Bench-Scale Fixed-Bed Column Study for the Removal of Dye-Contaminated Effluent Using Sewage-Sludge-Based Biochar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Sewage Sludge and Preparation of Adsorbent
2.2. BIE Collection and Characterization
2.3. Column Study
2.3.1. Experimental Set-Up
2.3.2. Kinetic Modeling
- Thomas Model
- Bohart–Adams model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorbent Preparation and Characterization
3.2. Column Study
3.2.1. Preliminary Study
3.2.2. Influence of Operation Conditions on Dye Removal
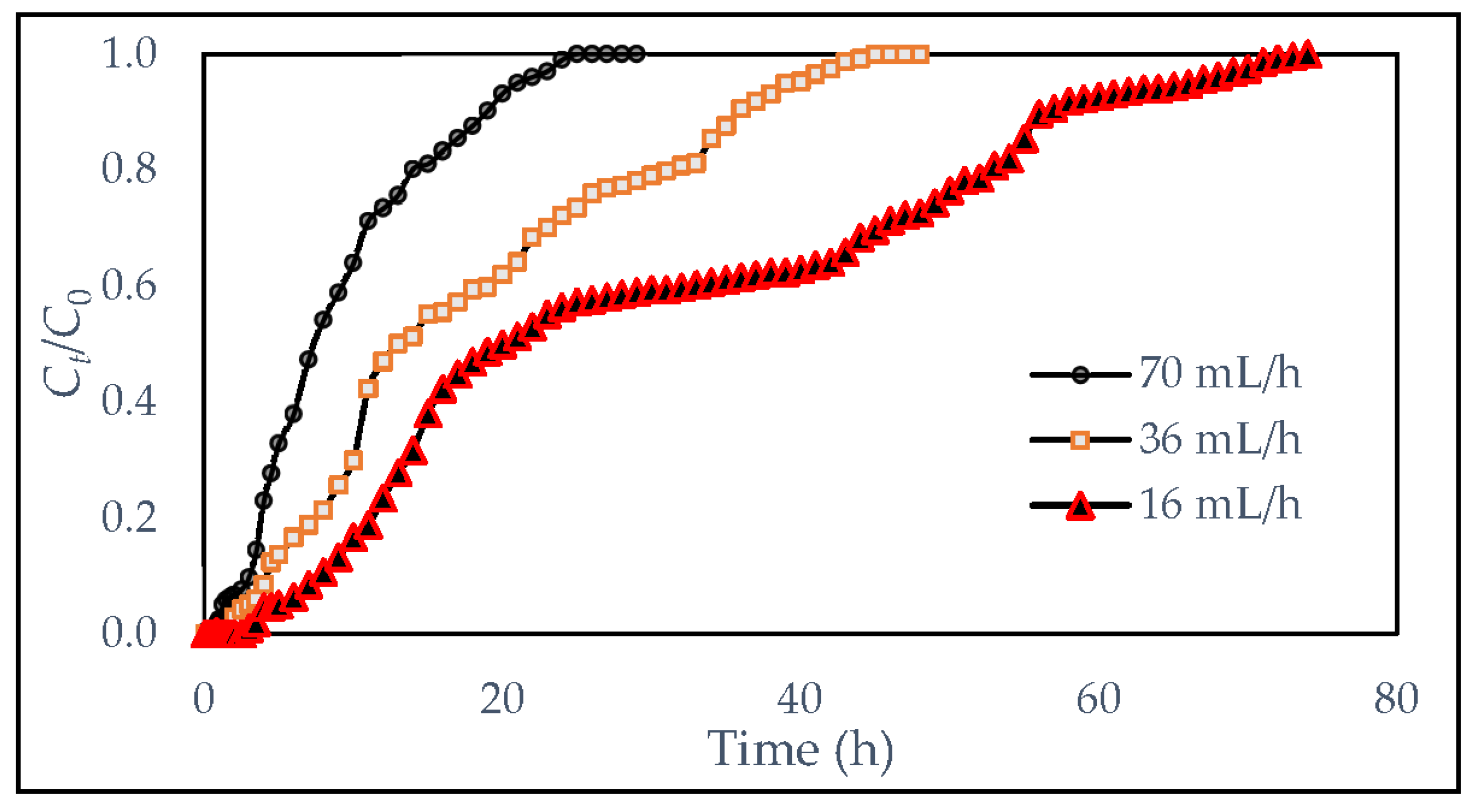
- Effect of feed-flow rate
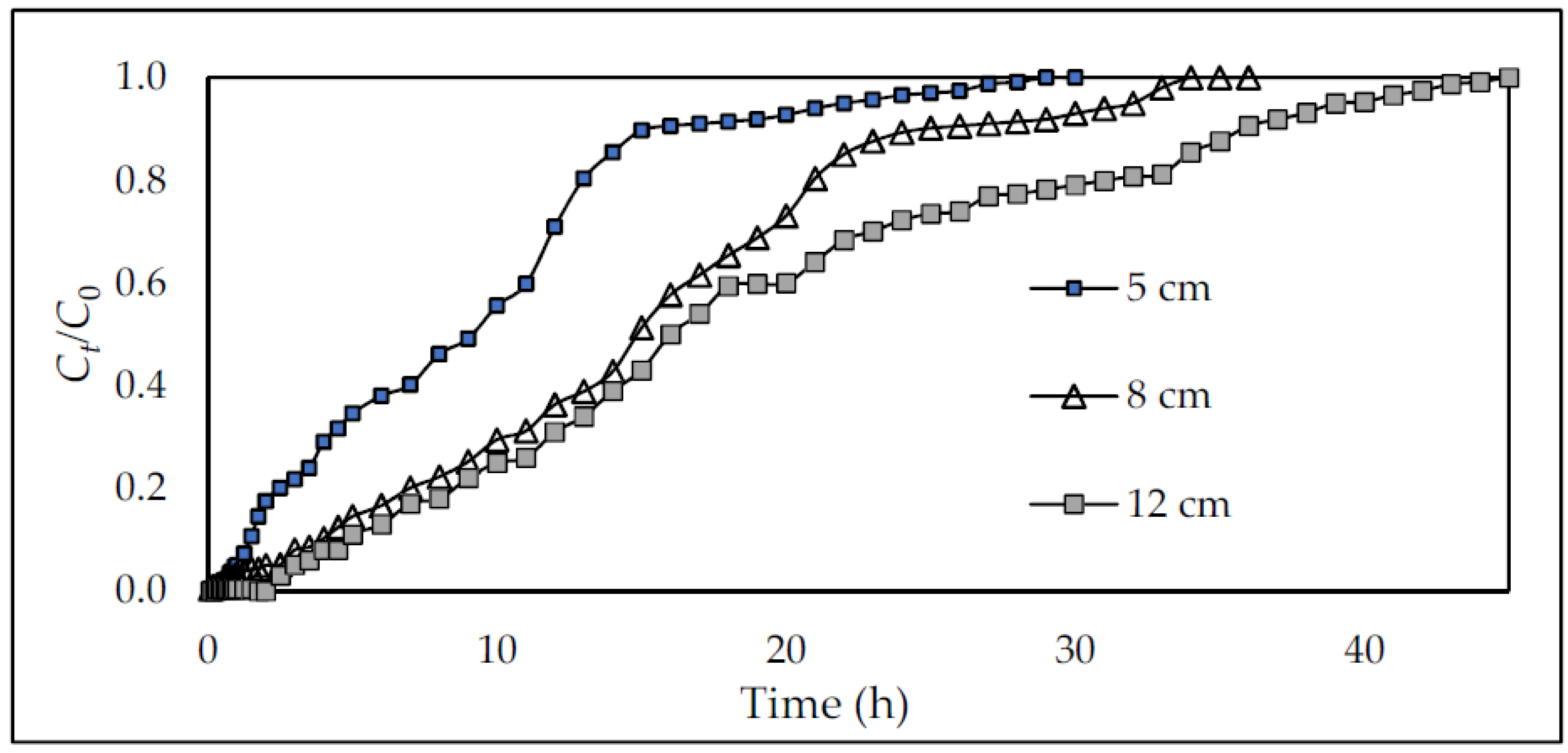
- Effect of bed depth
3.2.3. Breakthrough Curve Behavior Investigation
3.2.4. Mechanisms of Dyes Adsorption onto SSB
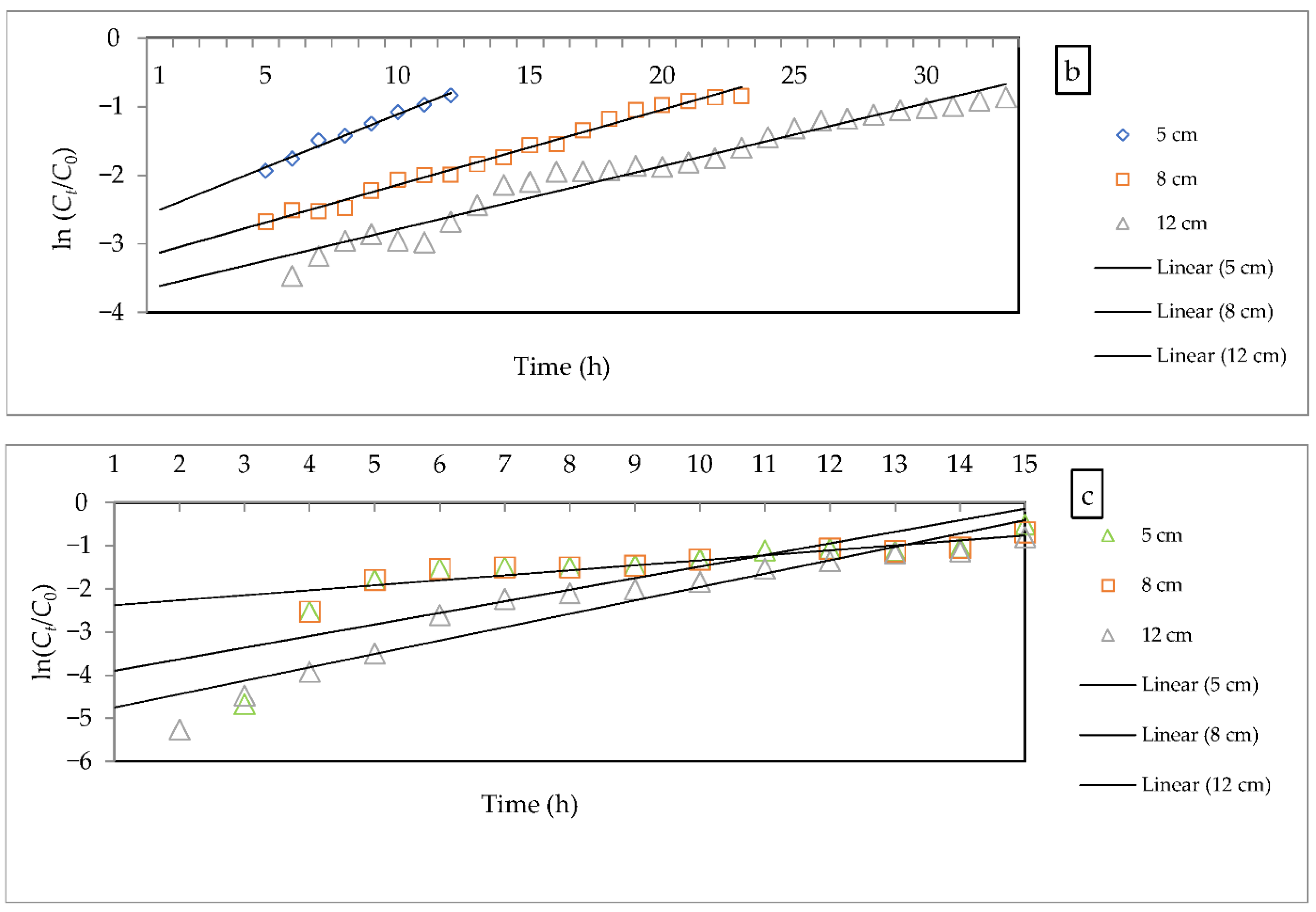
3.2.5. Evaluation of Kinetic Models
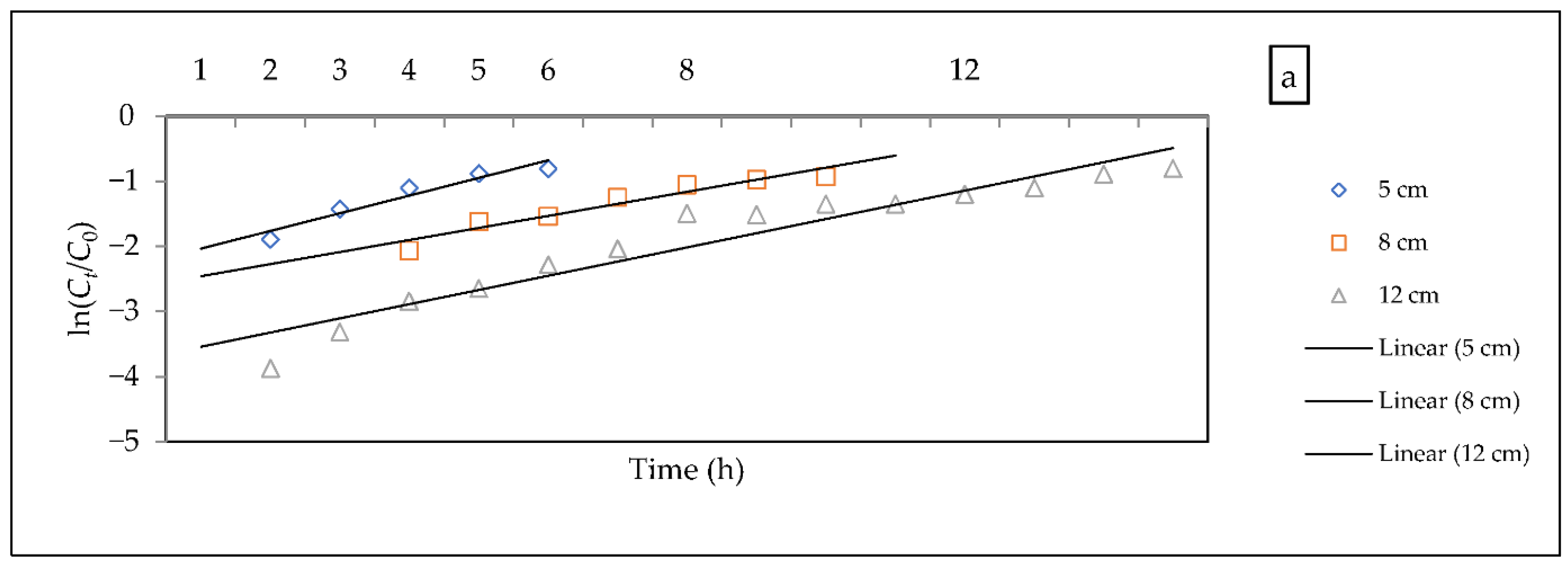
- Bohart–Adams model
- Thomas model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghaleb, A.A.S.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Ho, Y.-C.; Jagaba, A.H.; Noor, A.; Al-Sabaeei, A.M.; Almahbashi, N.M.Y. Response Surface Methodology to Optimize Methane Production from Mesophilic Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Oily-Biological Sludge and Sugarcane Bagasse. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahbashi, N.; Kutty, S.; Ayoub, M.; Noor, A.; Salihi, I.; Al-Nini, A.; Jagaba, A.; Aldhawi, B.; Ghaleb, A. Optimization of Preparation Conditions of Sewage sludge based Activated Carbon. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahbashi, N.M.Y.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Chua, Y.C.; Sholagberu, A.T.; Ghaleb, A.A.S.; Aminu, N. Kinetics of Nutrient Removal in an Integrated Suspended Growth Reactor. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2019, 11, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saeed, A.; Harun, N.; Sufian, S.; Siyal, A.; Zulfiqar, M.; Bilad, M.; Vagananthan, A.; Al-Fakih, A.; Ghaleb, A.; Almahbashi, N. Eucheuma cottonii Seaweed-Based Biochar for Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Miino, M.C.; Damiani, S. Treatments for color removal from wastewater: State of the art. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hairuddin, H.; Noor, N.L.M.; Ab Malik, A.M. Why do Microenterprise Refuse to Use Information Technology: A Case of Batik Microenterprises in Malaysia. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 57, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azha, S.F.; Ismail, S. Feasible and economical treatment of real hand-drawn batik/textile effluent using zwitterionic adsorbent coating: Removal performance and industrial application approach. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 102093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalik, W.F.; Ho, L.-N.; Ong, S.-A.; Voon, C.-H.; Wong, Y.-S.; Yusuf, S.Y.; Yusoff, N.A.; Lee, S.-L. Enhancement of simultaneous batik wastewater treatment and electricity generation in photocatalytic fuel cell. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 35164–35175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effendi, H.; Sari, R.D.; Hasibuan, S. Moringa oleifera as coagulant for batik effluent treatment. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Conference of the International Association for Impact Assessment, Firenze Fiera Congress and Exhibition Center, Florence, Italy, 20–23 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rashidi, H.; Sulaiman, N.N.; Hashim, N. Batik Industry Synthetic Wastewater Treatment Using Nanofiltration Membrane. Procedia Eng. 2012, 44, 2010–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.N.M.A.; Islam, M.A. The contribution of different vinyl sulphone-reactive dyes to an effluent. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2015, 9, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Burkinshaw, S.M.; Kabambe, O. Attempts to reduce water and chemical usage in the removal of bifunctional reactive dyes from cotton: Part 2 bis (vinyl sulfone), aminochlorotriazine/vinyl sulfone and bis (aminochlorotriazine/vinyl sulfone) dyes. Dyes and Pigments 2011, 88, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Gong, Y.; Gurav, R.; Tang, J. Chapter 9—Potential Application of Biochar for Bioremediation of Contaminated Systems Biochar Application; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.K.; Choi, T.R.; Gurav, R.; Bhatia, S.K.; Park, Y.L.; Kim, H.J.; Kan, E.; Yang, Y.H. Adsorption behavior of tetracycline onto Spirulina sp. (microalgae)-derived biochars produced at different temperatures. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.-H.; Chen, Y.-D.; Yang, Z.-K.; Nagarajan, D.; Chang, J.-S.; Ren, N.-Q. High-efficiency removal of lead from wastewater by biochar derived from anaerobic digestion sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.-J.; Huang, Q.-S.; Wang, C.; Ni, T.-Y.; Sun, J.; Wei, W. Competitive adsorption of heavy metals in aqueous solution onto biochar derived from anaerobically digested sludge. Chemosphere 2018, 219, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleb, A.; Kutty, S.; Salih, G.; Jagaba, A.; Noor, A.; Kumar, V.; Almahbashi, N.; Saeed, A.; Al-Dhawi, B.S. Sugarcane Bagasse as a Co-Substrate with Oil-Refinery Biological Sludge for Biogas Production Using Batch Mesophilic Anaerobic Co-Digestion Technology: Effect of Carbon/Nitrogen Ratio. Water 2021, 13, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosomi, M. New challenges on wastewater treatment. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2016, 18, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Zhang, R.; Ngo, H.H.; He, X.; Ma, J.; Nan, J.; Li, G. Life cycle assessment of sewage sludge treatment and disposal based on nutrient and energy recovery: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Pacheco, C.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; López-Peñalver, J. Optimization of the preparation process of biological sludge adsorbents for application in water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 217, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.; Saroha, A.K. Utilization of sludge based adsorbents for the removal of various pollutants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hii, K.; Baroutian, S.; Parthasarathy, R.; Gapes, D.; Eshtiaghi, N. A review of wet air oxidation and Thermal Hydrolysis technologies in sludge treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 155, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Kamran, K.; Quan, C.; Williams, P.T. Thermochemical conversion of sewage sludge: A critical review. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2020, 79, 100843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutty, S.; Almahbashi, N.; Nazrin, A.; Malek, M.; Noor, A.; Baloo, L.; Ghaleb, A. Adsorption kinetics of colour removal from palm oil mill effluent using wastewater sludge carbon in column studies. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraj, R.; Rajendran, V.; Gunalan, G.S. Preparation and characterization of activated carbons from Parthenium biomass by physical and chemical activation techniques. E-J. Chem. 2010, 7, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshwarisivaraj; Sivakumar, S.; Senthilkumar, P.; Subburam, V. Carbon from Cassava peel, an agricultural waste, as an adsorbent in the removal of dyes and metal ions from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 80, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, G.O.; Yehia, M.M.; Asaad, A.A. Assessment of activated carbon prepared from corncob by chemical activation with phosphoric acid. Water Resour. Ind. 2014, 7, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, M.; Negm, N.; Kana, M.A.; Hefni, H.; Moneem, M.A. Adsorption of aluminum and lead from wastewater by chitosan-tannic acid modified biopolymers: Isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics and process mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishayee, B.; Ruj, B.; Nandi, S.; Chatterjee, R.P.; Mallick, A.; Chakraborty, P.; Nayak, J.; Chakrabortty, S. Sorptive elimination of fluoride from contaminated groundwater in a fixed bed column: A kinetic model validation based study. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2021, 99, 100302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshni, K.; Soumen, D. A breakthrough column study for removal of malachite green using coco-peat. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2019, 21, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, M.; Safari, E.; Baghdadi, M.; Janmohammadi, M. Enhanced adsorption of heavy metals in groundwater using sand columns enriched with graphene oxide: Lab-scale experiments and process modeling. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, Z.; Saadi, R.; Fazaeli, R. Fixed-bed adsorption dynamics of Pb (II) adsorption from aqueous solution using nanostructured γ-alumina. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2013, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njaramba, L.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.; Cha, B.; Kim, N.; Yoon, Y.; Park, C.M. Remarkable adsorption for hazardous organic and inorganic contaminants by multifunctional amorphous core–shell structures of metal–organic framework-alginate composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttakin, M.; Mitra, S.; Thu, K.; Ito, K.; Saha, B.B. Theoretical framework to evaluate minimum desorption temperature for IUPAC classified adsorption isotherms. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 122, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Chang, F.-M.; Huang, B.; Song, Y.-P.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Wang, K.-J. Activated carbon preparation from pyrolysis char of sewage sludge and its adsorption performance for organic compounds in sewage. Fuel 2020, 266, 117053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, B.; Kończak, M.; Rakowska, M.; Oleszczuk, P. Engineered biochars from organic wastes for the adsorption of diclofenac, naproxen and triclosan from water systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Srivastava, V.C. Self-engineered iron oxide nanoparticle incorporated on mesoporous biochar derived from textile mill sludge for the removal of an emerging pharmaceutical pollutant. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 259, 113822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Chen, W.; Zhang, R.; Xing, Y. Enhanced Removal of Malachite Green Using Calcium-Functionalized Magnetic Biochar. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misran, E.; Okta, B.; Margaretha, S.E.; Purba, A.S. Banana stem based activated carbon as a low-cost adsorbent for methylene blue removal: Isotherm, kinetics, and reusability. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 1, 1946–1955, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, R.J.; Sivachidambaram, M.; Vijaya, J.J.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Muthumareeswaran, M.R. Synthesis of porous activated carbon powder formation from fruit peel and cow dung waste for modified electrode fabrication and application. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 142, 105800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davide, B.; Toni, V.; Henrik, R.; Lassi, U. Activated carbon from hydrolysis lignin: Effect of activation method on carbon properties. Biomass Bioenergy 2022, 159, 106387. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulhameed, A.S.; Firdaus, N.N.M.; Rangabhashiyam, S.; Jawad, A.H. Statistical modeling and mechanistic pathway for methylene blue dye removal by high surface area and mesoporous grass-based activated carbon using K2CO3 activator. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun’ichi, H.; Atsuo, K.; Katsuhiko, M.; Watkinson, A.P. Preparation of activated carbon from lignin by chemical activation. Carbon 2000, 38, 1873–1878. [Google Scholar]
- Işılay, O.; Mehmet, Ş.; Ramazan, O.; Erdem, M. Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from grape stalk by zinc chloride activation. Fuel Processing Technol. 2014, 125, 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, A.A.H.; Harun, N.Y.; Zulfani, N. Heavy metals capture from water sludge by kenaf fibre activated carbon in batch adsorption. Journal of Ecological Engineering 2020, 21, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, N.A.; Othman, N.; Yunus, Z.M.; Altowayti, W.A.H. An insight review of lignocellulosic materials as activated carbon precursor for textile wastewater treatment. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulla, B.A.; Belgin, G.; Özgür, S.; Kalderis, D. Evaluation of sewage sludge biochar and modified derivatives as novel SPE adsorbents for monitoring of bisphenol A. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128866. [Google Scholar]
- Cansado, I.P.; Mourão, P.A. Impact of the use of co-adjuvants agents during chemical activation on the performance of activated carbons in the removal of 4-chloro-2-methyl-phenoxyacetic acid. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Jingchun, T.; Kai, G.; Ruozhu, H.; Hang, Z.; Werner, D. Characterization of KOH modified biochars from different pyrolysis temperatures and enhanced adsorption of antibiotics. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14640–14648. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, D.S.; Georgin, J.; Netto, M.S.; Allasia, D.; Oliveira, M.L.; Foletto, E.L.; Dotto, G.L. Highly effective adsorption of synthetic phenol effluent by a novel activated carbon prepared from fruit wastes of the Ceiba speciosa forest species. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Yahyaoui, S.; Hanafy, H.; Seliem, M.K.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Dotto, G.; Sellaoui, L.; Li, Q. Effective adsorption of dyes on an activated carbon prepared from carboxymethyl cellulose: Experiments, characterization and advanced modelling. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 128116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, N.; Mohan, S. Development of nanoporous textile sludge based adsorbent for the dye removal from industrial textile effluent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 422, 126864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Hu, F.; Zhang, T.; Qiu, F.; Dai, H. Amine-functionalized magnetic bamboo-based activated carbon adsorptive removal of ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin: A batch and fixed-bed column study. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 249, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mery, M.; Ornella, A.; Agnese, G.; Maurizio, A.; Mentasti, E. Adsorption of heavy metals on vermiculite: Influence of pH and organic ligands. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 299, 537–546. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, S.J.; Tapre, R.W.; Patil, S.V.; Sawarkar, M.B. Adsorption of phenol from wastewater in fluidized bed using coconut shell activated carbon. Procedia Eng. 2013, 51, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawati, S.; Indriyanti, N.Y. Adsorption of Anionic and Cationic Dyes in Batik Wastewater Using Biomass Adsorbents: Literature Review. JKPK (Jurnal Kimia dan Pendidikan Kimia) 2021, 6, 274–291. [Google Scholar]
- Aris, M.; Hanny, V.; Nur, Z.; Agus, P.; Wicaksono, K.A. Performance of bioequalization-electrocatalytic integrated method for pollutants removal of hand-drawn batik wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 21, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Topare, N.S.; Bokil, S.A. Adsorption of textile industry effluent in a fixed bed column using activated carbon prepared from agro-waste materials. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarchia, C.A.; Debrassia, A.; Magrob, J.D.; Nedelkoc, N.; Ślawska-Waniewskac, A.; Dłużewskic, P.; Greneched, J.M.; Rodriguesa, C.A. Adsorption of Cr (VI) on crosslinked chitosan–Fe (III) complex in fixed-bed systems. J. Water Process Eng. 2015, 7, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Mubarak, M.F.; Keshawy, M.; Zayed, M.A.; Ataalla, M. Adsorption of Tartrazine anionic dye by novel fixed bed Core-Shell- polystyrene Divinylbenzene/Magnetite nanocomposite. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 61, 1335–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Rahimi, M.R.; Asfaram, A.; Ghaedi, M.; Javadian, H. Experimental design for the optimization of paraquat removal from aqueous media using a fixed-bed column packed with Pinus Eldarica stalks activated carbon. Chemosphere 2021, 291, 132670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zawahreh, K.; Barral, M.T.; Al-Degs, Y.; Paradelo, R. Competitive removal of textile dyes from solution by pine bark-compost in batch and fixed bed column experiments. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 27, 102421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samir, C.; Rahul, Y.; Prasanta, D.; Maiti, S. Fixed-bed adsorption of Reactive Orange 84 dye onto activated carbon prepared from empty cotton flower agro-waste. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2018, 28, 298–308. [Google Scholar]
- Alardhi, S.M.; Albayati, T.M.; Alrubaye, J.M. Adsorption of the methyl green dye pollutant from aqueous solution using mesoporous materials MCM-41 in a fixed-bed column. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B.; Li, Q.; Xu, X.; Fu, K. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by modified corn stalk: A fixed-bed column study. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 113, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naushad, M.; Alqadami, A.A.; Al-Kahtani, A.A.; Ahamad, T.; Awual, R.; Tatarchuk, T. Adsorption of textile dye using para-aminobenzoic acid modified activated carbon: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 296, 112075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birgani, P.M.; Ranjbar, N.; Abdullah, R.C.; Wong, K.T.; Lee, G.; Ibrahim, S.; Park, C.; Yoon, Y.; Jang, M. An efficient and economical treatment for batik textile wastewater containing high levels of silicate and organic pollutants using a sequential process of acidification, magnesium oxide, and palm shell-based activated carbon application. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 184, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daud, N.M.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Hasan, H.A.; Dhokikah, Y. Integrated physical-biological treatment system for batik industry wastewater: A review on process selection. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 152931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Carr, C.M. A critical review on recent advancements of the removal of reactive dyes from dyehouse effluent by ion-exchange adsorbents. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahbashi, N.; Kutty, S.; Jagaba, A.; Al-Nini, A.; Ali, M.; Saeed, A.; Ghaleb, A.; Rathnayake, U. Column Study for Adsorption of Copper and Cadmium Using Activated Carbon Derived from Sewage Sludge. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2022, 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, S.; Das, N.; Ramulu, T.; Sahoo, S.; Das, S.; Chaudhury, G.R. Removal of Cr(VI) by thermally activated weed Salvinia cucullata in a fixed-bed column. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, N.; Taghizadeh, M. Continuous fixed-bed adsorption of Mo(VI) from aqueous solutions by Mo(VI)-IIP: Breakthrough curves analysis and mathematical modeling. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Mondal, S.; De, S. Design and scaling up of fixed bed adsorption columns for lead removal by treated laterite. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 177, 760–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, G.; Abolghasemi, H.; Esmaieli, M.; Pouya, E.S. Aqueous phase adsorption of cephalexin by walnut shell-based activated carbon: A fixed-bed column study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 375, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Liu, H.; Cheng, C.; Li, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from wool waste and the comparison of muffle furnace and microwave heating methods. Powder Technol. 2013, 249, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, K.; Sathish, A.; Kumar, P.S. Packed bed column optimization and modeling studies for removal of chromium ions using chemically modified Lantana camara adsorbent. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2020, 33, 101069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika, R.; Jayalatha, T.; Jacob, S.; Rajeev, R.; George, B.K. Adsorption performance of packed bed column for the removal of perchlorate using modified activated carbon. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 117, 350–362. [Google Scholar]






| Parameters | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 9 |
| COD | mg/L | 115 |
| Color | Pt-Co | 234 |
| BET Result | Unit | SSB | BCSLN2 [36] | BCSLCO2 [36] | TSB [37] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BET surface area | m2/g | 117.6676 | 89.2 | 83.5 | 91 |
| Surface area of Micropore | m2/g | 16.0873 | - | - | - |
| Volume of Micropore | cm3/g | 0.006967 | 0.024 | 0.0206 | 0.2769 |
| BJH Adsorption average pore diameter | nm | 6.00933 | 6.19 | 5.86 | - |
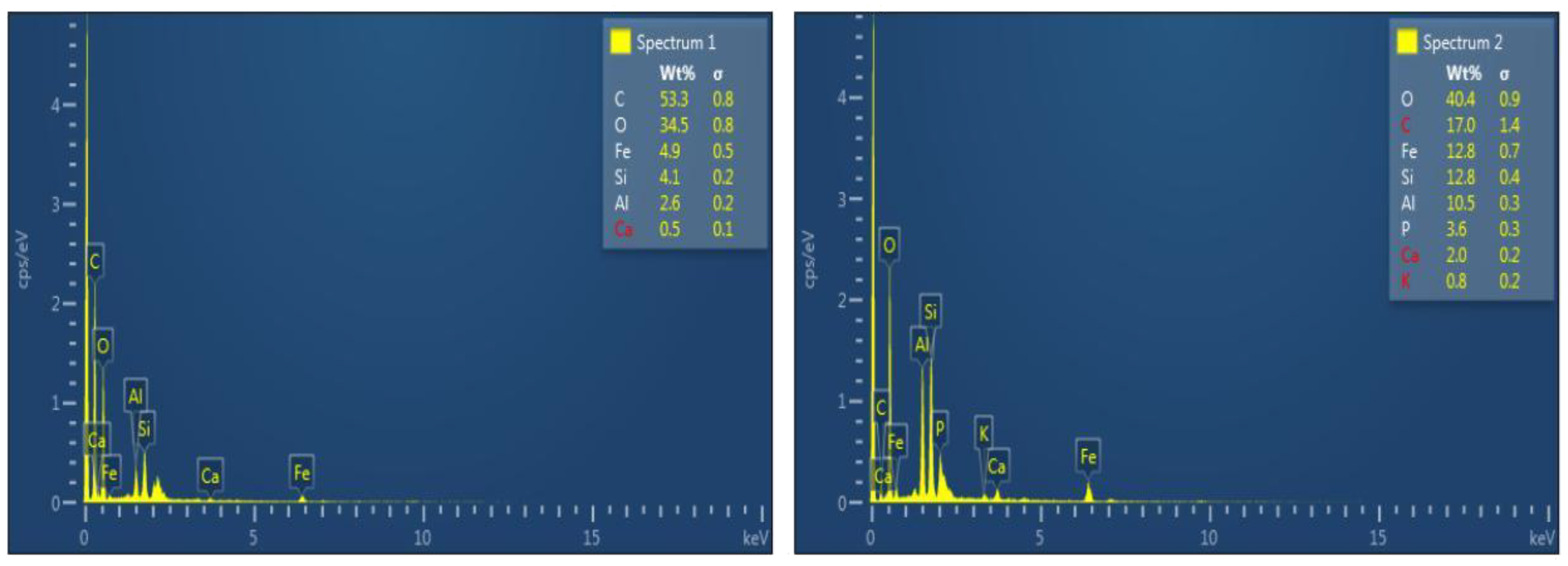
| Sample | Weightage of Elements (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Fe | Si | Al | Ca | P | K | |
| Raw sewage sludge | 53.3 | 34.5 | 4.9 | 4.1 | 2.6 | 0.5 | - | - |
| SSB | 17 | 40.4 | 12.8 | 12.8 | 10.5 | 2.0 | 3.6 | 0.8 |
| Flow Rate (mL/h) | Volume of Effluent | |
|---|---|---|
| (mL/Day) | (L/Day) | |
| 70 | 1680 | 1.68 |
| 36 | 864 | 0.864 |
| 16 | 384 | 0.384 |
| Flow Rate mL/h | Bed Depth (cm) | Breakthrough Point (min) | Exhausting Point (min) | Mass Transfer Zone (MTZ) (cm) | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70 | 5 | 35 | 1100 | 4.84 | 14.54 |
| 8 | 50 | 1220 | 7.67 | 19.45 | |
| 12 | 75 | 1260 | 11.29 | 27.44 | |
| 36 | 5 | 60 | 1320 | 4.77 | 19.33 |
| 8 | 110 | 2220 | 7.60 | 26.10 | |
| 12 | 175 | 2340 | 11.10 | 29.53 | |
| 16 | 5 | 125 | 3360 | 4.81 | 20.23 |
| 8 | 230 | 3540 | 7.48 | 29.32 | |
| 12 | 310 | 3960 | 11.06 | 42.30 |
| Flow Rate mL/h | Fitted Equation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70 | 5 | 2.82 | 8938.78 | 0.9287 | |
| 8 | 2.38 | 5818.95 | 0.927 | ||
| 12 | 2.27 | 4193.16 | 0.9167 | ||
| 36 | 5 | 1.61 | 5108.01 | 0.9871 | |
| 8 | 1.14 | 3333.68 | 0.9615 | ||
| 12 | 0.96 | 2676.19 | 0.953 | ||
| 16 | 5 | 2.28 | 1134 | 0.99 | |
| 8 | 2.33 | 925.59 | 0.97 | ||
| 12 | 2.4 | 705.94 | 0.94 |
| Flow Rate (mL/h) | Z (cm) | Fitted Equation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70 | 5 | 1.14 | 1.2 | 0.99 | y = −0.1092x + 0.9765 |
| 8 | 1.25 | 0.93 | 0.96 | y = −0.0749x + 0.9845 | |
| 12 | 1.81 | 0.87 | 0.98 | y = −0.1739x + 2.3439 | |
| 36 | 5 | 0.71 | 1.25 | 0.9 | y = −0.1199x + 1.5615 |
| 8 | 1.05 | 1.06 | 0.95 | y = −0.1008x + 2.4854 | |
| 12 | 1.06 | 0.62 | 0.98 | y = −0.1015x + 2.6268 | |
| 16 | 5 | 1.01 | 1.09 | 0.92 | y = −0.1193x + 1.5221 |
| 8 | 1.05 | 0.76 | 0.94 | y = −0.1334x + 2.0116 | |
| 12 | 1.1 | 0.52 | 0.90 | y = −0.2427x + 3.2833 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Mahbashi, N.M.Y.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Bilad, M.R.; Huda, N.; Kobun, R.; Noor, A.; Jagaba, A.H.; Al-Nini, A.; Ghaleb, A.A.S.; Al-dhawi, B.N.S. Bench-Scale Fixed-Bed Column Study for the Removal of Dye-Contaminated Effluent Using Sewage-Sludge-Based Biochar. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6484. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116484
Al-Mahbashi NMY, Kutty SRM, Bilad MR, Huda N, Kobun R, Noor A, Jagaba AH, Al-Nini A, Ghaleb AAS, Al-dhawi BNS. Bench-Scale Fixed-Bed Column Study for the Removal of Dye-Contaminated Effluent Using Sewage-Sludge-Based Biochar. Sustainability. 2022; 14(11):6484. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116484
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Mahbashi, Najib Mohammed Yahya, Shamsul Rahman Mohamed Kutty, Muhammad Roil Bilad, Nurul Huda, Rovina Kobun, Azmatullah Noor, Ahmad Hussaini Jagaba, Ahmed Al-Nini, Aiban Abdulhakim Saeed Ghaleb, and Baker Nasser Saleh Al-dhawi. 2022. "Bench-Scale Fixed-Bed Column Study for the Removal of Dye-Contaminated Effluent Using Sewage-Sludge-Based Biochar" Sustainability 14, no. 11: 6484. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116484
APA StyleAl-Mahbashi, N. M. Y., Kutty, S. R. M., Bilad, M. R., Huda, N., Kobun, R., Noor, A., Jagaba, A. H., Al-Nini, A., Ghaleb, A. A. S., & Al-dhawi, B. N. S. (2022). Bench-Scale Fixed-Bed Column Study for the Removal of Dye-Contaminated Effluent Using Sewage-Sludge-Based Biochar. Sustainability, 14(11), 6484. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116484










