Spanish Adaptation and Validation of the Child Adjustment and Parent Efficacy Scale
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Exploratory Factor Analysis
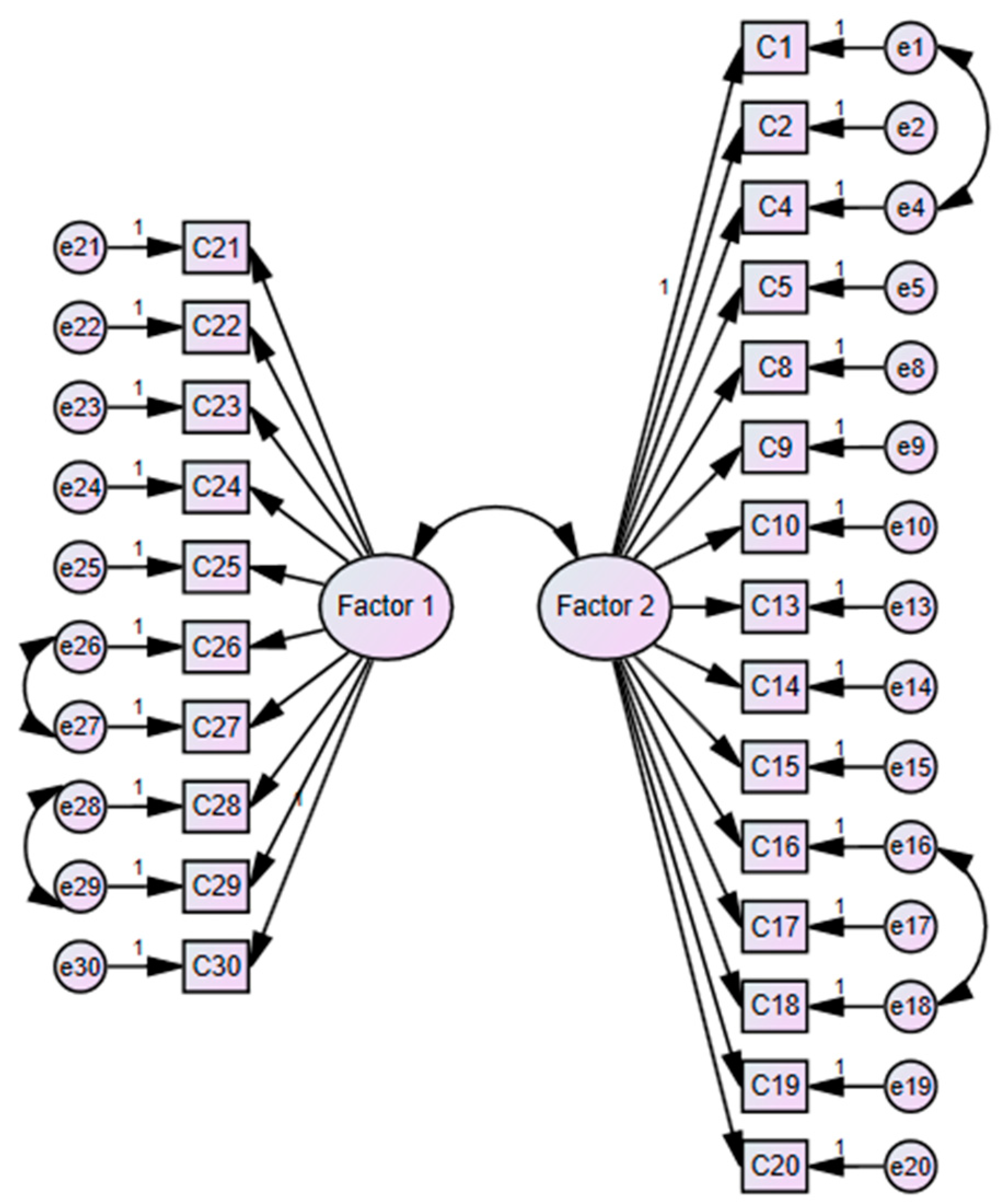
3.3. Confirmatory Factor Analysis
3.4. Reliability Analysis
3.5. Convergent and Discriminant Validity
3.6. Invariance of the Measurement Model
3.7. CAPES Self-Efficacy Scale
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Raw Score | Cut Score | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Child competence subscale a | ||
| ≤8.37 | ≤−1.645 | Significant incompetence |
| >8.37 and <11.39 | ≤−1.28 and >−1.645 | Moderate incompetence |
| >32.53 and <35.55 | ≥1.28 and <1.645 | Moderately high competence |
| ≥35.55 | ≥1.645 | Significantly high competence |
| Behavioural and emotional problems b | ||
| ≤0.83 | ≤−1.645 | Significantly high no-problems c |
| >0.83 and <3.08 | ≤−1.28 and >−1.645 | Moderately high no-problems c |
| >18.90 and <21.16 | ≥1.28 and <1.645 | Moderate deteriorate |
| ≥21.16 | ≥1.645 | Significant deteriorate |
References
- Maguire, S.A.; Williams, B.; Naughton, A.M.; Cowley, L.E.; Tempest, V.; Mann, M.K.; Teague, M.; Kemp, A.M. A systematic review of the emotional, behavioural and cognitive features exhibited by school-aged children experiencing neglect or emotional abuse. Child Care Health Dev. 2015, 41, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domitrovich, C.E.; Durlak, J.A.; Staley, K.C.; Weissberg, R.P. Social-Emotional Competence: An Essential Factor for Promoting Positive Adjustment and Reducing Risk in School Children. Child Dev. 2017, 88, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, R.; Novo, M.; Fariña, F.; Arce, R. Child-to-parent Violence and Parent-to-child Violence: A Meta-analytic Review. Eur. J. Psychol. Appl. Leg. Context 2019, 11, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barlow, J.; Bergman, H.; Kornør, H.; Wei, Y.; Bennett, C. Group-based parent training programmes for improving emotional and behavioural adjustment in young children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 8, CD003680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richman, N.; Graham, P.J. A Behavioural Screening Questionnaire for use with three-year-old children. Preliminary findings. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 1971, 12, 5–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyberg, S.M.; Ross, A.W. Assessment of child behavior problems: The validation of a new inventory. J. Clin. Child Psychol. 1978, 7, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.A.; Eyberg, S.M. The dyadic parent–child interaction coding system: Standardization and validation. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 1981, 49, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R. The Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire: A Research Note. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 1997, 38, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R. Psychometric Properties of the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2001, 40, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, T.M.; Ruffle, T.M. The Child Behavior Checklist and Related Forms for Assessing Behavioral/Emotional Problems and Competencies. Pediatr. Rev. 2000, 21, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rothbart, M.K.; Ahadi, S.A.; Hershey, K.L.; Fisher, P. Investigations of Temperament at Three to Seven Years: The Children’s Behavior Questionnaire. Child Dev. 2001, 72, 1394–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, G.; Spence, S.H.; McDonald, C. Can Parents and Teachers Provide a Reliable and Valid Report of Behavioral Inhibition? Child Dev. 2003, 74, 1899–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angalakuditi, M.; Wild, D.; Furtado, T. The translation and cultural adaptation of the Child Behavior Checklist for use in Israel (Hebrew), Korea, the US (Spanish), India (Malayalam and Kannada), and Spain. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2012, 5, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Pinto, I.; Santamaría, P.; Sánchez-Sánchez, F.; Carrasco, M.A.; Del Barrio, V. SENA: Sistema de Evaluación de Niños y Adolescentes [SENA: System for the Evaluation of Children and Adolescents]; TEA Ediciones: Madrid, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Morawska, A.; Sanders, M.R.; Haslam, D.; Filus, A.; Fletcher, R. Child Adjustment and Parent Efficacy Scale: Development and Initial Validation of a Parent Report Measure. Aust. Psychol. 2014, 49, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia, A.; Filus, A.; Calam, R.; Morawska, A.; Sanders, M.R. Validation of the Spanish version of the CAPES: A brief instrument for assessing child psychological difficulties and parental self-efficacy. Int. J. Behav. Dev. 2015, 40, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Morawska, A.; Sanders, M.R. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Group Triple P with Chinese Parents in Mainland China. Behav. Modif. 2016, 40, 825–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emser, T.S.; Mazzucchelli, T.G.; Christiansen, H.; Sanders, M.R. Child Adjustment and Parent Efficacy Scale-Developmental Disability (CAPES-DD): First psychometric evaluation of a new child and parenting assessment tool for children with a developmental disability. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2016, 53–54, 158–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.R.; Morawska, A. Family Background Questionnaire; Parenting and Family Support Centre: Brisbane, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Morawska, A.; Filus, A.; Haslam, D.; Sanders, M.R. The International Parenting Survey: Rationale, Development, and Potential Applications. Compr. Child Adolesc. Nurs. 2017, 42, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñiz, J.; Elosua, P.; Hambleton, R.K. Directrices para la traducción y adaptación de los tests: Segunda edición [International Test Commission Guidelines for test translation and adaptation: Second edition]. Psicothema 2013, 25, 151–157. Available online: http://www.psicothema.com/pdf/4093.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2021). [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fariña, F.; Arce, R.; Tomé, D.; Seijo, D. Validación del Cuestionario Actitud ante el Conflicto Parental: Autoinformada y Referenciada (ACPar). Revista Iberoamericana de Psicología y Salud 2020, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsuch, R.L. Exploratory Factor Analysis: Its Role in Item Analysis. J. Pers. Assess. 1997, 68, 532–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.A. Confirmatory Factor Analysis for Applied Research; Guilford: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fandiño, R.; Basanta, J.; Sanmarco, J.; Arce, R.; Fariña, F. Evaluation of the Executive Functioning and Psychological Adjustment of Child-to-Parent Offenders: Epidemiology and Quantification of Harm. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schermelleh-Engel, K.; Moosbrugger, H.; Müller, H. Evaluating the fit of structural equation models: Tests of significance and descriptive goodness-of-fit measures. Meth. Psychol. Res. Online 2003, 8, 23–74. Available online: http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~snijders/mpr_Schermelleh.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Hundleby, J.D.; Bernstein, I.H. Psychometric Theory, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Carmines, E.G.; Zeller, R.A. Reliability and Validity Assessment; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, G.W.; Rensvold, R.B. Evaluating Goodness-of-Fit Indexes for Testing Measurement Invariance. Struct. Equ. Model. 2002, 9, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.; Santo, R.M.; Guillemin, F. A review of guidelines for cross-cultural adaptation of questionnaires could not bring out a consensus. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2015, 68, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayorga, E.G.; Novo, M.; Fariña, F.; Arce, R. Destrezas cognitivas en menores infractores, de protección y normalizados: Un estudio de contraste. Revista Latinoamericana de Psicología 2020, 52, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, G.R.; Stapleton, L.M.; Mueller, R.O. The Reviewer’s Guide to Quantitative Methods in the Social Sciences; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bonett, D.G.; Wright, T.A. Cronbach’s alpha reliability: Interval estimation, hypothesis testing, and sample size planning. J. Organ. Behav. 2015, 36, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, M.; Fariña, F.; Seijo, D.; Vázquez, M.J.; Arce, R. Assessing the effects of a parental separation education program on mental health problems. Psicothema 2019, 31, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Gramaje, A.F.; Garcia, O.F.; Reyes, M.; Serra, E.; Garcia, F. Parenting Styles and Aggressive Adolescents: Relationships with Self-esteem and Personal Maladjustment. Eur. J. Psychol. Appl. Leg. Context 2019, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Podsakoff, N.P. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arce, R.; Fariña, F.; Seijo, D.; Novo, M. Assessing Impression Management with the MMPI-2 in Child Custody Litigation. Assessment 2015, 22, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-García, P.; Contreras, L.; Cano-Lozano, M.C. Types and intensity of postdivorce conflicts, the exercise of coparenting and its consequences on children. Revista Iberoamericana de Psicología y Salud 2019, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrás, T.; Seijo, D.; Fariña, F.; Novo, M.; Arce, R.; Cabanach, R.G. What and How Much Do Children Lose in Academic Settings Owing to Parental Separation? Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez, J.; Hidalgo, V.; López-Verdugo, I.; Jiménez, L. Beliefs about Child-Rearing and Development in Spain and Peru. A Comparative Analysis for Adapting Parenting Support Programs. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fariña, F.; Redondo, L.; Corrás, T.; Vilariño, M. Study of the Effects of Anchorage in Judicial Judgements in Child Custody Dispute Proceedings [Estudio de los efectos del anclaje en razonamientos judiciales en casos de disputa por la guarda y custodia]. Acción Psicológica 2017, 14, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fariña, F.; Seijo, D.; Arce, R.; Vázquez, M.J. Custodia compartida, corresponsabilidad parental y justicia terapéutica como nuevo paradigma. Anuario de Psicología Jurídica 2017, 27, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Abate, D.A. Use of solution-focused and family narrative approaches in working with high conflict families: Strategies and techniques that can be utilized in parenting coordination and co-parenting coaching. J. Child Custody 2016, 13, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.; Crouter, A.C.; Clements, M.L.; Boone-Holladay, T. Couples in Conflict; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]

| Variable | N (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age child | M = 7.13 (SD = 2.73). Range 2–12 | |
| Sex child | Male | 1311 (50.1%) |
| Female | 1289 (49.2%) | |
| Relationship to child | Father or foster father | 459 (17.5%) |
| Mother or foster mother | 2127 (81.2%) | |
| Stepfather | 2 (0.1%) | |
| Stepmother | 19 (0.7%) | |
| Other | 5 (0.2%) | |
| Marital status | Married | 1934 (73.9%) |
| Cohabiting | 353 (13.5%) | |
| Divorced | 222 (8.5%) | |
| Single | 84 (3.2%) | |
| Widow | 9 (0.3%) | |
| Other | 9 (0.3%) | |
| Family status | Both biological or adoptive parents | 2257 (86.2%) |
| One biological or adoptive parent and one stepparent | 91 (3.5%) | |
| Single parent family | 103 (3.9%) | |
| Other | 129 (4.9%) | |
| Children of previous relationships | Yes | 112 (4.3%) |
| No | 2294 (87.6%) |
| Items | M | SD | Skewness SE = 0.048 | Kurtosis SE = 0.096 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAPES1. Se altera o enfada cuando no se sale con la suya. | 1.56 | 0.80 | −0.36 | −0.33 |
| CAPES2. Se niega a realizar tareas del hogar cuando se le pide. | 2.10 | 0.73 | −0.64 | 0.46 |
| CAPES3. Se preocupa. | 1.54 | 0.90 | −0.13 | −0.73 |
| CAPES4. Le dan pataletas. | 2.13 | 0.81 | −0.64 | −0.18 |
| CAPES5. Se porta mal durante las comidas. | 2.27 | 0.76 | −0.96 | 0.73 |
| CAPES6. Discute o se pelea con otros niños/as o con sus hermanos/as. | 2.00 | 0.77 | −0.54 | 0.13 |
| CAPES7. Rechaza comerse la comida. | 2.11 | 0.80 | −0.73 | 0.26 |
| CAPES8. Tarda mucho en vestirse. | 1.97 | 0.86 | −0.54 | −0.33 |
| CAPES9. Me lastima a mi o a otros (golpea, araña, muerde, empuja…). | 2.69 | 0.58 | −2.02 | 4.18 |
| CAPES10. Interrumpe cuando hablo con otras personas. | 1.74 | 0.76 | −0.35 | −0.05 |
| CAPES11. Parece asustado o temeroso. | 2.49 | 0.68 | −1.34 | 1.66 |
| CAPES12. Tiene problemas de comportamiento en la guardería o el colegio. | 2.73 | 0.56 | −2.40 | 6.38 |
| CAPES13. Tiene dificultades para entretenerse sin la atención de un adulto. | 2.53 | 0.72 | −1.55 | 1.98 |
| CAPES14. Pega gritos, chillidos o es escandaloso. | 2.27 | 0.78 | −0.91 | 0.33 |
| CAPES15. Lloriquea o se queja. | 2.13 | 0.75 | −0.68 | 0.33 |
| CAPES16. Muestra una actitud desafiante cuando se le pide algo. | 2.44 | 0.68 | −1.15 | 1.20 |
| CAPES17. Llora más que otros/as niños/as de su edad. | 2.66 | 0.65 | −2.14 | 4.51 |
| CAPES18. Me contesta de forma grosera. | 2.58 | 0.63 | −1.54 | 2.45 |
| CAPES19. Aparenta estar descontento o triste. | 2.62 | 0.61 | −1.76 | 3.34 |
| CAPES20. Tiene dificultades para organizar las tareas y actividades. | 2.28 | 0.80 | −1.00 | 0.48 |
| CAPES21. Acepta las reglas y límites. | 1.82 | 1.01 | −0.26 | −1.13 |
| CAPES22. Se lleva bien con los miembros de la familia. | 2.34 | 1.08 | −1.39 | 0.33 |
| CAPES23. Es bondadoso/a y servicial con los demás. | 2.24 | 0.99 | −1.13 | 0.07 |
| CAPES24. Es capaz de entretenerse sin la constante atención adulta. | 2.09 | 1.02 | −0.84 | −0.48 |
| CAPES25. Coopera a la hora de dormirse. | 2.09 | 1.01 | −0.81 | −0.54 |
| CAPES26. Parece sentirse bien consigo mismo/a. | 2.28 | 0.98 | −1.26 | 0.41 |
| CAPES27. Se lleva bien con otros niños/as. | 2.36 | 0.97 | −1.46 | 0.94 |
| CAPES28. Expresa sus puntos de vista, ideas y necesidades de manera adecuada. | 2.15 | 0.95 | −0.94 | −0.10 |
| CAPES29. Puede realizar tareas pertinentes a su edad por sí mismo/a. | 2.35 | 0.97 | −1.40 | 0.75 |
| CAPES30. Obedece las instrucciones de los adultos. | 2.14 | 0.88 | −0.91 | 0.16 |
| Items | Factor | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| CAPES27 | 0.864 | |||||
| CAPES26 | 0.849 | |||||
| CAPES29 | 0.836 | |||||
| CAPES23 | 0.830 | |||||
| CAPES22 | 0.806 | |||||
| CAPES30 | 0.805 | |||||
| CAPES24 | 0.793 | |||||
| CAPES28 | 0.789 | |||||
| CAPES25 | 0.762 | |||||
| CAPES21 | 0.599 | |||||
| CAPES15 | 0.683 | |||||
| CAPES14 | 0.622 | |||||
| CAPES16 | 0.61 | |||||
| CAPES1 | 0.608 | |||||
| CAPES4 | 0.552 | −0.470 | ||||
| CAPES18 | 0.52 | −0.416 | ||||
| CAPES10 | 0.516 | |||||
| CAPES2 | 0.501 | |||||
| CAPES5 | 0.497 | 0.435 | ||||
| CAPES9 | 0.494 | |||||
| CAPES17 | 0.481 | 0.412 | ||||
| CAPES13 | 0.444 | −0.424 | ||||
| CAPES8 | 0.419 | |||||
| CAPES19 | 0.448 | 0.545 | ||||
| CAPES20 | 0.431 | 0.487 | ||||
| CAPES11 | 0.468 | |||||
| CAPES7 | 0.640 | |||||
| CAPES3 | 0.559 | |||||
| CAPES12 | 0.451 | −0.467 | ||||
| CAPES6 | ||||||
| Eigenvalues | 7.027 | 5.341 | 1.602 | 1.337 | 1.183 | 1.01 |
| Factor | Item | Standardized Regression Weights (λ) | Error Variances (δ) | Corrected Item-Total Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Child’s Competencies | CAPES 21 | 0.58 | 0.66 | 0.56 |
| CAPES 22 | 0.80 | 0.40 | 0.79 | |
| CAPES 23 | 0.81 | 0.33 | 0.81 | |
| CAPES 24 | 0.74 | 0.46 | 0.73 | |
| CAPES 25 | 0.74 | 0.46 | 0.72 | |
| CAPES 26 | 0.82 | 0.31 | 0.82 | |
| CAPES 27 | 0.86 | 0.22 | 0.86 | |
| CAPES 28 | 0.75 | 0.39 | 0.75 | |
| CAPES 29 | 0.83 | 0.29 | 0.82 | |
| CAPES 30 | 0.76 | 0.32 | 0.75 | |
| 2. Behavioural and Emotional Problems | CAPES 1 | 0.58 | 0.44 | 0.55 |
| CAPES 2 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.43 | |
| CAPES 4 | 0.57 | 0.45 | 0.52 | |
| CAPES 5 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.43 | |
| CAPES 8 | 0.44 | 0.64 | 0.4 | |
| CAPES 9 | 0.50 | 0.24 | 0.46 | |
| CAPES 10 | 0.52 | 0.44 | 0.45 | |
| CAPES 13 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.39 | |
| CAPES 14 | 0.64 | 0.38 | 0.58 | |
| CAPES 15 | 0.63 | 0.33 | 0.6 | |
| CAPES 16 | 0.58 | 0.31 | 0.55 | |
| CAPES 17 | 0.50 | 0.34 | 0.44 | |
| CAPES 18 | 0.50 | 0.31 | 0.49 | |
| CAPES 19 | 0.35 | 0.33 | 0.35 | |
| CAPES 20 | 0.48 | 0.55 | 0.42 |
| Factor | Cronbach’s Alpha (All Sample) | Cronbach’s Alpha (EFA Sample) | Cronbach’s Alpha (CFA Sample) | Composite Reliability (CFA Sample) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Child’s competencies | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.94 |
| 2. Behavioural and emotional problems | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.91 |
| Items | Standardised Regression Weights (Λ) | Error Variances (δ) | Corrected Item-Total Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| SE_C1 | 0.758 | 0.425 | 0.69 |
| SE_C2 | 0.768 | 0.41 | 0.71 |
| SE_C4 | 0.776 | 0.398 | 0.71 |
| SE_C5 | 0.78 | 0.392 | 0.71 |
| SE_C8 | 0.748 | 0.44 | 0.71 |
| SE_C9 | 0.847 | 0.283 | 0.79 |
| SE_C10 | 0.759 | 0.424 | 0.71 |
| SE_C13 | 0.853 | 0.272 | 0.81 |
| SE_C14 | 0.868 | 0.247 | 0.84 |
| SE_C15 | 0.902 | 0.186 | 0.84 |
| SE_C16 | 0.908 | 0.176 | 0.83 |
| SE_C17 | 0.901 | 0.188 | 0.83 |
| SE_C18 | 0.893 | 0.203 | 0.81 |
| SE_C19 | 0.862 | 0.257 | 0.72 |
| SE_C20 | 0.776 | 0.398 | 0.71 |
| Items | Minimum | Maximum | M | SD | Skewness | Skewness SE | Kurtosis | Kurtosis SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE_C1 | 0 | 10 | 7.84 | 2.16 | −1.29 | 0.06 | 1.60 | 0.13 |
| SE_C2 | 0 | 10 | 8.27 | 2.06 | −1.85 | 0.06 | 3.79 | 0.13 |
| SE_C4 | 0 | 10 | 7.91 | 2.39 | −1.54 | 0.07 | 2.08 | 0.13 |
| SE_C5 | 0 | 10 | 7.94 | 2.44 | −1.60 | 0.07 | 2.28 | 0.13 |
| SE_C8 | 0 | 10 | 7.89 | 2.25 | −1.43 | 0.07 | 2.09 | 0.14 |
| SE_C9 | 0 | 10 | 8.47 | 2.50 | −2.14 | 0.07 | 4.01 | 0.14 |
| SE_C10 | 0 | 10 | 7.68 | 2.22 | −1.32 | 0.07 | 1.74 | 0.14 |
| SE_C13 | 0 | 10 | 8.24 | 2.33 | −1.89 | 0.07 | 3.57 | 0.14 |
| SE_C14 | 0 | 10 | 7.93 | 2.35 | −1.56 | 0.07 | 2.26 | 0.14 |
| SE_C15 | 0 | 10 | 7.92 | 2.25 | −1.64 | 0.07 | 2.79 | 0.14 |
| SE_C16 | 0 | 10 | 8.18 | 2.32 | −1.92 | 0.07 | 3.75 | 0.14 |
| SE_C17 | 0 | 10 | 8.25 | 2.48 | −1.94 | 0.07 | 3.42 | 0.14 |
| SE_C18 | 0 | 10 | 8.32 | 2.47 | −2.04 | 0.07 | 3.78 | 0.14 |
| SE_C19 | 0 | 10 | 8.25 | 2.46 | −2.01 | 0.07 | 3.67 | 0.14 |
| SE_C20 | 0 | 10 | 7.91 | 2.53 | −1.66 | 0.07 | 2.33 | 0.14 |
| TOTAL | 0 | 10 | 8.13 | 1.97 | −2.17 | 0.08 | 5.36 | 0.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seijo, D.; Tomé, D.; Sanmarco, J.; Morawska, A.; Fariña, F. Spanish Adaptation and Validation of the Child Adjustment and Parent Efficacy Scale. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4647. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094647
Seijo D, Tomé D, Sanmarco J, Morawska A, Fariña F. Spanish Adaptation and Validation of the Child Adjustment and Parent Efficacy Scale. Sustainability. 2021; 13(9):4647. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094647
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeijo, Dolores, David Tomé, Jessica Sanmarco, Alina Morawska, and Francisca Fariña. 2021. "Spanish Adaptation and Validation of the Child Adjustment and Parent Efficacy Scale" Sustainability 13, no. 9: 4647. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094647
APA StyleSeijo, D., Tomé, D., Sanmarco, J., Morawska, A., & Fariña, F. (2021). Spanish Adaptation and Validation of the Child Adjustment and Parent Efficacy Scale. Sustainability, 13(9), 4647. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094647







