Abstract
Long-haul continental freight flows still heavily rely on unimodal road transport. Intermodal transport, combining road transport with other transport modes, has the potential to have lower operating costs and to be more environmentally sustainable. However, road transport benefits from its better flexibility and adaptability to sudden disruptions and uncertainties. To facilitate a modal shift towards intermodal transport, it is crucial to improve its resilience (i.e., capability to resist and recover from sudden disruptions). Synchromodality is an extension of intermodality in which decisions on modal choice and routing are not predefined long in advance but are taken based on real-time information and may provide a step in that direction. The conducted literature review investigates how uncertainty can be handled in intermodal and synchromodal freight transport networks. The literature is classified based on the planning level, which is either strategic, tactical or operational. The main focus is on the studied types of uncertainty and the proposed solution approaches. This work contributes to the research field by reviewing the literature on intermodal and synchromodal transport with uncertainty, presenting measures to mitigate the effects of uncertainty and proposing future research directions.
1. Introduction
In 2017, 73.3% of all inland freight transport was by road in the European Union, and this value is increasing [1] (p. 37). In an effort to reduce the environmental impact and costs, more efficient transport modes are being considered by logistics service providers. A combination of modes is often used in which high-capacity modes such as trains and ships perform long-haul transport and trucks perform first- and last-mile delivery. Intermodal transport is the transport of goods with at least two different modes, whereby the goods remain in the same loading unit throughout the whole trip [2]. Although no formal definition exists, this definition is widely adopted [3].
Intermodal transport is potentially cheaper and more sustainable than unimodal road transport [4]. This results from the lower costs and emissions per ton/km of trains, barges and ships compared to trucks. For instance, a study that compares road and coastal container transport in Taiwan concludes that emissions could be reduced by over 60% by switching from road to ships [5]. However, pre- and end-haulage are typically performed by trucks in intermodal transport. The cost and environmental benefits of the modal switch should therefore compensate for the additional trans-shipment operations, making it less attractive for short distances [6]. Apart from more energy-efficient transport modes, total emissions can also be reduced by consolidating shipments, which in turn increases fill-rates and reduces empty vehicle trips. Studies from Pan et al. [7] and Van Heeswijk et al. [6] indicate that intermodal transport with consolidation can lead to higher fill-rates and lower costs and emissions compared to road transport.
Despite having a higher operating cost than other modes, road transport remains heavily used. One reason is that logistics service providers are faced with many uncertainties that can lead to disruptions and variations. Supply chain disruptions are defined as unplanned and unanticipated events that disrupt the normal flow of goods in a supply chain [8,9]. Examples of disruptions are labour strikes, accidents, natural disasters and broken infrastructure. Besides disruptions, networks are also subject to normal variations (e.g., variations in travel times due to normal congestion). Although the distinction between them is not clear-cut, both aspects are the result of uncertainties.
As a result of these uncertainties, there is a need for flexibility and resilience. An exact definition of flexibility is not available, since its meaning varies depending on the literature. Evans [10] defines flexibility as the ability to make continuous adjustments in constantly changing conditions. It is a general term that encompasses concepts such as resilience and corrigibility, among others. Resilience is defined by Goetz and Szyliowicz [11] as the ability of an organisation to continue to function after unexpected changes, whereas corrigibility is the ability to learn and adapt to new conditions. For transport networks, Chen and Miller-Hooks [12] define resilience as the capability to resist and recover from disruptions. SteadieSeifi et al. [13] define a resilient freight transport network as one that can recover from any disruption by preventing, absorbing, or mitigating its effects. The last two definitions can be interpreted as a combination of resilience and corrigibility, which illustrates that the differences between these concepts are vague. A measure of resilience used by Chen and Miller-Hooks [12] and Miller-Hooks et al. [14] is the expected fraction of demand that can be satisfied post disaster. In this paper, this definition of resilience from Chen and Miller-Hooks [12] is used.
A review from Flodén et al. [15] on transport service choice indicates that cost is the most important factor when choosing the transport service. However, only alternatives that meet an adequate service quality are considered. Transport time and reliability are major components of service quality. Intermodal transport is slower than unimodal road transport, for instance due to trans-shipments and consolidation [16], and road transport is more flexible than other transport modes [17,18,19], thereby hindering a modal switch. Mitigating this lower flexibility is a key issue to facilitate a modal shift. Synchromodal transport is meant to resolve this issue by allowing more flexible planning and real-time updates. Synchromodal transport is an extension of intermodal transport with synchronised operations between carriers, by including real-time rerouting of loading units over the network to cope with uncertain events and operational or customer requirements [20]. According to Ambra et al. [21], synchromodality can be perceived as real-time, dynamic and optimised intermodal transport. In their review on developments on synchromodal transport related to the hinterland network of European Gateway Services (EGS), van Riessen et al. [22] report that the main challenge for a transportation network operator is the allocation of containers to inland services. They define the following three steps to enable synchromodal transport: integrated network planning, real-time planning and creating planning flexibility. Synchromodal transport has the potential to offer a better performance than intermodal transport on flexibility, reliability and capacity utilisation.
Compared to unimodal transport, intermodal networks have more sources of uncertainty with the additional use of terminals and trans-shipment [23]. Although many studies address uncertainties in intermodal networks, an extensive overview of the existing literature on the topic is missing. SteadieSeifi et al. [13] include but are not focused on uncertainty in their large-scale literature review on intermodal transport. The authors classify the literature into strategic, tactical and operational problems based on the planning horizon. These horizons correspond, respectively, to long-term, medium-term and short-term decisions. The strategic planning level regards the design of the physical network and the investment decisions in the infrastructure. The tactical level concerns the design of the service networks and planning routes. These decisions are made such that resources for a given network are allocated and utilised optimally [13,24]. The containers can be aggregated at this level. Operational planning problems address some of the same issues as tactical problems, such as routing and scheduling, but with individual containers and much shorter planning horizons, such as on a day-to-day basis or in real-time [25,26]. Another literature review by Elbert et al. [27] provides a detailed overview of the literature on both deterministic and stochastic tactical planning in a multimodal setting. Our study differs by specifically focusing on stochastic problems and by including all planning levels. The aim of this study is to provide an extensive overview of the literature on intermodal and synchromodal transport with uncertainty.
The main three contributions of our paper are: (1) an exhaustive overview of the literature on intermodal and synchromodal transport with uncertainty; (2) an overview of measures to mitigate the effects of uncertainty to facilitate the implementation of intermodal transport; and (3) the proposal of relevant future research directions. Our methodological approach is described in Section 2. The following sections each focus on one of the three planning levels. Section 3 investigates strategic planning problems, studies on tactical planning are reviewed in Section 4, and Section 5 addresses operational planning problems. Each of these sections is further divided into a discussion of the studied planning problems and a discussion of the proposed solution methods. Finally, Section 6 contains an in-depth overall discussion and presents future research opportunities for each planning level.
2. Methodology
This section describes the method that was used to identify relevant papers and the criteria to retain them. Searches are performed in the databases of Google Scholar and the Hasselt University library. Only peer-reviewed journal publications are considered. Academic literature is searched by looking up key words in the title. The title must contain the word multimodal, intermodal or synchromodal and at least one of the following words: uncertain(ty), stochastic(ity), random, disruption, perturbation or robust. This led to 561 results, of which 487 contain multimodal in their title, 70 contain intermodal and only 4 contain synchromodal. The ancestry approach is also used where literature that contains uncertainty is cited.
To retain the most relevant literature, only papers which meet the following criteria are kept: (1) the paper studies intermodal or synchromodal freight transport; (2) it contains at least one source of uncertainty and (3) it presents a planning model. The scope of this review is limited to network and flow planning in continental intermodal and synchromodal transport. For instance, the study from Pizzol [28] was not selected because although it includes uncertainty in an intermodal network, it focusses on the uncertainty of emissions rather than intermodal planning. Terminal operations and maritime transport are also left out of this review and therefore papers such as Carlo et al. [29,30,31] are omitted. Drone delivery concerns small packages, which is why studies of this transport mode are left out. This left us with 42 references, which are classified into different planning levels. Table 1 shows the number of studies on each planning level and type of uncertainty. Studies that consider multiple uncertain elements appear several times. The number of studies per year is shown in Figure 1. This figure indicates that the focus on uncertainty in intermodal transport planning is a recent development, with most of the research performed in the last ten years. The year 2018 appears as an outlier with the most publications. Figure A1 in Appendix A lists the number of studies per journal, which shows a vast range of journals with a single reference. Only the European Journal of Operational Research, Transport Research part B: Methodological and Transport Research part E: Logistics and Transportation Review contain three or more references.

Table 1.
Number of studies and types of uncertainty by planning level.
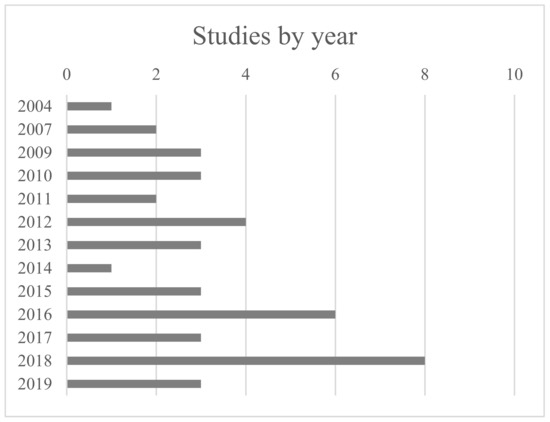
Figure 1.
Number of studies on intermodal and synchromodal transport planning with uncertainty per year.
3. Strategic Decisions
In their literature review on multimodal freight transport planning, SteadieSeifi et al. [13] conclude that research on strategic problems mostly addresses hub location problems, but only rarely considers uncertainties. The objective of hub location problems is to find the optimal locations of hubs to transport orders from their origin to their destination. Apart from direct shipping, orders can be consolidated at hubs to create economies of scale. In the context of intermodal transport, hubs can refer to intermodal terminals such as seaports and rail terminals. An example of a hub location problem is shown in Figure 2. For general overviews of hub location problems we refer to Alumur and Kara [32], Campbell and O’Kelly [33] and Farahani et al. [34]. In the following section (Section 3.1), studies on strategic planning problems that specifically account for uncertainties are discussed. Considered uncertainties are related to transit times, demand, terminal capacity, costs and hub failures. Section 3.2 gives an overview of the applied solution approaches to solve these problems. An overview of the literature on the strategic planning of intermodal transport with the type of uncertainty, solution methods and measures against uncertainty is given in Table 2. All papers in Table 2 study hub locations problems. Most studies do not take any active measures such as rerouting to mitigate the effects of uncertainty. Instead, the scenarios are generated from random distributions and the solution with the lowest expected cost is kept. This is referred to as “Scenario generation”. Three studies at the strategic level apply robust optimisation. One of these constructs solutions which remain feasible for any realisation of uncertainty, whereas the other two minimise the cost of the worst case scenario.
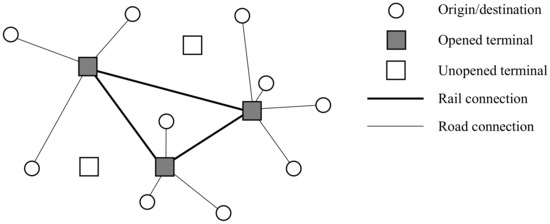
Figure 2.
Example of a hub location problem.

Table 2.
Strategic studies with uncertainty.
3.1. Planning Problems
Stochastic transit times are a first category of uncertainty considered at the strategic level. Sim et al. [35] investigate small package delivery companies and include time-windows. Deliveries have an origin and destination node. They must first be transported to a hub, then possibly to another hub, and finally to the destination. A hub-and-spoke network [42] is considered in which transport between two hubs is faster than between nonhub nodes. The objective is to minimise the longest path for a given minimum service level and number of hubs to be located. The model is applied on a case with up to 25 demand nodes and four facilities located in the US. The authors conclude that increased transit time variability leads to optimal locations for hubs closer to a central hub.
Ishfaq and Sox [36] study hub location problems while accounting for delays at hubs, which are a type of transit time uncertainty. Hubs are modelled as a queuing system with limited resources and time constraints. The more resources are available at a facility, the higher its processing capacity. Shipments need to be transported from an origin to a destination in a hub-and-spoke network that includes road and rail transport. They can be transported at lower cost on inter-hub connections. In contrast to Sim et al. [35], the number of hubs is not predetermined. A fixed cost is incurred per opened facility. The results of a case study of 25 US cities reveal an interaction effect between resources and time constraints. Differences in the amount of resources only affect the costs if the time constraints are strict, in which case lower resources lead to higher costs. The result is that more hubs are opened when resources per hub are lower and shipments are more spread out over facilities to reduce queue lengths. With smaller time-windows, fewer facilities are opened and more shipments only pass through a single facility. This is caused by more direct shipments, which are faster than inter-hub transport. The total costs are higher as a result because direct shipments are more expensive than inter-hub transport.
Stochastic demand is the second category of uncertainty. Karimi et al. [39] propose a mixed-integer linear program (MILP) for the hub location problem with stochastic demand and multiple commodities. Their model allows orders to be split and transported separately. The objective is to minimise costs, which include flow costs, costs for establishing and operating hubs and costs for new infrastructure. The number of hubs to build is not fixed. A sensitivity analysis shows that splitting orders results in total cost reductions of up to 50% by fully using vehicle capacities.
Meraklı and Yaman [37] investigate the robust uncapacitated hub location problem with demand uncertainty. To model demand, upper bounds are defined for inbound and outbound traffic at each node. The objective is to determine locations for a fixed number of hubs such that costs of the worst-case demand scenario are minimised. As the problem is uncapacitated, all demand is routed through the shortest path between its origin and destination. Three test instances are used with 25, 81 and up to 200 nodes. The problem is solved with a linear mixed integer programming formulation and two Benders decomposition based exact algorithms. The authors conclude that the optimal hub locations when uncertainty is accounted for are either identical or close to those in the deterministic case.
The third category of uncertainty is hub failures. Strategic studies without hub failures mitigate the expected effects of uncertainty by reducing their likelihood or impact, but do not provide an answer on how to resolve disruptions when they occur. Orders are either rejected or delivered late and a penalty cost is incurred. Studies that account for hub failures reroute flows from inoperative to operating facilities, thus presenting a solution in case of disruptions. A study on the expansion of intermodal networks from Fotuhi and Huynh [38] includes both stochastic demand and hub failures. These networks can be expanded by increasing the capacities or adding new terminals and links. Only existing infrastructure can be affected by disruptions, in which case their capacities are reduced. Fixed costs are incurred for infrastructure investments. Late deliveries incur a penalty cost and deliveries are not carried out if the delivery cost is higher than the penalty cost. The objective is to minimise total costs. Robust optimisation is used to solve the problem under uncertainty. It constructs a solution that remains feasible for any realisation of uncertainty. The paths are infeasible if they include a terminal which has not been selected to be built. The solution with the lowest optimality gap for all scenarios is chosen. The sum of losses by not choosing the optimal solution in each individual scenario is called regret. The test case includes a realistic-size rail–road network with 20 terminals, 10 potential locations for new terminals and 45 cities. Five demand scenarios are run based on forecasted demands from 2020 to 2040. The results suggest that expanding the rail network will cost less in the long run. New facilities are opened that provide sufficient capacity to absorb demand from disrupted facilities. Disruptions have a higher impact on total costs than demand uncertainty. As the robust function also includes the worst-case scenarios, regret is high in about 30% of experiments. If those scenarios are unlikely to happen, it may be better to exclude them.
Wang et al. [40] study the design of rail–road networks with fuzzy demand, cost and transit time uncertainty. The considered costs are hub construction costs, transport costs and trans-shipment costs. A hub-and-spoke network is designed with the following decisions: (1) determine the locations of intermodal hubs and (2) assign spokes to hubs. The weighted expected costs and the maximum time requirement are minimised in a biobjective optimisation formulation. A MILP is formulated which is solved with a memetic algorithm. The experiments are performed on a realistic dataset with 81 nodes. Compared to the deterministic model, the fuzzy model leads to better results.
Abbassi et al. [41] propose robust models for the intermodal terminal location problem. The study considers a road and maritime network where the location of ports must be determined. A deterministic case is compared against three models with each a different type of uncertainty, namely terminal operating costs, terminal capacities and transportation costs. Similarly to Meraklı and Yaman [37], the objective is to minimise the cost of the worst case scenario. Direct shipments are allowed. The share of direct unimodal shipments is slightly higher in instances with uncertainty at the terminals.
3.2. Solution Methods
Hub location problems are NP-hard, which means that finding an optimal solution is not always viable. The only studies that exclusively opt for an exact solution method are Karimi et al. [39], which uses an exact solver on a MILP, and Meraklı and Yaman [37], which compares their proposed Benders decomposition algorithms against a mixed integer programming formulation with a 10 h time limit. The mixed integer programming formulation can solve instances with up to 50 nodes within the time limit, compared to 200 node instances with the Benders decomposition algorithms. Ishfaq and Sox [36] use a nonlinear mixed integer solver for problems of up to five cities, but the high computational times render this method infeasible for larger problems. These larger problems are solved with a tabu search metaheuristic. To benchmark the heuristic performance, the results are compared against lower bounds that are obtained with a partial linear relaxation of one of the subproblems. The heuristic obtains solutions in less than one minute for problems of up to 15 cities and has an average optimality gap of 0.12%.
Due to the poor performance of exact solution methods, Sim et al. [35] also opt for a heuristic approach to solve the stochastic p-centre problem. They test three different heuristics: a radial heuristic based on the one from Dyer and Frieze [43], a randomised greedy local-search heuristic proposed by Teitz and Bart [44], and a combination of both in which the result from the radial heuristic serves as the initial solution for the Teitz–Bart heuristic. On average, the combined heuristics result in the lowest optimality gap and lower run times than the Teitz–Bart heuristic in the instances treated by Sim et al. [35]. Abbassi et al. [41] propose two solution methods: a simulated annealing metaheuristic and a hybrid approach in which the result of the metaheuristic serves as an initial solution for an exact method. Both approaches are compared against an exact method and the hybrid method leads to lower optimality gaps.
Fotuhi and Huynh [38] propose a genetic algorithm combined with column generation to obtain near-optimal solutions. The genetic algorithm is used to determine strategic decisions and flows are assigned with column generation. Wang et al. [40] use a memetic algorithm, which combines a genetic algorithm with two local search methods.
4. Tactical Decisions
Decisions at the tactical planning level involve allocating the resources optimally on a given network. These decisions consist of determining on which routes services are offered and the scheduling of those services, as well as routing freight [24]. SteadieSeifi et al. [13] identify two recurrent groups of models on tactical planning: Service Network Design (SND) and Network Flow Planning (NFP). NFP determines how to route orders within a given service network, whereas SND decides what services to offer to route orders. SND problems require two types of decisions. First, the service network is designed by deciding which services to offer and their frequency. Then, freight is routed through the selected services. The networks are typically modelled as a set of nodes that are connected with arcs. The orders have an origin and destination node. For every arc, a fixed cost is incurred if it is used in SND problems. These are the design costs for offering services on those arcs. Flow costs are variable and depend on the amount of freight routed through every arc. The objective of basic SND problems is to minimise the total cost, which is equal to the sum of the design and flow costs. NFP problems are similar to SND problems but exclude the design step. An example of a service network is shown in Figure 3. For more information on tactical planning, we refer to Wieberneit [45] and Elbert et al. [27]. Wieberneit [45] provides a literature review on SND which does not limit its scope to multimodal and stochastic problems. The review of Elbert et al. [27] focusses on tactical studies in a multimodal setting and also includes deterministic problems.
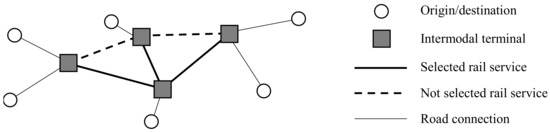
Figure 3.
Example of a service network.
4.1. Planning Problems
At the tactical level, uncertainties related to demand, transit times, capacity and costs are studied. However, the studied types of uncertainty differ between NFP and SND problems. Demand uncertainty is the most studied type of uncertainty for SND problems because the networks are usually set up in advance for longer periods of time. Therefore, complete demand information is not available yet. In contrast, stochastic demand is rarely studied in NFP problems since it is often assumed that demand is already known before routes are determined. Transit times and capacity are the most studied uncertainties for NFP, but are rarely included in studies on SND. Capacity uncertainty is modelled by lowering the capacities of links, nodes and intermodal terminals following disruptions. For severe disruptions such as disasters, capacities can also be set to zero. Only one study on SND considers capacity uncertainty, since the other studies assume that once a service is scheduled, it will never fail. One study on SND accounts for cost uncertainty by treating transport costs per arc as random variables within an interval [46].
Due to capacity restrictions and disruptions, it may be impossible to deliver all orders in time. A recurrent solution to deal with this problem is to impose a penalty cost for orders which cannot be delivered in time. These orders can either be delivered with a delay or handled by a subcontractor at the price of the penalty cost [19,47]. Both options can be used simultaneously if a delay leads to a missed transfer [48].
Although the objective of tactical planning problems is often to minimise costs, multi-objective optimisations are also used. Other elements in the objective function can include total transport time and emissions [19,49]. Demir et al. [19] minimise costs, time and greenhouse gas emissions by assigning different weights to each objective. The authors find that when only emissions are minimised, penalty costs and transportation costs are very high. Trucks must wait for electric trains, which have insufficient capacity to transport all loads at once. As an alternative, Sun et al. [47] include emissions in their objective function by adding emission costs. A different objective which does not include costs at all is to maximise the fraction of demand that can be satisfied following a disaster [12,14]. The remainder of this section is divided between studies on SND (Section 4.1.1) and NFP (Section 4.1.2).
4.1.1. Service Network Design
Studies on service network design with uncertainty are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Studies on Service Network Design (SND) with uncertainty.
Andersen and Christiansen [50] study travel time uncertainty in the European freight train network connecting Scandinavia with Italy. The proposed model supports strategic investment decisions in infrastructure for new railway lines and also models tactical scheduling decisions. Although infrastructure investments are required, these are not incorporated in the study, making it more of a tactical problem. Freight trains experience many delays in Germany due to congestion and lower priority than passenger trains, whereas truck transport through Switzerland and Austria is restricted leading to high travel times. The study assesses potential benefits on service quality of using the Polcorridor, a rail corridor through Poland. As a result of different track gauges between Poland and Czechia, two distinct locomotive fleets are needed as well as extra handling for container transfers. The required decisions are the selection of routes, train schedules and the number of stops at intermediate terminals. The fixed costs for the scheduled trains and used services are included. The variable costs are included for unit flows, repositioning moves, transport time based on the value of time and a penalty for the variability of the transport time. The last two costs are to include service quality in the objective. Demand varies but schedules must remain identical over all time periods. A trade-off needs to be made between excess capacity and lost revenue. Profits are maximised and solutions are obtained with a commercial solver. Fewer deliveries are performed when service quality is considered, because deliveries with high transport time or variability are rejected. Moreover, routes with less variability are chosen despite being longer and more expensive to operate.
Lium et al. [51] study demand stochasticity in service network design. A deterministic model is compared with a stochastic one. Both models include time-windows as a hard constraint, meaning orders must be delivered on time. The authors conclude that using deterministic formulations for stochastic models causes extra costs. Moreover, stochastic models generate solutions with more consolidation possibilities. As a result, the orders can be consolidated faster if the demand is lower than expected. Regarding demand correlation, as long as demand is not perfectly positively correlated, consolidation could be possible. The more negatively correlated, the higher the potential consolidation opportunities. For the same reason, hub-and-spoke networks are favoured over other network structures when dealing with stochasticity. Hoff et al. [52] study a realistically sized service network design problem in which demand becomes known gradually over time. The objective is to minimise the sum of service costs and the expected cost of sudden changes. Their model is based on the one from Lium et al. [51] but a metaheuristic is proposed instead of an exact solution method, which makes it possible to solve larger problem instances.
Crainic et al. [53], Bai et al. [55], Meng et al. [56] and Zhao et al. [58] develop two-stage stochastic programming formulations for the SND problem with stochastic demand. The services are selected in the first stage while demand is unknown. The demand materialises in the second stage, which is where routing decisions are made. Such an approach appears as “recourse” in Table 3. If insufficient capacity is available in the second stage, the excess demand can be outsourced at a higher cost.
Bai et al. [55] extend the study of Lium et al. [51] by considering rerouting to mitigate the costs of stochastic demand. Similarly to Lium et al. [51] and Hoff et al. [52], a scenario tree is used to account for stochasticity. Hard time constraints are kept and it is assumed that excess demand can be outsourced to an external network. In the first stage, the sum of the network setup costs and expected additional costs due to uncertainty are minimised. In the second stage, the optimal flow distribution between the network obtained in the first stage and the external network is generated. The vehicles are also switched between arcs in the model with rerouting. The second stage takes place once the disruption becomes known. As such, the study combines tactical with operational decisions. The stochastic SND model with rerouting is compared against the deterministic and stochastic models in Lium et al. [51]. The results indicate that including rerouting leads to larger cost reductions for correlated demand and requires fewer orders to be outsourced compared to the other models. A drawback of the proposed model is the high computational time. For large instances, the stochastic model without rerouting finds better solutions faster. Both stochastic models lead to the highest savings over the deterministic model when demand is correlated and highly uncertain. The total costs are lowest for all models when demand is clustered in space and time.
The two-stage model proposed by Zhao et al. [58] performs scheduling decisions in the first stage and routing decisions in the second stage. The model accounts for both stochastic demand and transit times. It is applied on a realistic network with 17 railway stations and three ports, of which two are rail–ship transfer hubs. The results indicate an increase in costs and decrease in punctuality as transit time variability increases.
Zhao et al. [48] study sea–rail intermodal container routing with stochastic travel and transfer times. The objective is to minimise total costs, which are composed of: (1) transport costs which depend on the mode and container quantity; (2) transfer costs for loading and unloading containers as well as changing modes; (3) inventory costs for containers waiting to be picked up in transfer hubs or at destination ports; (4) late delivery penalty costs which are proportional to the delay time; and (5) nonfulfilment penalty costs if delays lead to missed transfers. Lower limits on the probabilities of late arrivals at transfer hubs and deliveries are imposed, making it a chance-constrained stochastic problem. The model is applied on a realistically sized network between China and Singapore. The authors find that higher variability leads to higher total costs and more late deliveries. Compared to the deterministic case, routes are chosen with larger time buffers between mode changes to prevent missed transfers. The results of a sensitivity analysis indicate that it is always beneficial to have high on-time arrival probabilities at transfer hubs so as not to miss the next mode. In contrast, higher limits for on-time delivery probabilities lead to higher costs as variability increases, because the costs required to maintain the same service level outweigh penalty costs.
Meng et al. [56] investigate the amount of train, truck and barge capacity to procure under stochastic demand. The study is performed in the context of car manufacturers which need to ship cars between factories or to storage centres. Train and barge services have a limited capacity and fixed weekly schedules, whereas an unlimited number of trucks is available. The probability function of the demand is known and at the start of each week the demand becomes known. The amounts of train and barge capacity to book are determined for each week in the first stage. In the second stage, it is assumed that the demand of the whole week is known and cars are assigned to the services that were selected in the first stage. If the booked capacity is insufficient, the excess cars are shipped by truck. A case study is performed on a realistic Chinese network with 19 nodes, 17 train routes and 8 barge routes. The results indicate that only accounting for the expected value of demand leads to higher costs.
In their literature review on intermodal transport, Macharis and Bontekoning [23] conclude that the research focused on multiple decision makers is very limited, even though coordination is required for large networks. One such study from Puettmann and Stadtler [54] presents a cooperation scheme between an intermodal operator and two carriers, one for first-mile and one for last-mile drayage operations. Without cooperation, the different parties have no knowledge of the other parties’ capacities, costs and existing orders. In the studied cooperation method the, cost proposals are iteratively exchanged between the carriers and the intermodal operator. Due to long travel times for the long-haul, it is assumed that demand at the destination is not known yet at the departure time. The study estimates the effects of this demand uncertainty on cooperation. Performance is evaluated against the optimal situation, which is characterised by a fully centralised decision maker. With the proposed cooperation scheme, optimality gaps between 4% and 7% are obtained. This is a reduction of 65% to 75% compared to the optimality gaps of up to 20% in scenarios without cooperation. Compared to a deterministic setting, cooperative savings are only slightly lower with uncertain demand and decrease as uncertainty increases.
Differently from previous tactical studies with stochastic demand, Demir et al. [19] and Hrušovský et al. [57] include costs, total delivery times and emissions in the objective function. Both studies consider stochastic transit times, while Demir et al. [19] is one of the few studies which combines stochastic demand and transit times. The authors consider a network with road, rail and inland waterway transport. Demir et al. [19] experiment on a dataset with 10 terminals connected by 32 services. To account for stochasticity, the sample average approximation (SAA) approach is used to obtain a deterministic problem. The results indicate that rail and barge modes have a higher share in a deterministic setting compared to a stochastic one. This is caused by the stricter departure times of those modes as opposed to trucks that do not have fixed schedules. If a larger weight is given to delivery times in the objective function, the share of trucks also increases because they are faster.
Hrušovský et al. [57] assume departure times of rail and barge services are fixed, but travel times vary. A simulation optimisation approach is proposed in which solutions obtained from deterministic optimisation are used as input for the simulation step. Uncertainty is only considered in the simulation step where the performance of the deterministic solutions are evaluated over multiple scenarios. Experiments are conducted on the same instances as in Demir et al. [19]. The authors conclude that the SAA approach is much more sensitive to the instance size than the simulation–optimisation approach. Therefore, simulation–optimisation is better suited at solving large instances.
Similarly to Hrušovský et al. [57], Layeb et al. [59] apply a simulation–optimisation approach. However, both stochastic demand and travel times are included. The model is validated with a deterministic real-world case study from Demir et al. [19] using road, rail and inland waterway transport. It is modelled with Arena software and solved with Optquest. The simulation–optimisation model reaches 90% on time and in full deliveries. As demand and travel time distributions are skewed with fat tails, lognormal distributions are used for demand and railway travel times. For travel times, it is assumed that congestion occurs with a given probability of 20%. In case of congestion, the average travel times are assumed to be 20% longer. The main finding is that only the mean and variance of demand and transit times are not sufficient to set up reliable schedules, especially when empirical data displays skewness. The results indicate that ignoring stochasticity will lead to significantly higher costs, even when demand variability is low. This differs from Bai et al. [55], who found that costs are only slightly higher without accounting for stochasticity if demand variability is low.
Yang et al. [46] study how to plan intermodal hub-and-spoke networks with cost and travel time uncertainty. They present a MIP model which optimises both expected costs and maximum travel time. The network is uncapacitated and includes road, rail and air transport for long-haul transport between hubs. First and last mile deliveries are always performed by trucks. It is assumed that all hubs are directly connected to each other and shipments must pass through at least one hub. The required decisions are to select services and route freight on those services. The results indicate a trade-off between cost and maximum transport time. As the maximum travel time increases, air and truck transport decrease in favour of the cheaper but slower rail transport.
Sun et al. [60] examine the effect of rail capacity uncertainty on intermodal routing decisions. Trains follow a fixed schedule, whereas trucks are flexible and uncapacitated. Rail capacity constraints are modelled as fuzzy chance constraints, which are integrated in a MILP. A linear reformulation is performed on this MILP such that it can be solved with exact solution methods. This model is applied on a real large-scale Chinese rail–road intermodal network with 40 terminals and 118 arcs. The authors conclude that there is a trade-off between reliability and costs, because minimising costs results in infeasible decisions. The decisions are infeasible if the actual capacity is lower than what is required. All the test results lead to infeasible decisions when capacity uncertainty is not considered.
4.1.2. Network Flow Planning
Table 4 lists studies on network flow planning with the types of uncertainty and solution methods. Minimising costs during disruptions is the main objective of almost all studies on NFP. Li et al. [61] perform a multiobjective optimisation of an intermodal routing problem with cost and transit time uncertainty while accounting for risks. They identify three major objectives in the previous literature, namely costs, time and reliability, where reliability is measured by lost and damaged goods. Only the first two objectives are considered in their study. For each of these objectives, weighted subobjectives are added to account for risks. For the cost objective, these are to minimise the mean and standard deviation of the total cost and maximise the probability that the total cost of each selected route is within an acceptable threshold. The included costs are transport costs, transfer costs, holding costs and drayage costs. The subobjectives related to time are to minimise the mean and standard deviation of delivery times and maximise the probability of arriving within specified time-windows for just-in-time deliveries. The included transport modes are truck, train and barge. Different priorities are assigned to the objectives with an Analytic Hierarchy Process. The results indicate that the inventory costs are low at less than 3.7%. Despite accounting for only 2.7% of the total delivery time, transfers make up around 22.5% of total costs. The authors conclude that the share of barge transport is highest when delivery time windows are long because of the lower cost and speed compared to other transport modes.

Table 4.
Studies on Network Flow Planning (NFP) with uncertainty.
In addition to costs, Huang et al. [49] also minimise delays in their multiobjective optimisation problem. It is assumed that several carriers are involved in intermodal transport and successively handle goods. When a link becomes disrupted, its capacity is set to zero. The duration of this disruption is then estimated. No adjustments are needed if the duration is lower than the tolerance of the next carrier. If readjustments are needed, routes with the smallest deviation are chosen. Deviations are measured as the weighted sum of proportional changes in time and cost compared to the original route, with weights chosen depending on preferences. The total costs are the sum of the transport and transfer costs. The network is modelled as a state space which is solved with a depth-first search strategy. The method is applied on a small theoretical network, but no comparison is given with a cost minimisation objective.
Meng et al. [62] study liner ship fleet planning with stochastic demand. The objective is to determine the number and types of ships in the fleet and then assign them to routes such that profits are maximised. The routes must be decided under stochastic demand. It is possible to charter additional ships or charter out owned ships in case of overcapacity. The experiments are performed on eight ship routes operated by a global liner container shipping company and 36 ports. The results indicate that higher demand variability leads to higher costs.
Chen and Miller-Hooks [12] and Miller-Hooks et al. [14] consider disasters in an intermodal network, which are modelled by reducing arc capacities and increasing their transit time. On top of routing decisions, recovery actions can be used to mitigate the impact of disruptions. Miller-Hooks et al. [14] consider a given budget to allocate between pre- and postdisaster actions to maximise resilience, whereas Chen and Miller-Hooks [12] only consider postdisaster actions. Predisaster actions are performed before disasters occur and mitigate their impact. Examples include additional fire stations and retrofitting bridges to enhance their durability. Postdisaster actions are performed after a disaster. The objective is to maximise resilience, which the authors define as the fraction of demand that can be satisfied postdisaster. The authors conclude that postdisaster actions are more effective than predisaster actions and combining both is the most effective. Larger mitigations are obtained at the same cost with predisaster actions but low probabilities of individual scenarios render it inefficient to invest in them.
Li et al. [26] study a dynamic intermodal network with both demand and transit time uncertainty. The scope only encompasses long-haul transport between deep-sea terminals and inland terminals. Rail, road, barge and deep-sea transport are considered. Barges and trains operate under fixed schedules and transfer times at terminals are included. A receding horizon control approach is used, which means optimisation is applied to determine which actions should be taken, but only the ones of the current time period are implemented. The optimisation is performed at each time period with estimates based on the latest information. The authors assume decisions are taken by a single decision maker with access to current vehicle locations at all times. The objective is to determine container flows on each outgoing link of each node at each time step such that total costs are minimised. These costs include transport costs, transfer costs, storage costs and penalty costs for unfulfilled demand at the end of the planning horizon. The receding horizon intermodal container flow control (RIFC) model is applied on an intermodal connection from Rotterdam to Venlo over a time period of 24 h with one hour steps. A longer prediction horizon leads to better solutions up to a certain point, after which solutions stabilise. This comes at the cost of higher computation time. Variations in demand have no significant impact on the average computation time of the RIFC model. Higher demand increases the proportion of freight shipped on trains and barges because of capacity limitations for trucks. As the optimisations are based on estimated data, a sensitivity analysis is performed on the proportion of erroneous predictions. This reveals that the RIFC model is very robust to prediction errors, although the assumption was made that predictions within a given horizon are completely accurate.
In a study by Uddin and Huynh [17], the effects of disruptions on an intermodal network are investigated. This is done with a stochastic mixed-integer program in which total costs are minimised. Only the transfer costs at intermodal terminals, the transport costs and thepenalty costs for unsatisfied demand are considered. The model is applied on a small-scale theoretical network and on a large-scale real-life network in the US, which only includes freight transport on major highways and railroads. These networks consist of nodes, links and intermodal terminals where goods are transferred between the nodes. The types of examined disruption scenarios are: (1) link disruptions where several links have their capacity reduced by 50%; (2) node disruptions where all links connected to the disrupted node have capacity reductions of 80%; and (3) intermodal terminal disruptions with capacity reductions of 80%. For the theoretical network, node disruptions lead to the highest costs, closely followed by link disruptions. The total costs for terminal disruptions resulted in less than two thirds the cost of the other disruption types. This is explained by the network layout, which favours road transport, causing low terminal utilisation. In the large-scale network under link or node disruptions, most freight should be shipped by a combination of road and rail because of the lower rail costs and a robust network with sufficient excess capacity. With terminal disruptions, the majority of the freight is shipped by trucks at a slightly higher total cost.
Uddin and Huynh [18] extend their previous model by including multiple commodities, which have different transport and transfer costs, and stochastic capacity. In the event of disruptions, the capacity uncertainty is increased. Tests are performed with different required confidence levels. The results indicate that more uncertainty and higher confidence levels lead to higher costs. The total costs are the highest in the scenario where all terminals are disrupted, in which case all freight must be shipped by trucks. In case of lower required confidence levels with link and node disruptions, most freight is shipped by intermodal rail transport. For high required confidence levels, most freight is shipped by trucks because they can more easily find another route. The authors conclude that trucks should be used if reliability must be maximised, whereas intermodal rail transport should be used to minimise costs.
Sun et al. [47] include uncertain road travel times and rail capacity in their intermodal routing problem. The number of trucks is not restricted, but their transit times are uncertain because of traffic congestion. Trains do not suffer from congestion, but have a limited capacity. The included costs are the transport costs the, loading and unloading costs, the inventory costs for early deliveries, the penalty costs for delayed deliveries and the CO2 emission costs. In contrast to Zhao et al. [48], the loading and unloading times are omitted because they are low. Moreover, the CO2 emission costs are considered and a second model is proposed with biobjective optimisation of total costs and emissions, in which different weights are assigned to the objectives. A fuzzy chance constraint is added such that the probability of insufficient rail capacity remains lower than a given upper limit. The model is applied on a real-life network with major Chinese cities. The conclusion regarding emission costs is that current values are too low to have an impact. Including emissions directly in the objective function is more effective and can lead to 0.94% higher costs for a decrease in emissions of 3.90%, after which costs start increasing at a much higher rate. As is the case in Zhao et al. [48], higher reliability leads to higher costs.
4.2. Solution Methods
SND problems are NP-hard and, combined with the complexity of additional characteristics and the large sizes of real cases, exact solution methods are not always viable [24,63]. Exact solution methods are still used on small instances or with a time limit. Andersen and Christiansen [50] solve their MILP with a commercial solver. Lium et al. [51], Puettmann and Stadtler [54] and Bai et al. [55] use an exact method to solve their models, but only small instances are solved optimally. Lium et al. [51] and Bai et al. [55] also include time limits. Sun et al. [47] propose linear reformulations of their nonlinear model such that it can be solved with exact solution methods. The model is applied on a realistically sized network, but the number of orders is kept low due to the high computational complexity.
Hoff et al. [52] developed a metaheuristic to solve large service network design models in which demand becomes known gradually over time. Crainic et al. [53] propose a progressive hedging-based metaheuristic that decomposes the stochastic problem into deterministic scenarios, which can then be solved with exact methods.
Li et al. [61] solve their model with a kth shortest-path algorithm from Shier [64]. Li et al. [26] compare their linear program against an often used all-or-nothing (AON) approach, which is based on a greedy algorithm and assigns all demand to the least-cost route. Although it requires little computational time, the shortcomings of this AON approach are that it requires sufficient capacity and disregards congestion, potentially caused by the carriers’ own fleet. The results confirm that the AON approach finds a solution much faster, but at 10% to 25% higher cost in the tested instances.
The SAA method is applied by Meng et al. [56] on their two-stage stochastic programming model to obtain a deterministic problem. A metaheuristic solves the resulting deterministic problem with a dual decomposition algorithm and Lagrangian relaxation, which is similar to the decomposition approach from Crainic et al. [27,53]. Due to the high complexity and realistic network size, Zhao et al. [58] solve their two-stage chance-constrained stochastic programming with a hybrid heuristic which combines SAA and ant colony optimisation. A stopping criterion is set at a number of iterations based on the sample size. Zhao et al. [48] also use a hybrid heuristic and consider a realistically sized network. The heuristic combines a shortest path and genetic algorithm.
Yang et al. [46] solve their MIP model with a simulated annealing metaheuristic. On a small theoretical network with three hubs and 10 nodes, their metaheuristic obtains the optimal solutions faster than a commercial IP solver which uses branch and bound. The simulated annealing metaheuristic is compared against a genetic algorithm on a larger dataset with 50 to 100 nodes, which it also outperforms. The stochastic MIP in Uddin and Huynh [17] is solved with a SAA method, in which the expected objective value is estimated by taking random samples [65]. This is done for both the small theoretical and real-life networks. In the extension of this study, Uddin and Huynh [18] use an exact solver for their stochastic MIP.
Hrušovský et al. [57] and Layeb et al. [59] are the only studies to use simulation–optimisation. Hrušovský et al. [57] found that this approach is not as sensitive to the instance size and is able to solve large problems. Layeb et al. [59] conclude that it is able to obtain good solutions of more than 90% on time and in full deliveries within an hour.
5. Operational Decisions
5.1. Planning Problems
Operational problems consider partly the same issues as tactical problems, although with a different time horizon. Whereas tactical problems concern medium-term planning, operational problems focus on short-term planning. Medium-term schedules and routing decisions may be done at the tactical level, while adjustments are made at the operational level. Operational problems can be categorised into two main types: (1) real-time planning or replanning and (2) resource management. The first type includes scheduling and routing decisions based on real-time information such as new order arrivals, cancellations or disruptions. The second planning problem covers the allocation or repositioning of resources. These resources may be containers or vehicles.
5.1.1. Replanning
Table 5 provides an overview of the literature on replanning problems. The uncertainties studied in replanning problems are capacity, demand, travel times, departure times and order cancellations.

Table 5.
Studies on replanning with uncertainty.
Bock [66] provides a dynamic model to route freight which includes vehicle breakdowns, traffic congestion and street blockages as possible disturbance scenarios. Transport orders are assumed to arrive dynamically. Vehicle breakdowns are modelled by setting the route time to infinity. The planning is continuously updated, so a distinction is made between decisions that can still be changed and those that are fixed. These decisions are stored in two different plans: a relevant plan that contains fixed decisions and a theoretical plan that contains decisions which can still be changed in future periods. Both plans are updated in a rolling-horizon, where a new theoretical plan is generated based on the most recent information. As such, a static problem is considered during each planning period. If the theoretical plan outperforms the relevant plan for the next horizon, the theoretical plan becomes the relevant plan in the next period. Anticipation horizons of 90 s provide the best results for the instances used by Bock [66]. At longer anticipation horizons, capacities are almost completely used. Although this leads to better static solutions, they are also more vulnerable to disruptions due to a lack of buffer capacity.
Burgholzer et al. [67] study a real-life intermodal network in a microsimulation model which includes decisions taken by real-life participants. The arrival rates are stochastic and the routes are replanned in the event of disruptions, which are simulated by reducing capacity on links. Transport units (such as containers) have three options in case of disruptions: (1) stay on the disrupted link (take a free trace or wait until the disruption is over in case of 100% capacity reduction); (2) take an alternative link with the same transport mode; (3) switch to another transport mode. The objective is to minimise travel time. A case study is performed on parts of the Austrian road, rail and inland waterways network with a total of 110 links. The results indicate that road and rail transport are preferred over inland waterways in case of disruptions.
van Riessen et al. [69] study intermodal container transport with three types of disturbances: services which arrive or depart too early, too late or are cancelled. The network operator has a predetermined number of long-term barge and rail slots at fixed costs. Performance measures are defined as impact and relevance. Impact measures the extra cost as a result of disturbances, while relevance measures the difference between a fully updated and locally updated plan. In a fully updated plan, the whole schedule is reoptimized, compared to the locally updated plan in which only containers scheduled on the disturbed service are rescheduled. The schedules are made up to one week in advance and can be changed until six to nine hours before departure of a service. The model cannot solve disturbances beyond that point. The authors conclude that full updates only result in small cost reductions compared to local updates. Moreover, full updates are costly to implement even though the cost of reassigning containers was disregarded in this study.
Sun and Schonfeld [70] explore holding decisions with correlated vehicle arrivals at intermodal terminals. The main vehicles that perform long-haul transport visit multiple nodes. At the visited nodes, the containers from the feeder vehicles must be loaded onto the main vehicles and the containers that are delivered by the main vehicles are carried away by receiver vehicles. If a feeder vehicle is delayed, it is decided whether the main vehicle should depart or wait. Waiting leads to higher holding costs and runs the risk of arriving late at future terminals, whereas a missed-transfer cost is incurred when leaving. Containers that are left behind are picked up by the next service. Decisions are updated each time new information is available. Vehicle arrivals are assumed to be correlated due to effects such as adverse weather conditions. The authors conclude that the expected cost is not affected by correlations, but the variance is.
Rivera and Mes [71] study a periodical freight selection problem. Demand is stochastic and estimated with simulation. Freight can be transported with a single high-capacity transport mode or an unlimited number of trucks. The transport modes must be decided for new orders and this freight selection plan is updated each day. It can be considered as both a resource management and real-time planning problem. Cost reductions of up to 25% are obtained compared to single period optimisation.
Rivera and Mes [72] model drayage operations for synchromodal transport as a MILP, which is solved with a metaheuristic. In addition to a pickup-and-delivery problem with time-windows, empty and loaded containers are assigned to terminals. The schedules are updated dynamically as new information arrives. In static instances with clustered demand, the proposed solution method results in lower costs than a construction heuristic. For random demand, there are no significant differences. In dynamic instances, the proposed metaheuristic performs better for both clustered and random demand.
Escudero et al. [68] present a dynamic approach to solve daily drayage operations under transit time uncertainty. In contrast to Rivera and Mes [72], the real-time locations of the vehicles are considered, which requires constant monitoring. New solutions are generated each time an unexpected event happens or at fixed time intervals. Vehicles already on their way to a location are only reassigned to another location if the expected savings are above 10%. Operational cost reductions of up to 30% are achieved. Both this study and van Riessen et al. [69] assume that rescheduling leads to added costs. The model is applied on instances with clustered and random locations. Compared to static approaches, the dynamic approaches have the largest savings when locations are random.
Qu et al. [25] provide a model to reroute flows and reschedule services. The considered uncertainties are transit times, shipment release times and service break-downs. Major disruptions are not included. Sudden breakdowns lead to capacity reductions, as opposed to Bock [66]. Once an uncertain event occurs, complete information is assumed and replanning starts. New shipments are not accepted during replanning and unaffected decisions made before uncertain events are fixed. Similar to Bock [66], a static problem is solved at the replanning stage.
5.1.2. Resource Management
The literature on resource management is listed in Table 6 with the types of uncertainty and solution methods. Stochastic demand is the most studied uncertainty in resource management. Topaloglu and Powell [73] study this problem in the context of managing a fleet with different types of business jets. In an extension of Topaloglu and Powell [73], Topaloglu [74] presents a dynamic model for empty railcar repositioning with random load arrivals, random travel times and multiple vehicle types. It is solved with an approximation algorithm. The objective is to maximise profits.

Table 6.
Studies on resource management with uncertainty.
Lam et al. [75] use an approximate dynamic programming approach for the empty container repositioning problem with stochastic demand. Besides owned containers, additional ones can be leased per port per period and there is no limit on the maximum number available for lease. The proposed method results in less than half the costs compared to a heuristic that sends empty containers back to their region of origin whenever sufficient capacity is available.
Di Francesco et al. [76] study empty container repositioning under partial and complete port disruptions. Under partial disruptions, ships cannot berth, preventing loading and unloading. Containers can still be stored, sent out and received from land. Under complete disruptions, containers cannot be handled at all. Although these disruptions can be seen as capacity reductions, their consequences are much larger than those of capacity uncertainty studied in the literature on replanning.
van Riessen et al. [77] develop a method to create decision trees to support real-time container transport planning with stochastic order arrivals. When an order arrives to transport a container, the container is immediately allocated to a service (e.g., truck or train) by a decision tree. The decision trees are obtained with a machine learning technique that is trained using historical demand data. This method is compared to a first come, first serve approach that assigns orders to the earliest available service and a greedy approach for which incoming orders are assigned to the cheapest feasible service at their arrival. In 80% of cases, the decision tree outperforms the other approaches. As the decision trees in this study are based on historical data, they lead to better solutions when demand follows the same historical patterns.
5.2. Solution Methods
The addition of real-time information renders operational problems much more complex to solve. Moreover, fast algorithms are needed due to the short planning horizon. In contrast to studies on tactical problems, exact solution methods are rare in operational studies and only used on small instances. Qu et al. [25] model their problem as a MILP and consider a small test instance with six terminals, which is solved within seconds in CPLEX. van Riessen et al. [69] apply linear programming on an instance with ten terminals. Stochastic integer programming is used by Di Francesco et al. [76] on a network with five ports.
Metaheuristics are used by Bock [66], Escudero et al. [68] and van Riessen et al. [77] to generate decision trees. Escudero et al. [68] propose a genetic algorithm. Rivera and Mes [72] use a metaheuristic. The test instances from Bock [66] contain five hubs, between 210 and 399 depots and 57,100 routes. Escudero et al. [68] and Rivera and Mes [72] applied their heuristic on Solomon instances [78]. Sun and Schonfeld [70] apply a direct search method on small instances.
Lam et al. [75], Topaloglu [74] and Rivera and Mes [71] employ approximate dynamic programming. Lam et al. [75] conclude that methods yielding good results for small instances may not be extendable to larger instances. Topaloglu [74] concludes that linear approximations generally lead to poor solutions but have low run times, while piecewise-linear approximations are preferable in most situations.
6. Discussion and Future Research Directions
The previous sections reviewed the existing literature on intermodal and synchromodal transport planning with uncertainties, with each section focusing on a specific planning level. The current section presents a discussion of the most relevant findings of this study.
The review shows that there is a growing interest in studying the issue of uncertainty in inter- and synchromodal transport planning (e.g., more than half of the reviewed studies were published from 2015 onwards). Yet, it is clear that this topic still offers plenty of research challenges.
One of the objectives of this review was to identify the types of uncertainty already considered in the literature, which are listed by planning level in Table 1. The most studied types of uncertainty among all planning levels are stochastic demand and stochastic transit times. However, large differences are observed between planning levels. Only a few studies include hub failures and cost uncertainty, so more research could be done on those topics. Uncertain departure times and cancellations are included in a single study on operational planning, but might not have a significant impact on long-term planning. The need for more research attention on the issue of uncertainty is also clearly demonstrated by the fact that the number of studies that combine several types of uncertainty is still very limited. This is especially true for studies that combine more than two types of uncertainty.
Uncertainty is scarcely studied at the strategic level, which contains the fewest studies out of all planning levels. At this level, stochastic demand is the most studied, followed by stochastic transit times, costs and finally uncertain hub capacity and failures. Uncertain vehicle capacities are not studied at the strategic level, which could be a future research opportunity. Stochastic demand and transit times are jointly studied, as well as stochastic demand and hub failures. However, stochastic transit times and hub failures are not jointly studied. The optimal number of hubs is lower when including stochastic transit times if time-windows are strict, because more freight is delivered by faster direct shipping [36]. Meanwhile, it is optimal to have sufficient excess capacity in the case of hub failures, which might lead to more hubs [38]. Considering these opposite results, it would be interesting to research both uncertainty types simultaneously. Capacity utilisation can be increased by allowing orders to be split [39], which was shown to lower capacity requirements in a study that included stochastic demand. A research opportunity would be to investigate the possible interactions between splitable orders and uncertainties other than stochastic demand.
At the tactical level, the following insights are learned on the impact of uncertainty:
- To mitigate the effect of stochastic transit times, routes with lower transit time variability are chosen [50] and larger time buffers between successive departures are established [48].
- A measure against stochastic demand is to design service networks with increased consolidation opportunities [51,55].
- The share of road transport is higher when considering stochastic demand, transit times or capacity compared to a deterministic setting.
A clear difference is seen in types of uncertainty between SND and NFP problems. Most studies on SND include stochastic demand, whereas it is only included by a few studies on NFP. The opposite is true for capacity uncertainty, where only one study on SND assumes that the actual capacity can differ from the scheduled capacity, compared to six studies on NFP. This is because most studies on SND assume that service networks are determined in advance when demand is not known yet. In contrast, most studies on NFP assume demand is known before the planning starts. This distinction is not present for stochastic transit times. A future research opportunity would be to investigate vehicle capacity uncertainty in SND problems.
Differences in studied uncertainties between problem types are also observed at the operational level. An equal number of studies on replanning include stochastic transit times and demand, as opposed to studies on resource management where a greater focus is placed on stochastic demand. Research on capacity uncertainty in operational planning is scarce, with two studies on replanning and none on resource management. There are noticeably fewer studies on operational planning than tactical planning. In the case of replanning, a possible explanation is that it is only performed after the arrival of new information, at which point a deterministic problem could be considered. A measure against stochastic transit times and demand at the operational level is to include buffer capacity [66]. Similarly to the tactical level, road transport has a higher share when accounting for uncertainty [67].
Studies that integrate multiple planning levels are very limited. For instance, there are no studies that combine strategic decisions and tactical or operational decisions. At the tactical level, studies on SND with two-stage models could be regarded as a combination of tactical and operational decisions. Designing the service network in the first stage is a tactical decision made for several periods, whereas the short-term recovery actions in the second stage correspond to operational decisions. However, only one of these studies updates routes in the second stage [55]. In the other two-stage models, it is assumed that all excess demand is outsourced at a fixed cost. It would be interesting to further investigate the benefits of accounting for short-term recovery actions when making longer term decisions.
An ongoing challenge is to find efficient solution methods for large problem instances. Even though the planning problems are computationally difficult to solve, exact solution methods are frequently used in combination with small theoretical instances. Although valuable insights can be learned from these smaller instances, the solution methods are rarely suited to solve realistically sized problems. Different metaheuristics have been proposed that solve planning problems significantly faster than exact methods. An opportunity is to further research metaheuristics and to experiment on larger instances, which might lead to larger differences in computational time between algorithms. This could reveal which algorithms are better suited to solve real-sized problems, which is especially important for operational decisions with short planning horizons. Algorithms that can solve real-time transport planning problems are also a prerequisite of synchromodal transport [22].
Based on the current literature, it is not possible to determine the most efficient algorithm for each specific problem. Regarding metaheuristics, tabu-search, simulated annealing, genetic algorithms and ant-colony optimisation have been proposed, but a comparison between these methods is missing. Simulation–optimisation also showed promising results when applied on SND problems. The lack of a reference problem complicates the comparison between solution methods, since each study considers a different variant. Using benchmark data would also make it easier to identify more efficient solution methods. For the time being, most studies use their own datasets. It would be valuable to compare different solution methods, for instance in a meta-analysis, to gain insight into the most efficient one in specific situations.
Author Contributions
Methodology, T.D., Y.M., K.B. and A.C.; writing—original draft preparation, T.D.; writing—review and editing, Y.M., K.B. and A.C.; supervision, Y.M., K.B. and A.C.; funding acquisition, K.B. and A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the Strategic Basic Research project Data-driven logistics (S007318N), VLAIO (cSBO project DISpATch, HBC.2016.0412) and the Research Foundation Flanders (FWO—WOG, OR4Logistics). Yves Molenbruch is a postdoctoral researcher funded by the Research Foundation Flanders (FWO), grant number 1202719N.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
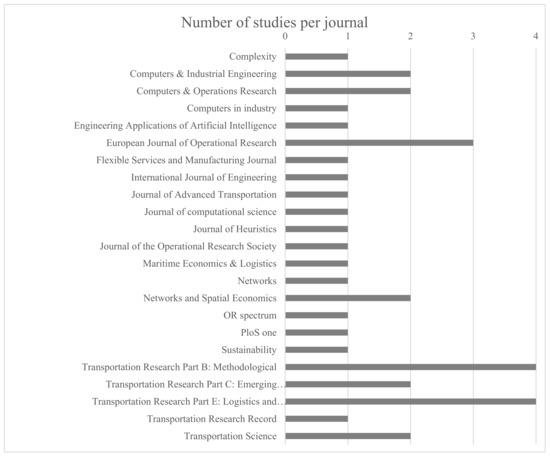
Figure A1.
Number of studies per journal.
References
- EUROSTAT. EU Transport in Figures; EUROSTAT: Luxembourg, 2019; p. 138. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, V. Should we keep on renaming a+ 35-year-old baby? J. Transp. Geogr. 2015, 46, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agamez-Arias, A.-D.-M.; Moyano-Fuentes, J. Intermodal transport in freight distribution: A literature review. Transp. Rev. 2017, 37, 782–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, T.-E.S.; Mathisen, T.A.; Jørgensen, F. Generalized transport costs in intermodal freight transport. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 54, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.-H.; Tseng, P.-H.; Lu, C.-S. Comparing carbon dioxide emissions of trucking and intermodal container transport in Taiwan. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2009, 14, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Heeswijk, W.; Mes, M.; Schutten, J.; Zijm, W. Freight consolidation in intermodal networks with reloads. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2018, 30, 452–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Ballot, E.; Fontane, F. The reduction of greenhouse gas emissions from freight transport by pooling supply chains. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 143, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craighead, C.W.; Blackhurst, J.; Rungtusanatham, M.J.; Handfield, R.B. The severity of supply chain disruptions: Design characteristics and mitigation capabilities. Decis. Sci. 2007, 38, 131–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, G. A conceptual framework for the analysis of vulnerability in supply chains. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2000, 30, 731–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.S. Strategic flexibility for high technology manoeuvres: A conceptual framework. J. Manag. Stud. 1991, 28, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, A.R.; Szyliowicz, J.S. Revisiting transportation planning and decision making theory: The case of Denver International Airport. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 1997, 31, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Miller-Hooks, E. Resilience: An indicator of recovery capability in intermodal freight transport. Transp. Sci. 2012, 46, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SteadieSeifi, M.; Dellaert, N.P.; Nuijten, W.; Van Woensel, T.; Raoufi, R. Multimodal freight transportation planning: A literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 233, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller-Hooks, E.; Zhang, X.; Faturechi, R. Measuring and maximizing resilience of freight transportation networks. Comput. Oper. Res. 2012, 39, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flodén, J.; Bärthel, F.; Sorkina, E. Transport buyers choice of transport service—A literature review of empirical results. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2017, 100, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommar, R.; Woxenius, J. Time perspectives on intermodal transport of consolidated cargo. Eur. J. Transp. Infrastruct. Res. 2007, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Huynh, N. Routing model for multicommodity freight in an intermodal network under disruptions. Transp. Res. Rec. 2016, 2548, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Huynh, N. Reliable Routing of Road-Rail Intermodal Freight under Uncertainty. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2019, 19, 929–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Burgholzer, W.; Hrušovský, M.; Arıkan, E.; Jammernegg, W.; Van Woensel, T. A green intermodal service network design problem with travel time uncertainty. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2016, 93, 789–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, K. Synchronic modalities–Critical success factors. In Logistics Handbook Edition; Evofenedex: Zoetermeer, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ambra, T.; Caris, A.; Macharis, C. Should I Stay or Should I Go? Assessing Intermodal and Synchromodal Resilience from a Decentralized Perspective. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Riessen, B.; Negenborn, R.R.; Dekker, R. Synchromodal container transportation: An overview of current topics and research opportunities. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Logistics, Barcelona, Spain, 27–29 July 2015; pp. 386–397. [Google Scholar]
- Macharis, C.; Bontekoning, Y.M. Opportunities for OR in intermodal freight transport research: A review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2004, 153, 400–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crainic, T.G. Service network design in freight transportation. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2000, 122, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Rezaei, J.; Maknoon, Y.; Tavasszy, L. Hinterland freight transportation replanning model under the framework of synchromodality. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2019, 131, 308–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Negenborn, R.R.; De Schutter, B. Intermodal freight transport planning–A receding horizon control approach. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2015, 60, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbert, R.; Müller, J.P.; Rentschler, J. Tactical network planning and design in multimodal transportation—A systematic literature review. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2020, 100462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzol, M. Deterministic and stochastic carbon footprint of intermodal ferry and truck freight transport across Scandinavian routes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 224, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlo, H.J.; Vis, I.F.; Roodbergen, K.J. Transport operations in container terminals: Literature overview, trends, research directions and classification scheme. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 236, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlo, H.J.; Vis, I.F.; Roodbergen, K.J. Seaside operations in container terminals: Literature overview, trends, and research directions. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2015, 27, 224–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlo, H.J.; Vis, I.F.; Roodbergen, K.J. Storage yard operations in container terminals: Literature overview, trends, and research directions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 235, 412–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alumur, S.; Kara, B.Y. Network hub location problems: The state of the art. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 190, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.F.; O’Kelly, M.E. Twenty-five years of hub location research. Transp. Sci. 2012, 46, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, R.Z.; Hekmatfar, M.; Arabani, A.B.; Nikbakhsh, E. Hub location problems: A review of models, classification, solution techniques, and applications. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2013, 64, 1096–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, T.; Lowe, T.J.; Thomas, B.W. The stochastic p-hub center problem with service-level constraints. Comput. Oper. Res. 2009, 36, 3166–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishfaq, R.; Sox, C.R. Design of intermodal logistics networks with hub delays. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2012, 220, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraklı, M.; Yaman, H. Robust intermodal hub location under polyhedral demand uncertainty. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2016, 86, 66–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotuhi, F.; Huynh, N. Reliable intermodal freight network expansion with demand uncertainties and network disruptions. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2017, 17, 405–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, B.; Bashiri, M.; Nikzad, E. Multi-commodity Multimodal Splittable Logistics Hub Location Problem with Stochastic Demands. Int. J. Eng. 2018, 31, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yang, K.; Yang, L.; Gao, Z. Modeling and optimization of a road–rail intermodal transport system under uncertain information. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 72, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbassi, A.; El hilali Alaoui, A.; Boukachour, J. Robust optimisation of the intermodal freight transport problem: Modeling and solving with an efficient hybrid approach. J. Comput. Sci. 2019, 30, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woxenius, J. Generic framework for transport network designs: Applications and treatment in intermodal freight transport literature. Transp. Rev. 2007, 27, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, M.E.; Frieze, A.M. A simple heuristic for the p-centre problem. Oper. Res. Lett. 1985, 3, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teitz, M.B.; Bart, P. Heuristic methods for estimating the generalized vertex median of a weighted graph. Oper. Res. 1968, 16, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieberneit, N. Service network design for freight transportation: A review. OR Spectr. 2008, 30, 77–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yang, L.; Gao, Z. Planning and optimization of intermodal hub-and-spoke network under mixed uncertainty. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2016, 95, 248–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hrušovský, M.; Zhang, C.; Lang, M. A time-dependent fuzzy programming approach for the green multimodal routing problem with rail service capacity uncertainty and road traffic congestion. Complexity 2018, 2018, 8645793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhang, X.; Whiteing, A. A chance-constrained stochastic approach to intermodal container routing problems. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L. A Decision Method for Disruption Management Problems in Intermodal Freight Transport. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Decision Technologies (IDT’2011), Beirut, Lebanon, 11–14 December 2011; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, J.; Christiansen, M. Designing new European rail freight services. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2009, 60, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lium, A.-G.; Crainic, T.G.; Wallace, S.W. A study of demand stochasticity in service network design. Transp. Sci. 2009, 43, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, A.; Lium, A.-G.; Løkketangen, A.; Crainic, T.G. A metaheuristic for stochastic service network design. J. Heuristics 2010, 16, 653–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crainic, T.G.; Fu, X.; Gendreau, M.; Rei, W.; Wallace, S.W. Progressive hedging-based metaheuristics for stochastic network design. Networks 2011, 58, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puettmann, C.; Stadtler, H. A collaborative planning approach for intermodal freight transportation. OR Spectr. 2010, 32, 809–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Wallace, S.W.; Li, J.; Chong, A.Y.-L. Stochastic service network design with rerouting. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2014, 60, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Hei, X.; Wang, S.; Mao, H. Carrying capacity procurement of rail and shipping services for automobile delivery with uncertain demand. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2015, 82, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrušovský, M.; Demir, E.; Jammernegg, W.; Van Woensel, T. Hybrid simulation and optimization approach for green intermodal transportation problem with travel time uncertainty. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2018, 30, 486–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xue, Q.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, X. A two-stage chance constrained approach with application to stochastic intermodal service network design problems. J. Adv. Transp. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layeb, S.B.; Jaoua, A.; Jbira, A.; Makhlouf, Y. A simulation-optimization approach for scheduling in stochastic freight transportation. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 126, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hong, Z.; Dong, K. How uncertain information on service capacity influences the intermodal routing decision: A fuzzy programming perspective. Information 2018, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Nachtmann, H.; Rossetti, M.D. WebShipCost-Quantifying Risk in Intermodal Transportation. In Proceedings of the IIE Annual Conference, Fayetteville, AR, USA, 8–10 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Wang, T.; Wang, S. Short-term liner ship fleet planning with container transshipment and uncertain container shipment demand. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2012, 223, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnanti, T.L.; Wong, R.T. Network design and transportation planning: Models and algorithms. Transp. Sci. 1984, 18, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shier, D.R. Iterative methods for determining the k shortest paths in a network. Networks 1976, 6, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleywegt, A.J.; Shapiro, A.; Homem-de-Mello, T. The sample average approximation method for stochastic discrete optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 2002, 12, 479–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, S. Real-time control of freight forwarder transportation networks by integrating multimodal transport chains. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 200, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgholzer, W.; Bauer, G.; Posset, M.; Jammernegg, W. Analysing the impact of disruptions in intermodal transport networks: A micro simulation-based model. Decis. Support. Syst. 2013, 54, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, A.; Muñuzuri, J.; Guadix, J.; Arango, C. Dynamic approach to solve the daily drayage problem with transit time uncertainty. Comput. Ind. 2013, 64, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Riessen, B.; Negenborn, R.R.; Lodewijks, G.; Dekker, R. Impact and relevance of transit disturbances on planning in intermodal container networks using disturbance cost analysis. Marit. Econ. Logist. 2015, 17, 440–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Schonfeld, P. Holding decisions for correlated vehicle arrivals at intermodal freight transfer terminals. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2016, 90, 218–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, A.E.P.; Mes, M.R. Anticipatory freight selection in intermodal long-haul round-trips. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2017, 105, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, A.E.P.; Mes, M.R. Scheduling drayage operations in synchromodal transport. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Logistics, Southampton, UK, 18–20 October 2017; pp. 404–419. [Google Scholar]
- Topaloglu, H.; Powell, W.B. Dynamic-programming approximations for stochastic time-staged integer multicommodity-flow problems. Inf. J. Comput. 2006, 18, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topaloglu, H. A parallelizable and approximate dynamic programming-based dynamic fleet management model with random travel times and multiple vehicle types. In Dynamic Fleet Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2007; pp. 65–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.-W.; Lee, L.-H.; Tang, L.-C. An approximate dynamic programming approach for the empty container allocation problem. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2007, 15, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Francesco, M.; Lai, M.; Zuddas, P. Maritime repositioning of empty containers under uncertain port disruptions. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2013, 64, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Riessen, B.; Negenborn, R.R.; Dekker, R. Real-time container transport planning with decision trees based on offline obtained optimal solutions. Decis. Support. Syst. 2016, 89, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.M. Algorithms for the vehicle routing and scheduling problems with time window constraints. Oper. Res. 1987, 35, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).