The Recovery of Phosphate and Ammonium from Biogas Slurry as Value-Added Fertilizer by Biochar and Struvite Co-Precipitation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Molar Ratio and pH Adjustment
2.2. Details of the Experiments
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.4. Phosphate and Ammonium Removal Efficiencies
3. Results
3.1. Recovery Efficiencies of Phosphate and Ammonium Using Biochar Contents
3.2. Recovery Efficiency of Phosphate and Ammonium at Different Temperature Intervals
3.3. Effects of Initial Phosphorus Concentration on Phosphate Recovery, Ammonium Recovery, and Their Residual Concentrations Using the Struvite Precipitation Method
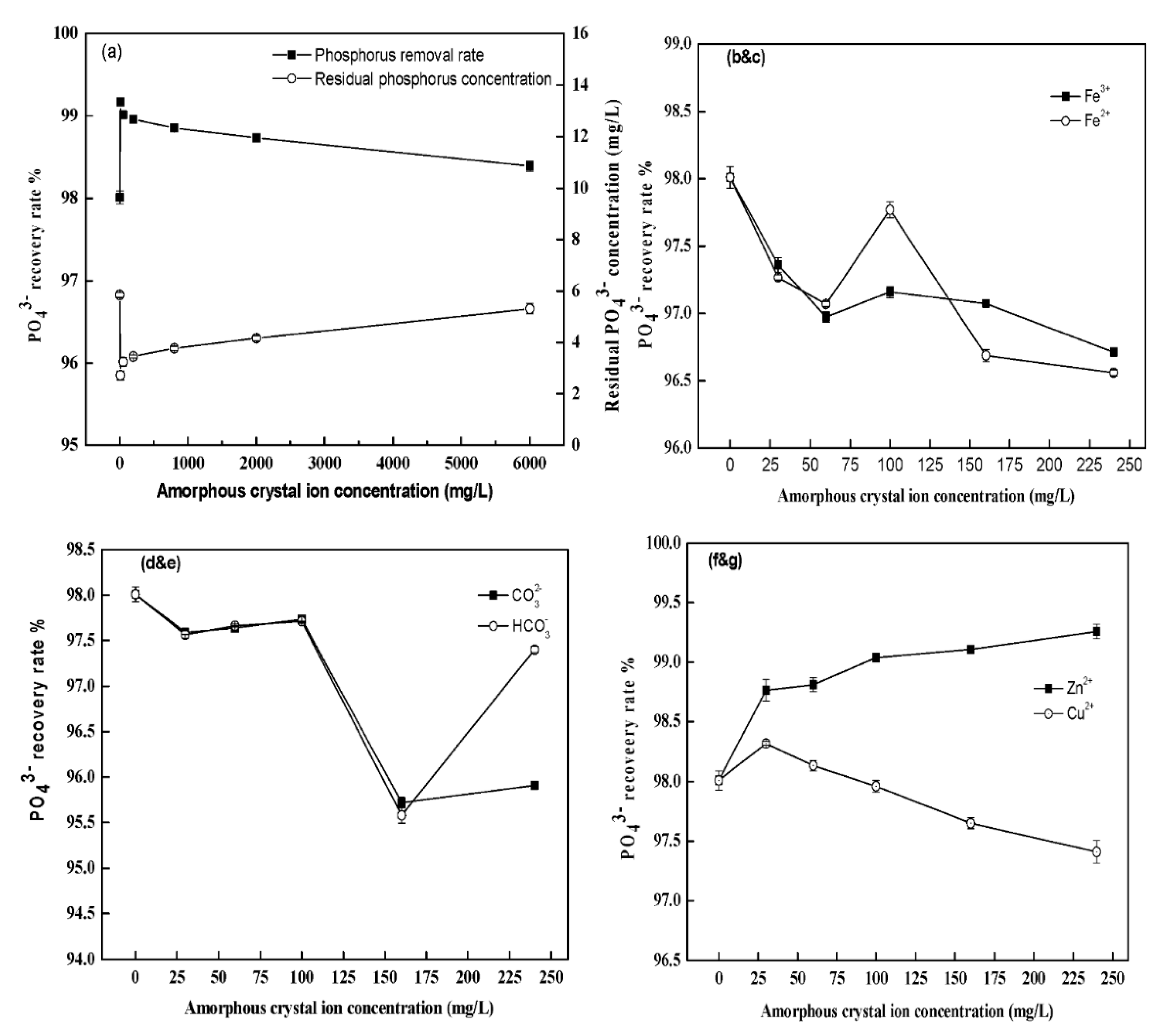
3.4. Effects of Different Ion Concentrations on the Removal Efficiencies of Phosphate and Ammonium
4. Discussion
4.1. Recovery Efficiency of Phosphate and Ammonium by Biochar Contents
4.2. Recovery Efficiency of Phosphate and Ammonium at Different Temperature Intervals
4.3. Effects of the Initial Phosphorus Concentration on Phosphate Recovery, Ammonium Recovery, and Their Residual Concentrations through the Struvite Precipitation Method
4.4. Effects of Different Ion Concentrations on the Removal Efficiencies of Phosphate and Ammonium
4.5. Commercialization and Applicability of This Study as Value-Added Fertilizer
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, Z.; Zhang, S.D.; Li, T.Q.; Zhao, F.L.; He, Z.L.; Zhao, H.P.; Yang, X.E.; Wang, H.L.; Zhao, J.; Rafiq, M.T. Sorption of am-monium and phosphate from aqueous solution by biochar derived from phytoremediation plants. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2013, 14, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, H.; Shen, F.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, L.; Xiao, H.; Deng, S. Biochar produced from oak sawdust by Lanthanum (La)-involved pyrolysis for adsorption of ammonium (NH4+), nitrate (NO3−), and phosphate (PO43−). Chemosphere 2015, 119, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, C.; Fletcher, L.; Singh, S.; Anyikude, K.; Ross, A. Phosphate and ammonium sorption capacity of biochar and hydrochar from different wastes. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lau, A. Reducing ammonia emission from poultry manure composting via struvite formation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2007, 82, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrar, M.M.; Xu, H.; Aziz, T.; Sun, N.; Mustafa, A.; Aslam, M.W.; Shah, S.A.A.; Mehmood, K.; Zhou, B.; Ma, X.; et al. Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry mediate sensitivity of carbon stabilization mechanisms along with surface layers of a Mollisol after long-term fertilization in Northeast China. J. Soils Sediments. 2021, 21, 705–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhang, X. Simultaneous ammonia nitrogen and phosphorus removal from micro-polluted water by biological aerated filters with different media. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Recovery of phosphate and ammonium as struvite from semiconductor wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 64, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.L.; Chen, S.H.; Wang, S.M.; Lin, L.F.; Yan, Y.J.; Zhang, Z.J.; Chen, J.S. Short Communication: Phosphorus recovery from synthetic swine wastewater by chemical precipitation using response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mat. 2010, 176, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-H.; Qiu, G.-L.; Yuan, P.; Cui, X.-Y.; Peng, J.-F.; Zeng, P.; Duan, L.; Xiang, L.-C.; Qian, F. Nutrients removal and recovery from anaerobically digested swine wastewater by struvite crystallization without chemical additions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Park, S.Y.; Li, Y. Nutrient recovery from wastewater streams bymicroalgae: Status and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 19, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.H.; Aswin, B.; Philiphi, D.R. Removal of nitrate, ammonia and phosphate from aqueous solutions in packed bed filter using biochar augmented sand media. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 120, 05004. [Google Scholar]
- Umar, W.; Ayub, M.A.; Rehman, M.Z.; Ahmad, H.R.; Farooqi, Z.R.; Shahzad, A.; Rehman, U.; Mustafa, A.; Nadeem, M. Nitrogen and phosphorus use efficiency in agroecosystems. In Resources Use Efficiency in Agriculture; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, D.; Geissler, B.; Mew, M.; Satalkina, L.; Zenk, L.; Tulsidas, H.; Barker, L.; El-Yahyaoui, A.; Hussein, A.; Taha, M.; et al. Unconventional uranium in China’s phosphate rock: Review and outlook. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 140, 110740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wang, J.; Xiang, S.; Huang, Z.; Ruan, R.; Liu, Y. Nutrient removal from digested swine wastewater by combining ammonia stripping with struvite precipitation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6725–6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Q. Recovery of ammonium-nitrogen from landfill leachate as a multi-nutrient fertilizer. Ecol. Eng. 2003, 20, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lupton, S. Markets for waste and waste–derived fertilizers. An empirical survey. J. Rural. Stud. 2017, 55, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.Z.; Yaseen, M.; Naveed, M.; Wang, X.; Fatima, K.; Saeed, Q.; Mustafa, A. Polymer-Paraburkholderiaphytofirmans PsJN coated diammonium phosphate enhanced microbial survival, phosphorous use efficiency, and production of wheat. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Mavinic, D.S.; Lo, K.V.; Koch, F.A. Production and basic morphology of struvite crystals from a pilot-scale crystallization process. Environ. Technol. 2006, 27, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egle, L.; Rechberger, H.; Zessner, M. Overview and description of technologies for recovering phosphorus from municipal wastewater. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 105, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.D.; Oldring, K.; Churchley, J.; Price, C.; Parsons, S.A. Chmical control of struvite precipitation. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 5, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ponce, R.; López-De-Sá, E.G.; Plaza, C. Lettuce response to phosphorus fertilization with struvite recovered from municipal wastewater. HortScience 2009, 44, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueno, Y.; Fujii, M. Three Years Experience of Operating and Selling Recovered Struvite from Full-Scale Plant. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuanyao, Y.; Huu, H.N.; Wenshan, G.; Yiwen, L.; Soon, W.C.; Dinh, D.N.; Heng, L.; Jie, W. A critical review on ammonium recovery from wastewater for sustainable wastewater management. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 749–758. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Xiao, D.; Pang, R.; Han, C.; Ding, L. Simultaneous removal of nutrients from simulated swine wastewater by adsorption of modified zeolite combined with struvite crystallization. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 256, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luján-Facundo, M.; Iborra-Clar, M.; Mendoza-Roca, J.; Also-Jesús, M. Alternatives for the management of pig slurry: Phosphorous recovery and biogas generation. J. Water Process. Eng. 2019, 30, 100473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, L.; Mangin, D.; Ferrer, J. Struvite formation from the supernatants of an anaerobic digestion pilotplant. J. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 1, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pang, Z. Application of struvite precipitation method in phosphorus and nitrogen removal from wastewater. J. China Biogas. 2004, 1, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.E.; Bowers, J.; Harrison, H. Releasing phosphorus from calcium for struvite fertilizer production from anaerobically digested dairy effluent. J. Water. Environ. Res. 2010, 1, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L. Study on the technology of chemical precipitation treatment of high concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater. J. Indust. Water Treatm. 2010, 6, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Dongmei, Z.; Lihua, C.; Xiaohui, G. Research on the influencing factors of struvite precipitation method used in pig farm wastewater pretreatment. J. South China Norm. Univ. 2012, 2, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman, J.N.; Zvomuya, F.; Cicek, N.; Flaten, D. Evaluation of manure-derived struvite as a phosphorus source for canola. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 3, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Boiarkina, I.; Huang, H.M.; Munir, T.; Wang, G.Q.; Young, B.R. Phosphorus recovery through struvite crystallization: Challanges for future design. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1244–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Ding, L. Recovery of phosphate and ammonia nitrogen from the anaerobic digestion supernatant of activated sludge by chemical precipitation. J. Clear Prod. 2015, 102, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N.O.; Mikkelsen, R.L.; Hesterberg, D.L. Struvite precipitation in anaerobic swine lagoon liquid: Effect of pH and Mg:P ratio and determination of rate constant. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 89, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, A.; Dastur, M.; Donald, S.M.; Frederic, A.K. Preliminary investigation into factors affecting controlled controlledstruvite crystallization at the bench scale. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2004, 3, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, Y.; Yuan, P.; Peng, J.; Fan, M. Modeling the crystallization of magnesium ammonium phosphate for phosphorus recovery. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safaa, M.R. Phosphate removal from aqueous solution using slag and fly ash. HBRC J. 2013, 3, 270–275. [Google Scholar]
- Chimenos, J.M.; Fernández, A.I.; Villalba, G.; Segarra, M.; Urruticoechea, A.; Artaza, B.; Espiell, F. Removal of ammonium and phosphates from wastewater resulting from the process of cochineal extraction using MgO-containing by-product. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratful, I.; Scrimshaw, M.; Lester, J. Conditions influencing the precipitation of magnesium ammonium phosphate. Water Res. 2001, 35, 4191–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Burken, J.G.; Zhang, X.J.; Surampalli, R. Engineered struvite precipitation: Impacts of component-ion molar ratios and pH. J. Environ. Eng. 2005, 131, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, P.W.A.; Han, Z.-Y.; Chen, Y.-X.; Wu, W.-X. Recovery of nitrogen and phosphorous as struvite from swine waste biogas digester effluent. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2007, 20, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hjorth, M.; Christensen, K.V.; Christensen, M.L.; Sommer, S.G. Solid-liquid separation of animal slurry in theory and practice: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 153–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prabhu, M.; Mutnuri, S. Cow urine as a potential source for struvite production. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2014, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miles, A.; Ellis, T.G. Struvite precipitation potential for nutrient recovery from anaerobically treated wastes. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Zhang, W.D.; Song, H.C.; Liu, S.Q.; Chen, L.Q.; Xia, C.F. Research on bacteriostastic activity of biogas broth on plantpathogenic microbe. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2005, 2, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.Z.; Cheng, G.L.; Lu, H.; Sun, Z.D. Influence of biogas fluid on cabbage quality, output and soil fertility. J. Changjiang Vegt. 2006, 9, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Plaza, C.; Sanz, R.; Clemente, C.; Fernández, J.M.; González, R.; Polo, A.; Colmenarejo, M.F. Greenhouse evaluation of struvite and sludges from municipal wastewater treatment works as phosphorus sources for plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 20, 8206–8212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Zebi, L.; Qingrong, L. Contents of selected nutrients and heavy metals in biogas slurry. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2007, 26, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F. Effect of household biogas project development on farmlan nutrient flow. J. Trans. CSAE 2009, 8, 192–199. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, C.A.; Dong, J. Advance on the using of biogas residue as fertilizer. J. Shand. Agric. Sci. 2011, 6, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Han, Z.; Yu, H.; Ye, Z.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, J. Struvite precipitation from biogas digestion slurry using a two-chamber electrolysis cell with a magnesium anode. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Cao, M. Pricin method and application effects of biogas slurry. J. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 1735–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Niu, D.; Cheng, H. Comprehensive utilizing of biogas residue. J. China Res. Comp. Utili. 2005, 12, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Wang, L.; Duan, L.; Zhu, S.; Ye, Z.; Yu, H. The electro coagulation pretreatment of biogas digestion slurry from swine farm prior to nano filtration concentration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, W.A.; Gordon, M.; Viktor, K.; Muataz, A.A.; Tareq, A.A. A state of the art review on phosphate removal from water by biochars. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 409, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.-A.; Guo, H.; Yang, Z.; Xin, S. Biogas slurry pricing method based on nutrient content. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 94, 12130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deenik, J.L.; McClellan, A.T.; Uehara, G. Biochar Volatile Matter Content Effects on Plant Growth and Nitrogen Transformations in a Tropical Soil. In Proceedings of the Western Nutrient Management Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 6–7 March 2009; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkhot, D.; Ghezzehei, T.A.; Berhe, A.A. Effectiveness of biochar for sorption of ammonium and phosphate from dairy effluent. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Wang, X.; Ji, X.; Peng, B.; Tan, C.; Huang, X. Phosphate reclaim from simulated and real eutrophic water by magnetic biochar derived from water hyacinth. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 187, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, J.R.; Mote, C.R.; Robinson, R.B. Thermodynamics of Struvite Formation. Trans. ASAE 1994, 37, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, X.; Xinqing, L.; Zhihong, Z. Biochar adsorption characteristics and kinetics of ammonium nitrogen in water. J. Earth Environ. 2011, 4, 511–516. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Yoshimasa, A.; Motoi, M. Removal and recovery of phosphate from water by calcium-silicate composites-novel adsorbents made from waste glass and shells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 8210–8218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Bao, J.; Hassan, M.A.; Irshad, S.; Talib, M.A.; Zheng, H. Efficient capture of phosphate and cadmium using biochar with multifunctional amino and carboxylic moieties: Kinetics and mechanism. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Rafeah, W.; Zainab, N.; Veronica, U. Removal of mercury, lead and copper from aqueous solution by activated carbon of palm oil empty fruit bunch. J. World Appl. Sci. 2009, 5, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J. Influencing factors and application of nitrogen and phosphorus removal by struvite method. J. Urban Roads Bridg. Flood Cont. 2009, 5, 254–257. [Google Scholar]
- Gadekar, S.; Pullammanappallil, P. Validation and applications of a chemical equilibrium model for struvite precipitation. Environ. Model. Assess. 2010, 15, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutchik, D.; Garrido, J.M. Struvite crystallization versus amorphous magnesium and calcium phosphate precipitation during the treatment of a saline industrial wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 2460–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laridi, R.; Auclair, J.C.; Benmooussa, H. Laboratory and pilot-scale phosphate and ammonium removal by controlled struvite precipitation following coagulation and flocculation of swine wastewater. J. Environ. Technol. 2005, 26, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianchao, K.; Kangping, C.; Yang, Y. Affecting factors and product properties of ammonia-nitrogen wastewater treatment by struvite precipitation method. J. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2010, 5, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hutnik, N.; Kozik, A.; Mazienczuk, A.; Piotrowski, K.; Wierzbowska, B.; Matynia, A. Phosphates (V) recovery from phosphorus mineral fertilizers industry wastewater by continuous struvite reaction crystallization process. J. Water. Res. 2013, 11, 3635–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Corre, K.S.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Hobbs, P.; Parsons, S.A. Impact of calcium on struvite crystal size, shape and purity. J. Cryst. Growth 2005, 283, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; King, J.; Li, W. A two-step fed SBR for treating swine manure. Process. Biochem. 2006, 41, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, A.; Kuru, B. Magnesium ammonium phosphate production from wastewater through Box-Behnken design and its effect on nutrient element uptake in plants. CLEAN-Soil Air Water 2013, 41, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, A.; Demir, S.; Sayilgan, E.; Eraslan, F.; Kucukyumuk, Z. Optimization of struvite fertilizer formation from baker’s yeast wastewater: Growth and nutrition of maize and tomato plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 3264–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Osada, T. Removal of phosphate, magnesium and calcium from swine wastewater through crystalli-zation enhanced by aeration. J. Water. Res. 2002, 36, 2991–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, A.; Blanco, F.; LaCalle, A.; Pinto, M. Struvite precipitation for ammonium removal from anaerobically treated effluents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlinger, K.N.; Young, T.M.; Schroeder, E.D. Kinetics effects on preferential struvite accumulation in wastewater. J. Environ. Eng. 2000, 4, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Cheng, X.; Wang, C. Removal and recovery of N, P and K from urine via ammonia stripping and precipitations of struvite and struvite-K. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 75, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booker, N.A.; Priestley, A.J.; Fraser, I.H. Struvite formation in wastewater treatment plants: Opportunities for nutrient recovery. Environ. Technol. 1999, 20, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.D.; Parsons, S.A. Struvite formation, control and recovery. Water Res. 2002, 36, 3925–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J. Aquatic Chemistry; Wiley-Inter Science: New York, NY, USA, 1970; p. 583. [Google Scholar]
- Asada, T.; Ishihara, S.; Yamane, T.; Toba, A.; Yamada, A.; Oikawa, K. Science of bamboo charcoal: Study on carbonizing temperature of bamboo charcoal and removal capability of harmful gases. J. Health Sci. 2002, 48, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taghizadeh-Toosi, A.; Clough, T.J.; Sherlock, R.R.; Condron, L.M. A wood based low-temperature biochar captures NH3-N generated from ruminant urine-N, retaining its bioavailability. Plant Soil 2012, 353, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, M.; Sardar, K.; Shams, A.B.; Saduf, M.; Alia, N.; Sheikh, S.A.; Anwarzeb, K. Removal of potentially toxic elements from aqueous solutions and industrial wastewater using activated carbon. J. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 2571–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, M.; Xie, T.; Li, J.; Xu, K.; Wang, C. Biochar as a carrier of struvite precipitation for nitrogen and phosphorus recovery from urine. J. Environ. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spokas, K.A.; Novak, J.M.; Venterea, R.T. Biochar’s role as an alternative N-fertilizer: Ammonia capture. Plant Soil 2012, 350, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, J.A.; Spokas, K.A.; Novak, J.M.; Lentz, R.D.; Cantrell, K.B. Biochar Elemental Composition and Factors Influencing Nutrient Retention. In Biochar for Envrionmental Management: Science, Technology and Implementation, 2nd ed.; Lehmann, J., Joseph, S., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2015; pp. 137–161. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, A.; Zimmerman, A.; Harris, W. Surface chemistry variations among a series of laboratory-produced biochars. Geoderma 2011, 163, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Xinrui, H.; Xingzu, W.; Dezhi, S. Influences of calcinations on the adsorptive removal of phosphate by Zn-Al layered double hydroxide from excess sludge liquor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 516–523. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Pan, Q.; Wang, J.; Xue, L.; Howard, A. Phosphorus and nitrogen adsorption capacities of biochars derived from feedstocks at different pyrolysis temperatures. Water 2019, 11, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, J.; Akindolie, M.S.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, Q.; Deng, F.; Cao, B.; Zhang, Y. One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of NaLa (CO3)2 decorated magnetic biochar for efficient phosphate removal from water: Kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics, mechanisms and reusability exploration. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, S.E.; Alling, V.; Martinsen, V.; Mulder, J.; Breedveld, G.D.; Cornelissen, G. The sorption and desorption of phosphate-P, ammonium-N and nitrate-N in cacao shell and corn cob biochars. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.-F.; Zhao, B.-W.; Diao, J.-R.; Zhong, J.-K.; Li, A.-B. Ammonium adsorption characteristics in aqueous solution by dairy manure biochar. Huanjing Kexue 2015, 36, 1678–1685. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.-S. Removal of lead from water using biochars prepared from hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, G.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Lehmann, J.; McBride, M.B.; Hay, A.G. Adsorption of copper and zinc by biochars produced from pyrolysis of hardwood and corn straw in aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8877–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.B.; Cao, X.H.; Liang, P.; Liu, Y.H. Adsorption of uranium from aqueous solution using biochar produced by hy-drothermal carbonization. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2013, 295, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xiao, X.; Yang, L.; Pan, B. Removal of ammonium from rare-earth wastewater using natural brucite as a magne-sium source of struvite precipitation. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türker, M.; Çelen, I. Removal of ammonia as struvite from anaerobic digester effluents and recycling of magnesium and phosphate. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1529–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, T.; Ogino, I.; Mukai, S.R. Immobilization of magnesium ammonium phosphate crystals within micro channels for efficient ammonia removal. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffer, Y.; Clark, T.; Pearce, P.; Parsons, S. Potential phosphorus recovery by struvite formation. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ding, L.; Ren, H.; Xiong, X. Ammonium nitrogen removal from coking wastewater by chemical precipitation recycle technology. Water Res. 2009, 43, 5209–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muster, T.; Douglas, G.; Sherman, N.; Seeber, A.; Wright, N.; Güzükara, Y. Towards effective phosphorus recycling from wastewater: Quantity and quality. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Min, K.J.; Lee, K.; Yu, M.S.; Park, K.Y. Effects of pH, molar ratios and pre-treatment on phosphorus recovery through struvite crystallization from effluent of anaerobically digested swine wastewater. Environ. Eng. Res. 2016, 22, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataki, S.; Baruah, D.C. Prospects and Issues of Phosphorus Recovery as Struvite from Waste Streams. In Handbook of Environmental Materials Management; Hussain, C., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.N.; Aziz, T.; Maqsood, M.A.; Bilal, H.M.; Raza, S.; Zia, M.; Mustafa, A.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y. Evaluating organic mate-rials coating on urea as potential nitrification inhibitors for enhanced nitrogen recovery and growth of maize (Zea mays). Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2019, 22, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Siciliano, A.; Limonti, C.; Curcio, G.M.; Molinari, M. Advances in struvite precipitation technologies for nutrients removal and recovery from aqueous waste and wastewater. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Fu, R.; Lv, H.; Zhu, G.; Lu, B.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Chen, H. Phosphate recovery from swine wastewater by a struvite precipitation electrolyzer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, P.; Gao, F. Highly efficient recovery of ammonium nitrogen from coking wastewater by coupling struvite precipitation and microwave radiation technology. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3688–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Ding, Y.; Qi, P.; You, H.; Jin, C. Effective removal of ammonia nitrogen from waste seawater using crystal seed enhanced struvite precipitation technology with response surface methodology for process optimization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, S.; Modinb, O.; Mijakovic, I. Technologies for biological removal and recovery of nitrogen from wastewater. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 43, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilken, V.; Zapka, O.; Muskolus, A. Product Quality: Fertilizing Efficiency, Results of Pot and Field Tests. In Report of the P-REX Project—Sustainable Sewage Sludge Management Fostering Phosphorus Recovery and Energy Efficiency; Institute of Agricultural and Urban Ecological Projects affiliated to Berlin Humboldt University (IASP): Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Etter, B.; Tilley, E.; Khadka, R.; Udert, K. Low-cost struvite production using source-separated urine in Nepal. Water Res. 2011, 45, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodlia, A.; Ikhlas, N.; Pandebesie, E.S.; Bagastyo, A.Y.; Herumurti, W. The effect of mixing rate on struvite recovery from the fertilizer industry. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 506, 012013. [Google Scholar]
- Wilsenach, J.; Schuurbiers, C.; van Loosdrecht, M. Phosphate and potassium recovery from source separated urine through struvite precipitation. Water Res. 2007, 41, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohui, J.; Jianwei, L.; Yanhui, Z. Comparison of adsorption effect of zirconium modified bentonite with different zirconium loading on phosphate in water. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 6, 2400–2411. [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeyan, T.; Rajgopal, S.; Miranda, L.R. Chromium adsorption from aqueous solution by Hevea Brasilinesis sawdust activated carbon. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 124, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, D.; Sheldarkar, S. Use of TNSAC in phosphate adsorption studies and relationships. Effects of adsorption operating variables and related relationships. Water. Res. 1993, 27, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobya, M.; Demirbas, E.; Bayramoglu, M. Modelling the effects of adsorbent dose and particle size on the adsorption of Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2004, 22, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, S.; Aydiner, C.; Demirbas, E.; Kobya, M.; Dizge, N. Modeling the effects of adsorbent dose and particle size on the adsorption of reactive textile dyes by fly ash. Desalination 2007, 212, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gethke, K.; Herbst, H.; Montag, D.; Bruszies, D.; Pinnekamp, J. Phosphorus recovery from human urine. Water Pract. Technol. 2006, 1, wpt2006070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, N.; Tang, S. Comparison of different K struvite crystallization processes for simul-taneous potassium and phosphate recovery from source-separated urine. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, B.; Zhao, N.; Li, J.; Dai, J. Alleviating Na+ effect on phosphate and potassium recovery from synthetic urine by K-struvite crystallization using different magnesium sources. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 655, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Yu, J.; Luo, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, P.; Zhang, Y. Simultaneous recovery of ammonium, potassium and magnesium from produced water by struvite precipitation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Sun, H.J.; Downs, R.T. Hazenite, KNaMg2(PO4)2·14H2O, a new biologically related phosphate mineral, from Mono Lake, California, USA. Am. Miner. 2011, 96, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampf, A.R.; Mills, S.J.; Nash, B.P.; Jensen, M.; Nikischer, T. Apexite, NaMg(PO4)·9H2O, a new struvite-type phase with a heteropolyhedral cluster. Am. Miner. 2015, 100, 2695–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageshwari, K.; Baishali, D.; Thirugnanam, A.; Balasubramanian, P. Effect of storage on physico chemical characteristics of urine for phosphate and ammonium recovery as struvite. J. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2020, 153, 105053. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Shi, C.; Shi, W.; Huang, X.; Ye, Y.; Jiang, W.; Kang, J.; Liu, D.; Ren, Y.; Li, D. Preferable phosphate removal by nano-La(III) hydroxides modified mesoporous rice husk biochars: Role of the host pore structure and point of zero charge. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Yu, G.; Mo, W.; Zhang, C.; Huang, H.; Li, S.; Gao, M.; Lu, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, H. Enhanced phosphate sequestration by Fe (iii) modified biochar derived from coconut shell. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 10425–10436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Lu, H.H.; Liu, Y.X.; Yang, S.M. Removal of phosphate from aqueous solution by SiO2– biochar nano composites prepared by pyrolysis of vermiculite treated algal biomass. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 83534–83546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.P.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Xia, S. Simultaneous recovery of phosphate, ammonium and humic acid from wastewater using a biochar supported Mg (OH)2 bentonite composite. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Gao, B.; Inyang, M.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Cao, X.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Yang, L. Removal of phosphate from aqueous solution by biochar derived from anaerobically digested sugar beet tailings. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Wang, J.J.; Zhou, B.; Awasthi, M.K.; Ali, A.; Zhang, Z.; Gaston, L.A.; Lahori, A.H.; Mahar, A. Enhancing phosphate adsorption by Mg/Al layered double hydroxide functionalized biochar with different Mg/Al ratios. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, R.; Zhang, H.; Tu, Z.; Li, R.; Li, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced removal of phosphate and ammonium by MgO-biochar composites with NH3 H2O hydrolysis pretreatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7493–7503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabdasli, I.; Parsons, S.A.; Tünay, O. Effect of major ions on induction time of struvite precipitation. Croat. Chem. Acta. 2006, 79, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Le Corre, K.S.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Hobbs, P.; Parsons, S.A. Phosphorus recovery from wastewater by struvite crystallization: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 433–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, Z.; Zeng, W.; Xu, H.; Li, S.; Peng, Y. Adsorption removal and reuse of phosphate from wastewater using a novel adsorbent of lanthanum-modified platanus biochar. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 140, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample Number | Biochar Type |
|---|---|
| CK | Blank |
| DG | Bean stem biochar |
| SH-1 | Water hyacinth root biochar |
| SH-2 | Water hyacinth stem and leaf biochar |
| HSK | Peanut shell biochar |
| MG-1 | Mushroom soil biochar (first batch) |
| MG-2 | Mushroom soil biochar (second batch) |
| SD | Rice Biochar |
| JM | Jimei block sludge biochar |
| TA-1 | Tongan City Sludge Biochar |
| TA-2 | Tongan Hydrothermal Sludge Biochar |
| TA-3 | Tong’an Hydrogel Sludge Biochar |
| XJ | Rubber wood biochar |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubar, A.A.; Huang, Q.; Sajjad, M.; Yang, C.; Lian, F.; Wang, J.; Kubar, K.A. The Recovery of Phosphate and Ammonium from Biogas Slurry as Value-Added Fertilizer by Biochar and Struvite Co-Precipitation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073827
Kubar AA, Huang Q, Sajjad M, Yang C, Lian F, Wang J, Kubar KA. The Recovery of Phosphate and Ammonium from Biogas Slurry as Value-Added Fertilizer by Biochar and Struvite Co-Precipitation. Sustainability. 2021; 13(7):3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073827
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubar, Aftab Ali, Qing Huang, Muhammad Sajjad, Chen Yang, Faqin Lian, Junfeng Wang, and Kashif Ali Kubar. 2021. "The Recovery of Phosphate and Ammonium from Biogas Slurry as Value-Added Fertilizer by Biochar and Struvite Co-Precipitation" Sustainability 13, no. 7: 3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073827
APA StyleKubar, A. A., Huang, Q., Sajjad, M., Yang, C., Lian, F., Wang, J., & Kubar, K. A. (2021). The Recovery of Phosphate and Ammonium from Biogas Slurry as Value-Added Fertilizer by Biochar and Struvite Co-Precipitation. Sustainability, 13(7), 3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073827







