College of Hydraulic Science and Engineering, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225009, China
Sustainability 2021, 13(9), 5236; https://doi.org/10.3390/su13095236 - 7 May 2021
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 2506
Abstract
Ecological compensation has recently gained significant attention as an economic incentive promoting natural resource management. However, there remain several challenges to its application. A key issue is the lack of a method clearly define the standard of ecological compensation. This study established an
[...] Read more.
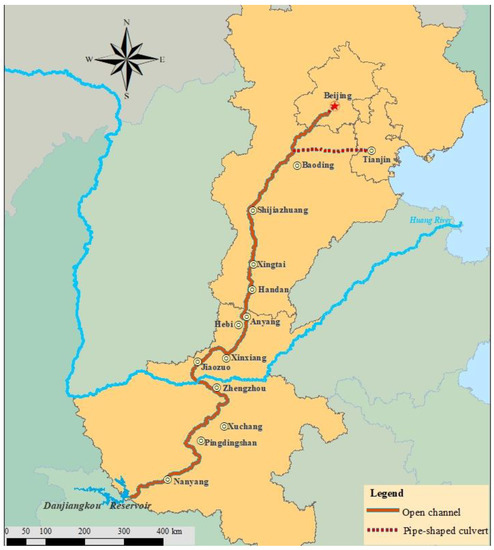
Ecological compensation has recently gained significant attention as an economic incentive promoting natural resource management. However, there remain several challenges to its application. A key issue is the lack of a method clearly define the standard of ecological compensation. This study established an accounting methodology for the ecological compensation standard for the water-receiving area in an inter-basin water diversion in China. Beijing, a major water-receiving area of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, was used as an example of the application of this approach. First, the evaluation index of ecosystem service value of the water-receiving area was selected, then, emergy theory was used to calculate the increment of ecological service value based on the characteristics of each indicator. The ecological service value due to the project was calculated to be 3.898 billion RMB, while the willingness-to-pay by the public was estimated at 915 million RMB. Therefore, the increment of ecological service value was the highest standard of compensation, and the public’s willingness-to-pay was the lower limit of ecological compensation. The final compensation standard can be determined through negotiation between suppliers and beneficiaries under the leadership of relevant governments and water-transfer authorities. Thus, this study aimed to provide a scientific basis for the construction of diversified ecological compensation mechanisms and promote sustainable development of the region.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Water, Economic Management and Governance Issues)
▼
Show Figures