A Topic-Based Bibliometric Review of Computers in Human Behavior: Contributors, Collaborations, and Research Topics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodologies
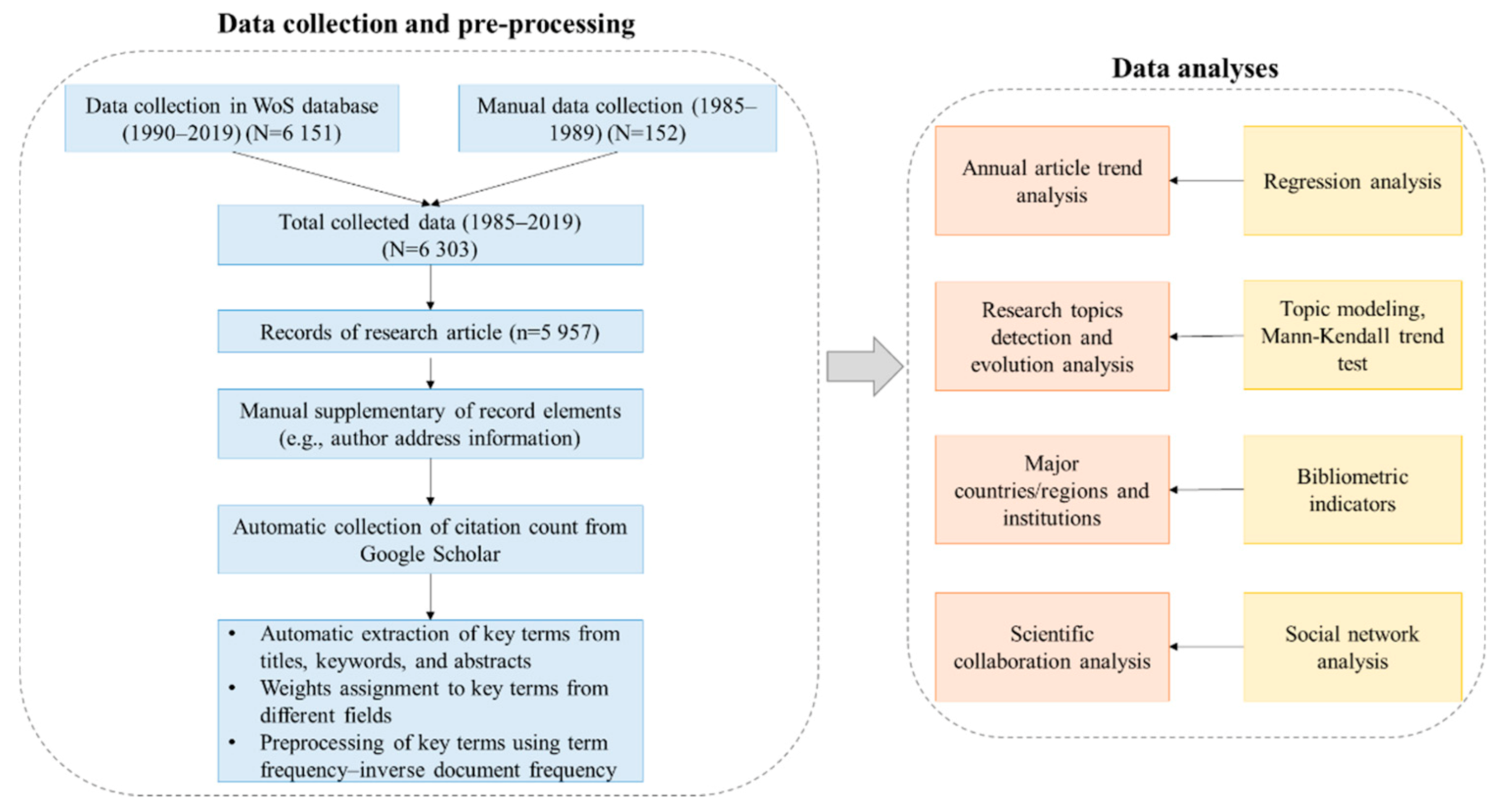
2.1. Data Collection and Pre-Processing
2.2. Performance Analyses
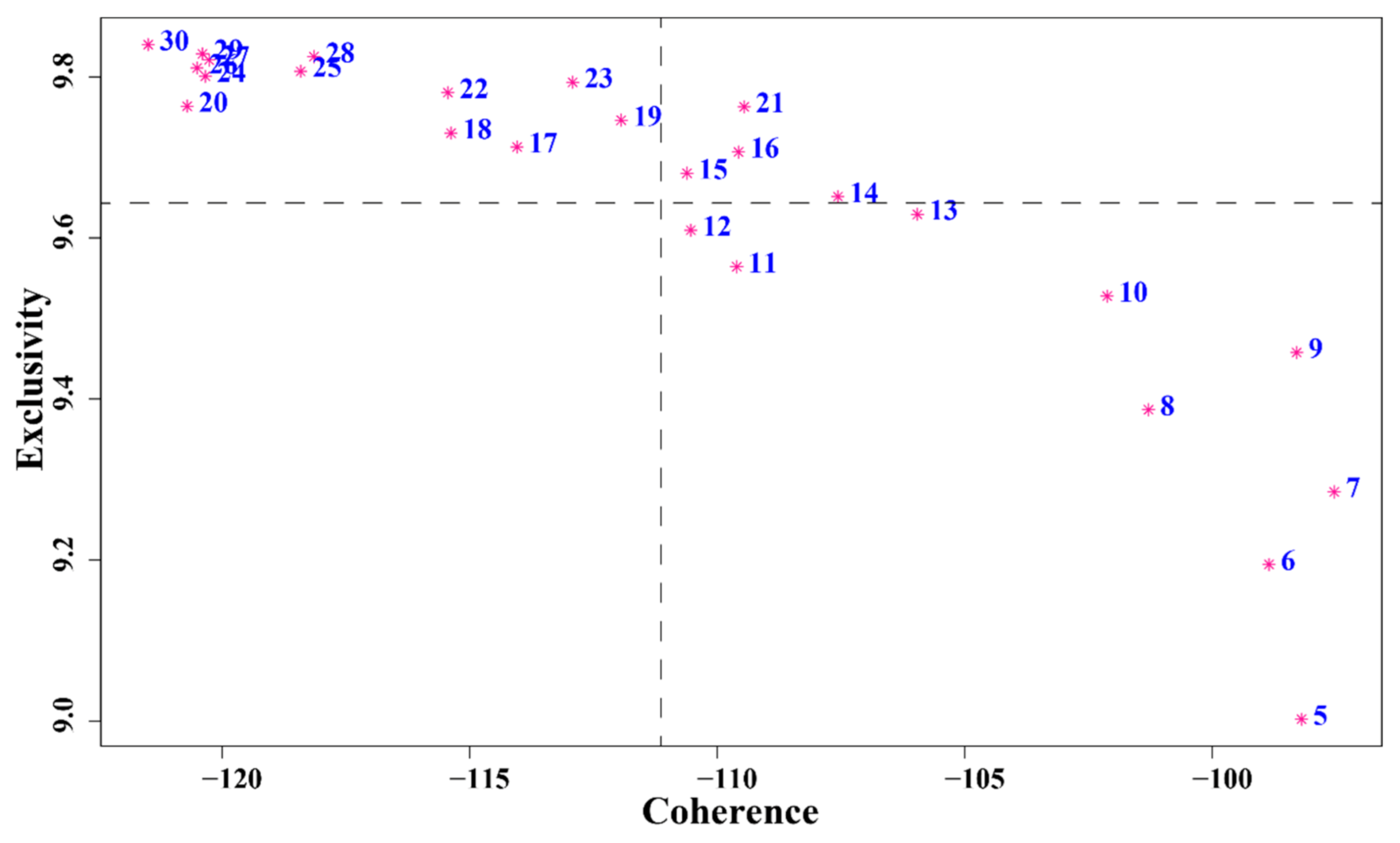
2.3. Topic Modeling and Evolution Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Trend of the Publications (RQ1)
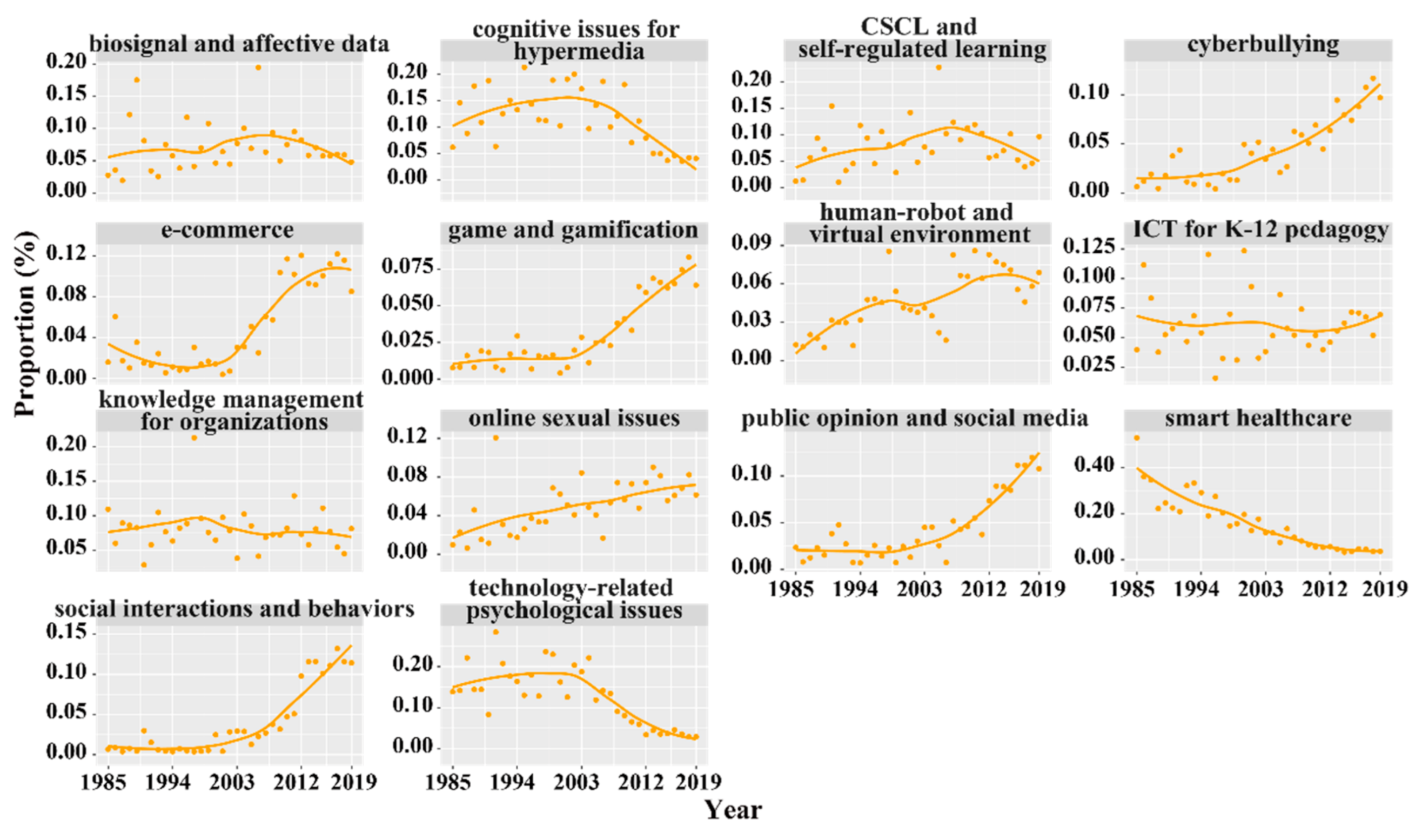
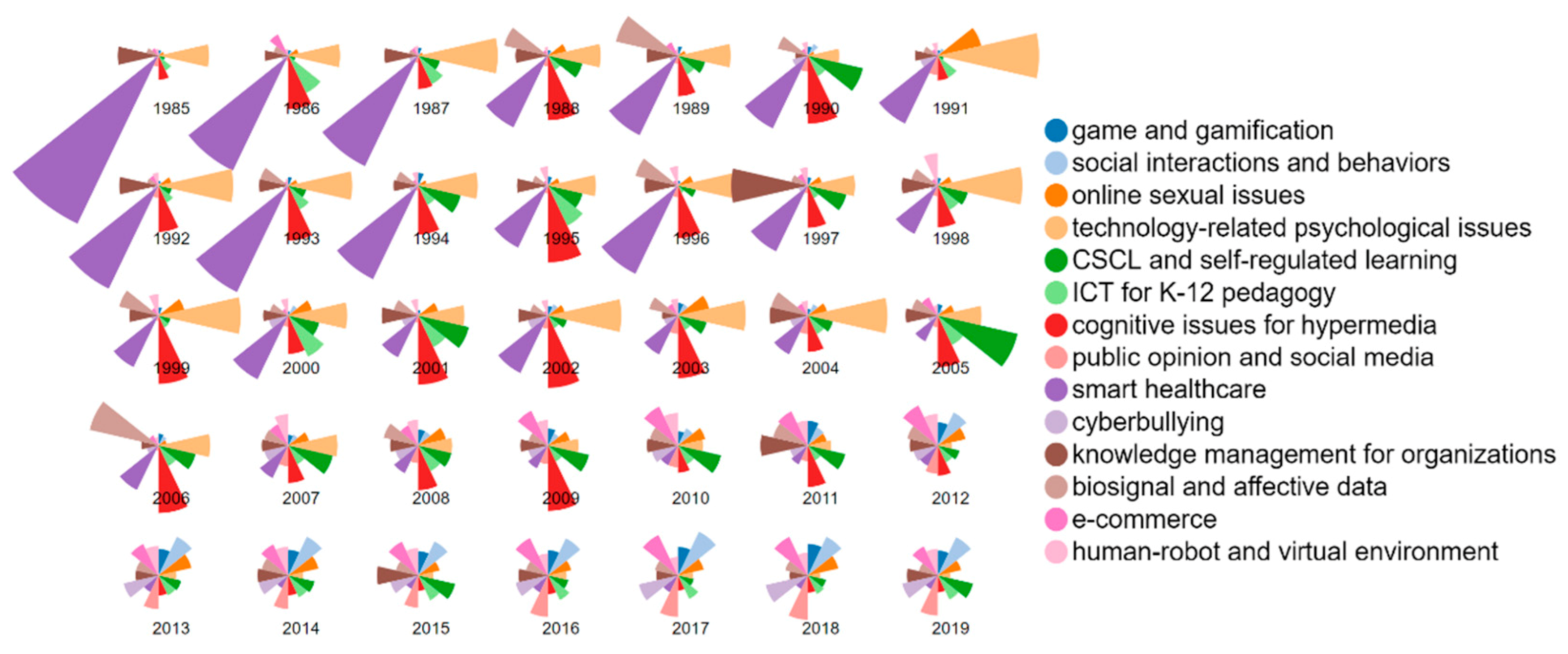
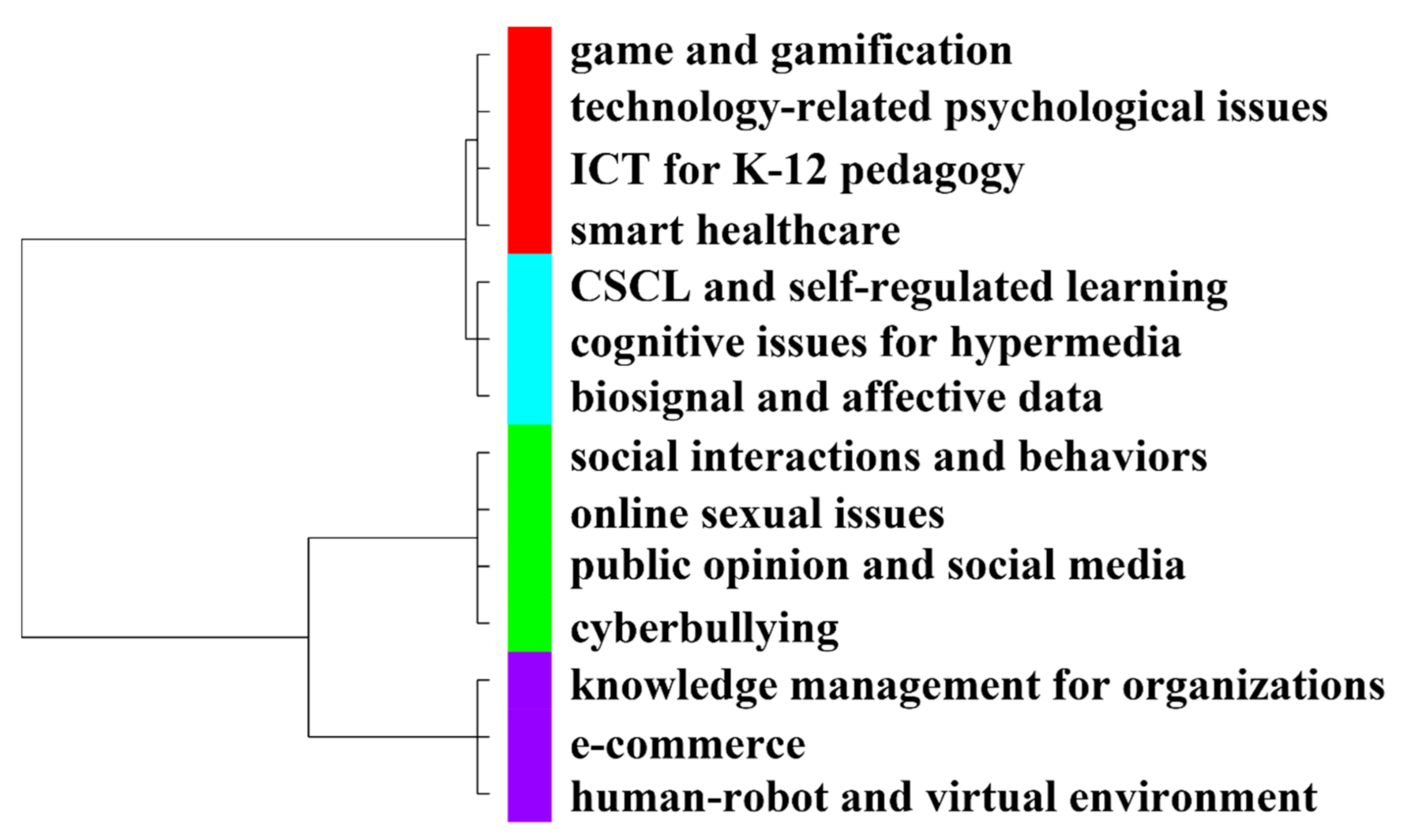
3.2. Topic Identification, Trends, and Correlations (RQ2)
3.3. Prolific Countries/Regions and Institutions (RQ3)
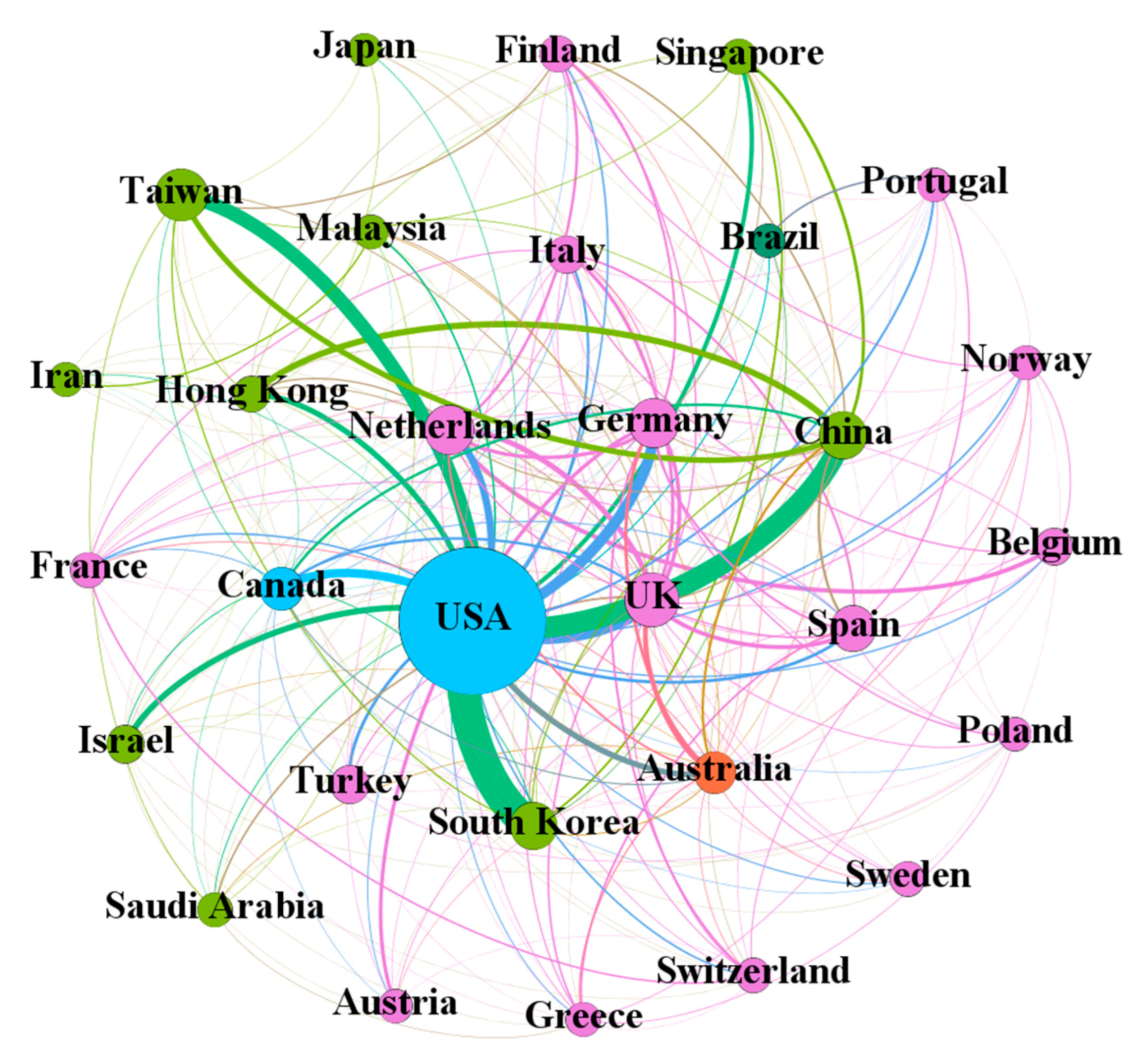
3.4. Scientific Collaborations (RQ4)
3.5. Topic Distributions across Countries/Regions and Institutions (RQ5)
4. Discussion
4.1. In Comparison with Vošner et al.
4.2. E-Commerce
4.3. Social Interactions and Behaviors
4.4. Public Opinion and Social Media
4.5. Cyberbullying
4.6. Online Sexual Issues
4.7. Human-Robot and Virtual Environments
4.8. Games and Gamification
4.9. Potential Inter-Topic Research Directions
4.10. Challenges and Suggestions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Studies | Aspects | Vošner et al. (2016) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vošner et al. (2016) | Period | 1985–2015 | |
| Country analysis | Methods | Most prolific countries | |
| Results | USA, Taiwan, the Netherlands, UK, Germany | ||
| Institution | Methods | Most prolific institutions | |
| Analysis | Results | State University System of Florida, Open University Netherlands, University of North Carolina, University of Twente, University of California System | |
| Collaboration analysis | Methods | Social network analysis | |
| Results | Close collaborators: Sungkyunkwan University and University of Southern California; University of Twente and Utrecht University; Open University of The Netherlands and Utrecht University | ||
| Topic analysis | Methods | Bibliometrics, keywords co-occurrence analysis | |
| Results | Human–computer interaction, attitudes and opinions about the computer use, internet and knowledge sharing, internet-based collaborative learning, psychological impact of computer use, and social media platforms | ||
| Our study | Period | 1985–2019 | |
| Country analysis | Methods | Most influential countries/regions ranked by H-index | |
| Results | USA, UK, Taiwan, South Korea, the Netherlands | ||
| Institution | Methods | Most influential institutions ranked by H-index | |
| Analysis | Results | Open University of Netherlands, Michigan State University, Sungkyunkwan University, Pennsylvania State University, University of Twente | |
| Collaboration analysis | Methods | Social network analysis | |
| Results | Countries/regions from the same continents, as well as institutions from the same countries/regions tended to collaborate more in conducting CHB research | ||
| Topic analysis | Methods | Structural topic model, Mann–Kendall test, affinity propagation clustering | |
| Results | 1. Top five topics: e-commerce, social interactions and behaviors, public opinion and social media, knowledge management for organizations, and cyberbullying | ||
| 2. Seven increasing topics: e-commerce, social interactions and behaviors, public opinion and social media, cyberbullying, online sexual issues, human-robot and virtual environment, and game and gamification | |||
| 3. Inter-topical research directions: (1) game and gamification, technology-related psychological issues, ICT for K-12 pedagogy, and smart healthcare; (2) CSCL and self-regulated learning, cognitive issues for hypermedia, and biosignal and affective data; (3) social interactions and behaviors, online sexual issues, public opinion and social media, and cyberbullying; (4) knowledge management for organizations, e-commerce, and human–robot and virtual environment | |||
References
- Shaw, H.; Ellis, D.A.; Ziegler, F.V. The Technology Integration Model (TIM). Predicting the continued use of technology. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 83, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katerina, T.; Nicolaos, P. Mouse behavioral patterns and keystroke dynamics in End-User Development: What can they tell us about users’ behavioral attributes? Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 83, 288–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K. WiAct: A passive WiFi-based human activity recognition system. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 20, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurangzeb, K.; Haider, I.; Khan, M.A.; Saba, T.; Javed, K.; Iqbal, T.; Rehman, A.; Ali, H.; Sarfraz, M.S. Human Behavior Analysis Based on Multi-Types Features Fusion and Von Nauman Entropy Based Features Reduction. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2019, 9, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hou, Y.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, C.; Dou, W.; Huang, Z.; Guo, Y. A Survey on Human Behavior Recognition Using Smartphone-Based Ultrasonic Signal. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 100581–100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Driscoll, M.P.; Nelson, D.W. The Past, Present, and Future of Research in Distance Education: Results of a Content Analysis. Am. J. Distance Educ. 2004, 18, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.E. About this article and new series. Educ. Technol. 2011, 51, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Zawacki-Richter, O.; Latchem, C. Exploring four decades of research in Computers & Education. Comput. Educ. 2018, 122, 136–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, H.; Wang, F.L.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Hao, T. A bibliometric analysis of natural language processing in medical research. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hao, J.; Chen, J.; Hua, S.; Hao, T. A Bibliometric Analysis of the Research Status of the Technology Enhanced Language Learning; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 169–179. [Google Scholar]
- Lemay, D.J.; Baek, C.; Doleck, T. Comparison of Learning Analytics and Educational Data Mining: A Topic Modeling Approach. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2021, 2, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabudi, T.; Pappas, I.; Olsen, D.H. AI-enabled Adaptive Learning Systems: A Systematic Mapping of the Literature. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2021, 2, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vošner, H.B.; Kokol, P.; Bobek, S.; Železnik, D.; Završnik, J. A bibliometric retrospective of the Journal Computers in Human Behavior (1991–2015). Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 65, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, K.D. Using structural topic modeling to identify latent topics and trends in aviation incident reports. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 87, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.W.; Börjeson, L. Gender diversity in the management field: Does it matter for research outcomes? Res. Policy 2019, 48, 1617–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Cheng, G.; Gong, T. Topics and trends in artificial intelligence assisted human brain research. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tao, X.; Wang, F.L.; Xie, H. Global research on artificial intelligence-enhanced human electroencephalogram analysis. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, H. A Structural Topic Modeling-Based Bibliometric Study of Sentiment Analysis Literature. Cogn. Comput. 2020, 12, 1097–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannigan, T.R.; Haans, R.F.J.; Vakili, K.; Tchalian, H.; Glaser, V.L.; Wang, M.S.; Kaplan, S.; Jennings, P.D. Topic Modeling in Management Research: Rendering New Theory from Textual Data. Acad. Manag. Ann. 2019, 13, 586–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zou, D.; Xie, H.; Wang, F.L. Past, present, and future of smart learning: A topic-based bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2021, 18, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zou, D.; Xie, H.; Cheng, K.S. Twenty years of personalized language learning: Topic modeling and knowledge mapping. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2021, 24, 205–222. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zou, D.; Cheng, G.; Xie, H. Detecting latent topics and trends in educational technologies over four decades using structural topic modeling: A retrospective of all volumes of Computers & Education. Comput. Educ. 2020, 151, 103855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zou, D.; Xie, H. Fifty years of British Journal of Educational Technology: A topic modeling based bibliometric perspective. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2020, 51, 692–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.E.; Stewart, B.M.; Tingley, D.; Lucas, C.; Leder-Luis, J.; Gadarian, S.K.; Albertson, B.; Rand, D.G. Structural Topic Models for Open-Ended Survey Responses. Am. J. Politics Sci. 2014, 58, 1064–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Non-parametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/pdf/1907187.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2020). [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, J.E. An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16569–16572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, S.; Ippolito, J.A.; Lopez, S.A.; Eloy, J.A.; Beebe, K.S. The Use of the h-Index in Academic Orthopaedic Surgery. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2017, 99, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Lu, L.Y.; Lu, W.-M.; Lin, B.J. Data envelopment analysis 1978–2010: A citation-based literature survey. Omega 2013, 41, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otte, E.; Rousseau, R. Social network analysis: A powerful strategy, also for the information sciences. J. Inf. Sci. 2002, 28, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In Proceedings of the Third International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; Available online: https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/ICWSM/article/view/13937 (accessed on 25 April 2020).
- Roberts, M.E.; Stewart, B.M.; Airoldi, E.M. A Model of Text for Experimentation in the Social Sciences. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2016, 111, 988–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J. Corporate funding and ideological polarization about climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Jiménez, E.; López-Catalán, L.; López-Catalán, B.; Domínguez-Fernández, G. Sustainable Development Goals and Education: A Bibliometric Mapping Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Gómez, A.; Ruiz-Palomo, D.; Fernández-Gámez, M.A.; García-Revilla, M.R. Sustainable Tourism Development and Economic Growth: Bibliometric Review and Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choshin, M.; Ghaffari, A. An investigation of the impact of effective factors on the success of e-commerce in small- and medium-sized companies. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 66, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.V.; Tran, A.; Nguyen, T. Understanding the discontinuance behavior of mobile shoppers as a consequence of technostress: An application of the stress-coping theory. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2019, 95, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, R. New Business Model for Company toWin the Competition. Am. J. Ind. Bus. Manag. 2014, 4, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.; Oliveira, T. Understanding the impact of m-banking on individual performance: DeLone & McLean and TTF perspective. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 61, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Fan, W.; Zhou, M. Social presence, trust, and social commerce purchase intention: An empirical research. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 56, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, K. Online communication with strong ties and subjective well-being in Japan. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 66, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenninger, H.; Cheung, C.M.; Krasnova, H. College-aged users behavioral strategies to reduce envy on social networking sites: A cross-cultural investigation. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2019, 97, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylski, A.K.; Murayama, K.; DeHaan, C.R.; Gladwell, V. Motivational, emotional, and behavioral correlates of fear of missing out. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2013, 29, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Brdiczka, O.; Liu, J. A study of Facebook behavior: What does it tell about your Neuroticism and Extraversion? Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 45, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanat-Maymon, Y.; Almog, L.; Cohen, R.; Amichai-Hamburger, Y. Contingent self-worth and Facebook addiction. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 88, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, N.; Burke, J. Sleeping with the frenemy: How restricting ‘bedroom use’ of smartphones impacts happiness and wellbeing. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 85, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalis, A.; Mikami, A.Y. Talking face-to-Facebook: Associations between online social interactions and offline relationships. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 89, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnidge, M. The role of news in promoting political disagreement on social media. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 52, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Lachlan, K.A.; Spence, P.R. Exploring extreme events on social media: A comparison of user reposting/retweeting behaviors on Twitter and Weibo. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 65, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, P.R.; Lachlan, K.A.; Rainear, A.M. Social media and crisis research: Data collection and directions. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 54, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.K.; Mahdavi, J.; Carvalho, M.; Fisher, S.; Russell, S.; Tippett, N. Cyberbullying: Its nature and impact in secondary school pupils. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2008, 49, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melander, L.A. College Students’ Perceptions of Intimate Partner Cyber Harassment. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2010, 13, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolak, J.; Mitchell, K.J.; Finkelhor, D. Does Online Harassment Constitute Bullying? An Exploration of Online Harassment by Known Peers and Online-Only Contacts. J. Adolesc. Health 2007, 41, S51–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.S.; Kim, D.H.; Thornberg, R.; Kang, J.H.; Morgan, J.T. Correlates of direct and indirect forms of cyberbullying victimization involving South Korean adolescents: An ecological perspective. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 87, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañaga, E.; Santiago, Y.; Anastasio, O.; Raúl, N. Loneliness, parent-child communication and cyberbullying victimization among Spanish youths. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 65, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappetta, K.C.; Barth, J.M. How gender role stereotypes affect attraction in an online dating scenario. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 63, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaughnessy, K.; Byers, E.S. Contextualizing cybersex experience: Heterosexually identified men and women’s desire for and experiences with cybersex with three types of partners. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 32, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzinikolaou, A.; Lievens, E. Towards a Legal Qualifcaton of Online Sexual Acts in which Children are Involved: Constructng a Typology. Eur. J. Law Technol. 2019, 10, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Guitton, M.J. Living in the Hutt Space: Immersive process in the Star Wars Role-Play community of Second Life. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2012, 28, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofari, C.; Guitton, M.J. Mapping virtual communities by their visual productions: The example of the Second Life Steampunk community. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 41, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzani, L.; Ripoll, P.; Peiró, J.M.; Van Dick, R. Loafing in the digital age: The role of computer mediated communication in the relation between perceived loafing and group affective outcomes. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 33, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudiello, I.; Zibetti, E.; Lefort, S.; Chetouani, M.; Ivaldi, S. Trust as indicator of robot functional and social acceptance. An experimental study on user conformation to iCub answers. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 61, 633–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerabeck, J.M.; Ferguson, C.J. The influence of solitary and cooperative violent video game play on aggressive and prosocial behavior. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2013, 29, 2573–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, L.D.; Misiak, M.; Behnke, M.; Dziekan, M.; Guzik, P. The Pikachu effect: Social and health gaming motivations lead to greater benefits of Pokémon GO use. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 75, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von der Emde, S.; Schneider, J.; Kötter, M. Technically speaking: Transforming language learning through virtual learning environments (MOOs). Mod. Lang J. 2001, 85, 210–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.W.Y.; So, H.C.F.; Choi, M.M.T.; Yan, V.C.M.; Wong, T.K.S. Artificial Intelligence in education: Using heart rate variability (HRV) as a biomarker to assess emotions objectively. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2021, 2, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, O.; Alikhani, I.; Järvelä, S.; Kirschner, P.A.; Juuso, I.; Seppänen, T. Multimodal data to design visual learning analytics for understanding regulation of learning. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2019, 100, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hee, C.; Jacobs, G.; Emmery, C.; De Smet, B.; Lefever, E.; Verhoeven, B.; de Pauw, G.; Daelemans, W.; Hoste, V. Automatic detection of cyberbullying in social media text. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaido, G.M. Cyberbullying on social media platforms among university students in the United Arab Emirates. Int. J. Adolesc. Youth 2020, 25, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.; Blazquez, M.; López, B.; Castro, M.; Cristobal, E.S.; Martin, S. Educational games for improving the teaching-learning process of a CLIL subject: Physics and chemistry in secondary education. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE) Proceedings, Madrid, Spain, 22–25 October 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Xie, H.; Hwang, G.-J. A multi-perspective study on Artificial Intelligence in Education: Grants, conferences, journals, software tools, institutions, and researchers. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, H.; Zou, D.; Hwang, G.-J. Application and theory gaps during the rise of Artificial Intelligence in Education. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2020, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ötting, S.K.; Maier, G.W. The importance of procedural justice in Human–Machine Interactions: Intelligent systems as new decision agents in organizations. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 89, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Terms | A1 (R) | A2 (R) | A3 (R) | A4 (R) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| internet | 1575 (1) | 242 (7) | 1333 (1) | 624 (2) |
| learning | 1374 (2) | 355 (2) | 1019 (3) | 467 (3) |
| medium | 1283 (3) | 90 (39) | 1193 (2) | 709 (1) |
| computer | 1246 (4) | 614 (1) | 632 (12) | 256 (22) |
| system | 1098 (5) | 331 (3) | 767 (5) | 343 (8) |
| group | 1071 (6) | 253 (4) | 818 (4) | 375 (6) |
| knowledge | 920 (7) | 201 (9) | 719 (7) | 307 (14) |
| cognitive | 872 (8) | 221 (8) | 651 (11) | 317 (12) |
| attitude | 849 (9) | 248 (6) | 601 (14) | 297 (16) |
| task | 780 (10) | 251 (5) | 529 (19) | 249 (25) |
| motivation | 768 (11) | 84 (45) | 684 (9) | 347 (7) |
| 749 (12) | 3 (2240) | 746 (6) | 432 (4) | |
| site | 744 (13) | 48 (140) | 696 (8) | 376 (5) |
| network | 706 (14) | 48 (140) | 658 (10) | 324 (11) |
| intention | 674 (15) | 51 (123) | 623 (13) | 338 (9) |
| gender | 664 (16) | 151 (13) | 513 (23) | 253 (23) |
| game | 658 (17) | 62 (86) | 596 (15) | 315 (13) |
| content | 641 (18) | 123 (22) | 518 (22) | 263 (19) |
| education | 633 (19) | 120 (25) | 513 (23) | 268 (18) |
| personality | 614 (20) | 89 (41) | 525 (20) | 259 (21) |
| acceptance | 613 (21) | 81 (49) | 532 (18) | 261 (20) |
| strategy | 612 (22) | 121 (24) | 491 (25) | 252 (24) |
| satisfaction | 606 (23) | 81 (49) | 525 (20) | 297 (16) |
| tool | 605 (24) | 140 (16) | 465 (28) | 192 (48) |
| problem | 589 (25) | 198 (10) | 391 (41) | 191 (49) |
| usage | 581 (26) | 91 (37) | 490 (26) | 228 (32) |
| control | 575 (27) | 132 (20) | 443 (29) | 230 (31) |
| adolescent | 569 (28) | 34 (218) | 535 (17) | 325 (10) |
| scale | 566 (29) | 149 (14) | 417 (32) | 234 (29) |
| networking | 548 (30) | 8 (1046) | 540 (16) | 298 (15) |
| quality | 538 (31) | 103 (35) | 435 (30) | 224 (34) |
| virtual | 535 (32) | 60 (90) | 475 (27) | 204 (44) |
| psychological | 502 (33) | 115 (30) | 387 (42) | 225 (33) |
| human | 501 (34) | 125 (21) | 376 (46) | 185 (51) |
| school | 496 (35) | 102 (36) | 394 (40) | 207 (41) |
| management | 486 (36) | 76 (57) | 410 (35) | 201 (47) |
| anxiety | 482 (37) | 187 (11) | 295 (61) | 167 (57) |
| life | 478 (38) | 52 (119) | 426 (31) | 237 (27) |
| age | 474 (39) | 67 (71) | 407 (36) | 224 (34) |
| service | 469 (40) | 65 (75) | 404 (37) | 203 (45) |
| Labels | Representative Terms | % | p | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| e-commerce | continuance, purchase, word-of-mouth, innovativeness, utilitarian, tam, ewom, price, externality, repurchase | 9.14 | 0.00002 | ↑↑↑↑ |
| social interactions and behaviors | smartphone, neuroticism, extraversion, extroversion, fb, networking, envy, fomo, narcissistic, sns | 8.85 | 0 | ↑↑↑↑ |
| public opinion and social media | political, crisis, tweet, cancer, incivility, election, lurking, breach, retweeting, presidential | 8.11 | 0 | ↑↑↑↑ |
| knowledge management for organizations | enterprise, technology-organization-environment, agile, turnover, governance, maturity, organizational, employee, fuzzy, coopetition | 7.79 | 0.3634 | ↓ |
| cyberbullying | cyberbullying, victimization, bullying, cyber, parental, adolescence, bystander, parenting, cybervictimization, pathological | 7.62 | 0 | ↑↑↑↑ |
| CSCL and self-regulated learning | self-regulated, cscl, srl, gstudy, collaborative, associative, collaborator, analytics, tutoring, apprenticeship | 7.50 | 0.3065 | ↑ |
| cognitive issues for hypermedia | hypermedia, cognitive-load, split-attention, landmark, solving, load, self-explanation, novice, hypertext, cognitive | 6.97 | 0.00216 | ↓↓↓ |
| smart healthcare | applicant, autism, aging, self-help, asd, writer, mmpi, psychotherapy, dementia, panic | 6.74 | 0 | ↓↓↓↓ |
| biosignal and affective data | banner, mouse, layout, seductive, eye, polychronicity, visual, engine, movement, eye-tracking | 6.60 | 0.4954 | ↑ |
| online sexual issues | sexting, dating, intimacy, sexual, ostracism, self-awareness, sext, im, chatbot, machiavellianism | 6.40 | 0.00001 | ↑↑↑↑ |
| technology-related psychological issues | cyberloafing, computer-related, technophobia, computerphobia, attitude, self-efficacy, instrument, validity, anxiety, psychometric | 6.22 | 0 | ↓↓↓↓ |
| ICT for K-12 pedagogy | ict, pre-service, flipped, k-12, pedagogy, lecture, efl, teacher, literacy, classroom | 6.20 | 0.6292 | ↑ |
| human-robot and virtual environment | robot, human-robot, robotic, team, humanoid, multicultural, virtual, agent, community, newcomer | 6.16 | 0.00003 | ↑↑↑↑ |
| game and gamification | game, player, playing, violent, garner, multiplayer, in-game, role-playing, warcraft, gameplay | 5.68 | 0 | ↑↑↑↑ |
| C/R | H | C (R) | ACP | A1 (R) | A2 (R) | A3 (R) | A4 (R) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 195 | 186,721 (1) | 78.06 | 2392 (1) | 658 (1) | 1734 (1) | 785 (1) |
| UK | 95 | 33,588 (3) | 72.23 | 465 (2) | 98 (3) | 367 (2) | 233 (2) |
| Taiwan | 94 | 38,665 (2) | 88.89 | 435 (3) | 90 (4) | 345 (3) | 178 (4) |
| South Korea | 86 | 24,236 (5) | 73.89 | 328 (7) | 20 (12) | 308 (5) | 148 (6) |
| The Netherlands | 85 | 28,385 (4) | 77.13 | 368 (4) | 105 (2) | 263 (7) | 132 (7) |
| Germany | 79 | 20,658 (8) | 56.29 | 367 (5) | 66 (5) | 301 (6) | 165 (5) |
| China | 74 | 20,247 (9) | 60.80 | 333 (6) | 15 (15) | 318 (4) | 204 (3) |
| Spain | 74 | 21,409 (7) | 74.34 | 288 (8) | 25 (10) | 263 (7) | 109 (8) |
| Canada | 70 | 24,007 (6) | 98.79 | 243 (9) | 59 (6) | 184 (9) | 77 (10) |
| Australia | 64 | 14,784 (10) | 68.76 | 215 (10) | 42 (7) | 173 (10) | 107 (9) |
| Israel | 56 | 12,148 (11) | 97.18 | 125 (13) | 37 (8) | 88 (14) | 46 (16) |
| Turkey | 55 | 9623 (12) | 67.77 | 142 (11) | 16 (14) | 126 (11) | 73 (11) |
| Finland | 49 | 7403 (14) | 70.50 | 105 (14) | 11 (18) | 94 (13) | 61 (13) |
| Italy | 45 | 5613 (17) | 43.18 | 130 (12) | 12 (17) | 118 (12) | 69 (12) |
| Belgium | 42 | 6039 (16) | 57.51 | 105 (14) | 17 (13) | 88 (14) | 55 (14) |
| Hong Kong | 40 | 8094 (13) | 94.12 | 86 (17) | 7 (22) | 79 (17) | 50 (15) |
| Singapore | 37 | 6416 (15) | 71.29 | 90 (16) | 6 (23) | 84 (16) | 45 (17) |
| France | 36 | 3936 (21) | 46.86 | 84 (18) | 13 (16) | 71 (18) | 33 (20) |
| Switzerland | 35 | 4687 (19) | 74.40 | 63 (23) | 9 (19) | 54 (22) | 29 (22) |
| Malaysia | 34 | 3580 (22) | 62.81 | 57 (25) | 3 (29) | 54 (22) | 29 (22) |
| Institutions | C/R | H | C (R) | ACP | A1 (R) | A2 (R) | A3 (R) | A4 (R) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open University of Netherlands | The Netherlands | 46 | 10,379 (1) | 136.57 | 76 (3) | 33 (1) | 43 (10) | 15 (26) |
| Michigan State University | USA | 40 | 8122 (2) | 86.40 | 94 (1) | 14 (9) | 80 (1) | 36 (2) |
| Sungkyunkwan University | South Korea | 40 | 5129 (10) | 84.08 | 61 (8) | 5 (65) | 56 (5) | 10 (68) |
| Pennsylvania State University | USA | 37 | 5019 (11) | 64.35 | 78 (2) | 12 (12) | 66 (2) | 35 (3) |
| University of Twente | The Netherlands | 36 | 5334 (6) | 74.08 | 72 (4) | 28 (2) | 44 (9) | 13 (38) |
| Utrecht University | The Netherlands | 35 | 5208 (8) | 81.38 | 64 (6) | 19 (5) | 45 (7) | 21 (8) |
| University of Amsterdam | The Netherlands | 34 | 4575 (13) | 75.00 | 61 (8) | 10 (19) | 51 (6) | 27 (5) |
| Knowledge Media Research Center | Germany | 33 | 3165 (27) | 65.94 | 48 (12) | 12 (12) | 36 (13) | 4 (257) |
| Nanyang Technological University | Singapore | 32 | 5142 (9) | 81.62 | 63 (7) | 5 (65) | 58 (4) | 31 (4) |
| National Taiwan Normal University | Taiwan | 31 | 2775 (35) | 40.81 | 68 (5) | 6 (50) | 62 (3) | 40 (1) |
| The Ohio State University | USA | 31 | 6150 (5) | 116.04 | 53 (10) | 8 (27) | 45 (7) | 14 (32) |
| National Sun Yat-sen University | Taiwan | 30 | 4936 (12) | 105.02 | 47 (13) | 18 (7) | 29 (31) | 11 (55) |
| University of Texas at Austin | USA | 30 | 6935 (3) | 133.37 | 52 (11) | 9 (23) | 43 (10) | 17 (15) |
| Erasmus University Rotterdam | The Netherlands | 29 | 3800 (16) | 102.70 | 37 (24) | 7 (37) | 30 (26) | 11 (55) |
| Kent State University | USA | 28 | 3794 (17) | 99.84 | 38 (19) | 8 (27) | 30 (26) | 13 (38) |
| National Taiwan University of Science and Technology | Taiwan | 28 | 6542 (4) | 155.76 | 42 (16) | 8 (27) | 34 (16) | 15 (26) |
| University of Southern California | USA | 28 | 3458 (20) | 76.84 | 45 (14) | 9 (23) | 36 (13) | 17 (15) |
| Florida State University | USA | 27 | 3134 (28) | 78.35 | 40 (18) | 21 (4) | 19 (64) | 11 (55) |
| University of California, Santa Barbara | USA | 27 | 3322 (23) | 87.42 | 38 (19) | 8 (27) | 30 (26) | 12 (46) |
| University of Alabama-Tuscaloosa | USA | 26 | 3686 (18) | 102.39 | 36 (26) | 3 (118) | 33 (20) | 11 (55) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Zou, D.; Xie, H.; Cheng, G. A Topic-Based Bibliometric Review of Computers in Human Behavior: Contributors, Collaborations, and Research Topics. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4859. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094859
Chen X, Zou D, Xie H, Cheng G. A Topic-Based Bibliometric Review of Computers in Human Behavior: Contributors, Collaborations, and Research Topics. Sustainability. 2021; 13(9):4859. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094859
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xieling, Di Zou, Haoran Xie, and Gary Cheng. 2021. "A Topic-Based Bibliometric Review of Computers in Human Behavior: Contributors, Collaborations, and Research Topics" Sustainability 13, no. 9: 4859. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094859
APA StyleChen, X., Zou, D., Xie, H., & Cheng, G. (2021). A Topic-Based Bibliometric Review of Computers in Human Behavior: Contributors, Collaborations, and Research Topics. Sustainability, 13(9), 4859. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094859








