Nitrogen Removal from Mature Landfill Leachate via Anammox Based Processes: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mature Landfill Leachate Treatment via Anammox-Based Processes
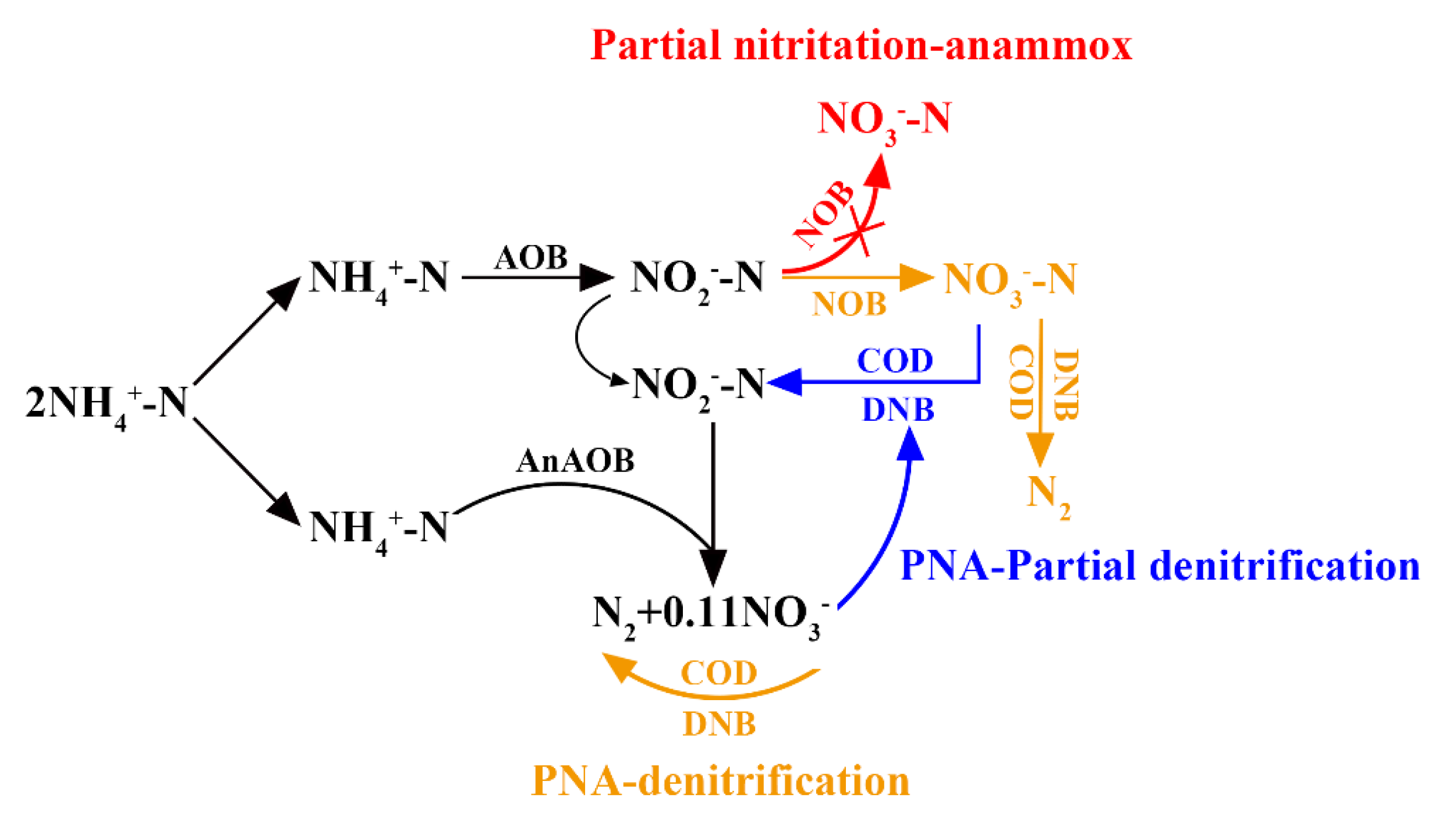
2.1. Partial Nitrification–Anammox Process
2.2. Coupling of Partial Nitrification–Anammox and Denitrification
2.3. Coupling of Partial Nitrification–Anammox and Partial Denitrification Process
| Process | Reactor | T (°C) | C/N | Influent (mg/L) | Effluent (mg/L) | NRE (%) | NRR kgN/(m3 d) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PN/A | SBR | 30 | 1.37 | NH4+ = 950 ± 20 TN = 1200 | TN = 37.6 | 96.1 | 0.397 | [23] |
| PN/A | USB | - | 1.2 | NH4+ = 900 ± 100 COD = 1300 ± 50 | TN < 60 | 96.3 | - | [22] |
| PN/A | SBR UASB | 25–33 | 1.75 | NH4+ = 1040 ± 300 TN = 1050 ± 350 COD = 1800 ± 200 | TN < 50 | 85.1 | 0.75 ± 0.12 | [18] |
| PN/A | SBBR | 25–30 | 0.7 | NH4+ = 3000 ± 100 COD = 3000 ± 100 | TN < 20 | 95 | 0.51 | [20] |
| SNAD | SBBR | 0.5 | NH4+ = 2004 ± 14.7 TN = 2024 ± 23.6 COD = 1026.8 ± 14.2 | TN < 120 | 94.9 | [27] | ||
| SPNAD | SBR | 0.85 | NH4+ = 1000 ± 250 TN = 1300 ± 75 COD = 1100 ± 200 | TN = 37 | 98.7 | 0.23 | [30] | |
| DN-PN/A | UASB | 1 | NH4+ = 2500 ± 250 COD = 2500 ± 250 | TN < 90 | 96 | 0.5 | [26] | |
| PN/A-PD/A | A/O UASB | - | NH4+ = 1500 ± 150 TN = 1400 ± 400 COD = 2300 ± 150 | TN = 15.7 | 98.8 | [34] | ||
| PN/A-PD/A | SBR | NH4+ = 804.9 COD = 1116 | TN = 19.2 | 87.9 | [32] | |||
| PN/A-PD/A | UASB A/O | 30–35 | 2–3 | NH4+ = 415 ± 15 TN = 430 ± 10 | TN = 20 | 92 | [35] |
3. Microbiological Analysis of Stable Nitrogen Removal Performance
4. Challenges in Anammox Based Processes for Treating Mature Landfill Leachate
4.1. Unstable Influent Condition
4.1.1. The Salinity and Heavy Metal
4.1.2. Organic Matter
4.1.3. High Strength Nitrogen
4.2. Difficulty in Operational Control
4.2.1. The Control of DO
4.2.2. The Control of C/N
4.3. The Seasonal Temperature Variation
5. Future Perspective
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kjeldsen, P.; Barlaz, M.A.; Rooker, A.P.; Baun, A.; Ledin, A.; Christensen, T.H. Present and long-term composition of MSW landfill leachate: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 32, 297–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, Y.; He, D.; Pan, X. Recent advances in municipal landfill leachate: A review focusing on its characteristics, treatment, and toxicity assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-pajooh, E.; Weichgrebe, D.; Cuff, G. Municipal landfill leachate characteristics and feasibility of retrofitting existing treatment systems with deammonification—A full scale survey. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 187, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.M.; Alfaia, R.G.D.S.M.; Campos, J.C. Landfill leachate treatment in Brazil—An overview. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, S.; Teixeira, P.; Oliveira, R.; Mota, M. Evaluation of Fenton and ozone-based advanced oxidation processes as mature landfill leachate pre-treatments. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chemlal, R.; Azzouz, L.; Kernani, R.; Abdi, N.; Lounici, H.; Grib, H.; Drouiche, N. Combination of advanced oxidation and biological processes for the landfill leachate treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iaconi, C.; Ramadori, R.; Lopez, A. Combined biological and chemical degradation for treating a mature municipal landfill leachate. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 31, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canziani, R.; Emondi, V.; Garavaglia, M.; Malpei, F.; Pasinetti, E.; Buttiglieri, G. Effect of oxygen concentration on biological nitrification and microbial kinetics in a cross-flow membrane bioreactor (MBR) and moving-bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) treating old landfill leachate. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 286, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Yang, G.; Tao, T.; Peng, Y. Recent advances in nitrogen removal from landfill leachate using biological treatments—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 235, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; Miao, L.; Ma, B.; Peng, Y. Biological nitrogen removal from landfill leachate using anaerobic-aerobic process: Denitritation via organics in raw leachate and intracellular storage polymers of microorganisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.C.; Daverey, A.; Huang, Y.T.; Sung, S.; Lin, J.G. Treatment of semiconductor wastewater using single-stage partial nitrification and anammox in a pilot-scale reactor. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 63, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, S.; Gilbert, E.M.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Joss, A.; Horn, H.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Full-scale partial nitritation/anammox experiences—An application survey. Water Res. 2014, 55, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hu, H.Y.; Chen, Q.Q.; Shi, M.L.; Jin, R.C. Successful start-up of the anammox process: Influence of the seeding strategy on performance and granule properties. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.J.; Han, B.; Cao, Y.; Wang, T.Y. Impact of substrate concentration on anammox-UBF reactors start-up. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 239, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.J.; Zheng, P.; Chai, L.Y.; Min, X.B. Thermodynamic and kinetic investigation of anaerobic bioprocesses on ANAMMOX under high organic conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 230, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetten, M.S.M.; Niftrik, L.V.; Strous, M.; Kartal, B.; Keltjens, J.T.; Op Den Camp, H.J.M. Biochemistry and molecular biology of anammox bacteria biochemistry and molecular biology of anammox bacteria. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 44, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; An, F.; Huang, J.; Shao, Z. Achieving stable two-stage mainstream partial-nitrification/anammox (PN/A) operation via intermittent aeration. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, S.; Ma, W.; Huang, P.; Huang, G.; Qin, Y.; Xu, B.; Ouyang, H. Long-term performance and microbial ecology of a two-stage PN-ANAMMOX process treating mature landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Miao, L.; Cao, T.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Han, J. Continuous-flow combined process of nitritation and ANAMMOX for treatment of landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Wang, S.; Cao, T.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z. Advanced nitrogen removal from landfill leachate via Anammox system based on Sequencing Biofilm Batch Reactor (SBBR): Effective protection of biofilm. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, S.; Li, S. Insight into the impacts of organics on anammox and their potential linking to system performance of sewage partial nitrification-anammox (PN/A): A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi, P.; Zhang, D.; Su, H.; Luo, W.; Quashie, F.K.; Kabutey, F.T.; Xiao, L.; Lai, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, J. Nitrogen removal from landfill leachate by single-stage anammox and partial-nitritation process: Effects of microaerobic condition on performance and microbial activities. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Ren, S. Advanced nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate via partial nitrification-Anammox biofilm reactor (PNABR) driven by high dissolved oxygen (DO): Protection mechanism of aerobic biofilm. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Du, R.; Zhou, Y. Coupling anammox with heterotrophic denitrification for enhanced nitrogen removal: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 2260–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, B.; Lin, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J. Robustness and microbial consortia succession of simultaneous partial nitrification, ANAMMOX and denitrification (SNAD) process for mature landfill leachate treatment under low temperature. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 132, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, M.Y.; Qiu, Q.C.; Huang, Y.; Li, B.L.; Yuan, Y.; Yuan, Y. The effect of different denitrification and partial nitrification-Anammox coupling forms on nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate at the pilot-scale. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; He, L.; Huang, W.; Zhou, J.; He, Q. Simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification (SNAD) process for nitrogen and refractory organic compounds removal from mature landfill leachate: Performance and metagenome-based microbial ecology. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294, 122166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Shen, L.; Meng, F. Response of microbial community structures and functions of nitrosifying consortia to biorefractory humic substances. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 4744–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ji, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Qin, G. Insight into the influence of microbial aggregate types on nitrogen removal performance and microbial community in the anammox process—A review and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H. Efficient step-feed partial nitrification, simultaneous Anammox and denitrification (SPNAD) equipped with real-time control parameters treating raw mature landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Peng, Y.; Ji, J.; Shi, L.; Gao, R.; Li, X. Partial denitrification providing nitrite: Opportunities of extending application for anammox. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 105001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Peng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L. Improving stability of mainstream Anammox in an innovative two-stage process for advanced nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, C.; Liang, D.; Peng, Y. A novel partial-denitrification strategy for post-anammox to effectively remove nitrogen from landfill leachate. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, L.; Shi, X.; Liu, T.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, J. Analysis of the impact of reflux ratio on coupled partial nitrification-anammox for co-treatment of mature landfill leachate and domestic wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, Z.; Huang, S.; Shen, M.; Yan, Z.; Li, J.; Peng, Y. Low energy treatment of landfill leachate using simultaneous partial nitrification and partial denitrification with anaerobic ammonia oxidation. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Ren, S.; Peng, Y. Simultaneous Ammonium oxidation denitrifying (SAD) in an innovative three-stage process for energy-efficient mature landfill leachate treatment with external sludge reduction. Water Res. 2020, 169, 121615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Ren, S.; Qiu, J. New insights into co-treatment of mature landfill leachate with municipal sewage via integrated partial nitrification, Anammox and denitratation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H. High-efficient nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate and waste activated sludge (WAS)reduction via partial nitrification and integrated fermentation-denitritation process (PNIFD). Water Res. 2019, 160, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strous, M.; Van Gerven, E.; Zheng, P.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S.M. Ammonium removal from concentrated waste streams with the anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) process in different reactor configurations. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, R.; Sheng, X.; Chen, L.; Wu, G.; Hu, H.; Zhan, X. Start up of partial nitritation-anammox process using intermittently aerated sequencing batch reactor: Performance and microbial community dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhat, P.T.; Biec, H.N.; Van, T.T.T.; van Tuan, D.; Trung, N.L.H.; Nghi, V.T.K.; Dan, N.P. Stability of partial nitritation in a sequencing batch reactor fed with high ammonium strength old urban landfill leachate. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 124, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.Z.; Peng, Y.; Miao, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, B. A novel simultaneous partial nitrification Anammox and denitrification (SNAD) with intermittent aeration for cost-effective nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yuan, C.; Zhu, T.; Wang, Y. Effect of humic acid on the single-stage nitrogen removal using anammox and partial nitritation (SNAP) process: Performance and bacterial communities. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Elela, S.I.; Kamel, M.M.; Fawzy, M.E. Biological treatment of saline wastewater using a salt-tolerant microorganism. Desalination 2010, 250, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Jin, R.C.; Yang, G.F.; Yu, J.J.; Xing, B.S.; Zhang, Q.Q. Impacts of transient salinity shock loads on Anammox process performance. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 112, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Kim, W.; Lim, H.; Bae, H. Shift in bacterial community structure in response to salinity in a continuous anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) reactor. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2020, 147, 104873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Vossenberg, J.; Woebken, D.; Maalcke, W.J.; Wessels, H.J.C.T.; Dutilh, B.E.; Kartal, B.; Janssen-Megens, E.M.; Roeselers, G.; Yan, J.; Speth, D.; et al. The metagenome of the marine anammox bacterium “Candidatus Scalindua profunda” illustrates the versatility of this globally important nitrogen cycle bacterium. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1275–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dale, O.R.; Tobias, C.R.; Song, B. Biogeographical distribution of diverse anaerobic ammonium oxidizing (anammox) bacteria in Cape Fear River Estuary. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1194–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Mi, W.; Ito, H.; Kawagoshi, Y. Probing the dynamics of three freshwater Anammox genera at different salinity levels in a partial nitritation and Anammox sequencing batch reactor treating landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Liu, T.; Xiao, H.; Wang, S. Treatment performance and N2O emission in the UASB-A/O shortcut biological nitrogen removal system for landfill leachate at different salinity. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 32, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Yin, C.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, F. Increased salinity triggers significant changes in the functional proteins of Anammox bacteria within a biofilm community. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Lin, X.; Yan, Y.; Ma, X.; Wu, M.; Han, H. 16S rRNA gene high-throughput sequencing reveals shift in nitrogen conversion related microorganisms in a CANON system in response to salt stress. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qi, P.; Qiang, Z.; Dong, H.; Gao, D.; Wang, D. Is anammox a promising treatment process for nitrogen removal from nitrogen-rich saline wastewater? Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Sugano, T.; Song, Y.; Xie, C.; Chen, Y.; Xue, Y.; Li, Y.Y. The performance of freshwater one-stage partial nitritation/anammox process with the increase of salinity up to 3.0%. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 311, 123489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, A.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Sethupathi, S.; Lim, J.W. An overview of heavily polluted landfill leachate treatment using food waste as an alternative and renewable source of activated carbon. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 98, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Li, G.F.; Shi, Z.J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, B.C.; Fan, N.S.; Jin, R.C. Co-inhibition of salinity and Ni(II) in the anammox-UASB reactor. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Xu, J.J.; Deng, R.; Ji, Z.Q.; Wu, Y.H.; Jin, R.C. Evaluation of the inhibitory effects of heavy metals on anammox activity: A batch test study. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, M.; Deng, Q.; Cai, T. Combination and performance of forward osmosis and membrane distillation (FO-MD) for treatment of high salinity landfill leachate. Desalination 2017, 420, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.; Zhou, K.; Peng, C.; Chen, W. Characterization and treatment of landfill leachate: A review. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.; Fernández, I.; Suárez-Ojeda, M.E.; Carrera, J. Inhibition of the anammox activity by aromatic compounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.F.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Jin, R.C. Changes in the nitrogen removal performance and the properties of granular sludge in an Anammox system under oxytetracycline (OTC) stress. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Z.; Ma, Y. Performance of the nitrogen removal, bioactivity and microbial community responded to elevated norfloxacin antibiotic in an Anammox biofilm system. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.F.; Jin, R.C. The joint inhibitory effects of phenol, copper (II), oxytetracycline (OTC) and sulfide on Anammox activity. Proc. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 126, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulikowska, D.; Klimiuk, E. The effect of landfill age on municipal leachate composition. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5981–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, S.M.; Sun, W.; Sierra-Alvarez, R.; Field, J.A. Toluene-nitrite inhibition synergy of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing (anammox) activity. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamchoi, N.; Nitisoravut, S.; Schmidt, J.E. Inactivation of ANAMMOX communities under concurrent operation of anaerobic ammonium oxidation (ANAMMOX) and denitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3331–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, S.; Terada, A.; Smets, B.F. Heterotrophic activity compromises autotrophic nitrogen removal in membrane-aerated biofilms: Results of a modeling study. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, D.; Zapata, A.; Brunetti, G.; del Moro, G.; di Iaconi, C.; Oller, I.; Malato, S.; Mascolo, G. Comparison of several combined/integrated biological-AOPs setups for the treatment of municipal landfill leachate: Minimization of operating costs and effluent toxicity. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, T.; Li, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, S. A metabolomic view of how low nitrogen strength favors anammox biomass yield and nitrogen removal capability. Water Res. 2018, 143, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.H.; Shin, H.S.; Park, H. Characterization of humic substances present in landfill leachates with different landfill ages and its implications. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4023–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhang, B.; Ou, H.; Hu, Z.; Wang, W. Inhibitory effect of salinity and humic acid on the performance of anaerobic ammonium oxidation process and recovery of anammox activity. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2021, 38, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.Y. Process stability and the recovery control associated with inhibition factors in a UASB-anammox reactor with a long-term operation. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 203, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Q.; Ma, H.; Li, Y.Y. Operation stability and recovery performance in an Anammox EGSB reactor after pH shock. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 90, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Peng, L.; Wang, D.; Ni, B. The roles of free ammonia (FA) in biological wastewater treatment processes: A review. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Liu, J.; Ye, M.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.Y. Towards advanced nitrogen removal and optimal energy recovery from leachate: A critical review of anammox-based processes. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 612–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, S.; Huang, G.; Xu, B. Achieving stable partial nitritation using endpoint pH control in an SBR treating landfill leachate. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2014, 92, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichel, A.; Moreno, R.; Figueroa, M.; Campos, J.L.; Mendez, R.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Val del Rio, A. How to cope with NOB activity and pig manure inhibition in a partial nitritation-anammox process? Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Qing, X.; He, Q. Effects of dissolved oxygen on microbial community of single-stage autotrophic nitrogen removal system treating simulating mature landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarró, J.; Hernández-del Amo, E.; Gich, F.; Ruscalleda, M.; Balaguer, M.D.; Colprim, J. Nitrous oxide reduction genetic potential from the microbial community of an intermittently aerated partial nitritation SBR treating mature landfill leachate. Water Res. 2013, 47, 7066–7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Duc, L.; Ito, H.; Hama, T.; Kim, J.; Kawagoshi, Y. A novel reactor combining anammox and Fenton-like reactions for the simultaneous removal of organic carbon and nitrogen at different organic carbon to nitrogen ratios. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 110832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Kambey, C.; Nguyen, V.K. Performance of anammox processes for wastewater treatment: A critical review on effects of operational conditions and environmental stresses. Water. 2020, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weralupitiya, C.; Wanigatunge, R.; Joseph, S.; Athapattu, B.C.L.; Lee, T.H.; Kumar Biswas, J.; Ginige, M.P.; Shiung Lam, S.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Vithanage, M. Anammox bacteria in treating ammonium rich wastewater: Recent perspective and appraisal. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 334, 125240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotti, T.; Kleerebezem, R.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Effect of temperature change on anammox activity. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2015, 112, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosta, J.; Fernández, I.; Vázquez-Padín, J.R.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Campos, J.L.; Mata-Álvarez, J.; Méndez, R. Short- and long-term effects of temperature on the Anammox process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hulle, S.W.H.; Volcke, E.I.P.; Teruel, J.L.; Donckels, B.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Vanrolleghem, P.A. Influence of temperature and pH on the kinetics of the Sharon nitritation process. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2007, 82, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yan, Z.; Huang, S.; Li, J.; Su, B.; Wang, C.; Peng, Y. Rapid start-up and stable maintenance of partial nitrification–anaerobic ammonium oxidation treatment of landfill leachate at low temperatures. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, M.Y.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yuan, Y. Influence of seasonal temperature change on autotrophic nitrogen removal for mature landfill leachate treatment with high-ammonia by partial nitrification-Anammox process. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 102, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Yu, G.; Liu, Z.; Tang, J.; Liu, J. Fast start-up of the CANON process with a SABF and the effects of pH and temperature on nitrogen removal and microbial activity. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 254, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-J.; Zheng, P.; Wang, C.-H.; Mahmood, Q.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Chen, X.-G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.-W. Performance of high-loaded Anammox UASB reactors containing granular sludge. Water Res. 2011, 45, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureni, M.; Falås, P.; Robin, O.; Wick, A.; Weissbrodt, D.G.; Nielsen, J.L.; Ternes, T.A.; Morgenroth, E.; Joss, A. Mainstream Partial Nitritation and Anammox: Long-Term Process Stability and Effluent Quality at Low Temperatures. Water Res. 2016, 101, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Ruiz, M.J.; Maza-Márquez, P.; González-López, J.; Osorio, F. Nitrogen removal capacity and bacterial community dynamics of a canon biofilter system at different organic matter concentrations. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dapena-Mora, A.; Fernández, I.; Campos, J.L.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Méndez, R.; Jetten, M.S.M. Evaluation of activity and inhibition effects on anammox process by batch tests based on the nitrogen gas production. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2007, 40, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Z.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Guo, Q.; Chen, Q.-Q.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Jin, R.-C. Anaerobic Ammonium-oxidizing bacteria gain antibiotic resistance during long-term acclimatization. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Graaf, A.A.; Mulder, A.; de Bruijn, P.; Jetten, M.S.; Robertson, L.A.; Kuenen, J.G. Anaerobic oxidation of Ammonium is a biologically mediated process. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández, I.; Bravo, J.I.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Pereira, A.; Campos, J.L.; Méndez, R.; Melo, L.F. Influence of the shear stress and salinity on anammox biofilms formation: Modelling results. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 37, 1955–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Windey, K.; de Bo, I.; Verstraete, W. Oxygen-limited autotrophic nitrification–denitrification (OLAND) in a rotating biological contactor treating high-salinity wastewater. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4512–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Li, Y.; Shan, X.; Abbas, G.; Zeng, Z.; Kang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, M. A holistic analysis of Anammox process in response to salinity: From adaptation to collapse. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 215, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.-C.; Ma, C.; Mahmood, Q.; Yang, G.-F.; Zheng, P. Anammox in a UASB reactor treating saline wastewater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2011, 89, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ma, C.; Ji, Y.-X.; Ni, W.-M.; Jin, R.-C. Evaluation of the efficacy and regulation measures of the anammox process under salty conditions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 132, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, B.; Koleva, M.; Arsov, R.; van der Star, W.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Strous, M. Adaptation of a freshwater anammox population to high salinity wastewater. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 126, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.-F.; Ni, W.-M.; Wu, K.; Wang, H.; Yang, B.-E.; Jia, X.-Y.; Jin, R.-C. The effect of Cu(II) stress on the activity, performance and recovery on the anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (Anammox) process. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 226, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Yang, C.-C.; Xu, J.-L.; Hu, H.-Y.; Huang, M.; Shi, M.-L.; Jin, R.-C. Individual and combined effects of substrate, heavy metal and hydraulic shocks on an anammox system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 154, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Guo, Q.; Wang, J.-J.; Wang, H.-Z.; Jin, R.-C. Analyzing the revolution of anaerobic Ammonium oxidation (Anammox) performance and sludge characteristics under zinc inhibition. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 3221–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Z.; Qiao, S.; Zhou, J.; Tang, X.; Cheng, Y. Inhibition and recovery of anammox biomass subjected to short-term exposure of Cd, Ag, Hg and Pb. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Val del Río, Á.; da Silva, T.; Martins, T.H.; Foresti, E.; Campos, J.L.; Méndez, R.; Mosquera-Corral, A. Partial nitritation-anammox granules: Short-term inhibitory effects of seven metals on Anammox activity. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.W.; Yang, X.R.; Li, H.; Marshall, C.W.; Zheng, B.X.; Yan, Y.; Su, J.Q.; Zhu, Y.G. Electron shuttles enhance anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron(III) reduction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9298–9307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yan, Z.; Li, J.; Huang, S.; Li, Z.; Shen, M.; Peng, Y. Low temperature advanced nitrogen and sulfate removal from landfill leachate by nitrite-anammox and sulfate-anammox. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, R.M.; Liang, J.; Cui, L.; Zhang, D.; Otitoju, T.A.; Elsalahi, R.H.; Song, X. Novel simultaneous anaerobic ammonium and sulfate removal process: A review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, T.; Liao, C.; Li, N.; Wang, X. A promising destiny for Feammox: From biogeochemical ammonium oxidation to wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Su, Q.; Peng, L.; Sun, L.; Zhao, Q.; Diao, X.; Lu, H. Elemental sulfur-driven autotrophic denitrification for advanced nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate after PN/A pretreatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Hou, S.; Huang, X.; Fang, Z.; Tong, Y.; Yang, H. Insights into the microbial community structure of anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste landfill leachate for methane production by adaptive thermophilic granular sludge. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 39, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmadewanthi, I.D.A.A.; Chrystiadini, G.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Abdullah, S.R.S. Impact of degraded solid waste utilization as a daily cover for landfill on the formation of methane and leachate. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 15, 100797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harb, R.; Laçin, D.; Subaşı, I.; Erguder, T.H. Denitrifying anaerobic methane oxidation (DAMO) cultures: Factors affecting their enrichment, performance and integration with anammox bacteria. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Ding, J.; Lu, Y.Z.; Ding, Z.W.; Zeng, R.J. Nitrogen source effects on the denitrifying anaerobic methane oxidation culture and anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria enrichment process. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 3895–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, R.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, T. A novel additional carbon source derived from rotten fruits: Application for the denitrification from mature landfill leachate and evaluation the economic benefits. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Inhibitor | Types | Reactor | Concentration | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic matter | Nontoxic | UASB | 700 mg L−1 Sucrose | Nitrogen removal efficiency decreased by 98% | [89] |
| MBBR | 533 mg L−1 COD | No interruption because nitrogen load was less | [90] | ||
| Biofilter | 400 mg L−1 Acetate | Partial inhibition of nitrogen removal rate and increase in the heterotrophic bacteria | [91] | ||
| Serum vials | 50 mmol L−1 Acetate | Nitrogen removal efficiency decreased by 70% | [92] | ||
| Toxic | UASB | 50 mg L−1 Oxytetracycline | Activity loss of 90.4% | [61] | |
| 150 mg L−1 Amoxicillin | Severely inhibited | [93] | |||
| Serum vials | 20 mg L−1 Chloramophenicol | Activity decreased by 36% | [94] | ||
| 200 mg L−1 Chloramophenicol | Activity decreased by 98% | ||||
| 100 mg L−1 Penicillin | Activity decreased by 36% | ||||
| Salinity | NaCl | SBR | 5 g L−1 | Favored the formation of anammox biofilm | [95] |
| 15 g L−1 | Obversed inhibitory effect | ||||
| RBC | 6 g L−1 | No remarkable loss of activity | [96] | ||
| 30 g L−1 | Activity decreased by 95% (nonadapted) and 59% (adapted) | ||||
| UASB | 35.1 g L−1 | Anammox performance collapsed | [97] | ||
| 30 g L−1 | Activity decreased by 67.5% (nonadapted) and 45.1% (adapted) | [98] | |||
| 5–30 g L−1 | Performance degraded at NaCl higher than 15 g/L | [99] | |||
| 90% NaCl and 10% KCl | SBR | 10 g L−1 | Maximum activity | [100] | |
| 45 g L−1 | Decreased by 85% | ||||
| 60 g L−1 | The activity was lost | ||||
| Na2SO4 | Serum vials | 11.36 g L−1 | Inhibition by 50% | [92] | |
| CaCl2 | SBR | 5 g L−1 | Favored the formation of anammox biofilm | [95] | |
| Heavy metal | Cu | Serum flask | 12.6 mg L−1 | Inhibition by 50% | [101] |
| UASB | 5.95 mg L−1 | No significant inhibition | [102] | ||
| Zn | Serum flask | 20.0 mg L−1 | Activity decreased by 20.1% | [57] | |
| UASB | 25 mg L−1 | Inhibition by 50% | [103] | ||
| Hg | Serum vials | 60.35 mg L−1 | Inhibition by 50% | [104] | |
| Ag | 11.52 mg L−1 | ||||
| Cd | 11.16 mg L−1 | ||||
| Mn | Serum vials | 175.8 mg L−1 | Inhibition by 50% | [105] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, W.; Wang, L.; Cheng, L.; Yang, W.; Gao, D. Nitrogen Removal from Mature Landfill Leachate via Anammox Based Processes: A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14020995
Deng W, Wang L, Cheng L, Yang W, Gao D. Nitrogen Removal from Mature Landfill Leachate via Anammox Based Processes: A Review. Sustainability. 2022; 14(2):995. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14020995
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Weifeng, Litao Wang, Lang Cheng, Wenbo Yang, and Dawen Gao. 2022. "Nitrogen Removal from Mature Landfill Leachate via Anammox Based Processes: A Review" Sustainability 14, no. 2: 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14020995
APA StyleDeng, W., Wang, L., Cheng, L., Yang, W., & Gao, D. (2022). Nitrogen Removal from Mature Landfill Leachate via Anammox Based Processes: A Review. Sustainability, 14(2), 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14020995






