The Application of Advanced Information Technologies in Civil Infrastructure Construction and Maintenance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
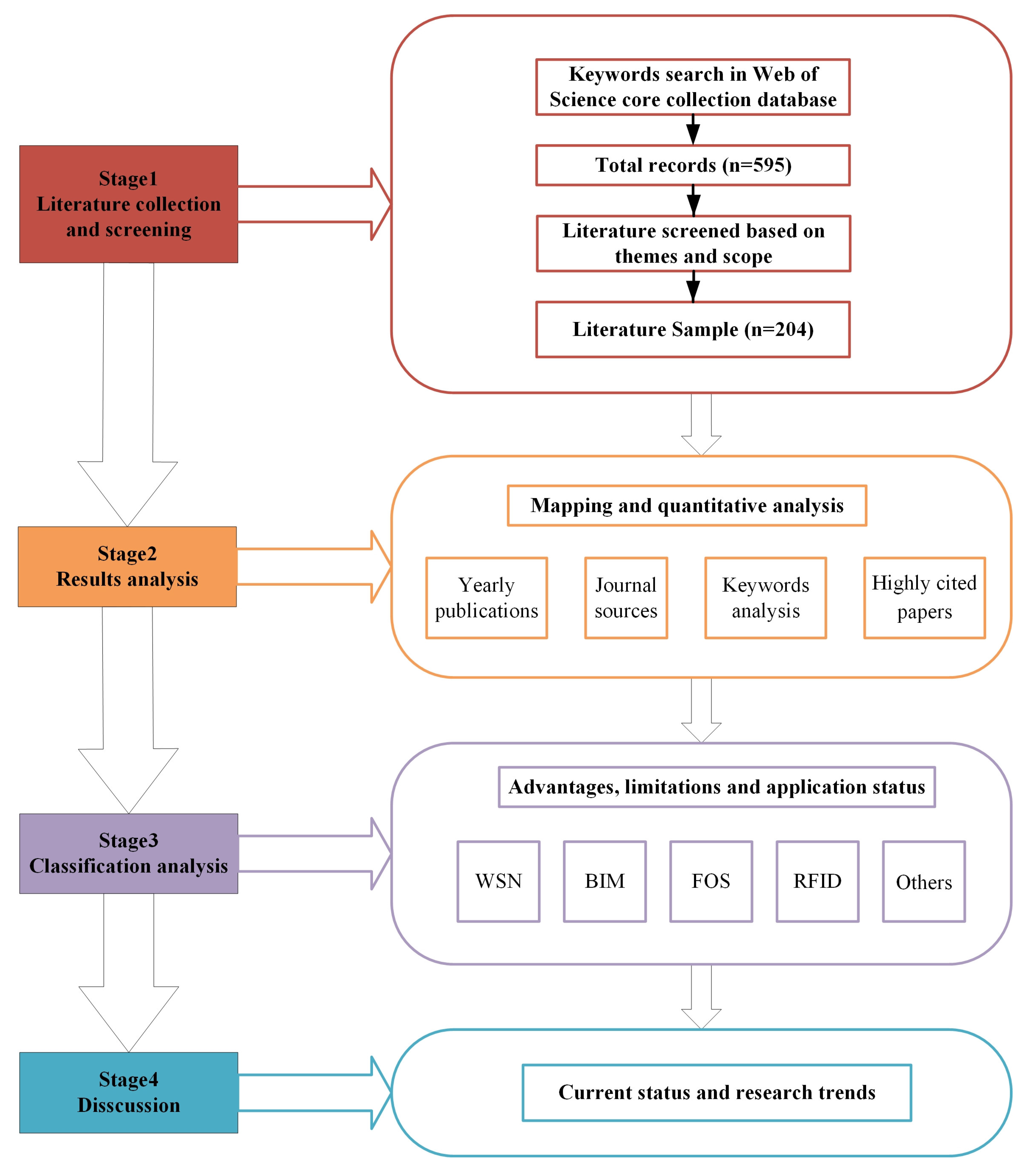
2. Methodologies
- (1)
- Literature collection and screening
- (2)
- Analysis of the Results
- (3)
- Classification analysis
- (4)
- Finally, based on the above analysis results, the current status and research trends of this research were discovered.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Number of Annual Publications
3.2. Analysis of Journal Source
3.3. Analysis of Keywords
3.4. Analysis of Paper Citations
4. Classified Analysis of Information Technologies in Civil Infrastructure
4.1. Wireless Sensor Networks
4.1.1. Advantages
4.1.2. Applications
Structural Health Monitoring
Pipeline Damage Detection
Water Quality Monitoring
Traffic Safety Maintenance
4.1.3. Challenges and Limitations
4.2. Building Information Modelling
4.2.1. Advantages
3D Visualization
Improve the Efficiency and Accuracy of Information Exchange
Life Cycle Management
Integrating Emerging Technologies
4.2.2. Applications
Planning and Design Phase
Construction Phase
Maintenance Phase
4.2.3. Challenges and Limitations
Application of Obstacles
Need for Interoperability
4.3. Fiber Optic Sensing
4.3.1. Advantages
4.3.2. Classification
Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing
Applications
Fiber Bragg Grating
Applications
4.4. Radio Frequency Identification
4.4.1. Advantages
4.4.2. Applications
Proximity Monitoring and Safety Warning
Tracking and Monitoring
Pipeline Monitoring and Maintenance
4.4.3. Limitations
4.5. Other Advanced Information Technologies
4.5.1. IoT and Sensors
Concrete Structure Monitoring
Road Surface Monitoring
Other Application Areas
4.5.2. Computer Vision
Applications
Construction Site Monitoring
Safety Inspection
Structural Health Monitoring
4.5.3. Geographic Information System
Applications
4.5.4. Micro-Electro-Mechanical System
Advantages
Applications
5. Discussions
5.1. Application of Information Technologies in Different Phases
5.2. Status of Research and Potential Future Research Directions
5.2.1. Sensor Deployment Optimization
5.2.2. Power Supply and Maintenance
5.2.3. Data-Centric Engineering
5.2.4. To Achieve Full Interoperability
5.2.5. Future of Civil Infrastructure: Multidisciplinary Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soga, K.; Schooling, J. Infrastructure sensing. Interface Focus 2016, 6, 201600234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costin, A.; Adibfar, A.; Hu, H.; Chen, S.S. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for transportation infrastructure - Lit-erature review, applications, challenges, and recommendations. Autom. Constr. 2018, 94, 257–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Lv, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhang, R.; Lin, Y. Optimizing the ultra-dense 5G base stations in urban outdoor areas: Coupling GIS and heuristic optimization. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Hou, H.; Liu, G.-J.; Zhang, S. Storing E-waste in Green Infrastructure to Reduce Perceived Value Loss through Landfill Siting and Landscaping: A Case Study in Nanjing, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, L.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, H.; Love, P.E. A CNN-based 3D patch registration approach for integrating sequential models in support of progress monitoring. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2019, 41, 100923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, T.; Nehdi, M.L. Data acquisition technologies for construction progress tracking. Autom. Constr. 2016, 70, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, A.Y.; Huang, Y.-N.; Han, J.-Y.; Lai, J.-S.; Kang, S.-C.; Wu, T.-H.; Wen, M.-C.; Tsai, M.-H. A review of rotorcraft Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) developments and applications in civil engineering. Smart Struct. Syst. 2014, 13, 1065–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Rashidi, A.; Brilakis, I.; Vela, P. Comparison of Image-Based and Time-of-Flight-Based Technologies for Three-Dimensional Reconstruction of Infrastructure. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2013, 139, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, B.-W.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, D.-K.; Choi, P.-H. Proximity Warning and Excavator Control System for Prevention of Collision Accidents. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Marks, E.; Cho, Y.K.; Suryanto, W. Performance Test of Wireless Technologies for Personnel and Equipment Proximity Sensing in Work Zones. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2016, 142, 04015049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celaya-Echarri, M.; Azpilicueta, L.; Lopez-Iturri, P.; Picallo, I.; Aguirre, E.; Astrain, J.J.; Villadangos, J.; Falcone, F. Radio Wave Propagation and WSN Deployment in Complex Utility Tunnel Environments dagger. Sensors 2020, 20, 6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Shao, C.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, H.; Yang, X.; Lou, X.; Li, J.; Hui, G.; Zhao, Z. Simulating study on RHCRP protocol in utility tunnel WSN. Wirel. Netw. 2020, 26, 2797–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayadi, A.; Ghorbel, O.; BenSalah, M.S.; Abid, M. Spatio-temporal correlations for damages identification and localiza-tion in water pipeline systems based on WSNs. Comput. Netw. 2020, 171, 107134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, R.; Ren, L.; Song, G. A novel OFDR-based distributed optical fiber sensing tape: Design, optimization, calibration and application. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 105017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidovic, I.; Marschnig, S. Optical Fibres for Condition Monitoring of Railway Infrastructure-Encouraging Data Source or Errant Effort? Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-Z.; Wu, G.; Feng, D.-C.; Wang, Z.; Cao, X.-Y. Multi-Cross-Reference Method for Highway-Bridge Damage Identification Based on Long-Gauge Fiber Bragg-Grating Sensors. J. Bridg. Eng. 2020, 25, 04020023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Cheng, H.; Kong, Q.; Chen, X. Bond-Slip Monitoring of Concrete Structures Using Smart Sensors—A Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodge, V.J.; O’Keefe, S.; Weeks, M.; Moulds, A. Wireless Sensor Networks for Condition Monitoring in the Railway Industry: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2015, 16, 1088–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, A.B.; Abdaoui, A.; Elfouly, T.; Ahmed, M.H.; Badawy, A.; Shehata, M.S. Structural Health Monitoring Using Wire-less Sensor Networks: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 1403–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, B.; Paya-Zaforteza, I.; Calderon, P.A.; Adam, J.M. Analysis of the strain transfer in a new FBG sensor for Struc-tural Health Monitoring. Eng. Struct. 2011, 33, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bocca, M.; Eriksson, L.M.; Mahmood, A.; Jantti, R.; Kullaa, J. A Synchronized Wireless Sensor Network for Experi-mental Modal Analysis in Structural Health Monitoring. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2011, 26, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wright, G.; Cheng, J.C.P.; Li, X.; Liu, R. A State-of-the-Art Review on the Integration of Building In-formation Modeling (BIM) and Geographic Information System (GIS). ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mottola, L.; Picco, G.P.; Ceriotti, M.; Guna, S.; Murphy, A.L. Not all Wireless Sensor Networks are Created Equal: A Comparative Study on Tunnels. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. 2010, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teizer, J. Status quo and open challenges in vision-based sensing and tracking of temporary resources on infrastruc-ture construction sites. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2015, 29, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sony, S.; LaVenture, S.; Sadhu, A. A literature review of next-generation smart sensing technology in structural health monitoring. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Adeli, H. Wireless smart sensors for monitoring the health condi-tion of civil infrastructure. Sci. Iran. 2018, 25, 2913–2925. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-H.; Wu, Y.; Soga, K.; Wham Brad, P.; Pariya-Ekkasut, C.; Berger, B.; O’Rourke, T.D. Buried Wireless Sensor Network for Monitoring Pipeline Joint Leakage Caused by Large Ground Movements. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2019, 10, 04019023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, L.B.; Latif, R.M.A.; Farhan, M.; Aldabbas, H. Smart City Based Autonomous Water Quality Monitoring System Using WSN. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 115, 1805–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhao, K.; Yang, H. Development of a Novel Piezoelectric Sensing System for Pavement Dynamic Load Identification. Sensors 2019, 19, 4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furkan, M.O.; Mao, Q.; Livadiotis, S.; Mazzotti, M.; Aktan, A.E.; Sumitro, S.P.; Bartoli, I. Towards rapid and robust meas-urements of highway structures deformation using a wireless sensing system derived from wired sensor. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2020, 10, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.E.; Asikuzzaman, M.; Khan, I.U.; Ra, I.; Hossain, M.S.; Shah, S.B.H. Comparative Study of IoT-Based Topology Maintenance Protocol in a Wireless Sensor Network for Structural Health Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, H.Y.; Lopez, R.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z. Comparative Analysis on the Adoption and Use of BIM in Road Infrastructure Projects. J. Manag. Eng. 2016, 32, 05016021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetemi, E.; Ordieres-Mere, J.; Nuur, C. An Institutional Approach to Digitalization in Sustainability-Oriented Infra-structure Projects: The Limits of the Building Information Model. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundan, M.R.; Khademi, K.; Bahmanoo, S.; Wakil, K.; Mohamad, E.T.; Khorami, M. Practical use of computational building information modeling in repairing and maintenance of hospital building- case study. Smart Struct. Syst. 2018, 22, 575–586. [Google Scholar]
- Boddupalli, C.; Sadhu, A.; Rezazadeh Azar, E.; Pattyson, S. Improved visualization of infrastructure monitoring data using building information modeling. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2019, 15, 1247–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hu, R.; Guo, X.; Wu, F. Building Information Modeling-Based Secondary Development System for 3D Modeling of Underground Pipelines. CMES-Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2020, 123, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, K. Establishment and application of intelligent city building information model based on BP neural net-work model. Comput. Commun. 2020, 153, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, I.; Akinci, B.; González-Jorge, H.; Díaz-Vilariño, L.; Arias, P. A semi-automated method for extracting vertical clearance and cross sections in tunnels using mobile LiDAR data. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 59, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.; Hisham, M. Implementing earned value management using bridge information modeling. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2014, 18, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, C.; Yun, N.; Song, H. Application of 3D Bridge Information Modeling to Design and Construction of Bridges. Procedia Eng. 2011, 14, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Shou, W.; Wang, X.; Xu, B.; Kim, M.J.; Wu, P. A BIM-based approach for automated tower crane layout planning. Autom. Constr. 2015, 59, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chong, H.-Y. Setting new trends of integrated Building Information Modelling (BIM) for construction industry. Constr. Innov. Inf. Process Manag. 2015, 15, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chan, N.K.; Huang, T.; Skitmore, M.; Yang, J. Virtual prototyping for planning bridge construction. Autom. Constr. 2012, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Yung, P.; Luo, H.; Truijens, M. An innovative method for project control in LNG project through 5D CAD: A case study. Autom. Constr. 2014, 45, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Hu, D.; Zhang, Z. Dynamic BIM-augmented UAV safety inspection for water diversion project. Comput. Ind. 2019, 108, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, H.-Y.; Wang, J.; Shou, W.; Wang, X.; Guo, J. Improving Quality and Performance of Facility Management Using Building Information Modelling; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Liu, Y. E-maintenance platform design for public infrastructure maintenance based on IFC ontology and Se-mantic Web services. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2020, 32, e52046SI. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marefat, A.; Toosi, H.; Hasankhanlo, R.M. A BIM approach for construction safety: Applications, barriers and solution. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2019, 26, 1855–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flora, M.; Froech, G.; Gaechter, W. Optimization of construction management in underground construction using digi-tal infrastructure information models. Bautechnik 2020, 97, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costin, A.; Eastman, C. Need for Interoperability to Enable Seamless Information Exchanges in Smart and Sustainable Urban Systems. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2019, 33, 04019008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, R.; Marzouk, H.; Haddara, M.; Gu, X. Multi-channel random decrement smart sensing system for concrete bridge girders damage location identification. Eng. Struct. 2017, 143, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.-H.; Shi, B.; Yan, J.-F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.-C.; Wang, B.-J. Fiber Bragg grating-based performance monitoring of a slope model subjected to seepage. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 95027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.W.; Su, Y.H.; Han, J.P. Structural Health Monitoring of Civil Infrastructure Using Optical Fiber Sensing Tech-nology: A Comprehensive Review. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 652329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, J.H.; Jin, W.L.; He, Y.; Cleland, D.J.; Bai, Y. A novel method of embedding distributed optical fiber sensors for structural health monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 12501812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soga, K.; Luo, L. Distributed fiber optics sensors for civil engineering infrastructure sensing. J. Struct. Integr. Maint. 2018, 3, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassil, A.; Wang, X.; Chapeleau, X.; Niederleithinger, E.; Abraham, O.; LeDuc, D. Distributed Fiber Optics Sensing and Coda Wave Interferometry Techniques for Damage Monitoring in Concrete Structures. Sensors 2019, 19, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Zhang, G.; Hou, S.; Cai, C.S. Geopolymer-Based Smart Adhesives for Infrastructure Health Monitoring: Concept and Feasibility. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Soga, K.; Kechavarzi, C. Distributed fibre optic sensing of a deep excavation adjacent to pre-existing tunnels. Géotechnique Lett. 2018, 8, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Murro, V.; Pelecanos, L.; Soga, K.; Kechavarzi, C.; Morton, R.F.; Scibile, L. Long-term Deformation Monitoring of CERN Concrete-lined Tunnels using Distributed Fibre-Optic Sensing. Geotech. Eng. 2019, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Bao, Y.; Meng, W.; Chen, G. In-situ monitoring of corrosion-induced expansion and mass loss of steel bar in steel fiber reinforced concrete using a distributed fiber optic sensor. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 165, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, B. Structural health monitoring of a newly built high-piled wharf in a harbor with fiber Bragg grating sensor technology: Design and deployment. Smart Struct. Syst. 2017, 20, 163–173. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, C.; Hong, W.; Liu, J.; Wu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Li, S. Bridge Assessment and Health Monitoring with Distributed Long-Gauge FBG Sensors. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2013, 9, 494260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.; Felix, C.; Figueiras, J. Fiber-optic-based displacement transducer to measure bridge deflections. Struct. Health Monit-Int. J. 2011, 10, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, P.; Lima, H.; Varum, H.; Andre, P. Optical fiber sensors for static and dynamic health monitoring of civil en-gineering infrastructures: Abode wall case study. Measurement 2012, 45, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; He, J.; Ou, J. Integrated Optical Fiber Sensing System by Combing Large-Scale Distributed BOTDA/R and Localized FBGs. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2012, 8, 804394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardroud, J.M. Influence of RFID technology on automated management of construction materials and components. Sci. Iran. 2012, 19, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taneja, S.; Akinci, B.; Garrett, J.H.; Soibelman, L.; Ergen, E.; Pradhan, A.; Tang, P.; Berges, M.; Atasoy, G.; Liu, X.; et al. Sensing and Field Data Capture for Construction and Facility Operations. J. Construction Eng. Manag. 2011, 137, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanmu, A.; Olatunji, O.; Love, P.E.D.; Duy, N.; Matthews, J. Auto-generated site layout: An integrated approach to re-al-time sensing of temporary facilities in infrastructure projects. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2016, 12, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Sharma, G.; Boudriga, N.; Iyengar, S.; Prabakar, N. Autonomous pipeline monitoring and maintenance system: A RFID-based approach. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2015, 262, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazyad, A.S.; Seddiq, Y.M.; Alotaibi, A.M.; Al-Nasheri, A.Y.; BenSaleh, M.S.; Obeid, A.M.; Qasim, S.M. A Proposed Scalable Design and Simulation of Wireless Sensor Network-Based Long-Distance Water Pipeline Leakage Monitoring System. Sensors 2014, 14, 3557–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, L.; Bell, S.J. High-Resolution Monitoring of Weather Impacts on Infrastructure Networks Using the Internet of Things. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 6, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandharipande, A.; Calabrese, F.; Lim, H.B.; Rajagopal, R. Guest Editorial Special Issue on Sensing Technologies for Intelligent Urban Infrastructures. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, J.; Niederleithinger, E.; Mielentz, F.; Grothe, S.; Wiggenhauser, H. Monitoring of concrete constructions by em-bedded ultrasonic sensors. Bautechnik 2014, 91, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’alessandro, A.; Ubertini, F.; García-Macías, E.; Triguero, R.C.; Downey, A.; Laflamme, S.; Meoni, A.; Materazzi, A.L. Static and Dynamic Strain Monitoring of Reinforced Concrete Components through Embedded Carbon Nanotube Cement-Based Sensors. Shock Vib. 2017, 2017, 3648403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, J.; Haber, R.; Muñoz, J.J.; Matía, F.; García, Á. Smart Sensing of Pavement Temperature Based on Low-Cost Sensors and V2I Communications. Sensors 2018, 18, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sattar, S.; Li, S.; Chapman, M. Road Surface Monitoring Using Smartphone Sensors: A Review. Sensors 2018, 18, 3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Wang, Z.; Hu, S.; Lepine, J.; Na, X.; Ainalis, D.; Stettler, M. An Automated Machine-Learning Approach for Road Pothole Detection Using Smartphone Sensor Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Majhi, S. Characterisation of road bumps using smartphones. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2016, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vij, D.; Aggarwal, N. Smartphone based traffic state detection using acoustic analysis and crowdsourcing. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 138, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Padillo, J.; Morillo, J.G.; Ramirez-Faz, J.; Roldán, M.T.; Montesinos, P. Design and Implementation of a Pressure Monitoring System Based on IoT for Water Supply Networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zymelka, D.; Togashi, K.; Kobayashi, T. Concentric Array of Printed Strain Sensors for Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors 2020, 20, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dabous, S.A.; Feroz, S. Condition monitoring of bridges with non-contact testing technologies. Autom. Constr. 2020, 116, 103224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackl, J.; Adey, B.T.; Woźniak, M.; Schümperlin, O. Use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Photogrammetry to Obtain Topographical Information to Improve Bridge Risk Assessment. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2018, 24, 40170411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnisarman, S.; Lopes, S.; Madathil, K.C.; Piratla, K.; Gramopadhye, A. A survey of automation-enabled hu-man-in-the-loop systems for infrastructure visual inspection. Autom. Constr. 2019, 97, 52–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarapu, K.; Shashi, M.; Keesara, V.R. UAV in Construction Site Monitoring and Concrete Strength Estimation. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2020, 49, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Chen, Y.; Bouferguene, A.; Zaman, H.; Al-Hussein, M.; Kurach, L. A deep learning-based framework for an au-tomated defect detection system for sewer pipes. Autom. Constr. 2020, 109, 102967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagvozda, M.; Dimter, S.; Moser, V.; Barišić, I. Application of GIS technology in pavement management systems. J. Croat. Assoc. Civ. Eng. 2019, 71, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Ni, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, T.; Shen, D.; Wang, J. Web3DGIS-Based System for Reservoir Landslide Monitoring and Early Warning. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Afferden, M.; Cardona, J.A.; Lee, M.-Y.; Subah, A.; Müller, R.A. A new approach to implementing decentralized wastewater treatment concepts. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaselskis, E.J.; Schexnayder, C.J.; Fiori, C.; Becker, T.C.; Hung, W.; Beckman, C.; Kaewmoracharoen, M.; Recavarren, G.C.; Celaya, M.; Alarcon, D. Innovative Technologies Used to Investigate Segments of the Inca Road. J. Prof. Issues Eng. Educ. Pract. 2013, 139, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, H.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Kim, S.; Taylor, P.C.; Prokudin, M.; Buss, A. Highway Infrastructure Health Monitoring Using Micro-Electromechanical Sensors and Systems (MEMS). J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2013, 19, S188–S201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondolo, F.; Cesetti, A.; Matta, E.; Quattrone, A.; Sabia, D. Smart reinforcement steel bars with low-cost MEMS sensors for the structural health monitoring of RC structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 173, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoerbinger, S.; Immitzer, M.; Obriejetan, M.; Rauch, H.P. GIS-based assessment of ecosystem service demand con-cerning green infrastructure line-side vegetation. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 121, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibaut, A.; Zazula, D. Sustainable management of construction site big visual data. Sustain. Sci. 2018, 13, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseoglu, O.; Keskin, B.; Ozorhon, B. Challenges and Enablers in BIM-Enabled Digital Transformation in Mega Pro-jects: The Istanbul New Airport Project Case Study. Buildings 2019, 9, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neath, S.; Hulse, R.; Codd, A. Building information modelling in practice: Transforming Gatwick airport, UK. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng-Civ. Eng. 2014, 167, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.; Butler, C.; Khan, S.; Coyle, B. Corrib onshore gas pipeline, Ireland—using BIM on a large infrastructure project. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng-Civ. Eng. 2014, 167, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, A.; Karan, E. Video to BrIM: Automated 3D As-Built Documentation of Bridges. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2018, 32, 040180263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canete, E.; Chen, J.; Diaz, M.; Llopis, L.; Rubio, B. Wireless sensor networks and structural health monitoring: Experi-ences with slab track infrastructures. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2019, 15, 15501477198260023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, J.; Zou, X.; Xu, W. ePave: A Self-Powered Wireless Sensor for Smart and Autonomous Pavement. Sensors 2017, 17, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, A.B.; Ravisankar, K.; Senthil, R.; Parivallal, S. Wireless strain sensing system for assessing condition of civ-il infrastructure facilities. Gradevinar 2016, 68, 221–227. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Yao, T.; Ren, M.; Rong, J.; Liu, C.; Jia, L. Physical topology optimization of infrastructure health monitoring sen-sor network for high-speed rail. Measurement 2016, 79, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Rong, J. Wireless Sensor Networks of Infrastructure Health Monitoring for High-Speed Railway. Shock Vib. 2015, 2016, 5194324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haque, M.E.; Zain, M.F.; Hannan, M.A.; Rahman, M.H. Building structural health monitoring using dense and sparse topology wireless sensor network. Smart Struct. Syst. 2015, 16, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.-B.; Cho, S.; Park, H.-J.; Min, J.; Park, J. Smart wireless sensing and assessment for civil infrastructure. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2013, 10, 534–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.N.; Song, G.B.; Kim, J.T.; Yi, T.H. Sensing Methodologies and Sensor Networks for Health Monitoring of Civil Infrastruc-tures. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2012, 8, 358286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Hu, B.; Lv, H. Infrastructure Monitoring and Operation for Smart Cities Based on IoT System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, W.W.; Lynch, J.P.; Zekkos, D. Applications of UAVs in Civil Infrastructure. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2019, 25, 040190022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canete, E.; Chen, J.; Diaz, M.; Llopis, L.; Rubio, B. Sensor4PRI: A Sensor Platform for the Protection of Railway Infra-structures. Sensors 2015, 15, 4996–5019. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Lozano, J.; Martín-Guzmán, M.; Martín-Ávila, J.; García-Cerezo, A. A Wireless Sensor Network for Urban Traffic Characterization and Trend Monitoring. Sensors 2015, 15, 26143–26169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merschbrock, C.; Munkvold, B.E. Effective digital collaboration in the construction industry – A case study of BIM deployment in a hospital construction project. Comput. Ind. 2015, 73, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Kim, C.; Kim, H. RFID and CCTV-Based Material Delivery Monitoring for Cable-Stayed Bridge Construction. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2012, 26, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderegg, P.; Broennimann, R.; Meier, U. Reference data for long-term monitoring of infrastructures. Bautechnik 2018, 95, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gue, C.Y.; Wilcock, M.; Alhaddad, M.M.; Elshafie, M.Z.E.B.; Soga, K.; Mair, R.J. The monitoring of an existing cast iron tunnel with distributed fibre optic sensing (DFOS). J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2015, 5, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asundi, A. The Smart Bridge-Condition Monitoring for Military Bridge. J. Indian Inst. science 2014, 94, 261–271. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, C.; Min, J. Smart sensing, monitoring, and damage detection for civil infrastructures. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2011, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianidis, E.; Valari, E.; Pagani, A.; Carrillo, I.; Kounoudes, A.; Michail, K.; Smagas, K. Augmented Reality Geovisuali-sation for Underground Utilities. PFG-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2020, 88, 173–185. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.C.; Cheng, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.-J.; Flatt, J.E.; Habib, A.; Bullock, D. Evaluating the Accuracy of Mobile LiDAR for Mapping Airfield Infrastructure. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2019, 2673, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, K.; Ando, T. Reduction of Piping Management Person-Hours through Use of AR Technology at Shipbuilding Sites. Fujitsu Sci. Tech. J. 2019, 55, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bazán, Á.M.; Alberti, M.G.; Álvarez, A.A.; Trigueros, J.A. New Perspectives for BIM Usage in Transportation Infrastructure Projects. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Sakurai, R.; Sakai, H. Forest road planning using precision geographic data under climate change. Int. J. For. Eng. 2018, 30, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovina, O.; Teizer, J.; Pradhananga, N. Heat map generation for predictive safety planning: Preventing struck-by and near miss interactions between workers-on-foot and construction equipment. Autom. Constr. 2016, 71, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkinson, C.L.; Bayraktar, M.E.; Ahmad, I. The use of computing technology in highway construction as a total jobsite management tool. Autom. Constr. 2010, 19, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.; Seco, F.; Milanés, V.; Jiménez, A.; Díaz, J.C.; De Pedro, T. An RFID-Based Intelligent Vehicle Speed Controller Using Active Traffic Signals. Sensors 2010, 10, 5872–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, E.; Capozzoli, L.; De Martino, G.; Grimaldi, S. Urban geophysical approach to characterize the subsoil of the main square in San Benedetto del Tronto town (Italy). Eng. Geol. 2019, 257, 105133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaa, F.A.; Al, K.; Niver, E. Decision Analysis of Preferred Methods for Locating Underground Conduits. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2014, 5, 040130172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, P.E.; Zhou, J.; Matthews, J. Project controls for electrical, instrumentation and control systems: Enabling role of digital system information modelling. Autom. Constr. 2019, 103, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Z.; He, Q. Using Vehicle Interior Noise Classification for Monitoring Urban Rail Transit Infrastructure. Sensors 2020, 20, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matarazzo, T.J.; Santi, P.; Pakzad, S.N.; Carter, K.; Ratti, C.; Moaveni, B.; Osgood, C.; Jacob, N. Crowdsensing Framework for Monitoring Bridge Vibrations Using Moving Smartphones. Proc. IEEE 2018, 106, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, T.; Usui, T.; Watabe, K.; Nguyen, M.-D.; Matsumoto, K.; Shimoyama, I. Elastic Wave Measurement Using a MEMS AE Sensor. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corva, D.M.; Hosseini, S.S.; Collins, F.; Adams, S.D.; Gates, W.P.; Kouzani, A.Z. Miniature Resistance Measurement De-vice for Structural Health Monitoring of Reinforced Concrete Infrastructure. Sensors 2020, 20, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viljamaa, E.; Peltomaa, I. Intensified construction process control using information integration. Autom. Constr. 2014, 39, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Gonzalez-Prelcic, N.; Heath, R.W.; Ghosh, A. Leveraging Sensing at the Infrastructure for mmWave Communication. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2020, 58, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerario, A.; Varasano, A. An IoT Smart Infrastructure for S. Domenico Church in Matera’s “Sassi’’: A Multiscale Perspective to Built Heritage Conservation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshandah, M.; Huang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Lu, P. Internal crack detection in concrete pavement using discrete strain sensors. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2020, 10, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftherakis, D.; Vicen-Bueno, R. Sensors to Increase the Security of Underwater Communication Cables: A Review of Underwater Monitoring Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, H.; Thakar, S.K.; Oseng, M.L.; Nguyen, C.M.; Jebali, C.; Kouki, A.B.; Chiao, J.C. Development and Characterization of a Novel Interdigitated Capacitive Strain Sensor for Structural Health Monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 6542–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, R.W.; Schumacher, T.; Algernon, D.; Kee, S. Strategies for maintenance of highway bridges in the US - with the support of nondestructive testing and structural health monitoring. Bautechnik 2011, 88, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.A.; Mechitov, K.A.; Sim, S.H.; Spencer, B.F., Jr.; Agha, G.A. Enabling framework for structural health monitoring using smart sensors. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2011, 18, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.; Lee, J.; Koo, K. Smart structure technologies for civil infrastructures in Korea: Recent research and applications. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2011, 7, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnam, A.; Wickramasinghe, D.C.; Ghaffar, M.A.A.; Tuong, T.V.; Tang, Y.H.; Isa, H.B.M. Automated progress monitor-ing system for linear infrastructure projects using satellite remote sensing. Autom. Constr. 2016, 68, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Zhu, Z. Line Segment Grouping and Linking: A Key Step Toward Automated Photogrammetry for Non-Contact Site Surveying. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2015, 79, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soilan, M.; Riveiro, B.; Martinez-Sanchez, J.; Arias, P. Segmentation and classification of road markings using MLS data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 123, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, A.; Tuccillo, M.E.; Martel, K.D.; Matthews, J.C.; Feeney, C. Demonstration and Evaluation of State-of-the-Art Wastewater Collection Systems Condition Assessment Technologies. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2014, 5, 040130182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyczkowski, M.; Szustakowski, M.; Ciurapinski, W.; Palka, N.; Kastek, M. Integrated optoelectronics security system for critical infrastructure protection. Prz. Elektrotechniczny 2010, 86, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Mascarenas, D.D.L.; Ballor, J.P.; McClain, O.L.; Mellor, M.A.; Shen, C.; Bleck, B.; Morales, J.; Yeong, L.R.; Narushof, B.; Shelton, P.; et al. Augmented reality for next generation infrastructure inspection. Struct. Health Monit. Int. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Shin, M.; Lim, S.; Park, J.; Kim, J.; Paik, J. Intelligent Image-Based Railway Inspection System Using Deep Learning-Based Object Detection and Weber Contrast-Based Image Comparison. Sensors 2019, 19, 4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alhaddad, M.; Dewhirst, M.; Soga, K.; Devriendt, M. A new photogrammetric system for high-precision monitoring of tunnel deformations. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Transp. 2019, 172, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.; Hendy, C. Improved Structural Health Monitoring of London’s Docklands Light Railway Bridges Using Digital Image Correlation. Struct. Eng. Int. 2017, 27, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Jian, X.; Yan, B.; Su, D. Infrastructure Safety Oriented Traffic Load Monitoring Using Multi-Sensor and Single Camera for Short and Medium Span Bridges. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Peng, B.; He, L.; Fan, K.; Li, Z.; Tong, L. Road Extraction from Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing Images Based on Improved Neural Networks. Sensors 2019, 19, 4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerra, E.; Munguía, R.; Grau, A. UAV Visual and Laser Sensors Fusion for Detection and Positioning in Industrial Applications. Sensors 2018, 18, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeon, J.; Rew, Y.; Choi, K.; Kang, J. Environmental Effects of Accelerated Pavement Repair Using 3D Printing: Life Cycle Assessment Approach. J. Manag. Eng. 2020, 36, 040200033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, S.M.; Ahmad, J.; Hussain, S.; Zoha, A.; Abbasi, Q.H.; Imran, M.A. Mobility Prediction-Based Optimisation and Encryption of Passenger Traffic-Flows Using Machine Learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaaslan, E.; Bagci, U.; Catbas, F.N. Artificial Intelligence Assisted Infrastructure Assessment using Mixed Reality Systems. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2019, 2673, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, G.; Li, Y.E.; Zhao, Y.; Martin, E.R. Urban Near-Surface Seismic Monitoring Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL086115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mcmahon, P.; Zhang, T.; Dwight, R. Requirements for Big Data Adoption for Railway Asset Management. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 15543–15564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, A.; Hajizadeh, S.; Su, Z.; Naeimi, M.; Nunez, A.; Dollevoet, R.; De Schutter, B.; Li, Z. A decision support ap-proach for condition-based maintenance of rails based on big data analysis. Transp. Res. Part C-Emerg. Technol. 2018, 95, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nam, B.H.; Ii, K.H.S.; Cho, B.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Youn, H. A Potential Technology for Road Sinkhole Assessment: The Rolling Dynamic Deflectometer. J. Test. Eval. 2019, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, I.; Abdel-Jaber, H.; Glisic, B. Quantitative Attribute Analyses with Ground Penetrating Radar for Infrastructure Assessments and Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors 2019, 19, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thodesen, C.C.; Lerfald, B.O.; Hoff, I. Review of Asphalt Pavement Evaluation Methods and Cur-Rent Applications in Norway. Balt. J. Road Bridge Eng. 2012, 7, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, J.V.M.; Larocca, A.P.C.; Neto, J.O.D.A.; Cunha, A.L.; dos Santos, M.C.; Schaal, R.E. Vibration monitoring of a small concrete bridge using wavelet transforms on GPS data. J. Civ. Struct. Heal. Monit. 2019, 9, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrile, V.; Fotia, A.; Leonardi, G.; Pucinotti, R. Geomatics and Soft Computing Techniques for Infrastructural Monitoring. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Gafy, M.A.; Abdelrazig, Y.A.; Abdelhamid, T.S. Environmental Impact Assessment for Transportation Projects: Case Study Using Remote-Sensing Technology, Geographic Information Systems, and Spatial Modeling. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2011, 137, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.W.; Peng, Y.H.; Tseng, Y.C. An Infrastructure-less Framework for Preventing Rear-End Collisions by Vehicular Sensor Networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2011, 15, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.S.; Ghosh, A.; Johnson, E.A.; Krishnamachari, B. Energy-efficient deployment strategies in structural health mon-itoring using wireless sensor networks. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2013, 20, 971–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, S.; Sun, G. Optimal Energy Resources Allocation Method of Wireless Sensor Networks for Intelligent Railway Systems. Sensors 2020, 20, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| No. | Journals | Number of Papers | Total Citations | Norm. Citations | Avg. Citations | Avg. Norm. Citations | Avg. Pub. Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sensors | 26 | 249 | 25.58 | 9.58 | 0.98 | 2018 |
| 2 | Automation in Construction | 16 | 268 | 25.22 | 16.75 | 1.58 | 2017 |
| 3 | Smart Structures and Systems | 7 | 162 | 10.50 | 23.14 | 1.50 | 2015 |
| 4 | Journal of Civil Structural Health Monitoring | 6 | 32 | 1.60 | 5.33 | 0.27 | 2018 |
| 5 | Structural Control and Health Monitoring | 5 | 149 | 11.64 | 29.80 | 2.33 | 2014 |
| 6 | Structure and Infrastructure Engineering | 5 | 50 | 2.60 | 10.00 | 0.52 | 2015 |
| 7 | International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks | 5 | 20 | 1.68 | 4.00 | 0.34 | 2014 |
| 8 | Sustainability | 5 | 6 | 1.57 | 1.20 | 0.31 | 2019 |
| 9 | Applied Sciences-Basel | 5 | 8 | 0.85 | 1.60 | 0.17 | 2019 |
| No. | Keywords | Occurrences | Total Link Strength | Avg. Citations | Avg. Norm. Citations | Avg. Pub. Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Structural health monitoring | 44 | 93 | 20.41 | 1.56 | 2016 |
| 2 | Wireless sensor networks | 43 | 79 | 19.84 | 1.62 | 2017 |
| 3 | Information technology | 28 | 77 | 10.32 | 0.81 | 2017 |
| 4 | BIM | 27 | 73 | 16.81 | 1.09 | 2018 |
| 5 | Fiber optics sensing | 23 | 44 | 16.70 | 1.06 | 2016 |
| 6 | Management | 19 | 62 | 10.11 | 0.82 | 2017 |
| 7 | RFID | 19 | 62 | 19.05 | 1.13 | 2015 |
| 8 | Design | 18 | 62 | 20.83 | 1.28 | 2017 |
| 9 | Infrastructure | 17 | 54 | 11.82 | 0.80 | 2017 |
| 10 | Construction | 16 | 60 | 18.50 | 1.19 | 2017 |
| 11 | Bridges | 14 | 35 | 17.29 | 1.28 | 2016 |
| 12 | Visualization | 11 | 39 | 11.73 | 0.76 | 2018 |
| 13 | Crack detection | 10 | 24 | 9.70 | 1.17 | 2018 |
| 14 | Damage detection | 10 | 31 | 23.70 | 1.71 | 2017 |
| 15 | Internet of things | 10 | 25 | 6.50 | 1.06 | 2019 |
| 16 | Inspection | 9 | 30 | 19.22 | 1.85 | 2016 |
| 17 | GIS | 8 | 20 | 12.63 | 0.65 | 2018 |
| 18 | Maintenance | 8 | 22 | 22.38 | 1.13 | 2016 |
| 19 | Algorithm | 7 | 16 | 30.86 | 2.85 | 2017 |
| 20 | Tracking | 7 | 23 | 27.86 | 1.65 | 2015 |
| No. | Author | Title | Journal | Total Citations | Norm. Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hodge et al. [18] | Wireless Sensor Networks for Condition Monitoring in the Railway Industry: A Survey | IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems | 172 | 5.47 |
| 2 | Liu et al. [7] | A Review of Rotorcraft Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Developments and Applications in Civil Engineering | Smart Structures and Systems | 114 | 6.12 |
| 3 | Noel et al. [19] | Structural Health Monitoring Using Wireless Sensor Networks: A Comprehensive Survey | IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials | 107 | 5.66 |
| 4 | Torres et al. [20] | Analysis of the Strain Transfer in a New FBG Sensor for Structural Health Monitoring | Engineering Structures | 74 | 2.61 |
| 5 | Bocca et al. [21] | A Synchronized Wireless Sensor Network for Experimental Modal Analysis in Structural Health Monitoring | Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering | 72 | 2.54 |
| 6 | Liu et al. [22] | A State-of-the-Art Review on the Integration of Building Information Modelling (BIM) and Geographic Information System (GIS) | ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information | 70 | 3.70 |
| 7 | Mottola et al. [23] | Not all Wireless Sensor Networks are Created Equal: A Comparative Study on Tunnels | ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks | 69 | 2.98 |
| 8 | Park et al. [10] | Performance Test of Wireless Technologies for Personnel and Equipment Proximity Sensing in Work Zones | Journal of Construction Engineering and Management | 66 | 3.65 |
| 9 | Dai et al. [8] | Comparison of Image-Based and Time-of-Flight-Based Technologies for Three-Dimensional Reconstruction of Infrastructure | Journal of Construction Engineering and Management | 59 | 4.18 |
| 10 | Teizer et al. [24] | Status Quo and Open Challenges in Vision-based Sensing and Tracking of Temporary Resources on Infrastructure Construction Sites | Advanced Engineering Informatics | 56 | 1.78 |
| 11 | Sony et al. [25] | A Literature Review of Next-generation Smart Sensing Technology in Structural Health Monitoring | Structural Control & Health Monitoring | 52 | 6.77 |
| Classification | Advantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| DFOS | capable of measuring continuous strain and temperature over a long distance; Lower costs | long distance or large range measurements |
| FBG | linear, small size, high resolution and automatic signal transmission | localized measurement |
| Planning and Design | Construction | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. GIS | 1. BIM | 1. WSN |
| (Site selection [3,4,89], roadside vegetation management [93], and road investigation [90]) | (Information sharing [47], construction management optimization [47,94], schedule monitoring [5], digital delivery [95,96], 3D visualization [97] and LCM [39,98]) | (SHM [11,12,13,18,19,21,23,27,30,52,70,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106], information collection [107,108,109], quality monitoring [28] and traffic trend forecast [110]) |
| 2. BIM | 2. RFID | 2. FOS |
| (Aid decision making [37], information sharing [47], collaborative design [111], 3D visualization [97] and LCM [39,98]) | (Proximity sensing and safety warning [9,10], data collection and material tracking [66,67,68,112]) | (SHM [14,15,16,17,20,51,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,113,114,115,116]) |
| 3. GNSS, GIS, AR and VR | 3. CV | 3. BIM |
| (Visualization of underground facilities [117], investigation of road [90]) | (Data collection [24,108], visual inspection [38,84,112,118], quality control, schedule monitoring [5,6,7,8], efficiency improvement [119] and SHM [85]) | (Expansion, update and maintenance [34,120], 3D visualization [36], safety inspection [45], SHM [35], asset management [96] and LCM [39,98]) |
| 4. CV | 4. GPS | 4. RFID |
| (Planning [7,121], investigation of road [90]) | (safety warning [122], material tracking [66] and site management [123]) | (Leakage monitoring [70], object location [66,68,69] and proximity sensing [124]) |
| 5. GPR | 5. System information model | 5. Smartphone sensor |
| (Exploration of underground structure [125,126], investigation of road [90]) | (Schedule monitoring [127]) | (Road detection [76,77,78], track wear assessment [128], traffic condition detection [79] and vibration monitoring [129]) |
| 6. FOS | 6. MEMS | |
| (Strain monitoring [58]) | (Assessment performance and condition [130], SHM [91,92,131]) | |
| 7. ICT, AI | 7. IoT and smart sensors | |
| (Schedule monitoring [132], site management [123] and communication [133]) | (SHM [25,73,74,75,81,116,134,135,136,137,138,139,140], information collection [107]) | |
| 8. Satellite remote sensing | 8. CV | |
| (Schedule monitoring [141]) | (Data collection [83,142], visual inspection [7,38,84,86,143,144,145,146], SHM [25,147,148,149], safety inspection [8,45,150], road extraction [151] and pipeline positioning [152]) | |
| 9. 3D printing | ||
| (Road repair [153]) | ||
| 10. AI, ML | ||
| (Passenger flow forecast [154], infrastructure assessment [155]) | ||
| 11. DAS | ||
| (Earthquake monitoring [156]) | ||
| 12. Big data | ||
| (Asset management [157], maintenance of railway condition [158]) | ||
| 13. GPR | ||
| (Exploration of underground structure [125], SHM [159,160,161]) | ||
| 14. GPS | ||
| (Vibration monitoring [162]) | ||
| 15. GIS | ||
| (SHM [163], pavement Management [87] and environmental impact assessment [164]) | ||
| 16. Remote sensing | ||
| (Environmental impact assessment [164]) | ||
| 17. Vehicular sensor networks | ||
| (Preventing rear-end collisions [165]) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.Z.; Guo, Z.; Su, D.; Xiao, B.; Tam, V.W.Y. The Application of Advanced Information Technologies in Civil Infrastructure Construction and Maintenance. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7761. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137761
Li CZ, Guo Z, Su D, Xiao B, Tam VWY. The Application of Advanced Information Technologies in Civil Infrastructure Construction and Maintenance. Sustainability. 2022; 14(13):7761. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137761
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Clyde Zhengdao, Zhenchao Guo, Dong Su, Bing Xiao, and Vivian W. Y. Tam. 2022. "The Application of Advanced Information Technologies in Civil Infrastructure Construction and Maintenance" Sustainability 14, no. 13: 7761. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137761
APA StyleLi, C. Z., Guo, Z., Su, D., Xiao, B., & Tam, V. W. Y. (2022). The Application of Advanced Information Technologies in Civil Infrastructure Construction and Maintenance. Sustainability, 14(13), 7761. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137761







