A Review of Farmland Soil Health Assessment Methods: Current Status and a Novel Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
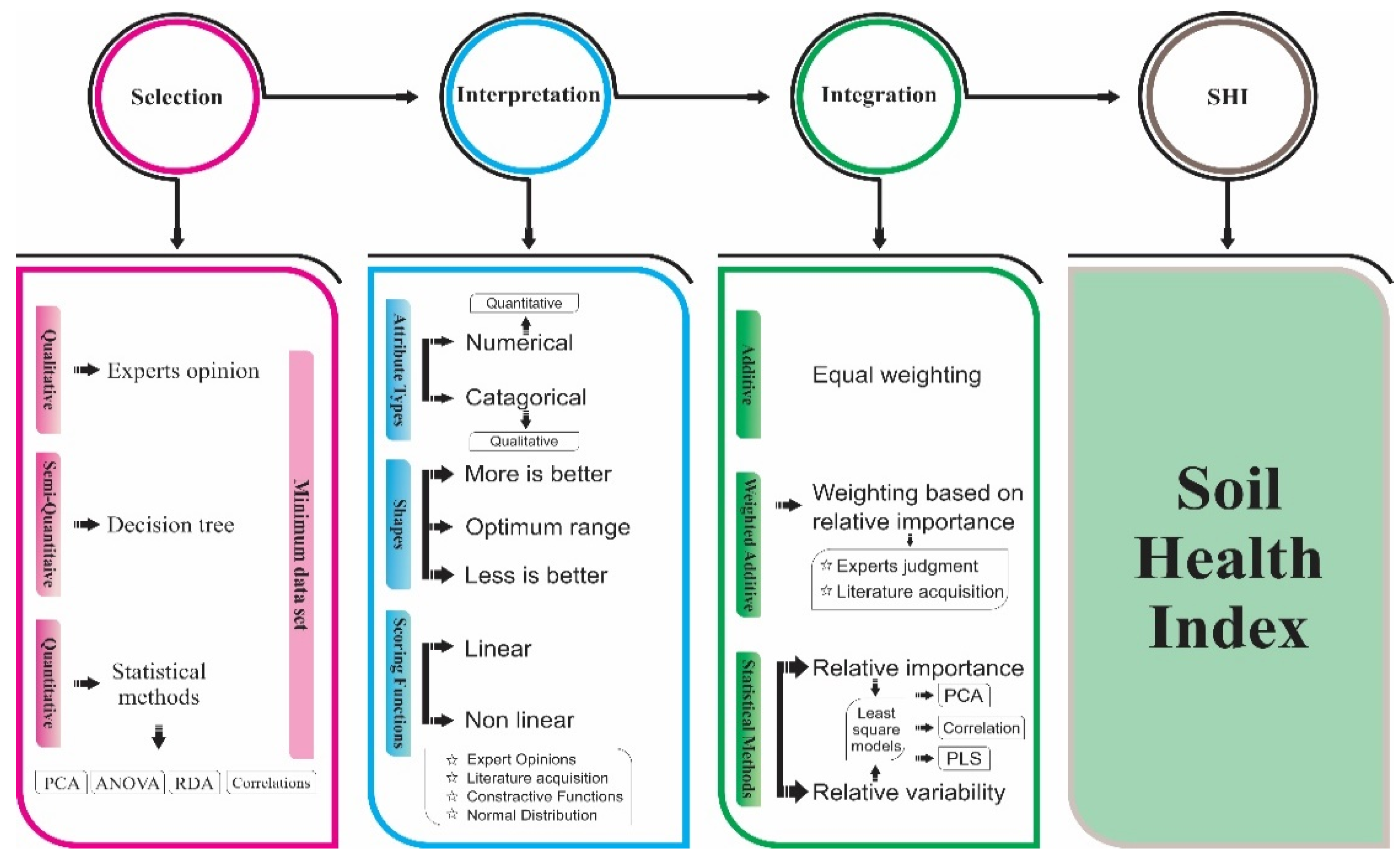
2. Conceptual Framework of Existing SHIs
2.1. Selection of Attributes
2.2. Interpretation of Attributes
2.3. Integration of Attributes
3. Common Soil Health Assessment Methods
3.1. Comprehensive Assessment of Soil Health (CASH)
3.2. Soil Management Assessment Framework (SMAF)
3.3. Meta-Analytic Hierarchy Process (Meta-AHP)
3.4. Soil Indicator Assessment (SINDI)
3.5. Other Soil Health Assessment Methods
3.6. Visual Soil Assessment Approaches
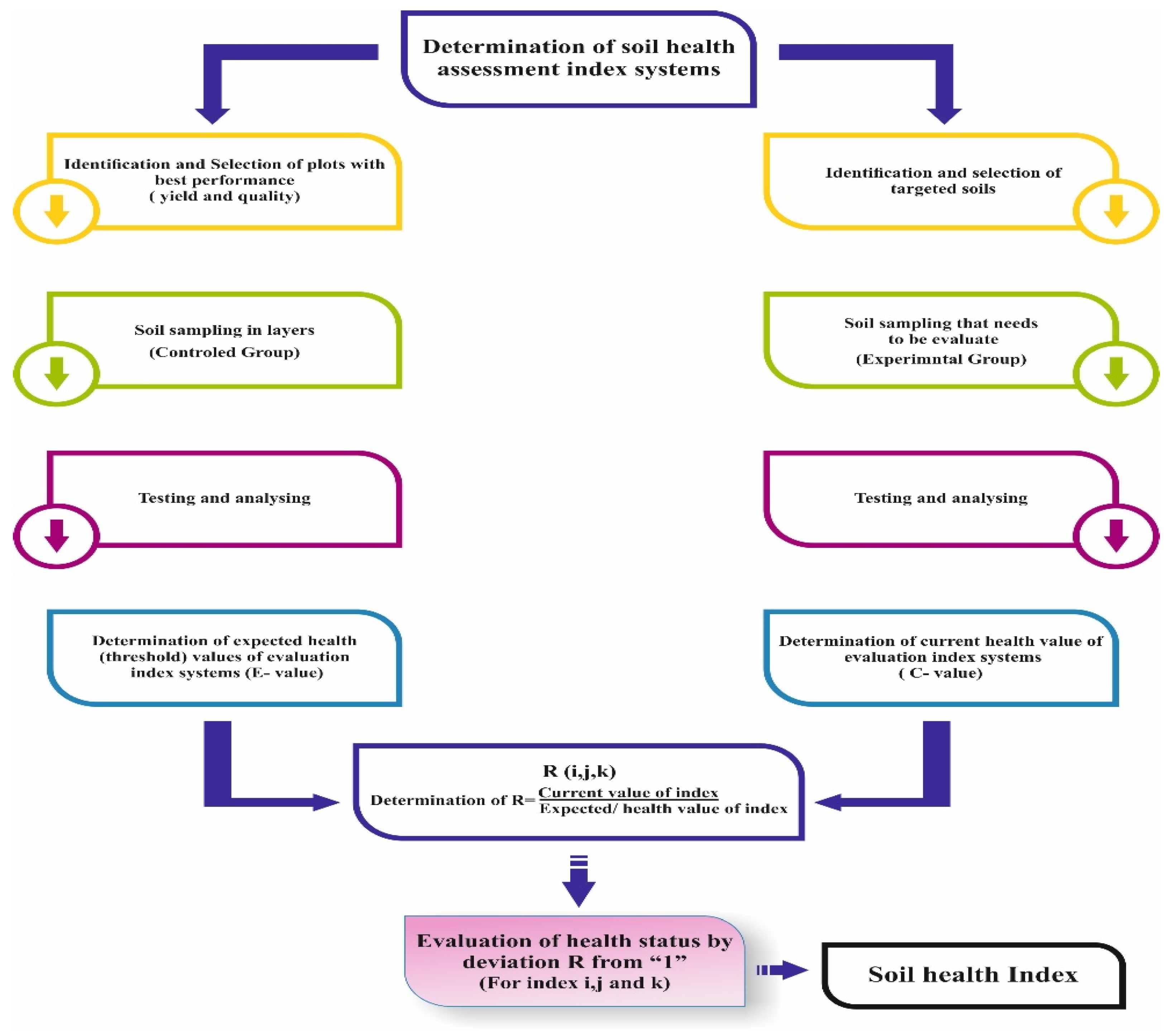
4. A New Soil Health Assessment Approach
4.1. Design and Description
4.2. Determination of Current Value (C)and Health Value or Expected Value (E)
- Soil function index-i: The attributes like field water capacity and the wilting coefficient will be measured by pressure membrane instruments from ring knife soil samples, while soil bulk density is measured directly using the same soil samples, whereas soil organic matter, cation exchange capacity (CEC), pH, and enzyme activity will be determined by conventional analytical methods using composite soil samples, and soil microbial biomass, functional genes, and groups will be determined by high-throughput sequencing using composite refrigerated soil samples.
- Soil nutrient index-j: The total and available amount of soil macro and micro elements will be determined through conventional analytical methods as described by Liu et al. [90].
- Soil output index-k: The yield and income should be calculated through conventional tools and sale registration calculations, respectively, whereas the product quality should be measured according to the corresponding product quality measurement method. The analytical results of both high-performing soils and targeted soils will represent the E and C values.
4.3. Evaluation of Soil Health
- a.
- Current value of function index (Ci)/Expected value of function index (Ei) = Ri
- b.
- Current value of nutrition index (Cj)/Expected value of nutrition index (Ej) = Rj
- c.
- Current value of output index (Ck)/Expected value of output index (Ek) = Rk
4.4. The Advantages of This System and Method
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrea, F.; Bini, C.; Amaducci, S. Soil and Ecosystem Services: Current Knowledge and Evidences from Italian Case Studies. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 123, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Bolan, N.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Kirkham, M.B.; O’Connor, D. Sustainable Soil Use and Management: An Interdisciplinary and Systematic Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, K.; Zhao, R. Bibliometric Analysis of Research on Soil Health from 1999 to 2018. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinot, O.; Levy, G.J.; Steinberger, Y.; Svoray, T.; Eshel, G. Soil Health Assessment: A Critical Review of Current Methodologies and a Proposed New Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Lun, F.; Liu, M.; Xiao, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Qi, W.; Sun, D. Rapid Diagnosis of Agricultural Soil Health: A Novel Soil Health Index Based on Natural Soil Productivity and Human Management. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moebius-Clune, B.N.; Moebius-Clune, D.J.; Gugino, B.K.; Idowu, O.J.; Schindelbeck, R.R.; Ristow, A.J.; van Es, H.M.; Thies, J.E.; Shayler, H.A.; McBride, M.B.; et al. Comprehensive Assessment of Soil Health–The Cornell Framework Manual; Edition 3.1.; Cornell University: Geneva, NY, USA, 2016; p. 123. [Google Scholar]
- Norris, C.E.; Bean, G.M.; Cappellazzi, S.B.; Cope, M.; Greub, K.L.H.; Liptzin, D.; Rieke, E.L.; Tracy, P.W.; Morgan, C.L.S.; Honeycutt, C.W. Introducing the North American Project to Evaluate Soil Health Measurements. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 3195–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, J.; Ren, L.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, J.; Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Peng, Q.; Huang, H.; Chen, A. Diagnosis of soil contamination using microbiological indices: A review on heavy metal pollution—ScienceDirect. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 242, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pheap, S.; Lefèvre, C.; Thoumazeau, A.; Leng, V.; Boulakia, S.; Koy, R.; Hok, L.; Lienhard, P.; Brauman, A.; Tivet, F. Multi-Functional Assessment of Soil Health under Conservation Agriculture in Cambodia. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 194, 104349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igalavithana, A.D.; Lee, S.S.; Niazi, N.K.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, K.H.; Park, J.H.; Moon, D.H.; Ok, Y.S. Assessment of Soil Health in Urban Agriculture: Soil Enzymes and Microbial Properties. Sustainable 2017, 9, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bünemann, E.K.; Bongiorno, G.; Bai, Z.; Creamer, R.E.; De Deyn, G.; de Goede, R.; Fleskens, L.; Geissen, V.; Kuyper, T.W.; Mäder, P.; et al. Soil Quality—A Critical Review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilburne, L.; Sparling, G.; Schipper, L. Soil Quality Monitoring in New Zealand: Development of an Interpretative Framework. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 104, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Wang, C.; Liu, M.; Zhang, D.; Li, K.; Li, N. A New Method for Soil Health Assessment Based on Analytic Hierarchy Process and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2771–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Min, X.; Yang, Z.; Chai, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Physicochemical and Biological Quality of Soil in Hexavalent Chromium-Contaminated Soils as Affected by Chemical and Microbial Remediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paul Obade, V.; Lal, R. Towards a Standard Technique for Soil Quality Assessment. Geoderma 2016, 265, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, J.; Mills, J.; Dibari, C.; Ferrise, R.; Ghaley, B.B.; Hansen, J.G.; Iglesias, A.; Karaczun, Z.; McVittie, A.; Merante, P.; et al. Communicating Soil Carbon Science to Farmers: Incorporating Credibility, Salience and Communicating Soil Carbon Science to Farmers: Incorporating Credibility, Salience and Legitimacy. J. Rural Stud. 2016, 48, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuckle, J.G.; Roesch-McNally, G. Cover Crop Adoption in Iowa: The Role of Perceived Practice Characteristics. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 70, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eanes, F.R.; Singh, A.S.; Bulla, B.R.; Ranjan, P.; Fales, M.; Wickerham, B.; Doran, P.J.; Prokopy, L.S. Land Use Policy Crop Advisers as Conservation Intermediaries: Perceptions and Policy Implications for Relying on Nontraditional Partners to Increase U. S. Farmers ’ Adoption of Soil and Water Conservation Practices. Land Use Policy 2019, 81, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitter, H.; Kirchner, M.; Schmid, E.; Schönhart, M. The Participation of Agricultural Stakeholders in Assessing Regional Vulnerability of Cropland to Soil Water Erosion in Austria. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2013, 14, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnall, D.K.; McIntosh, W.A.; Morgan, C.L.; Woodward, R.T.; Cisneros, M.; Black, M.; Kiella, E.M.; Ale, S. Farmers’ Insights on Soil Health Indicators and Adoption. Agrosystems Geosci. Environ. 2020, 3, e20066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.R.; Veum, K.S.; Parker, P.A.; Holan, S.H.; Karlen, D.L.; Amsili, J.P.; Es, H.M.; Wills, S.A.; Seybold, C.A.; Moorman, T.B. The Soil Health Assessment Protocol and Evaluation Applied to Soil Organic Carbon. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 85, 1196–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brussaard, L. Ecosystem Services Provided by the Soil Biota. Soil Ecol. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.A.; Martin, S. Identifying Critical Limits for Soil Quality Indicators in Agro-Ecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 88, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Singh, S.; Walker, F.R.; Eash, N.S.; Buschermohle, M.J.; Duncan, L.A.; Jagadamma, S. Soil Health and Soil Fertility Assessment by the Haney Soil Health Test in an Agricultural Soil in West Tennessee. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2019, 50, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hose, T.; Cougnon, M.; De Vliegher, A.; Vandecasteele, B.; Viaene, N.; Cornelis, W.; Van Bockstaele, E.; Reheul, D. The Positive Relationship between Soil Quality and Crop Production: A Case Study on the Effect of Farm Compost Application. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 75, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giasson, E.; Sarmento, E.C.; Weber, E.; Flores, C.A.; Hasenack, H. Árvores de Decisão Para o Mapeamento Digital de Solos Em Encostas Basálticas Subtropicais. Sci. Agric. 2011, 68, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fine, A.K.; van Es, H.M.; Schindelbeck, R.R. Statistics, Scoring Functions, and Regional Analysis of a Comprehensive Soil Health Database. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.K.; Bali, S.K.; Zaeen, A.A. A Case Study of Potential Reasons of Increased Soil Phosphorus Levels in the Northeast United States. Agronomy 2017, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrews, S.S.; Carroll, C.R. Designing a Soil Quality Assessment Tool for Sustainable Agroecosystem Management. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oudenhoven, A.P.E.; Petz, K.; Alkemade, R.; Hein, L.; De Groot, R.S. Framework for Systematic Indicator Selection to Assess Effects of Land Management on Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 21, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bone, J.; Head, M.; Barraclough, D.; Archer, M.; Scheib, C.; Flight, D.; Voulvoulis, N. Soil Quality Assessment under Emerging Regulatory Requirements. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bone, J.; Barraclough, D.; Eggleton, P.; Head, M.; Jones, D.T.; Voulvoulis, N. Prioritising Soil Quality Assessment through the Screening of Sites: The Use of Publicly Collected Data. Land Degrad. Dev. 2014, 25, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.C.R.; Brussaard, L.; Totola, M.R.; Hoogmoed, W.B.; de Goede, R.G.M. A Functional Evaluation of Three Indicator Sets for Assessing Soil Quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.G.; Huggins, D.R.; Carpenter-Boggs, L.A.; Reganold, J.P. Evaluating Measures to Assess Soil Health in Long-Term Agroecosystem Trials. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhou, D. Selecting the Minimum Data Set and Quantitative Soil Quality Indexing of Alkaline Soils under Different Land Uses in Northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO-ITPS Protocol for the Assessment of Sustainable Soil Management. 2020. Available online: https://www.fao.org/global-soil-partnership/resources/highlights/detail/en/c/1370578/ (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Zvomuya, F.; Janzen, H.H.; Larney, F.J.; Olson, B.M. A Long-Term Field Bioassay of Soil Quality Indicators in a Semiarid Environment. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2008, 72, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, J.C.; Kalra, N.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Naher, U.A.; Haque, M.M. Soil Health Assessment Methods and Relationship with Wheat Yield. Open J. Soil Sci. 2019, 09, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doran, J.W.; Parkin, T.B. Quantitative Indicators of Soil Quality: A Minimum Data Set. Methods Assess. Soil Qual. 1996, 49, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Bossio, D.A.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Rillig, M.C. The Concept and Future Prospects of Soil Health. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, J.C.; Gamero, C.A.; Rodrigues, J.G.L.; Mirás-Avalos, J.M. Determination of the Quality Index of a Paleudult under Sunflower Culture and Different Management Systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 112, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, J.W.; Parkin, T.B.; Doran, J.W.; Jones, A.J. Methods for Assessing Soil Quality. Choice Rev. Online 1997, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Karlen, D.L.; Mitchell, J.P. A Comparison of Soil Quality Indexing Methods for Vegetable Production Systems in Northern California. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 90, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido Moncada, M.; Gabriels, D.; Cornelis, W.M. Data-Driven Analysis of Soil Quality Indicators Using Limited Data. Geoderma 2014, 235–236, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.A.; Pregibon, D. Tree-Based Models. In Statistical Models in S; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; pp. 377–419. [Google Scholar]
- Debeljak, M.; Cortet, J.; Demšar, D.; Krogh, P.H.; Džeroski, S. Hierarchical Classification of Environmental Factors and Agricultural Practices Affecting Soil Fauna under Cropping Systems Using Bt Maize. Pedobiologia 2007, 51, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada, M.P.; Gabriëls, D.; Lobo, D.; Rey, J.C.; Cornelis, W. Visual Field Assessment of Soil Structural Quality in Tropical Soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 139, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachepsky, Y.A.; Rawls, W.J. Soil Structure and Pedotransfer Functions. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2003, 54, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, M.S.; Holden, N.M. Quantitative Soil Quality Indexing of Temperate Arable Management Systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 150, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Lv, Z.; Liu, G. Assessing Soil Quality for Sustainable Cropland Management Based on Factor Analysis and Fuzzy Sets: A Case Study in the Lhasa River Valley, Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClellan Maaz, T.; Heck, R.H.; Glazer, C.T.; Loo, M.K.; Zayas, J.R.; Krenz, A.R.; Beckstrom, T.B.; Crow, S.E.; Deenik, J.L. Measuring the Unmeasurable: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach to Assessing Soil Health. SSRN Electron. J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, O.J.; van Es, H.M.; Abawi, G.S.; Wolfe, D.W.; Ball, J.I.; Gugino, B.K.; Moebius, B.N.; Schindelbeck, R.R.; Bilgili, A. V Farmer-Oriented Assessment of Soil Quality Using Field, Laboratory, and VNIR Spectroscopy Methods. Plant Soil 2008, 307, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, L. Haney Test Interpretation Guide v1.0. Available online: https://www.wardlab.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/Haney-Rev-1.0-Interpretation-Guide-PDF.pdf (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Mohanty, M.; Painuli, D.K.; Misra, A.K.; Ghosh, P.K. Soil Quality Effects of Tillage and Residue under Rice-Wheat Cropping on a Vertisol in India. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 92, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Karlen, D.L.; Cambardella, C.A. The Soil Management Assessment Framework. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 1945–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, J.W.; Parkin, T.B.; Doran, J.W.; Coleman, D.C.; Bazdicek, D.F.; Stewart, B.A.; Karlen, D.L.; Stott, D.E.; Doran, J.W.; Coleman, D.C.; et al. Defining Soil Quality for a Sustainable Environment 1994. Available online: https://acsess.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/book/10.2136/sssaspecpub35 (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Sharma, K.L.; Sharma, S.C.; Bawa, S.S.; Singh, S.; Chandrika, D.S.; Sharma, V.; Khokhar, A.; Grace, J.K.; Rao, C.S.; Maruthi Sankar, G.R.; et al. Combined Effect of Tillage and Organic Fertilization on Soil Quality Key Indicators and Indices in Alluvial Soils of Indo-Gangetic Plains under Rainfed Maize–Wheat System. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2015, 61, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoray, T.; Hassid, I.; Atkinson, P.M.; Moebius-Clune, B.N.; van Es, H.M. Mapping Soil Health over Large Agriculturally Important Areas. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 1420–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Masto, R.E.; Yadav, A.; George, J.; Ram, L.C.; Shukla, S.P. Soil Quality Index for Evaluation of Reclaimed Coal Mine Spoil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, H.; Xie, Y.; Jia, X.; Su, T.; Li, J.; Shen, Y. Assessment of Soil Quality Indexes for Different Land Use Types in Typical Steppe in the Loess Hilly Area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, T.; Page, T.; Hubacek, K.; Smith, L.; Hiscock, K. The Role of Expert Opinion in Environmental Modelling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 36, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Lal, R. Comparison of Soil Quality Index Using Three Methods. PLoS One 2014, 9, 105981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cherubin, M.R.; Karlen, D.L.; Cerri, C.E.P.; Franco, A.L.C.; Tormena, C.A.; Davies, C.A.; Cerri, C.C. Soil Quality Indexing Strategies for Evaluating Sugarcane Expansion in Brazil. PLoS One 2016, 11, 150860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilburne, L.R.; Hewitt, A.E.; Sparling, G.P.; Selvarajah, N. Soil Quality in New Zealand: Policy and the Science Response. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 1768–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soil Navigator - Pillar1 - Landmark2020. Available online: https://landmark2020.eu/pillars/soil-navigator-pillar1/ (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Shepherd, T.G.; Ross, C.W.; Basher, L.R.; Saggar, S. Visual Soil Assessment; Horizons. mw & Landcare Research: Palmerston North, New Zealand, 2000; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, L.; Schindler, U.; Graham Shepherd, T.; Ball, B.C.; Smolentseva, E.; Pachikin, K.; Hu, C.; Hennings, V.; Sheudshen, A.K.; Behrendt, A.; et al. The Muencheberg Soil Quality Rating for Assessing the Quality of Global Farmland. In Proceedings of the Environmental Science and Engineering (Subseries: Environmental Science); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 235–248. [Google Scholar]
- Roger-Estrade, J.; Richard, G.; Caneill, J.; Boizard, H.; Coquet, Y.; Defossez, P.; Manichon, H. Morphological Characterisation of Soil Structure in Tilled Fields: From a Diagnosis Method to the Modelling of Structural Changes over Time. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, B.C.; Batey, T.; Munkholm, L.J. Field Assessment of Soil Structural Quality - A Development of the Peerlkamp Test. Soil Use Manag. 2007, 23, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, R.M.L.; Ball, B.C.; Tormena, C.A. Improvements in the Visual Evaluation of Soil Structure. Soil Use Manag. 2011, 27, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, D.C. Rapid Assessment of Soil Compaction Damage I. The SOILpak Score, a Semi-Quantitative Measure of Soil Structural Form. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2001, 39, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q. Advances in Agricultural Soil Quality Assessment Tools and Applications. Chinese J. Soil Sci. 2013, 2, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Anderson, I.C.; Singh, B.K. Response of Soil Properties and Microbial Communities to Agriculture: Implications for Primary Productivity and Soil Health Indicators. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SINDI. Available online: https://sindi.landcareresearch.co.nz/ (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- ISQAPER. Available online: https://www.isqaper-project.eu/ (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Huber, S.; Syed, B.; Freudenschub, A.; Ernstsen, V.; Loveland, P. Proposal for a European Soil Monitoring and Assessment Framework; Technical Report 61 EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2001; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- ENVASSO—ESDAC—European Commission. Available online: https://esdac.jrc.ec.europa.eu/projects/envasso (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Recare Project. Available online: http://www.recare-project.eu/ (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Huber, S.; Prokop, G.; Arrouays, D.; Banko, G.; Bispo, A.; Jones, R.J.A.; Kibblewhite, M.G.; Lexer, W.; Möller, A.; Rickson, R.J.; et al. Environmental Assessment of Soil for Monitoring: Volume I Indicators and Criteria; European Communities: Luxembourg, 2008; Volume I, p. 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Caspari, T.; Gonzalez, M.R.; Batjes, N.H.; Mäder, P.; Bünemann, E.K.; de Goede, R.; Brussaard, L.; Xu, M.; Ferreira, C.S.S.; et al. Effects of Agricultural Management Practices on Soil Quality: A Review of Long-Term Experiments for Europe and China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedeoğlu, M.; Başayiğit, L.; Yüksel, M.; Kaya, F. Assessment of the Vegetation Indices on Sentinel-2A Images for Predicting the Soil Productivity Potential in Bursa, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The GROW Observatory—The GROW Observatory. Available online: https://growobservatory.org/ (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Mueller, L.; Kay, B.D.; Hu, C.; Li, Y.; Schindler, U.; Behrendt, A.; Shepherd, T.G.; Ball, B.C. Visual Assessment of Soil Structure: Evaluation of Methodologies on Sites in Canada, China and Germany. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 103, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boizard, H.; Laon-reims-mons, U.A. Visual Soil Structure Assessment-Detailed Report. COSPAR Inf. Bull. 1985, 1985, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batey, T. Soil profile description and evaluation. In Soil and Environmental Analysis: Physical Methods, 2nd ed.; Smith, K.A., Mullins, C.E., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Emmet-Booth, J.P.; Forristal, P.D.; Fenton, O.; Ball, B.C.; Holden, N.M. A Review of Visual Soil Evaluation Techniques for Soil Structure. Soil Use Manag. 2016, 32, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarry, D. A Methodology of Visual-Soil Field Assessment Tool to Support, Enhance, and Contribute to the LADA Program. Rome, Italy Food Agric. Organ. 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Romig, D.E.; Garlynd, M.J.; Harris, R.F. Farmer-based Assessment of Soil Quality: A Soil Health Scorecard. Methods Assess. soil Qual. 1997, 49, 39–60. [Google Scholar]
- Abdollahi, L.; Hansen, E.M.; Rickson, R.J.; Munkholm, L.J. Overall Assessment of Soil Quality on Humid Sandy Loams: Effects of Location, Rotation and Tillage. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 145, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.S.; Jiang, N.H.; Zhang, L.D.; Liu, Z.L. Soil Physical and Chemical Analysis and Description of Soil Profiles. China Stand. Methods Press Beijing China 1996, 24, 266. [Google Scholar]
| Analytical Soil Health Assessment Methods | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Methods | Country | Pros/Principle | Cons |
| Comprehensive Assessment of Soil Health (CASH) | USA Moebius-Clune et al. [6] | Evaluate soil health, address soil health degradation | Does not consider the weight of attributes, high accuracy on the field, and low at a regional scale. |
| Soil Management Assessment Framework (SMAF) | USA Andrews et al. [55] | Evaluate quality and vulnerability to change and management practices | The selection of attributes is not flexible, Development of MDS confronts subjectivity |
| Meta-Analytic Hierarchy Process (Meta-AHP) | China Xue et al. [13] | Consistent and sensitive SH assessment approach for different land use treatments | May confront lack of simplicity and methodological transparency, required competent expert |
| Soil Indicator Assessment (SINDI) | New ZealandLilburne et al. [64] | The online tool, easy to access, compares the measured properties with the database information. Use for environmental reporting | Has regional limitations, uses a single attribute as the assessment unit |
| Quantifying Soil Attributes and ES | Israel Rinot et al. [4] | Use of soil ecosystem services (ES) as a target value, quantify the relative contribution of indicators to each ES | This framework is still at the theoretical stage and has not been used widely. |
| Soil Navigator decision support model | EU EU LANDMARK project [65] | Data mining and machine learning techniques assess basic soil properties, metrological and management parameters | May confront lack of simplicity, Required competent expert Regional limitations |
| Visual soil health assessment methods | |||
| Visual Soil Assessment (VSA) | New Zealand Shepherd et al. [66] | Assess soil quality Spade method | The result of the visual assessment is different from the laboratory as well as it couldn’t predict the biochemical characteristics of soil solely. |
| Muencheberg Soil Quality Rating (M-SQR) | Germany Mueller et al. [67] | Assess yield potential concerning soil properties Pit method | |
| Profil cultural | France Roger Estrade et al. [68] | Assess soil structure, trench method | |
| Peerlkamp | UK Ball et al. [69] | Assess soil structure, Spade method | |
| VESS | Brazil Guimaraes et al. [70] | Assess soil structure, Spade method | |
| SOILpak | Australia McKenzie [71] | Assess soil structure, root growth Spade method | |
| The Ratio (Ri, Rj, Rk) Deviated From “1,” and Their Health Grading | Classification of Soil General Health Status | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ratio(Ri, Rj, Rk) | Level and Their Health Grading | Number of Indicatorsq = m + n + p * | Health Level |
| 0, Health | ≥80% of indicators meet level “0” | Healthy | |
| 1, Sub health | ≥20% of indicators meet level “1” | Sub healthy | |
| 2, Weak | ≥20% of indicators meet level “2” | Weak | |
| 3, Degraded | ≥20% of indicators meet level “3” | Degraded | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain, Z.; Deng, L.; Wang, X.; Cui, R.; Liu, G. A Review of Farmland Soil Health Assessment Methods: Current Status and a Novel Approach. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9300. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159300
Hussain Z, Deng L, Wang X, Cui R, Liu G. A Review of Farmland Soil Health Assessment Methods: Current Status and a Novel Approach. Sustainability. 2022; 14(15):9300. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159300
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain, Zakir, Limei Deng, Xuan Wang, Rongyang Cui, and Gangcai Liu. 2022. "A Review of Farmland Soil Health Assessment Methods: Current Status and a Novel Approach" Sustainability 14, no. 15: 9300. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159300
APA StyleHussain, Z., Deng, L., Wang, X., Cui, R., & Liu, G. (2022). A Review of Farmland Soil Health Assessment Methods: Current Status and a Novel Approach. Sustainability, 14(15), 9300. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159300








