Abstract
In order to elucidate the impact of fortunei forest environment on overall health, the effect of the Cryptomeria fortunei forest environment on mice was examined. Using an OFT (Open Field Test), the behavior of mice in fortunei forest and in an indoor environment (used as a control) was analyzed, while minor changes in climate, oxygen, and suspended particulate matter were observed and recorded simultaneously. The results indicated that the two environments were significantly different in regard to relative humidity, wind speed, and the oxygen content of air, while there were no significant differences in temperature. Importantly, spontaneous activity behavioral indicators in mice were significantly different. Mice in the Cryptomeria fortunei environment (LS group) spent less time in the corners and near walls in comparison to mice in the indoor environment (CK group). Compared with indoor control mice, for the mice exposed to forest environments total distance traveled, central grid distance, frequency of movement through the central grid, frequency of standing, and body mass significantly increased; The number of fecal grains significantly decreased. The spontaneous activity behavioral indicators changed over time stages. In the early stages there were no differences, but after accumulation of environmental effects in the late stages, significant differences were evident. The above results showed that the Cryptomeria fortunei forest environment increased excitability and cognitive ability of mice, was able to effectively alleviate anxiety, and was able to emotionally relax and improve the appetite of the mice.
1. Introduction
With the enhancement of living standards in recent years, the demand for modern healthcare has become increasingly urgent. Recent data from the World Health Organization has shown that there are approximately 150 million people worldwide living with mental illnesses. Depression is a common and well-known mental illness, and approximately 1 million individuals commit suicide every year [1,2]. People love the forest because of its exquisite landscape, fresh air, and comfort. Walking in the forest and breathing in aromas released from trees is not only for recreation, but also for relaxation [3,4,5]. Forests are associated with increased physical activity and decreased overweight and obesity of urban dwellers [6,7,8], and people are increasingly using urban forests for health promotion [1,9]. The impact of forests on health has become a topic of captivating interest in the research world and is gradually being studied in-depth. Many experimental studies have demonstrated that forest bathing can provide physiological and psychological benefits, which can decrease cerebral blood flow in the prefrontal cortex; lower blood pressure, pulse rate, and levels of salivary cortisol, along with other stress hormones; suppress sympathetic nervous activity; and increase parasympathetic nervous activity [10,11,12,13]. Lee Qing at Nippon Medical School in Japan reported that enhanced human natural killer (NK) activity and intracellular anticancer proteins as a result of forest therapy [14,15], immunity disproportion and enhancement in proinflammatory cytokines might be linked with the development of depression [16]. This research was the focus of much public attention, and forest therapy became recognized as a relaxation activity. Akazawa Natural Recreation Forest is the birthplace of Japan’s forest bathing. The primary tree species in this forest is Japanese cedar. Related research has shown that Japanese cedar and China Cryptomeria were similar species and had similar ecological characteristics [17]. In China, Cryptomeria fortunei are a precious species in warm temperate and high altitude zones, and are distributed in the provinces and regions south of the Yangtze. Cryptomeria fortunei display a straight trunk, beautiful tree-shape, and have great ecological and aesthetic value. Additionally, Cryptomeria bark has detoxification, insecticide, and anti-itching effects, which can be used to treat stubborn psoriasis and burns, along with other ailments. These characteristics make the study of Cryptomeria fortunei highly significant in regard to health benefits. Many domestic and foreign scholars have focused on Cryptomeria resource management [18,19], forest protection, cultivation, and biological activity of extracted essential oils, which include anti-moth [20], anti-mosquito [21], anti-termite [22] and antibacterial activity [23]. The research of Miyazaki Liang Wen has shown that Cryptomeria can release beneficial phytoncides, one being alpha-pinene, which is expressed in large quantities and had relaxation and stress-relieving effects. However, there are relatively few studies focused on evaluating the impact of natural Cryptomeria forest stands on health.
Humans are complex social animals and are affected by political, economic, environmental, and other factors. Therefore, experiments based on the human subject are difficult to carry out, and it is important to establish a simple and valid method. The open-field test is not only simple, but it also has strong validity, being widely used for the detection of anti-anxiety and depression medications in the pharmacology field [24]. The advantages of the test are that animals can be easily placed into a novel environment and that their basic behavioral parameters can be easily observed and measured [25,26,27]. Laboratory white mice are mostly inbred strains with less inter-individual differences [28,29]. Their genome sequences, physiological characteristics, and biochemical metabolism are highly similar to those of humans. Therefore, they can serve as a valid animal model for studies on the effects of different urban forests on human health.
In recent years, the relationship between forest and health focuses on the empirical study of the human body in a forest environment or urban forests [30,31,32]. There was also an emulation experiment of indoor controlled mice [33,34,35], but there were few reports about the mice on the real forest environment. The innovation point of this study is to use a commonly used method in clinical medicine, and the mice were in real forest environments; then we investigated the mice spontaneous-activity change after the influence of the forest environment and monitored forest environment factors (including air temperature, relative humidity, wind speed, light, air oxygen concentration, air particles). The aim of this study was to elucidate the impact of these forests on human health. Our preliminary studies on comparative analysis of the effects of arborvitae, cedar, camphor, and Pinus bungeana foliage volatiles on spontaneous behavior of mice under indoor conditions showed that an open-field test was the preferred method for this research. The decision to use Kunming mice in this study was based upon previous studies from a medical perspective. The function of the forest in regard to health was well-investigated and provided a theoretical basis for enhanced disease prevention and health promotion in urban residents. This study also provided a theoretical basis and scientific support for improving mental state and relieving stress and anxiety.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
Twenty (10 male and 10 female) 4-week-old Kunming mice (weighing 18–24 g) were used for the study. All animal experiments were carried out in accordance with the UK Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act, 1986 (amended 2013), and Shandong Analysis and Test Center Laboratory Animal Welfare Ethics Review Committee approved the study protocol on 1 December 2017. All efforts were made to minimize the number of animals used and their suffering. In order to adapt to the environment, all the animals were maintained for 3 days in laboratory before the experiment. During the adaptation period, mice were housed in groups of five according to sex. Cages were 290 mm × 180 mm × 160 mm with adequate food and water provided. Cages with mice were suspended from 09:00 to 15:00 in the Cryptomeria forest and indoor environments.
2.2. Simulation Box
A 31.5 cm × 13 cm × 17 cm squirrel trapping cage was adjusted by covering the bottom of the cage with planks to prevent the spilling of mice feces. Wire was attached to the top ends to suspend the cage (Figure 1).
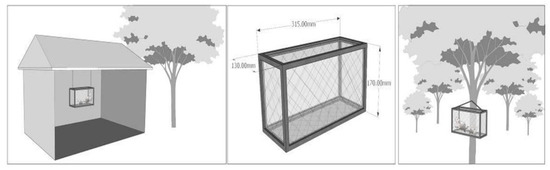
Figure 1.
Indoor and outdoor simulation box. The left picture is a schematic diagram of the experimental site of the control group, the middle picture is a schematic diagram of the box scale, and the right picture is a schematic diagram of the environment of the Cryptomeria fortunei forest.
2.3. Study Area and Sites
Study sites were in Fuzhou City Qishan Forest Park, which is located southwest of South Island town in Minhou County, Fujian Province (east longitude 119°, north latitude 25–26°), with an area of approximately 3587 km2. Its altitude primarily ranges from 400 to 800 m, with the highest elevation being 1010 m. The diversity of plant and animal species is very rich, and the forest vegetation is well maintained with three structural layers (tree, shrub, and grass). The forest coverage rate is 89.33%, with typical stands consisting of coniferous trees, mixed broad-leaved trees, evergreen trees, and bamboo. Qishan belongs to a pleasant, warm, and humid subtropical monsoon climate, with abundant rainfall and a frost-free period of 326 days. It has mild climate, with an average annual temperature of around 16~20 °C, average annual sunshine of 1700~1980 h, average annual rainfall of 900~2100 mm, and an average relative humidity of about 77%. This park is only 23 km away from the Fuzhou City Center and is close to the urban main roads. Traveling from neighboring areas in Fuzhou Qishan is very convenient and therefore the park has potential for the development of forest bathing.
The selected Cryptomeria forest locations in Qishan Forest Park had an area of 12,000 m2 of pure forest with a canopy density of 0.9, forest age of 25 years, an average tree height about 18.5 m, and an average tree diameter of 22 cm. The herbaceous layer consisted mainly of ferns.
The selected indoor environment was a residential room at the Qishan Forest Park Twin Peaks Village. The room had an area of about 20 m2, and was quiet, clean, and odor-free.
2.4. Methods
The open field test is a widely used method in the fields of neurology, pharmacology, behavioral pharmacology, toxicology, etc. It is a classic behavior test used to evaluate states of locomotor activity and anxiety because of its simple operation, data-rich nature, and quantitative outputs for exploration behavior and anxiety [36,37]. The spontaneous activity test indicator is used to evaluate the stimulation or inhibition of central nervous system activity. When the central nervous system is in the excited state, the total distance increases [38,39]. When the central nervous system is suppressed, the total distance decreases. The total distance and average speed are considered the key data to reflect spontaneous activity [40].
The Super-Maze animal behavior video analysis system was used in this study, and it consisted mainly of cameras, computers, image acquisition, and analysis software. The size of the open field arena was 50 cm × 50 cm × 50 cm and was made of medical-grade organic material. The arena had a black bottom, white walls, and an open top to allow simultaneous tracking of the spontaneous activity of 8 mice with real-time synchronization record video and mouse activity trajectories. The automatic video analysis system effectively eliminated the need for manual counting, thus reducing subjective errors and differences in observations between animal groups while increasing the reliability of test results. Automatic recording indicators included total distance traveled, distance of each grid, average speed, latent period, rest time, the number of times entered. The open field arena was divided into 16 grids, with grid numbers 6, 7, 10, and 11 defined as the center area and the remaining grids defined as corner areas (Figure 2). Video cameras tracked and recorded mice in the center area. Each test group was carried out at the same time.
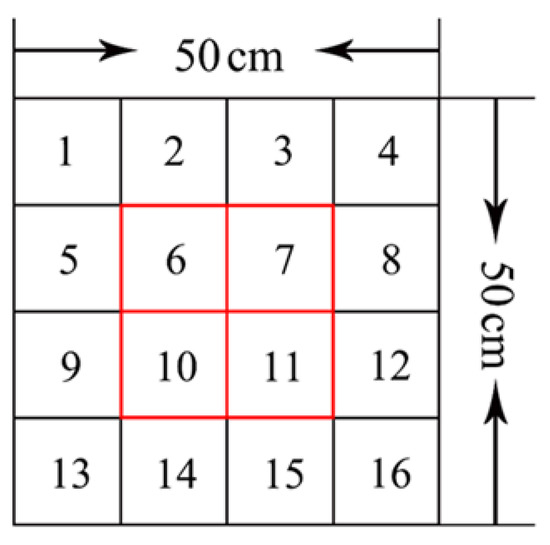
Figure 2.
Sketches of the 16 grids.
Mice were randomized into treatment and control groups. Each group consisted of 5 male and 5 female mice, and the tail of each mouse was labelled with a black marker. Each mouse was weighed before 9:00 a.m. each day and then placed in the respective simulation box. During experimentation, 10 of these mice were placed in the outdoor simulation box and hung in Cryptomeria forest, and 10 were hung in the indoor environment.
Experimental mice were hung for 6 h continuously (from 9:00 a.m. to 15:00 p.m.) without food. Two groups of mice were brought back into the open field test room to observe spontaneous behavior after 15:00 p.m. Individual tests were 5 min in duration and persisted for 6 days. After each test, the open-field arena bottom was cleaned with 75% alcohol to ensure that no residual urine and feces were present during the testing of other mice and did not affect the results.
Experimentation took place in late September in the summer of 2013 when weather was sunny and breezy. Observations were taken once every 2 h over a 6 h period (from 9:00 a.m. to 15:00 p.m.). NK5920 and TES1332A were used to measure temperature, relative humidity, average wind speed, and light intensity at each site. A British Dustmate dust detector was used to measure the concentration of TSP (total suspended particulate), PM10 (inhalable particles), PM2.5 (fine particulate matter), PM1 at the height of 1.2 to 1.5 m. Sampling lasted 2 min and was repeated 3 times at each site.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The significance test and one-way ANOVA analysis were performed using the SPSS 18.0 software package for Windows with a significance at the 5% level. Resulting charts were composed using Excel 2003. (LS: Representative samples of mice hanging in the stand of Cryptomeria fortunei, CK: Representative samples of mice hanging in the room. Significant levels: p values of <0.05 were considered statistically significant; p values of <0.01 were considered statistically extremely significant.)
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Spontaneous Behavioral Indicators
In this study, all the open-field tests were 5 min. The total distance and average speeds were consistent among all tests; therefore, only the differences in the total distance were analyzed. The results showed that the total distances of LS (Cryptomeria group) mice were significantly higher than that of CK (the control group) mice during 6 tests (Figure 3). The total distances of the CK group mice were 6.83%, 8.94%, 9.03%, 25.27%, 30.95%, and 31.49% less than the LS group mice, with the difference between the 2 groups gradually increasing. Trends over the 6-day period were strongly displayed at first, but weakened over time. ANOVA results showed that the total distance differences between the LS group and the CK group between the 4th and 5th days of experimentation were significant (p = 0.022, p = 0.014, respectively). The total distance differences of 2 groups on the 6th day were highly significant (p = 0.009). This analysis showed that the Cryptomeria forest environment had a growing influence on experimental mice. As the number of tests increased, the differences in total distance between the two groups became increasingly apparent. Therefore, the Cryptomeria forest environment may increase the total activity of mice, enhancing the excitability of the central nervous system.
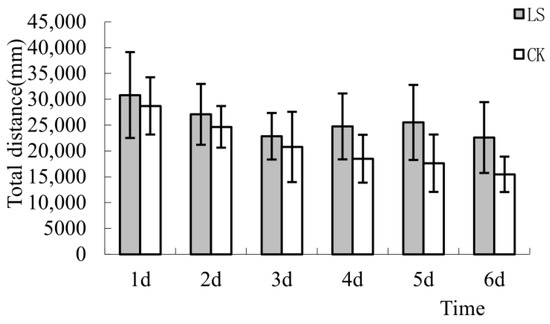
Figure 3.
Comparison of the total distance. LS: Representative samples of mice hanging in the stand of Cryptomeria fortunei; CK: Representative samples of mice hanging in the room.
Thigmotaxis is defined as avoidance of the central region and moving in corners, which is the natural reaction of rodents displaying fear in a novel environment [41]. The study of thigmotaxis can provide in-depth fundamental research data for the study of other anxiety symptoms [42]. A large number of clinical trials have shown that anti-anxiety drugs could effectively reduce this avoidance in rodents [43]. In the Open Field Test (OFT), the activity of animals in the central region or in corners can effectively reflect the desire of animals to explore and adapt to new environments. If there is a strong desire to explore and adapt to the environment, the anxiety level of the animals is lower [44]. The results showed that the central grid distances of the LS group mice were significantly higher than those of the CK group mice during 6 tests. The central grid distances of the LS group mice were 44.8%, 71.8%, 90.1%, 82.8%, 158%, and 28.3% higher than those of the CK group mice (Figure 4). ANOVA results showed that the central grid distance of 2 groups on the 3rd, 4th, and 5th days were significantly different (p = 0.028, 0.005, and 0.016, respectively). These results showed that the mice living in the Cryptomeria stand environment increased their exploration activity and environmental adaptability.
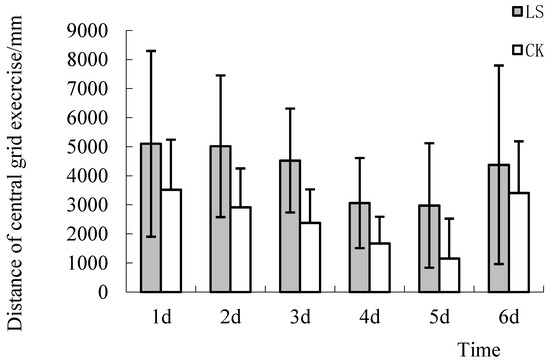
Figure 4.
Comparison of the central grid distance. LS: Representative samples of mice hanging in the stand of Cryptomeria fortunei; CK: Representative samples of mice hanging in the room.
In the open analysis system, grids 6, 7, 10, and 11 were defined as the central grid. The average frequency of movement through the central grid was calculated. ANOVA results showed that this frequency for the two groups on the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th days were significantly different (p = 0.04,0.046, 0.011, and 0.029, respectively). The frequency of movement through the central grid of the LS group mice were 26.4%, 63.2%, 85.2%, 124%, 67.8%, and 30.9% higher than the CK group mice (Figure 5). The results showed that the Cryptomeria stand environment significantly enhanced the ability of mice to explore, which was consistent with results of the central grid distance.
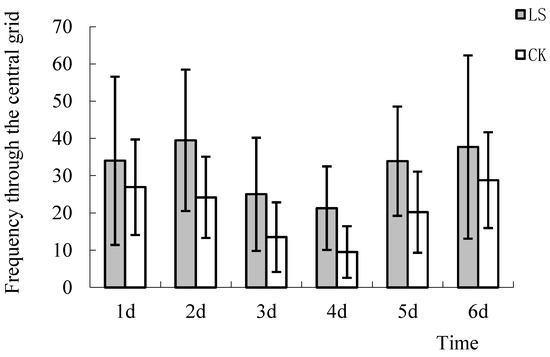
Figure 5.
Comparison of frequency through the central grid. LS: Representative samples of mice hanging in the stand of Cryptomeria fortunei; CK: Representative samples of mice hanging in the room.
The duration of time spent in corners and near walls is often used to evaluate anxiety in rodents [43,45]. If these activities last a long time, this indicates that the mice have depression and anxiety tendencies. The duration of locomotor activity in corners and near walls for the LS group mice was less than that of the CK group (Figure 6). The duration of locomotor activity in corners and near walls of LS group mice were 2.9%, 7.1%, 3.8%, 6.6%, 6.9%, and 1.6% lower than that of the CK group mice. The duration of time in corners and near walls of 2 groups on the 2nd, 4th, and 6th days was significantly different (p = 0.004, 0.006, and 0.009, respectively). This demonstrated that the Cryptomeria stand environment could play an anti-depressant and anti-anxiety role in mice.
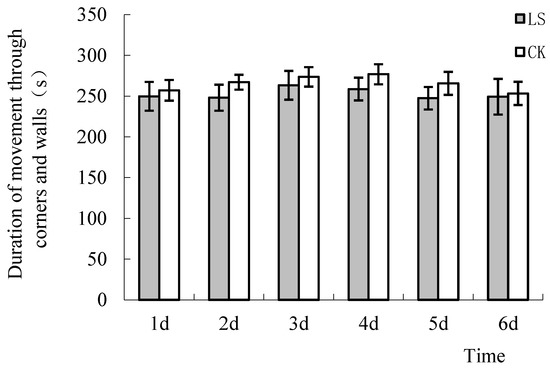
Figure 6.
Activity in the corners and walls. LS: Representative samples of mice hanging in the stand of Cryptomeria fortunei; CK: Representative samples of mice hanging in the room.
There are many behaviors observed in open-field tests, including standing, jumping, self-grooming and rotation. Standing implies that the mouse lifts both of its forefeet off the floor [43]. In this study, only the times of mice standing were calculated. The results showed that the LS group mice engaged in the standing behavior more than the CK group (Figure 7). The standing times of the 2 groups on the 1st and 2nd days were significantly different (p = 0.035 and 0.007, respectively). The standing times of the LS group mice were 24.3%, 41.5%, 27.3%, 13.4%, 23.1%, and 17.6% more than the CK group mice. Trends showed that the standing times of 2 groups declined each day until the 6th day. The sudden increase in this behavior on the last test day was due to unrelated weather factors. The city of Fuzhou experienced rainy weather for a few days, which resulted in testing inconsistencies on the 5th and 6th days.
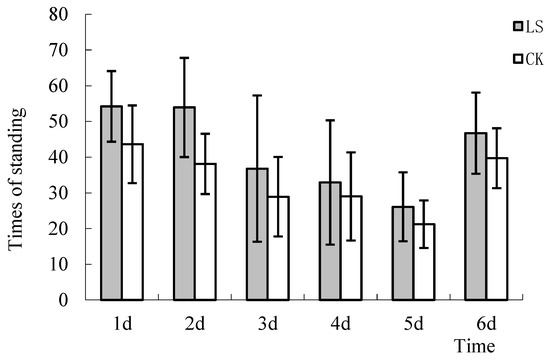
Figure 7.
Comparison of the number of standing. LS: Representative samples of mice hanging in the stand of Cryptomeria fortunei; CK: Representative samples of mice hanging in the room.
3.2. Analysis of Changes in Body Mass
The weights of the LS group and the CK group were 21.74 g ± 1.90 and 20.38 g ± 4.32, respectively, after mice were randomized at the beginning of the trial. Early experiments on the mice showed that the differences between the two groups were not significant (p = 0.374). Trends showed that growth occurred with the increase of the testing time. However, the growth rate of the LS group was larger than that of the CK group after the 4th day, and the weight differences between the two groups were significant (p = 0.012, p = 0.003, p = 0.001, for the 4th, 5th, and 6th days, respectively) (Figure 8). ANOVA and LSD multiple comparisons showed that the body mass of the LS group between the 1st and 3rd days, the 1st and 4th days, the 1st and 5th days, and the 1st and 6th days was highly significant (p = 0.001, p = 0.000, p = 0.000, and p = 0.000, respectively). The body mass of the LS group mice was 6.68%, 12.7%,19.3%, 23.7%, 25.2%, and 27.3% larger than the CK group mice. The above analysis showed that the Cryptomeria forest stand environment could increase the appetite of mice.
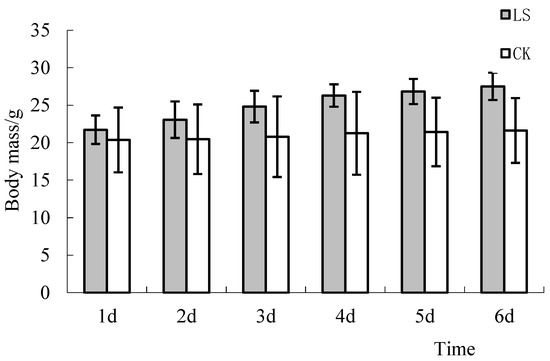
Figure 8.
Comparison of body mass changes. LS: Representative samples of mice hanging in the stand of Cryptomeria fortunei; CK: Representative samples of mice hanging in the room.
3.3. Analysis of the Fecal Grains
The number of mice fecal grains in the simulation boxes was calculated before the OFT, which gave total fecal grains for each group (Figure 9). When compared, the biggest difference between the CK group and LS group was 30.1%. As the number of tests increased, the difference in the trends of the two groups were first reduced and then stabilized. However, the trend reduction for the LS group was to a larger extent. This may be due to the fast changing of the LS group mice from the initial tension state to the adaptation state. The number of fecal grains was used as a conventional indicator to reflect the level of tension in a rodent. In the beginning of the trial, increased tension was caused by the introduction of mice to novel environments. This tension diminished with repeated testing. The Cryptomeria stand environment played a tension-relieving role in mice.
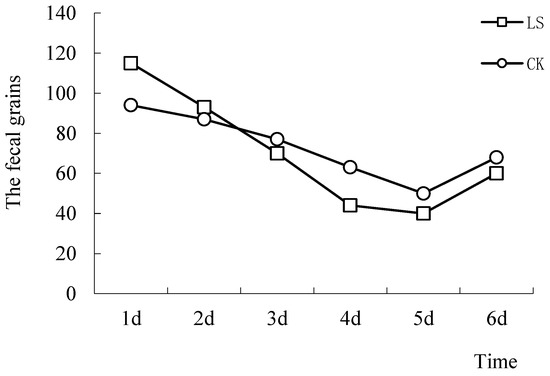
Figure 9.
Comparison of fecal grains. LS: Representative samples of mice hanging in the stand of Cryptomeria fortunei; CK: Representative samples of mice hanging in the room.
3.4. Typical Trajectories
Trajectories show the areas of spontaneous mice activity during testing from a starting position to a destination. This reflects the overall intuitive status of mice (Figure 10). Trajectories were representative of the average level of activity for each test group. The LS group of mice exhibited a relatively large amount of exercise and more frequent activity in the central region, while the CK group favored the corners of the region.
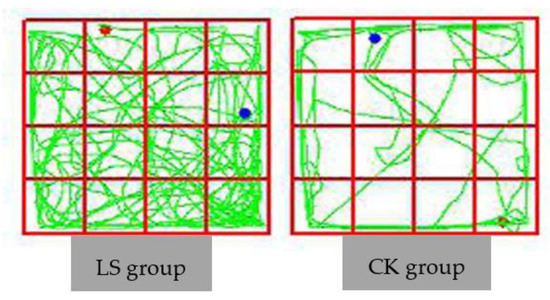
Figure 10.
Comparison of trajectories of the two groups. LS group: Representative samples of mice hanging in the stand of Cryptomeria fortunei; CK group: Representative samples of mice hanging in the room.
When mice are in a novel environment, measured characteristics are always strong at first but weaken over time due to decreased excitability and exploration of mice with the increase of OFT and familiarity with the environment [46,47,48]. On the 6th testing day, there was an apparent change in the variation curves of the central grid distance, frequency of movement through the central grid, standing time, and fecal grains, which was due to continuous rain during the 5th and 6th test days.
The OFT is not just a simple method to monitor mouse movement. Mice mood is affected by many internal factors and external factors. In terms of internal factors, gender, health status, strains, and social competition due to food and water are important. In terms of test operator factors, the crawling away of mice from the operator and the extent to which the operator is gentle would affect the mood of mice. Because of this, the same batch of test animals was monitored by the same operator throughout the experiment in order to avoid the impact of such factors. In terms of external environmental factors, the difference between the two environments was the primary cause of emotional changes in mice. Suitable temperature, humidity, light, wind speed, high oxygen content, and low particulate matter were key factors affecting spontaneous behavior in mice. Additionally, maybe plant essence and negative air ion were main influencing factors. The impact of many other environmental factors in Cryptomeria forest ecosystems on health needs further studying.
3.5. Difference Analysis of the Environment
Average values for temperature, relative humidity, wind speed, and light intensity were analyzed over time, showing significant variation. Temperature in the indoor environment was higher than in the Cryptomeria forest (Figure 11A), but the trend showed a steady rise in temperature from 9:00 a.m. to 15:00 p.m. The differences in temperature between the two environments for each period were not significant. The range of relative humidity in the Cryptomeria forest was relatively large in comparison to that of the indoor environment, which changed smoothly. The differences of relative humidity between the two environments from 9:00 a.m. to 23:00 p.m. were significant (Figure 11B). During the trial, the wind speeds in the two environments were in a breeze state (Figure 11C). Therefore, the effect of wind could be ignored. However, the differences in the wind speed between the two environments in each period were significant. The differences in the light intensity between the two sites were highly significant (Figure 11D). Light intensity in Cryptomeria forest is affected not only by changes in solar elevation angle and azimuth, but also by stand canopy density, community structure and species characteristics. The illumination in the indoor environment was weak with relatively small changes, which closely followed changes in the weather conditions. When comparing the microclimate of the two test environments, there were significant differences in light intensity, wind speed, and relative humidity.
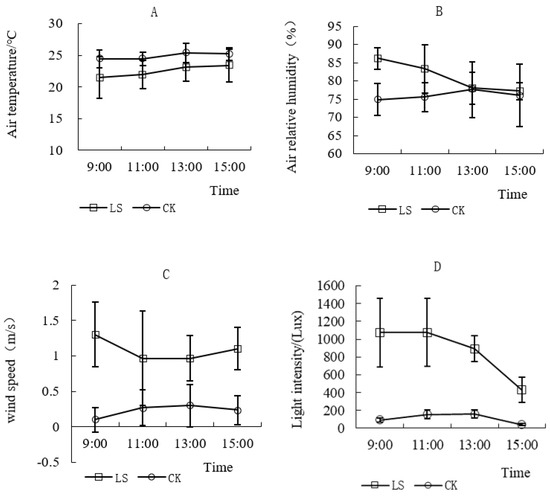
Figure 11.
Comparison of microclimate factors in two kinds of environments. (A) Comparison of air temperature in two kinds of environments; (B) Comparison of relative humidity in two kinds of environments; (C) Comparison of wind speed in two kinds of environments; (D) Comparison of light intensity in two kinds of environments; LS Representative the environment of Cryptomeria fortunei; CK Representative the environment of the room.
The oxygen concentrations in the two environments were very different (Figure 12). The oxygen concentration in the indoor environment was essentially unchanged from 9:00 a.m. to 15:00 p.m., but the oxygen concentration gradually increased, reaching 23.54% at 15:00 p.m., in the Cryptomeria forest. The differences in oxygen concentrations in the two environments at 13:00 and 15:00 were significant (p = 0.004; p = 0.000, respectively).
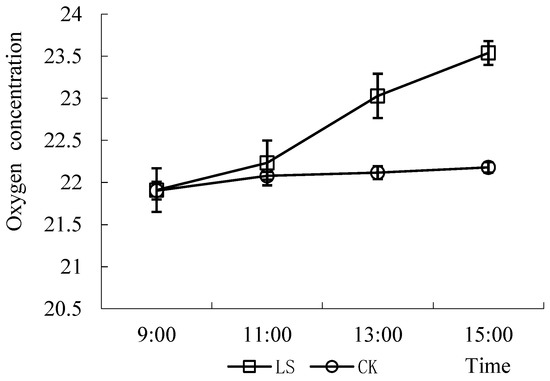
Figure 12.
Comparison of Oxygen concentration in two kinds of environments. LS: Representative the environment of Cryptomeria fortunei; CK: Representative the environment of the room.
The analysis showed that the differences of TSP, PM10, PM2.5, and PM1 were significant between the Cryptomeria forest and the indoor environment (Figure 13), and the concentration of each particle in the indoor environment was higher than in the Cryptomeria forest. This was due to strong wind, which is conducive to the spread of particulate matter, or else the release of volatile species from Cryptomeria could attract dust particles to the plant.
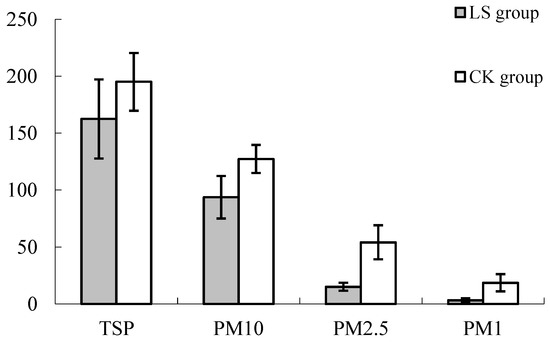
Figure 13.
Comparison of Particulate matter in two kinds of environments. LS group: Representative the environment of Cryptomeria fortunei; CK group: Representative the environment of the room.
4. Discussion
In this study, the excitability, exploratory ability, cognitive ability, and emotional state of mice in the Cryptomeria cedar forest environment were greatly improved. The results of the study are similar to the effect of the forest environment on the human body. Hassan et al. found that young adults’ mood improved, and their anxiety lessened after they walked for 15 min in a bamboo forest [49]. Bratman et al. suggested that the forest environment influenced the surveyed participants, causing a decrease in the negative subscales of POMS and an increase in the positive (vigor) subscale [50]. Wolf et al. found that the human health benefits of exposure to trees and forests abound and include restorative capacities such as stress reduction as well as improvement in clinical mental-health outcomes [51].
In addition, the difference between the control group and the experimental group in the spontaneous activity index gradually increases with the accumulation of time. There is evidence that even a short period spent in a forest can help people reduce stress, recover their attentional capabilities, and shift towards more positive emotions [52,53,54,55,56,57,58]. Forest bath can increase the NK cell activity, the number of NK cells and the level of anticancer proteins in the cells, and improve the immune function of the human body, and this effect lasts for at least 7 days [31]. It was found that short-term forest bathing (2 days) can significantly improve people’s bad mood, significantly reduce the level of oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease [5]. In addition, some scholars have carried out a 4-day forest bathing supplementary therapy for patients with chronic heart failure. It could be observed that the brain natriuretic peptide level of the subjects gradually decreases. Brain natriuretic peptide level is the same as inflammation and oxidative stress, and it is a biomarker of heart failure [59]. The above shows that the duration of each scholar’s research on the relationship between the environment and human health is different. The impact of forests on the human body has a cumulative effect over time. But there must be a threshold or a turning point in time. The long-term health effects of exposure to forest environments were unclear because we only had 6 days for our experiments. Thus, the test period should be extended in future studies.
This study was an extension of previous research [60]. Plants, including arborvitae, cypress, camphor, cedar, and privet branches and leaves, were treated by pruning in previous studies. The results showed that 6 kinds of tree species volatiles had a catalytic role in improving central nervous system excitability and exploration ability in mice. However, the role of camphor and Pinus bungeana volatiles had certain threshold concentrations that, when exceeded, inhibited spontaneous activity of mice. The effects seen in the previous study were obvious, but the plant material had been pruned. The type and concentration of plant volatiles released certainly changed, and furthermore these early studies were carried out under indoor environment conditions. In this study, outdoor simulation was used to explore the effect of natural stand conditions on mice. The impact on the health of mice is not only limited to volatiles, but also to other factors in the environment, such as air oxygen content, air particles, air negative ions, etc. There were no differences in the concentration levels of volatiles and stand density. At present, the results could not be evaluated quantitatively, but only analyzed qualitatively.
Depression is considered one of the most important global health challenges [61]. Depression is understood as a combination of symptoms. There are also several levels of symptoms [62,63]. However, the exact pathogenesis is still elusive. In recent years, many theories have been proposed, including the monoamine theory, dysfunction in hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis hypothesis, and neurotrophic theory inflammatory theory [64,65,66,67]. Studies demonstrated that immune system activation played a major role in the development of depression [68,69]. Common treatments for depression are psychotherapy and antidepressants [70]. Although these two methods have been proven to be efficient in ameliorating depressive symptoms, they also present some disadvantages—the use of antidepressants can have secondary effects such as gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., metabolic abnormalities) [71]. Specifically, this research has found encouraging results regarding the potential of forest therapy to prevent and treat depression. Less research has explored direct links between forest therapy and depression. The limitations of the research method still cannot distinguish whether it is to prevent or treat depression, which requires a certain medical foundation for more in-depth research and exploration.
5. Conclusions
The results of this study show that there were significant differences in the relative humidity, wind speed, air oxygen content, and particulate matter between the indoor and the Cryptomeria forest environments. Mice living in the two environments were significantly affected in regard to excitability, cognitive ability, anti-anxiety, tension relief, and appetite. The change of test index was slightly different at different stages with the cumulative effects of the forest environment day by day. These results showed that the Cryptomeria fortunei forest environment increased the excitability and cognitive ability of the mice and was also able to effectively alleviate anxiety, emotionally relax, and improve the appetite of mice.
In this study, healthy Kunming mice were used in an OFT. A comfortable environment could promote excitability, enhance exploratory ability, relieve tension, and regulate the central nervous system. The development of forest bathing could play a preventive role in human health, but does it have therapeutic functions in regard to health care? To construct mouse models on treatment of depression and anxiety, studies on unhealthy mice living in the forest environment are necessary. The development of techniques, professional methods, and the medical basis of conclusions are critical for future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W.; methodology, Y.W.; investigation, Y.W.; resources, Y.W. and D.Y.; data curation, Y.W. and Z.J.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.W.; writing—review and editing, Y.L.; supervision, Y.W. and C.L.; project administration, Y.W. and F.H.; funding acquisition, F.H. and Y.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 41801196) and Young Doctor Fund Project of Shandong Academy of Sciences (2020 QN0028).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by Shandong Analysis and Test Center Laboratory Animal Welfare Ethics Review Committee (protocol code ECAESDATC-2017-056 and date of approval on 1 December 2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
We agree to deposit our data to a public repository.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Qishan Forest Park for providing the experimental site and Shandong Analysis and Test Center, which provided training guidance about raising mice and treated them after the experiment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Abel, J.L.; Rissman, E.F. Running-Induced Epigenetic and Gene Expression Changes in the Adolescent Brain. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2013, 31, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, A.J.; Charlson, F.J.; Norman, R.E.; Flaxman, A.D.; Patten, S.B.; Vos, T.; Whiteford, H.A. The Epidemiological Modelling of Major Depressive Disorder: Application for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohira, H.; Takagi, S.; Masui, K.; Oishi, M. Effects on Shinrin-Yoku (Forest-Air Bathing and Walking) on Mental and Physical Health. Bull. Tokai Women Univ. 1999, 19, 217–232. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Xu, J.; Hu, D. Effects of VOCs from Leaves of Acer Truncatum Bunge and Cedrus Deodara on Human Physiology and Psychology. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 19, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.X.; Lan, X.G.; Cao, Y.B.; Chen, Z.M.; He, Z.H.; Lv, Y.D.; Wang, Y.Z.; Hu, X.L.; Wang, G.F.; Yan, J. Effects of Short-Term Forest Bathing on Human Health in a Broad-Leaved Evergreen Forest in Zhejiang Province, China. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2012, 25, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- James, P.; Banay, R.F.; Hart, J.E.; Laden, F. A Review of the Health Benefits of Greenness. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2015, 2, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellaway, A.; Macintyre, S.; Bonnefoy, X. Graffiti, Greenery, and Obesity in Adults: Secondary Analysis of European Cross Sectional Survey. BMJ 2005, 331, 611–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lachowycz, K.; Jones, A.P. Greenspace and Obesity: A Systematic Review of the Evidence. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, e183–e189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo, F.J.; Kroeger, T.; Wagner, J.E. Urban Forests and Pollution Mitigation: Analyzing Ecosystem Services and Disservices. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2078–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunetsugu, Y.; Park, B.-J.; Ishii, H.; Hirano, H.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. Physiological Effects of Shinrin-Yoku (Taking in the Atmosphere of the Forest) in an Old-Growth Broadleaf Forest in Yamagata Prefecture, Japan. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2007, 26, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, B.J.; Tsunetsugu, Y.; Kasetani, T.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. The Physiological Effects of Shinrin-Yoku (Taking in the Forest Atmosphere or Forest Bathing): Evidence from Field Experiments in 24 Forests across Japan. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2010, 15, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sung, J.; Woo, J.-M.; Kim, W.; Lim, S.-K.; Chung, E.-J. The Effect of Cognitive Behavior Therapy-Based “Forest Therapy” Program on Blood Pressure, Salivary Cortisol Level, and Quality of Life in Elderly Hypertensive Patients. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2012, 34, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, B.-J.; Tsunetsugu, Y.; Ohira, T.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. Effect of Forest Bathing on Physiological and Psychological Responses in Young Japanese Male Subjects. Public Health 2011, 125, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Morimoto, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Inagaki, H.; Katsumata, M.; Hirata, Y.; Hirata, K.; Shimizu, T.; Li, Y.J.; Wakayama, Y.; et al. A Forest Bathing Trip Increases Human Natural Killer Activity and Expression of Anti-Cancer Proteins in Female Subjects. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2008, 22, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q. Forest Medicine; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, T.; Behl, T.; Mehta, V.; Uddin, M.S.; Bungau, S. Molecular Insights into the Therapeutic Promise of Targeting HMGB1 in Depression. Pharmacol. Rep. 2021, 73, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y. The Origin and Natural Distribution of Cryptomeria. J. Sichuan For. Sci. Technol. 2007, 28, 92–94. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Huang, L.; Jiang, C.; Chen, B. The New Model of Density of Cryptomeria Fortunei Plantation. J. Fujian Coll. For. 2005, 25, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, A.; Da, L.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, M. Community Structure and Regeneration Pattern of Cryptomeria Fortunei in Mount Tianmu of Zhejiang, China. J. Zhejiang For. Coll. 2004, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Lai, W.-C.; Chu, F.-H.; Lin, C.-T.; Shen, S.-Y.; Chang, S.-T. Essential Oil from the Leaves of Cryptomeria Japonica Acts as a Silverfish (Lepisma Saccharina) Repellent and Insecticide. J. Wood Sci. 2006, 52, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-S.; Chang, H.-T.; Wu, C.-L.; Chang, S.-T. Anti-Termitic Activities of Essential Oils from Coniferous Trees against Coptotermes Formosanus. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-S.; Chang, H.-T.; Chang, S.-T.; Tsai, K.-H.; Chen, W.-J. Bioactivity of Selected Plant Essential Oils against the Yellow Fever Mosquito Aedes Aegypti Larvae. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 89, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-S.; Lin, H.-Y.; Chang, S.-T. Chemical Composition and Antifungal Activity of Essential Oils from Different Tissues of Japanese Cedar (Cryptomeria Japonica). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, R.G. Ethologically-Based Animal Models of Anxiety Disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 1990, 46, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polissidis, A.; Zelelak, S.; Nikita, M.; Alexakos, P.; Stasinopoulou, M.; Kakazanis, Z.-I.; Kostomitsopoulos, N. Assessing the Exploratory and Anxiety-Related Behaviors of Mice. Do Different Caging Systems Affect the Outcome of Behavioral Tests? Physiol. Behav. 2017, 177, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thippeswamy, B.S.; Mishra, B.; Veerapur, V.P.; Gupta, G. Anxiolytic Activity of Nymphaea Alba Linn. in Mice as Experimental Models of Anxiety. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2011, 43, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brenes, J.C.; Padilla, M.; Fornaguera, J. A Detailed Analysis of Open-Field Habituation and Behavioral and Neurochemical Antidepressant-like Effects in Postweaning Enriched Rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 197, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, H.; Iguchi, Y. Ethological and Multi-Behavioral Analysis of Learning and Memory Performance in Laboratory Rodent Models. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 135, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, R.J. Animal Welfare Beyond the Cage … and Beyond the Evidence? J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2010, 13, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, G.-X.; Cao, Y.-B.; Lan, X.-G.; He, Z.-H.; Chen, Z.-M.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Hu, X.-L.; Lv, Y.-D.; Wang, G.-F.; Yan, J. Therapeutic Effect of Forest Bathing on Human Hypertension in the Elderly. J. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Morimoto, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Inagaki, H.; Katsumata, M.; Hirata, Y.; Hirata, K.; Suzuki, H.; Li, Y.J.; Wakayama, Y.; et al. Visiting a Forest, but Not a City, Increases Human Natural Killer Activity and Expression of Anti-Cancer Proteins. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2008, 21, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Kawada, T. Effect of forest therapy on the human psycho-neuro-endocrino-immune network. Nihon Eiseigaku Zassh. Jpn. J. Hyg. 2011, 66, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Li, K.; Liu, H.; Jing, T.; Song, X.; Xue, L.; Li, C.; Shen, W. The Effect of VOCs from the Branches and Leaves of Pistacia Chinensis Bunge and Juniperus Chinensis Cv. Kaizuka on Mouse Behavior. BioResources 2016, 11, 10226–10239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Qie, G.; Dung, J.; Jiang, J. Effect of VOCs from Branch and Leaf of Cinnamomum Camphora on Spontaneous of Mice. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2012, 21, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Qie, G.; Dung, J.; Jiang, J. Effect of VOCs from Branch and Leaf of Platycladus Orientalis on Locomotor Activity in Mice. Sci. Sil. Sin. 2011, 47, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, P.C.; Bergner, C.L.; Smolinsky, A.N.; Dufour, B.D.; Egan, R.J.; LaPorte, J.L.; Kalueff, A.V. Experimental Models of Anxiety for Drug Discovery and Brain Research. In Mouse Models for Drug Discovery: Methods and Protocols; Proetzel, G., Wiles, M.V., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Carey, R.; Damianopoulos, E.; De Palma, G. 8-OH DPAT Can Restore the Locomotor Stimulant Effects of Cocaine Blocked by Haloperidol. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2000, 66, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Su, M.; Shi, X.; Wang, H. Effects of Righting Cream on Locomotor Activity of Mice. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2012, 23, 2340–2342. [Google Scholar]
- Uzbay, I.T.; Coskun, I.; Kayir, H.; Ozturk, N.; Ozturk, Y. Extract of Hypericum Perforatum Blocks Caffeine-Induced Locomotor Activity in Mice: A Possible Role of Nitric Oxide. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, K.; Spencer, C.; Kaasik, K.; Lee, C.C.; Lupski, J.R.; Paylor, R. Behavioral Characterization of Mouse Models for Smith–Magenis Syndrome and Dup(17)(P11.2p11.2). Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Treit, D.; Fundytus, M. Thigmotaxis as a Test for Anxiolytic Activity in Rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1988, 31, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, J.N. Behavioral Phenotyping of Transgenic and Knockout Mice: Experimental Design and Evaluation of General Health, Sensory Functions, Motor Abilities, and Specific Behavioral Tests1Published on the World Wide Web on 2 December 1998.1. Brain Res. 1999, 835, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choleris, E.; Thomas, A.W.; Kavaliers, M.; Prato, F.S. A Detailed Ethological Analysis of the Mouse Open Field Test: Effects of Diazepam, Chlordiazepoxide and an Extremely Low Frequency Pulsed Magnetic Field. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2001, 25, 235–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoli, Q.; Wenjuan, L. Methods and Strategies of Anxiety and Depression Animal Models Study. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 2005, 13, 327. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.-H.; Wang, C.; Yangcheng, H.-Y.; Liu, R.-Y.; Zhou, J.-N. Age-Related Changes in Anxiety Are Task-Specific in the Senescence-Accelerated Prone Mouse 8. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 91, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chao, Y.; Wei, E. A New Model for Evaluating Locomotor Activity and Central Depressive Drugs in Different Strain Mice. Bull. Sci. Technol. 2003, 19, 292–296. [Google Scholar]
- Belzung, C. Measuring Rodent Exploratory Behavior. In Handbook of Molecular-Genetic Techniques for Brain and Behavior Research (Techniques in the Behavioral and Neural Sciences); Crusio, W.E., Gerlai, R.T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, P.A. Relationships between Exploratory Behaviour and Fear: A Review. Br. J. Med. Psychol. 1973, 64, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Tao, J.; Li, G.; Jiang, M.; Aii, L.; Zhihui, J.; Zongfang, L.; Qibing, C. Effects of Walking in Bamboo Forest and City Environments on Brainwave Activity in Young Adults. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, e9653857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratman, G.N.; Daily, G.C.; Levy, B.J.; Gross, J.J. The Benefits of Nature Experience: Improved Affect and Cognition. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 138, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, K.L.; Lam, S.T.; McKeen, J.K.; Richardson, G.R.A.; van den Bosch, M.; Bardekjian, A.C. Urban Trees and Human Health: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djernis, D.; Lerstrup, I.; Poulsen, D.; Stigsdotter, U.; Dahlgaard, J.; O’Toole, M. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Nature-Based Mindfulness: Effects of Moving Mindfulness Training into an Outdoor Natural Setting. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotera, Y.; Richardson, M.; Sheffield, D. Effects of Shinrin-Yoku (Forest Bathing) and Nature Therapy on Mental Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2020, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, S. The Restorative Benefits of Nature: Toward an Integrative Framework. J. Environ. Psychol. 1995, 15, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Choi, H.; Bang, K.-S.; Kim, S.; Song, M.; Lee, B. Effects of Forest Therapy on Depressive Symptoms among Adults: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajoo, K.S.; Karam, D.S.; Abdullah, M.Z. The Physiological and Psychosocial Effects of Forest Therapy: A Systematic Review. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 54, 126744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-P.; Hsieh, H. Beyond Restorative Benefits: Evaluating the Effect of Forest Therapy on Creativity. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 51, 126670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Yan, Q.; Pan, Y.; Gu, X.; Liu, Y. Medical Empirical Research on Forest Bathing (Shinrin-Yoku): A Systematic Review. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2019, 24, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mao, G.X.; Cao, Y.B.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.M.; Dong, J.H.; Chen, S.S.; Wu, Q.; Lyu, X.L.; Jia, B.B.; Yan, J.; et al. Additive Benefits of Twice Forest Bathing Trips in Elderly Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Qie, G.; Dong, J.; Jiang, J. Comparative Analysis on Effects of VOCs from Branches and Leaves of Four Conifer Species on Locomotor Activity of Mice. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2013, 49, 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Cipriani, A.; Furukawa, T.A.; Salanti, G.; Chaimani, A.; Atkinson, L.Z.; Ogawa, Y.; Leucht, S.; Ruhe, H.G.; Turner, E.H.; Higgins, J.P.T.; et al. Comparative Efficacy and Acceptability of 21 Antidepressant Drugs for the Acute Treatment of Adults With Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. FOC 2018, 16, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, E.I. The 52 Symptoms of Major Depression: Lack of Content Overlap among Seven Common Depression Scales. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 208, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Leemput, I.A.; Wichers, M.; Cramer, A.O.J.; Borsboom, D.; Tuerlinckx, F.; Kuppens, P.; van Nes, E.H.; Viechtbauer, W.; Giltay, E.J.; Aggen, S.H.; et al. Critical Slowing down as Early Warning for the Onset and Termination of Depression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rana, T.; Behl, T.; Sehgal, A.; Mehta, V.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Bungau, S. Elucidating the Possible Role of FoxO in Depression. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 2761–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, T.; Behl, T.; Sehgal, A.; Mehta, V.; Singh, S.; Kumar, R.; Bungau, S. Integrating Endocannabinoid Signalling In Depression. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 71, 2022–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, T.; Behl, T.; Sehgal, A.; Srivastava, P.; Bungau, S. Unfolding the Role of BDNF as a Biomarker for Treatment of Depression. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 71, 2008–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dindelegan, C.M.; Faur, D.; Purza, L.; Bumbu, A.; Sabau, M. Distress in Neurocognitive Disorders Due to Alzheimer’s Disease and Stroke. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 2501–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.H.; Raison, C.L. The Role of Inflammation in Depression: From Evolutionary Imperative to Modern Treatment Target. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dantzer, R. Depression and Inflammation: An Intricate Relationship. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 71, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuijpers, P. The Challenges of Improving Treatments for Depression. JAMA 2018, 320, 2529–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.F.; Sharma, M.S.; Brunoni, A.R.; Vieta, E.; Fava, G.A. The Safety, Tolerability and Risks Associated with the Use of Newer Generation Antidepressant Drugs: A Critical Review of the Literature. Psychother. Psychosom. 2016, 85, 270–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).