Degradation of Tetracycline in Water by Fe-Modified Sterculia Foetida Biochar Activated Peroxodisulfate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
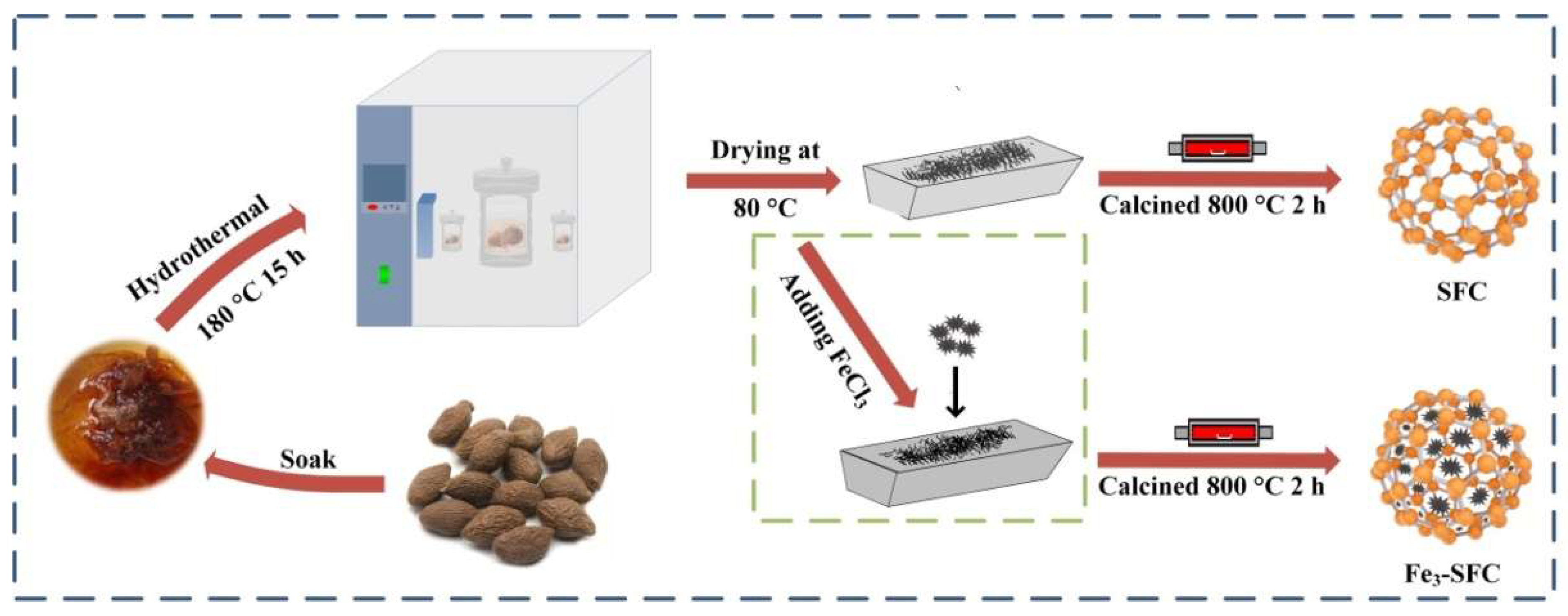
2.2. Biochar-Based Catalyst Synthesis
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Catalytic Degradation Experiment
2.5. Electrochemical Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
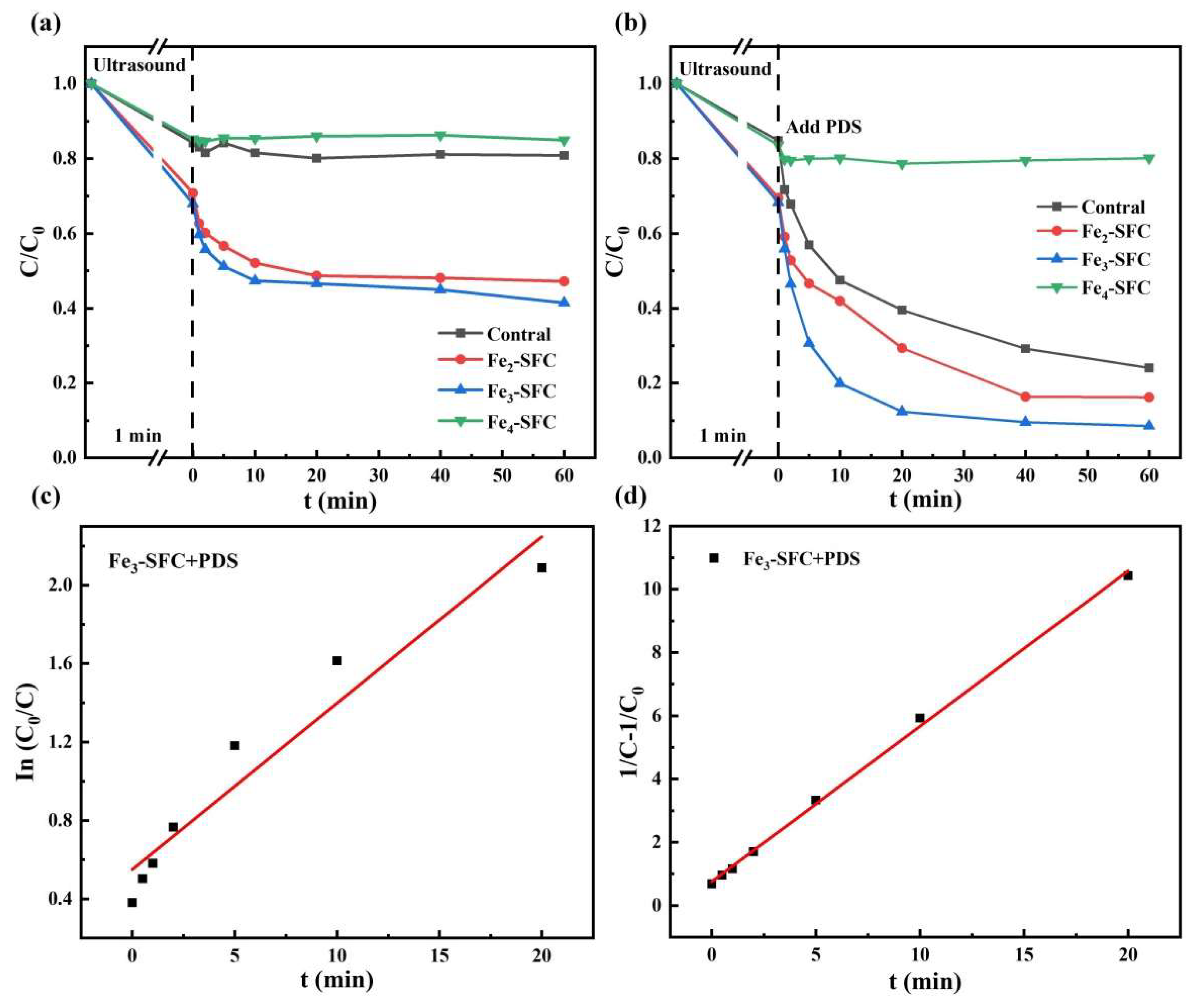
3.2. TC Degradation
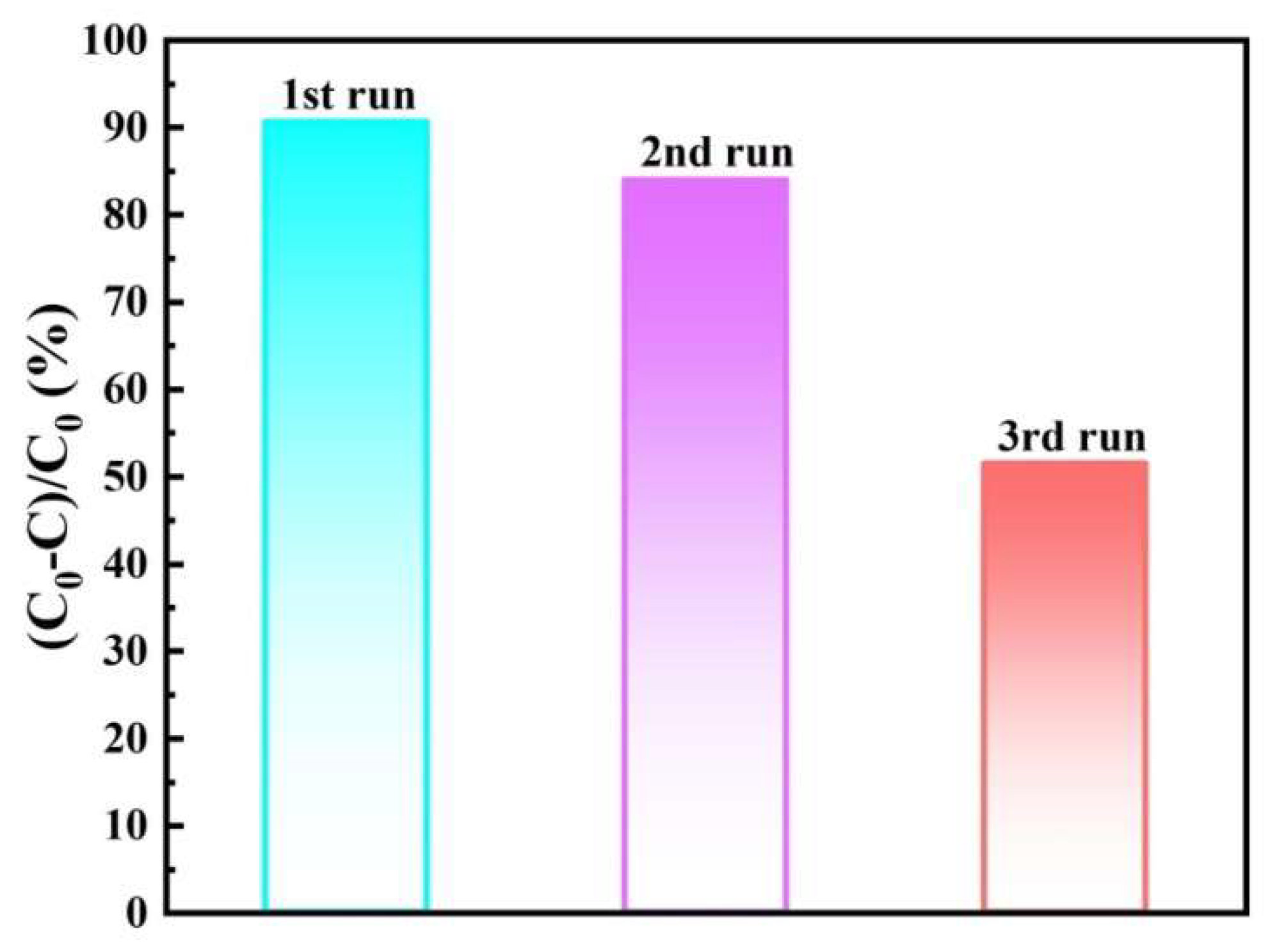
3.3. Reaction Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yue, Y.; Shen, C.; Ge, Y. Biochar accelerates the removal of tetracyclines and their intermediates by altering soil properties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Mei, Q.; Tao, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhao, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. A smartphone-integrated ratiometric fluorescence sensing platform for visual and quantitative point-of-care testing of tetracycline. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 148, 111791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Z.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, X.; Ge, M.; Liu, D.; Wang, C.; He, Z. A Review on Application of Biochar in the Removal of Pharmaceutical Pollutants through Adsorption and Persulfate-Based AOPs. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, X.; Sun, W.; Li, S.; Yang, C.; Li, C.; Lu, Z. Degradation of tetracycline by medium pressure UV-activated peroxymonosulfate process: Influencing factors, degradation pathways, and toxicity evaluation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, B.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Modification of activated carbon by the alkaline treatment to remove the dyes from wastewater: Mechanism, isotherm and kinetic. Desalination Water Treat. 2012, 47, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Lv, W.; Liu, G. Construction of carbon dots modified MoO3/g-C3N4 Z-scheme photocatalyst with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity for the degradation of tetracycline. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 229, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Qi, J.; Tian, J.; Gao, S.; Cui, F. Construction of Ag/g-C3N4 photocatalysts with visible-light photocatalytic activity for sulfamethoxazole degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 341, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Hayati, B.; Arami, M. Textile dye removal from single and ternary systems using date stones: Kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 4638–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, R.K.; Agrawal, K.; Verma, P. Multifaceted Role of Microalgae for Municipal Wastewater Treatment: A Futuristic Outlook toward Wastewater Management. Clean Soil Air Water 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Nasar, A. Utilization of Jackfruit Peel as a Low-cost Adsorbent for the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Synthetically Polluted Water. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2021, 17, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ji, G.; Li, A. Degradation of antibiotic pollutants by persulfate activated with various carbon materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Han, D.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shang, J. Persulfate activation by sulfide-modified nanoscale iron supported by biochar (S-nZVI/BC) for degradation of ciprofloxacin. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235, 116202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Lu, X.; Yan, B.; Li, N.; Chen, G.; Cheng, Z.; Hou, L.A.; Wang, S.; Duan, X. Sludge-derived biochar toward sustainable Peroxymonosulfate Activation: Regulation of active sites and synergistic production of reaction oxygen species. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 440, 135897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Wang, C. Peroxymonosulfate catalytic degradation of persistent organic pollutants by engineered catalyst of self-doped iron/carbon nanocomposite derived from waste toner powder. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 291, 120963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, R.; Sun, R.; Yang, J.; Sillanpää, M. A review on persulfates activation by functional biochar for organic contaminants removal: Synthesis, characterizations, radical determination, and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.-e.; Guan, J.; Feng, Q.; Wu, X.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, W.; Tong, S.; Zhou, N.; Gong, D. Accelerated polysulfide redox kinetics revealed by ternary sandwich-type S@Co/N-doped carbon nanosheet for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries. Carbon 2018, 128, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M. Photocatalytic degradation of dyes using carbon nanotube and titania nanoparticle. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oveisi, M.; Asli, M.A.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Carbon nanotube based metal-organic framework nanocomposites: Synthesis and their photocatalytic activity for decolorization of colored wastewater. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2019, 487, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.-L.; Ma, X.-W.; Wu, X.-Q.; Yuan, L.; Lai, Y.-L.; Tong, Z.-H. Degradation of imidazolium ionic liquids in a thermally activated persulfate system. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 128624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-Q.; Gao, N.-Y.; Chu, W.-H.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Zhang, J.; Yin, D.-Q. UV-activated persulfate oxidation of sulfamethoxypyridazine: Kinetics, degradation pathways and impact on DBP formation during subsequent chlorination. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Saffar-Dastgerdi, M.H. Clean Laccase immobilized nanobiocatalysts (graphene oxide-zeolite nanocomposites): From production to detailed biocatalytic degradation of organic pollutant. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 268, 118443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wu, T.; Liu, Z.; Tang, W.; Xiao, S.; Shao, B.; Liang, Q.; He, Q.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, C.; et al. Carbon nanotube-based materials for persulfate activation to degrade organic contaminants: Properties, mechanisms and modification insights. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Xu, X.; Qamar Zaman, W.; Hu, X.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H.; Cao, X. Different mechanisms between biochar and activated carbon for the persulfate catalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole: Roles of radicals in solution or solid phase. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 121908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Dai, H.; Ji, J.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H. Resource utilization of luffa sponge to produce biochar for effective degradation of organic contaminants through persulfate activation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 288, 120650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Wang, C.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Tong, S. Persulfate activation for efficient degradation of norfloxacin by a rGO-Fe3O4 composite. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 102, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Décima, M.A.; Marzeddu, S.; Barchiesi, M.; Di Marcantonio, C.; Chiavola, A.; Boni, M.R. A Review on the Removal of Carbamazepine from Aqueous Solution by Using Activated Carbon and Biochar. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Moghimi, F.; Arami, M.; Mazaheri, F. Silk degumming using microwave irradiation as an environmentally friendly surface modification method. Fibers Polym. 2010, 11, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Najafi, F.; Neshat, A. Poly (amidoamine-co-acrylic acid) copolymer: Synthesis, characterization and dye removal ability. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 42, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magioglou, E.; Frontistis, Z.; Vakros, J.; Manariotis, I.; Mantzavinos, D. Activation of Persulfate by Biochars from Valorized Olive Stones for the Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole. Catalysts 2019, 9, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Abdollahi, K.; Panahi, R.; Rahmanian, N.; Shakeri, M.; Mokhtarani, B. Applications of Biocatalysts for Sustainable Oxidation of Phenolic Pollutants: A Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.H.; Chen, Y.D.; Li, R.; Zhang, C.; Ge, Y.; Cao, G.; Ma, M.; Duan, X.; Wang, S.; Ren, N.Q. N-doped graphitic biochars from C-phycocyanin extracted Spirulina residue for catalytic persulfate activation toward nonradical disinfection and organic oxidation. Water Res. 2019, 159, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Ma, T.; Shang, Y.; Gao, B.; Jin, B.; Dan, H.; Li, Q.; Yue, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. In-situ pyrolysis of Enteromorpha as carbocatalyst for catalytic removal of organic contaminants: Considering the intrinsic N/Fe in Enteromorpha and non-radical reaction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 250, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, H.; Jiang, M.; Bai, Y.; Yang, X.; Shu, H. Sheet-like structure FeF 3/graphene composite as novel cathode material for Na ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 38277–38282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajershojaei, K.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Khosravi, A. Immobilization of laccase enzyme onto titania nanoparticle and decolorization of dyes from single and binary systems. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2015, 20, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, B.; Min, Z.; Qian, D.; Jiang, J.; Li, J. Fe-doped CoSe2 nanoparticles encapsulated in N-doped bamboo-like carbon nanotubes as an efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 265, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashkoor, F.; Nasar, A. Environmental application of agro-waste derived materials for the treatment of dye-polluted water: A Review. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2021, 17, 904–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddeeg, S.M.; Tahoon, M.A.; Alsaiari, N.S.; Shabbir, M.; Rebah, F.B. Application of functionalized nanomaterials as effective adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals from wastewater: A review. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2021, 17, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; He, Z.; Wei, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, R.; Hu, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, G. Wood-Derived Monolithic Carbon Materials and Their Functional Applications. Clean Soil Air Water 2022, 50, 2100420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, N.A.; El-Khouly, S.M.; El-Shafey, O.I. Modified carbon nanostructures obtained from sugarcane bagasse hydrochar for treating chromium-polluted water. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2021, 17, 975–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Taghizadeh, A.; Taghizadeh, M.; Baglou, M.A.S. Surface modified montmorillonite with cationic surfactants: Preparation, characterization, and dye adsorption from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M. Synthesis of magnetic carbon nanotube and photocatalytic dye degradation ability. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 5595–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Wang, B.; Ma, L.; Fu, P.; Xie, L.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, W. Air pre-oxidation induced high yield N-doped porous biochar for improving toluene adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Q. Sustainable mechanisms of biochar derived from brewers’ spent grain and sewage sludge for ammonia–nitrogen capture. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 3927–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Fan, S.; Xu, H. Effect of Fe-N modification on the properties of biochars and their adsorption behavior on tetracycline removal from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Jing, F.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, B.; Guo, D. Simultaneous recovery of nitrogen and phosphorus from biogas slurry by Fe-modified biochar. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Sadeghi, U.; Maleki, A.; Hayati, B.; Najafi, F. Synthesis of cationic polymeric adsorbent and dye removal isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2745–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, G.; Haydar, S. Textile Effluent Treatment Using Natural Coagulant Opuntia stricta in Comparison with Alum. Clean Soil Air Water 2021, 49, 2000342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, R.; Wang, L.; Luo, D.; Wang, C. Efficient degradation of toxic mixed dyes through peroxymonosulfate activation by copper/iron nanoparticles loaded on 3D carbon: Synthesis, characterizations, and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza Samarghandi, M.; Tari, K.; Shabanloo, A.; Salari, M.; Zolghadr Nasab, H. Synergistic degradation of acid blue 113 dye in a thermally activated persulfate (TAP)/ZnO-GAC oxidation system: Degradation pathway and application for real textile wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 247, 116931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ma, W.; Ren, Z.; Du, Y.; Xu, P.; Han, X. Prussian blue analogues derived porous nitrogen-doped carbon microspheres as high-performance metal-free peroxymonosulfate activators for non-radical-dominated degradation of organic pollutants. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, R.; Sun, R.; Yang, J.; Dionysiou, D.D. Microplastics separation and subsequent carbonization: Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic performance of iron/carbon nanocomposite. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahi, N.; Aber, S.; Vatanpour, V.; Mahmoodi, N.M. The effect of amine functionalization of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles used as additives on the morphology and the permeation properties of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration nanocomposite membranes. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 154, 388–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Jia, X.; Kang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wei, J.; Guo, A.; Ge, M.; He, Z. Activation of peroxydisulfate by black fungus-derived N-doped biochar for tetracycline degradation via non-radical dominated oxidation pathway. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 31, 102007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Hayati, B.; Bahrami, H.; Arami, M. Dye adsorption and desorption properties of Mentha pulegium in single and binary systems. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tan, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Ye, S.; Yin, Z.; Hu, X.; Liu, N. Catalytic degradation of estrogen by persulfate activated with iron-doped graphitic biochar: Process variables effects and matrix effects. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, D.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Teng, J. Adsorption pore structure and its fractal characteristics of coals by N2 adsorption/desorption and FESEM image analyses. Fuel 2019, 257, 116031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jia, Y.; Zhou, M.; Su, X.; Sun, J. High-efficiency degradation of organic pollutants with Fe, N co-doped biochar catalysts via persulfate activation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, M.; Cui, K.; Cui, M.; Ding, Y.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Li, X. Enhanced norfloxacin degradation by iron and nitrogen co-doped biochar: Revealing the radical and nonradical co-dominant mechanism of persulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Guo, Y.; Qiao, S.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, J. 2-Methylimidazole as a nitrogen source assisted synthesis of a nano-rod-shaped Fe/FeN@N-C catalyst with plentiful FeN active sites and enhanced ORR activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 533, 147481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Miao, D.; Wei, Q.; Li, H.; Ma, L.; Zhou, K.; Liu, L.; Yu, Z. Persulfate enhanced electrochemical oxidation of highly toxic cyanide-containing organic wastewater using boron-doped diamond anode. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, R.; Ding, Y.; Ren, Z.; Fu, M.; Cao, X.; Zeng, G. Singlet oxygen-dominated activation of peroxymonosulfate by passion fruit shell derived biochar for catalytic degradation of tetracycline through a non-radical oxidation pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Li, Q.; Ye, Y.; Pan, F.; Zhang, D.; Xia, D. Degradation of cephalexin by persulfate activated with magnetic loofah biochar: Performance and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 272, 118971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Du, J.; Wu, Q.; Chang, J.-S.; Ren, N. Singlet oxygen-dominated peroxydisulfate activation by sludge-derived biochar for sulfamethoxazole degradation through a nonradical oxidation pathway: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yan, L.; Li, X.; Yan, T.; Song, W.; Hou, T.; Tong, C.; Mu, J.; Xu, M. Goethite/biochar-activated peroxymonosulfate enhances tetracycline degradation: Inherent roles of radical and non-radical processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 147102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, X.; Dai, H.; Wei, Y.; Xu, G.; Hu, F. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by single atom Co-N-C catalysts for high-efficient removal of chloroquine phosphate via non-radical pathways: Electron-transfer mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Ren, X.; Dong, W.; Chen, H.; Cai, T.; Zeng, W.; Li, W.; Tang, L. Soybean residue based biochar prepared by ball milling assisted alkali activation to activate peroxydisulfate for the degradation of tetracycline. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 599, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, G.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, K.; Zhang, W.; Song, J. Renewable and robust biomass waste-derived Co-doped carbon aerogels for PMS activation: Catalytic mechanisms and phytotoxicity assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, N.; Fatehizadeh, A.; Amin, M.M.; Pourzamani, H.R.; Ebrahimi, A.; Taheri, E.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Application of UV/chlorine processes for the DR83:1 degradation from wastewater: Effect of coexisting anions. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Huang, F.; Hu, L.; Sun, W.; Li, E.; Xiong, D.; Zhong, H.; He, Z. Efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate by a novel catalyst prepared directly from electrolytic manganese slag for degradation of recalcitrant organic pollutes. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, G.; Liu, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P. Enhanced degradation of Bisphenol A (BPA) by peroxymonosulfate with Co3O4-Bi2O3 catalyst activation: Effects of pH, inorganic anions, and water matrix. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Deng, Y.; Gong, D.; Tang, R.; Zheng, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Su, L.; Liao, C.; Yang, L. Magnetically modified in-situ N-doped Enteromorpha prolifera derived biochar for peroxydisulfate activation: Electron transfer induced singlet oxygen non-radical pathway. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Yi, Y.; Ying, G.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Activation of persulfate for highly efficient degradation of metronidazole using Fe(II)-rich potassium doped magnetic biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 152089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X. Magnetic ball-milled FeS@biochar as persulfate activator for degradation of tetracycline. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 126997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Guo, T.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G. Efficient activation of persulfate by a magnetic recyclable rape straw biochar catalyst for the degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride in water. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Shen, M.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Gong, B.; Liu, H.; Huang, Z. Resource utilization of piggery sludge to prepare recyclable magnetic biochar for highly efficient degradation of tetracycline through peroxymonosulfate activation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Shao, T.; Shang, J. Degradation of tetracycline in water by biochar supported nanosized iron activated persulfate. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Park, K.-H.; Kim, W.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, H.-J.; Hong, S.W.; Park, H.-J.; Lee, S.; et al. Photosensitized Production of Singlet Oxygen via C60 Fullerene Covalently Attached to Functionalized Silica-coated Stainless-Steel Mesh: Remote Bacterial and Viral Inactivation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 270, 118862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Ma, S.; Zhao, P.; Xu, S.; Zhan, S. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by graphitized hierarchical porous biochar and MnFe2O4 magnetic nanoarchitecture for organic pollutants degradation: Structure dependence and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Mao, X.; Wang, D. Degradation of 2,4-DCP using persulfate and iron/E-carbon micro-electrolysis coupling system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xue, J.; Han, C.; Liu, N.; Ma, K.; Zhang, R.; Wu, X.; Dai, L.; Wang, L.; He, Z. A hafnium oxide-coated dendrite-free zinc anode for rechargeable aqueous zinc-ion batteries. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 599, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; He, T.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Long, F.; Xiang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wu, J.; Wu, X. The MnO@N-doped carbon composite derived from electrospinning as cathode material for aqueous zinc ion battery. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 873, 114368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Zeng, G.; Tan, X.; Wu, H.; Liang, J.; Song, B.; Tang, N.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Q.; et al. Nitrogen-doped biochar fiber with graphitization from Boehmeria nivea for promoted peroxymonosulfate activation and non-radical degradation pathways with enhancing electron transfer. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 269, 118850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liang, S.; Gao, J.; Guo, S.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Xu, G.; Wu, X.; Chen, G.; Zhou, J. Manipulating the ion-transfer kinetics and interface stability for high-performance zinc metal anodes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Bin, Q.; Shen, Y.; Huang, J.; He, D.; Chen, W. In-situ formed N-doped bamboo-like carbon nanotubes encapsulated with Fe nanoparticles supported by biochar as highly efficient catalyst for activation of persulfate (PS) toward degradation of organic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 402, 126090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Li, C.; Yao, M.; He, Z.; Wu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Dai, L.; Wang, L. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of Li1+xTi2−xFex(PO4)3/C anode for aqueous lithium ion battery. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.; Zhu, L.; Li, F.; Xu, G. Self-Supporting Electrode Composed of SnSe Nanosheets, Thermally Treated Protein, and Reduced Graphene Oxide with Enhanced Pseudocapacitance for Advanced Sodium-Ion Batteries. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 5642–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Tang, M.; He, M.; Jiang, N.; Xu, C.; Lin, D.; Zheng, Q. Core-shell MnO2@CoS nanosheets with oxygen vacancies for high-performance supercapattery. J. Power Sources 2020, 446, 227335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Huang, X.; Ma, F.; Wang, L.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Catalytic Removal of Aqueous Contaminants on N-Doped Graphitic Biochars: Inherent Roles of Adsorption and Nonradical Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8649–8658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, J.; Xu, Z.; Liu, M.; Tang, S.; Yang, C.; Qian, D. Facile synthesis of Ag@Cu2O heterogeneous nanocrystals decorated N-doped reduced graphene oxide with enhanced electrocatalytic activity for ultrasensitive detection of H2O2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 260, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Li, R.; Wang, B.; Ma, M.; Zhong, X. An annularly-distributed poly-stable array for broadband vibrational energy. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 332, 113106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Fan, K.; Zhao, D.; Liu, B.; Jiang, J.; Qian, D.; Yang, C.; Li, J. N-doped carbon coated anatase TiO2 nanoparticles as superior Na-ion battery anodes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 517, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tong, X.; Feng, J.B. Fabrication of sewage sludge-derived magnetic nanocomposites as heterogeneous catalyst for persulfate activation of Orange G degradation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 529, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, H.; Hu, Q.; Wei, S.; Gu, H.; Guo, Z. Electrospun iron/cobalt alloy nanoparticles on carbon nanofibers towards exhaustive electrocatalytic degradation of tetracycline in wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Sample | Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|
| SFC | 558.5050 | 0.5649 |
| Fe3-SFC | 959.2110 | 1.0152 |
| Fitting Formula | Dynamical Equation | k | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order kinetic | −ln(C0/Ct) = 0.085t + 0.549 | 0.085 min−1 | 0.924 |
| Pseudo-second-order kinetic | 1/Ct − 1/C0 = 0.491t + 0.756 | 0.491·L mg−1·min−1 | 0.998 |
| Catalysts | Target Pollutants | Catalyst Dosage (G/L) | Pollutant Concentration (Mg/L) | Persulfatedosage (G/L) | Reaction Time | Degradation Conditions | D.E. (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3-SFC | Tetracycline | 0.1 | 10 | 0.4 | 1 h | pH: 6.93 T: 25 °C | 91.50 | This work |
| KOH activation biochar | Tetracycline | 0.2 | 50 | 2 | 3 h | pH: 7 T: 25 °C | 82.36 | [66] |
| Goethite/ biochar | Tetracycline | 0.5 | 20 | 0.1 | 1 h | pH: 7 T: 25 °C | 66.71 | [64] |
| N-doped Enteromorpha prolifera-derived magnetic biochar | Tetracycline | 0.2 | 50 | 0.4 | 5 h | pH: 4 T: 25 °C | 87.2 | [71] |
| Passion fruit shell-derived biochar | Tetracycline | 0.4 | 20 | 0.1 | 2 h | pH: 7 T: 25 °C | 90.91 | [61] |
| Black fungus-derived N-doped biochar | Tetracycline | 0.3 | 20 | 0.4 | 1 h | pH: 6.9 T: 25 °C | 89.8 | [53] |
| Fe(II)-rich potassium-doped magnetic biochar | Metronidazole | 0.5 | 20 | 10 mM | 120 min | pH: 6.5 T: 25 °C | 98.4 | [72] |
| Fe, N co-doped biochar (Fe-N-BC) | Acid orange | 0.2 | 20 | 1 mM | 40 min | pH: 3 T: 25 °C | 100 | [57] |
| Composite of iron sulfide and biochar (FeS@BC) | Tetracycline | 0.3 | 200 | 10 mM | 30 min | pH: 3.6 T: 25 °C | 87.4 | [73] |
| Magnetic rape straw biochar (MRSB) | Tetracycline hydrochloride | 1 | 20 | 8 mM | 120 min | pH: 5.68 T: 25 °C | 98.02 | [74] |
| Magnetic biochar was prepared from dewatered piggery sludge | Tetracycline | 0.75 | 6.7 | 20 mg/L | 120 min | pH: 7 T: 25 °C | 66.87 | [75] |
| Biochar supported nanosized iron (nFe(0)/BC) | Tetracycline | 0.4 | 100 | 1 mM | 240 min | pH: 5 T: 25 °C | 97.68 | [76] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Jia, X.; Kang, Z.; Kang, X.; Ge, M.; Zhang, D.; Wei, J.; Wang, C.; He, Z. Degradation of Tetracycline in Water by Fe-Modified Sterculia Foetida Biochar Activated Peroxodisulfate. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12097. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912097
Zhang Y, Jia X, Kang Z, Kang X, Ge M, Zhang D, Wei J, Wang C, He Z. Degradation of Tetracycline in Water by Fe-Modified Sterculia Foetida Biochar Activated Peroxodisulfate. Sustainability. 2022; 14(19):12097. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912097
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuchen, Xigai Jia, Ziyang Kang, Xiaoxuan Kang, Ming Ge, Dongbin Zhang, Jilun Wei, Chongqing Wang, and Zhangxing He. 2022. "Degradation of Tetracycline in Water by Fe-Modified Sterculia Foetida Biochar Activated Peroxodisulfate" Sustainability 14, no. 19: 12097. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912097
APA StyleZhang, Y., Jia, X., Kang, Z., Kang, X., Ge, M., Zhang, D., Wei, J., Wang, C., & He, Z. (2022). Degradation of Tetracycline in Water by Fe-Modified Sterculia Foetida Biochar Activated Peroxodisulfate. Sustainability, 14(19), 12097. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912097







