Can Environmental Regulation Improve High-Quality Economic Development in China? The Mediating Effects of Digital Economy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypotheses
3.1. Environmental Regulation and High-Quality Economic Development
3.1.1. Formal Environmental Regulation
3.1.2. Informal Environmental Regulation
3.2. Digital Economy and High-Quality Economic Development
3.3. Environmental Regulation, Digital Economy, and High-Quality Economic Development
3.3.1. Formal Environmental Regulation
3.3.2. Informal Environmental Regulation
3.4. Spatial Spillover Effect of Environmental Regulation on High-Quality Economic Development
4. Methods, Variables, and Data
4.1. Methods
4.1.1. Mediation Model
4.1.2. Threshold Model
φ3lnFormi,t × I(lnDigecoi,t > θ2) + φkXi,t + μi + εi,t
φ3lnInFormi,t × I(lnDigecoi,t > θ2) + φkXi,t + μi + εi,t
4.1.3. Spatial Durbin Model
ρ5lnXi,t + ρ6(WlnXi,t) + μi + δt + εi,t
ρ5lnXi,t + ρ6(WlnXi,t) + μi + δt + εi,t
4.2. Variables
4.2.1. High-Quality Economic Development
4.2.2. Dual Environmental Regulation
4.2.3. Digital Economy
4.2.4. Control Variables
4.3. Data
5. Empirical Results
5.1. Analysis of Mediating Effects
5.2. Analysis of Threshold Effects
5.3. Analysis of Spatial Spillover Effects
5.4. Robustness Tests
5.5. Discussion of Results
6. Conclusions and Policy Recommendations
6.1. Discussion and Concluding Remarks
6.2. Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, S.D.; Zhang, Y.Y. Promoting Common Prosperity in High-Quality Development: A Political Economy Interpretation. Soc. Sci. Xinjiang 2022, 4, 30–40+188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, D.H.; Jin, D.C. The Impact of Environmental Regulation on Capacity Utilization: Analysis of Moderating Mediating Effect Based on Technological Innovation. Reform 2021, 8, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, Y. New Normal and New Economy: A New Growth Engine for China. IJEPS 2020, 14, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chen, D.K. Air Pollution, Government Regulations and High-Quality Economic Development. Econ. Res. J. 2018, 53, 20–34. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Shu, Y.; Jin, X. Environmental Regulation, Carbon Emissions and Green Total Factor Productivity: A Case Study of China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 2577–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, N. Environmental Regulation and Environmental Productivity: The Case of China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, B. The Digital Economy: What is New and What is Not? Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2004, 15, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, W. Does Environmental Regulation Policy Help Improve Business Performance of Manufacturing Enterprises? Evidence from China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, D.; Chen, W. Can the Digital Economy Promote FinTech Development? Growth Change 2022, 53, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, J. Study on the “High-Quality Development” Economics. CPE 2018, 1, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M. Changes Unseen in a Century, High-Quality Development, and the Construction of a New Development Pattern. J. Manag. World 2020, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Tao, W.; Shen, Z. Improving High-Quality Development with Environmental Regulation and Industrial Structure in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 366, 132997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Q.; Ren, M.; Wei, Q.; Guo, X.H.; Yi, C. Data-Intelligence Empowerment: A New Leap of Information Systems Research. J. Manag. World 2022, 38, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Xie, T.; Wang, Z.; Ma, L. Digital Economy: An Innovation Driver for Total Factor Productivity. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 139, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Ding, Z.; Wang, H.; Zou, L. Can Environmental Regulation Improve Firm Total Factor Productivity? The Mediating Effects of Credit Resource Allocation. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, R.; Esposito, P.; Lasinio, C.J. Environmental Regulation and Productivity Growth: Main Policy Challenges. Int. Econ. 2021, 165, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, A.J.; McConnell, V.D. The Impact of Environmental Regulations on Industry Productivity: Direct and Indirect Effects. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 1990, 18, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y. The U-shaped Relationship between Environmental Regulation and the Quality of Economic Growth: Theoretical Mechanism and Empirical Test. Jianghai. Acad. J. 2019, 4, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, R.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, J. Different Types of Environmental Regulations and Heterogeneous Influence on “Green” Productivity: Evidence from China. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 132, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.G.; Zhou, T.; Chen, R.J.; Gan, T.Q. Environmental Regulatory Reform and High-quality Economic Development—Based on Adjustments of Pollution Charge for Industry. Res. Econ. Manag. 2019, 40, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Song, Y.T.; Yang, C.D. The Impact of Environmental Regulations on the Quality of Economic Growth: Promote or Restrain?-From the Perspective of Total Factor Productivity. Contemp. Econ. Manag. 2019, 41, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.Q.; Chu, C.J.; Gao, J.N. Effect of Environmental Regulation and Industrial Structure Upgrade on High-Quality Economic Development. China Popul. Res. Environ. 2020, 30, 84–94. [Google Scholar]
- Shangguan, X.M.; Ge, B.H. Digital Finance, Environmental Regulation and High-Quality Economic Development. Mod. Financ. Econ. 2021, 41, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, X.M.; Ge, B.H. Scientific and Technological Innovation, Environmental Regulation and High-Quality Economic Development. China Popul. Res. Environ. 2020, 30, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.J.; Lin, C. Study on the Relationship between Environmental Regulation and the Quality of China’s Economic Growth-A perspective Based on Environmental Kuznets Curve. Shanghai. J. Econ. 2018, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Hu, X.P. Research on the Effects of Environmental Regulation on the Quality of China’s Economic Growth. China Popul. Res. Environ. 2019, 29, 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Yu, Z.; Wei, Y.D.; Wang, M. Internet Access, Spillover and Regional Development in China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Jiang, F.X.; Wei, Z.T. Can the Digital Economy Become a New Driving Force for the High-Quality Economic Development? Inq. Econ. Issues. 2021, 1, 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.; Liu, C.; Zheng, C.; Li, F. Digital Economy, Technological Innovation and High-Quality Economic Development: Based on Spatial Effect and Mediation Effect. Sustainability 2021, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hytha, D.A. Technology Innovation and the Rebirth of Self-Regulation: How the Internet of Things, Cloud Computing, Blockchain, and Artificial Intelligence Solve Big Problems Managing Environmental Regulation and Resources. Int. J. Commun. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.S.; Li, F.P.; Li, X. Environmental Regulation, Digital Inclusive Finance and Urban Industrial Upgrading-Analysis Based on Spatial Spillover Effect and Regulation Effect. Inq. Econ. Issues. 2022, 1, 50–66. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, X.P.; Hao, L.F. Impact of Dual Environmental Regulations on Carbon Emission Intensity under the Constraint of Technological Innovation. China Popul. Res. Environ. 2021, 31, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q. Research on the Emission Reduction Effect of Formal and Informal Environmental Regulation-Take the Yangtze River Economic Belt as an Example. Mod. Econ. Res. 2018, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Wang, R. Effect of Environmental Regulation on Industrial Solid Waste Pollution in China: From the Perspective of Formal Environmental Regulation and Informal Environmental Regulation. IJERPH 2020, 17, 7798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, W.; Yuan, K.; Zhang, X. Can Informal Environmental Regulation Promote Industrial Structure Upgrading? Evidence from China. Appl. Econ. 2022, 54, 2161–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.F. Research on the Mechanism of Digital Economy Driving High-Quality Economic Development: A Theoretical Analysis Framework. Mod. Econ. Res. 2020, 1, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.J.; Sun, B.W. Digital Economy Promotes High-Quality Economic Development: A Theoretical Analysis Framework. Economist 2019, 2, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, S.S. Digital Economy, Entrepreneurship, and High-Quality Economic Development: Empirical Evidence from Urban China. J. Manag. World. 2020, 36, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.B.; Pang, C.; Liu, J.Z. Structural Changes in Outsourcing and High-Quality Economic Development in the Digital Era-An Inframarginal Analysis to the Division of Labor. China Ind. Econ. 2020, 17, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.-H.; Choi, M.J. Ecological Views of Big Data: Perspectives and Issues. Telemat. Inform. 2015, 32, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, X.; Huang, S. Impacts on Environmental Quality and Required Environmental Regulation Adjustments: A Perspective of Directed Technical Change Driven by Big Data. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 124126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Salman, M.; Lu, Z. Heterogeneous Impacts of Environmental Regulations and Foreign Direct Investment on Green Innovation across Different Regions in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Ximei, W. Digital Economy and Environmental Sustainability: How does ICT Affect Ecological Footprint and What is the Role of Economic Complexity? Review 2022. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-1593054/v1 (accessed on 10 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- Lun, X.B.; Liu, Y. Digital Government, Digital Economy and Green Technology Innovation. J. Shanxi. Univ. Financ. Econ. 2022, 44, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. The Relationship between Industrial Restructuring and China’s Regional Haze Pollution: A Spatial Spillover Perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 115808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S.; Haynes, K.E.; Dinc, M. Geographic and Network Neighbors: Spillover Effects of Telecommunications Infrastructure. J. Reg. Sci. 2002, 42, 339–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.L.; Chu, S.B. Local Government Competition, Environmental Regulation and Regional Ecological Efficiency. World. Econ. 2014, 37, 88–110. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Han, F. Does the Agglomeration of Producer Services Promote the Quality of Urban Economic Growth? J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2019, 36, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Zhao, L.; An, P. Effect of Environmental Regulation on High-quality Economic Development in China—An Empirical Analysis Based on Dynamic Spatial Durbin Model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 54661–54678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Zhou, S.S. Dual Environmental Regulation, Government Subsidy and Enterprise Innovation Output. China Popul. Res. Environ. 2019, 29, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, G. Environmental Decentralization, Digital Finance and Green Technology Innovation. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2022, 61, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI). Available online: https://navi.cnki.net/knavi/yearbooks/YZGCA/detail (accessed on 3 September 2022).
- Baidu Index. Available online: https://index.baidu.com/v2/index.html#/ (accessed on 3 September 2022).
- Institute of Digital Finance Peking University. Available online: https://www.idf.pku.edu.cn/zsbz/515313.htm (accessed on 3 September 2022).
- Wind. Available online: https://www.wind.com.cn/ (accessed on 3 September 2022).
- Wang, X.X.; Lei, H.Y.; Wang, S.S. Environmental Regulation, Technological Innovation and High Quality Development of Green Economy. Stat. Decis. 2022, 38, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
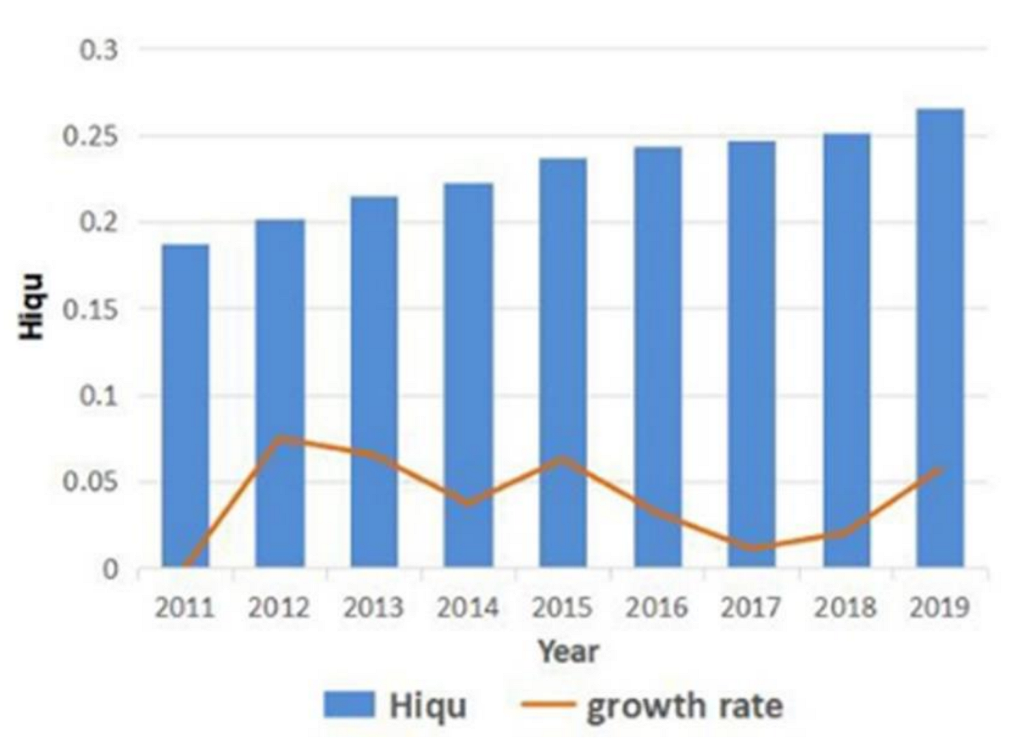
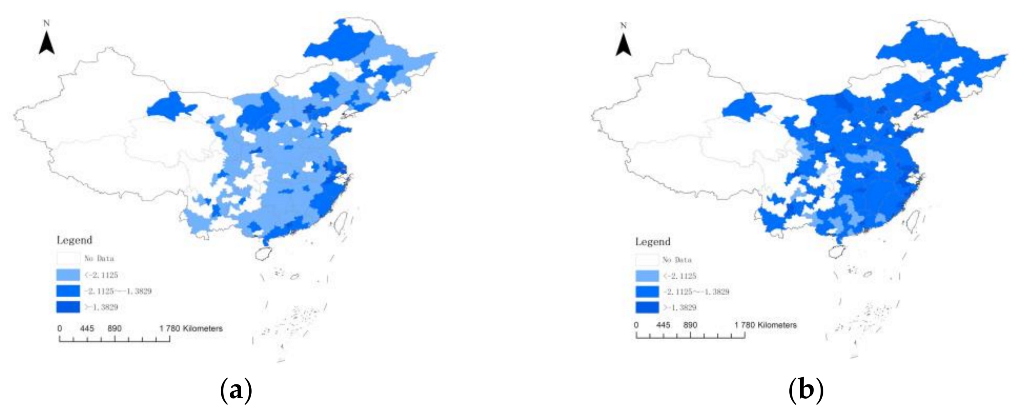
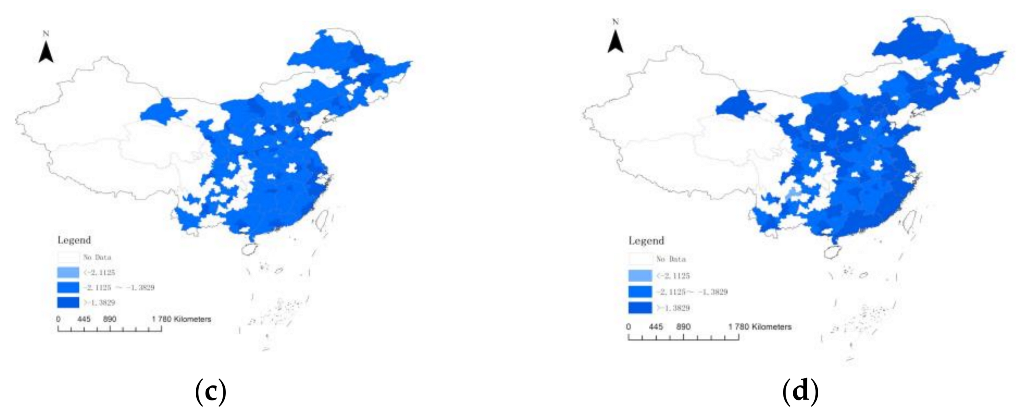

| Variables | Measurement | |
|---|---|---|
| Formal environmental regulation (Form) | The proportion of environment-related word frequencies in city government work reports | |
| Informal environmental regulation (Inform) | The search index of environment-related terms in the Baidu index | |
| Digital economy (Digeco) | The development of the Internet | The level of Internet penetration |
| The proportion of related employees | ||
| Internet-related output | ||
| The level of cell phone penetration | ||
| Digital transactions | The published Digital Financial Inclusion Index | |
| High-quality economic development (Hiqu) | economic efficiency and equity | Inclusive TFP |
| industrial development quality | The optimization of industrial structure | |
| The rationalization of industrial structure | ||
| The level of productive service industry | ||
| scientific innovation | Total expenditures on science and technology | |
| residents’ welfare | GDP per capita | |
| education expenditure per capita | ||
| hospital beds per capita | ||
| environmental quality | solid waste utilization | |
| sewage treatment | ||
| PM2.5 concentration | ||
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std | Min | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explained variables | lnHiqu | 2 124 | −1.477 | 0.239 | −2.389 | −0.547 |
| Explanatory variables | lnForm | 2 124 | −7.516 | 0.419 | −9.099 | −6.331 |
| lnInform | 2 124 | 3.273 | 1.131 | 1.099 | 6.230 | |
| Mediating variables | lnDigeco | 2 124 | −1.671 | 0.450 | −3.948 | −0.319 |
| Control variables | lnGovern | 2 124 | −1.847 | 0.455 | −4.321 | 0.302 |
| lnFore | 2 124 | −6.584 | 1.128 | −9.199 | −3.660 | |
| lnUrban | 2 124 | −1.245 | 0.632 | −3.060 | 0.134 | |
| lnFinan | 2 124 | −0.157 | 0.490 | −2.136 | 2.008 | |
| lnInfras | 2 124 | 1.204 | 0.828 | −1.708 | 3.688 | |
| Variable | Formal Environmental Regulation | Informal Environmental Regulation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnHiqu | lnDigeco | lnHiqu | lnHiqu | lnDigeco | lnHiqu | |
| lnForm | 0.058 *** (6.16) | 0.235 *** (10.80) | −0.002 (−0.21) | |||
| lnInform | 0.041 *** (7.86) | 0.129 *** (10.56) | 0.009 ** (2.05) | |||
| lnDigeco | 0.254 *** (31.44) | 0.250 *** (30.98) | ||||
| lnGovern | 0.108 *** (6.40) | 0.161 *** (4.13) | 0.067 *** (4.88) | 0.101 *** (6.01) | 0.129 *** (3.32) | 0.068 *** (5.00) |
| lnFore | −0.019 *** (−4.86) | −0.015 (−1.61) | −0.015 *** (−4.83) | −0.020 *** (−4.97) | −0.017 * (−1.82) | −0.015 *** (−4.80) |
| lnUrban | 0.084 *** (5.52) | 0.144 *** (4.12) | 0.047 *** (3.82) | 0.076 *** (5.03) | 0.123 *** (3.49) | 0.045 *** (3.68) |
| lnFinan | 0.223 *** (19.27) | 0.702 *** (26.27) | 0.045 *** (4.07) | 0.211 *** (17.99) | 0.680 *** (24.89) | 0.041 *** (3.75) |
| lnInfras | 0.118 *** (11.81) | 0.395 *** (17.19) | 0.017 ** (1.97) | 0.106 *** (10.50) | 0.363 *** (15.49) | 0.015 * (1.73) |
| Constant | −0.969 *** (−11.11) | 0.113 (0.56) | −0.998 *** (−14.12) | −1.555 *** (−32.91) | −2.143 *** (−19.15) | −1.019 *** (−24.17) |
| Fix Effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Period | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| N | 236 | 236 | 236 | 236 | 236 | 236 |
| R-square | 0.370 | 0.516 | 0.568 | 0.454 | 0.554 | 0.589 |
| Explanatory Variable | Threshold Variable | Threshold Type | F-Statistic | p Value | Bootstrap | Crit10 | Crit5 | Crit1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnForm | lnDigeco | Single | 262.72 | 0.000 | 300 | 40.4895 | 45.0650 | 52.5770 |
| Double | 153.58 | 0.000 | 300 | 29.9799 | 35.5802 | 47.2357 | ||
| Triple | 114.62 | 0.763 | 300 | 189.8428 | 201.8964 | 221.4062 | ||
| lnInfrom | lnDigeco | Single | 265.72 | 0.000 | 300 | 58.0153 | 63.6067 | 84.7343 |
| Double | 128.96 | 0.000 | 300 | 25.7757 | 28.8882 | 37.8720 | ||
| Triple | 86.49 | 0.833 | 300 | 141.6841 | 155.6759 | 179.2047 |
| Explanatory Variables | Threshold Value | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|
| lnForm | −2.1125 | (−2.1300, −2.0943) |
| −1.3829 | (−1.3838, −1.3805) | |
| lnInfrom | −2.1125 | (−2.1169, −2.1062) |
| −1.2602 | (−1.2691, −1.2583) |
| Variable | Formal Environmental Regulation | Variable | Informal Environmental Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| lnForm (lnDigeco < −2.1125) | 0.037 *** (4.30) | lnInfrom (lnDigeco < −2.1125) | 0.0004 (0.08) |
| lnForm (−2.1125 ≤ lnDigeco ≤ −1.3829) | 0.022 ** (2.46) | lnInfrom (−2.1125 ≤ lnDigeco ≤ −1.2602) | 0.041 *** (8.48) |
| lnForm (lnDigeco > −1.3829) | 0.011 (1.25) | lnInfrom (lnDigeco > −1.2602) | 0.062 *** (12.43) |
| lnGovern | 0.098 *** (6.36) | lnGovern | 0.086 *** (5.63) |
| lnFore | −0.018 *** (−4.93) | lnFore | −0.021 *** (−5.91) |
| lnUrban | 0.069*** (4.97) | lnUrban | 0.050*** (3.62) |
| lnFinan | 0.140 *** (12.32) | lnFinan | 0.138 *** (12.03) |
| lnInfras | 0.065 *** (6.88) | lnInfras | 0.063 *** (6.64) |
| constant | −1.223 *** (−15.14) | constant | −1.583 *** (−36.45) |
| N | 236 | N | 236 |
| R-square | 0.442 | R-square | 0.532 |
| Year | The Geographic Matrix (W1) | Proximity Weight Matrix (W2) | Economic-Distance Matrix (W3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 0.250 *** (5.956) | 0.065 *** (8.977) | 0.226 *** (29.859) |
| 2012 | 0.257 *** (5.567) | 0.067 *** (9.348) | 0.243 *** (32.124) |
| 2013 | 0.301 *** (6.503) | 0.044 *** (6.306) | 0.260 *** (34.314) |
| 2014 | 0.266 *** (5.778) | 0.033 *** (4.851) | 0.281 *** (37.138) |
| 2015 | 0.266 *** (5.763) | 0.022 *** (3.461) | 0.269 *** (35.500) |
| 2016 | 0.272 *** (5.892) | 0.043 *** (6.210) | 0.263 *** (34.775) |
| 2017 | 0.265 *** (5.733) | 0.034 *** (4.986) | 0.257 *** (33.984) |
| 2018 | 0.312 *** (6.740) | 0.046 *** (6.584) | 0.278 *** (36.654) |
| 2019 | 0.275 *** (5.956) | 0.039 *** (5.592) | 0.261 *** (34.444) |
| Variable | lnForm | lnInform | Variable | lnForm | lnInform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y-1 | 1.050 *** (91.01) | 0.526 *** (28.83) | SR_Dire | 0.001 (0.26) | 0.009 ** (2.26) |
| lnForm | 0.002 (0.40) | - | SR_Indi | −0.023 *** (−2.57) | 0.013 * (1.76) |
| lnInform | - | 0.009 ** (1.99) | SR_Total | −0.022 * (−2.18) | 0.022 *** (3.04) |
| WlnX_ | −0.021 ** (−2.39) | 0.007 * (1.70) | LR_Dire | 0.826 (0.05) | 0.023 *** (2.59) |
| ρ | 0.087 *** (5.40) | 0.265 *** (11.35) | LR_Indi | −0.682 (−0.04) | 0.055 ** (2.26) |
| Control | yes | yes | LR_Total | 0.144 ** (2.12) | 0.078 *** (2.91) |
| R-square | 0.610 | 0.662 | Log L | 2101.202 | 2629.291 |
| Variables | Proximity Weight Matrix | Economic-Distance Matrix | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnForm | lnInform | lnForm | lnInform | |
| y-1 | 0.533 *** (26.94) | 0.562 *** (28.60) | 0.533 *** (26.68) | 0.533 *** (26.65) |
| lnForm | 0.003 (0.48) | - | 0.002 (0.28) | - |
| lnInform | - | 0.003 (0.66) | - | 0.001 (0.03) |
| Wlnx_ | −0.240 (−0.27) | 0.037 *** (3.41) | −0.093 (−0.84) | 0.084 *** (6.46) |
| ρ | 0.534 *** (7.35) | 0.712 *** (11.24) | 0.286 * (1.89) | 0.477 *** (7.70) |
| Control | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.680 | 0.685 | 0.566 | 0.684 |
| Log L | 2650.634 | 2639.890 | 2462.422 | 2653.728 |
| Variables | Control Fixed Effects | Instrumental Variable | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnForm | 0.051 *** (5.90) | 0.059 *** (6.55) | ||||
| lnInform | 0.048 *** (10.08) | 0.054 *** (11.44) | ||||
| L.lnForm | 0.059 *** (5.98) | |||||
| L.lnInform | - | 0.048 *** (9.34) | ||||
| Control | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Province fixed effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Province × Year fixed effect | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No |
| City fixed effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 236 | 236 | 236 | 236 | 236 | 236 |
| Period | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| R-squared | 0.487 | 0.487 | 0.495 | 0.494 | 0.438 | 0.455 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Zhang, G. Can Environmental Regulation Improve High-Quality Economic Development in China? The Mediating Effects of Digital Economy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912143
Wang J, Zhang G. Can Environmental Regulation Improve High-Quality Economic Development in China? The Mediating Effects of Digital Economy. Sustainability. 2022; 14(19):12143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912143
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jun, and Guixiang Zhang. 2022. "Can Environmental Regulation Improve High-Quality Economic Development in China? The Mediating Effects of Digital Economy" Sustainability 14, no. 19: 12143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912143
APA StyleWang, J., & Zhang, G. (2022). Can Environmental Regulation Improve High-Quality Economic Development in China? The Mediating Effects of Digital Economy. Sustainability, 14(19), 12143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912143






