Influence of Cerium and Nickel Co-Doping on ZnO Nanostructures for Electrochemical Behavior of H2O2 Sensing Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of Co-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles
2.3. Material Analysis and Instrumentations
2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Analysis
3.2. XPS Analysis
3.3. Optical Properties
3.3.1. UV-Vis Reflectance Spectroscopy
3.3.2. Photoluminescence (PL) Analysis
3.4. FT-IR Analysis
3.5. Morphological Characterization
3.6. Electrochemical Characterization
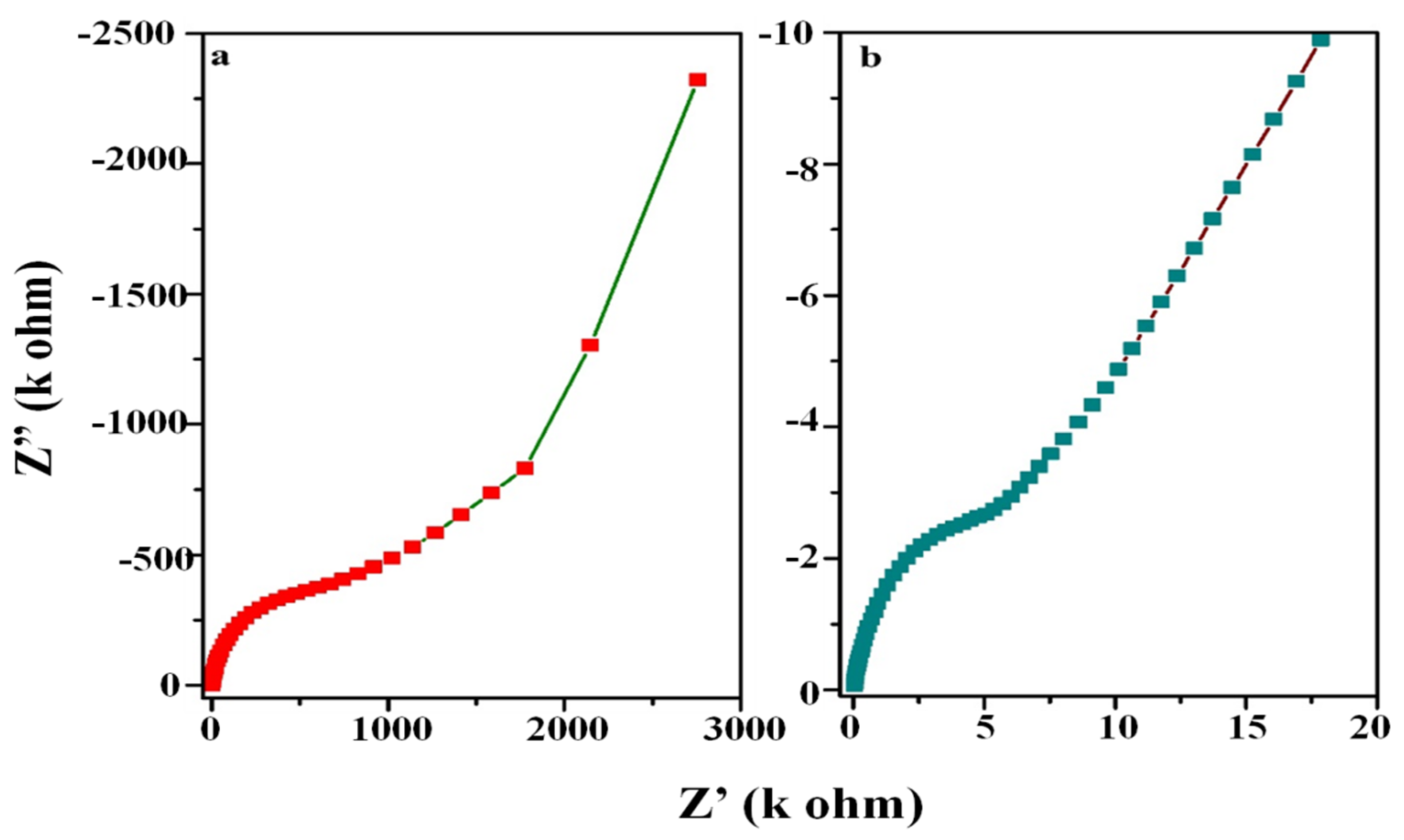
3.7. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
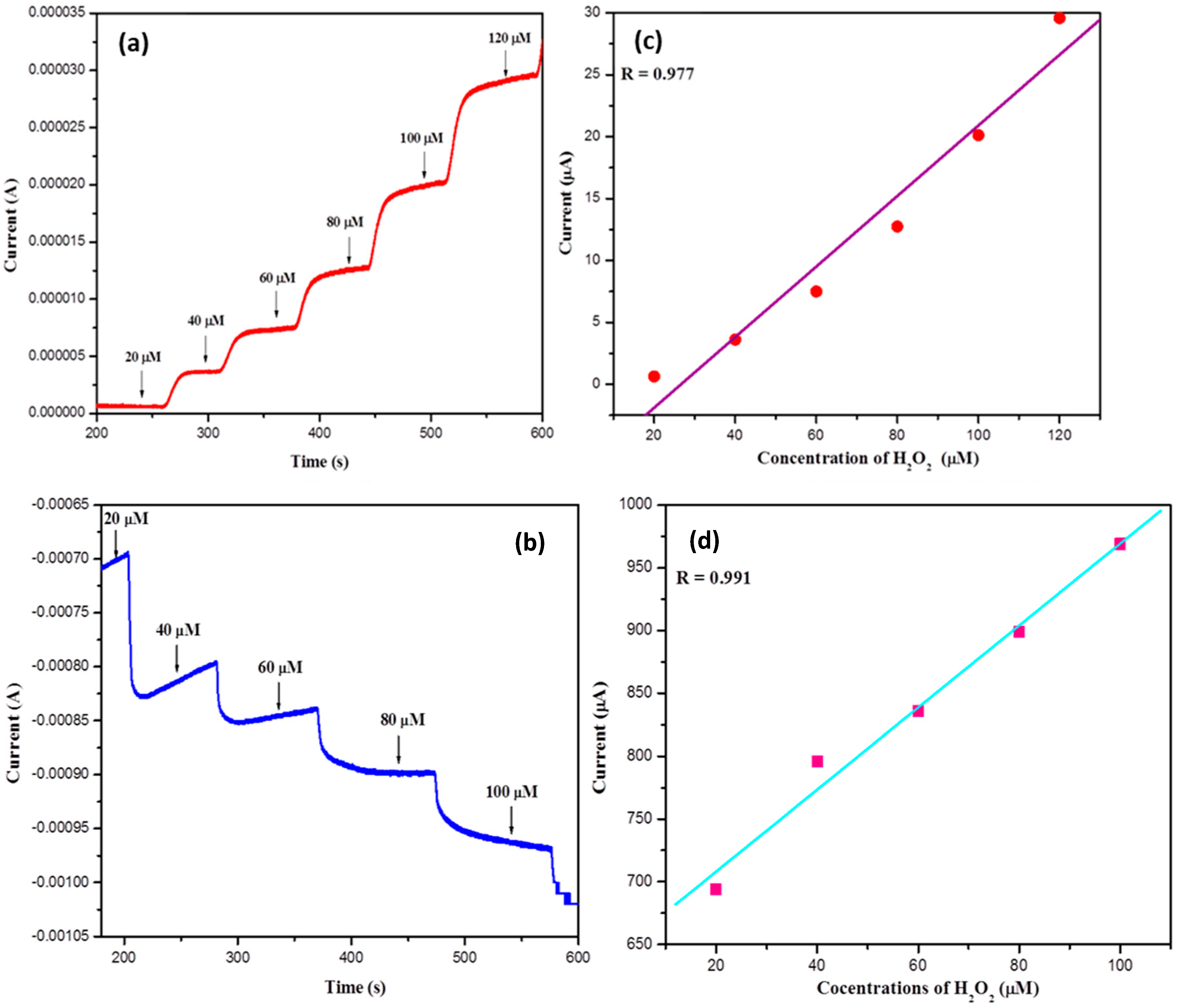
3.8. Electrochemical Performance of Bare and Ce/Ni-ZnOfor H2O2 Sensing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hammad, T.M.; Salem, J.K. Synthesis and characterization of Mg-doped ZnO hollow spheres. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 2205–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.X.; Sun, X.W.; Zhang, X.H.; Ke, L.; Chua, S.J. Photoluminescent properties of copper-doped zinc oxide nanowires. Nanotechnology 2004, 15, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingshirn, C. ZnO: Material, Physics and Applications. ChemPhysChem 2007, 8, 782–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.L.; Song, J.H. Piezoelectric Nanogenerators Based on Zinc Oxide Nanowire Arrays. Science 2006, 312, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.J.; Wang, J.B.; Zhong, X.L.; Zhou, G.C.; Yan, H.L. Synthesis, structure, and room-temperature ferromagnetism of Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 6464–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ding, M.H.; Sun, S. Preparation and Characterization of ZnO Nanoparticles Supported on Amorphous SiO2. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seetha, M.; Bharathi, S.; Raj, A.D.; Mangalaraj, D.; Nataraj, D. Optical investigations on indium oxide nano-particles prepared through precipitation method. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 1578–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Bao, C.G.; Yao, W.J.; Ma, S.Q.; Zhang, L.L.; Hou, S.Z. Influence of deposition temperature on the crystallinity of Al-doped ZnO thin films at glass substrates prepared by RF magnetron sputtering method. Superlattices Microstruct. 2011, 49, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, M. Defect-induced room temperature ferromagnetism in Fe and Na co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 2012, 521, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.; Liu, R.; Wang, Q. Optical and structural analysis of rare earth and Li co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 550, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.F.; Wang, Y.X.; Yang, K.; Zhang, X.R.; Song, Y.L. Enhanced upconverted photoluminescence in Er3+ and Yb3+ codopedZnO nanocrystals with and without Li+ ions. Opt. Commun. 2008, 281, 5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.H.; Lia, X.; Yang, J.H.; Yang, L.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yan, Y.S.; Han, Q.; Wei, M.B.; Gao, M.; Liu, X.Y.; et al. Rapid synthesis and luminescence of the Eu3+, Er3+ co-doped ZnO quantum-dot chain via chemical precipitation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 9574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamilalagan, E.; Selvi, S.V.; Chen, S.-M.; Akilarasan, M.; Maheshwaran, S.; Chen, T.-W.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M.; Al-Onazi, W.A.; Elshikh, M.S.; Liu, X. Fabrication of p-n Junction (Ni/Zn)O and Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO) Nanocomposites for the Electrocatalysis of Analgesic Drug (Acetaminophen) Detection in Pharmaceutical and Biological Samples. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 036501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renganathan, V.; Balaji, R.; Chen, S.M.; Kogularasu, S.; Akilarasan, M. Bifunctional bimetallic heterojunction material based on Al2O3/ZnO micro flowers for electrochemical sensing and catalysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 176, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogularasua, S.; Akilarasana, M.; Chena, S.-M.; Chena, T.-W.; Lou, B.-S. Urea-based morphological engineering of ZnO; for the biosensing enhancement towards dopamine and uric acid in food and biological samples. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 227, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Coffetti, D.; Crotti, E.; Coppola, L.; Meoni, A.; Ubertini, F. Self-Sensing Properties of Green Alkali-Activated Binders with Carbon-Based Nanoinclusions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Liu, X.F.; Zhu, H.C.; Wu, Z.B.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.P.; Yu, R.H. Raman and highly ultraviolet red-sifted near band edge properties of LaCe co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tana, W.K.; Razak, K.A.; Lockman, Z.; Kawamura, G.; Muto, H.; Matsuda, A. Photoluminescence properties of rod-like Ce-doped ZnO nanostructured films formed by hot-water treatment of sol-gel derived coating. Opt. Mater. 2013, 35, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ri, K.H.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhou, W.L.; Gao, J.X.; Wang, X.J.; Yu, J. The structural properties of Al-doped ZnO films depending on the thickness and their effect on the electrical properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 258, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.K.; Lee, T.I.; Kar, J.P.; Lee, M.J.; Park, K.I.; Ahn, K.J.; Yeom, K.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Myoung, J.M. Effect of deposition power on structural and electrical properties of Al-doped ZnO films using pulsed direct-current magnetron sputtering with single cylindrical target. Mat. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 2011, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-C.; Peng, K.-C.; Yeh, T.-Y.; Lee, S.-L. On the Structure and Characterization of Al, Sc-Co-Doped ZnO-Films Varying with 0–2.37 wt.% Sc Contents. Thin Solid Film. 2009, 517, 4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larachi, F.; Pierre, J.; Adnot, A.; Bernis, A. Ce 3d XPS study of composite CexMn1−xO2− y wet oxidation catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 195, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galtayries, A.; Blanco, G.; Cifredo, G.A.; Finol, D.; Gatica, J.M.; Pintado, J.M. XPS Analysis and Microstructural Characterization of a Ce/Tb Mixed Oxide Supported on a Lanthana-modified Transition Alumina. Surf. Interface Anal. 1999, 27, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Zhao, R.; Chen, G. A highly sensitive H2O2 sensor based on zinc oxide nanorod arrays film sensing interface. Analyst 2010, 135, 1992–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Z. Tin Oxide Nanorod Array-Based Electrochemical Hydrogen Peroxide Biosensor Biosens. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Komazaki, Y.; Inoue, T.; Tanaka, S. Automated measurement system for H2O2 in the atmosphere by diffusion scrubber sampling and HPLC analysis of Ti(IV)-PAR-H2O2 complex. Analyst 2001, 5, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Liu, D. Facile synthesis of copper oxide nanostructures and their application in non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 208, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivalingam, D.; Gopalakrishnan, J.B.; Krishnan, U.M.; Madanagurusamy, S.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Nanostructured ZnO thin film for hydrogen peroxide sensing. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2011, 43, 1804–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Gong, Y.; Luo, Y.; Tian, Y. WO3 nanostructures facilitate electron transfer of enzyme: Application to detection of H2O2 with high selectivity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2465–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratoddi, I.; Macagnano, A.; Battocchio, C.; Zampetti, E.; Venditti, I.; Russo, M.V.; Bearzotti, A. Platinum nanoparticles on electrospuntitania nanofibers as hydrogen sensing materials working at room temperature. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 9177–9184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Qin, L.; Hao, Y.; Guo, Q.; Mu, F.; Yan, Z. Application of tubular tetrapod magnesium oxide in a biosensor for hydrogen peroxide. Microchim. Acta 2012, 178, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Deng, M.; Li, G.; Chen, S.; Wang, L. Electrochemical behavior of cuprous oxide-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites and their application in nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensing. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 88, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hardan, N.H.; Jalar, A.; Hamid, M.A.A.; Keng, L.K.; Shamsudin, R.; Majlis, B.Y. The room-temperature sensing performance of ZnO nanorods for 2-methoxyethanol solvent. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannadasan, N.; Shanmugam, N.; Cholan, S.; Sathishkumar, K.; Poonguzhali, R.; Viruthagiri, G. Synergistic effect of bimetal ions (Ce, Pb) incorporation on optical, structural, and sensory activity of ZnO nanocrystals. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2015, 19, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, X.; Wang, X.; Shiu, K.-K.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, H. Highly sensitive graphene–Pt nanocomposites amperometric biosensor and its application in living cell H2O2 detection. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.X.; Zhu, G.P.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Tan, S.T.; Sun, X.W.; Smith, T.A. Growth and spectra analysis of ZnO nanotubes. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 094303–094305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, F.; Fu, L. Application of biosynthesized ZnO nanoparticles on an electrochemical H2O2 biosensor. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 52, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aydoğdu, G.; Zeybek, D.K.; Pekyardımcı, Ş.; Kılıç, E. A novel amperometric biosensor based on ZnO nanoparticles-modified carbon paste electrode for determination of glucose in human serum. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2013, 41, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yuri, I.; Gan, X.; Suzuki, I.; Li, G. Electrochemical study of the effect of nano-zinc oxide on microperoxidase and its application to more sensitive hydrogen peroxide biosensor preparation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1600–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
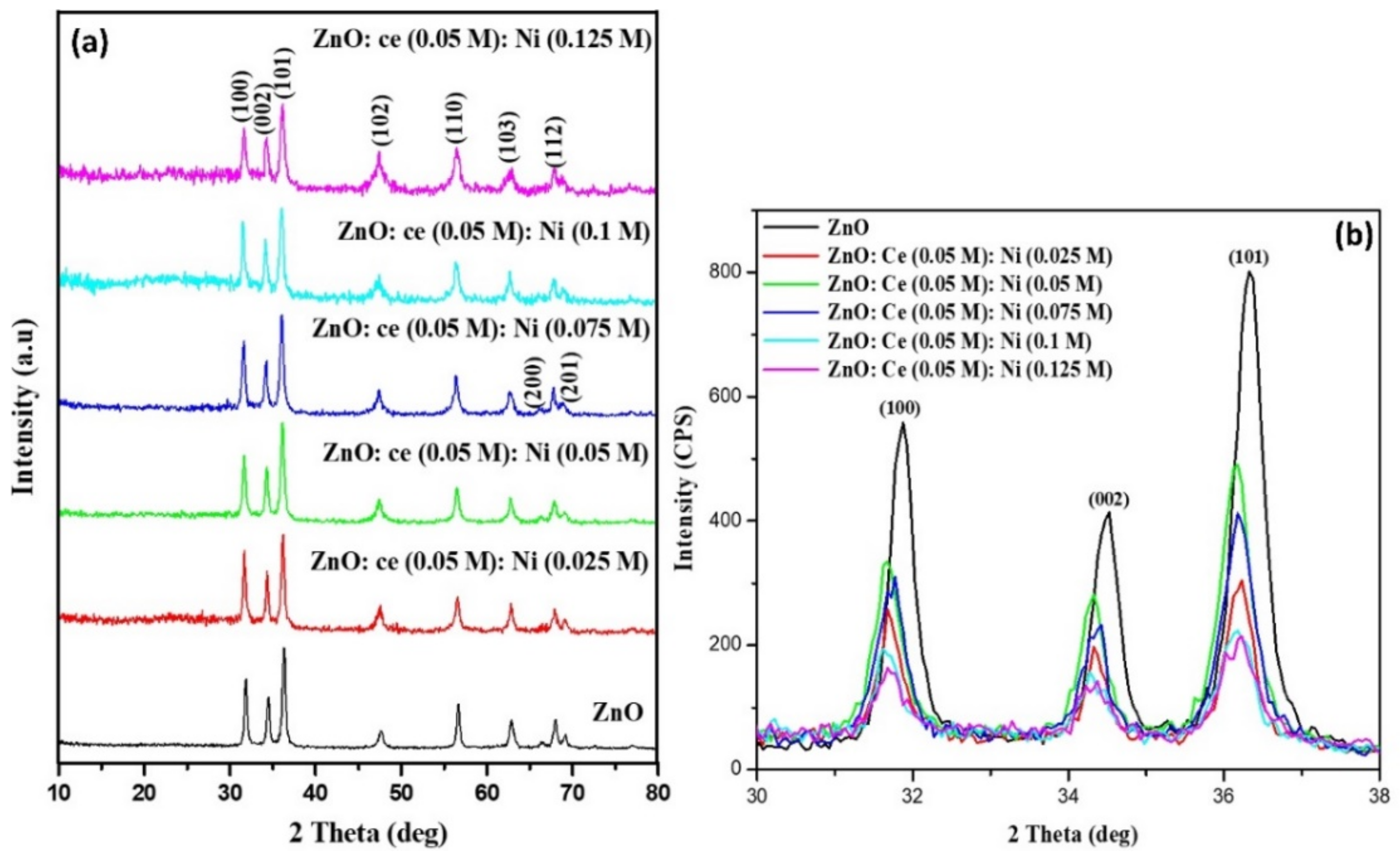

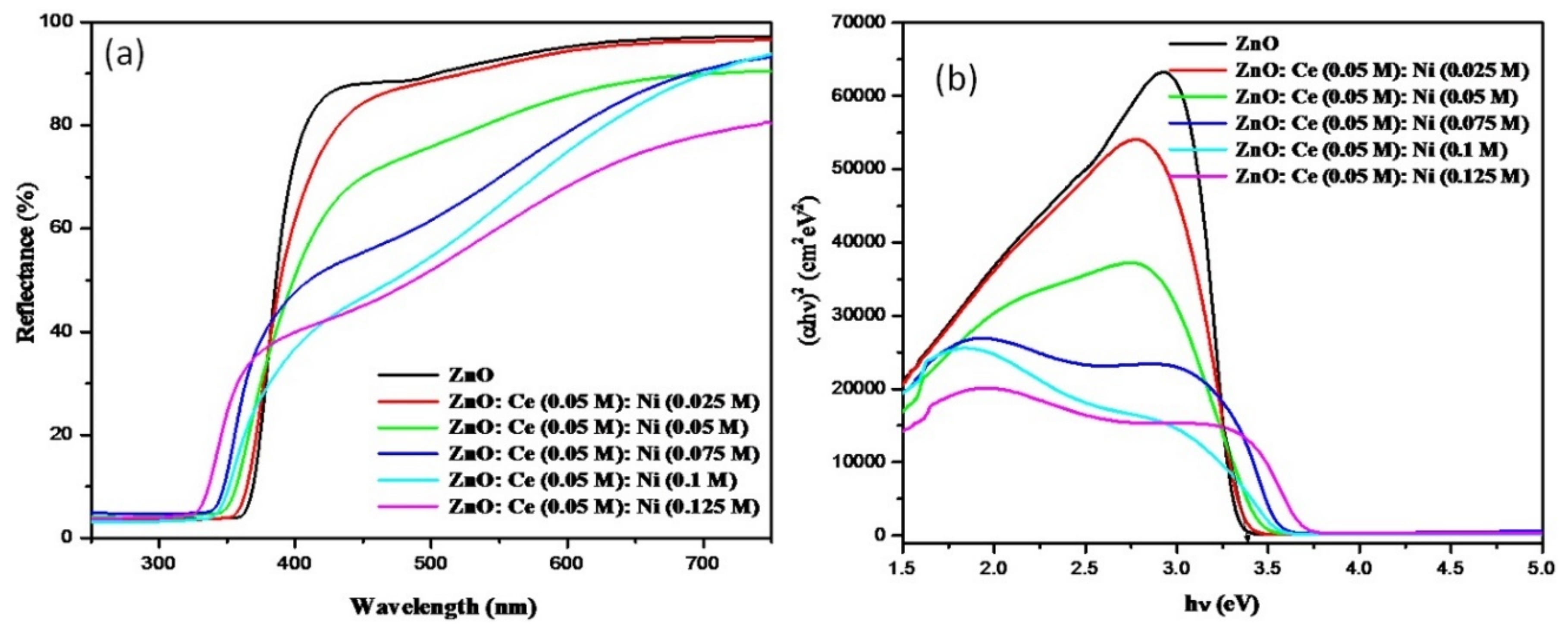
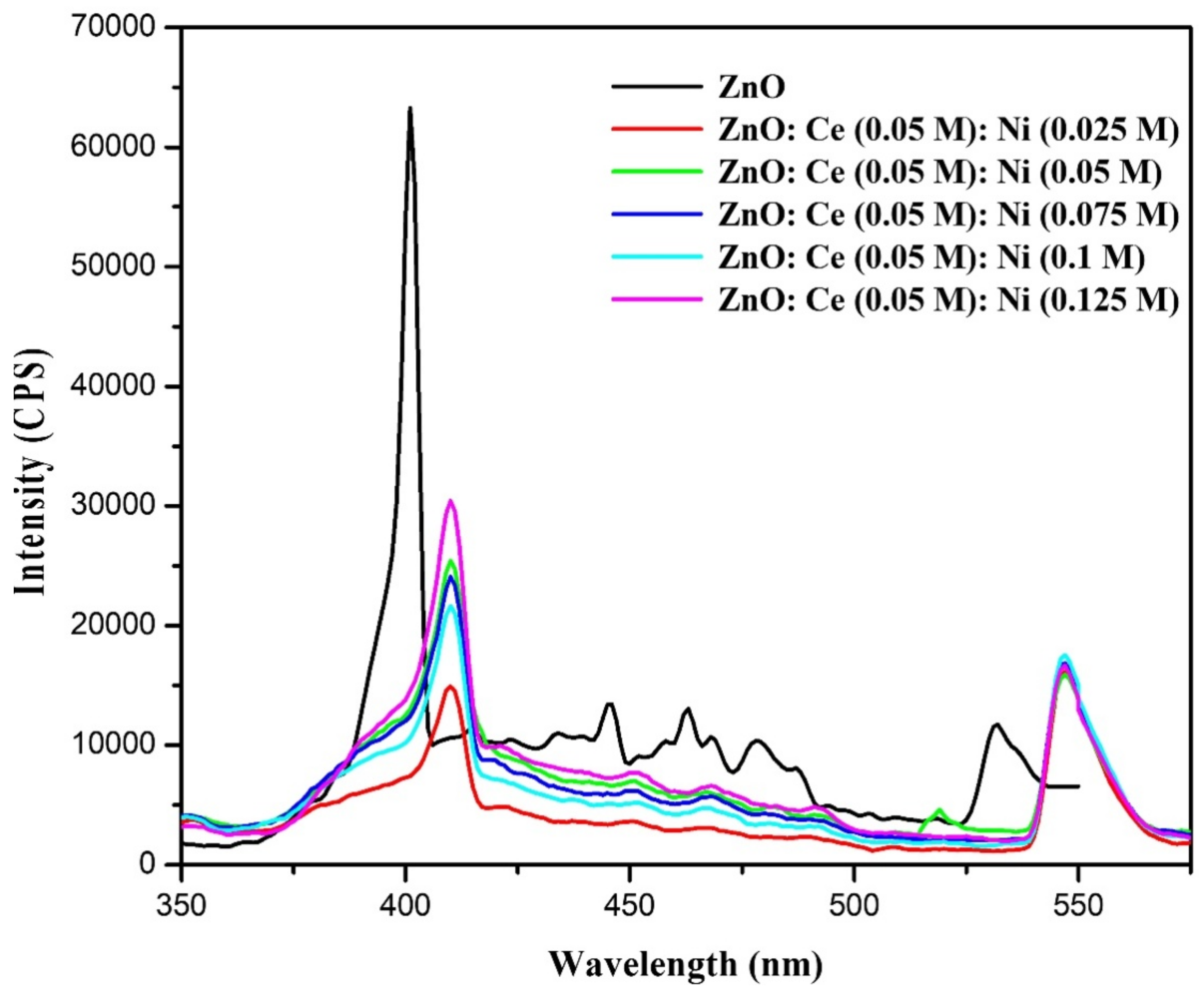

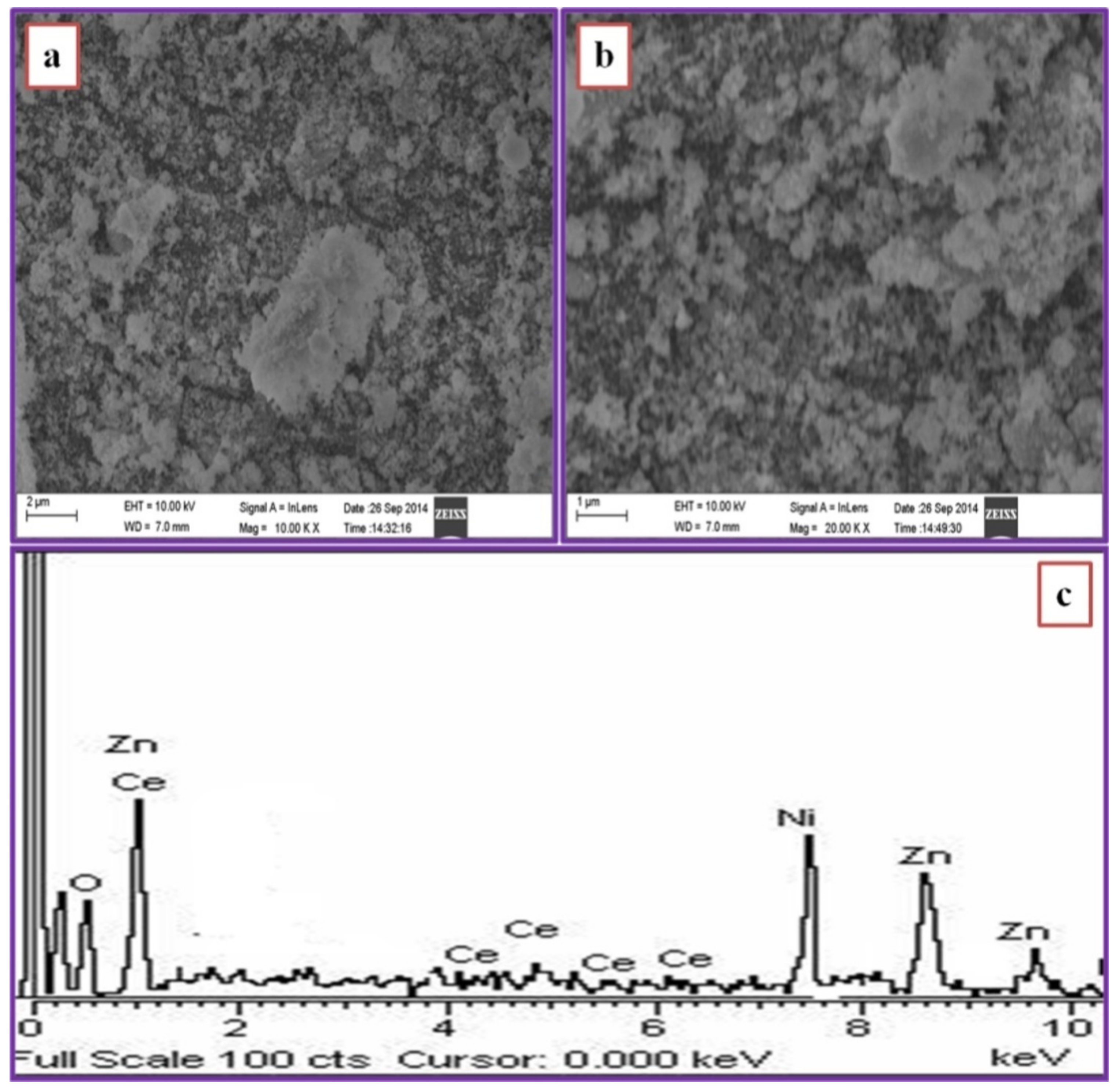


| Samples | Particle Size (nm) | Lattice Parameters (Å) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a = b | c | c/a | ||
| ZnO | 24 | 3.242 | 5.204 | 1.604 |
| ZnO: Ce (0.05 M): Ni (0.025 M) | 17.99 | 3.257 | 5.220 | 1.602 |
| ZnO: Ce (0.05 M): Ni (0.05 M) | 16.86 | 3.260 | 5.227 | 1.603 |
| ZnO: Ce (0.05 M): Ni (0.075 M) | 15.85 | 3.256 | 5.224 | 1.604 |
| ZnO: Ce (0.05 M): Ni (0.1 M) | 14.64 | 3.260 | 5.226 | 1.603 |
| ZnO: Ce (0.05 M): Ni (0.125 M) | 11.19 | 3.256 | 5.224 | 1.604 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shanmugam, N.; Thirumal, V.; Kannadasan, N.; Murugavel, K.; Jayashri, N.; Kim, J.; Choi, D. Influence of Cerium and Nickel Co-Doping on ZnO Nanostructures for Electrochemical Behavior of H2O2 Sensing Applications. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6353. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106353
Shanmugam N, Thirumal V, Kannadasan N, Murugavel K, Jayashri N, Kim J, Choi D. Influence of Cerium and Nickel Co-Doping on ZnO Nanostructures for Electrochemical Behavior of H2O2 Sensing Applications. Sustainability. 2022; 14(10):6353. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106353
Chicago/Turabian StyleShanmugam, Nadana, Vediyappan Thirumal, Natesan Kannadasan, Kandasamy Murugavel, Natarajan Jayashri, Jinho Kim, and Dongjin Choi. 2022. "Influence of Cerium and Nickel Co-Doping on ZnO Nanostructures for Electrochemical Behavior of H2O2 Sensing Applications" Sustainability 14, no. 10: 6353. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106353
APA StyleShanmugam, N., Thirumal, V., Kannadasan, N., Murugavel, K., Jayashri, N., Kim, J., & Choi, D. (2022). Influence of Cerium and Nickel Co-Doping on ZnO Nanostructures for Electrochemical Behavior of H2O2 Sensing Applications. Sustainability, 14(10), 6353. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106353






