Evaluation of Rwanda’s Energy Resources
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Current Status of Rwanda
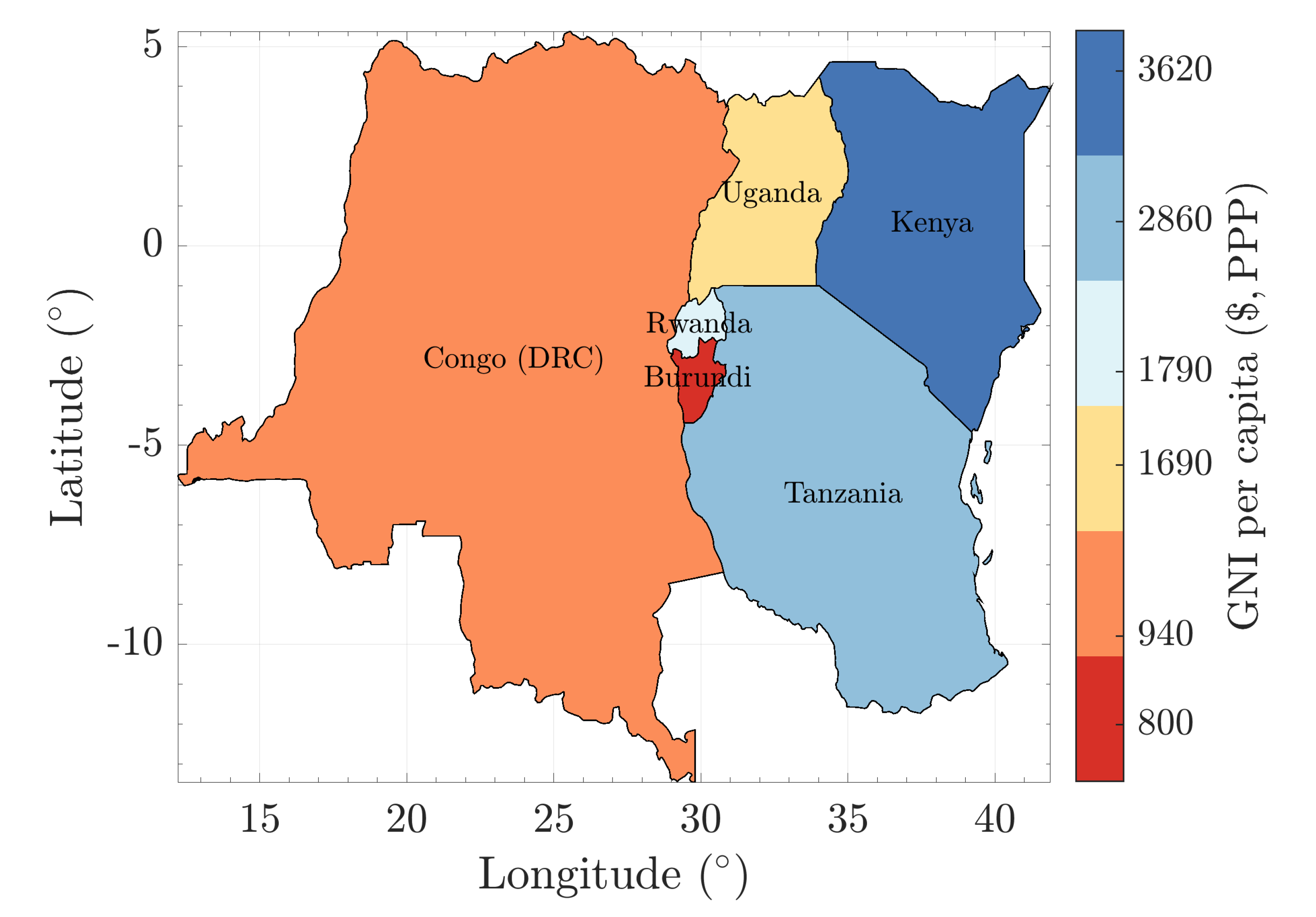
2.1. Economy
2.2. Population
2.3. Environment
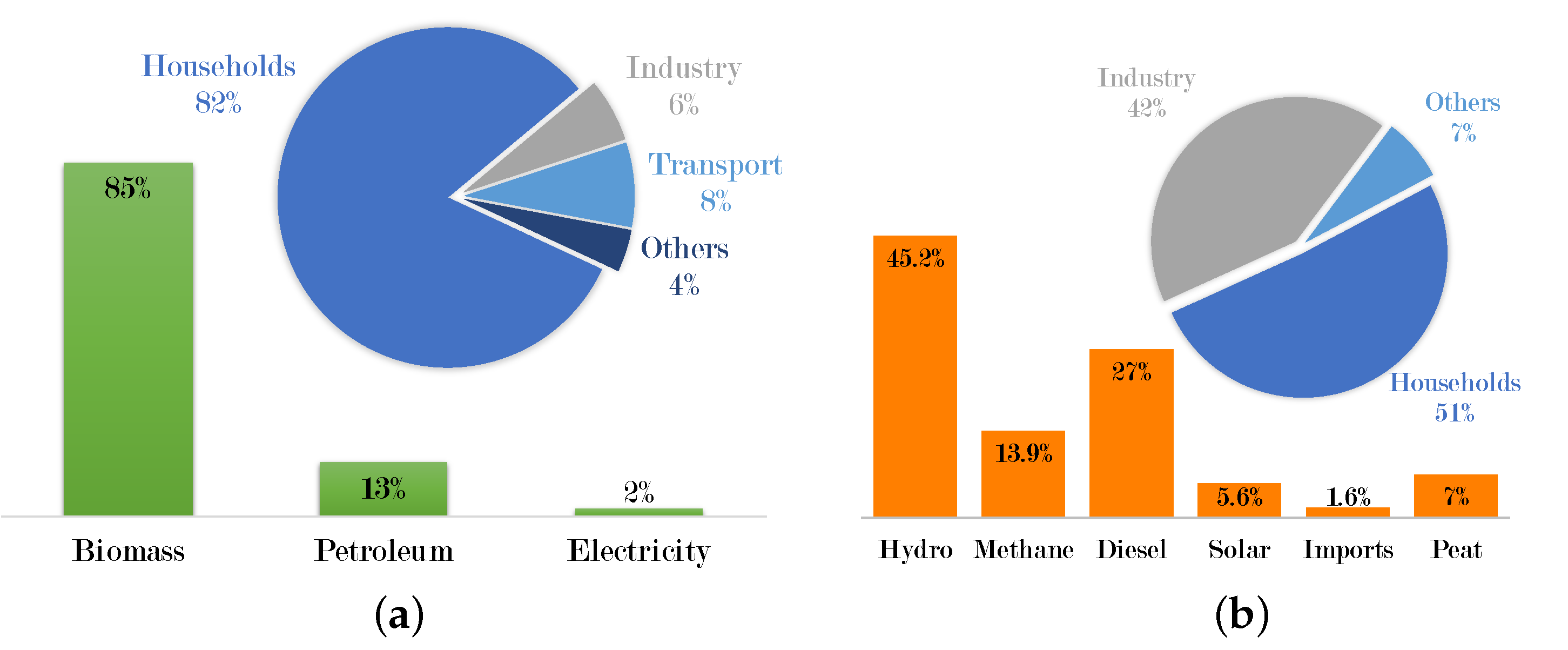
2.4. Energy
2.5. Energy–Environmental Crisis
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results and Discussions
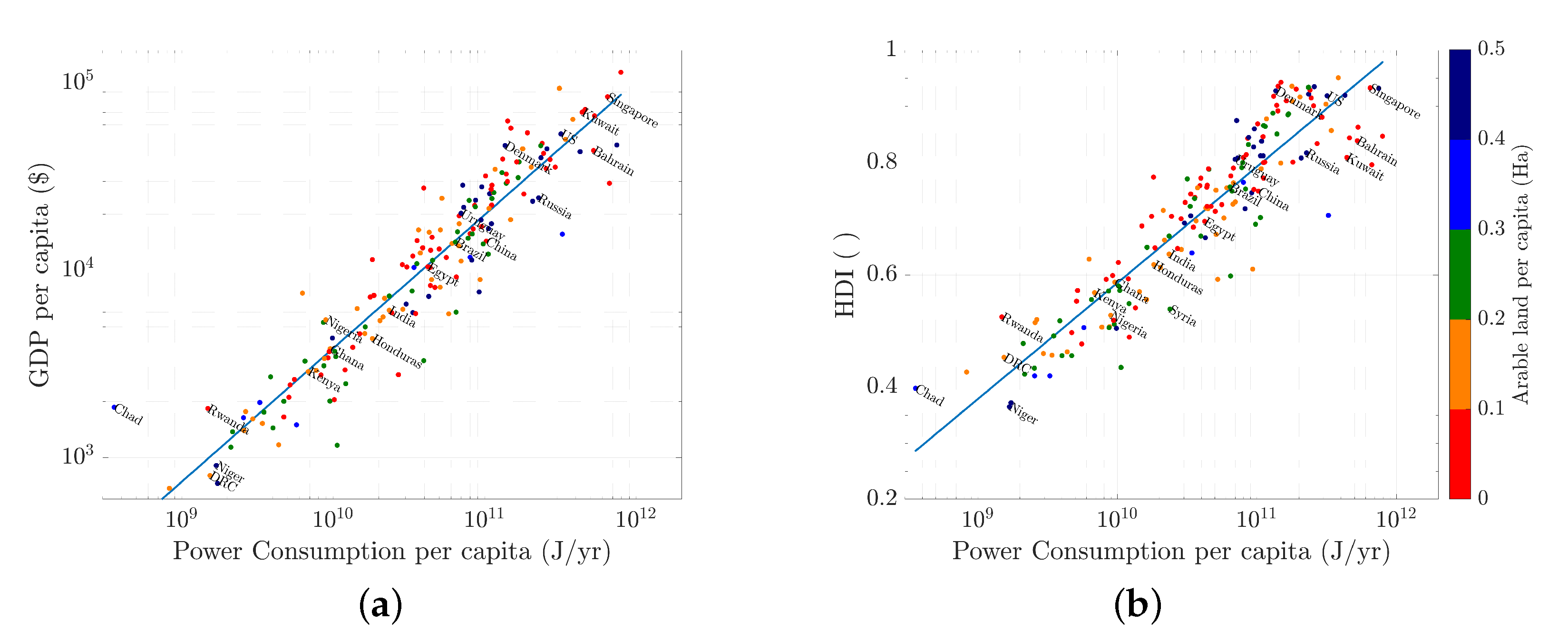
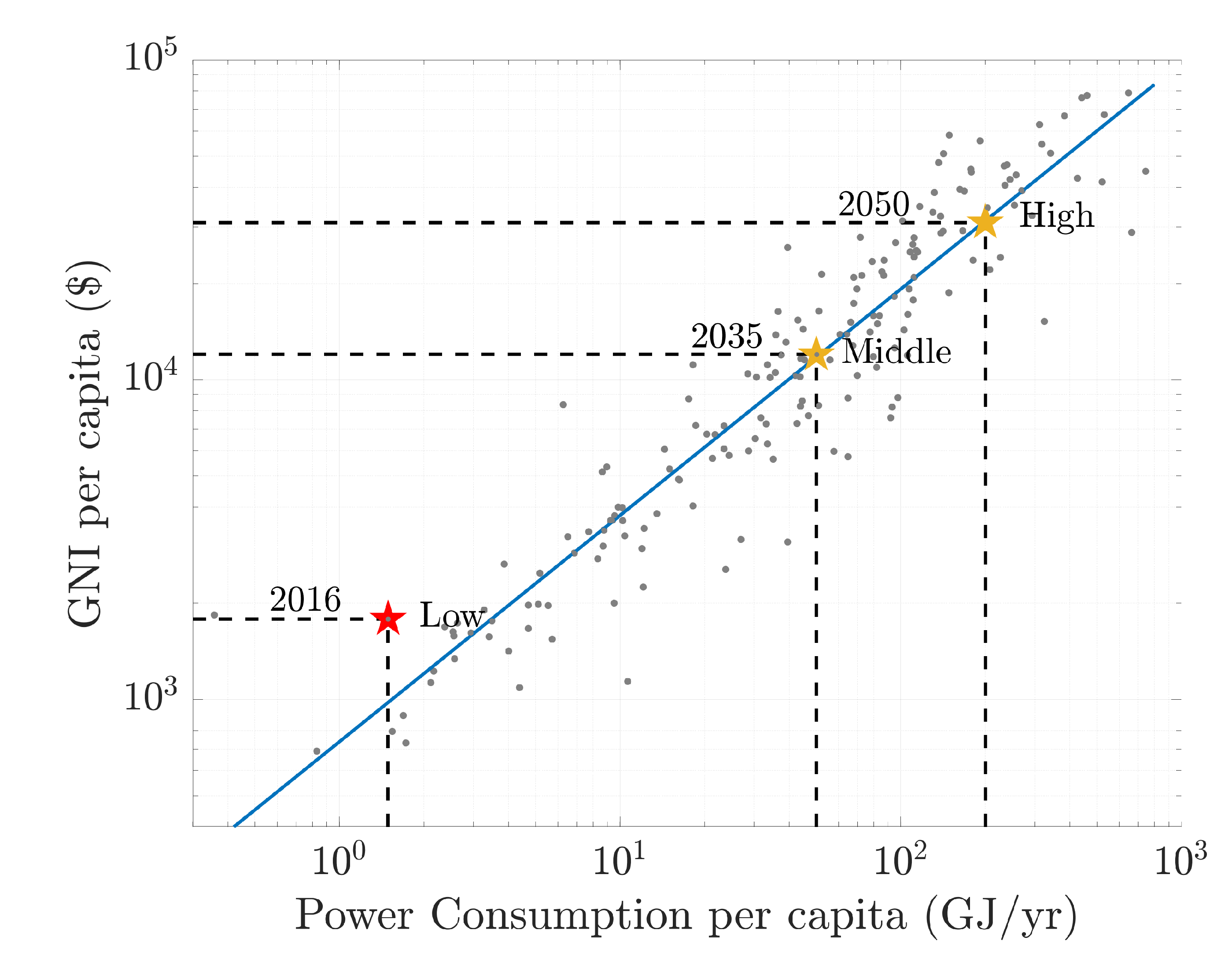
4.1. Developmental Goals and Requirements
4.2. Available Resources
4.3. Required Resources
4.4. Feasibility of Proposed Scenario
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hagens, N. Economics for the future—Beyond the superorganism. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 169, 106520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R. A Short History of Progress; Carroll and Graf Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, C.A.S.; Klitgaard, K.A. Energy and the Wealth of Nations: Understanding the Biophysical Economy; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Callen, T. Gross Domestic Product (GDP): An Economy’s All—Back to Basics: GDP Definition. 2020. Available online: https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fandd/basics/gdp.htm (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- UN. Human Development Index (HDI)|Human Development Reports. 2018. Available online: http://hdr.undp.org/en/content/human-development-index-hdi (accessed on 8 April 2020).
- Bolson, N.; Yutkin, M.; Rees, W.; Patzek, T. Resilience rankings and trajectories of world’s countries. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 195, 107383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EIA. International—U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). 2020. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/international/data/world (accessed on 6 April 2020).
- FAO. FAOSTAT—Land Use. 2019. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/RL (accessed on 21 April 2020).
- UN/WHO. About the Sustainable Development Goals—United Nations Sustainable Development. 2016. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/ (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- The World Bank. Rwanda Overview. 2015. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/rwanda/overview (accessed on 16 April 2020).
- Bank, W. GDP per Capita, PPP (Current International $)—Rwanda|Data. 2020. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.PCAP.PP.CD?locations=RW (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- MININFRA. Energy Sector Strategic Plan 2018/19–2023/24; Technical Report; MININFRA: Kigali, Rwanda, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rwanda Environment Management Authority (REMA). Rwanda State of the Environment and Outlook Report; Technical Report; REMA: Kigali, Rwanda, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Population, Total—Rwanda|Data. 2020. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.TOTL?locations=RW (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Population Pyramid. Population of Rwanda. 2020. Available online: https://www.populationpyramid.net/rwanda/ (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Worldometer. Rwanda Demographics 2020 (Population, Age, Sex, Trends)—Worldometer, 2020. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/demographics/rwanda-demographics/ (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- UNHCR. UNHCR Rwanda. 2018. Available online: https://www.unhcr.org/en-us/rwanda.html (accessed on 2 June 2020).
- World Bank. GNI per Capita. 2020. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GNP.PCAP.PP.CD?locations=RW-XM-XP-XD (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Greene, C.A.; Thirumalai, K.; Kearney, K.A.; Delgado, J.M.; Schwanghart, W.; Wolfenbarger, N.S.; Thyng, K.M.; Gwyther, D.E.; Gardner, A.S.; Blankenship, D.D. The Climate Data Toolbox for MATLAB. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2019, 20, 3774–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connolly-Boutin, L.; Smit, B. Climate change, food security, and livelihoods in sub-Saharan Africa. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2016, 16, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serdeczny, O.; Adams, S.; Baarsch, F.; Coumou, D.; Robinson, A.; Hare, W.; Schaeffer, M.; Perrette, M.; Reinhardt, J. Climate change impacts in Sub-Saharan Africa: From physical changes to their social repercussions. Reg. Environ. Change 2017, 17, 1585–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D.; Burgess, M. Soil Erosion Threatens Food Production. Agriculture 2013, 3, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boonstra, W.J.; de Boer, F.W. The Historical Dynamics of Social–Ecological Traps. AMBIO 2014, 43, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Capellán-Pérez, I.; de Castro, C.; Arto, I. Assessing vulnerabilities and limits in the transition to renewable energies: Land requirements under 100% solar energy scenarios. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 760–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kisioh, H. Gishwati Forest Reserve Three Years Interim Management Plan; Technical Report; Rwanda Natural Resources Authority: Kigali, Rwanda, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Musabyimana, T. The Landscape Approach to Forest Restoration and Conservation (LAFREC) Project in Rwanda (Gishwati and Mukura Forest Reserves): Social Assessment; Technical Report; REMA: Kigali, Rwanda, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- NASA. Gishwati Forest, Rwanda. 2009. Available online: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/38644/gishwati-forest-rwanda (accessed on 26 October 2020).
- Mongabay. Deforestation statistics for Rwanda. 2018. Available online: https://rainforests.mongabay.com/deforestation/archive/Rwanda.htm (accessed on 26 October 2020).
- World Bank. Forest Area (% of Land Area). 2015. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/AG.LND.FRST.ZS?locations=RW (accessed on 26 October 2020).
- European Union Energy Iniative. Biomass Energy Strategy (Best), Rwanda Volume 1-Executive Summary; Technical Report; European Union Energy Iniative: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bimenyimana, S.; Asemota, G.N.O.; Li, L. The State of the Power Sector in Rwanda: A Progressive Sector with Ambitious Targets. Front. Energy Res. 2018, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwanda Energy Group. Rwanda Least Cost Power Development Plan 2019–2040; Technical Report; Rwanda Energy Group: Kigali, Rwanda, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bolson, N.; Prieto, P.; Patzek, T. Capacity Factors: Values and Implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- World Data. Energy Consumption in Rwanda. 2020. Available online: https://www.worlddata.info/africa/rwanda/energy-consumption.php (accessed on 19 April 2020).
- Rwanda Energy Group. Tariffs. 2020. Available online: https://www.reg.rw/customer-service/tariffs/ (accessed on 4 May 2020).
- World Bank. Access to electricity (% of population)—Rwanda|Data. 2019. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/EG.ELC.ACCS.ZS?locations=RW (accessed on 12 August 2021).
- MININFRA. Rural Electrification Strategy; Technical Report; MININFRA: Kigali, Rwanda, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Disch, D.; Bronckaers, J. An Analysis of the Off-Grid Lighting Market in Rwanda: Sales, Distribution and Marketing; Technical Report; GVEP International: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Collings, S.; Munyehirwe, A. Pay-as-you-go solar pv in rwanda: Evidence of benefits to users and issues of affordability. Field Actions Sci. Rep. 2016, 2016, 94–103. [Google Scholar]
- Rwanda Energy Group. Facts & Figures Details. 2020. Available online: http://www.reg.rw/facts-figures/facts-figures-details/facts/installed-generation-capacity-on-the-national-grid/ (accessed on 19 April 2020).
- MININFRA. Biomass Energy Strategy 2019–2030; Technical Report; MININFRA: Kigali, Rwanda, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Household Cookstoves, Environment, Health, and Climate Change; Technical Report; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jeuland, M.A.; Pattanayak, S.K. Benefits and Costs of Improved Cookstoves: Assessing the Implications of Variability in Health, Forest and Climate Impacts. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mugabo, A. Low LPG Gas Uptake Blamed on High Prices as Consumers Opt for Firewood, Charcoal—Rwanda Today. 2020. Available online: http://rwandatoday.africa/business/Low-LPG-gas-uptake-blamed-on-high-prices/4383192-4947496-k50nx9z/index.html (accessed on 4 May 2020).
- Decker, C.T.; Johannes, A.C.; Alvey, J.B.; Masters, B.C.; Lux, S.M.; Page, M.A.; Chu, D.; Smith, K.C.; Wolf, K.T.; Roege, P. Opportunities for Waste Heat Recovery at Contingency Bases Construction Engineering; Technical Report; US Army Corps of Engineers: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Buningwire, W. Rwanda Energy Group Announces Rwf 19bn Power Loss. 2019. Available online: https://www.ktpress.rw/2019/01/rwanda-energy-group-announces-rwf-19bn-power-loss/ (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Wang, R. Sankey Diagram. 2020. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/75813-sankey-diagram (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Bolson, N.; Yutkin, M.; Patzek, T. Energy efficiency and sustainability assessment for methane harvesting from Lake Kivu. Energy 2021, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. National Income—Gross National Income. 2021. Available online: https://data.oecd.org/natincome/gross-national-income.htm (accessed on 11 August 2021).
- OECD. GDP and Spending—Gross Domestic Product (GDP). 2021. Available online: https://data.oecd.org/gdp/gross-domestic-product-gdp.htm (accessed on 11 August 2021).
- UNDP. Human Development Data Center. 2020. Available online: http://hdr.undp.org/en/data (accessed on 8 April 2020).
- MININFRA, Ministry of Infrastructure of Rwanda. Rwanda Atomic Energy Board to Coordinate Nuclear Energy Technologies. 2020. Available online: https://www.mininfra.gov.rw/updates/news-details/rwanda-atomic-energy-board-to-coordinate-nuclear-energy-technologies-minister-gatete (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- ROSATOM. Nuclear Science Aids Rwanda in Reaching Ambitious Economic Goals and Better Life. 2021. Available online: https://rusatom-overseas.com/media/mass-media-about-us/nuclear-science-aids-rwanda-in-reaching-ambitious-economic-goals-and-better-life.html (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- IAEA; NEA. IUREP Orientation Phase Mission: RWANDA; Technical Report; IAEA and NEA: Paris, France, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- NEA; IAEA. Uranium 2020 Resources, Production and Demand (Red Book); Technical Report; NEA and IAEA: Paris, France, 2020; Available online: https://www.oecd-nea.org/jcms/pl_52718/uranium-2020-resources-production-and-demand?details=true (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- IRENA. Solar Pv in Africa: Costs and Markets; Technical Report; IRENA: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- IEA. Snapshot 2020. Available online: https://iea-pvps.org/snapshot-reports/snapshot-2020/ (accessed on 28 May 2020).
- Golubkova, K.; Winning, A. Russia’s Rosatom, Rwanda Sign Deal to Build Nuclear Science Center. 2019. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/article/us-russia-rwanda-nuclear/russias-rosatom-rwanda-sign-deal-to-build-nuclear-science-center-idUSKBN1X32DV (accessed on 28 May 2020).
- Inyenyeri. Inyenyeri a Rwandan Social Benefit Company. 2020. Available online: https://cleancooking.org/sector-directory/inyenyeri/ (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- Mimi Moto. Mimi Moto—Clean Cooking for All. 2020. Available online: https://mimimoto.nl/ (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- Jagger, P.; Das, I. Implementation and scale-up of a biomass pellet and improved cookstove enterprise in Rwanda. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2018, 46, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uwimana, J. Some Rwandans Left Behind, as Eco-Friendly Initiatives Lead to Rise in Energy Costs. 2018. Available online: https://globalpressjournal.com/africa/rwanda/rwandans-left-behind-eco-friendly-initiatives-lead-rise-energy-costs/ (accessed on 3 May 2020).
- Coelho, S.T.; Sanches-Pereira, A.; Tudeschini, L.G.; Goldemberg, J. The energy transition history of fuelwood replacement for liquefied petroleum gas in Brazilian households from 1920 to 2016. Energy Policy 2018, 123, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobarak, A.M.; Dwivedi, P.; Bailis, R.; Hildemann, L.; Miller, G. Low demand for nontraditional cookstove technologies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10815–10820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Havugimana, L. The transition from cooking with charcoal to LPG gas in Rwanda (2018–2024). IRPJ 2019. Available online: https://irpj.euclid.int/articles/the-transition-from-cooking-with-charcoal-to-lpg-gas-in-rwanda-2018-2024/# (accessed on 13 May 2020).
- Byanyima, N.; Naluwagga, A.; Bechtel, K. Fuel Use and Emissions Report for Canarumwe and Canamake Iviguruye Stoves; Technical Report; Centre for Research in Energy and Energy Conservation, 2014; Available online: http://catalog.cleancookstoves.org/media/W1siZiIsIjIwMTcvMTIvMTEvMjAvMTIvNDMvNjAwL1Rlc3QgUmVwb3J0IGZvciBDYW5hbWFrZSBhbmQgQ2FuYXJ1bXdlICBzdG92ZXMtTWFyY2gyMDE0LnBkZiJdXQ/Test%20Report%20for%20Canamake%20and%20Canarumwe%20%20stoves-March2014.pdf?sha=c34e5927143e9228 (accessed on 4 May 2020).
- Alliance, C.C. Clean Cooking Catalog. 2020. Available online: http://catalog.cleancookstoves.org/stoves (accessed on 4 May 2020).
- Irena. Measuring Small-Scale Biogas Capacity and Production. Technical Report. 2016. Available online: https://www.irena.org/publications/2016/Dec/Measuring-small-scale-biogas-capacity-and-production (accessed on 3 May 2020).
- Enea Consulting. Domestic Biogas Diffusion in Rwanda—Key Learnings for Scale Up. Technical Report. 2016. Available online: https://www.enea-consulting.com/static/94b8aa5abb921b5a3a2fdf0c8db77053/enea-domestic-biogas-diffusion-in-rwanda.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Commoner, B.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Holdren, J.P. Response. Bull. At. Sci. 1972, 28, 17–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Dieu Iyakaremye, J.; Harerimana, L.; Das, D.; Mugwaneza, F.; Bosco Ndikubwimana, J. Evaluation and comparison of the performance characteristics of improved firewood stove for rural households of Rwanda. East Afr. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9. Available online: http://eajournalv2.unilak.ac.rw/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/1_-IyakaremyePaper31.pdf (accessed on 11 May 2020).
- Urmee, T.; Gyamfi, S. A review of improved Cookstove technologies and programs. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

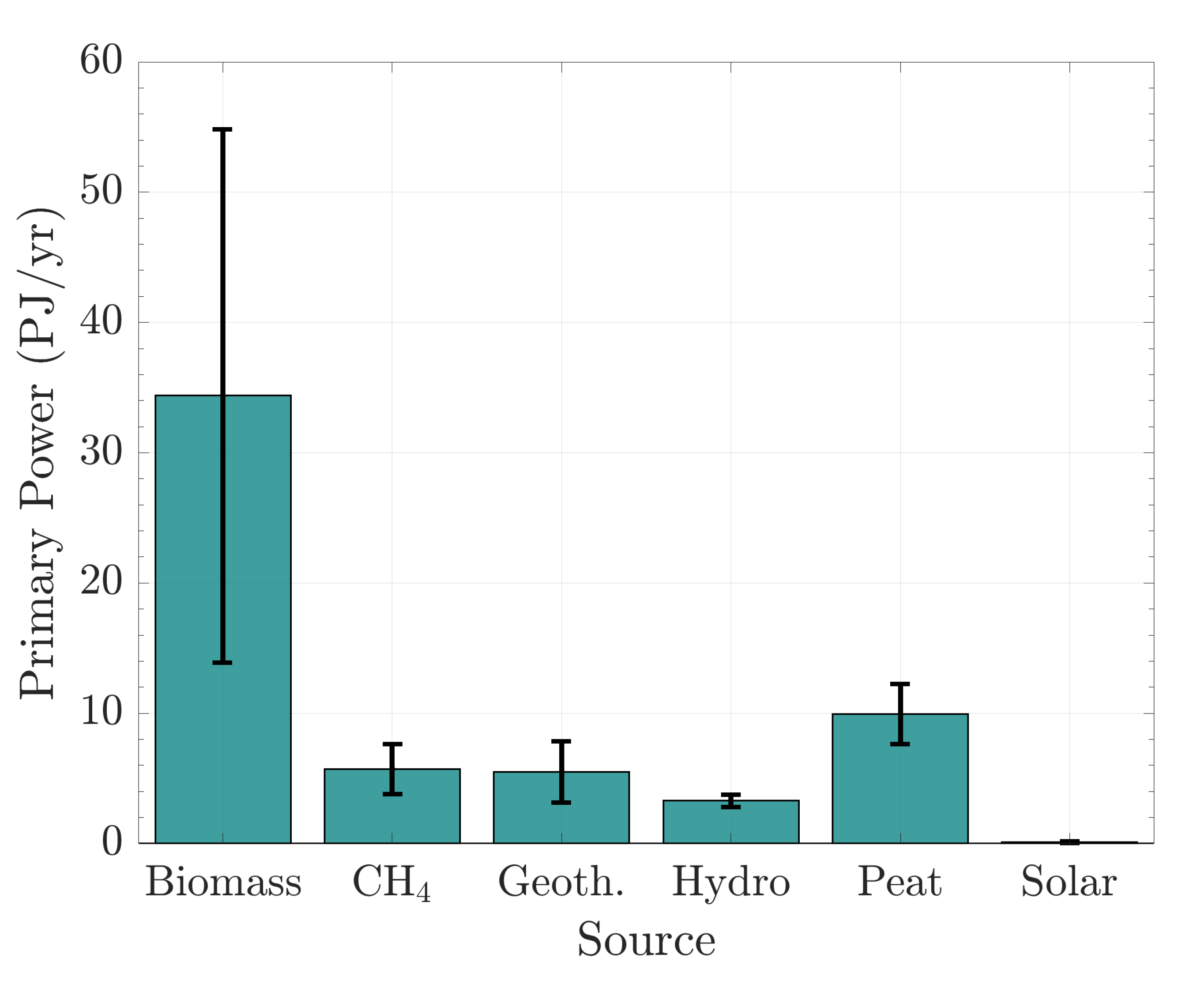
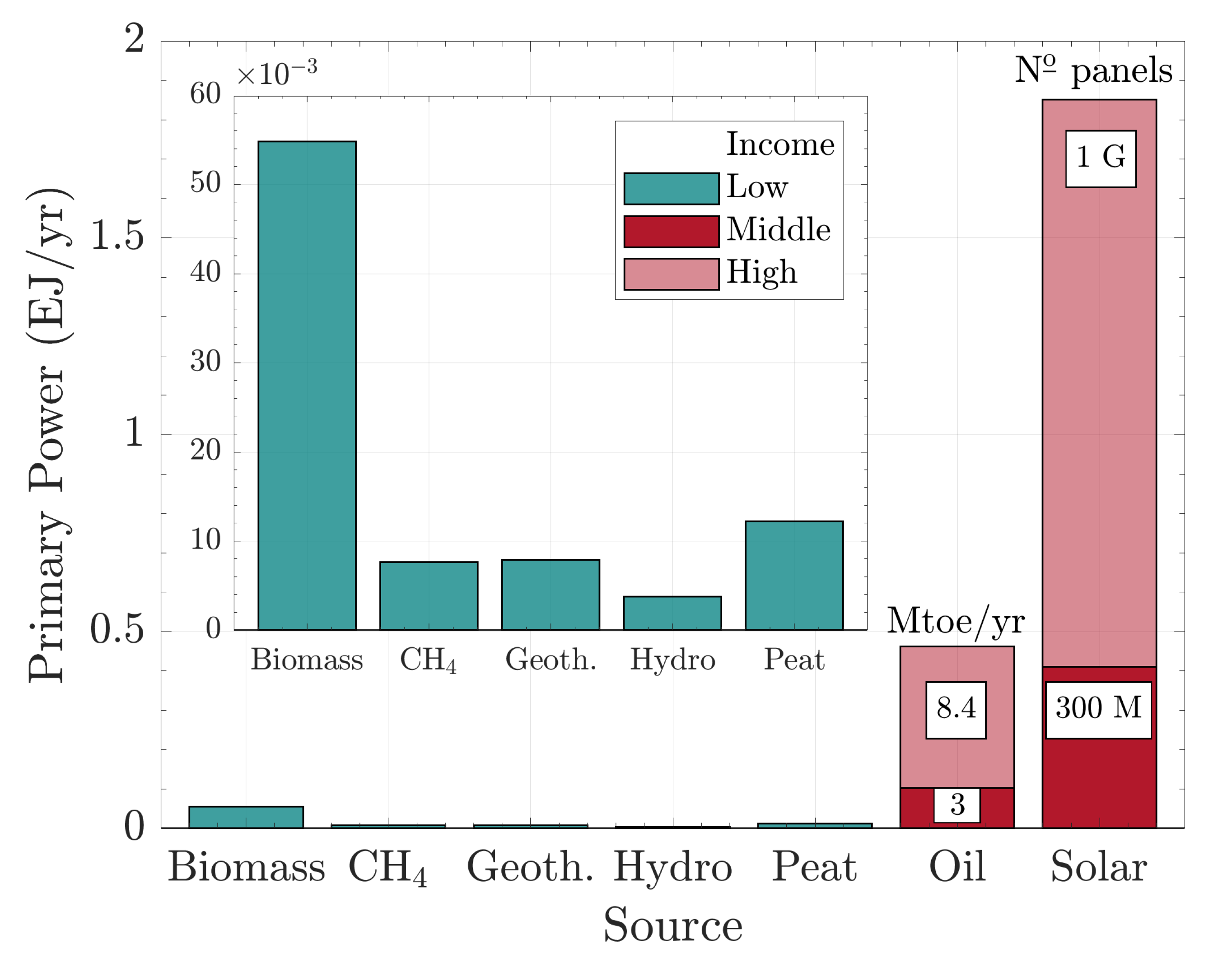
| Resource | Potential (MW) | Installed (MW) |
|---|---|---|
| Hydropower | 300–400 | 98.5 |
| Methane | 140–180 | 30 |
| Peat | 120–160 | 15 |
| Geothermal | 47 | - |
| Solar | TBD | 12 |
| Biomass | TBD | - |
| Wind | TBD | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bolson, N.; Patzek, T. Evaluation of Rwanda’s Energy Resources. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6440. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116440
Bolson N, Patzek T. Evaluation of Rwanda’s Energy Resources. Sustainability. 2022; 14(11):6440. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116440
Chicago/Turabian StyleBolson, Natanael, and Tadeusz Patzek. 2022. "Evaluation of Rwanda’s Energy Resources" Sustainability 14, no. 11: 6440. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116440
APA StyleBolson, N., & Patzek, T. (2022). Evaluation of Rwanda’s Energy Resources. Sustainability, 14(11), 6440. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116440






