Quantitative Source Apportionment and Uncertainty Analysis of Heavy Metal(loid)s in the Topsoil of the Nansi Lake Nature Reserve
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
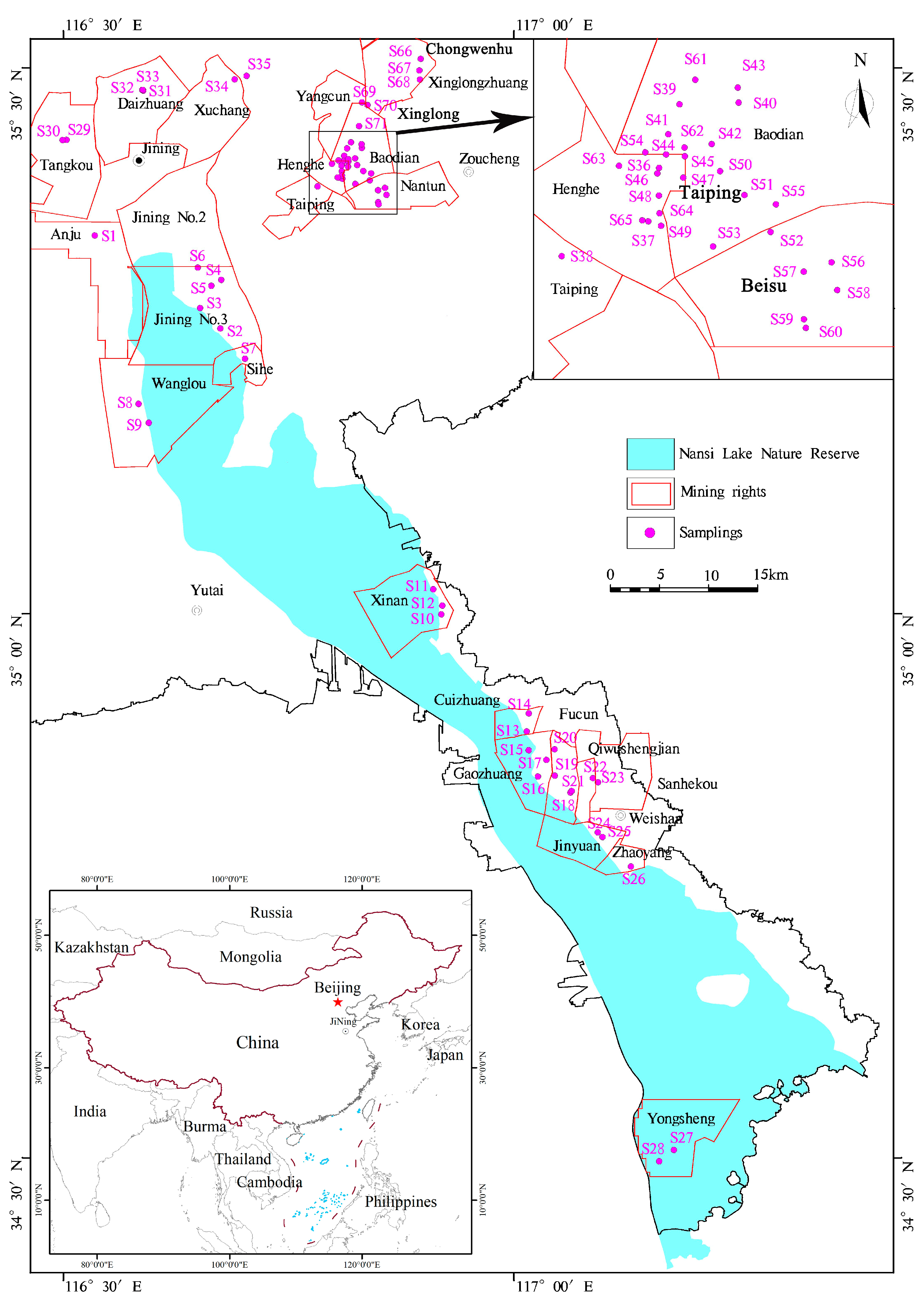
2.1. Study Area and Site Description
2.2. Sample Preparation and Chemical Analysis
2.3. Contamination Assessment and Potential Ecological Risk
2.4. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) Model Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Contamination and Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metal(loid)s
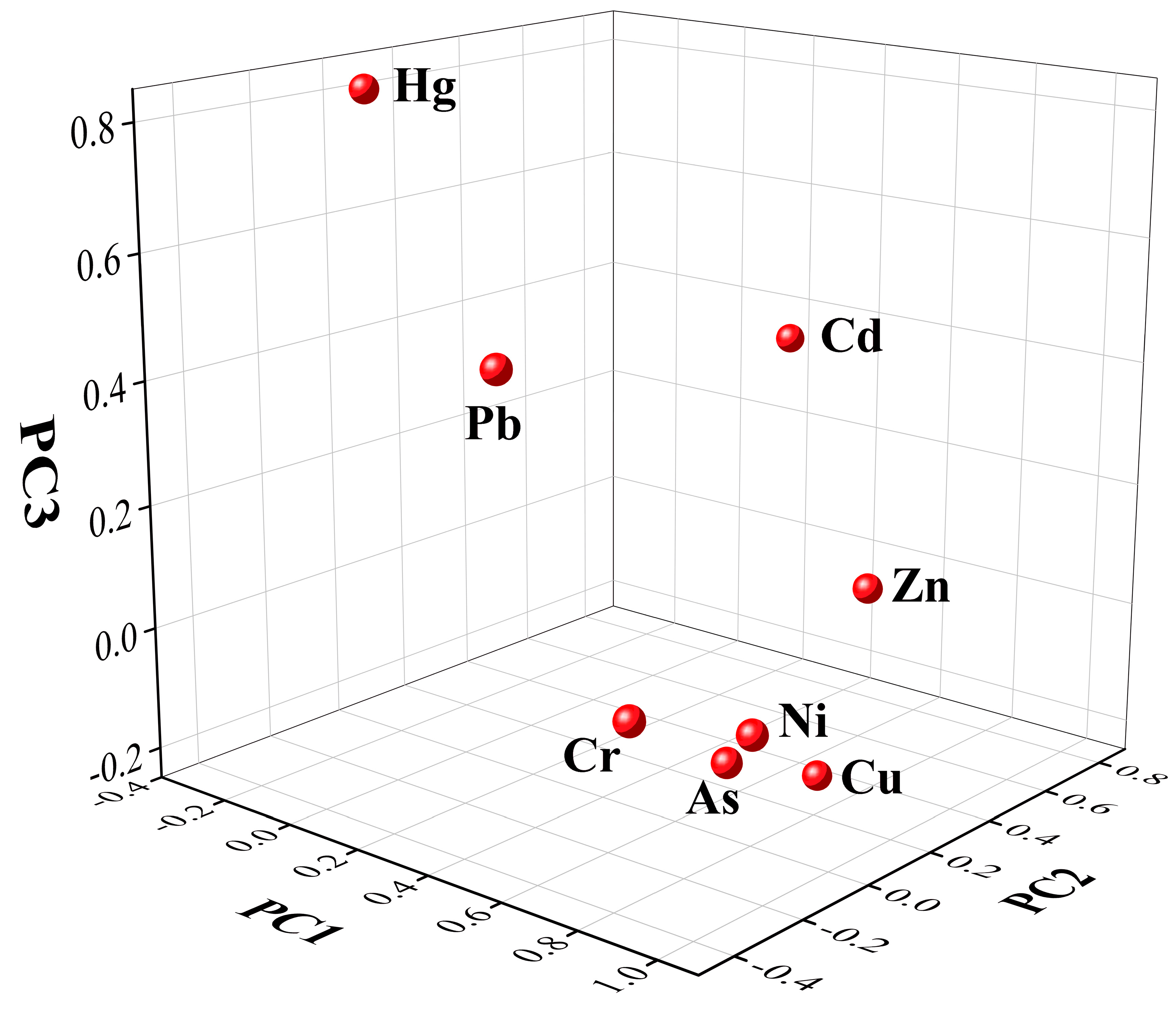
3.2. Source Identification Using PCA
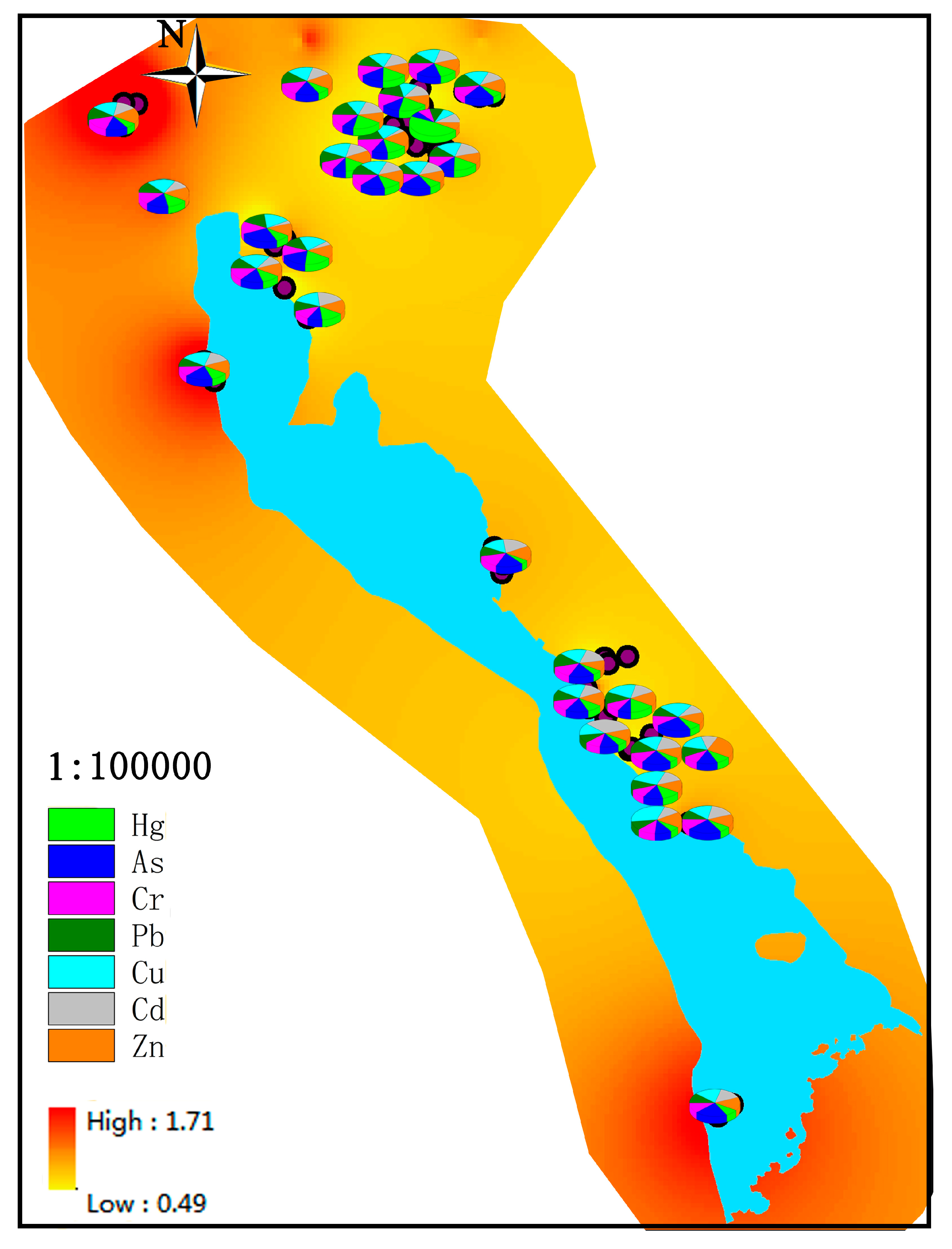
3.3. Quantitative Source Apportionment of Heavy Metal(loid)s
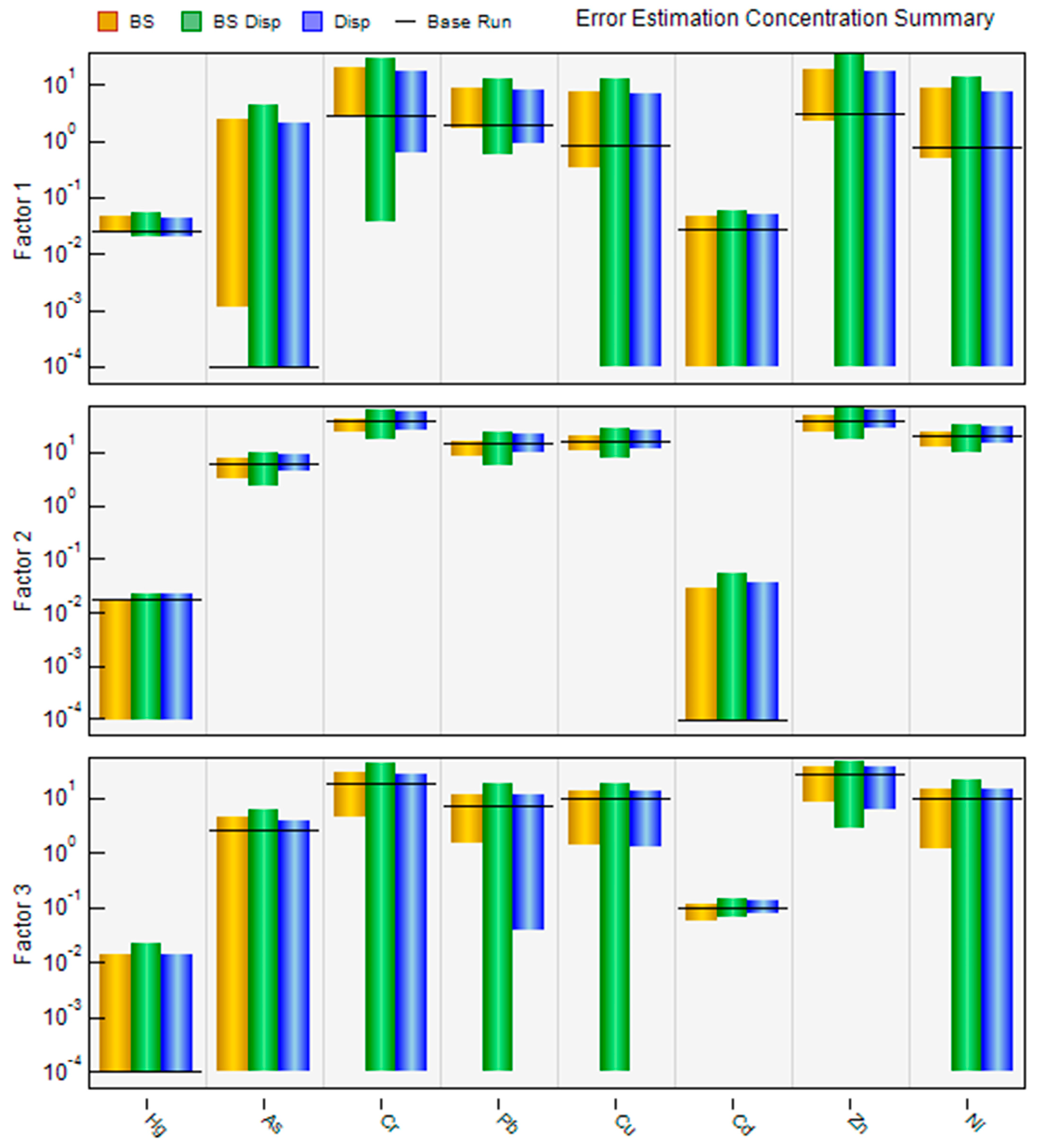
3.4. Uncertainty Analysis in Source Apportionment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). Soil Screening Guidance: User’s Guide; Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; p. 20460.
- USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). Regional screening levels (RSLs)—Generic Tables. 2019. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/regional-screening-levels-rsls-generic-tables (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Peng, S.; Dai, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Q.; Liang, B.; Zheng, T. Dynamics of ecological risks associated with heavy metal(loid)s in sediments during the construction process of the Yangtze River deepwater channel. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Gui, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Fang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of shallow groundwater in Suxian mining area, Huaibei coalfield, China. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2020, 7, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, H.; Han, J.; Jiang, B.; Gao, J. Understanding of mineral change mechanisms in coal mine groundwater reservoir and their influences on effluent water quality: A experimental study. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2020, 8, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewińska-Preis, L.; Szram, E.; Fabiańska, J.; Monika, N.A.; Misz-Kennan, M.; Abramowicz, A.; Kruszewski, Ł.; Kita, A. Selected ions and major and trace elements as contaminants in coal-waste dump water from the Lower and Upper Silesian Coal Basins (Poland). Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2021, 8, 790–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Gui, H.; Fang, P.; Li, G. Groundwater contamination and human health risk based on Monte Carlo simulation in a typical mining area in Northern Anhui Province, China. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2021, 8, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Fan, L.; Xia, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, J.; Gao, S.; Wu, B.; Peng, J.; Ji, Y. Impact of coal mining on groundwater of Luohe Formation in Binchang mining area. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2021, 8, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Shen, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, E.; Meng, X.; Wang, J. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the sediments of Nansihu Lake Catchment, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 161, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Chen, K.; Yuan, Z.; Bi, J.; Huang, L. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in surface sediments of Six Major Chinese freshwater lakes. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhuang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Jiao, K.; Wang, M.; Chen, Q. Calculation of Thallium’s toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index: A case study. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.; Samantha, C.Y.; Alexander, L.F.; Wang, Q.; Song, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Lai, X. Distribution, contamination status, and source apportionment of trace metalsin lake sediments under the influence of the South-to-North Water Transfer Project, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Shen, J.; Zhang, E.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L. A geochemical record of recent anthropogenic nutrient loading and enhanced productivity in Lake Nansihu, China. J. Paleolimnol. 2010, 44, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, L.; Bo, X. Characteristics of sediments and pore water in Lake Nansi Wetland. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2010, 31, 939–945. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Huang, G.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Li, Y. An inexact two-stage stochastic programming model for water resources management in Nansihu Lake Basin, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 127, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, W.; Sun, X.; Guo, H.; Shan, R. Comparison of the SWAT and InVEST models to determine hydrological ecosystem service spatial patterns, priorities and trade-offs in a complex basin. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blifford, I.H., Jr.; Meeker, G.O. A factor analysis model of large scale contamination. Atmos. Environ. 1967, 1, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y. Source Apportionment of PM2.5 in Atmosphere in Changchun Using PMF and PCA/APCS Methods; JiLin University: Changchun, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, J.G.; Robinson, N.F.; Chow, J.C.; Henry, R.C.; Kim, B.M.; Pace, T.G.; Meyer, E.L.; Nguyen, Q. The USEPA/DRI chemical mass balance receptor model. CMB 7.0. Environ. Softw. 1990, 5, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, S.; Saral, A.; Ertürk, F.; Kuzu, L. Combined use of Principal ComponentAnalysis (PCA) and Chemical Mass Balance (CMB) for source identification andsource apportionment in air contamination modeling studies. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 212, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, H.; Teng, Y.; Dong, J. Contamination characteristics and source apportionment of soil heavy metal(loid)s in Lalin River basin. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fang, H.; Wu, J.; Lin, J.; Lan, W.; Chen, J. Distribution and source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in farmland soils using PMF and lead isotopiccomposition. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, D.; O’ Connor, D.; Nathanail, P.; Tian, L.; Ma, Y. Integrated GIS and multi-variate statistical analysis for regional scale assessment of heavy metal soil con-tamination: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; He, K.; Sun, Z.; Chen, G.; Cheng, H. Quantitative source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in the agricultural soils of an industrializing region and associated model uncertainty. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122244. [Google Scholar]
- DZ/T 0064.1~0064.80-93; Method for Inspection of Underground Water Quality. The Geological and Mining Industry of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1993.
- HJ 803-2016; Soil and Sediment—Determination of Aqua Regia Extracts of 12 Metal Elements—Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. National Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- DZ/T 0279.3-2016; Analysis Methods for Regional Geochemical Sample—Part 3: Determination of 15 Elements including Barium, Beryllium, Bismuth, etc. by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. The Geological and Mining Industry of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- HJ 680-2013; Soil and Sediment—Determination of Mercury, Arsenic, Selenium, Bismuth, Antimony—Microwave Dissolution/Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry. National Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Wu, P.; Yang, F.; Sun, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risks in urban soils around an electronics manufacturing facility. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic contamination control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Analysis of different modes of factor analysis as least squares fit problems. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1993, 18, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.G.; Wade, K.S.; Hafner, H.R. Multivariate Receptor Modeling Workbook; Sonoma Technology Inc.: Petaluma, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, W.F.; Schauer, J.J. Impact of species uncertainty perturbation on the solution stability of positive matrix factorization of atmospheric particulate matter data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6015–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatero, P.; Eberly, S.; Brown, S.G.; Norris, G.A. Methods for estimating uncertainty in factor analytic solutions. Atmos. Meas. Techmiques 2014, 7, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polissar, A.V.; Hopke, P.K.; Paatero, P.; Malm, W.C.; Sisler, J.F. Atmospheric aerosol over Alaska 2. Elemental composition and sources. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 19045–19057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manta, D.S.; Angelone, M.; Bellanca, A.; Neri, R.; Sprovieri, M. heavy metal(loid)s inurban soils: A case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 300, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE). Soil Environmental Quality. Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Development Land (GB36600-2018); Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Nowak, B. Contents and relationship of elements in human hair for a non-in-dustrialised population in Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 209, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tri Mursito, A.; Widodo; Nor Arifin, D. Characterization of bio-coal briquettes blended from low quality coal and biomass waste treated by Garant® bio-activator and its application for fuel combustion. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2020, 7, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilal, I.; Abdugheni, A.; Shi, Q.; Liu, S.; Nijat, K.; Li, H. contamination and source identification of heavy metal(loid)s in surrounding soils of Eastern Junggar Coalfield based on PMF model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Hu, Y. Lead (Pb) isotopic fingerprinting and its applications in lead pollution studies in China: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1134–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Lin, C.; Hu, G.; Yu, R.; Hao, C.; Chen, F. Source Appointment of heavy metal(loid)s in Agricultural Soils of Jiulong River Basin Based on Positive Matrix Factorization. Environ. Sci. 2019, 41, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
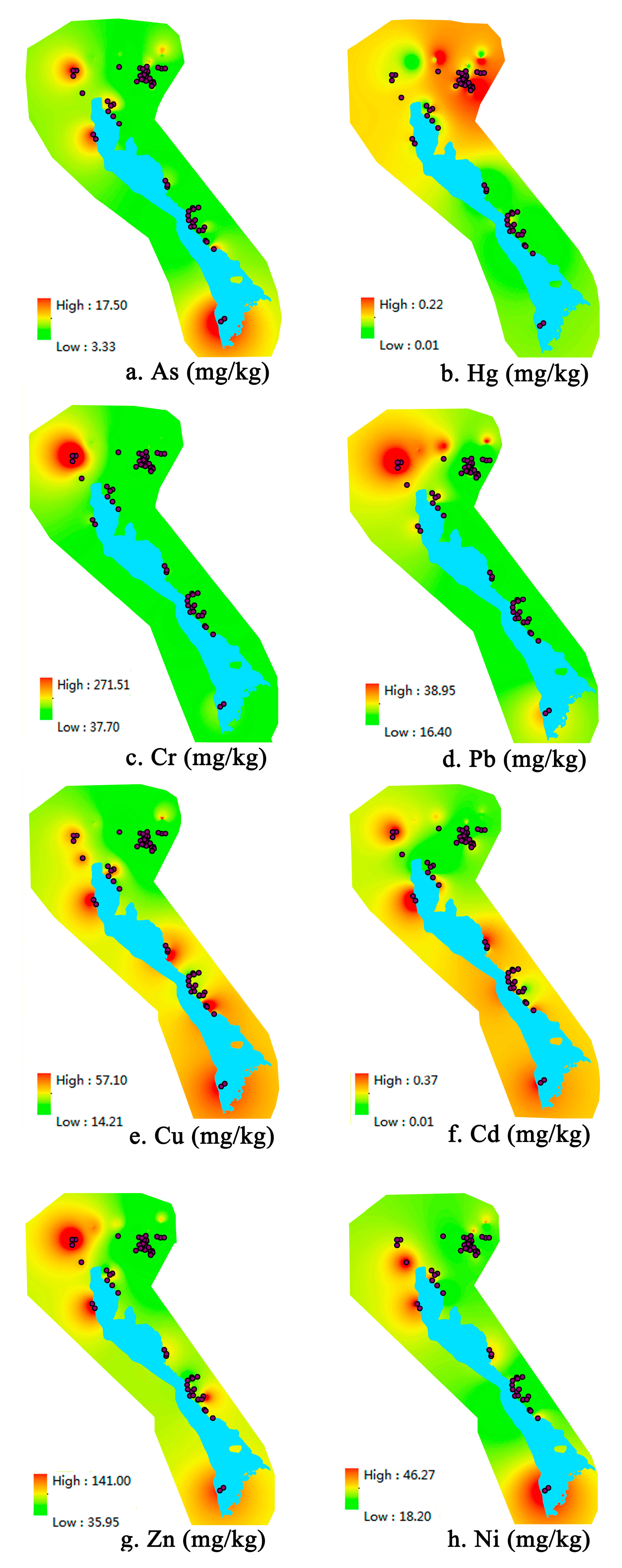


| Metal | Mean (mg/kg) | Median (mg/kg) | Min (mg/kg) | Max (mg/kg) | SD (mg/kg) | CV | BV (mg/kg) | RSV (mg/kg) | RIV (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hg | 0.043 | 0.033 | 0.014 | 0.221 | 0.033 | 0.767 | 0.042 | 38 | 82 |
| As | 9.361 | 9.180 | 3.330 | 17.500 | 3.237 | 0.346 | 8.700 | 60 | 140 |
| Cd | 0.129 | 0.130 | 0.010 | 0.370 | 0.057 | 0.446 | 0.142 | 65 | 172 |
| Cr | 62.541 | 58.330 | 37.700 | 271.510 | 27.576 | 0.441 | 64.500 | 5.7 | 78 |
| Cu | 28.542 | 27.300 | 14.210 | 57.100 | 8.851 | 0.310 | 24.200 | 18,000 | 36,000 |
| Ni | 30.008 | 28.360 | 18.200 | 46.270 | 6.683 | 0.223 | 28.300 | 900 | 2000 |
| Pb | 24.172 | 23.250 | 16.400 | 38.950 | 4.510 | 0.187 | 25.200 | 800 | 2500 |
| Zn | 70.865 | 69.400 | 35.950 | 141.000 | 20.516 | 0.290 | 64.600 | — | — |
| Sampling | Average | Potential Ecological Risk Index (Eri) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sites | RI | Very High | High | Considerable | Moderate | Low | ||
| (Location) | Eri ≥ 320 | 160 ≤ Eri < 320 | 80 ≤ Eri < 160 | 40 ≤ Eri < 80 | Eri < 40 | |||
| Risk Index (RI) | Moderate 150 ≤ RI < 300 | 5 | 182.99 | _ | _ | Hg | _ | Cd > As > Cu > Pb > Cr > Zn |
| Low RI < 150 | 68 | 85.73 | _ | _ | _ | _ | Hg > Cd > As > Cu > Pb > Cr > Zn | |
| Heavy Metal | Hg | As | Cr | Pb | Cu | Cd | Zn | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hg | 1.000 | |||||||
| As | −0.189 | 1.000 | ||||||
| Cr | −0.121 | 0.651 | 1.000 | |||||
| Pb | 0.062 | 0.243 | 0.458 | 1.000 | ||||
| Cu | −0.217 | 0.440 | 0.449 | 0.129 | 1.000 | |||
| Cd | 0.048 | 0.152 | 0.032 | 0.066 | 0.175 | 1.000 | ||
| Zn | −0.118 | 0.514 | 0.373 | 0.294 | 0.665 | 0.369 | 1.000 | |
| Ni | −0.164 | 0.781 | 0.924 | 0.403 | 0.622 | 0.159 | 0.576 | 1.000 |
| Heavy Metal | Ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | |
| Hg | −0.228 | −0.043 | 0.819 |
| As | 0.811 | −0.088 | −0.093 |
| Cr | 0.838 | −0.399 | 0.049 |
| Pb | 0.474 | −0.372 | 0.508 |
| Cu | 0.732 | 0.295 | −0.221 |
| Cd | 0.268 | 0.751 | 0.362 |
| Zn | 0.750 | 0.429 | 0.064 |
| Ni | 0.949 | −0.176 | −0.003 |
| Heavy Metal | Factor in Concentration | Contribution in Percentage (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Contribution 1 | Contribution 2 | Contribution 3 | |
| Hg | 0.02504 | 0.01723 | 0.00000 | 59.20% | 40.80% | 0.00% |
| As | 0.00005 | 6.09300 | 2.58060 | 0.00% | 70.20% | 29.80% |
| Cr | 2.76840 | 37.73500 | 18.89400 | 4.70% | 63.50% | 31.80% |
| Pb | 1.90740 | 14.37000 | 7.17350 | 8.10% | 61.30% | 30.60% |
| Cu | 0.79278 | 16.15400 | 9.83200 | 3.00% | 60.30% | 36.70% |
| Cd | 0.02591 | 0.00000 | 0.10232 | 20.20% | 0.00% | 79.80% |
| Zn | 3.00330 | 37.80700 | 26.95500 | 4.40% | 55.80% | 39.80% |
| Ni | 0.77940 | 19.99300 | 9.71800 | 2.50% | 65.60% | 31.90% |
| Factor | Heavy Metal | BS | DISP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5th | 50th | 95th | Interval Ratio | Min | Average | Max | Interval Ratio | ||
| Factor 1 | Hg | 0.0244 | 0.0325 | 0.0451 | 0.637 | 0.02504 | 0.03418 | 0.04126 | 0.475 |
| As | 0.0011 | 1.2308 | 2.4740 | 2.009 | 0.00002 | 1.16867 | 1.56590 | 1.340 | |
| Cr | 2.6323 | 10.7840 | 19.5690 | 1.571 | 2.75010 | 10.43553 | 13.78000 | 1.057 | |
| Pb | 1.6896 | 5.0176 | 8.5531 | 1.368 | 1.90080 | 5.01321 | 6.50330 | 0.918 | |
| Cu | 0.3259 | 4.1168 | 7.4248 | 1.724 | 0.77330 | 3.88880 | 5.32650 | 1.171 | |
| Cd | 0 | 0.0282 | 0.0446 | 1.582 | 0.00083 | 0.02556 | 0.03841 | 1.470 | |
| Zn | 2.2259 | 10.4550 | 18.3690 | 1.544 | 2.93200 | 10.26777 | 14.16600 | 1.094 | |
| Ni | 0.4666 | 5.0028 | 8.6742 | 1.641 | 0.77153 | 4.71017 | 6.28870 | 1.171 | |
| Factor 2 | Hg | 0 | 0.0026 | 0.0181 | 6.962 | 0 | 0.00467 | 0.01723 | 3.690 |
| As | 3.1642 | 5.2158 | 7.4058 | 0.813 | 5.15180 | 5.92057 | 7.28570 | 0.360 | |
| Cr | 23.1000 | 32.2040 | 42.4230 | 0.600 | 30.80900 | 36.01925 | 44.48800 | 0.380 | |
| Pb | 8.1691 | 12.1920 | 15.9350 | 0.637 | 11.26700 | 13.34705 | 16.34000 | 0.380 | |
| Cu | 10.7700 | 14.4090 | 19.2580 | 0.589 | 13.64000 | 15.90855 | 20.08900 | 0.405 | |
| Cd | 0 | 0.0048 | 0.0289 | 6.021 | 0 | 0.00774 | 0.02818 | 3.641 | |
| Zn | 23.7500 | 33.5330 | 46.1960 | 0.669 | 31.84300 | 37.46710 | 48.00100 | 0.431 | |
| Ni | 11.9220 | 17.2700 | 22.8240 | 0.631 | 16.65500 | 19.32430 | 23.91900 | 0.376 | |
| Factor 3 | Hg | 0 | 0.0015 | 0.0137 | 9.133 | 0 | 0.00343 | 0.00874 | 2.548 |
| As | 0 | 2.1763 | 4.5688 | 2.099 | 0 | 1.58178 | 2.59360 | 1.640 | |
| Cr | 4.4281 | 16.3160 | 30.2640 | 1.583 | 3.40650 | 12.93514 | 19.00100 | 1.206 | |
| Pb | 1.5249 | 6.6370 | 12.0000 | 1.578 | 1.57850 | 5.08928 | 7.21500 | 1.108 | |
| Cu | 1.4240 | 8.3097 | 13.5840 | 1.463 | 2.78080 | 6.98031 | 9.89200 | 1.019 | |
| Cd | 0.0592 | 0.0919 | 0.1118 | 0.572 | 0.08944 | 0.09512 | 0.10320 | 0.145 | |
| Zn | 8.7346 | 23.1260 | 37.8070 | 1.257 | 10.21500 | 20.03585 | 27.13000 | 0.844 | |
| Ni | 1.2433 | 8.1707 | 15.1690 | 1.704 | 1.31880 | 6.45064 | 9.77180 | 1.310 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, G.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, H.; Mei, A.; Gao, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. Quantitative Source Apportionment and Uncertainty Analysis of Heavy Metal(loid)s in the Topsoil of the Nansi Lake Nature Reserve. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6679. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116679
Zhao D, Wu Q, Zheng G, Zeng Y, Wang H, Mei A, Gao S, Zhang X, Zhang Y. Quantitative Source Apportionment and Uncertainty Analysis of Heavy Metal(loid)s in the Topsoil of the Nansi Lake Nature Reserve. Sustainability. 2022; 14(11):6679. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116679
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Di, Qiang Wu, Guodong Zheng, Yifan Zeng, Hanyuan Wang, Aoshuang Mei, Shuai Gao, Xiaohui Zhang, and Yao Zhang. 2022. "Quantitative Source Apportionment and Uncertainty Analysis of Heavy Metal(loid)s in the Topsoil of the Nansi Lake Nature Reserve" Sustainability 14, no. 11: 6679. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116679
APA StyleZhao, D., Wu, Q., Zheng, G., Zeng, Y., Wang, H., Mei, A., Gao, S., Zhang, X., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Quantitative Source Apportionment and Uncertainty Analysis of Heavy Metal(loid)s in the Topsoil of the Nansi Lake Nature Reserve. Sustainability, 14(11), 6679. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116679






