Hydrochemical Characteristics and the Relationship between Surface and Groundwater in a Typical ‘Mountain–Oasis’ Ecosystem in Central Asia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.1.1. Climate Pattern
2.1.2. Social and Economic Characteristics
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.2.1. Sample Collection
2.2.2. Sample Testing and Laboratory Analysis
2.3. Analysis Method
3. Results
3.1. General Hydrochemical Characteristics of the Study Area
3.1.1. pH and TDS
3.1.2. Major Ions Concentrations
3.2. Seasonal and Spatial Variations of Stable Isotope
3.2.1. δD and δ18O in River Water
3.2.2. δD and δ18O in Groundwater
3.2.3. δD and δ18O in Precipitation and Glacial Water
3.3. Hydrochemical Types in Surface Water and Groundwater
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors Controlling Hydrochemical Processes
4.2. Relationship between Surface Water and Groundwater
4.3. Ion Ratio of Dissolved Minerals and Cation Exchange
4.4. Effects of Human Activities
4.5. Differences from the Other Regions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panneerselvam, B.; Paramasivam, S.K.; Karuppannan, S.; Ravichndran, N.; Selvaraj, P. A GIS-based evaluation of hydrochemical characterisation of groundwater in hard rock region, South Tamil Nadu, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wu, J.; He, S. Hydrochemical characteristics and quality evaluation of groundwater in terms of health risks in Luohe aquifer in Wuqi County of the Chinese Loess Plateau, northwest China. HERA Int. J. 2019, 25, 32–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Hong, Y.; Bi, X.; Yang, Y. Statistical analysis of groundwater chemistry of the Tarim River lower reaches, Northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 65, 1807–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Wu, J.; Abuduwaili, J. Hydrochemical and isotopic characters of surface water in agricultural oases of the Tianshan Mountains, Northwest China. Arid. Land Res. Manag. 2016, 30, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.E. Linking DPSIR Model and Water Quality Indices to Achieve Sustainable Development Goals in Groundwater Resources. Hydrology 2021, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, A.A. On the Retrieval of the Water Quality Parameters from Sentinel-3/2 and Landsat-8 OLI in the Nile Delta’s Coastal and Inland Waters. Water 2022, 14, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.E. Meta-evaluation of water quality indices. application into groundwater resources. Water 2020, 12, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Chen, W.; Shen, Y. The seasonal and spatial distribution of hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and its controlling factors in the eastern Loess Plateau. Earth Sci. Inform. 2021, 14, 2293–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Xia, Z.; Li, X.; Kayumba, P.M. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the dried-up river oasis of the Tarim Basin, Central Asia. J. Arid. Land 2021, 13, 977–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Joseph, S.; Thrivikramji, K.P. Hydrochemical variations of a tropical mountain river system in a rain shadow region of the southern Western Ghats, Kerala, India. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 63, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuba, R.; Tijani, M.N.; Snow, D. Hydrochemistry and stable isotopes (18O and 2H) characteristics of groundwater in Lokoja and its environs, central Nigeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emenike, P.C.; Nnaji, C.C.; Tenebe, I.T. Assessment of geospatial and hydrochemical interactions of groundwater quality, southwestern Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chukwura, U.O.; Udom, G.J.; Cuthbert, S.J.; Hursthouse, A.S. Evaluation of hydrochemical characteristics and flow directions of groundwater quality in Udi Local Government Area Enugu State, Nigeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 4541–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannous, M.; Jahnke, C.; Troeger, U.; Falk, M.; Bzuer, F. Hydrochemistry and environmental isotopes (18O, 2H, 3H, 3He/4He) of groundwater and floodwater in the great area of Hurghada, Eastern Desert of Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, G.; Sheng, Y.; Shi, Z.; Sun, X. Groundwater microbial communities and their connection to hydrochemical environment in Golmud, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, P.; Huang, X.; Zhang, B.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Meng, X.; et al. Groundwater sources, flow patterns, and hydrochemistry of the Central Yinchuan Plain, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. Spatial characteristics of surface water and groundwater using water stable isotope in the Tarim River Basin, northwestern China. Ecohydrology 2013, 6, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Gao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wu, G.; Li, F. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of groundwater in the Yishu River basin. Acta Geophys. 2020, 68, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos Trans. AGU 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ni, J.; Song, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, F.; Cao, Y. Analysis of coastal groundwater hydrochemistry evolution based on groundwater flow system division. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Zheng, F.; Zhao, X.; Xia, X.; Teng, Y. Identification of hydrochemical genesis and screening of typical groundwater pollutants impacting human health: A case study in Northeast China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1202–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Qian, H.; Shi, Z.; Wang, H. Long-term monitoring of hydrochemical characteristics and nitrogen pollution in the groundwater of Yinchuan area, Yinchuan basin of northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Qian, H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M. Insights into hydrological and hydrochemical processes in response to water replenishment for lakes in arid regions. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; He, S.; He, X.; Tian, R. Seasonal hydrochemical characterization and groundwater quality delineation based on matter element extension analysis in a paper wastewater irrigation area, northwest China. Expo. Health 2018, 10, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Su, Y.; Feng, Q. The hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater and surface water in the Heihe River Basin, northwest China. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Stotler, R.L.; Zhang, Y. Spatial and temporal characteristics of stable isotopes in the Tarim River Basin. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2016, 52, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, Y. Isotopic and hydrochemical composition of runoff in the Urumqi River, Tianshan Mountains, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 1521–1537. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Hao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q. Identifying evaporation fractionation and streamflow components based on stable isotopes in the Kaidu River Basin with mountain–oasis system in north-west China. Hydrol. Processes 2018, 32, 2423–2434. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, R.J.; Hiscock, K.M.; Lovett, A.A.; Dugdale, S.J.; Sünnenberg, G.; Vrain, E. Temporal hydrochemical dynamics of the River Wensum, UK: Observations from long-term high-resolution monitoring (2011–2018). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Q.; Kong, Y.; Cheng, A.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, X. Contributions of local terrestrial evaporation and transpiration to precipitation using δ18O and D-excess as a proxy in Shiyang inland river basin in China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 146, 140–151. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Q.; Song, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y. The influence from the shrinking cryosphere and strengthening evopotranspiration on hydrologic process in a cold basin, Qilian Mountains. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 144, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Xu, Z.; Liu, H.; Ren, J.; Fan, W.; Lu, N.; Dong, X. Evaluation on dynamic change and interrelations of ecosystem services in a typical mountain-oasis-desert region. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Hou, Y.; Wang, B.; Bi, X.; Bo, L.; Zhang, X. Scenario analysis of ecosystem service changes and interactions in a mountain-oasis-desert system: A case study in Altay Prefecture, China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, Z.; Haximu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Aji, R. An ecological risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments of Bosten Lake, northwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7255–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wu, B.; Yang, P. Assessing the changes in land use and ecosystem services in an oasis agricultural region of Yanqi Basin, Northwest China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 8343–8357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, X. Hydroclimatic changes of Lake Bosten in Northwest China during the last decades. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.; Xia, Z.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, D. Exploring annual lake dynamics in Xinjiang (China): Spatiotemporal features and driving climate factors from 2000 to 2019. Clim. Chang. 2021, 166, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Lu, J.; Liu, Z.; Tong, Y.; Li, S. Concentration and distribution of antibiotics in water–sediment system of Bosten Lake, Xinjiang. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ye, Q. Climate classification over China based on Köppen climate classification in the context of ENSO. Clim. Chang. Res. 2019, 15, 352. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, D.; Shen, X. Spatial-temporal variations of Köppen climate types in China. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2021, 32, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, W.; Du, P.; Liu, T.; Bao, A.; Chwn, X.; Liu, J.; Qin, C. Impacts of climate change and agricultural activities on water quality in the Lower Kaidu River Basin, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asadi, E.; Isazadeh, M.; Samadianfard, S.; Ramli, M.F.; Mosavi, A.; Nabipour, N.; Shamshirband, S.; Hajnal, E.; Chau, K.W. Groundwater quality assessment for sustainable drinking and irrigation. Sustainability 2019, 12, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Ma, L.; Abuduwaili, J.; Lin, L. Distributions, Relationship and Assessment of Major Ions and Potentially Toxic Elements in Waters of Bosten Lake, the Former Largest Inland and Freshwater Lake of China. Water 2020, 2, 2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, H.; Jia, S.; Lv, A. Possible Hydrochemical Processes Influencing Dissolved Solids in Surface Water and Groundwater of the Kaidu River Basin, Northwest China. Water 2020, 2, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, P.; Qu, S.; Liao, F.; Wang, G. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and dominant water-rock interactions in the Delingha Area, Qaidam Basin, Northwest China. Water 2020, 12, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, X.; Yang, Y. Hydrochemical and stable isotopic spatiotemporal variation characteristics and their environmental significance in the Kashi River Mountain Area of Ili, Xinjiang, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 799–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Han, C.; Yuan, S.; Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, C. Assessment of the hydrochemistry, water quality, and human health risk of groundwater in the northwest of Nansi Lake Catchment, north China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 961–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunanidhi, D.; Aravinthasamy, P.; Deepali, M.; Subramani, T.; Bellows, B.C.; Li, P. Groundwater quality evolution based on geochemical modeling and aptness testing for ingestion using entropy water quality and total hazard indexes in an urban-industrial area (Tiruppur) of Southern India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 18523–18538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Song, X. Water transfer imposes hydrochemical impacts on groundwater by altering the interaction of groundwater and surface water. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Xiao, J.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y. Evaluation of groundwater geochemical characteristics and quality in the central and Northern Shaanxi Province, China. Acta Geochim. 2020, 39, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiphei, S.P.; Kurakalva, R.M.; Sahadevan, D.K. Water quality index and GIS-based technique for assessment of groundwater quality in Wanaparthy watershed, Telangana India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 45041–45062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Qian, H.; Xu, P.; Hou, K. Hydrochemical characteristic of groundwater and its impact on crop yields in the Baojixia irrigation area, China. Water 2020, 12, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, X.; Meng, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y. Appraising groundwater quality and health risks from contamination in a Semiarid region of Northwest China. Expos. Health 2016, 8, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, P.; Qian, H.; Yang, F. Hydrogeochemistry and fluoride contamination in Jiaokou Irrigation District, Central China: Assessment based on multivariate statistical approach and human health risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Sun, Z. Evaluation of shallow groundwater contamination and associated human health risk in an alluvial plain impacted by agricultural and industrial activities, mid-west China. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Fan, W.; Yang, C.; Li, E.; Wang, Z. Impact of land use on shallow groundwater quality characteristics associated with human health risks in a typical agricultural area in Central China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1712–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Fan, Y.; Sun, C.; Fang, G. Hydrological and water cycle processes of inland river basins in the arid region of Northwest China. J. Arid Land 2019, 11, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Jia, W.; Zhu, G.; Shi, Y.; Yang, L.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, F. Hydrochemical characteristics and ion sources of river water in the upstream of the Shiyang River, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Feng, Q.; Liu, W.; Li, Z.; Wen, X.; Si, J.; Xi, H.; Guo, R.; Jia, B. Stable isotopic and geochemical identification of groundwater evolution and recharge sources in the arid Shule River Basin of Northwestern China. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 4703–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W. Hydrochemistry of inland rivers in the north Tibetan Plateau: Constraints and weathering rate estimation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Ji, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lei, M. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and groundwater quality assessment in the plain area of Yarkant River Basin in Xinjiang, PR China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 31704–31716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
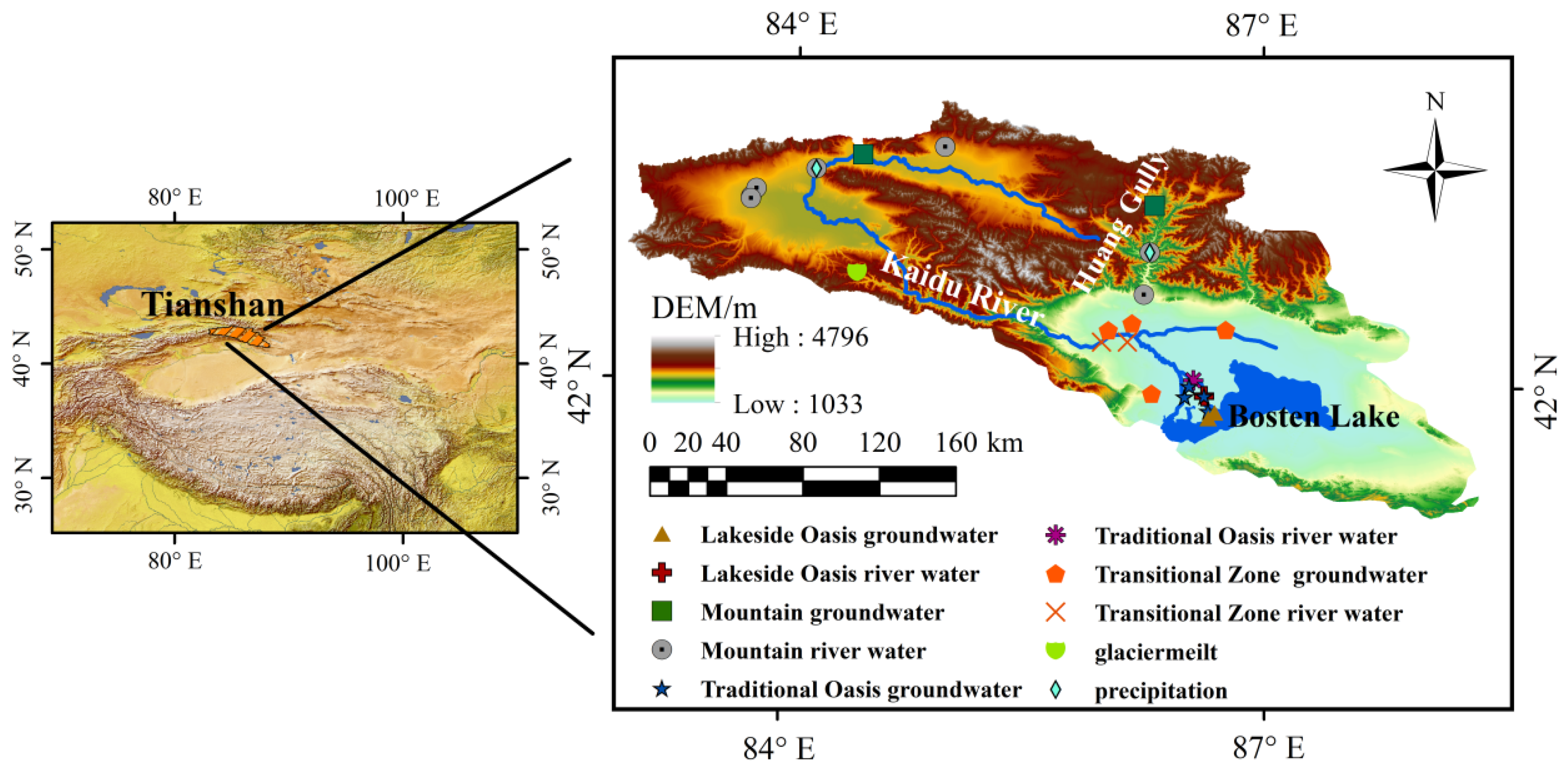









| Type of Sample | Regions | Samples | Longtitude | Latitude | Number of Samples | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface water | River water | Traditional oasis area | O1 | 86.55 | 42.05 | 4 |
| Lakeside area | O2 | 86.62 | 41.98 | 4 | ||
| Transition zone | O3 | 86.14 | 42.23 | 4 | ||
| O4 | 85.97 | 42.23 | 4 | |||
| Mountain area | M1 | 86.24 | 42.45 | 4 | ||
| M2 | 86.27 | 42.65 | 4 | |||
| M3 | 84.95 | 43.13 | 4 | |||
| M4 | 84.95 | 43.13 | 4 | |||
| M5 | 84.13 | 43.01 | 4 | |||
| M6 | 83.72 | 42.87 | 4 | |||
| M7 | 83.75 | 42.91 | 3 | |||
| M8 | 83.72 | 42.86 | 3 | |||
| Precipitation | P1 | 86.27 | 42.65 | 7 | ||
| P2 | 84.13 | 43.01 | 6 | |||
| Glacier water | G1 | 84.41 | 42.53 | 12 | ||
| Groundwater | Traditional oasis area | La1 | 86.65 | 41.91 | 4 | |
| La2 | 86.50 | 41.97 | 4 | |||
| La3 | 86.53 | 42.02 | 4 | |||
| La4 | 86.62 | 41.98 | 4 | |||
| Lakeside area | Lb1 | 86.69 | 41.90 | 4 | ||
| Lb2 | 86.65 | 41.87 | 4 | |||
| Transition zone | Lc1 | 86.76 | 42.29 | 4 | ||
| Lc2 | 86.16 | 42.32 | 4 | |||
| Lc3 | 86.01 | 42.29 | 4 | |||
| Lc4 | 86.29 | 41.99 | 4 | |||
| Mountain area | MG1 | 86.30 | 42.87 | 4 | ||
| MG2 | 84.43 | 43.09 | 4 | |||
| Season | Type | pH | TDS (mg/L) | Ca2+ (mg/L) | Mg2+ (mg/L) | Na+ (mg/L) | K+ (mg/L) | HCO3− (mg/L) | Cl− (mg/L) | SO42− (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | groundwater | max | 8.22 | 771.00 | 64.60 | 26.37 | 100.48 | 5.54 | 305.95 | 64.58 | 174.13 |
| min | 7.77 | 204.00 | 4.31 | 2.15 | 4.96 | 0.94 | 111.87 | 2.85 | 10.99 | ||
| ave | 8.01 | 522.00 | 35.07 | 12.91 | 49.01 | 3.01 | 193.94 | 37.36 | 72.15 | ||
| river water | max | 8.23 | 444.00 | 68.83 | 14.33 | 16.82 | 2.45 | 217.40 | 23.62 | 63.42 | |
| min | 7.59 | 255.00 | 33.32 | 7.39 | 6.74 | 1.50 | 78.13 | 6.13 | 15.93 | ||
| ave | 8.01 | 327.62 | 49.82 | 10.74 | 11.49 | 2.46 | 180.83 | 11.31 | 39.16 | ||
| precipitation | max | 7.38 | 141.40 | 17.74 | 1.43 | 6.18 | 2.87 | 52.00 | 17.10 | 18.94 | |
| min | 6.17 | 56.20 | 10.32 | 0.39 | 1.09 | 0.76 | 29.41 | 7.13 | 4.20 | ||
| ave | 6.52 | 88.48 | 15.36 | 0.82 | 2.64 | 1.31 | 37.85 | 12.42 | 7.96 | ||
| glacier water | max | 7.68 | 71.10 | 7.89 | 0.40 | 2.31 | 2.38 | 50.53 | 3.16 | 1.80 | |
| min | 7.07 | 62.30 | 4.12 | 0.35 | 0.76 | 0.69 | 31.53 | 0.86 | 1.26 | ||
| ave | 7.38 | 66.70 | 6.00 | 0.38 | 1.53 | 1.54 | 41.03 | 2.01 | 1.53 | ||
| Summer | groundwater | max | 8.10 | 645.00 | 99.91 | 31.06 | 106.69 | 5.01 | 313.89 | 101.06 | 201.72 |
| min | 7.75 | 137.90 | 18.93 | 5.43 | 6.23 | 0.69 | 109.40 | 2.74 | 11.24 | ||
| ave | 7.97 | 451.09 | 50.45 | 14.93 | 53.37 | 2.73 | 189.22 | 42.19 | 82.88 | ||
| river water | max | 8.19 | 353.00 | 56.77 | 11.71 | 10.94 | 1.86 | 188.65 | 14.64 | 54.32 | |
| min | 7.44 | 114.80 | 13.99 | 1.34 | 0.68 | 0.44 | 49.61 | 0.82 | 8.98 | ||
| ave | 7.80 | 236.82 | 38.67 | 7.35 | 5.90 | 1.23 | 137.54 | 5.44 | 27.15 | ||
| precipitation | max | 6.73 | 75.20 | 11.63 | 0.55 | 1.02 | 1.27 | 41.43 | 15.47 | 3.34 | |
| min | 5.94 | 18.30 | 2.85 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.21 | 11.79 | 0.93 | 1.02 | ||
| ave | 6.18 | 37.72 | 5.75 | 0.25 | 0.41 | 0.67 | 22.66 | 5.21 | 1.81 | ||
| glacier water | max | 6.84 | 95.00 | 4.44 | 0.58 | 0.05 | 0.63 | 35.92 | 2.26 | 3.49 | |
| min | 6.73 | 60.00 | 2.62 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 23.95 | 1.16 | 1.27 | ||
| ave | 6.78 | 70.00 | 3.07 | 0.42 | 0.03 | 0.29 | 32.09 | 1.51 | 1.91 | ||
| Autumn | groundwater | max | 7.92 | 1049.35 | 81.41 | 28.34 | 219.32 | 7.57 | 182.10 | 121.91 | 423.75 |
| min | 7.70 | 149.50 | 15.21 | 4.87 | 5.37 | 0.61 | 110.70 | 2.61 | 12.16 | ||
| ave | 7.81 | 482.76 | 41.44 | 13.60 | 70.96 | 2.68 | 159.57 | 50.38 | 113.73 | ||
| river water | max | 7.99 | 434.00 | 63.10 | 16.05 | 36.66 | 3.17 | 275.44 | 20.34 | 60.50 | |
| min | 7.69 | 142.10 | 31.42 | 2.91 | 5.29 | 0.80 | 112.00 | 1.74 | 8.41 | ||
| ave | 7.87 | 273.36 | 46.45 | 10.48 | 11.80 | 1.64 | 170.40 | 9.09 | 36.87 | ||
| precipitation | max | 6.47 | 130.10 | 3.88 | 0.31 | 0.89 | 3.06 | 63.58 | 49.81 | 11.49 | |
| min | 6.40 | 70.60 | 3.76 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.45 | 52.59 | 6.84 | 1.68 | ||
| ave | 6.43 | 104.07 | 3.81 | 0.21 | 0.48 | 1.59 | 58.77 | 31.01 | 7.20 | ||
| glacier water | max | 6.91 | 78.34 | 3.95 | 0.46 | 0.31 | 0.56 | 35.66 | 1.83 | 2.52 | |
| min | 6.84 | 60.84 | 3.05 | 0.34 | 0.12 | 0.32 | 34.00 | 1.28 | 1.41 | ||
| ave | 6.87 | 67.09 | 3.36 | 0.39 | 0.22 | 0.41 | 34.70 | 1.45 | 1.82 | ||
| Winter | groundwater | max | 8.23 | 1077.30 | 66.05 | 60.68 | 113.62 | 5.49 | 314.23 | 118.61 | 207.06 |
| min | 7.97 | 119.58 | 19.91 | 2.14 | 6.27 | 1.88 | 147.47 | 9.77 | 38.63 | ||
| ave | 8.11 | 606.32 | 44.92 | 24.22 | 55.56 | 3.62 | 225.33 | 53.12 | 100.17 | ||
| river water | max | 8.30 | 798.00 | 67.56 | 34.76 | 17.54 | 2.35 | 214.63 | 24.29 | 69.75 | |
| min | 7.91 | 64.45 | 21.41 | 0.52 | 2.52 | 0.37 | 49.87 | 0.0 | 7.49 | ||
| ave | 8.16 | 337.88 | 44.19 | 11.53 | 7.85 | 1.61 | 170.83 | 16.07 | 32.82 |
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Ave | Max | Min | Ave | Max | Min | Ave | Max | Min | Ave | ||
| δD (‰) | groundwater | −59.60 | −94.24 | −69.12 | −53.69 | −94.05 | −68.55 | −51.29 | −69.63 | −63.86 | −60.23 | −75.81 | −68.31 |
| river water | −61.44 | −99.36 | −79.49 | −58.35 | −71.06 | −63.97 | −57.52 | −73.24 | −66.76 | −61.41 | −76.14 | −70.69 | |
| precipitation | −38.47 | −76.00 | −60.95 | 6.22 | −56.9 | −24.15 | −13.79 | −61.32 | −40.13 | ||||
| glacier water | −70.05 | −153.40 | −111.72 | −60.19 | −67.34 | −63.11 | −66.34 | −70.2 | −67.96 | ||||
| δ18O (‰) | groundwater | −9.01 | −13.86 | −10.43 | −7.85 | −13.54 | −10.33 | −7.5 | −10.75 | −9.74 | −9.53 | −11.7 | −10.38 |
| river water | −9.15 | −15.06 | −11.62 | −9.34 | −11.01 | −10 | −9.39 | −10.82 | −10.35 | −9.52 | −11.75 | −10.75 | |
| precipitation | −6.02 | −11.12 | −8.74 | 0.24 | −9.49 | −3.94 | −2.7 | −9.13 | −6.74 | ||||
| glacier water | −9.97 | −20.31 | −15.14 | −9.65 | −10.57 | −10.04 | −10.33 | −10.8 | −10.5 | ||||
| Location | Surface Water | Groundwater | References | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | TDS (mg/L) | δ18O (‰) | δD (‰) | pH | TDS (mg/L) | δ18O (‰) | δD (‰) | |||
| Hexi corridor region | Shiyang River | 7.0~8.4 | 64~353 | −10.0~−1.8 | −60.6~−14.5 | 7.0~8.5 | 231~20,897 | −11.3~−5.0 | −86.2~−28.5 | [58] |
| Heihe River | 7.2~8.1 | 31~2157 | −29.7~1.9 | −216.3~38.7 | 7.2~8.1 | 293~5157 | −9.7~−3.7 | −58.0~−42.0 | [25] | |
| Shule River | 7.2~7.8 | 19~980 | −29.0~3.8 | −233.1~36.5 | 7.6~7.9 | 117~2382 | −11.9~−6.9 | −63.1~−9.4 | [18,59] | |
| North slope of Tianshan | Urumqi River | 6.0~8.5 | 125~304 | −36.2~0.0 | −67.5~−44.0 | 7.0~7.9 | 128~245 | −9.0~−8.9 | −61.0~−57.0 | [27] |
| Yili River | 7.2~8.4 | 303~321 | −11.6~−10.9 | −77.0~−72.0 | [46,60] | |||||
| Tarim Basin | Tarim River | 7.4~8.5 | 253~3220 | −25.74~8.48 | −96.1~51.9 | 7.2~8.8 | 450~27,495 | [9,17,26] | ||
| Yarkant River | 7.4~8.3 | 273~3344 | 6.4~8.6 | 522~9014 | [61] | |||||
| Study area | 7.4~8.3 | 64~798 | −15.0~−9.2 | −99.4~−61.4 | 7.7~8.3 | 19~1077 | −13.8~−7.8 | −94.2~−51.3 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, C.; Wang, S.; Chen, W. Hydrochemical Characteristics and the Relationship between Surface and Groundwater in a Typical ‘Mountain–Oasis’ Ecosystem in Central Asia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7453. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127453
Sun C, Wang S, Chen W. Hydrochemical Characteristics and the Relationship between Surface and Groundwater in a Typical ‘Mountain–Oasis’ Ecosystem in Central Asia. Sustainability. 2022; 14(12):7453. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127453
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Congjian, Shiyu Wang, and Wei Chen. 2022. "Hydrochemical Characteristics and the Relationship between Surface and Groundwater in a Typical ‘Mountain–Oasis’ Ecosystem in Central Asia" Sustainability 14, no. 12: 7453. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127453
APA StyleSun, C., Wang, S., & Chen, W. (2022). Hydrochemical Characteristics and the Relationship between Surface and Groundwater in a Typical ‘Mountain–Oasis’ Ecosystem in Central Asia. Sustainability, 14(12), 7453. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127453








