Experimental Winter Monitoring of a Light-Weight Green Roof Assembly for Building Retrofit
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Objectives
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Green Roof Stratigraphy
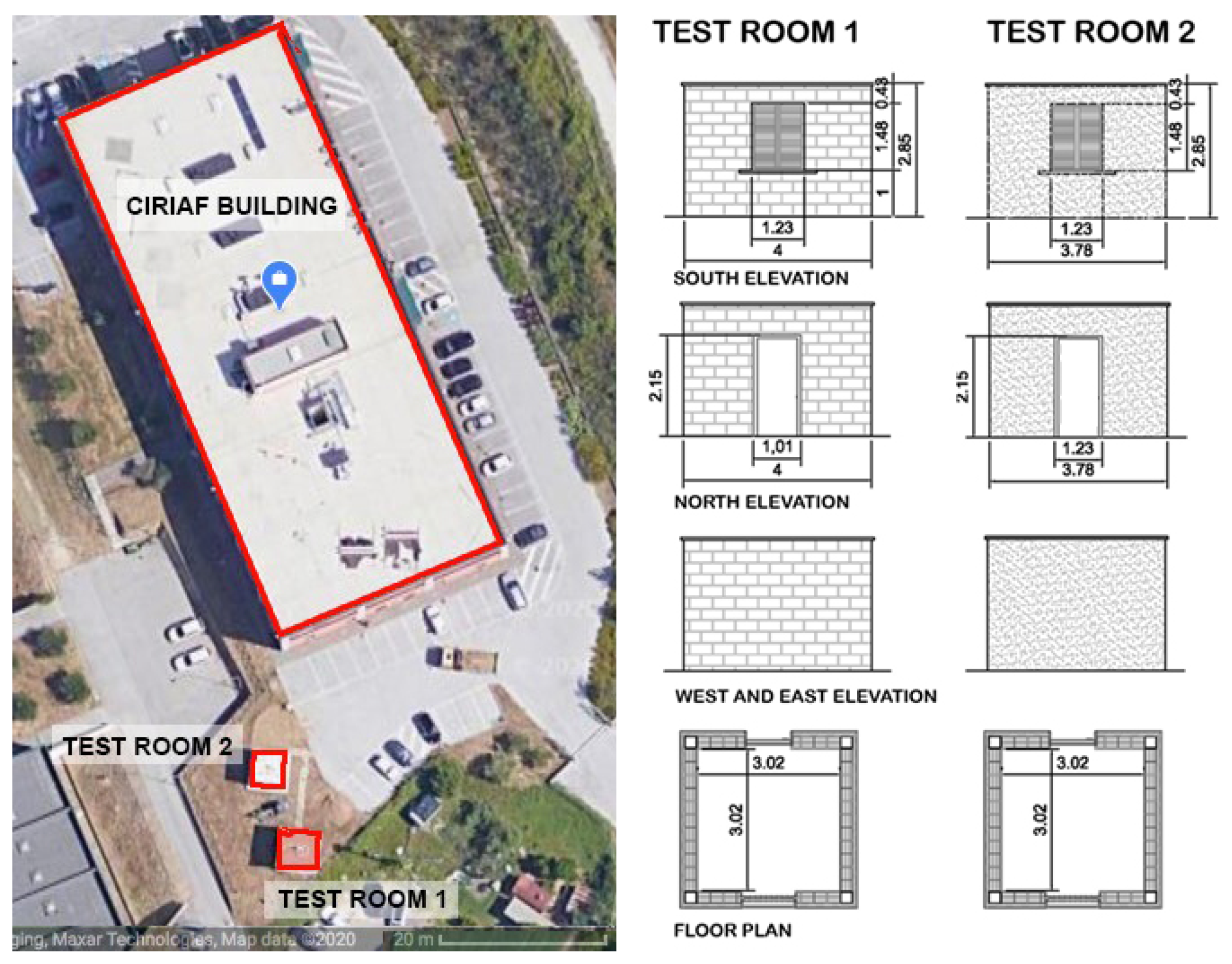
3.2. Case Study
- -
- -
- -
- Test-room 2 (TR2-green) with green extensive lightweight assembly installed on 18 September 2019 and ongoing. The system is described in previous Section 3.1.
3.3. Experimental Methodology
4. Results and Discussion
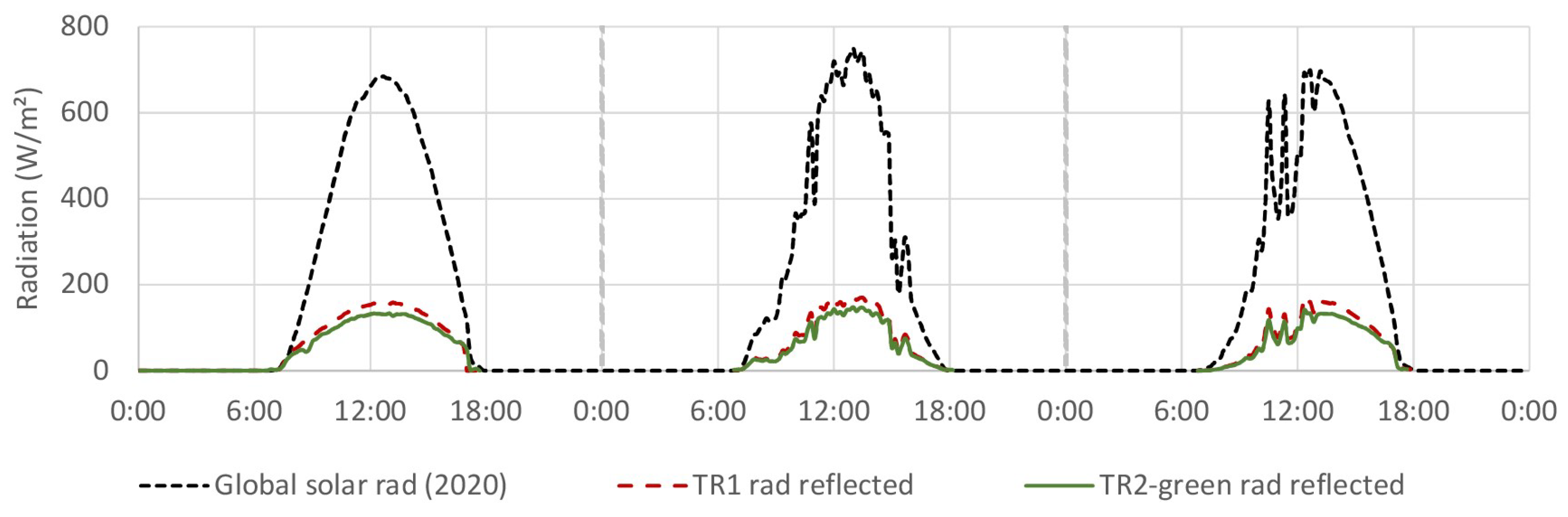
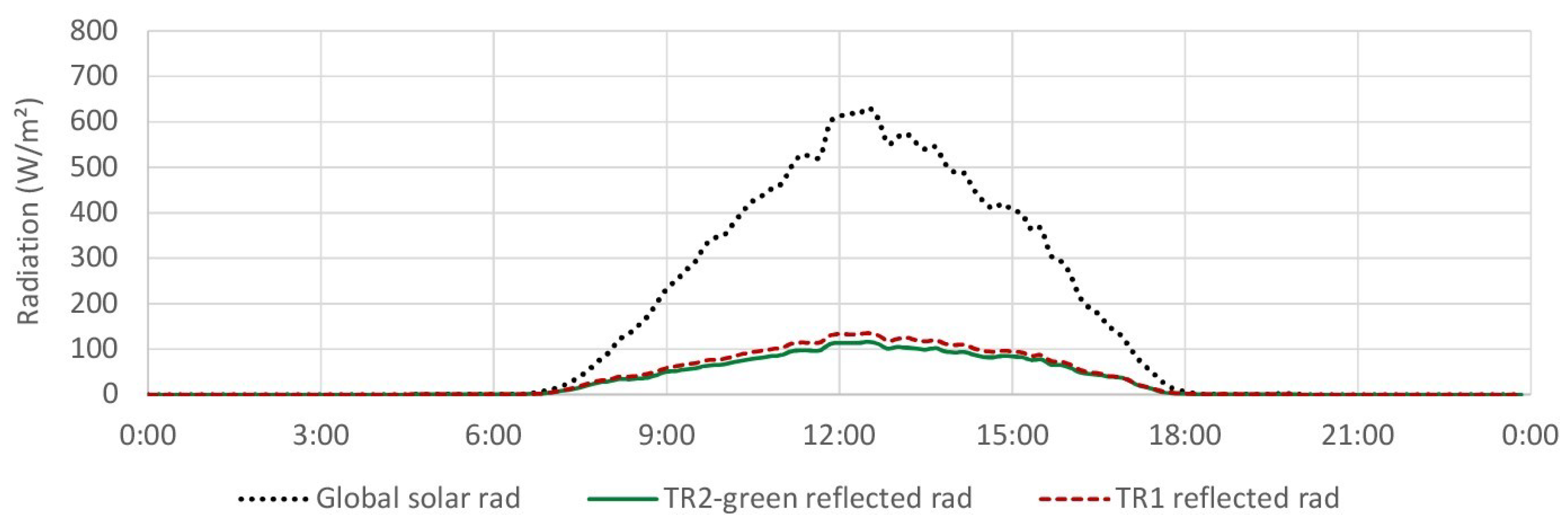
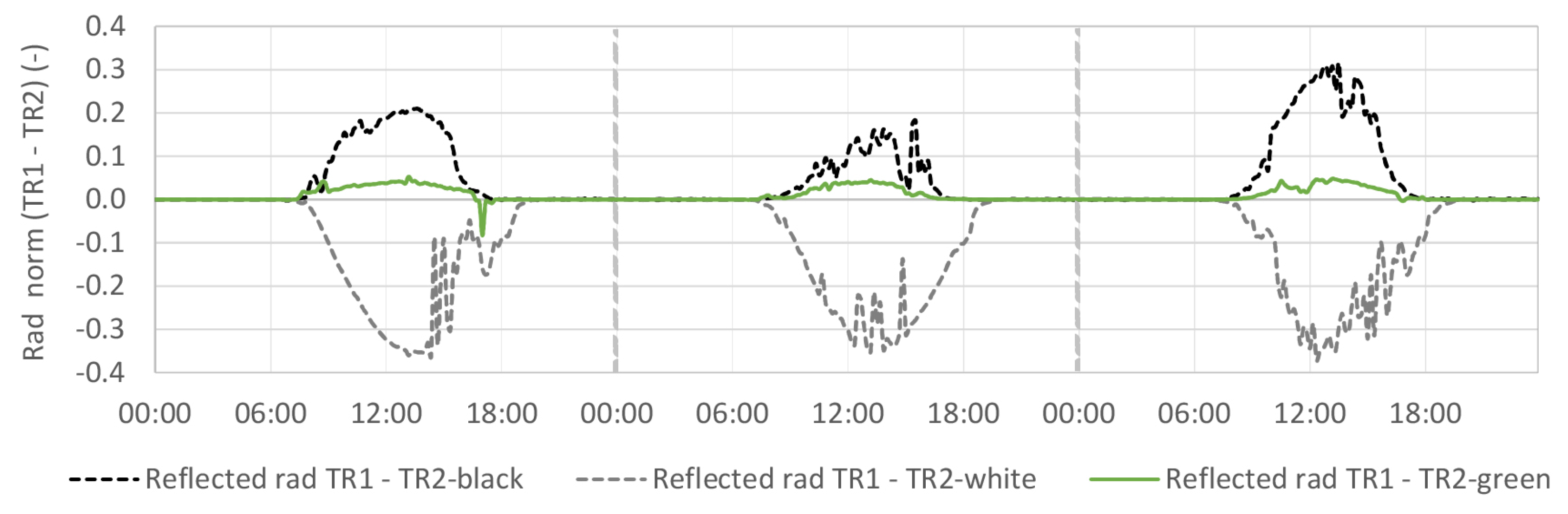
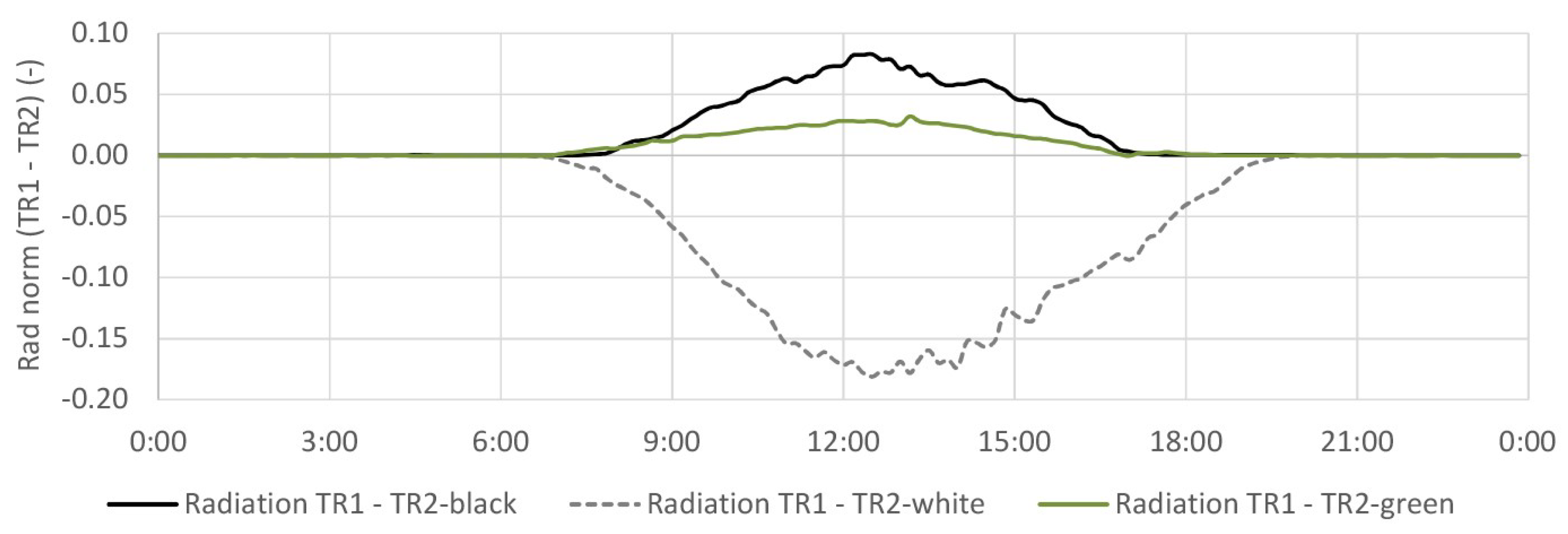
4.1. Global Reflected Radiation
4.1.1. TR2-Green Compared with Tiled Roof (TR1)
4.1.2. TR2-Green Compared with Black and White Coating
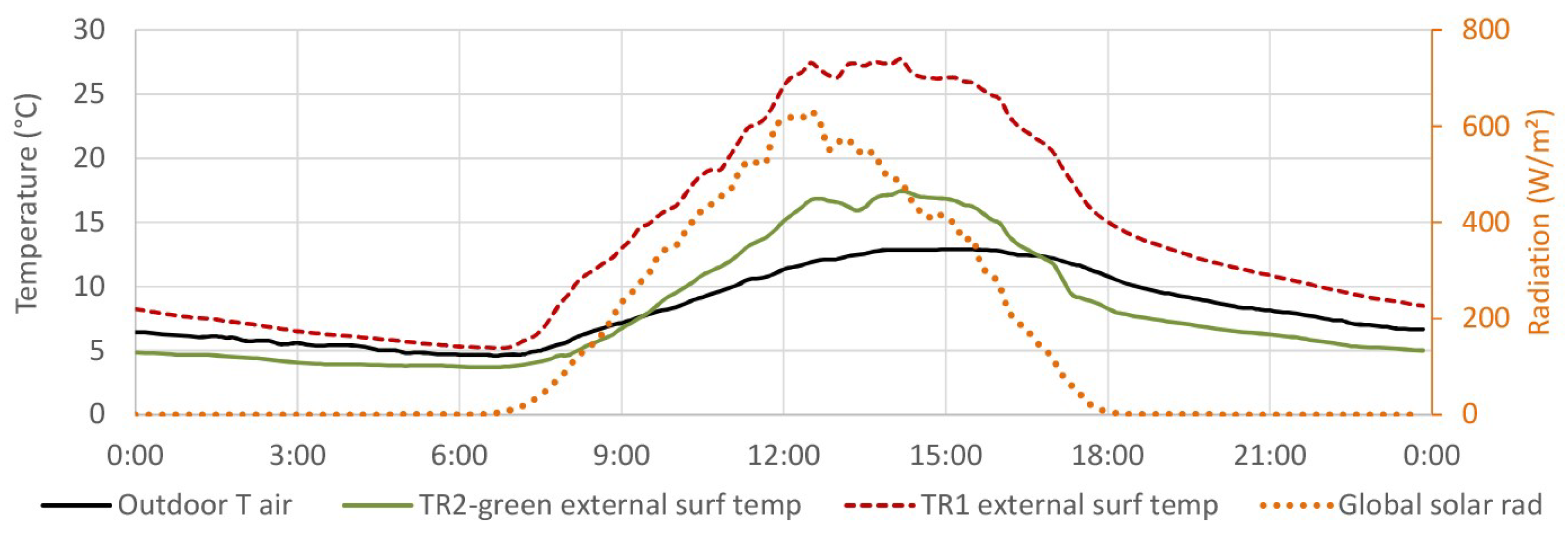
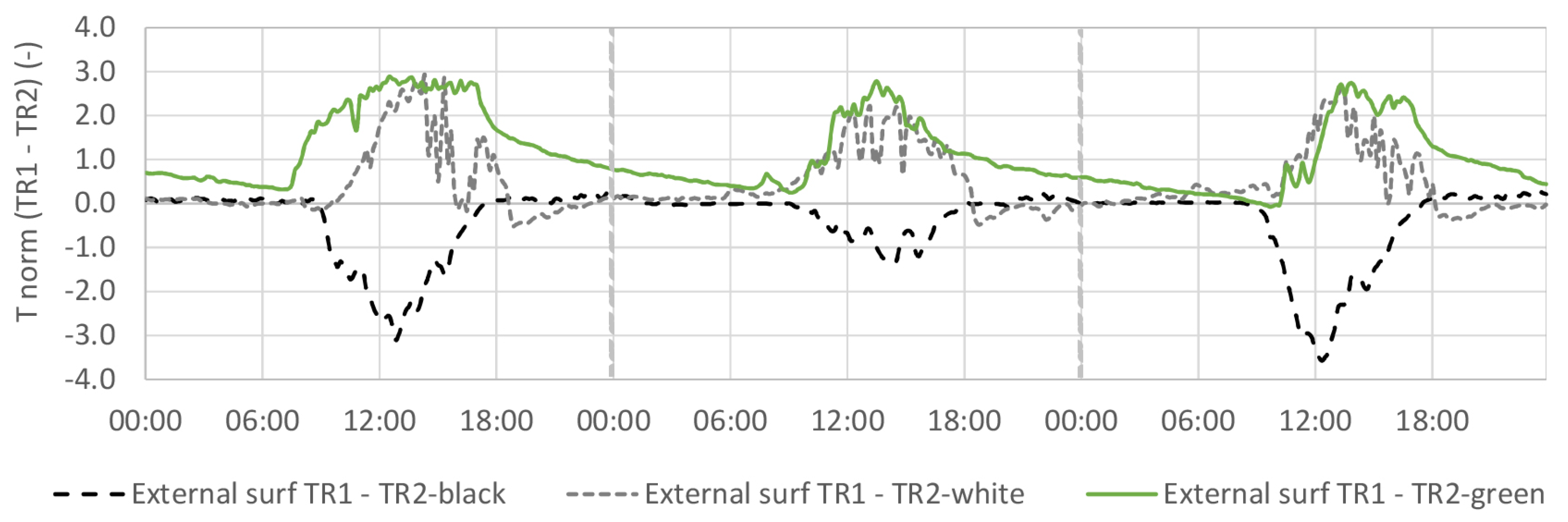
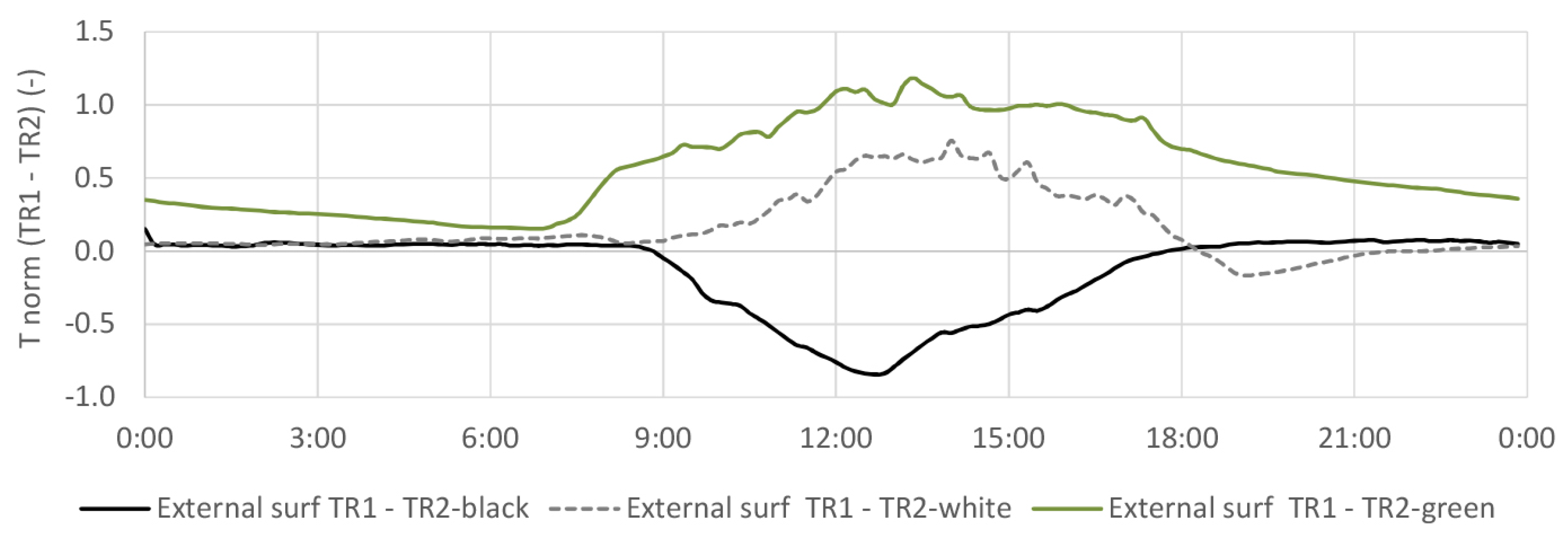
4.2. External Surface Temperature
4.2.1. TR2-Green Compared with Tiled Roof (TR1)
4.2.2. TR2-Green Compared with Black and White Coating
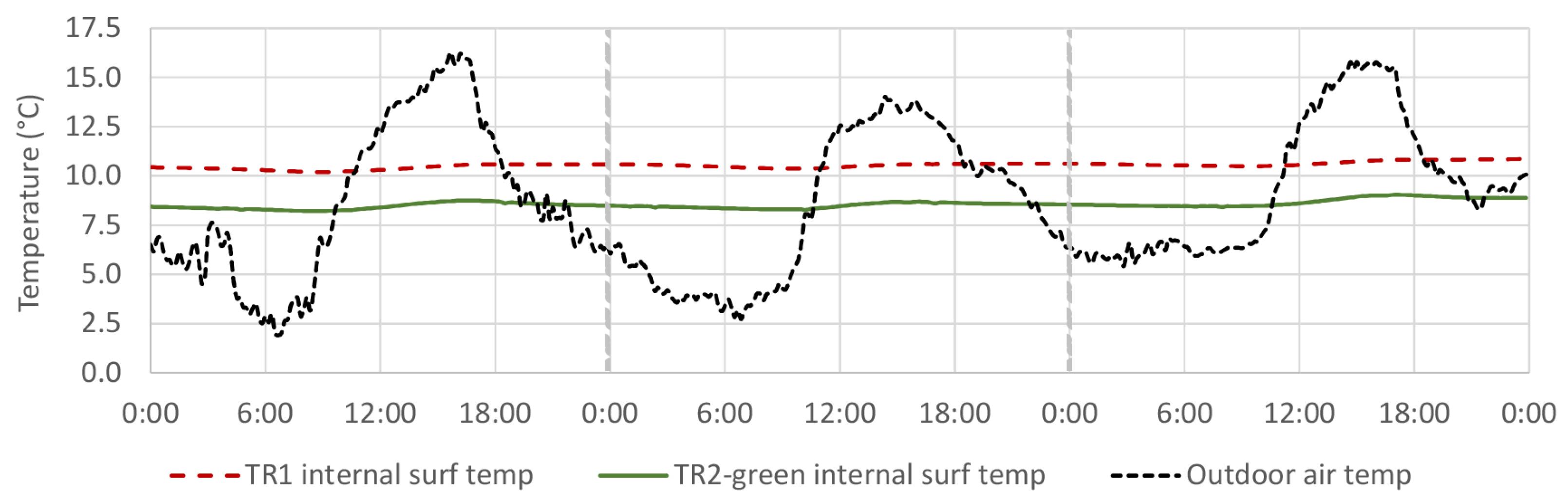
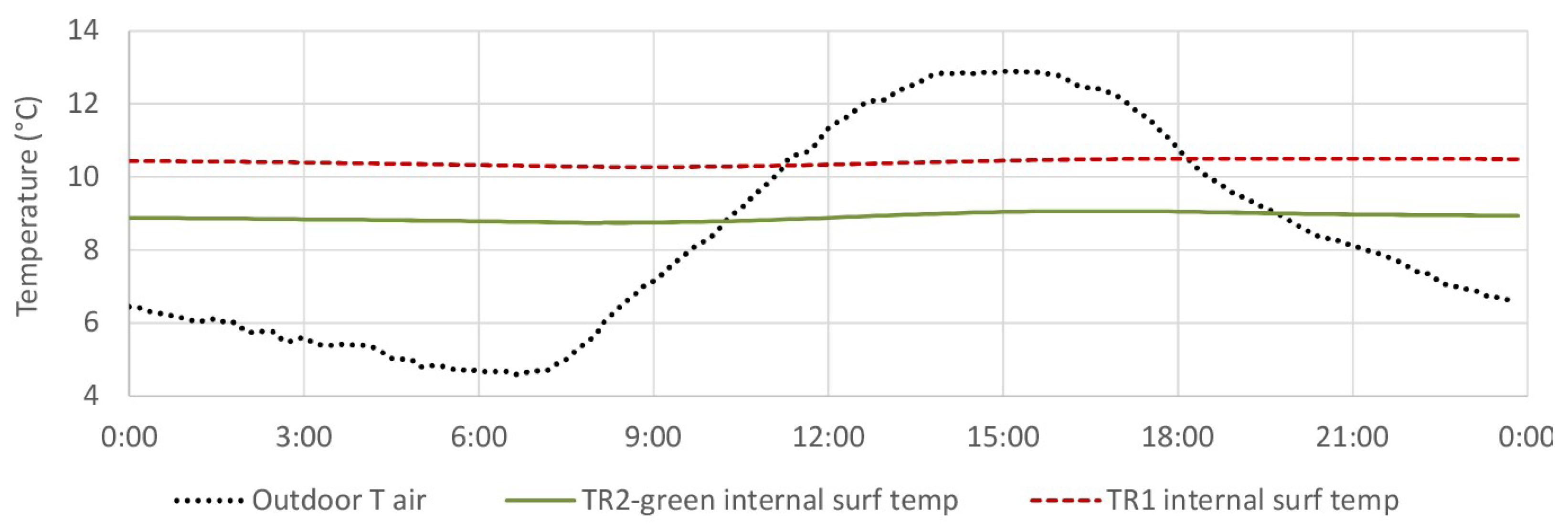
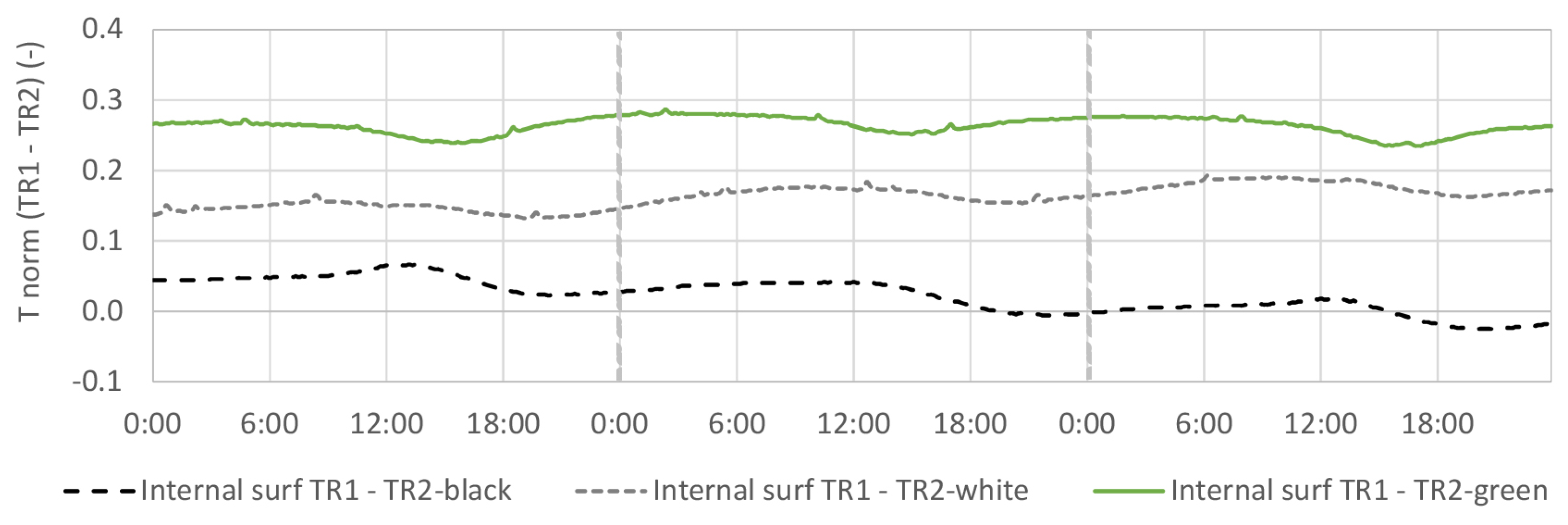
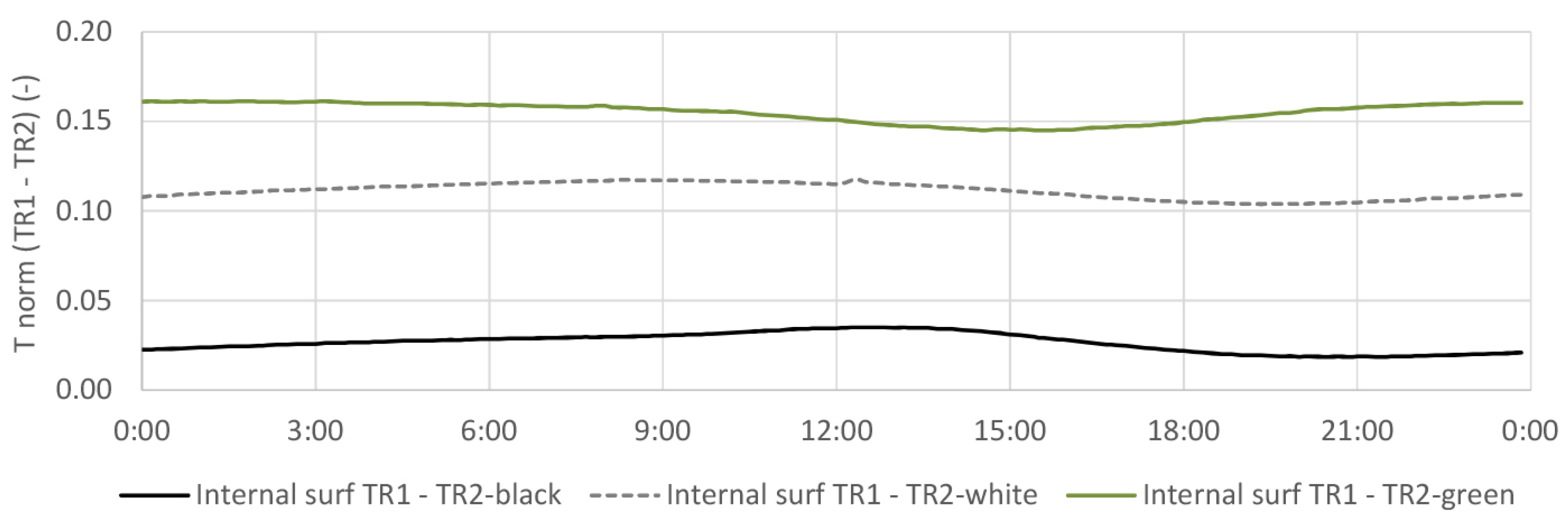
4.3. Internal Surface Temperature
4.3.1. TR2-Green Compared with Tiled Roof (TR1)
4.3.2. TR2-Green Compared with Black and White Coating
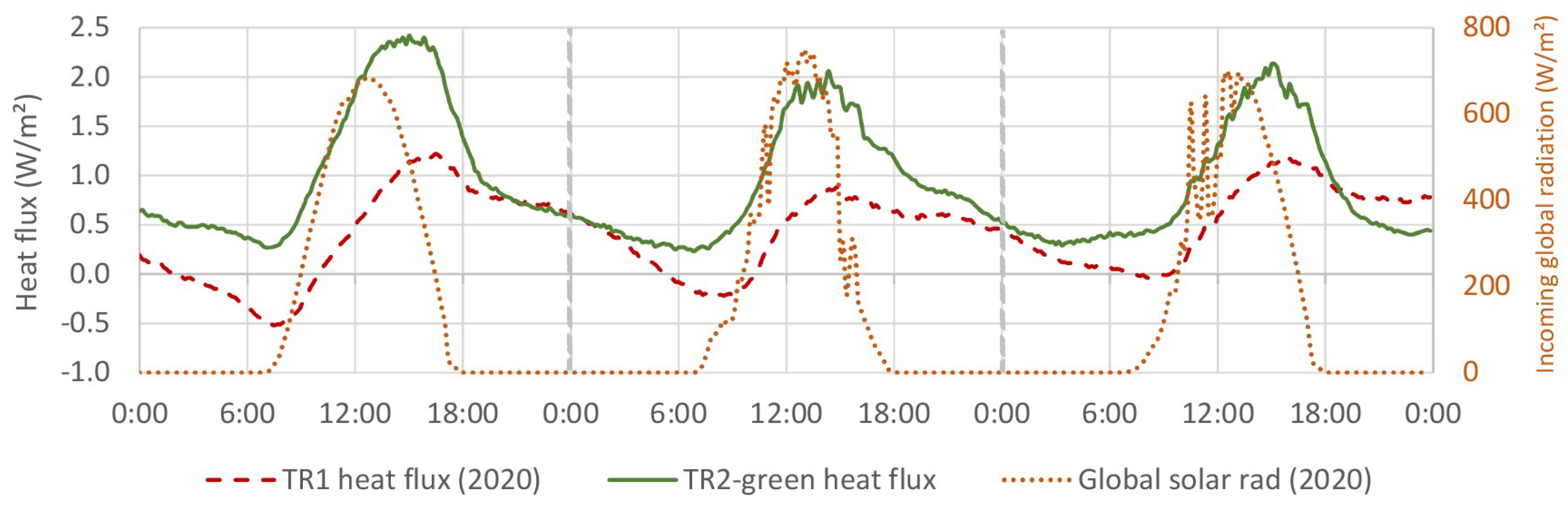
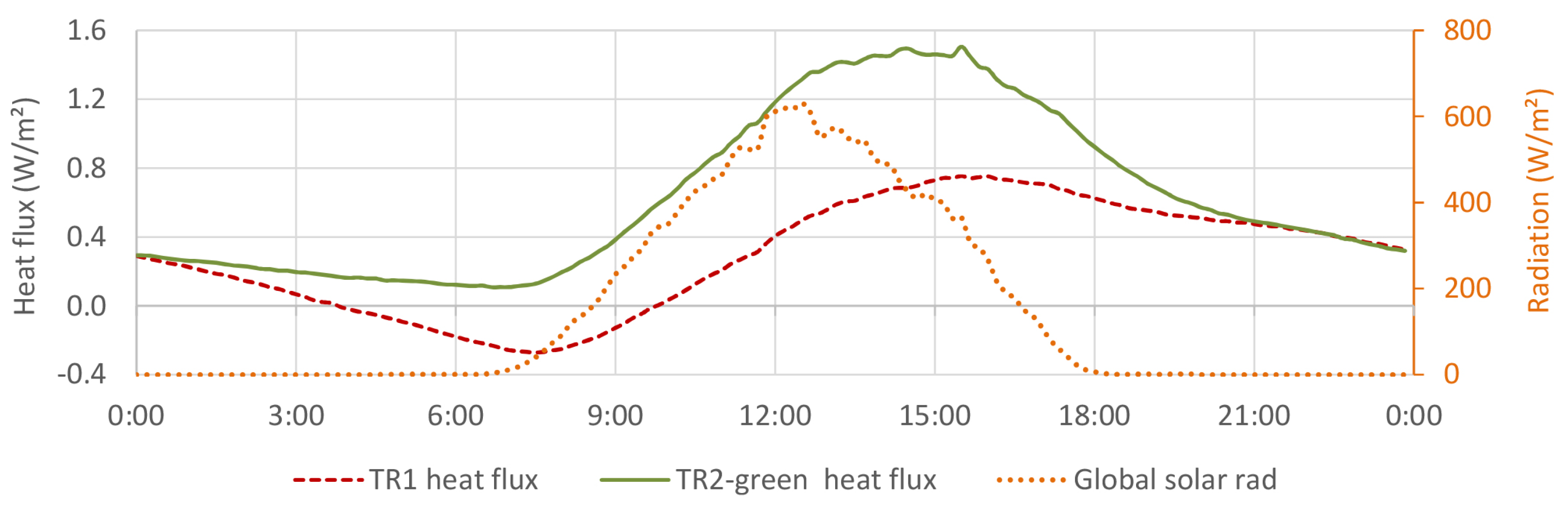
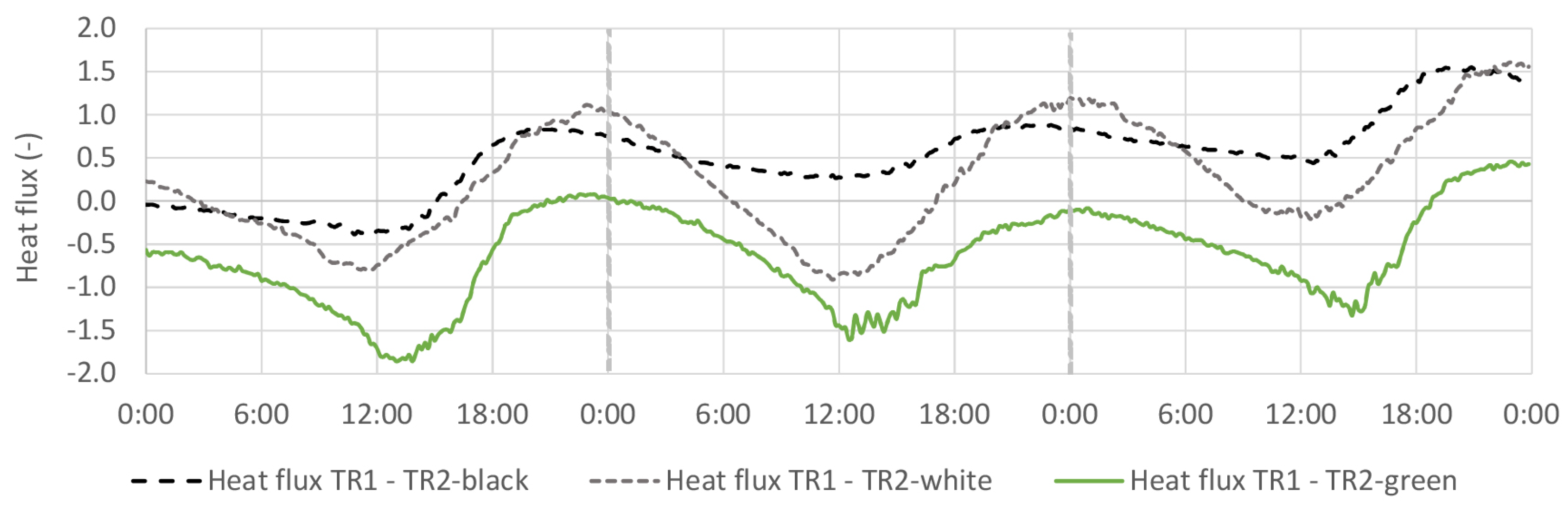
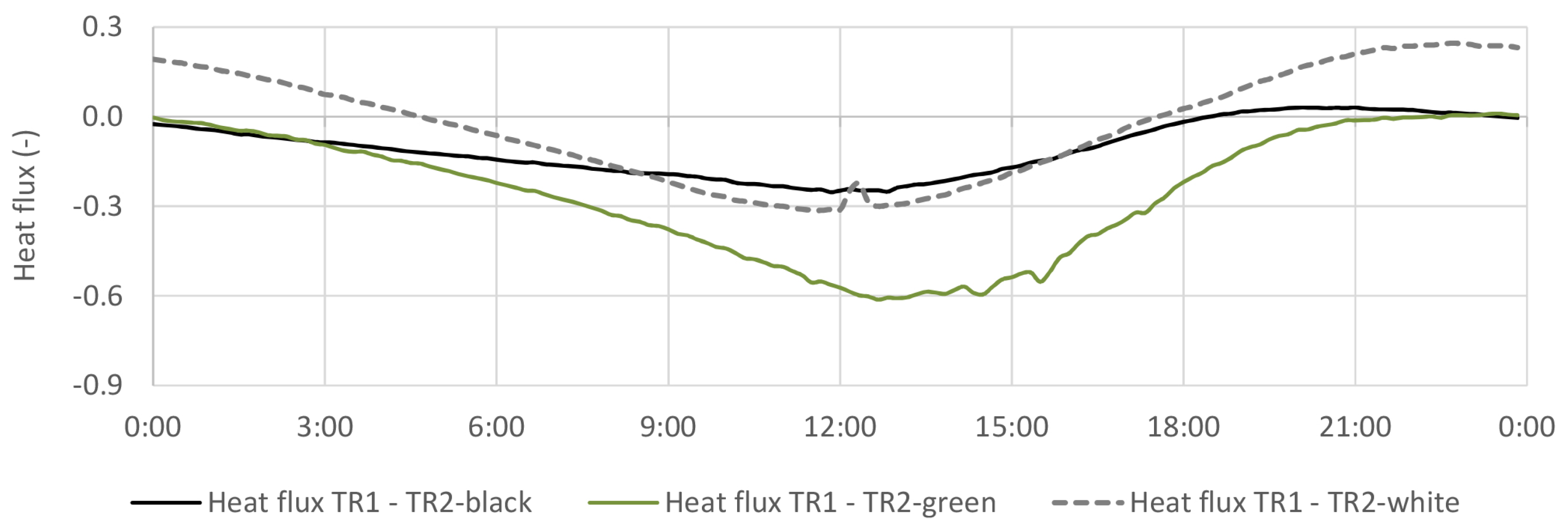
4.4. Thermal Flux
4.4.1. TR2-Green Compared with Tiled Roof (TR1)
4.4.2. TR2-Green Compared with Black and White Coating
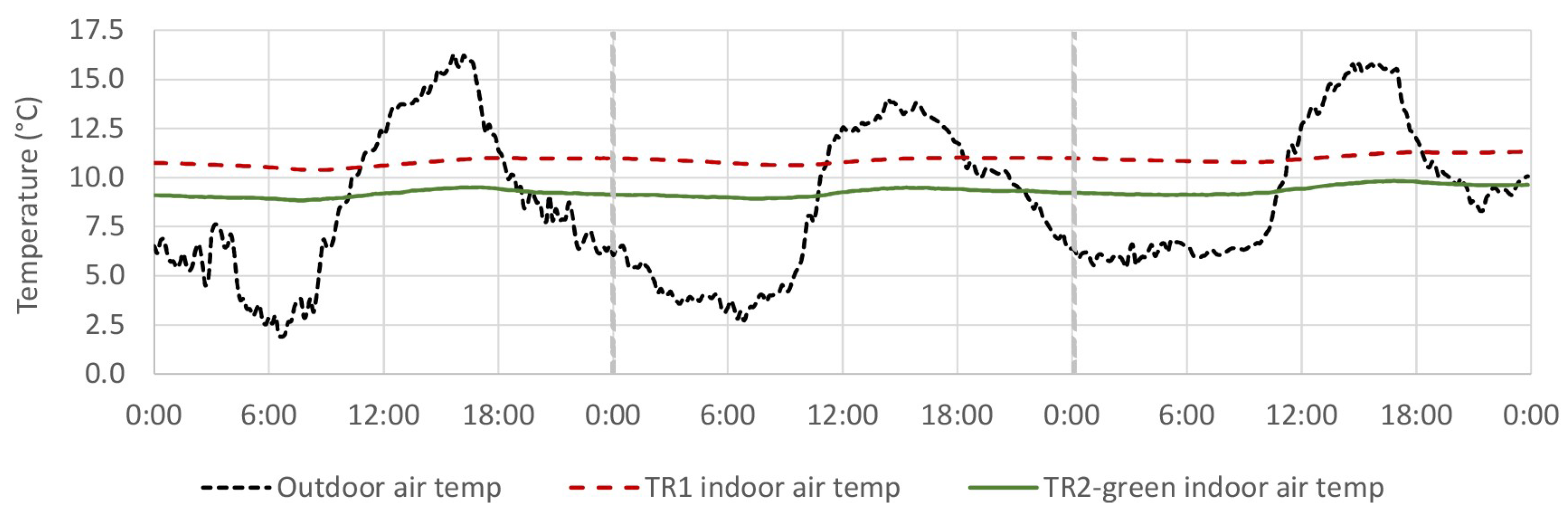
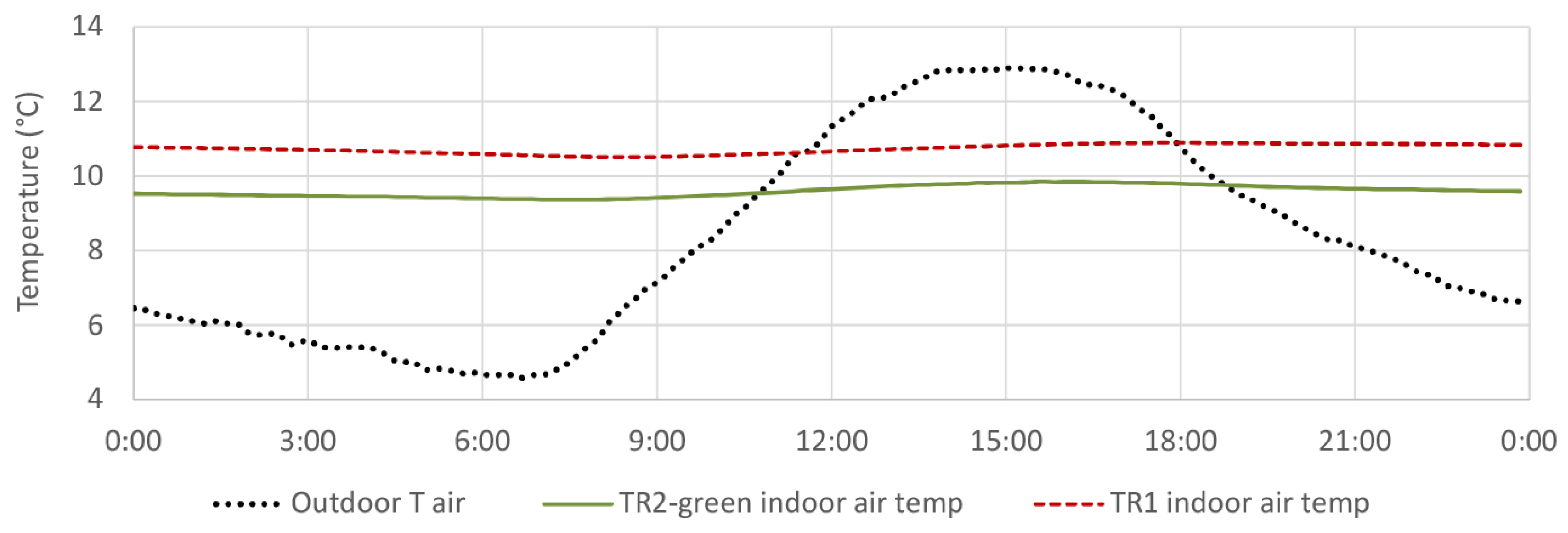
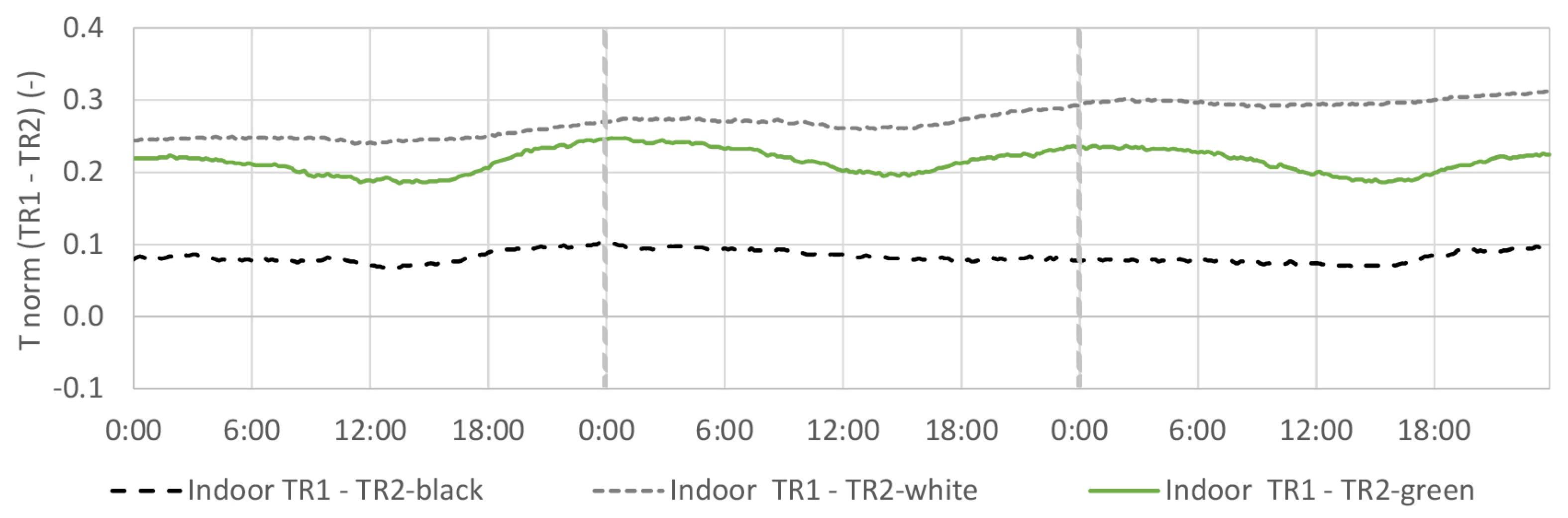
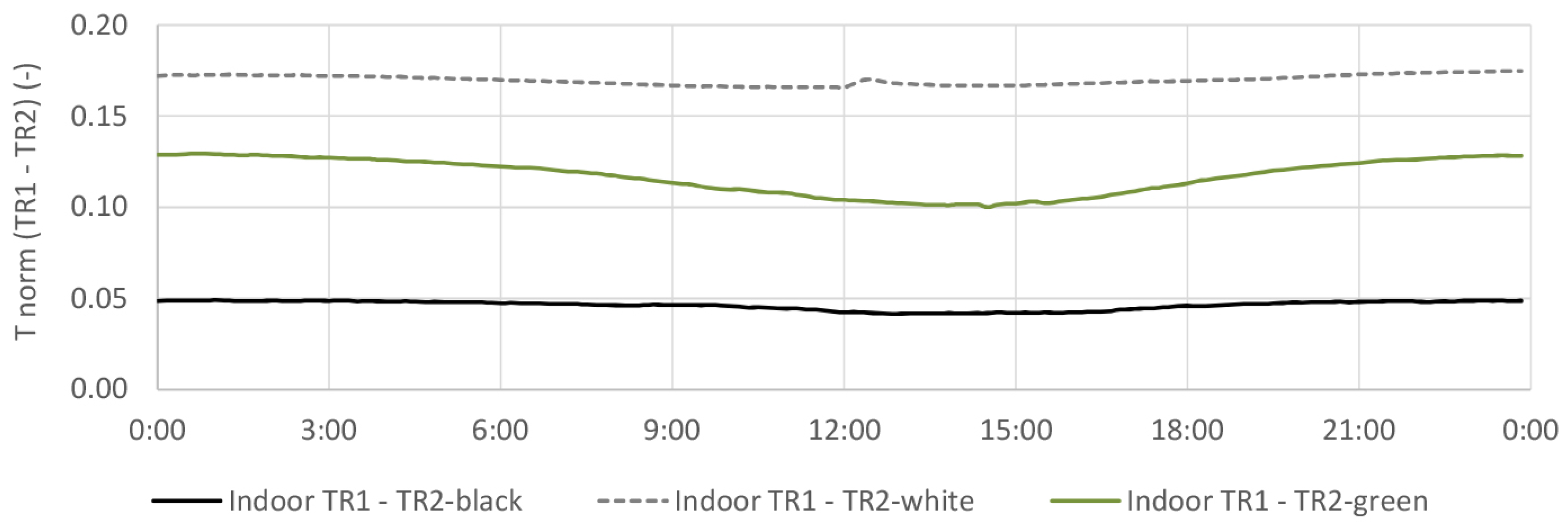
4.5. Indoor Air Temperature
4.5.1. TR2-Green Compared with Tiled Roof (TR1)
4.5.2. TR2-Green Compared with Black and White Coating
4.6. Discussion over the Obtained Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TR | Test-room |
| TR1 | Test-room 1 (reference prototype building) |
| TR2 | Test-room 2 (modified-black, -white, -green prototype building) |
| U-value | Thermal transmittance |
| Thermal conductivity | |
| Density | |
| C | Specific heat capacity |
| d | Thickness |
| CIRIAF | Interuniversity Research Center |
| , | Normalized reflected radiation |
| , | Normalized external surface temperature |
| , | Reflected radiation |
| R | Maximum incoming solar radiation |
| R | Average incoming solar radiation |
| Te1, Te2 | External surface temperatures |
| T | Maximum outdoor air temperature |
| T | Average outdoor air temperature |
| Ti1, Ti2 | Internal surface temperatures |
| Ta1, Ta2 | Indoor air temperatures |
| Normalized reflected radiation difference | |
| , | Normalized external and internal surface temperature difference |
| Normalized indoor air temperature difference | |
| Normalized heat flux difference | |
| LAI | Leaf area index |
| UHI | Urban heat island |
References
- Lundholm, J.T.; Peck, S.W. Introduction: Frontiers of green roof ecology. Urban Ecosyst. 2008, 11, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascone, S. Green roof design: State of the art on technology and materials. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scharf, B.; Zluwa, I. Case study investigation of the building physical properties of seven different green roof systems. Energy Build. 2017, 151, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, B.G.; Hanslin, H.M.; Muthanna, T.M. Green roof performance potential in cold and wet regions. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andenæs, E.; Kvande, T.; Muthanna, T.M.; Lohne, J. Performance of blue-green roofs in cold climates: A scoping review. Buildings 2018, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oberndorfer, E.; Lundholm, J.; Bass, B.; Coffman, R.R.; Doshi, H.; Dunnett, N.; Gaffin, S.; Köhler, M.; Liu, K.K.Y.; Rowe, B. Green Roofs as Urban Ecosystems: Ecological Structures, Functions, and Services. BioScience 2007, 57, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M.; Pavlou, C.; Doukas, P.; Mihalakakou, G.; Synnefa, A.; Hatzibiros, A.; Patargias, P. Investigating and analysing the energy and environmental performance of an experimental green roof system installed in a nursery school building in Athens, Greece. Energy 2007, 32, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleghani, M. Outdoor thermal comfort by different heat mitigation strategies—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2011–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, C.Y. Effect of vegetation biomass structure on thermal performance of tropical green roof. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 8, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Bou-Zeid, E.; Oppenheimer, M. The effectiveness of cool and green roofs as urban heat island mitigation strategies. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizotto, S.; Lamberts, R. Investigation of green roof thermal performance in temperate climate: A case study of an experimental building in Florianópolis city, Southern Brazil. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 1712–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U.; GhaffarianHoseini, A.H.; GhaffarianHoseini, A. State-of-the-art analysis of the environmental benefits of green roofs. Appl. Energy 2014, 115, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Renterghem, T. Green roofs for noise reduction: Literature review and new approaches. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE 2017—46th International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering: Taming Noise and Moving Quiet, Hong Kong, China, 27–30 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shafique, M.; Xue, X.; Luo, X. An overview of carbon sequestration of green roofs in urban areas. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 47, 126515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, S.S.; Sailor, D.J. Development and application of a building energy performance metric for green roof systems. Energy Build. 2013, 60, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, A.; Colonia, A.; Mesa, J.; Maury, H.; Maury-Ramírez, A. State-of-the-art green roofs: Technical performance and certifications for sustainable construction. Coatings 2020, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, K.J.; Lee, K.E.; Sargent, L.; Johnson, K.A.; Rayner, J.; Farrell, C.; Miller, R.E.; Williams, N.S. Appraising the psychological benefits of green roofs for city residents and workers. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 44, 126399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, L.; Corrao, R.; Heiselberg, P.K. The effects of vegetation on indoor thermal comfort: The application of a multi-scale simulation methodology on a residential neighborhood renovation case study. Energy Build. 2017, 146, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Xing, Q.; Long, P.; Lin, Y.; Hu, J.; Tan, H. Influence of vertical greenery systems and green roofs on the indoor operative temperature of air-conditioned rooms. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 31, 101373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarin, R.M.; Castellotti, F.; Busato, F. Experimental measurements and numerical modelling of a green roof. Energy Build. 2005, 37, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M. Cooling the cities—A review of reflective and green roof mitigation technologies to fight heat island and improve comfort in urban environments. Sol. Energy 2014, 103, 682–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castleton, H.F.; Stovin, V.; Beck, S.B.; Davison, J.B. Green roofs; Building energy savings and the potential for retrofit. Energy Build. 2010, 42, 1582–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisello, A.L.; Rossi, F.; Cotana, F. Summer and winter effect of innovative cool roof tiles on the dynamic thermal behavior of buildings. Energies 2014, 7, 2343–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pianella, A.; Aye, L.; Chen, Z.; Williams, N.S. Substrate depth, vegetation and irrigation affect green roof thermal performance in a mediterranean type climate. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Orazio, M.; Di Perna, C.; Di Giuseppe, E. Green roof yearly performance: A case study in a highly insulated building under temperate climate. Energy Build. 2012, 55, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niachou, A.; Papakonstantinou, K.; Santamouris, M.; Tsangrassoulis, A.; Mihalakakou, G. Analysis of the green roof thermal properties and investigation of its energy performance. Energy Build. 2001, 33, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takebayashi, H.; Moriyama, M. Surface heat budget on green roof and high reflection roof for mitigation of urban heat island. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pisello, A.L.; Piselli, C.; Cotana, F. Thermal-physics and energy performance of an innovative green roof system: The Cool-Green Roof. Sol. Energy 2015, 116, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindi Pratopronto. Available online: http://www.pratopronto.it/index.phpoption=com_content&view=article&id=51&Itemid=57 (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- RecycleTherm Km0. Isolante Termoacustico in Fibre Tessili Riciclate a Filiera Corta; Manifattura Maiano s.p.a.: Via Maiano, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pisello, A.L.; Cotana, F.; Nicolini, A.; Buratti, C. Effect of dynamic characteristics of building envelope on thermal-energy performance in winter conditions: In field experiment. Energy Build. 2014, 80, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousis, I.; Fabiani, C.; Gobbi, L.; Pisello, A.L. Phosphorescent-based pavements for counteracting urban overheating—A proof of concept. Sol. Energy 2020, 202, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisello, A.L.; Castaldo, V.L.; Cotana, F. Dynamic thermal-energy performance analysis of a prototype building with integrated phase change materials. Energy Procedia 2015, 81, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pisello, A.L.; Castaldo, V.L.; Piselli, C.; Fabiani, C.; Cotana, F. Thermal performance of coupled cool roof and cool façade: Experimental monitoring and analytical optimization procedure. Energy Build. 2017, 157, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, V.; Ballarini, I.; Corgnati, S.P. Typology Approach for Building Stock: National Scientific Report on the TABULA Activities in Italy; Politecnico di Torino: Turin, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pisello, A.L. High-albedo Roof Coatings for Reducing Building Cooling Needs; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 243–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.L.; Jim, C.Y. Seasonal and diurnal thermal performance of a subtropical extensive green roof: The impacts of background weather parameters. Sustainability 2015, 7, 11098–11113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.; Baskaran, B. Thermal Performance of Green Roofs in Cold Climates. In Proceedings of the World Sustainable Building Conference, Tokyo, Japan, 27–29 September 2005; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Guattari, C.; Evangelisti, L.; Asdrubali, F.; De Lieto Vollaro, R.L. Experimental evaluation and numerical simulation of the thermal performance of a green roof. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandoval, V.; Suárez, F.; Vera, S.; Pinto, C.; Victorero, F.; Bonilla, C.; Gironás, J.; Bustamante, W.; Rojas, V.; Pastén, P. Impact of the properties of a green roof substrate on its hydraulic and thermal behavior. Energy Procedia 2015, 78, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Issa, R.J.; Leitch, K.; Chang, B. Experimental Heat Transfer Study on Green Roofs in a Semiarid Climate during Summer. J. Constr. Eng. 2015, 2015, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayata, T.; Tabares-Velasco, P.C.; Srebric, J. An investigation of sensible heat fluxes at a green roof in a laboratory setup. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libessart, L.; Kenai, M.A. Measuring thermal conductivity of green-walls components in controlled conditions. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 19, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellazzi, A.; Barozzi, B.; Pollastro, M.C.; Meroni, I. Thermal resistance of growing media for green roofs: To what extent does the absence of specific reference values potentially affect the global thermal resistance of the green roof? An experimental example. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiolo, M.; Pirouz, B.; Bruno, R.; Palermo, S.A.; Arcuri, N.; Piro, P. The role of the extensive green roofs on decreasing building energy consumption in the mediterranean climate. Sustainability 2020, 12, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, C.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Y. Theoretical and experimental analysis of the energy balance of extensive green roofs. Energy Build. 2010, 42, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo Del Barrio, E. Analysis of the green roofs cooling potential in buildings. Energy Build. 1998, 27, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teemusk, A.; Mander, Ü. Greenroof potential to reduce temperature fluctuations of a roof membrane: A case study from Estonia. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascone, S.; Coma, J.; Gagliano, A.; Pérez, G. The evapotranspiration process in green roofs: A review. Build. Environ. 2019, 147, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
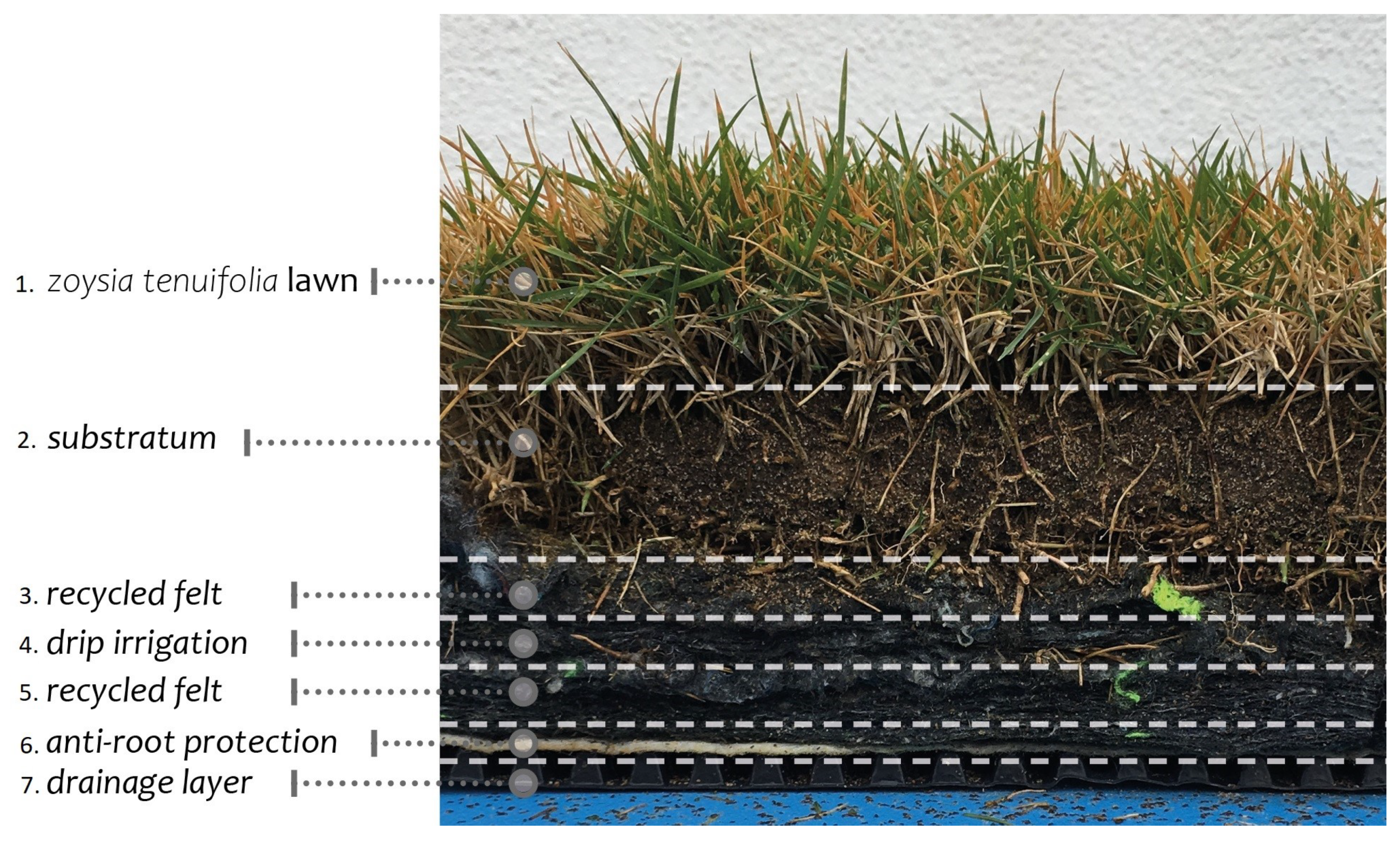


| Main Thermophysical Properties | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layers Green Roof | C | d | |||
| [W/m · K] | [kg/m] | [J·kgK] | [m] | ||
| (1–2) turfgrass | 1. zoysia tenuifolia | 0.32 | 1600 | 1720 | 0.18 |
| 2. substratum | |||||
| (3–5) felt layer | 3. recycled felt [30] | ||||
| 4. irrigation drip | 0.036 | 80 | 1300 | 0.06 | |
| 5. recycled felt [30] | |||||
| 6. anti-root protection layer | 0.05 | 120 | 1300 | 0.01 | |
| 7. drainage layer | 0.25 | 1700 | 1400 | 0.7 | |
| Main Thermophysical Properties | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layers | C | d | R | ||
| [W/m · K] | [kg/m] | [J·kgK] | [m] | [mK·W] | |
| TR1 | 0.25 | ||||
| Clay tile | 1.00 | 2000 | 800 | 0.015 | |
| Mineral wool | 0.04 | 160 | 1030 | 0.015 | |
| Air gap | 1.3 | 0.05 | 0.23 | ||
| Mineral wool | 0.038 | 60 | 1030 | 0.08 | |
| Aerated concrete slab | 0.16 | 500 | 1290 | 0.20 | |
| Gypsum plastering | 0.4 | 600 | 1000 | 0.015 | |
| TR2 | 0.25 | ||||
| Bitumen sheet | 0.23 | 1100 | 1000 | 0.01 | |
| Mineral wool | 0.04 | 160 | 1030 | 0.10 | |
| Aerated concrete slab | 0.16 | 500 | 1290 | 0.20 | |
| Gypsum plastering | 0.40 | 600 | 1000 | 0.015 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frota de Albuquerque Landi, F.; Fabiani, C.; Pisello, A.L. Experimental Winter Monitoring of a Light-Weight Green Roof Assembly for Building Retrofit. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4604. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094604
Frota de Albuquerque Landi F, Fabiani C, Pisello AL. Experimental Winter Monitoring of a Light-Weight Green Roof Assembly for Building Retrofit. Sustainability. 2021; 13(9):4604. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094604
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrota de Albuquerque Landi, Fabiana, Claudia Fabiani, and Anna Laura Pisello. 2021. "Experimental Winter Monitoring of a Light-Weight Green Roof Assembly for Building Retrofit" Sustainability 13, no. 9: 4604. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094604
APA StyleFrota de Albuquerque Landi, F., Fabiani, C., & Pisello, A. L. (2021). Experimental Winter Monitoring of a Light-Weight Green Roof Assembly for Building Retrofit. Sustainability, 13(9), 4604. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094604








