Deciphering the Effects of Waste Amendments on Particulate Organic Carbon and Soil C-Mineralization Dynamics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Soil Incubation Experiment
2.3. Soil Mineralization Experiment
2.4. Determination of Soil Properties, SOC and POC
2.5. Data Process
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Different Amounts of Waste Amendments on SOC and POC
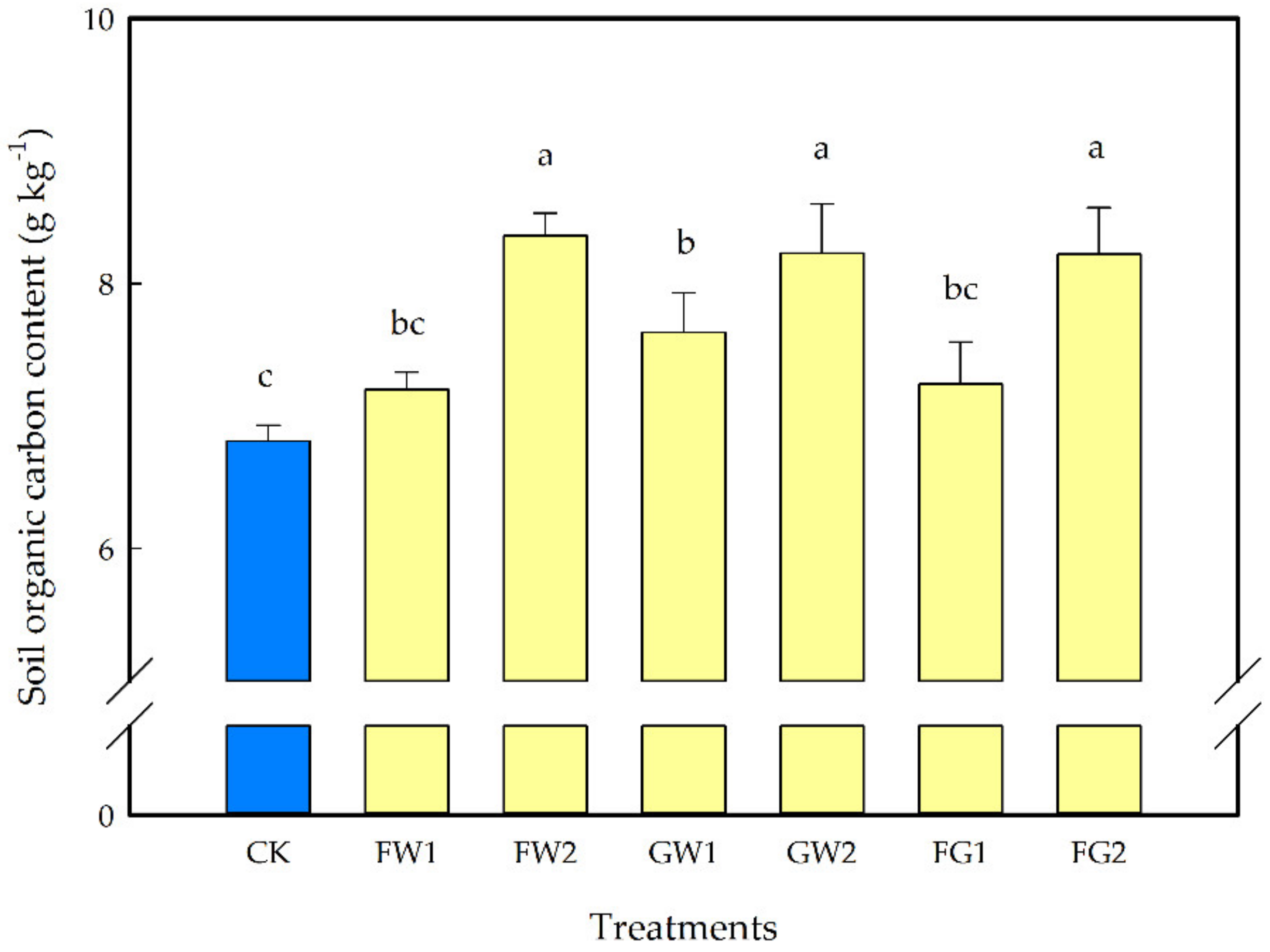
3.1.1. Effect of Different Amounts of Waste Amendments on SOC
3.1.2. Effect of Different Amount of Waste Amendments on POC
3.2. Effect of Different Amounts of Waste Amendments on Soil Organic Carbon Mineralization
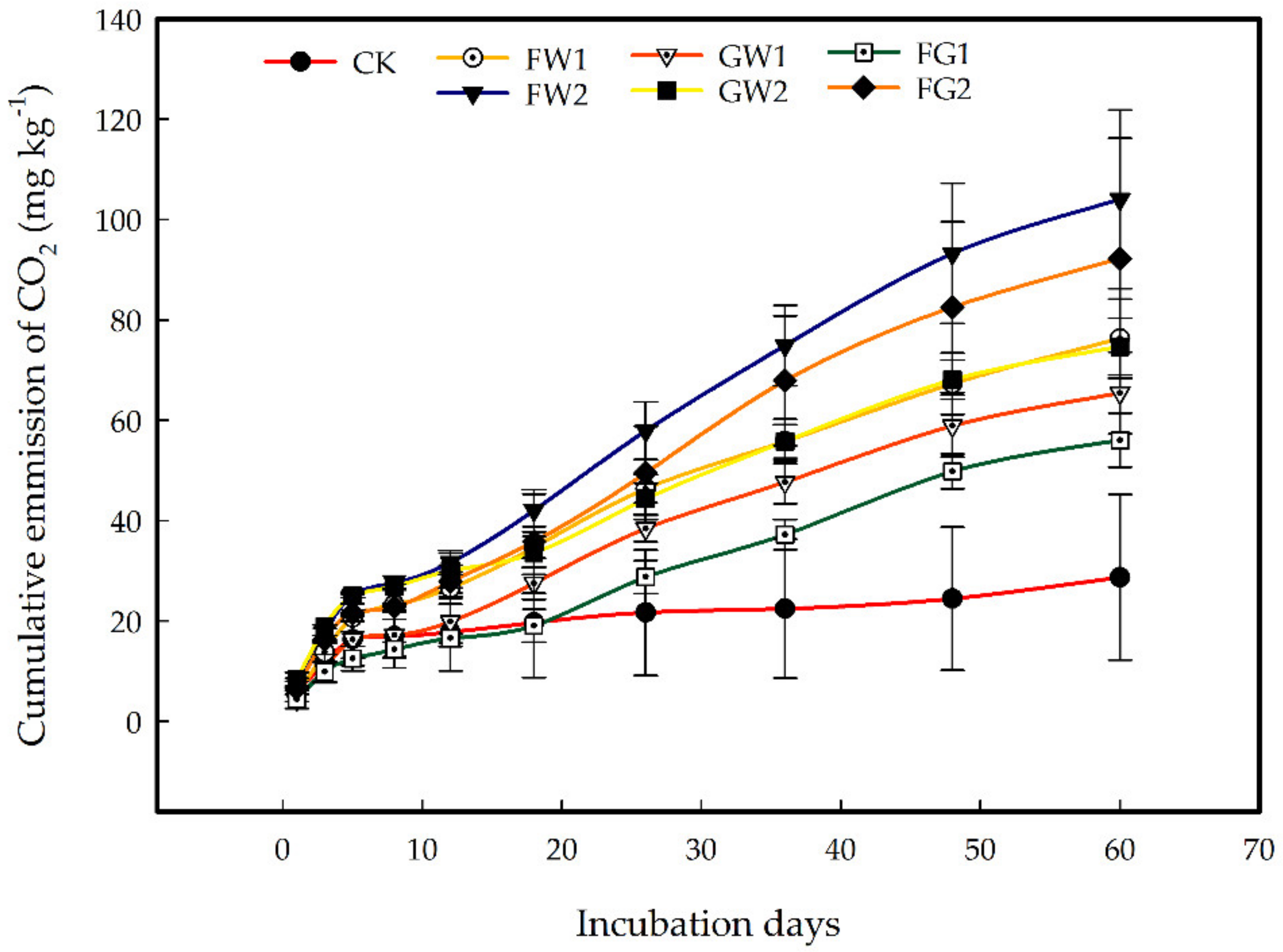
3.2.1. Effect of Different Amounts of Waste Amendments on Cumulative Emissions of CO2
3.2.2. Simulation of SOC Mineralization
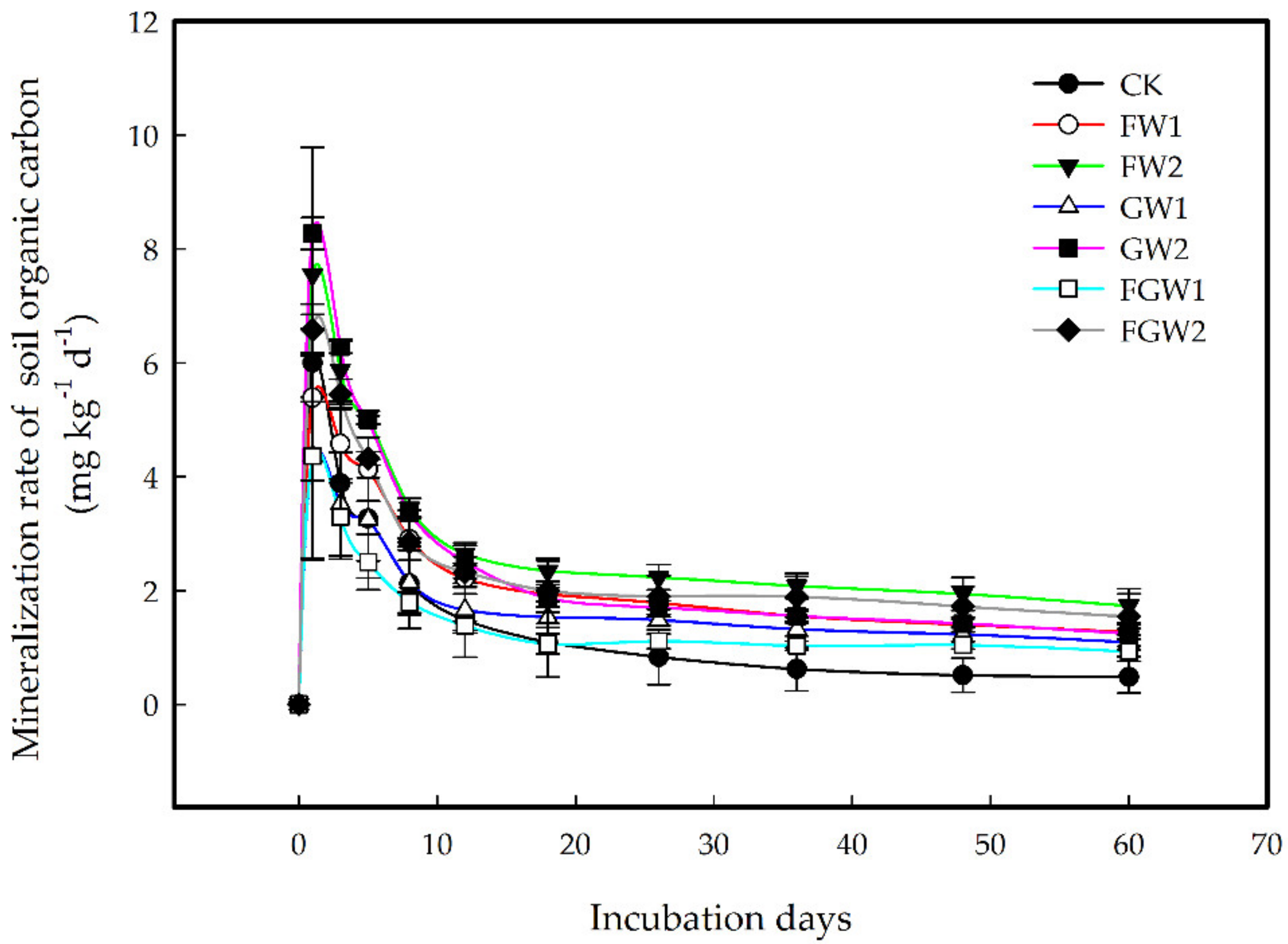
3.2.3. Effect of Different Amounts of Waste Amendments on the Soil Mineralization Rate
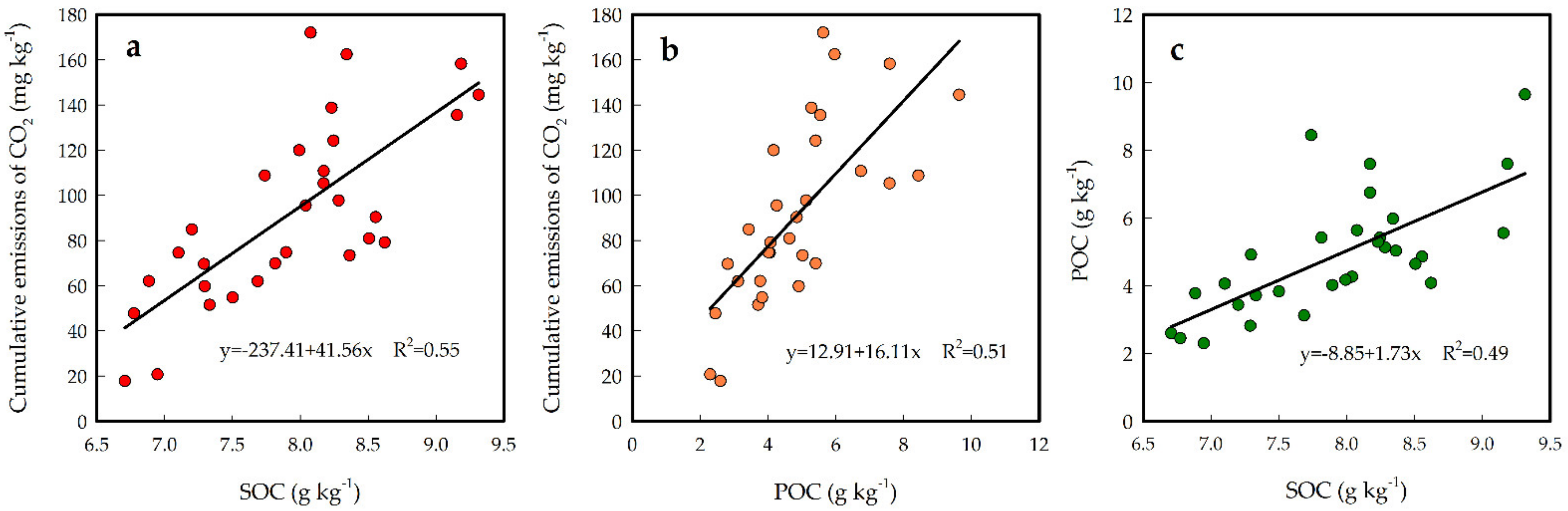
3.3. Correlation Analysis among SOC, POC and Cumulative Emissions of CO2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Statistics Bureau of the People’s Republic of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Amritha, P.K.; Anilkumar, P.P. Development of landscaped landfills using organic waste for sustainable urban waste management. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amritha, P.K.; Kumar, P.A. Productive landscapes as a sustainable organic waste management option in urban areas. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2019, 21, 709–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, D.L. Research on Policy Expression and Evolution Logic in the Change of Municipal Solid Waste Management Policy in China: An Empirical Analysis Based on 169 Policy Texts from 1986 to 2018. Adm. Trib. 2020, 2, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H.T.; Ye, X.H.; Li, J.Q.; Lu, J.; Fan, Q.F.; Yu, N.; Zhang, Y.L.; Dang, X.L.; Zhang, Y.L. Effects of straw return in deep soils with urea addition on the soil organic carbon fractions in a semi-arid temperate cornfield. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Q.; Hu, N.J.; Yang, M.F.; Zhan, X.H.; Zhang, Z.W. Effects of different tillage and straw return on soil organic carbon in a rice-wheat rotation system. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubar, K.A.; Huang, L.; Lu, J.W.; Li, X.K.; Xue, B.; Yin, Z.Y. Long-term tillage and straw returning effects on organic C fractions and chemical composition of SOC in rice-rape cropping system. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 65, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.H.; Ma, J.; Liu, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.C.; Yang, Z.L.; Guo, M.X. Variability of aboveground litter inputs alters soil carbon and nitrogen in a coniferous-broadleaf mixed forest of central China. Forests 2019, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.S.; Huang, W.J.; Mayes, M.A.; Zhou, G.Y. Soil moisture drives microbial controls on carbon decomposition in two subtropical forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 130, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, V.; Traversa, A.; Senesi, N. Forest Soil Organic Carbon Dynamics as Affected by Plant Species and Their Corresponding Litters: A Fluorescence Spectroscopy Approach. Plant Soil 2013, 374, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.Y.; Cheon, J.L.; Ahn, J.H. Effect of Food Waste Compost on the Antler-Type Fruiting Body Yield of Ganoderma lucidum. Mycobiology 2013, 41, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Q.; Zhang, W.; Guo, J.; Wu, S.; Tan, T.; Wang, F.; Dong, R. Performance and kinetic evaluation of a semi-continuously fed anaerobic digester treating food waste: Effect of trace elements on the digester recovery and stability. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Zhao, B.; Ren, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Hou, J.; He, L. Effects of Food Waste Soil Conditioner on Organic Carbon Distribution in Orchard Soil. Res. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 485–493. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Hou, J.; Hao, Y.; Meng, F.; Li, M.; Fan, H. Effect of Exogenous Organic Carbon Prepared from Food Waste on Soil Aggregates. Res. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 166–174. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Li, F.; Chu, H. Effects of Food Waste Compost on Soil Microbial Populations, Tomato Yield, and Tomato Quality. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2014, 45, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedra, F.; Polo, A.; Ribeiro, A.; Domingues, H. Effects of municipal solid waste compost and sewage sludge on mineralization of soil organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E.; Sparks, D.L.; Page, A.L.; Helmke, P.A.; Loeppert, R.H.; Soltanpour, P.N.; Tabatabai, M.A.; Johnston, C.T.; Sumner, M.E. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. Methods Soil Anal. Part 3 Chem. Methods 1996, 9, 961–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Garten, C.T.; Post, W.M.; Hanson, P.J.; Cooper, L.W. Forest soil carbon inventories and dynamics along an elevation gradient in the southern Appalachian Mountains. Biogeochemistry 1999, 45, 115–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saviozzi, A.; Vanni, G.; Cardelli, R. Carbon mineralization kinetics in soils under urban environment. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 73, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.J.; Brown, R.N.; Amador, J.A. Growing food with garbage: Effects of six waste amendments on soil and vegetable crops. Hortscience 2017, 52, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morlat, R.; Chaussod, R. Long-term additions of organic amendmentsin a Loire Valley Vineyard: I. Effects on properties of a calcareous sandy soil. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2008, 59, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piccolo, A.; Mbagwu, J.S.C. Effects of different organic waste amendments on soil microaggregates stability and molecular sizes of humic substances. Plant Soil 1990, 123, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.J.; Wu, J.G.; Zhao, J.H.; Li, J.M.; Hu, J.; Yaa, O.K. Effects of Solid Organic Wastes on Soil Particulate Organic Carbon Structure Under Different Water Conditions. Clean 2019, 47, 1900187.1–1900187.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, L.; Iovieno, P.; Zaccardelli, M.; Morra, L.; Costantini, E. Soil organic matter dynamic as affected by municipal food waste compost fertilization in southern Italy. In Proceedings of the 5th International Congress of the European Society for Soil Conservation” Soils Changing in a Changing World: The Soils of Tomorrow”, Palermo, Italy, 25–30 June 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovieno, P.; Morra, L.; Leone, A.; Pagano, L.; Alfani, A. Effect of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil respiration and enzyme activities of two Mediterranean horticultural soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2009, 45, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.M.; Reynolds, W.D.; Drury, C.F.; Fleming, R.; Tan, C.S.; Denholm, K.; Yang, J.Y. Organic carbon and nitrogen stocks in a clay loam soil 10 years after a single compost application. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 94, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Evanylo, G.K. The effects of long-term application of organic amendments on soil organic carbon accumulation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrar, M.M.; Xu, H.; Aziz, T.; Sun, N.; Adnan, M.; Aslam, M.W.; Syed, A.; Khalid, M.; Zhou, B.; Ma, X.; et al. Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry mediate sensitivity of carbon stabilization mechanisms along with surface layers of a Mollisol after long-term fertilization in Northeast China. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 705–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.A.; Xu, M.; Abrar, M.M.; Shi, S. Long-term fertilization affects functional soil organic carbon protection mechanisms in a soil profile of Chinese loess plateau soil. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, M.A.; Xu, M.G.; Syed, A.A.; Muhammad, W.A.; Tariq, A.; Adnan, M.; Muhammad, N.A.; Zhou, B.; Ma, X. Variations in the profile distribution and protection mechanisms of organic carbon under long-term fertilization in a Chinese Mollisol. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138181. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, A.; Xu, M.; Atizaz, S.; Nuez-Delgado, A. Soil aggregation and soil aggregate stability regulate organic carbon and nitrogen storage in a red soil of southern China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.J.; Wu, J.G.; Li, J.M.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L. Effect of Exogenous Organic Carbon on Soil Organic Carbon and Particulate Organic Carbon in Black Soil. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 31, 278–287. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.D.; Wu, J.G. Infrared Spectrum Characteristics of Particulate Organic Carbon in Soil Fertilizing with Different Organic Materials. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 49(3), 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbi, S.M.F.; Wilson, B.R.; Lockwood, P.V.; Daniel, H.; Young, I.M. Soil organic carbon mineralization rates in aggregates under contrasting land uses. Geoderma 2014, 216, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Zhong, M. Soil moisture alters the response of soil organic carbon mineralization to litter addition. Ecosystems 2016, 19, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Han, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil organic carbon mineralization and microbial community structure. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adnan, M.; Xu, H.; Muhammad, M.A.; Syed, A.; Sun, N.; Qudsia, S.; Muhammad, K.; Muhammad, N.; Manuel, C.; Gao, H.; et al. Long-term fertilization enhanced carbon mineralization and maize biomass through physical protection of organic carbon in fractions under continuous maize cropping. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.S.; Li, L.J.; Ye, R.; Zhu-Barker, X.; Horwath, W.R. The temperature sensitivity of organic carbon mineralization is affected by exogenous carbon inputs and soil organic carbon content. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2017, 81, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leirós, M.C.; Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Seoane, S.; Gil-Sotres, F. Dependence of mineralization of soil organic matter on temperature and moisture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Yu, D.P.; Zhou, W.M.; Zhou, L.; Bao, Y.; Meng, Y.Y.; Dai, L.M. Variations of soil aggregates and soil organic carbon mineralization across forest types on the northern slope of Changbai Mountain. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, A.H.; Usman, A.R.A.; Al-Omran, A.; Ok, Y.S.; Ahmad, M.; Al-Wabel, M.I. Carbon mineralization and nutrient availability in calcareous sandy soils amended with woody waste biochar. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setia, R.; Marschner, P.; Baldock, J.; Chittleborough, D.; Verma, V. Relationships between carbon dioxide emission and soil properties in salt-affected landscapes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Soil | Food Waste Compost | Garden Waste Compost |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.84 | 7.22 | 7.18 |
| EC (mS cm−1) | 0.24 | 3.59 | 0.62 |
| Organic carbon content (g kg−1) | 6.75 | 292.10 | 349.60 |
| Total N (g kg−1) | 1.42 | 21.00 | 9.69 |
| C/N ratio | 4.75 | 13.90 | 36.10 |
| Treatments Number | Soil (%) | Food Waste Compost (%) | Garden Waste Compost (%) | Amendment Carbon (g kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| FW1 | 100 | 1.00 | 0 | 2.92 |
| FW2 | 100 | 2.00 | 0 | 5.84 |
| GW1 | 100 | 0 | 0.84 | 2.92 |
| GW2 | 100 | 0 | 1.67 | 5.84 |
| FGW1 | 100 | 0.50 | 0.42 | 2.92 |
| FGW2 | 100 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 5.84 |
| Incubation Time | CK | FW1 | FW2 | GW1 | GW2 | FGW1 | FGW2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 2.84 ± 0.50 | A | 5.82 ± 0.45 | A | 6.54 ± 0.55 | AB | 5.29 ± 0.99 | A | 8.47 ± 0.87 | A | 4.97 ± 1.30 | A | 5.65 ± 1.12 | AB |
| c | b | ab | b | a | b | b | ||||||||
| 12 d | 2.05 ± 0.50 | C | 4.51 ± 0.16 | B | 5.59 ± 1.96 | AB | 3.75 ± 0.03 | AB | 5.88 ± 1.27 | BC | 3.80 ± 0.47 | A | 6.34 ± 0.62 | A |
| c | ab | ab | bc | ab | bc | a | ||||||||
| 18 d | 2.07 ± 0.10 | C | 3.90 ± 0.47 | B | 6.72 ± 0.22 | AB | 2.87 ± 0.24 | B | 4.21 ± 0.12 | D | 3.55 ± 1.09 | A | 4.25 ± 0.41 | B |
| d | bc | a | cd | b | bc | b | ||||||||
| 26 d | 2.59 ± 0.10 | AB | 4.10 ± 0.28 | B | 7.60 ± 0.78 | A | 3.70 ± 0.09 | AB | 4.08 ± 0.01 | D | 3.28 ± 0.30 | A | 4.81 ± 0.43 | AB |
| d | bc | a | cd | bc | cd | b | ||||||||
| 36 d | 1.82 ± 0.12 | C | 4.18 ± 0.65 | B | 5.12 ± 0.07 | B | 4.08 ± 0.82 | AB | 6.54 ± 0.09 | B | 3.84 ± 0.01 | A | 4.93 ± 0.65 | AB |
| d | bc | b | bc | a | c | bc | ||||||||
| 48 d | 1.95 ± 0.13 | C | 3.35 ± 0.18 | B | 5.26 ± 0.65 | AB | 3.38 ± 0.40 | B | 4.53 ± 0.04 | CD | 3.37 ± 0.01 | A | 4.75 ± 1.28 | AB |
| c | b | a | b | ab | b | ab | ||||||||
| 60 d | 2.44 ± 0.21 | B | 3.43 ± 0.88 | B | 5.13 ± 0.39 | B | 4.01 ± 1.27 | AB | 5.02 ± 0.55 | BCD | 3.77 ± 0.08 | A | 4.17 ± 0.13 | B |
| c | bc | a | abc | ab | abc | ab | ||||||||
| Treatments Number | C1 (mg kg−1) | K (mg d−1) | C2 (mg kg−1) | H (mg d−1) | C1 + C2 (mg kg−1) | C1/(C1 + C2) (%) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 23.24 | 0.19 | 0.8324 | ||||
| FW1 | 12.12 | 0.54 | 139.24 | 0.0104 | 151.36 | 8.01% | 0.9973 |
| FW2 | 12.71 | 0.77 | 280.44 | 0.0068 | 293.14 | 4.33% | 0.9948 |
| GW1 | 7.28 | 0.74 | 129.36 | 0.0102 | 136.64 | 5.33% | 0.9954 |
| GW2 | 18.17 | 0.62 | 333.28 | 0.0032 | 351.45 | 5.17% | 0.9934 |
| FGW1 | 8.23 | 1.08 | 185.64 | 0.0114 | 193.87 | 4.24% | 0.9930 |
| FGW2 | 10.49 | 0.89 | 272.91 | 0.0061 | 283.40 | 3.70% | 0.9942 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, H.; Liang, J. Deciphering the Effects of Waste Amendments on Particulate Organic Carbon and Soil C-Mineralization Dynamics. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073790
Ma X, Zhang Q, Wu H, Liang J. Deciphering the Effects of Waste Amendments on Particulate Organic Carbon and Soil C-Mineralization Dynamics. Sustainability. 2021; 13(7):3790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073790
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xiang, Qingqing Zhang, Haibing Wu, and Jing Liang. 2021. "Deciphering the Effects of Waste Amendments on Particulate Organic Carbon and Soil C-Mineralization Dynamics" Sustainability 13, no. 7: 3790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073790
APA StyleMa, X., Zhang, Q., Wu, H., & Liang, J. (2021). Deciphering the Effects of Waste Amendments on Particulate Organic Carbon and Soil C-Mineralization Dynamics. Sustainability, 13(7), 3790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073790





