Financial-Economic Analysis of Cultural Companies in Small and Medium-Sized Cities in Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Cultural Sector in Spain: Urban Concentration and Neglect of Small and Medium Cities
3. Data, Methodology and Hypotheses
- (1)
- Distinctive financial-economic characteristics of companies will exist depending on the sub-sector in which they operate.
- (2)
- Certain financial-economic variables of the companies will permit profiles of the various culture sub-sectors to be drawn.
- (3)
- Significant differences in the financial-economic variables will be found between intra- and extra-metropolitan cities.
4. Financial-Economic Analysis of Cultural Companies
5. Differentiating Features in the Financial-Economic Structure of Cultural Companies
5.1. Results of the Factor Analysis
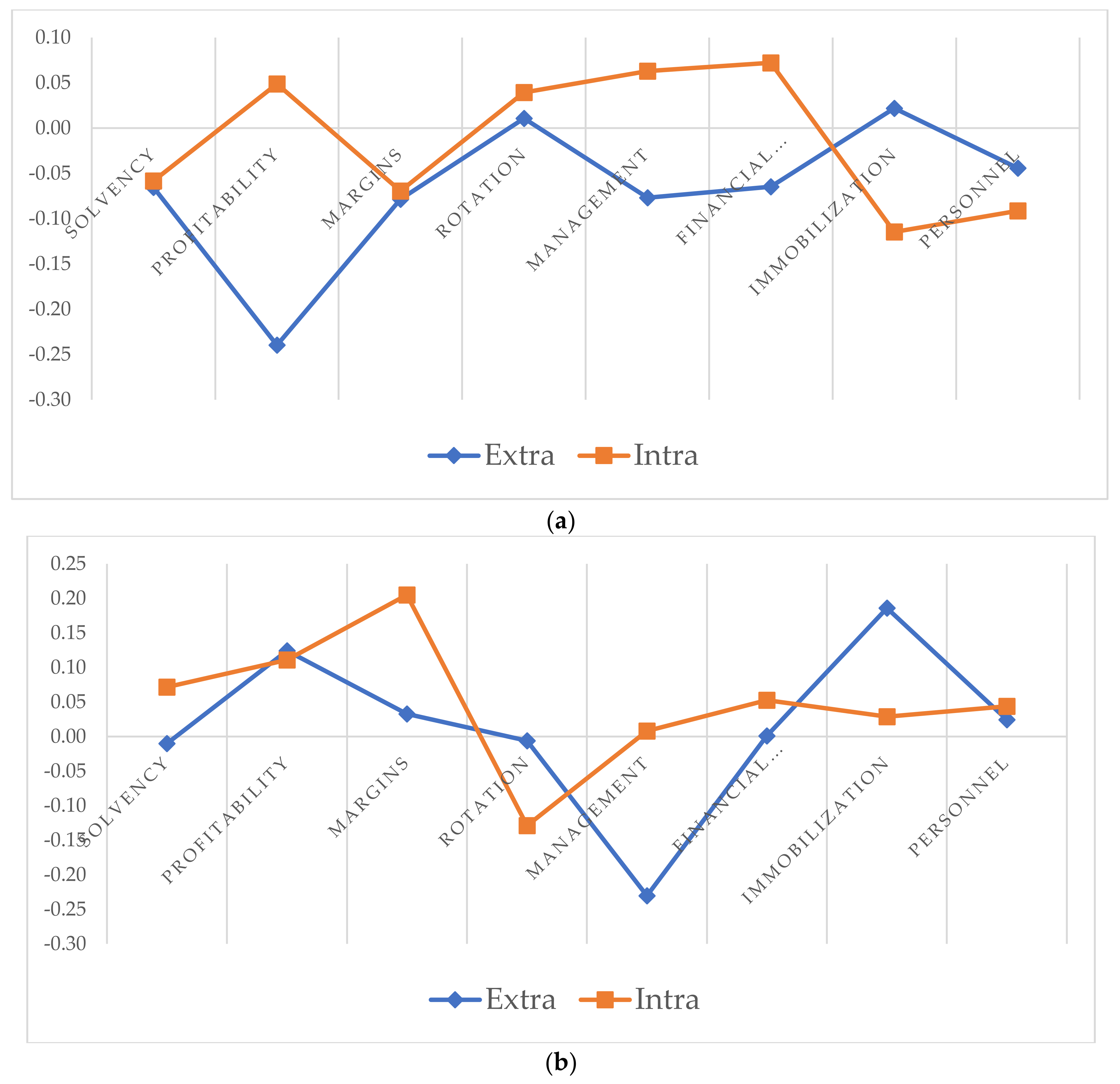
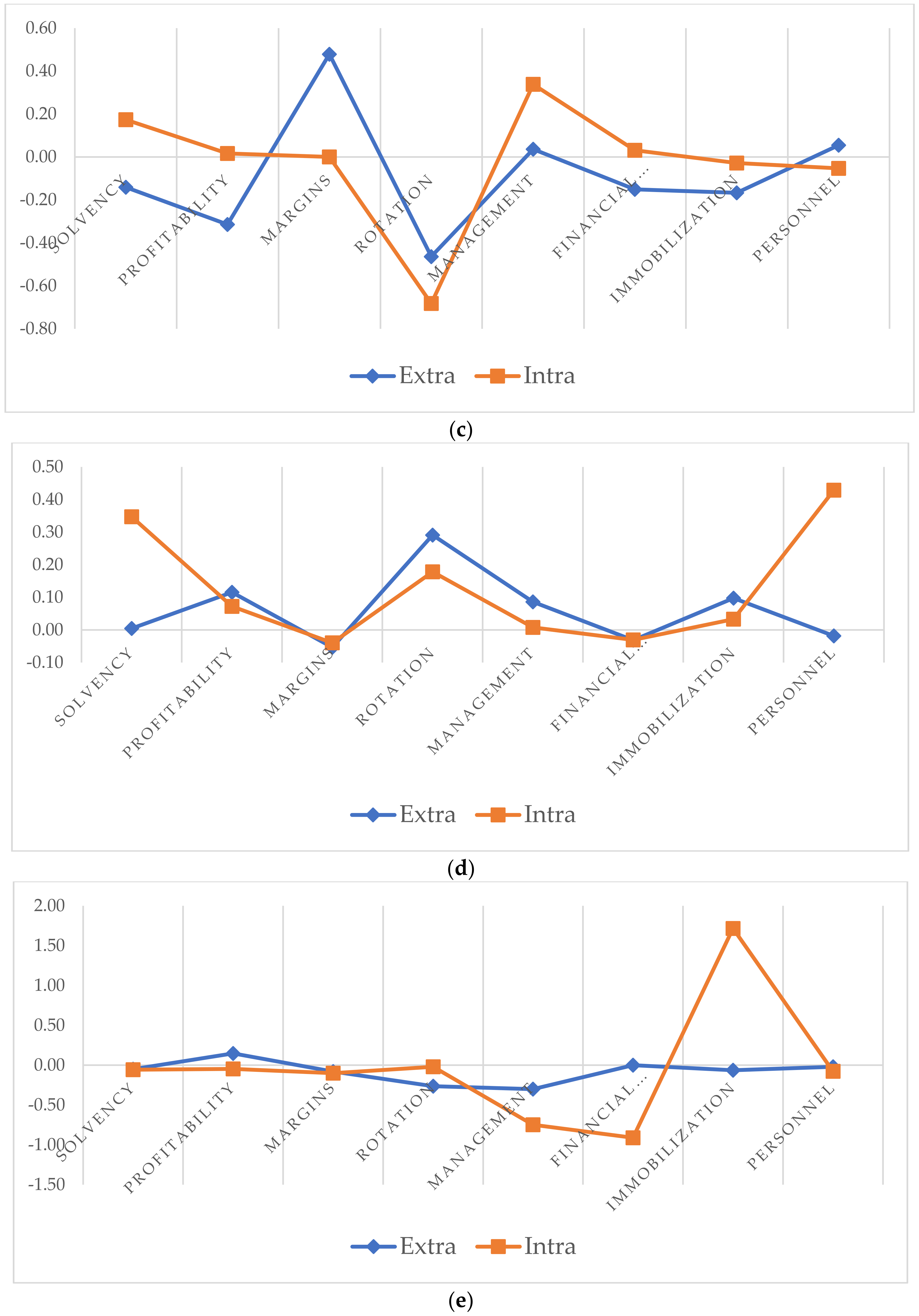
5.2. The Intra–Extra-Metropolitan Situation as a Factor of Differentiation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Province | Municipality | Extra- vs. Intra-Metropolitan City |
|---|---|---|
| A Coruña | FERROL | Extra |
| SANTIAGO DE COMPOSTELA | Extra | |
| Albacete | ALBACETE | Extra |
| Alicante | ALCOY/ALCOI | Extra |
| BENIDORM | Extra | |
| ELDA | Extra | |
| ORIHUELA | Extra | |
| TORREVIEJA | Extra | |
| Almería | ALMERIA | Extra |
| EL EJIDO | Extra | |
| ROQUETAS DE MAR | Extra | |
| Asturias | AVILES | Intra |
| SIERO | Intra | |
| Avila | AVILA | Extra |
| Badajoz | BADAJOZ | Extra |
| MERIDA | Extra | |
| Barcelona | CASTELLDEFELS | Intra |
| CERDANYOLA DEL VALLES | Intra | |
| CORNELLA DE LLOBREGAT | Intra | |
| EL PRAT DE LLOBREGAT | Intra | |
| GRANOLLERS | Intra | |
| MANRESA | Extra | |
| MATARO | Intra | |
| MOLLET DEL VALLES | Intra | |
| RUBI | Intra | |
| SANT BOI DE LLOBREGAT | Intra | |
| SANT CUGAT DEL VALLES | Intra | |
| SANTA COLOMA DE GRAMENET | Intra | |
| SITGES | Intra | |
| VILADECANS | Intra | |
| VILANOVA I LA GELTRU | Extra | |
| Burgos | BURGOS | Extra |
| Cáceres | CACERES | Extra |
| Cádiz | ALGECIRAS | Extra |
| CADIZ | Intra | |
| CHICLANA DE LA FRONTERA | Intra | |
| EL PUERTO DE SANTA MARIA | Intra | |
| LA LINEA DE LA CONCEPCION | Extra | |
| SAN FERNANDO | Intra | |
| SANLUCAR DE BARRAMEDA | Extra | |
| Cantabria | SANTANDER | Extra |
| TORRELAVEGA | Extra | |
| Castellón | VILA-REAL | Extra |
| Ciudad Real | CIUDAD REAL | Extra |
| Cuenca | CUENCA | Extra |
| Girona | GIRONA | Extra |
| TORRENT | Intra | |
| Granada | MOTRIL | Extra |
| Guadalajara | GUADALAJARA | Extra |
| Guipuzcoa | DONOSTIA-SAN SEBASTIAN | Extra |
| IRUN | Extra | |
| Huelva | HUELVA | Extra |
| Huesca | HUESCA | Extra |
| Jaen | JAEN | Extra |
| LINARES | Extra | |
| La Rioja | LOGROÑO | Extra |
| Las Palmas de Gran Canaria | ARRECIFE | Extra |
| SAN BARTOLOME DE TIRAJANA | Extra | |
| SANTA LUCIA DE TIRAJANA | Extra | |
| TELDE | Intra | |
| León | LEON | Extra |
| PONFERRADA | Extra | |
| Lleida | LLEIDA | Extra |
| Lugo | LUGO | Extra |
| Madrid | ALCALA DE HENARES | Intra |
| ALCOBENDAS | Intra | |
| ALCORCON | Intra | |
| ARANJUEZ | Extra | |
| ARGANDA DEL REY | Intra | |
| BOADILLA DEL MONTE | Intra | |
| COLLADO VILLALBA | Intra | |
| COSLADA | Intra | |
| FUENLABRADA | Intra | |
| GETAFE | Intra | |
| LAS ROZAS DE MADRID | Intra | |
| LEGANES | Intra | |
| MAJADAHONDA | Intra | |
| PARLA | Intra | |
| PINTO | Intra | |
| POZUELO DE ALARCON | Intra | |
| RIVAS-VACIAMADRID | Intra | |
| SAN SEBASTIAN DE LOS REYES | Intra | |
| TORREJON DE ARDOZ | Intra | |
| VALDEMORO | Intra | |
| Málaga | BENALMADENA | Extra |
| ESTEPONA | Extra | |
| FUENGIROLA | Extra | |
| MARBELLA | Extra | |
| MIJAS | Extra | |
| TORREMOLINOS | Extra | |
| VELEZ-MALAGA | Extra | |
| Murcia | LORCA | Extra |
| MOLINA DE SEGURA | Intra | |
| Ourense | OURENSE | Extra |
| Palencia | PALENCIA | Extra |
| Pontevedra | PONTEVEDRA | Extra |
| Salamanca | SALAMANCA | Extra |
| Santa Cruz de Tenerife | ARONA | Extra |
| SAN CRISTOBAL DE LA LAGUNA | Intra | |
| Segovia | SEGOVIA | Extra |
| Sevilla | ALCALA DE GUADAIRA | Intra |
| DOS HERMANAS | Intra | |
| UTRERA | Extra | |
| Tarragona | REUS | Extra |
| TARRAGONA | Extra | |
| Toledo | TALAVERA DE LA REINA | Extra |
| TOLEDO | Extra | |
| Valencia | GANDIA | Extra |
| PATERNA | Intra | |
| SAGUNTO/SAGUNT | Extra | |
| TORRENT | Intra | |
| Vizcaya | BARAKALDO | Intra |
| GETXO | Intra | |
| Zamora | ZAMORA | Extra |
References
- Scott, A.J. The Cultural Economy of Cities. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 1997, 21, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, P. Creative Cities and Economic Development. Urban Stud. 2000, 37, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.J. Creative Cities: Conceptual Issues and Policy Questions. J. Urban Aff. 2006, 28, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, A.C.; Jeffcutt, P. (Eds.) Creativity, innovation and the cultural economy: Snake oil for the twenty-first century? In Creativity, Innovation and the Cultural Economy; Routledge: London, UK, 2009; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Green Paper-Unlocking the Potential of Cultural and Creative Industries; COM (2010)183; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2010; Available online: https://op.europa.eu/es/publication-detail/-/publication/1cb6f484-074b-4913-87b3-344ccf020eef/language-en (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Herrero Prieto, L.C. La contribución de la cultura y las artes al desarrollo económico regional. Investig. Reg. 2011, 19, 177–202. [Google Scholar]
- Sacco, P.; Ferilli, G.; Blessi, G.T. Understanding culture-led local development: A critique of alternative theoretical explanations. Urban Stud. 2013, 51, 2806–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés-Ochoa, E.; Canizalez-Ramírez, P.M. Industrias culturales y crecimiento económico. Un modelo para el estudio del surgimiento de clusters creativos. Econ. Soc. Territ. 2015, 15, 185–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lazzeretti, L.; Capone, F.; Innocenti, N. Exploring the intellectual structure of creative economy research and local economic development: A co-citation analysis. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2017, 25, 1693–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murciano, M.; González Saavedra, C. Las industrias culturales y creativas en España: Una aproximación cuantitativa. In Las Industrias Culturales Y Creativas En Iberoamérica: Evolución Y Perspectivas; Cátedra Iberoamericana ‘Alejandro Roemmers’ de Industrias Culturales y Creativas de la Universidad Miguel Hernández de Elche, Fundación Iberoamericana de Industrias Culturales y Creativas, Eds.; Facultad de Ciencias Sociales y Jurídicas: Elche, Spain, 2018; pp. 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- Naciones Unidas. Resolución Aprobada Por La Asamblea General El 19 De Diciembre De 2019 (Sobre La Base Del Informe De La Segunda Comisión (A/74/379)); Naciones Unidas: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, P.; Lazzeretti, L. Creative Cities, Cultural Clusters and Local Economic Development; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Moral, S.; Díez-Pisonero, R.; Gago-García, C.; Arellano-Espinar, A. Sectores estratégicos en la economía del conocimiento y desarrollo en la ciudad de Madrid y su región. Rev. Estud. Andal. 2019, 8, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommaas, H. Cultural Clusters and the Post-industrial City: Towards the Remapping of Urban Cultural Policy. Urban Stud. 2004, 41, 507–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorentzen, M.; Frederiksen, L. Why do cultural industries cluster? Localization, urbanization, products and projects. In Creative Cities, Cultural Clusters and Local Economic Development; Cooke, P., Lazzeretti, L., Eds.; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2008; pp. 155–179. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzeretti, L.; Boix, R.; Capone, F. Why Do Creative Industries Cluster? An Analysis of the Determinants of Clustering of Creative In-Dustries; Working Paper in Economics, nº 09.02, 2009; Institut d’Estudis Regionals i Metropolitans de Barcelona (IERMB): Barcelona, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez Barquero, A. Industrialización endógena en áreas rurales. Crisis, autonomías y desarrollo regional. In Actas del IX Reunión de Estudios Regionales; Servizo de Publicacións e Intercambio Científico de la USC, Ed.; Universidade de Santiago de Compostela: Galicia, Spain, 1985; pp. 113–145. [Google Scholar]
- Escalona-Orcao, A.; García, B.S.-V.; Navarro-Pérez, M.; Pinillos-García, M.; Conejos-Sevillano, A. Cultural Dynamism and Business Vitality in Medium-Sized Cities—Evidence and Proposals for Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrado, D.; Escalona, A.; Escolano, S.; Sánchez, B. Creative clusters outside and within metropolitan areas: A comparative analysis. In Proceedings of the Fifth Global Conference on Economic Geography of Creative Industries IV (Session 97), Köln, Germany, 24–28 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Montalto, V.; Moura, C.J.T.; Langedijk, S.; Saisana, M. Culture counts: An empirical approach to measure the cultural and creative vitality of European cities. Cities 2019, 89, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boal San Miguel, I. Cultura, Creatividad y Disparidades Territoriales: Nuevas Perspectivas de Análisis. Ph.D. Thesis, Departamento de Economía Aplicada, Universidad de Valladolid, Valladolid, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Boal, I.; Herrero, L.C. Where are the artists? Analysing economies of agglomeration in Castile and León, Spain. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2017, 97, 995–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, I.B.-S.; Herrero-Prieto, L. A Spatial–Temporal Analysis of Cultural and Creative Industries with Micro-Geographic Disaggregation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorentzen, A.; van Heur, B. (Eds.) Introduction: Cultural political economy of small cities. In Cultural Political Economy of Small Cities; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Statistics on Cultural Industries: Framework for the Elaboration of National Data Capacity Building Projects; UNESCO: Bangkok, Thailand, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio de Cultura y Deporte. Cuenta Satélite de la Cultura en España 2019; MCD: Madrid, Spain, 2020.
- Ministerio de Cultura y Deporte. Anuario de Estadísticas Culturales 2020; MCD: Madrid, Spain, 2021.
- Boix, R.; Lazzeretti, L. Las industrias creativas en España: Una panorámica. Investig. Reg. J. Reg. Res. 2012, 22, 181–206. [Google Scholar]
- Gámir, A. La industria cultural y los grupos multimedia en España, estructura y pautas de distribución territorial. An. Geogr. Ucm 2005, 25, 179–202. [Google Scholar]
- García García, A.; Fernández Salinas, V.; Caravaca Barroso, I.; González Romero, G. Cultural resources and creative industries in Spanish medium-sized cities. Braz. Geogr. J. Geosci. Humanit. Res. Medium 2012, 3, 50–69. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzeretti, L.; Parrilli, M.D.; Cooke, P.; Curbelo, J. New focus of economic reactivation in Spain: Creative industries in the Basque country. In Innovation, Global Change and Territorial Resilience; Cooke, P., Davide, M., Curbelo, J., Eds.; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, R.; Sánchez, S.; Abad, L.; García, I. Sistema urbano y sociedad del conocimiento: Hacia una tipología de las ciudades españolas. Investig. Reg. J. Reg. Res. 2009, 16, 117–142. [Google Scholar]
- Méndez, R.; Michelini, J.J.; Prada, J.; Tébar, J. Economía creativa y desarrollo urbano en España: Una aproximación a sus lógicas espaciales. EURE 2012, 38, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelini, J.; Méndez, R. Economía creativa y estrategias de promoción en la región metropolitana de Madrid. In Crisis Económica e Impactos Territoriales; AGE y University de Girona: Girona, Spain, 2012; pp. 370–391. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero, G.; Navarro, C. Industrias culturales en ciudades españolas. Un primer acercamiento. Rev. Estud. Reg. 2012, 94, 71–103. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, D.; Jayne, M. (Eds.) Conceptualizing small cities. In Small Cities: Urban Experience beyond the Metropolis; Routledge: London, UK, 2006; pp. 15–32. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, G.; Foord, J. Small cities for a small country: Sustaining the cultural renaissance? In Small Cities: Urban Experience beyond the Metropolis; Bell, D., Jayne, M., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2006; pp. 151–168. [Google Scholar]
- Selada, C.; Cunha, I.; Tomaz, E. Creative-based strategies in small cities: A case-study approach. Redige 2011, 2, 79–111. [Google Scholar]
- Barrado-Timón, D.; Palacios, A.; Hidalgo-Giralt, C. Medium and Small Cities, Culture and the Economy of Culture. A Review of the Approach to the Case of Spain in Light of International Scientific Scholarship. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Indicadores Cultura 2030; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2020; Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000373570 (accessed on 27 April 2021).
- Escalona-Orcao, A.; Barrado-Timón, D.A.; Escolano-Utrilla, S.; Sánchez-Valverde, B.; Navarro-Pérez, M.; Pinillos-García, M.; Sáez-Pérez, L.A. Cultural and Creative Ecosystems in Medium-Sized Cities: Evolution in Times of Economic Crisis and Pandemic. Sustainability 2020, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ayuso, M. Técnicas de análisis factorial aplicadas al análisis de la información financiera: Fundamentos, limitaciones, hallazgo y evidencia empírica española. Rev. Española Financ. Contab. 1996, 86, 57–101. [Google Scholar]
- Muro, R. Dos años de estancamiento previos a la pandemia. Un nuevo punto de partida. In Informe Sobre las Artes Escénicas En España: Distribución, Programación Y Públicos; Academia de las Artes Escénicas en España, Ed.; Academia de las Artes Escénicas en España: Madrid, Spain, 2020; pp. 11–21. [Google Scholar]


| Indicator (a) | Absolute Value | % of National Total (Spain) |
|---|---|---|
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP) (b) | €29,432 million (cultural activities) €40,838 million (activities related to intellectual property) | 2.4% (cultural activities) 3.4% (activities related to intellectual property) |
| Gross Value Added (GVA) (b) | €28,181 million (cultural activities) €38,631 million (activities related to intellectual property) | 2.6% (cultural activities) 3.3% (activities related to intellectual property) |
| Employment | 710,200 persons | 3.6% (of total employment in Spain) |
| Number of businesses | 127,581 | 3.8% (of national companies) |
| Public investment (liquidated expenditure on culture) (b) | €696 million (Central Administration) €1178 million (Autonomous Community Administrations) €3476 million (Local Administrations) | 0.06% of GDP 0.10% of GDP 0.29% of GDP |
| Household cultural consumption expenditure | €12,451.5 million | 2.2% of the total estimated expenditure on goods and services |
| Foreign trade of cultural goods | €2054.4 million (Exports) €2165.0 million (Imports) | 0.7% of total Exports 0.7% of total Imports |
| Criteria | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Balance Sheet | Annual Turnover | Staff | |
| Micro | <1,000,000 € | <2,000,000 € | <10 |
| Small | <10,000,000 € | <10,000,000 € | <50 |
| Medium | <43,000,000 € | <50,000,000 € | <250 |
| Large | ≥43,000,000 € | ≥50,000,000 € | ≥250 |
| Statistics | Age in Years of the Company | Size of the Company | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microbusiness | Small | Medium | Large | ||
| Mean | 16 | 16 | 23 | 27 | 23 |
| Median | 15 | 15 | 22 | 20 | 24 |
| Maximum | 100 | 82 | 82 | 100 | 37 |
| Minimum | 1 | 1 | 2 | 10 | 3 |
| Standard deviation | 10 | 9 | 13 | 20 | 12 |
| No. of firms | 2543 | 2318 | 195 | 23 | 7 |
| CNAE Code 2009 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | 59 | 60 | 90 | 91 | |
| Leverage coefficient, liquidity, and solvency | |||||
| Leverage coefficient (%) | 83.008 | 106.052 | 97.959 | 97.255 | 66.402 |
| Cost of Debt ratio (%) | 2.077 | 4.034 | 1.205 | 7.381 | 1.391 |
| Guarantee ratio (%) | 1.472 | 1.632 | 2.122 | 1.540 | 2.521 |
| Debt Quality ratio (%) | 76.418 | 78.395 | 81.060 | 78.738 | 79.125 |
| Financial Expenses on Sales (%) | 1.896 | 114.693 | 18.911 | 2.594 | 1.107 |
| Liquidity ratio (%) | 1.080 | 1.254 | 1.685 | 1.241 | 1.171 |
| Solvency ratio (%) | 4.965 | 8.314 | 7.461 | 22.641 | 4.386 |
| Short-term Solvency (%) | 3.832 | 8.061 | 7.520 | 23.058 | 4.684 |
| Acid Test (%) | 1.069 | 1.264 | 1.707 | 1.241 | 1.255 |
| Payment Period (days) | 149.593 | 637.322 | 767.747 | 392.308 | 153.293 |
| Working Capital ratio (%) | 16.050 | 15.600 | 21.850 | 14.200 | 14.950 |
| Self-financing ratio generated by Assets (%) | 0.167 | 4.772 | −0.197 | −6.627 | −3.708 |
| Self-financing ratio generated by Sales (%) | −0.011 | −151.228 | −284.207 | 1.719 | 2.508 |
| Efficiency | |||||
| Personnel expenses (%) | 22.299 | 86.229 | 19.641 | 79.608 | 15.303 |
| Worker Costs over Operating Income (%) | 36.746 | 61.786 | 141.135 | 69.537 | 48.380 |
| Fixed Assets ratio (%) | 32.336 | 326.123 | 8.563 | 74.208 | 143.281 |
| Sales ratio over Total Assets (%) | 1.391 | 1.238 | 0.962 | 1.685 | 1.489 |
| Ratio of Participation of Current Assets over Total Assets (%) | 61.857 | 60.381 | 62.853 | 62.128 | 54.546 |
| Profitability | |||||
| Economic Profitability (ROA) (%) | 3.920 | 4.954 | 3.623 | 5.804 | 8.870 |
| Operating Profitability (%) | 6.199 | 6.418 | 6.316 | 5.589 | 2.435 |
| Financial Profitability (ROE) (%) | 7.941 | 10.406 | 8.025 | 11.331 | 3.607 |
| Asset Turnover ratio | 1.089 | 0.718 | 0.614 | 1.095 | 0.829 |
| Profit Margin (%) | 0.036 | 0.069 | 0.059 | 0.053 | 0.107 |
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy | 0.735 | |
|---|---|---|
| Bartlett’s test of sphericity | Approx. Chi squared | 65,587.616 |
| gl | 231 | |
| Sig. | 0.000 | |
| Variables | Commonality | Factors | Own Value | % of Variation | % Accumulated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leverage coefficient (%) | 0.603 | 1 | 6.037 | 26.246 | 26.246 |
| Cost of Debt ratio (%) | 0.793 | 2 | 4.474 | 19.453 | 45.699 |
| Guarantee ratio (%) | 0.901 | 3 | 3.296 | 14.331 | 60.031 |
| Debt Quality ratio (%) | 0.597 | 4 | 2.167 | 9.421 | 69.452 |
| Financial Expenses on Sales (%) | 0.754 | 5 | 1.151 | 5.006 | 74.458 |
| Liquidity ratio (%) | 0.969 | 6 | 0.992 | 4.312 | 78.770 |
| Solvency ratio (%) | 0.968 | 7 | 0.975 | 4.239 | 83.009 |
| Short-term Solvency (%) | 0.968 | 8 | 0.950 | 4.132 | 87.142 |
| Acid Test (%) | 0.969 | ||||
| Payment Period (days) | 0.760 | ||||
| Working Capital ratio (%) | 0.748 | ||||
| Personnel expenses (%) | 0.992 | ||||
| Worker Costs over Operating Income (%) | 0.831 | ||||
| Fixed Assets ratio (%) | 0.934 | ||||
| Sales ratio over Total Assets (%) | 0.983 | ||||
| Self-financing ratio generated by Assets (%) | 0.945 | ||||
| Self-financing ratio generated by Sales (%) | 0.827 | ||||
| Ratio of Participation of Current Assets over Total Assets (%) | 0.761 | ||||
| Economic Profitability (ROA) (%) | 0.939 | ||||
| Operating Profitability (%) | 0.946 | ||||
| Financial Profitability (ROE) (%) | 0.968 | ||||
| Asset Turnover ratio (%) | 0.983 | ||||
| Profit Margin (%) | 0.903 |
| Factor 1. Solvency | Factor 2. Profitability | Factor 3. Margins | Factor 4. Rotation | ||||
| Liquidity ratio | 0.972 | Operating Profitability | 0.963 | Profit Margin | −0.926 | Sales ratio over Total Assets | 0.962 |
| Acid Test | 0.972 | Self-financing ratio generated by Assets | 0.963 | Worker Costs over Operating Income | 0.892 | Asset Turnover ratio | 0.962 |
| Solvency ratio | 0.971 | Economic Profitability (ROA) | 0.961 | Self-financing ratio generated by Sales | −0.876 | ||
| Short-term Solvency | 0.971 | Working Capital ratio | 0.744 | Payment Period | 0.845 | ||
| Guarantee ratio | 0.949 | Leverage coefficient | −0.711 | Financial Expenses on Sales | 0.843 | ||
| Cost of Debt ratio | 0.888 | ||||||
| Factor 5. Management | Factor 6. Financial Structure | Factor 7. Inmobilization | Factor 8. Personnel | ||||
| Ratio of Participation of Current Assets over Total Assets | 0.842 | Financial Profitability (ROE) | 0.981 | Fixed Assets ratio | 0.959 | Personnel expenses | 0.994 |
| Debt Quality ratio | 0.735 | ||||||
| Wilks’ Lambda | F | gl1 | gl2 | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solvency | 0.993 | 2.088 | 4 | 1276 | 0.080 |
| Profitability | 0.991 | 2.816 | 4 | 1276 | 0.024 |
| Margins | 0.987 | 4.360 | 4 | 1276 | 0.002 |
| Rotation | 0.964 | 11.844 | 4 | 1276 | 0.000 |
| Management | 0.992 | 2.694 | 4 | 1276 | 0.030 |
| Financial Structure | 0.997 | 1.111 | 4 | 1276 | 0.350 |
| Immobilization | 0.987 | 4.345 | 4 | 1276 | 0.002 |
| Personnel | 0.991 | 2.832 | 4 | 1276 | 0.024 |
| CNAE Code 2009 | Predicted Group Membership | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | 59 | 60 | 90 | 91 | |||
| Original | % | 18 | 99.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.4 |
| 59 | 95.7 | 0.4 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1.2 | ||
| 60 | 93.9 | 0.0 | 5.1 | 1.0 | 0.0 | ||
| 90 | 94.9 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 4.3 | 0.4 | ||
| 91 | 91.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 8.7 | ||
| Variables | CNAE Code 2009 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | 59 | 60 | 90 | 91 | |
| Rotation | 0.0315 (4.656%) | −0.076 (4.64%) | −0.572 (20.42%) | 0.254 (14.46%) | −0.170 (3.91%) |
| Immobilization | −0.068 (10.42%) | 0.103 (6.25%) | −0.121 (4.31%) | 0.072 (4.12%) | 0.644 (14.77%) |
| Personnel | −0.076 (11.56%) | 0.0364 (2.21%) | 0.011 (0.38%) | 0.178 (10.12%) | −0.042 (0.96%) |
| Management | 0.015 (2.25%) | −0.102 (6.17%) | 0.152 (5.44%) | 0.051 (2.92%) | −0.485 (11.12%) |
| Margins | −0.074 (11.30%) | 0.130 (7.88%) | 0.313 (11.19%) | −0.052 (2.96%) | −0.088 (2.01%) |
| Profitability | −0.053 (8.12%) | 0.118 (7.17%) | −0.199 (7.11%) | 0.101 (5,76%) | 0.077 (1.77%) |
| (Constant) | −0.656 (51.69%) | −1.647 (65.68%) | −2.801 (51.15%) | −1.756 (59.66%) | −4.361 (65.47%) |
| Tests of Equality of Group Means | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Variables | F | df1 | df2 | Sig. |
| Extra | Solvency | 1481 | 4 | 554 | 0.207 |
| Profitability | 2948 | 4 | 554 | 0.020 | |
| Margins | 6996 | 4 | 554 | 0.000 | |
| Rotation | 6328 | 4 | 554 | 0.000 | |
| Management | 1891 | 4 | 554 | 0.110 | |
| Financial Structure | 0.151 | 4 | 554 | 0.963 | |
| Immobilization | 0.896 | 4 | 554 | 0.466 | |
| Personnel | 0.892 | 4 | 554 | 0.468 | |
| Intra | Solvency | 2264 | 4 | 717 | 0.061 |
| Profitability | 0.344 | 4 | 717 | 0.848 | |
| Margins | 1559 | 4 | 717 | 0.183 | |
| Rotation | 6222 | 4 | 717 | 0.000 | |
| Management | 2379 | 4 | 717 | 0.050 | |
| Financial Structure | 5777 | 4 | 717 | 0.000 | |
| Immobilization | 15,632 | 4 | 717 | 0.000 | |
| Personnel | 3512 | 4 | 717 | 0.008 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cea-D’Ancona, F.; Sáez-Cala, A.; Palacios, A. Financial-Economic Analysis of Cultural Companies in Small and Medium-Sized Cities in Spain. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6524. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116524
Cea-D’Ancona F, Sáez-Cala A, Palacios A. Financial-Economic Analysis of Cultural Companies in Small and Medium-Sized Cities in Spain. Sustainability. 2022; 14(11):6524. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116524
Chicago/Turabian StyleCea-D’Ancona, Francisca, Antonia Sáez-Cala, and Antonio Palacios. 2022. "Financial-Economic Analysis of Cultural Companies in Small and Medium-Sized Cities in Spain" Sustainability 14, no. 11: 6524. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116524
APA StyleCea-D’Ancona, F., Sáez-Cala, A., & Palacios, A. (2022). Financial-Economic Analysis of Cultural Companies in Small and Medium-Sized Cities in Spain. Sustainability, 14(11), 6524. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116524







