Residues from Water Precipitation via Ferric Hydroxide Threaten Soil Fertility
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kliestik, T.; Nica, E.; Musa, H.; Poliak, M.; Mihai, E.A. Networked, Smart, and Responsive Devices in Industry 4.0 Manufacturing Systems. Econ. Manag. Financ. Mark. 2020, 15, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Beever, J.; Brightman, A.O. Reflexive Principlism as an Effective Approach for Developing Ethical Reasoning in Engineering. Sci. Eng. Ethics 2015, 22, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winn, M.L.; Angell, L.C. Towards a Process Model of Corporate Greening. Organ. Stud. 2000, 21, 1119–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroušek, J.; Kolář, L.; Strunecký, O.; Kopecký, M.; Bartoš, P.; Maroušková, A.; Cudlínová, E.; Konvalina, P.; Šoch, M. Modified biochars present an economic challenge to phosphate management in wastewater treatment plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 123015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroušek, J.; Rowland, Z.; Valášková, K.; Král, P. Techno-economic assessment of potato waste management in developing economies. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2020, 22, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliestik, T.; Valaskova, K.; Nica, E.; Kovacova, M.; Lazaroiu, G. Advanced methods of earnings management: Monotonic trends and change-points under spotlight in the Visegrad countries. Oecon. Copernic. 2020, 11, 371–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliestik, T.; Misankova, M.; Valaskova, K.; Svabova, L. Bankruptcy Prevention: New Effort to Reflect on Legal and Social Changes. Sci. Eng. Ethics 2017, 24, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, M.A.; Burbano, V.C. The Drivers of Greenwashing. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2011, 54, 64–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mardoyan, A.; Braun, P. Analysis of Czech Subsidies for Solid Biofuels. Int. J. Green Energy 2015, 12, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacova, M.; Kliestik, T.; Valaskova, K.; Durana, P.; Juhaszova, Z. Systematic review of variables applied in bankruptcy prediction models of Visegrad group countries. Oecon. Copernic. 2019, 10, 743–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Grady, P.F. Thales of Miletus: The Beginnings of Western Science and Philosophy; Routledge: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zaman, S.; Begum, A.; Rabbani, K.S.; Bari, L. Low cost and sustainable surface water purification methods using Moringa seeds and scallop powder followed by bio-sand filtration. Water Supply 2016, 17, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Nagpal, G.; Agrawal, S. Rachna Water purification by using Adsorbents: A Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 11, 187–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.E. Plasma-based water purification: Challenges and prospects for the future. Phys. Plasmas 2017, 24, 055501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortajada, C.; van Rensburg, P. Drink more recycled wastewater. Nature 2020, 577, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maroušek, J.; Kwan, J.T.H. Use of pressure manifestations following the water plasma expansion for phytomass disintegration. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marasova, J.; Vallušová, A.; Vasileva, E.S.; de Saint Julien, D.P. CSR Practices: The Case of Veolia in Three European Countries. In Responsible Organizations in the Global Context; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 175–197. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, E.; Kliestik, T.; Musa, H.; Durana, P. Product decision-making information systems, real-time big data analytics, and deep learning-enabled smart process planning in sustainable industry 4.0. J. Self-Gov. Manag. Econ. 2020, 8, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bolisetty, S.; Peydayesh, M.; Mezzenga, R. Sustainable technologies for water purification from heavy metals: Review and analysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, R.J.; Birnbaum, L.; Cantor, K.P.; Rose, J.B.; Butterworth, B.E.; Pegram, R.; Tuomisto, J. Water Chlorination: Essential Process or Cancer Hazard? Toxicol. Sci. 1995, 28, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccaro, P.; Mancini, G.; Vagliasindi, F.G. Water intended for human consumption—Part I: Compliance with European water quality standards. Desalination 2005, 176, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exley, C. Aluminum Should Now Be Considered a Primary Etiological Factor in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Rep. 2017, 1, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, R.; Fan, C.; Sun, J.; Shang, C. Oxidation of iron sulfide and surface-bound iron to regenerate granular ferric hydroxide for in-situ hydrogen sulfide control by persulfate, chlorine and peroxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 336, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.D.C.; Zhou, J.L.; Li, W.; Long, G. Progress in manufacture and properties of construction materials incorporating water treatment sludge: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 145, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroušek, J.; Strunecký, O.; Stehel, V. Biochar farming: Defining economically perspective applications. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, T.S.; Hinsinger, P.; Turner, B.L. Phosphorus in soils and plants–facing phosphorus scarcity. Plant Soil 2016, 401, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordell, D. Global phosphorus scarcity: A food secure future? J. Nutr. Intermed. Metab. 2017, 8, 61–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroušek, J.; Stehel, V.; Vochozka, M.; Kolář, L.; Maroušková, A.; Strunecký, O.; Peterka, J.; Kopecký, M.; Shreedhar, S. Ferrous sludge from water clarification: Changes in waste management practices advisable. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSmidt, E.; Ghyselbrecht, K.; Zhang, Y.; Pinoy, L.; Van Der Bruggen, B.; Verstraete, W.; Rabaey, K.; Meesschaert, B. Global Phosphorus Scarcity and Full-Scale P-Recovery Techniques: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 336–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, D.; Kammann, C.; Grünhage, L.; Muller, C. Simple Biotoxicity Tests for Evaluation of Carbonaceous Soil Additives: Establishment and Reproducibility of Four Test Procedures. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroušek, J. Novel technique to enhance the disintegration effect of the pressure waves on oilseeds. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valaskova, K.; Throne, O.; Kral, P.; Michalkova, L. Deep learning-enabled smart process planning in cyber-physical system-based manufacturing. J. Self-Gov. Manag. Econ. 2020, 8, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Stávková, J.; Maroušek, J. Novel sorbent shows promising financial results on P recovery from sludge water. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordell, D.; White, S. Life’s bottleneck: Sustaining the world’s phosphorus for a food secure future. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2014, 39, 161–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Giles, C.D.; Darch, T.; George, T.S.; Blackwell, M.S.A.; Stutter, M.; Shand, C.; Lumsdon, D.; Cooper, P.; Wendler, R.; et al. Opportunities for mobilizing recalcitrant phosphorus from agricultural soils: A review. Plant Soil 2018, 427, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hancock, J. Environmental Human Rights: Power, Ethics and Law; Routledge: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Maroušek, J.; Myšková, K.; Žák, J. Managing Environmental Innovation: Case Study on Biorefinery Concept; Revista Técnica de la Facultad de Ingeniería Universidad del Zulia: Caracas, Venezuela, 2015; Volume 38, pp. 216–220. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.; Lan, Y.; Tratnyek, P.G.; Johnson, R.L.; Filip, J.; O’Carroll, D.M.; Garcia, A.N.; Agrawal, A. Sulfidation of Iron-Based Materials: A Review of Processes and Implications for Water Treatment and Remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13070–13085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-H.; Wang, S.-Y. Application of water treatment sludge in the manufacturing of lightweight aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herreño, L.C.F.; Solano, D.M.V.; Sarabia, K.D.R.; Pérez, J.O.C.; Quintero, A.A.M. Drinking water treatment sludge as a partial substitute for clays in non-structural brick production. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1409, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, P.A.; Bays, C.L. Critical Thinking Development in Undergraduate Engineering Students from Freshman through Senior Year: A 3-Cohort Longitudinal Study. Am. J. Eng. Educ. 2015, 6, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroušek, J.; Maroušková, A.; Kůs, T. Shower cooler reduces pollutants release in production of competitive cement substitute at low cost. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Effects 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glæsner, N.; Helming, K.; De Vries, W. Do Current European Policies Prevent Soil Threats and Support Soil Functions? Sustainability 2014, 6, 9538–9563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Psacharopoulos, G. The social cost of an outdated law: Article 16 of the Greek constitution. Eur. J. Law Econ. 2003, 16, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroušek, J. Study on commercial scale steam explosion of winter Brassica napus straw. Int. J. Green Energy 2013, 10, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.D. Moral Relevance and Moral Conflict; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Funk, C. Mixed messages about public trust in science. Issues Sci. Technol. 2017, 34, 86–88. [Google Scholar]
- Maroušek, J. Finding the optimal parameters for the steam explosion process of hay. Revista Técnica de la Facultad de Ingeniería Universidad del Zulia 2012, 35, 170–178. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, Z.; Yi, F.; Naz, A.S.; Saleem, A. An investigation of justice in supply chain trust and relationship commitment-An empirical study of Pakistan. J. Compet. 2015, 7, 71–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, J.; He, H. Adsorbents based on montmorillonite for contaminant removal from water: A review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 123, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramus, C.A.; Montiel, I. When Are Corporate Environmental Policies a Form of Greenwashing? Bus. Soc. 2005, 44, 377–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatankhah, S.; Zarra-Nezhad, M.; Amirnejad, G. An empirical assessment of willingness to accept “low-cost” air transport services: Evidence from the Middle East. J. Tour. Serv. 2019, 10, 79–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenhard, R.; Malcho, M.; Jandačka, J. Modelling of heat transfer in the evaporator and condenser of the working fluid in the heat pipe. Heat Transf. Eng. 2019, 40, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapolsky, R.M. Behave: The Biology of Humans at Our Best and Worst; Penguin: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Stutter, M.I.; Shand, C.A.; George, T.S.; Blackwell, M.S.A.; Dixon, L.; Bol, R.; Mackay, R.L.; Richardson, A.E.; Condron, L.M.; Haygarth, P.M. Land use and soil factors affecting accumulation of phosphorus species in temperate soils. Geoderma 2015, 257–258, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandačka, J.; Mičieta, J.; Holubčík, M.; Nosek, R. Experimental Determination of Bed Temperatures during Wood Pellet Combustion. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 2919–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencsik, A.; Kosár, S.T.; Máchová, R. Corporate Culture in Service Companies that Support Knowledge Sharing. J. Tour. Serv. 2018, 9, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muo, I.; Azeez, A.A. Green entrepreneurship: Literature review and agenda for future research. Int. J. Entrep. Knowl. 2019, 7, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroušek, J. Pretreatment of sunflower stalks for biogas production. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2013, 15, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, F.; Kienhues, D.; Bromme, R. Trust in science and the science of trust. In Trust and Communication in a Digitized World; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 143–159. [Google Scholar]
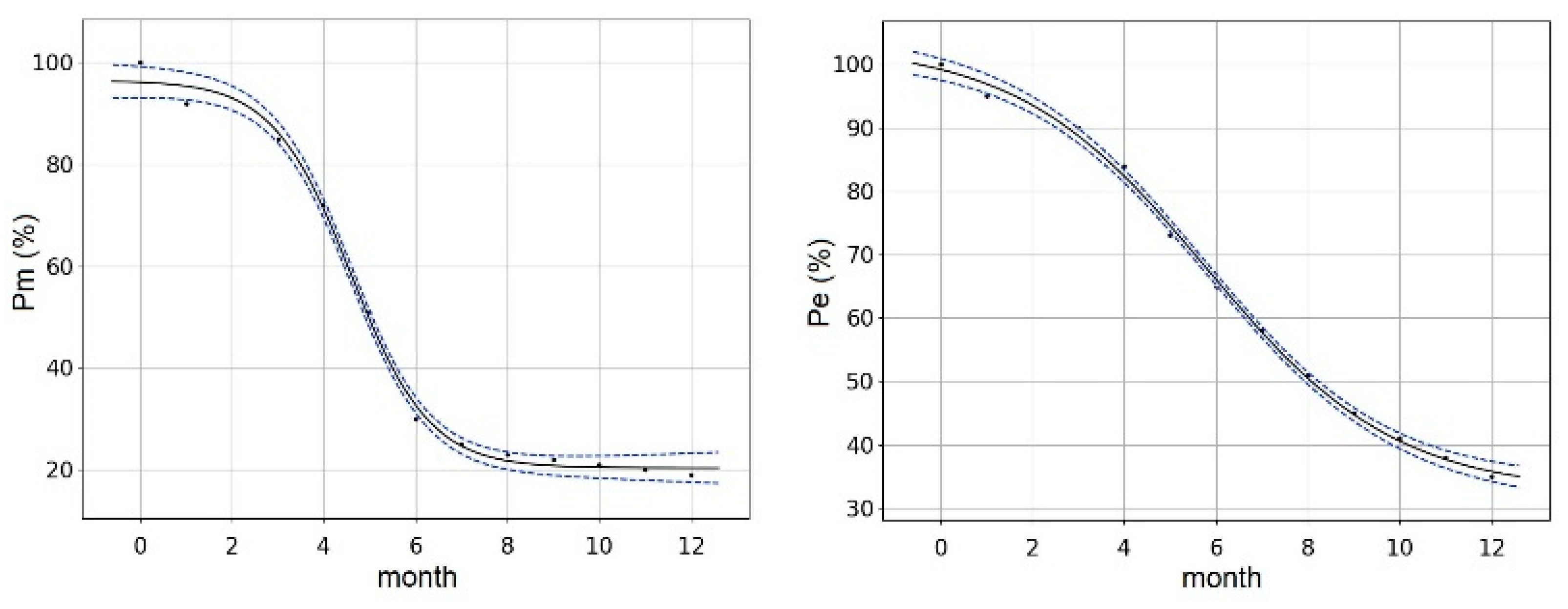
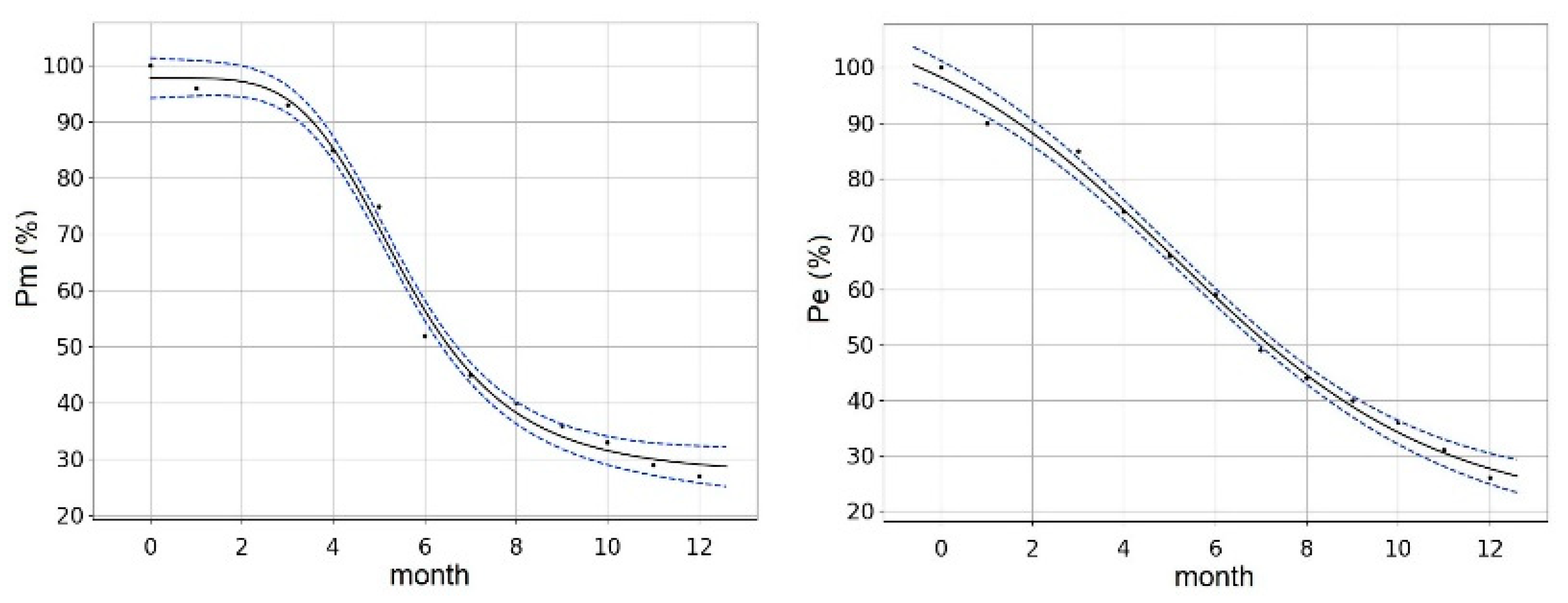
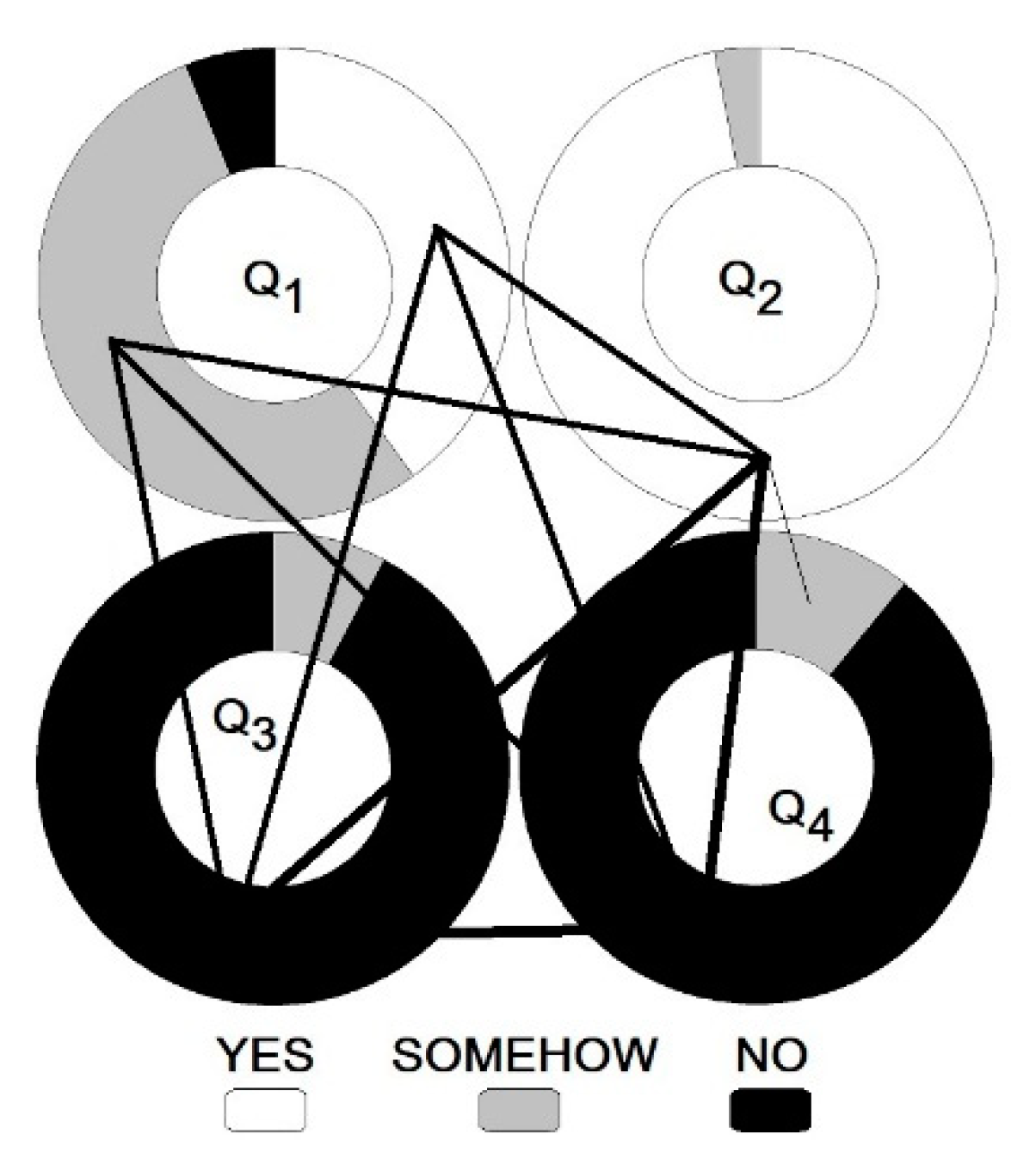
| A (13) | CZ (14) | F (9) | DE (16) | GB (3) | I (7) | CH (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 (mg.kg−1) | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 1.0 ± 0.5 | 0.9 ± 0.4 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 0.9 ± 0.2 |
| CaO (mg.kg−1) | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.3 |
| Cell (mg.kg−1) | 2.0 ± 0.4 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 2.2 ± 0.5 | 1.9 ± 0.3 | 1.9 ± 0.6 | 1.9 ± 0.3 | 2.1 ± 0.4 |
| Fe2O3 (mg.kg−1) | 8.9 ± 0.9 | 5.3 ± 1.2 | 9.8 ± 1.5 | 8.3 ± 3.6 | 9.9 ± 2.1 | 7.0 ± 2.4 | 8.3 ± 1.0 |
| Lign (mg.kg−1) | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 1.5 ± 0.2 |
| MgO (mg.kg−1) | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.0 |
| MnO2 (mg.kg−1) | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.2 | 0.1 ± 0.1 |
| Cox (mg.kg−1) | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 2.2 ± 0.1 |
| P2O5 (mg.kg−1) | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| SiO2 (mg.kg−1) | 3.6 ± 0.3 | 3.7 ± 0.4 | 3.3 ± 0.5 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | 3.6 ± 0.3 | 3.3 ± 0.3 | 3.4 ± 0.4 |
| S (mg.kg−1) | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| VS (mg.kg−1) | 21.0 ± 3.1 | 19.7 ± 4.4 | 22.5 ± 3.5 | 19.1 ± 2.9 | 16.7 ± 3.4 | 20.3 ± 2.2 | 19.5 ± 4.4 |
| I. | II. | III. | IV. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC0 (%) | 92 | 85 | 81 | 77 |
| HCfs (%) | 91 | 80 | 73 | 66 |
| GC0 (%) | 96 | 94 | 92 | 91 |
| GCfs (%) | 93 | 82 | 68 | 60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brabenec, T.; Maroušková, A.; Zoubek, T.; Filip, M. Residues from Water Precipitation via Ferric Hydroxide Threaten Soil Fertility. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4327. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084327
Brabenec T, Maroušková A, Zoubek T, Filip M. Residues from Water Precipitation via Ferric Hydroxide Threaten Soil Fertility. Sustainability. 2021; 13(8):4327. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084327
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrabenec, Tomáš, Anna Maroušková, Tomáš Zoubek, and Martin Filip. 2021. "Residues from Water Precipitation via Ferric Hydroxide Threaten Soil Fertility" Sustainability 13, no. 8: 4327. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084327
APA StyleBrabenec, T., Maroušková, A., Zoubek, T., & Filip, M. (2021). Residues from Water Precipitation via Ferric Hydroxide Threaten Soil Fertility. Sustainability, 13(8), 4327. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084327






