Transformation of Industry Ecosystems in Cities and Regions: A Generic Pathway for Smart and Green Transition
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Problem Definition
1.1. Problem Definition
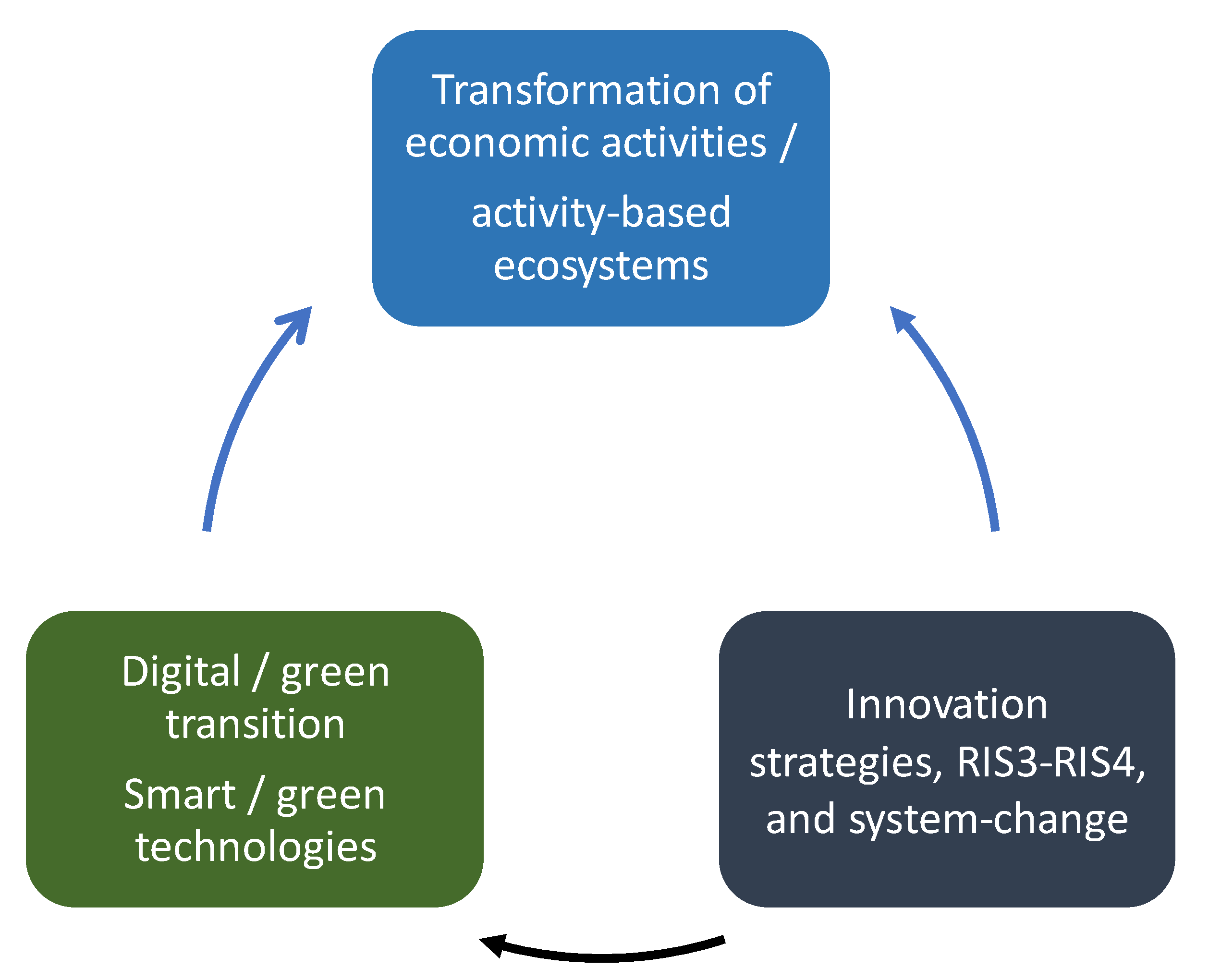
1.2. A Generic Pathway towards Smart and Green Transition
2. Pathways for Industrial Transformation: Related Works
3. Towards a Generic Pathway of Transition: Evidence from the Case Studies
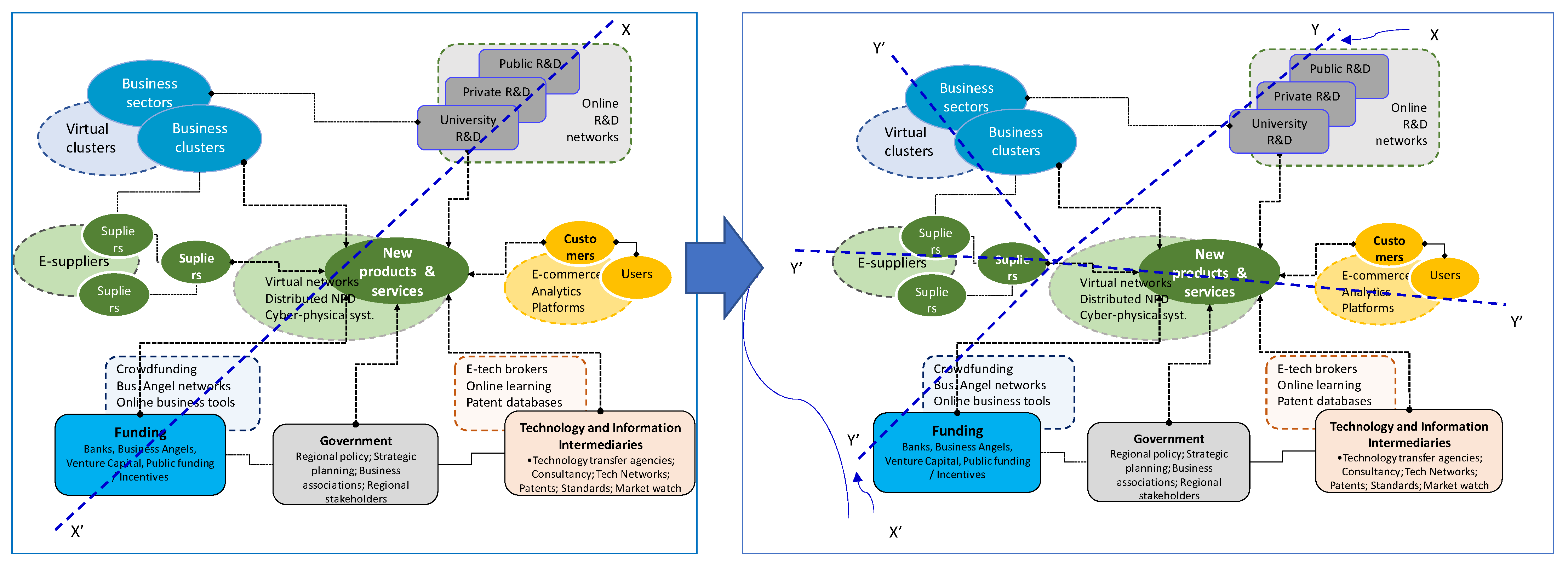
3.1. Generic Pathway Instances and Hypotheses from a Multilevel Perspective
3.2. Evidence from the Case Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission. The European Green Deal; COM(2019) 640 Final; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pontikakis, D.; Fernandez, T.; Janssen, M.; Guy, K.; Marques Santos, A.; Boden, M.; Moncada-Paternò-Castello, P. Projecting Opportunities for INdustrial Transitions (POINT): Concepts, Rationales and Methodological Guidelines for Territorial Reviews of Industrial Transition; No JRC121439; Joint Research Centre: Ispra, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, A.G.; Dalenogare, L.S.; Ayala, N.F. Industry 4.0 technologies: Implementation patterns in manufacturing companies. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 210, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyzbun, K.; Beitz, S.; Barnes, K. Industry transformation. In Drivers of Change: For the Australian Labour Market to 2030: Proceedings of an Expert Scenario Forum; The Academy of the Social Sciences in Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2014; pp. 17–35. [Google Scholar]
- Oztemel, E.; Gursev, S. Literature review of Industry 4.0 and related technologies. J. Intell. Manuf. 2020, 31, 127–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. NACE Rev 2. Statistical Classification of Economic Activities in the European Community; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2008; Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/documents/3859598/5902521/KS-RA-07-015-EN.PDF (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Stephany, F. One size does not fit all: Constructing complementary digital reskilling strategies using online labour market data. Big Data Soc. 2021, 8, 20539517211003120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oqubay, A.; Ohno, K. How Nations Learn: Technological Learning, Industrial Policy, and Catch-Up; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; p. 368. [Google Scholar]
- Adner, R.; Kapoor, R. Value creation in innovation ecosystems: How the structure of technological interdependence affects firm performance in new technology generations. Strateg. Manag. J. 2010, 31, 306–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, M.; Kajikawa, Y.; Tomita, J.; Matsumoto, Y. A review of the ecosystem concept—Towards coherent ecosystem design. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawer, A. The organization of technological platforms. In Technology and Organization: Essays in Honour of Joan Woodward; Phillips, N., Sewell, G., Griffiths, D., Eds.; Research in the Sociology of Organizations; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2010; Volume 29, pp. 287–296. [Google Scholar]
- Castellani, S. Everything You Need to Know about Digital Platforms. Available online: http://stephane-castellani.com/everything-you-need-to-know-about-digital-platforms/ (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Gawer, A.; Cusumano, M.A. Platform leadership: How Intel, Microsoft, and Cisco Drive Industry Innovation; Harvard Business School Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; Volume 5, pp. 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Gawer, A.; Cusumano, M.A. Industry platforms and ecosystem innovation. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2014, 31, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geels, F.W. Socio-technical transitions to sustainability: A review of criticisms and elaborations of the Multi-Level Perspective. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 39, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Propris, L.; Bailey, D. Pathways of regional transformation and Industry 4.0. Reg. Stud. 2021, 55, 1617–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystrov, A.V.; Radaikin, A.G.; Fedoseev, E.V. Formation of organizational and economic model of cross-industry ecosystems. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 666, p. 062112. [Google Scholar]
- D’Amico, G.; Arbolino, R.; Shi, L.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Ioppolo, G. Digitalisation driven urban metabolism circularity: A review and analysis of circular city initiatives. Land Use Policy 2022, 112, 105819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T. State of the Art and Future Perspectives in Smart and Sustainable Urban Development; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. A New Industrial Strategy for Europe; COM(2020) 102 Final; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 10 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Landabaso, M. Guest editorial on research and innovation strategies for smart specialisation in Europe: Theory and practice of new innovation policy approaches. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2014, 17, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellandi, M.; De Propris, L. Local productive systems’ transitions to industry 4.0. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Lopes, S.I.; Fernandez-Carames, T.M. Green IoT and edge AI as key technological enablers for a sustainable digital transition towards a smart circular economy: An industry 5.0 use case. Sensors 2021, 21, 5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komninos, N.; Panori, A.; Kakderi, C. Smart cities beyond algorithmic logic: Digital platforms, user engagement and data science. In Smart Cities in the Post-algorithmic Era; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Izzo, F.; Tomnyuk, V.; Lombardo, R. 4.0 digital transition and human capital: Evidence from the Italian fintech market. Int. J. Manpow. 2021, 43, 910–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favoretto, C.; Mendes, G.H.; Oliveira, M.G.; Cauchick-Miguel, P.A.; Coreynen, W. From servitization to digital servitization: How digitalization transforms companies’ transition towards services. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2022, 102, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadir, B.A.; Broberg, O. Human well-being and system performance in the transition to industry 4.0. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2020, 76, 102936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamim, S.; Cang, S.; Yu, H.; Li, Y. Management approaches for Industry 4.0: A human resource management perspective. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 5309–5316. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Turowski, K. A survey of current challenges in manufacturing industry and preparation for industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the First International Scientific Conference “Intelligent Information Technologies for Industry (IITI’16), Sochi, Russia, 16–21 May 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Rojko, K.; Erman, N.; Jelovac, D. Impacts of the transformation to industry 4.0 in the manufacturing sector: The case of the US. Organizacija. Home 2020, 53, 287–305. [Google Scholar]
- Martynov, V.V.; Shavaleeva, D.N.; Zaytseva, A.A. Information technology as the basis for transformation into a digital society and industry 5.0. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference “Quality Management, Transport and Information Security, Information Technologies” (IT&QM&IS), Sochi, Russia, 23–27 September 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 539–543. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.; An, Y. Analyzing influencing factors of green transformation in China’s manufacturing industry under environmental regulation: A structural equation model. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddi, M. The European Green Deal: Assessing Its Current State and Future Implementation; FIIA Working Paper; FIIA: Helsinki, Finland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rivas, S.; Urraca, R.; Bertoldi, P.; Thiel, C. Towards the EU Green Deal: Local key factors to achieve ambitious 2030 climate targets. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjærseth, J.B. Towards a European Green Deal: The evolution of EU climate and energy policy mixes. Int. Environ. Agreem. Politics Law Econ. 2021, 21, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortright, J. New growth theory, new growth theory, technology and learning: Technology and learning. A practitioner’s guide a practitioner’s guide. Rev. Econ. Dev. Lit. Pract. 2001, 1, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Acs, Z.; Sanders, M. Endogenous growth theory and regional extensions. In Handbook of Regional Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 615–634. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. OECD Science, Technology and Innovation Outlook 2016; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2016; Available online: https://doi.org/10.1787/sti_in_outlook-2016-en (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Geels, F.W. Technological transitions as evolutionary reconfiguration processes: A multi-level perspective and a case-study. Res. Policy 2002, 31, 1257–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geels, F.W. Transformative Innovation and Socio-Technical Transitions to Address Grand Challenges; European Commission R&I Paper Series; Working Paper; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Schot, J.; Geels, F.W. Strategic niche management and sustainable innovation journeys: Theory, findings, research agenda, and policy. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2008, 20, 537–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.M.; Rohracher, H. Legitimizing research, technology and innovation policies for transformative change: Combining insights from innovation systems and multi-level perspective in a comprehensive ‘failures’ framework. Res. Policy 2012, 41, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schot, J.; Steinmueller, W.E. Three frames for innovation policy: R&D, systems of innovation and transformative change. Res. Policy 2018, 47, 1554–1567. [Google Scholar]
- Tukker, A. Leapfrogging into the future: Developing for sustainability. Int. J. Innov. Sustain. Dev. 2005, 1, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.; Sauter, R. Sustainable innovation through leapfrogging: A review of the evidence. Int. J. Technol. Glob. 2011, 5, 170–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Gibbs, D. Sustainability transitions and leapfrogging in latecomer cities: The development of solar thermal energy in Dezhou, China. Reg. Stud. 2018, 52, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.B.; Yigitcanlar, T. Participatory Governance of Smart Cities: Insights from e-Participation of Putrajaya and Petaling Jaya, Malaysia. Smart Cities 2022, 5, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A. Moving from Industry 2.0 to Industry 4.0: A case study from India on leapfrogging in smart manufacturing. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 21, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primi, A.; Toselli, M. A global perspective on industry 4.0 and development: New gaps or opportunities to leapfrog? J. Econ. Policy Reform 2020, 23, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komninos, N.; Kakderi, C.; Collado, A.; Papadaki, I.; Panori, A. Digital transformation of city ecosystems: Platforms shaping engagement and externalities across vertical markets. J. Urban. Technol. 2021, 28, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komninos, N.; Kakderi, C.; Mora, L.; Panori, A.; Sefertzi, E. Towards high impact smart cities: A universal architecture based on connected intelligence spaces. J. Knowl. Econ. 2022, 13, 1169–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Dey, S. Global manufacturing value networks: Assessing the critical roles of platform ecosystems and industry 4.0. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2021, 32, 1290–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, J.; Jacobides, M.G.; Reeves, M. The myths and realities of business ecosystems. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2019, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Okano, M.T.; Antunes, S.N.; Fernandes, M.E. Digital transformation in the manufacturing industry under the optics of digital platforms and ecosystems. Indep. J. Manag. Prod. 2021, 12, 1139–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, K.I.; Müller, J.M. (Eds.) Digital Business Models in Industrial Ecosystems: Lessons Learned from Industry 4.0 Across Europe; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Andreoni, A.; Lazonick, W. Local Ecosystems and Social Conditions of Innovative Enterprise. In The Oxford Handbook of Industrial Hubs and Economic Development; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 77–97. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Updating the 2020 New Industrial Strategy: Building a Stronger Single Market for Europe’s Recovery; COM(2021) 350 Final; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 5 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rip, A.; Kemp, R. Technological change. Hum. Choice Clim. Chang. 1998, 2, 327–399. [Google Scholar]
- Geels, F.W. Technological Transitions and System Innovations: A Co-Evolutionary and Socio-Technical Analysis; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Geels, F.W.; Schot, J. Typology of sociotechnical transition pathways. Res. Policy 2007, 36, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genus, A.; Coles, A.M. Rethinking the multi-level perspective of technological transitions. Res. Policy 2008, 37, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geels, F.W.; Kern, F.; Fuchs, G.; Hinderer, N.; Kungl, G.; Mylan, J.; Wassermann, S. The enactment of socio-technical transition pathways: A reformulated typology and a comparative multi-level analysis of the German and UK low-carbon electricity transitions 1990–2014. Res. Policy 2016, 45, 896–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geels, F.W.; Schot, J. Taxonomy of transition pathways in socio-technical transitions. In Proceedings of the On Exploring Socio-Technical Transitions to Sustainability’ Workshop; Institute of Commonwealth Studies: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Marinelli, E.; Fernández Sirera, T.; Pontikakis, D. Towards a Transformative Smart Specialisation Strategy: Lessons from Catalonia, Bulgaria and Greece; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Veldhuizen, C. Smart Specialisation as a transition management framework: Driving sustainability-focused regional innovation policy? Res. Policy 2020, 49, 103982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhout, F.; Smith, A.; Stirling, A. Socio-technological regimes and transition contexts. Syst. Innov. Transit. Sustain. Theory Evid. Policy 2004, 44, 48–75. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.; Stirling, A.; Berkhout, F. The governance of sustainable socio-technical transitions. Res. Policy 2005, 34, 1491–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foray, D.; Goddard, J.; Goenaga Beldarrain, X.; Landabaso, M.; McCann, P.; Morgan, K.; Ortgea-Argiles, R. Guide to Research and Innovation Strategies for Smart Specialisation (RIS 3), Smart Specialisation Platform; IPTS Institute for Prospective Technological Studies, Joint Research Centre of the European Commission: Seville, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Komninos, N.; Tsampoulatidis, I.; Kakderi, C.; Nikolopoulos, S.; Kompatsiaris, I. Projects for smart cities: Ecosystems, connected intelligence and innovation for the radical transformation of cities. In Smart Cities and Smart Communities; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 33–68. [Google Scholar]
- Komninos, N.; Kakderi, C.; Panori, A.; Psaltoglou, A.; Chatziparadeisis, A. Ecosystems and functioning EDP for S3 2021–2027 in Greece. Report to the European Commission, DG Regional and Urban Policy. 2020. Available online: https://www.komninos.eu/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/ECOSYSTEMS-and-EDP-2021-2027-in-GREECE-v2020-05-16-Final.pdf (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- Komninos, N. Ecosystems and functioning EDP for S3 2021–2027 in Cyprus. Report to the European Commission, DG Regional and Urban Policy. 2020. Available online: https://www.komninos.eu/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/ECOSYSTEMS-and-EDP-2021-2027-in-CYPRUS-v2020-05-16-FINAL.pdf (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- Kakderi, C.; Komninos, N.; Panori, A.; Psaltoglou, A. Smart Specialisation 2.0: Driving public funds towards platforms and ecosystems. In Proceedings of the International Symposium: New Metropolitan Perspectives, Reggio Calabria, Italy, 18–23 May 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- Foray, D. From smart specialisation to smart specialisation policy. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2014, 17, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.; Maroulis, N. From Strategy to Implementation: The Real Challenge for Smart Specialisation Policy. In Advances in the Theory and Practice of Smart Specialisation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 293–318. [Google Scholar]
- Komninos, N.; Kakderi, C.; Panori, A.; Garcia, E.; Fellnhofer, K.; Reid, A.; Cvijanović, V.; Roman, M.; Deakin, M.; Mora, L.; et al. Intelligence and co-creation in Smart Specialisation Strategies: Towards the next stage of RIS3. archiDOCT 2021, 17, 25361. [Google Scholar]
- Panori, A.; Kakderi, C.; Dimitriadis, I. Combining technological relatedness and sectoral specialization for improving prioritization in Smart Specialisation. Reg. Stud. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschma, R.; Frenken, K. Technological relatedness and regional branching. In Beyond Territory: Dynamic Geographies of Knowledge Creation, Diffusion, and Innovation; Bathelt, H., Feldman, M.P., Kogler, D.F., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 64–81. [Google Scholar]
- Srnicek, N. Platform Capitalism; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Komninos, N.; Tsarchopoulos, P.; Kakderi, C. New services design for smart cities: A planning roadmap for user-driven innovation. In Proceedings of the 2014 ACM International Workshop on Wireless and Mobile Technologies for Smart Cities, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 11 August 2014; pp. 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, C.; Lee, J.H.; Sonthikorn, P.; Vongbunyong, S. Frugal innovation and leapfrogging innovation approach to the industry 4.0 challenge for a developing country. Asian J. Technol. Innov. 2021, 29, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bilali, H. The multi-level perspective in research on sustainability transitions in agriculture and food systems: A systematic review. Agriculture 2019, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komninos, N.; Panori, A. The creation of city smartness: Architectures of intelligence in smart cities and smart ecosystems. In Smart Cities in the Post-Algorithmic Era; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
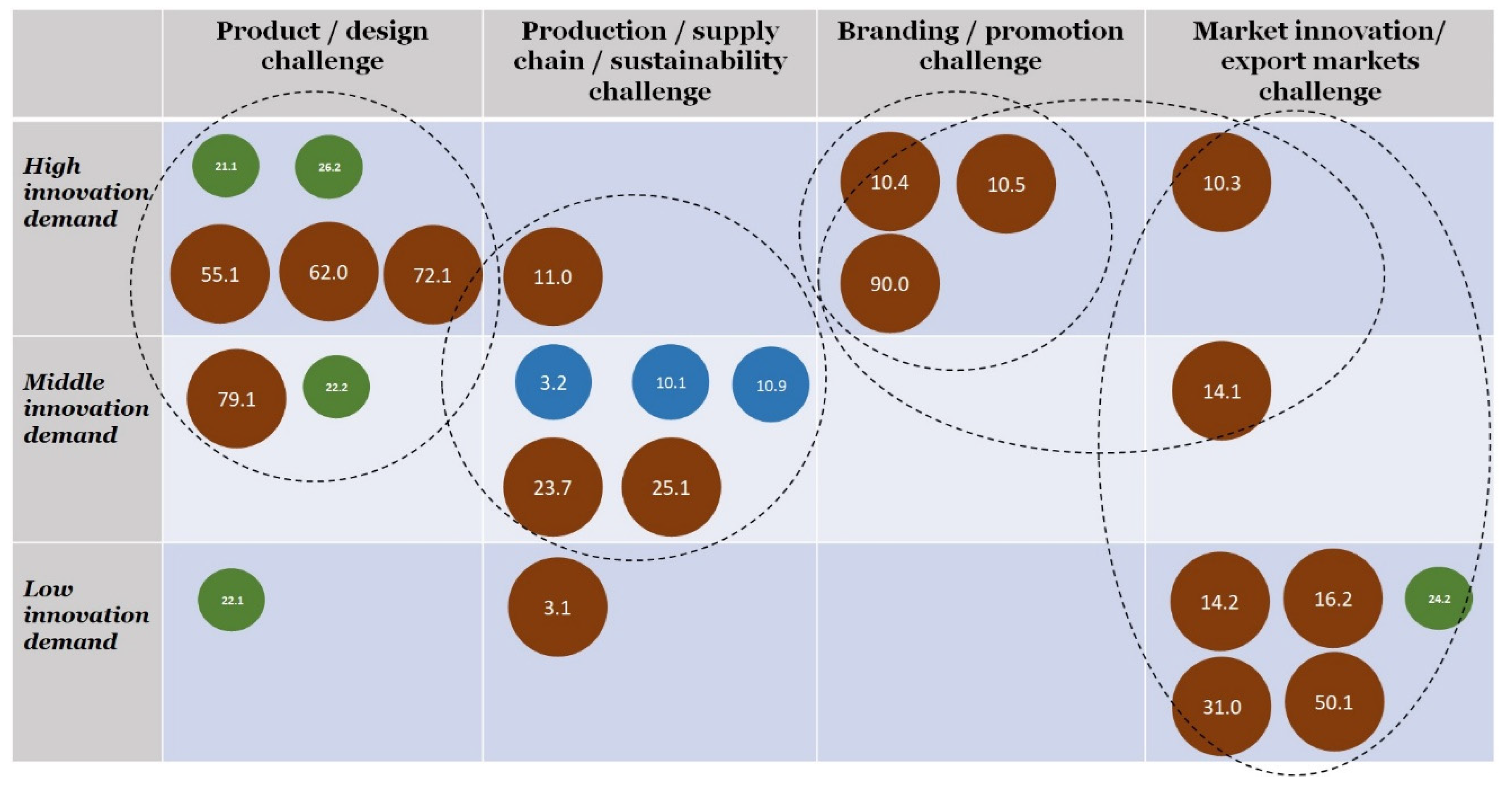
| Top10 per Number of Companies | Top10 per Employment | Top10 per Specialisation on Companies | Top10 per Specialisation on Employment | NACE | Top10 per Number of Companies | Top10 per Employment | Top10 per LQ on Companies | Top10 per LQ on Employment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NACE | Index | NACE | Index | NACE | Index | NACE | Index | ||||||
| 55.1 | 1077 | 55.1 | 20,284 | 10.4 | 8.12 | 10.4 | 6.39 |  | 55.1 | 1077 | 20,284 | 2.51 | 2.97 |
| 10.7 | 591 | 10.7 | 3241 | 30.3 | 4.55 | 55.1 | 2.97 | 10.4 | 466 | 1237 | 8.12 | 6.39 | |
| 72.1 | 499 | 79.1 | 2570 | 23.4 | 3.55 | 50.1 | 2.80 | 72.1 | 499 | 1323 | 1.98 | 1.69 | |
| 10.4 | 466 | 50.1 | 1707 | 32.2 | 3.18 | 23.4 | 2.30 | 79.1 | 378 | 2570 | 2.14 | 2.04 | |
| 79.1 | 378 | 72.1 | 1323 | 55.1 | 2.51 | 79.1 | 2.04 | 16.2 | 208 | 1.79 | |||
| 62.0 | 351 | 10.4 | 1237 | 79.1 | 2.14 | 72.1 | 1.69 | 50.1 | 1707 | 2.80 | |||
| 90.0 | 269 | 10.1 | 791 | 72.1 | 1.98 | 32.2 | 1.65 | 10.1 | 791 | 1.14 | |||
| 31.0 | 235 | 31.0 | 699 | 25.2 | 1.88 | 13.9 | 1.51 | 10.5 | 95 | 1.87 | |||
| 16.2 | 208 | 62.0 | 663 | 10.5 | 1.87 | 10.1 | 1.14 | 23.4 | 3.55 | 2.30 | |||
| 10.5 | 95 | 61.2 | 624 | 16.2 | 1.79 | 28.3 | 1.13 | 32.2 | 3.18 | 1.65 | |||
| NACE | Name | Number of Regions | NACE | Name | Number of Regions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55.1 | Hotels and similar accommodation | 8 | 63.9 | Other information service activities | 1 |
| 11.0 | Manufacture of beverages | 8 | 61.3 | Satellite telecommunications activities | 1 |
| 10.5 | Manufacture of dairy products | 7 | 61.1 | Wired telecommunications activities | 1 |
| 03.1 | Fishing | 7 | 50.2 | Sea and coastal freight water transport | 1 |
| 16.2 | Manufacture of products of wood, cork, straw, and plaiting materials | 6 | 32.2 | Manufacture of musical instruments | 1 |
| 31.0 | Manufacture of furniture | 5 | 32.1 | Manufacture of jewellery, bijouterie, and related articles | 1 |
| 03.2 | Aquaculture | 5 | 30.3 | Manufacture of air and spacecraft and related machinery | 1 |
| 25.1 | Manufacture of structural metal products | 4 | 29.1 | Manufacture of motor vehicles | 1 |
| 23.4 | Manufacture of other porcelain and ceramic products | 4 | 28.9 | Manufacture of other special-purpose machinery | 1 |
| 10.9 | Manufacture of prepared animal feeds | 4 | 26.7 | Manufacture of optical instruments and photographic equipment | 1 |
| 10.7 | Manufacture of bakery and farinaceous products | 4 | 26.2 | Manufacture of computers and peripheral equipment | 1 |
| 10.6 | Manufacture of grain mill products, starches, and starch products | 4 | 26.1 | Manufacture of electronic components and boards | 1 |
| 10.3 | Processing and preserving of fruit and vegetables | 4 | 24.3 | Manufacture of other products of first processing of steel | 1 |
| 90.0 | Creative, arts, and entertainment activities | 3 | 24.2 | Manufacture of tubes, pipes, hollow profiles, and related fittings of steel | 1 |
| 79.1 | Travel agency and tour operator activities | 3 | 23.6 | Manufacture of articles of concrete, cement, and plaster | 1 |
| 72.1 | Research and experimental development on natural sciences and engineering | 3 | 23.3 | Manufacture of clay building materials | 1 |
| 50.1 | Sea and coastal passenger water transport | 3 | 22.2 | Manufacture of plastic products | 1 |
| 23.7 | Cutting, shaping, and finishing of stone | 3 | 21.1 | Manufacture of basic pharmaceutical products | 1 |
| 16.1 | Sawmilling and planning of wood | 3 | 20.5 | Manufacture of other chemical products | 1 |
| 10.4 | Manufacture of vegetable and animal oils and fats | 3 | 18.2 | Reproduction of recorded media | 1 |
| 10.2 | Processing and preserving of fish, crustaceans, and molluscs | 3 | 15.1 | Tanning and dressing of leather; manufacture of luggage, handbags, saddlery, and harness; etc. | 1 |
| 10.1 | Processing and preserving of meat and production of meat products | 3 | 14.2 | Manufacture of articles of fur | 1 |
| 62.0 | Computer programming, consultancy, and related activities | 2 | 14.1 | Manufacture of wearing apparel, except fur apparel | 1 |
| 28.3 | Manufacture of agricultural and forestry machinery | 2 | 13.3 | Finishing of textiles | 1 |
| 22.1 | Manufacture of rubber products | 2 | 10.1 | Processing and preserving of meat and production of meat products | 1 |
| 10.8 | Manufacture of other food products | 2 |
| REGION | Industry Group/Ecosystem | Size of Ecosystem | Mature/ Emerging | R&D and Innovation Demand | Innovation Platform | Regional/Interregional |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East Macedonia and Thrace | 22.2 Manufacture of plastics | Small | Mature | Medium | New product and materials | Regional |
| 23.7 Cutting, shaping of stone | Large | Mature | Medium | Brand and by-products | Interregional | |
| 26.2 Manufacture of computers | Small | Emerging | High | No | Regional | |
| Central Macedonia | 10.3 Processing fruit and vegetables | Large | Mature | High | Brand and packaging | Interregional |
| 14.1 Manufacture of wearing apparel | Large | Mature | Medium | Brand and design | Regional | |
| 25.1 Manufacture of structural metal products | Large | Mature | Medium | Materials | Regional | |
| West Macedonia | 16.2 Manufacture of products of wood | Large | Mature | Low | Brand and eco-quality | Interregional |
| 14.2 Manufacture of fur | Large | Mature | Low | Export | Regional | |
| Epirus | 10.1 Processing of meat | Medium | Mature | Medium | Brand and packaging | Interregional |
| 10.5 Manufacture of dairy products | Large | Mature | High | Brand and packaging | Interregional | |
| Thessaly | 22.1 Manufacture of rubber products | Small | Emerging | Low | No | Regional |
| 31.0 Manufacture of furniture | Large | Mature | Low | Commercial infra | Interregional | |
| Sterea Ellada | 24.2 Manufacture of tubes of steel | Small | Mature | Low | New product | Regional |
| Ionian Islands | 79.1 Travel and tour operator activities | Large | Mature | High | New product | Interregional |
| Attica | 90.0 Creative, art activities | Large | Mature | High | Digital infrastructure | Interregional |
| 62.0 Computer programming | Large | Emerging | High | Market and infrastructure | Regional | |
| 21.1 Manufacture of pharmaceutical products | Small | Emerging | High | New product | Regional | |
| Western Greece | 03.2 Aquaculture | Medium | Mature | Medium | Brand and new product | Interregional |
| 10.9 Manufacture of prepared animal feeds | Medium | Mature | Medium | Production and supply chain | Interregional | |
| Peloponnese | 11.0 Manufacture of beverages | Large | Mature | High | Production and by-products | Interregional |
| North Aegean | 10.4 Manufacture of vegetable oils and fats | Large | Mature | High | Brand and quality | Interregional |
| 03.1 Fishing | Large | Mature | Low | Brand and Infrastructure | Interregional | |
| South Aegean | 50.1 Sea passenger water transport | Large | Mature | Low | Infrastructure | Interregional |
| Crete | 55.1 Hotels and similar accommodation | Large | Mature | High | Market access | Interregional |
| 72.1 Research in natural sciences and engineering | Large | Emerging | Medium | Infrastructure | Interregional |
| Smart Technologies | Green Technologies | Smart–Green Technologies | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company level |
|
|
|
| Ecosystem level |
|
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Komninos, N. Transformation of Industry Ecosystems in Cities and Regions: A Generic Pathway for Smart and Green Transition. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9694. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159694
Komninos N. Transformation of Industry Ecosystems in Cities and Regions: A Generic Pathway for Smart and Green Transition. Sustainability. 2022; 14(15):9694. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159694
Chicago/Turabian StyleKomninos, Nicos. 2022. "Transformation of Industry Ecosystems in Cities and Regions: A Generic Pathway for Smart and Green Transition" Sustainability 14, no. 15: 9694. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159694
APA StyleKomninos, N. (2022). Transformation of Industry Ecosystems in Cities and Regions: A Generic Pathway for Smart and Green Transition. Sustainability, 14(15), 9694. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159694






