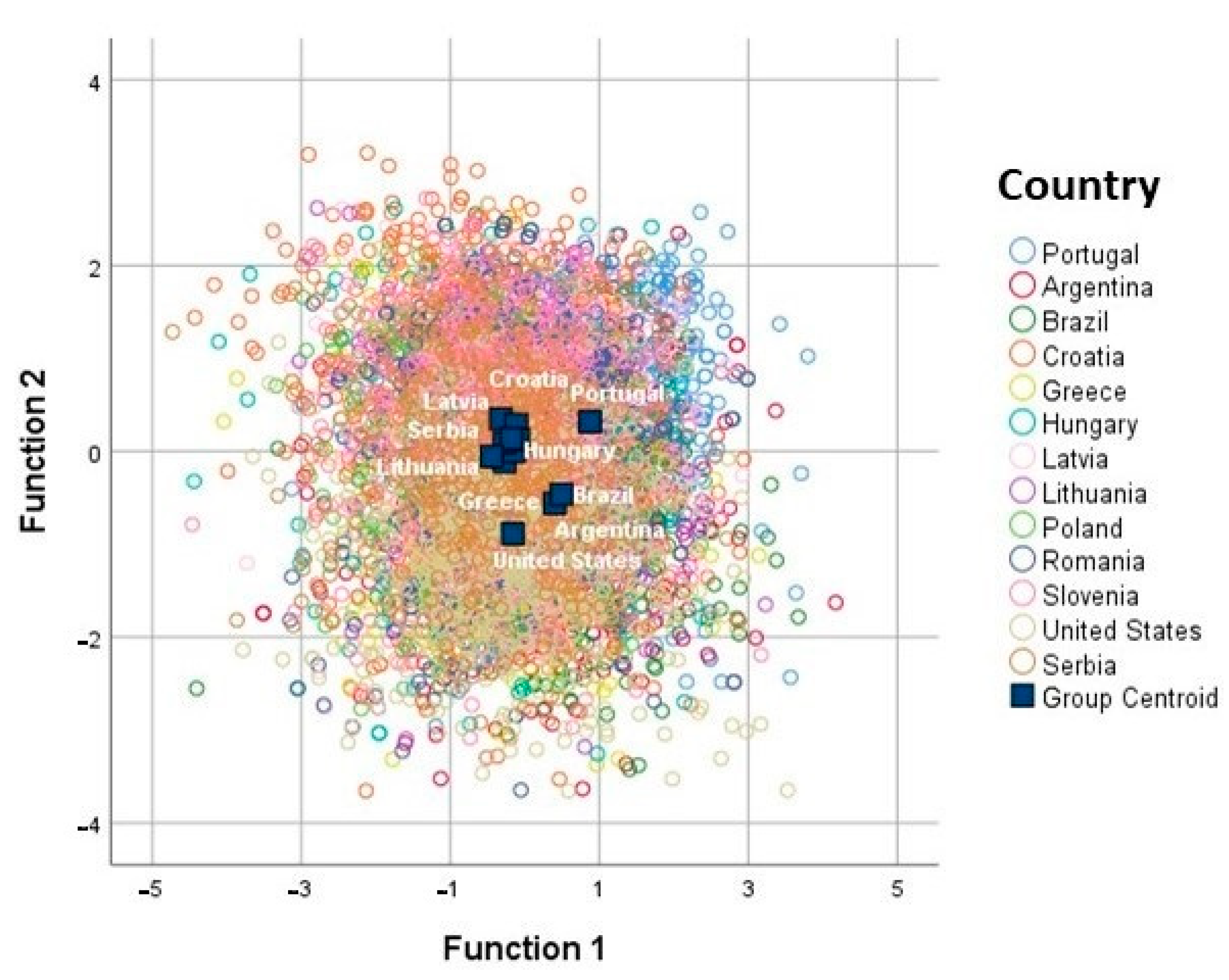
3.6. Discriminant Function Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pohlmann, C.R.; Scavarda, A.J.; Alves, M.B.; Korzenowski, A.L. The Role of the Focal Company in Sustainable Development Goals: A Brazilian Food Poultry Supply Chain Case Study. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bajada, C.; Arshinder, K. Redesigning a Food Supply Chain for Environmental Sustainability—An Analysis of Resource Use and Recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiné, R.P.F.; Correia, P.; Coelho, C.; Costa, C.A. The Role of Edible Insects to Mitigate Challenges for Sustainability. Open Agric. 2021, 6, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiné, R.P.F.; Gaião, D.; Costa, D.V.T.A.; Correia, P.M.R.; Guerra, L.T.; Correia, H.E.; Costa, C.A. Bridges between Family Farming and Organic Farming: A Study Case of the Iberian Peninsula. Open Agric. 2019, 4, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarkar, D.; Kar, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Shikha; Rakshit, A.; Tripathi, V.K.; Dubey, P.K.; Abhilash, P.C. Low Input Sustainable Agriculture: A Viable Climate-Smart Option for Boosting Food Production in a Warming World. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, D.W.; Fanning, A.L.; Lamb, W.F.; Steinberger, J.K. A Good Life for All within Planetary Boundaries. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dania, W.A.P.; Xing, K.; Amer, Y. Collaboration Behavioural Factors for Sustainable Agri-Food Supply Chains: A Systematic Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiné, R.P.F.; Florença, S.G.; Barroca, M.J.; Anjos, O. The Duality of Innovation and Food Development versus Purely Traditional Foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, A.; Behdani, B.; Fogliano, V.; Luning, P.A. A Systems Approach to Dynamic Performance Assessment in New Food Product Development. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.; Li, B.; Singh, T.; Shi, K. Predictability of Stock Market Returns: New Evidence from Developed and Developing Countries. Glob. Financ. J. 2021, 100624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhoushy, S. Consumers’ Sustainable Food Choices: Antecedents and Motivational Imbalance. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 89, 102554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iris, G.; Abraham, H.; Doron, K. Examination of the Relationship between Dietary Choice and Consumer Preferences for Sustainable Near-Food Products in Israel. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowd, K.; Burke, K.J. The Influence of Ethical Values and Food Choice Motivations on Intentions to Purchase Sustainably Sourced Foods. Appetite 2013, 69, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W.; Rockström, J.; Loken, B.; Springmann, M.; Lang, T.; Vermeulen, S.; Garnett, T.; Tilman, D.; DeClerck, F.; Wood, A.; et al. Food in the Anthropocene: The EAT–Lancet Commission on Healthy Diets from Sustainable Food Systems. Lancet 2019, 393, 447–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/WHO. Sustainable Healthy Diets: Guiding Principles; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fardet, A.; Rock, E. How to Protect Both Health and Food System Sustainability? A Holistic ‘Global Health’-Based Approach via the 3V Rule Proposal. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 3028–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feil, A.A.; da Silva, C.C.C.; Sindelar, F.C.W.; Barden, J.E.; Dalmoro, M. Profiles of Sustainable Food Consumption: Consumer Behavior toward Organic Food in Southern Region of Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, A.; Sütterlin, B.; Siegrist, M. Consumer Segmentation Based on Stated Environmentally-Friendly Behavior in the Food Domain. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 25, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrão, A.C.; Guine, R.P.F.; Correia, P.; Ferreira, M.; Duarte, J.; Lima, J. Development of A Questionnaire To Assess People’s Food Choices Determinants. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 15, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, R.; Witte, J. Statistics, 9th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.H.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-13-813263-7. [Google Scholar]
- Maroco, J.; Garcia-Marques, T. Qual a fiabilidade do alfa de Cronbach? Questões antigas e soluções modernas? Laboratório Psicol. 2006, 4, 65–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, F.B. Educational Measurements Their Interpretation; Wadsworth Pub. Co: Marceline, MO, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri, N.; Simeone, M.; Russo, C.; Perito, M.A. Profiling Young Consumers’ Perceptions of GMO Products: A Case Study on Italian Undergraduate Students. Int. J. Gastron. Food. Sci. 2020, 21, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, C.; Tufi, E. Consumer Behavior Under Conflicting Information Provided by Interested Parties: Implications for Equilibrium in the Market for Credence Goods. Recent Pat. Food Nutr. Agric. 2016, 8, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covino, D. GMOs and the Issue of Coexistence in Italy. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 46, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgili, M.; Bilirgen, H.; Ozbek, A.; Ekinci, F.; Demirdelen, T. The Role of Hydropower Installations for Sustainable Energy Development in Turkey and the World. Renew. Energy 2018, 126, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. Total Primary Energy Supply (TPES) by Source, World 1990–2017; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantas, A.; Stamford, L.; Azapagic, A. Economic Sustainability of Food Supply Chains: Life Cycle Costs and Value Added in the Confectionary and Frozen Desserts Sectors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aschemann-Witzel, J.; Zielke, S. Can’t Buy Me Green? A Review of Consumer Perceptions of and Behavior Toward the Price of Organic Food. J. Consum. Aff. 2017, 51, 211–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchfield, S.G.; Schulz, K.G.; Kelaher, B.P. The Influence of Plastic Pollution and Ocean Change on Detrital Decomposition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, G.; Styles, D.; Lens, P.N.L. Recycling of European Plastic Is a Pathway for Plastic Debris in the Ocean. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, G.; Failler, P. Governing Plastic Pollution in the Oceans: Institutional Challenges and Areas for Action. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 112, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilkes-Hoffman, L.S.; Lane, J.L.; Grant, T.; Pratt, S.; Lant, P.A.; Laycock, B. Environmental Impact of Biodegradable Food Packaging When Considering Food Waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J.B.; Ambrosi, A.; Tessaro, I.C. Development of Biodegradable Starch-Based Foams Incorporated with Grape Stalks for Food Packaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 225, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamdem, D.P.; Shen, Z.; Nabinejad, O.; Shu, Z. Development of Biodegradable Composite Chitosan-Based Films Incorporated with Xylan and Carvacrol for Food Packaging Application. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 21, 100344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teigiserova, D.A.; Hamelin, L.; Thomsen, M. Towards Transparent Valorization of Food Surplus, Waste and Loss: Clarifying Definitions, Food Waste Hierarchy, and Role in the Circular Economy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 136033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searchinger, T.; Waite, R.; Hanson, C.; Ranganathan, J.; Dumas, P.; Matthews, E. Creating a Sustainable Food Future; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-56973-953-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kummu, M.; Moel, H.; Porkka, M.; Siebert, S.; Olli, V.; Ward, P. Lost Food, Wasted Resources: Global Food Supply Chain Losses and Their Impacts on Freshwater, Cropland, and Fertiliser Use. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 438C, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midgley, J.L. Anticipatory Practice and the Making of Surplus Food. Geoforum 2019, 99, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.J.; Rashidi, T.H.; Dixit, V.V. Estimating Surplus Food Supply for Food Rescue and Delivery Operations. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2017, 57, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papargyropoulou, E.; Lozano, R.; Steinberger, J.K.; Wright, N.; bin Ujang, Z. The Food Waste Hierarchy as a Framework for the Management of Food Surplus and Food Waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 76, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedeurwaerdere, T.; De Schutter, O.; Hudon, M.; Mathijs, E.; Annaert, B.; Avermaete, T.; Bleeckx, T.; de Callataÿ, C.; De Snijder, P.; Fernández-Wulff, P.; et al. The Governance Features of Social Enterprise and Social Network Activities of Collective Food Buying Groups. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 140, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garrett, J.J. Future Visions: A Sustainable and Healthy Local Food Production System. Rangelands 2016, 38, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hang, M.Y.L.P.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Leach, M.; Yang, A. Designing Integrated Local Production Systems: A Study on the Food-Energy-Water Nexus. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 1065–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu-Mag, R.M.; Petrescu, D.C.; Reti, K.-O. My Land Is My Food: Exploring Social Function of Large Land Deals Using Food Security–Land Deals Relation in Five Eastern European Countries. Land Use Policy 2019, 82, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, K.; Hamm, U. Information Search Behaviour and Its Determinants: The Case of Ethical Attributes of Organic Food. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2012, 36, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornish, A.R.; Briley, D.; Wilson, B.J.; Raubenheimer, D.; Schlosberg, D.; McGreevy, P.D. The Price of Good Welfare: Does Informing Consumers about What on-Package Labels Mean for Animal Welfare Influence Their Purchase Intentions? Appetite 2020, 148, 104577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.J.; Cranfield, J.; Chen, C.; Widowski, T. Heterogeneous Informational and Attitudinal Impacts on Consumer Preferences for Eggs from Welfare Enhanced Cage Systems. Food Policy 2020, 101979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Sharma, C.; Bryant, R.; Mohan, M.S.; Al-Marashdeh, O.; Harrison, R.; Torrico, D.D. Animal Welfare Information Affects Consumers’ Hedonic and Emotional Responses towards Milk. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estévez-Moreno, L.X.; María, G.A.; Sepúlveda, W.S.; Villarroel, M.; Miranda-de la Lama, G.C. Attitudes of Meat Consumers in Mexico and Spain about Farm Animal Welfare: A Cross-Cultural Study. Meat Sci. 2021, 173, 108377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Gudiño, J.; Blanco-Penedo, I.; Gispert, M.; Brun, A.; Perea, J.; Font-i-Furnols, M. Understanding Consumers’ Perceptions towards Iberian Pig Production and Animal Welfare. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunert, K.G. Drivers of Food Choice: A Cognitive Structure Approach to the Determinants of Food Choice and Implications for Affecting Behavior Change. Nutrition 2018, 55–56, S4–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzone, L.; Hilton, D.; Sale, L.; Cohen, D. Socio-Demographics, Implicit Attitudes, Explicit Attitudes, and Sustainable Consumption in Supermarket Shopping. J. Econ. Psychol. 2016, 55, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Tang, C.; Huang, Z.; Hussain, Z.; Are, K.S.; Abegunrin, T.P.; Qin, Z.; Guo, H. Increase in Farm Size Significantly Accelerated Stream Channel Erosion and Associated Nutrient Losses from an Intensive Agricultural Watershed. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 295, 106900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Mu, Y. Significant Influence of the Intensive Agricultural Activities on Atmospheric PM2.5 during Autumn Harvest Seasons in a Rural Area of the North China Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 241, 117844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golosov, V.N.; Collins, A.L.; Dobrovolskaya, N.G.; Bazhenova, O.I.; Ryzhov, Y.V.; Sidorchuk, A.Y. Soil Loss on the Arable Lands of the Forest-Steppe and Steppe Zones of European Russia and Siberia during the Period of Intensive Agriculture. Geoderma 2021, 381, 114678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.R.; Uddin, M.T.; Roy, M.K. Assessment of Organic Shrimp Farming Sustainability from Economic and Environmental Viewpoints in Bangladesh. Environ. Res. 2020, 180, 108879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wai Hui, C.; You, F. Multi-Objective Economic-Resource-Production Optimization of Sustainable Organic Mixed Farming Systems with Nutrient Recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 304–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Meyer-Höfer, M.; von der Wense, V.; Spiller, A. Characterising Convinced Sustainable Food Consumers. Br. Food J. 2015, 117, 1082–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, M.C.; Ynion, J.; Cuevas, R.P.; Samaddar, A.; Ray, A.C.; Mohanty, S.K.; Demont, M. Expert Elicitation Database Capturing Diversity and Cultural Drivers of Food Choice and Nutritional Implications in Eastern India. Data Brief 2020, 33, 106330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaddar, A.; Cuevas, R.P.; Custodio, M.C.; Ynion, J.; Ray, A.C.; Mohanty, S.K.; Demont, M. Capturing Diversity and Cultural Drivers of Food Choice in Eastern India. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2020, 22, 100249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas, R.P.; de Guia, A.; Demont, M. Developing a Framework of Gastronomic Systems Research to Unravel Drivers of Food Choice. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2017, 9, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civitello, L. Cuisine and Culture: A History of Food and People, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kittler, P.G.; Sucher, K.P.; Nelms, M. Food and Culture; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-538-73497-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hendry, L.C.; Stevenson, M.; MacBryde, J.; Ball, P.; Sayed, M.; Liu, L. Local Food Supply Chain Resilience to Constitutional Change: The Brexit Effect. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2019, 39, 429–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomé, K.M.; Cappellesso, G.; Ramos, E.L.A.; de Lima, D.S.C. Food Supply Chains and Short Food Supply Chains: Coexistence Conceptual Framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilbery, B.; Maye, D. Food Supply Chains and Sustainability: Evidence from Specialist Food Producers in the Scottish/English Borders. Land Use Policy 2005, 22, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Agostinho, F.; Duan, H.; Song, G.; Wang, X.; Giannetti, B.F.; Santagata, R.; Casazza, M.; Lega, M. Environmental Impacts Characterization of Packaging Waste Generated by Urban Food Delivery Services. A Big-Data Analysis in Jing-Jin-Ji Region (China). Waste Manag. 2020, 117, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rubio, A.; Almenar, E.; Hernandez-Muñoz, P.; Lagarón, J.M.; Catalá, R.; Gavara, R. Overview of Active Polymer-Based Packaging Technologies for Food Applications. Food Rev. Int. 2004, 20, 357–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastrinos, N.; Weber, K.M. Sustainable Development Goals in the Research and Innovation Policy of the European Union. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 157, 120056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC. Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council Establishing Horizon Europe—The Framework Programme for Research and Innovation, Laying Down Its Rules for Participation and Dissemination COM(2018) 435 Final; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Georgescu, M.; Tarcea, M.; Hardmas, R.; Seni, G.; Teodorescu, C.; Szasz, S.; Guiné, R.; Abram, Z. Romanian Population Perception about Food Risk Behavior Starting from Their Social and Cultural Profile. Bull. Univ. Agric. Sci. Vet. Med. Cluj-Napoca. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 77, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarić, M.M.; Jakšić, K.; Čulin, J.; Guiné, R.P.F. Environmental and Political Determinants of Food Choices: A Preliminary Study in a Croatian Sample. Environments 2020, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongprawmas, R.; Mora, C.; Pellegrini, N.; Guiné, R.P.F.; Carini, E.; Sogari, G.; Vittadini, E. Food Choice Determinants and Perceptions of a Healthy Diet among Italian Consumers. Foods 2021, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable/Group | n | % | Variable/Group | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age group | Living environment | ||||
| Young Adults | 4988 | 49.5 | Urban | 7020 | 69.7 |
| Middle-aged Adults | 3495 | 34.7 | Suburban/Rural | 3047 | 30.3 |
| Senior Adults/Elderly | 1584 | 15.8 | Country | ||
| Sex | Argentina | 522 | 5.2 | ||
| Women | 7117 | 70.7 | Brazil | 665 | 6.6 |
| Men | 2950 | 29.3 | Croatia | 1538 | 15.3 |
| Education | Greece | 498 | 4.9 | ||
| Up to secondary School | 3917 | 38.9 | Hungary | 500 | 5.0 |
| University | 6150 | 61.1 | Latvia | 636 | 6.3 |
| Marital status | Lithuania | 507 | 5.0 | ||
| Married | 4804 | 47.7 | Poland | 586 | 5.8 |
| Single/Divorced/Widowed | 5443 | 52.3 | Portugal | 1314 | 13.1 |
| Professional area | Romania | 821 | 8.2 | ||
| Nutrition | 937 | 9.3 | Serbia | 498 | 4.9 |
| Food | 1048 | 10.4 | Slovenia | 1092 | 10.8 |
| Agriculture | 356 | 3.5 | United States | 890 | 8.9 |
| Sport | 349 | 3.5 | |||
| Psychology | 438 | 4.4 | |||
| Health | 1823 | 18.1 | |||
| Others | 5116 | 50.8 |
| Variable/Group | Not Influenced (%) | Influenced (%) | Chi-Square p-Value | Cramer’s Coefficient, V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age group | <0.0005 | 0.164 | ||
| Young Adults | 34.8 | 65.2 | ||
| Middle-aged Adults | 22.9 | 77.1 | ||
| Senior Adults/Elderly | 16.2 | 83.8 | ||
| Sex | <0.0005 | 0.114 | ||
| Women | 24.4 | 75.6 | ||
| Men | 35.7 | 64.3 | ||
| Marital status | <0.0005 | 0.124 | ||
| Married | 21.9 | 78.1 | ||
| Single/Divorced/Widowed | 33.0 | 67.0 | ||
| Education | <0.0005 | 0.070 | ||
| Up to secondary School | 31.7 | 68.3 | ||
| University | 25.2 | 74.8 | ||
| Professional area | <0.0005 | 0.080 | ||
| Nutrition | 28.5 | 71.5 | ||
| Food | 27.5 | 72.5 | ||
| Agriculture | 24.7 | 75.3 | ||
| Sport | 36.4 | 63.6 | ||
| Psychology | 41.6 | 58.4 | ||
| Health | 28.0 | 72.0 | ||
| Others | 26.0 | 74.0 |
| Variable/Group | Not Influenced (%) | Influenced (%) | Chi-Square p-Value | Cramer´s Coefficient, V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Living environment | <0.0005 | 0.038 | ||
| Urban | 26.6 | 73.4 | ||
| Suburban/Rural | 30.3 | 69.7 | ||
| Country | <0.0005 | 0.258 | ||
| Argentina | 34.1 | 65.9 | ||
| Brazil | 28.4 | 71.6 | ||
| Croatia | 29.7 | 70.3 | ||
| Greece | 28.7 | 71.3 | ||
| Hungary | 43.8 | 56.2 | ||
| Latvia | 32.5 | 67.5 | ||
| Lithuania | 30.0 | 70.0 | ||
| Poland | 24.4 | 75.6 | ||
| Portugal | 7.7 | 92.3 | ||
| Romania | 19.7 | 80.3 | ||
| Serbia | 32.1 | 67.9 | ||
| Slovenia | 20.2 | 79.8 | ||
| United States | 51.7 | 48.3 |
| Function | Eigenvalue | % Variance Explained | Canonical Correlation | Wilks’ Lambda | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0.169 | 36.0 | 0.380 | 0.643 | <0.0005 |
| F2 | 0.142 | 30.4 | 0.353 | 0.751 | <0.0005 |
| F3 | 0.067 | 14.2 | 0.250 | 0.858 | <0.0005 |
| F4 | 0.044 | 9.4 | 0.206 | 0.915 | <0.0005 |
| F5 | 0.031 | 6.6 | 0.173 | 0.955 | <0.0005 |
| F6 | 0.016 | 3.4 | 0.124 | 0.985 | <0.0005 |
| Functions | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables 1 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 |
| RIP | 0.751 * | 0.384 | 0.113 | 0.367 | −0.111 | 0.358 |
| SNR | 0.716 * | 0.287 | −0.154 | 0.280 | 0.497 | −0.235 |
| MP | 0.685 * | 0.226 | 0.180 | 0.264 | 0.250 | 0.561 |
| SE | 0.311 | 0.901 * | 0.212 | 0.126 | −0.161 | −0.069 |
| PB | −0.110 | 0.771 * | −0.159 | 0.494 | 0.261 | 0.235 |
| RL | 0.324 | 0.097 | 0.562 | 0.688 * | 0.309 | −0.013 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guiné, R.P.F.; Bartkiene, E.; Florença, S.G.; Djekić, I.; Bizjak, M.Č.; Tarcea, M.; Leal, M.; Ferreira, V.; Rumbak, I.; Orfanos, P.; et al. Environmental Issues as Drivers for Food Choice: Study from a Multinational Framework. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052869
Guiné RPF, Bartkiene E, Florença SG, Djekić I, Bizjak MČ, Tarcea M, Leal M, Ferreira V, Rumbak I, Orfanos P, et al. Environmental Issues as Drivers for Food Choice: Study from a Multinational Framework. Sustainability. 2021; 13(5):2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052869
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuiné, Raquel P. F., Elena Bartkiene, Sofia G. Florença, Ilija Djekić, Maša Černelič Bizjak, Monica Tarcea, Marcela Leal, Vanessa Ferreira, Ivana Rumbak, Panagiotis Orfanos, and et al. 2021. "Environmental Issues as Drivers for Food Choice: Study from a Multinational Framework" Sustainability 13, no. 5: 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052869
APA StyleGuiné, R. P. F., Bartkiene, E., Florença, S. G., Djekić, I., Bizjak, M. Č., Tarcea, M., Leal, M., Ferreira, V., Rumbak, I., Orfanos, P., Szűcs, V., Klava, D., Korzeniowska, M., Isoldi, K., Correia, P., Ferreira, M., & Cardoso, A. P. (2021). Environmental Issues as Drivers for Food Choice: Study from a Multinational Framework. Sustainability, 13(5), 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052869