Decomposition of Formic Acid and Acetic Acid into Hydrogen Using Graphitic Carbon Nitride Supported Single Metal Catalyst
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of Modified Graphitic Carbon Nitride Based Monometallic Catalyst
2.3. Catalysts Characterization
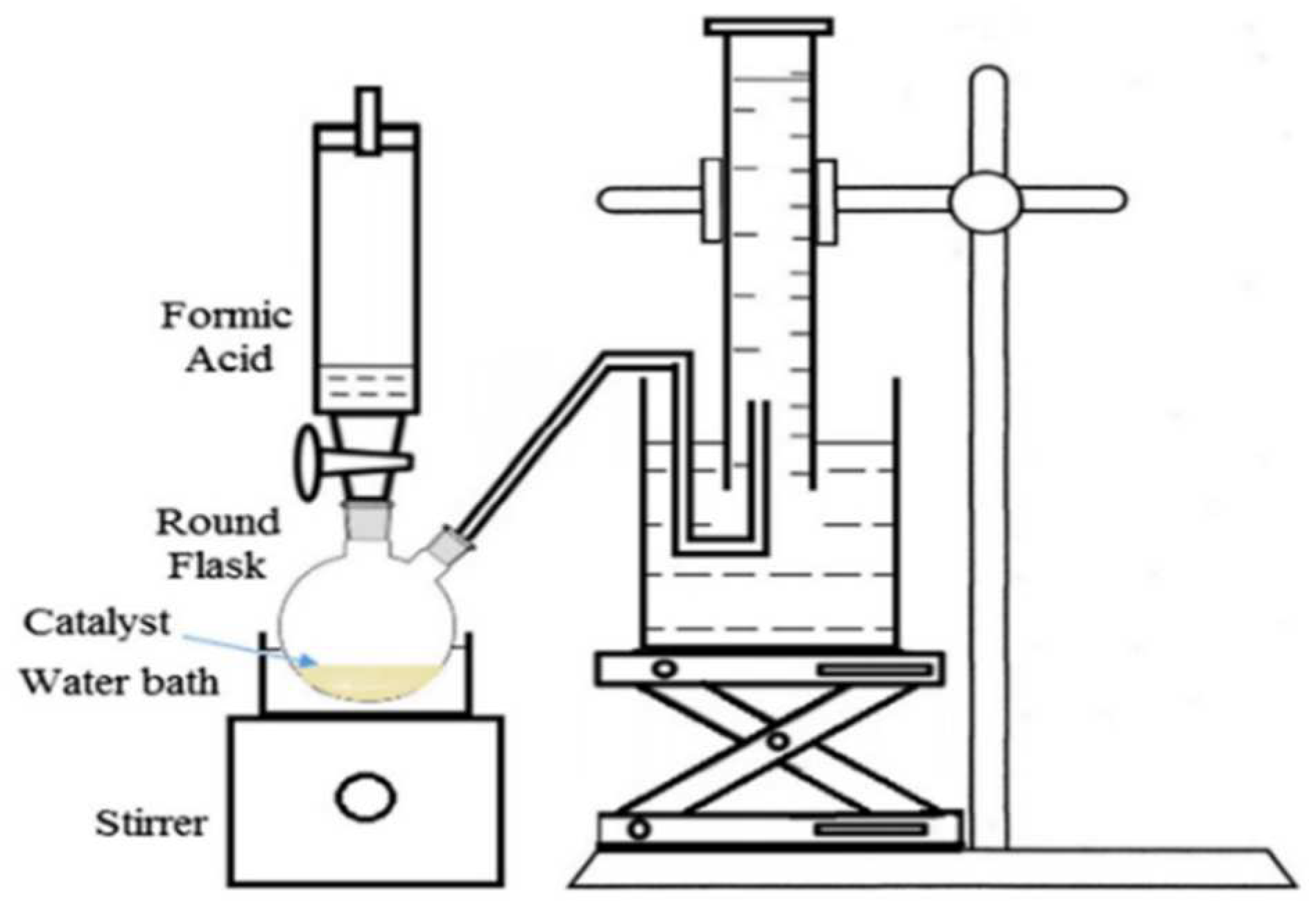
2.4. Catalysts Testing
3. Results and Discussion
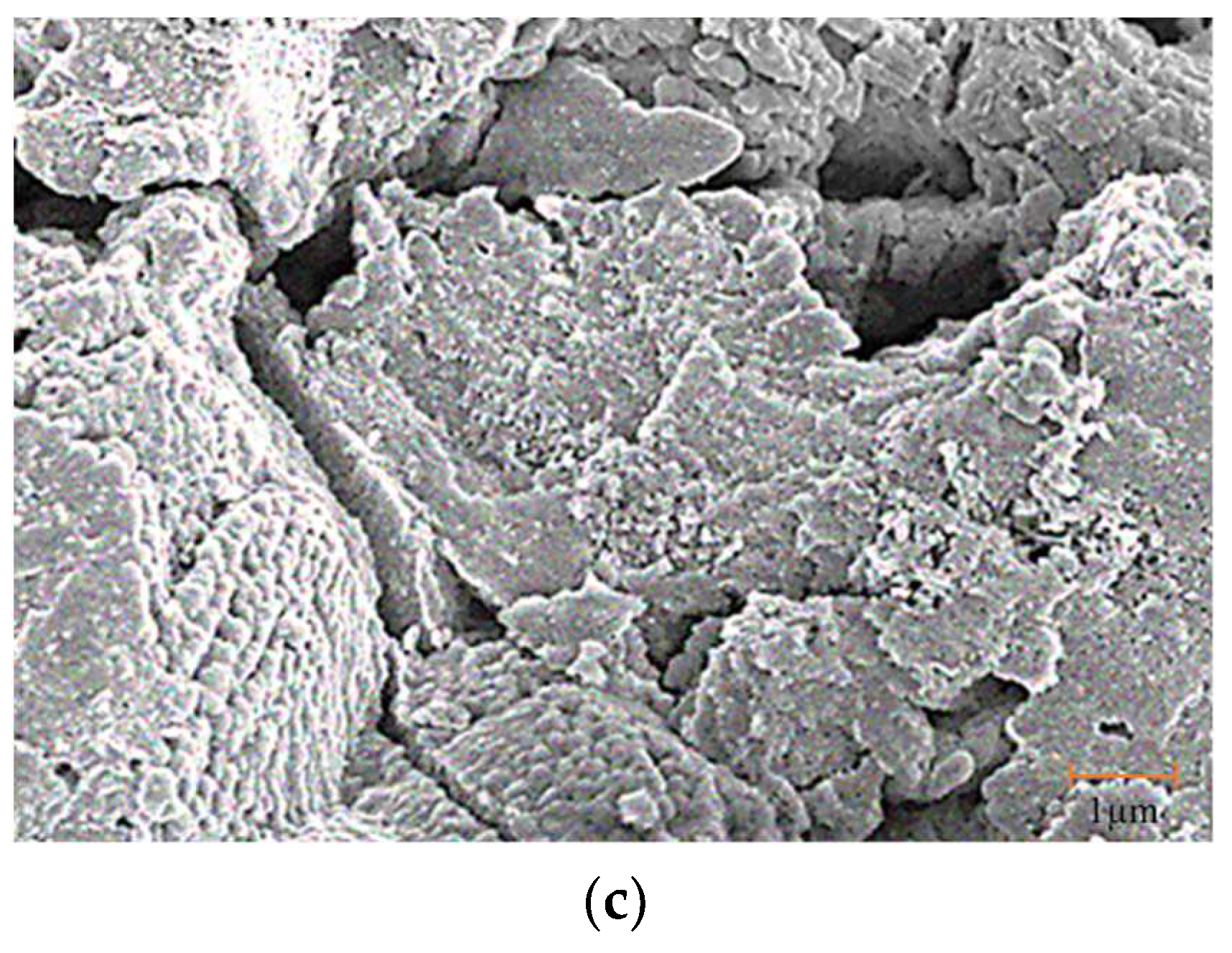
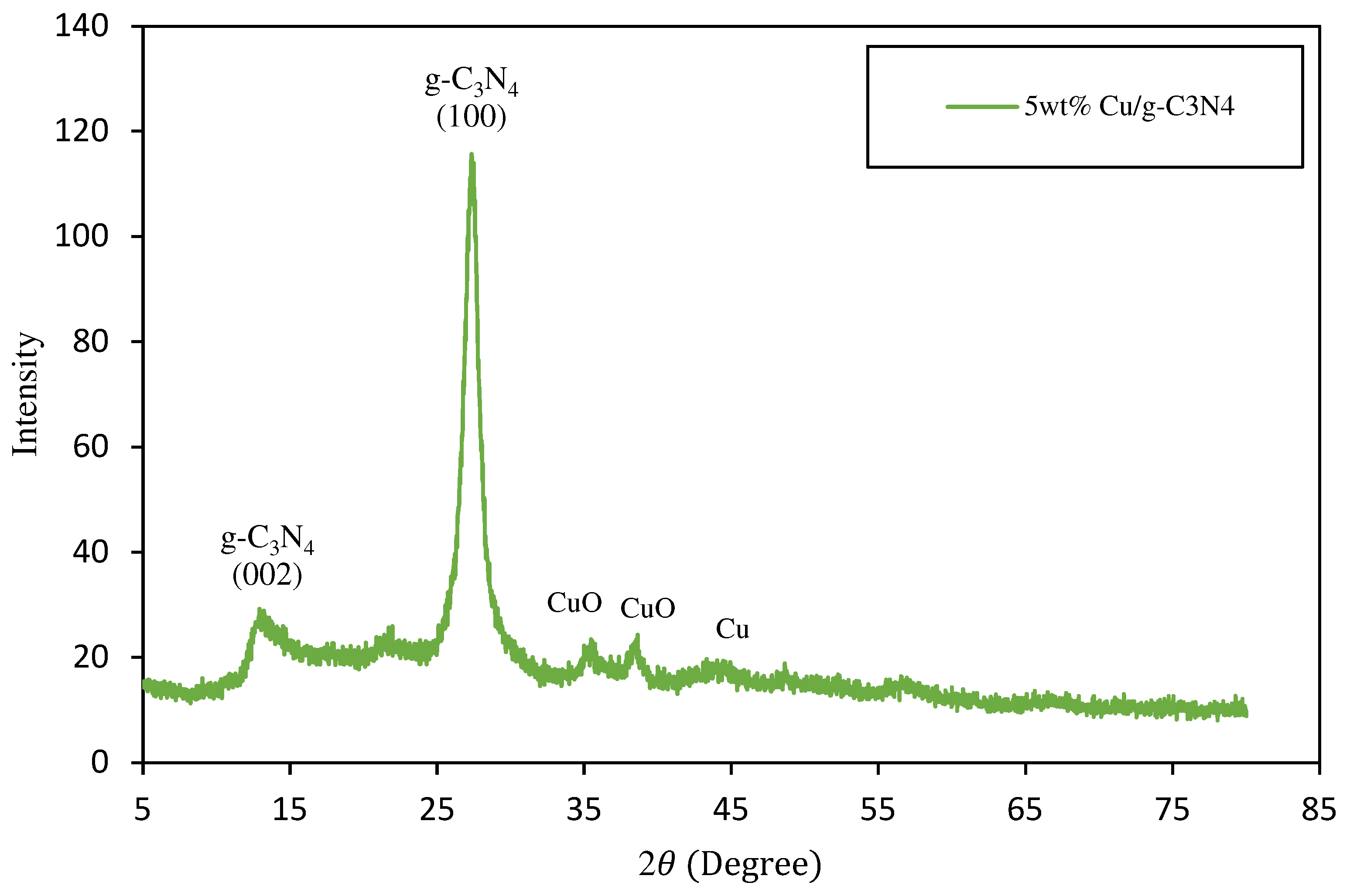
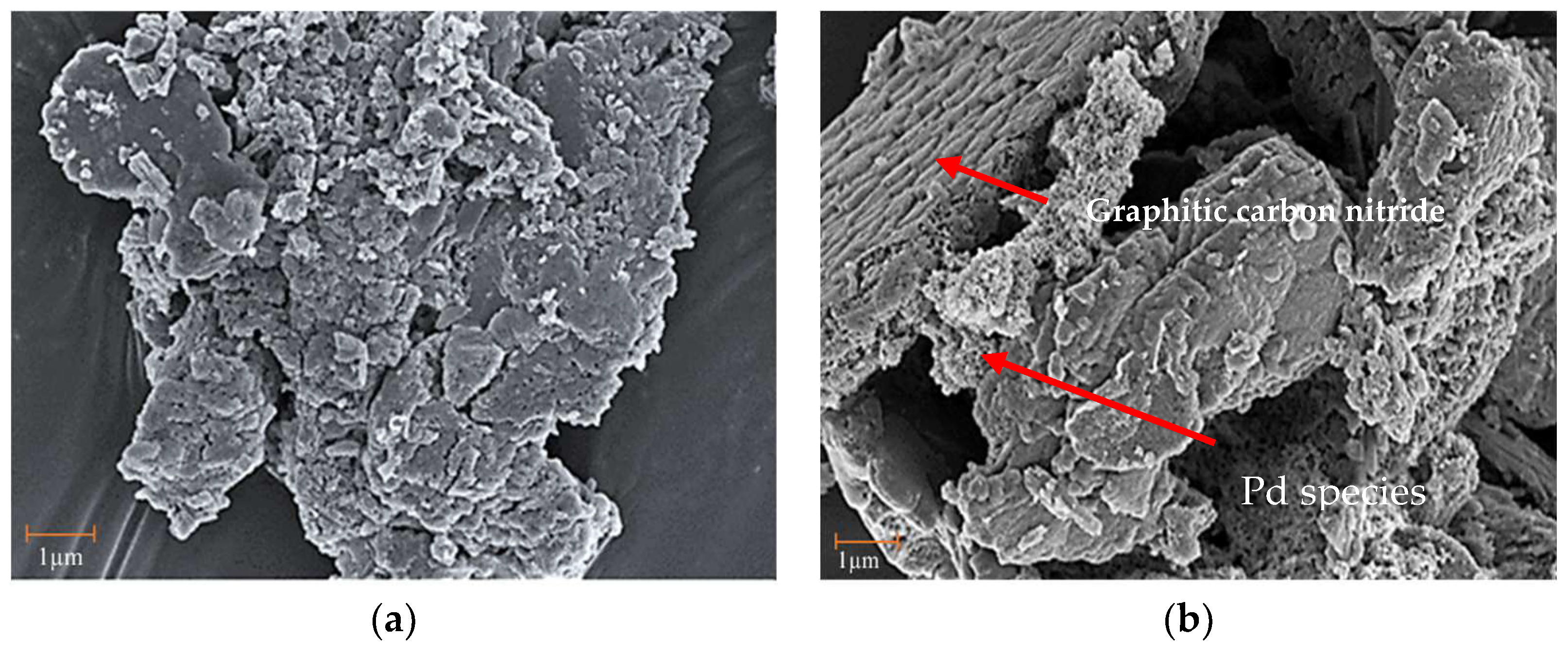
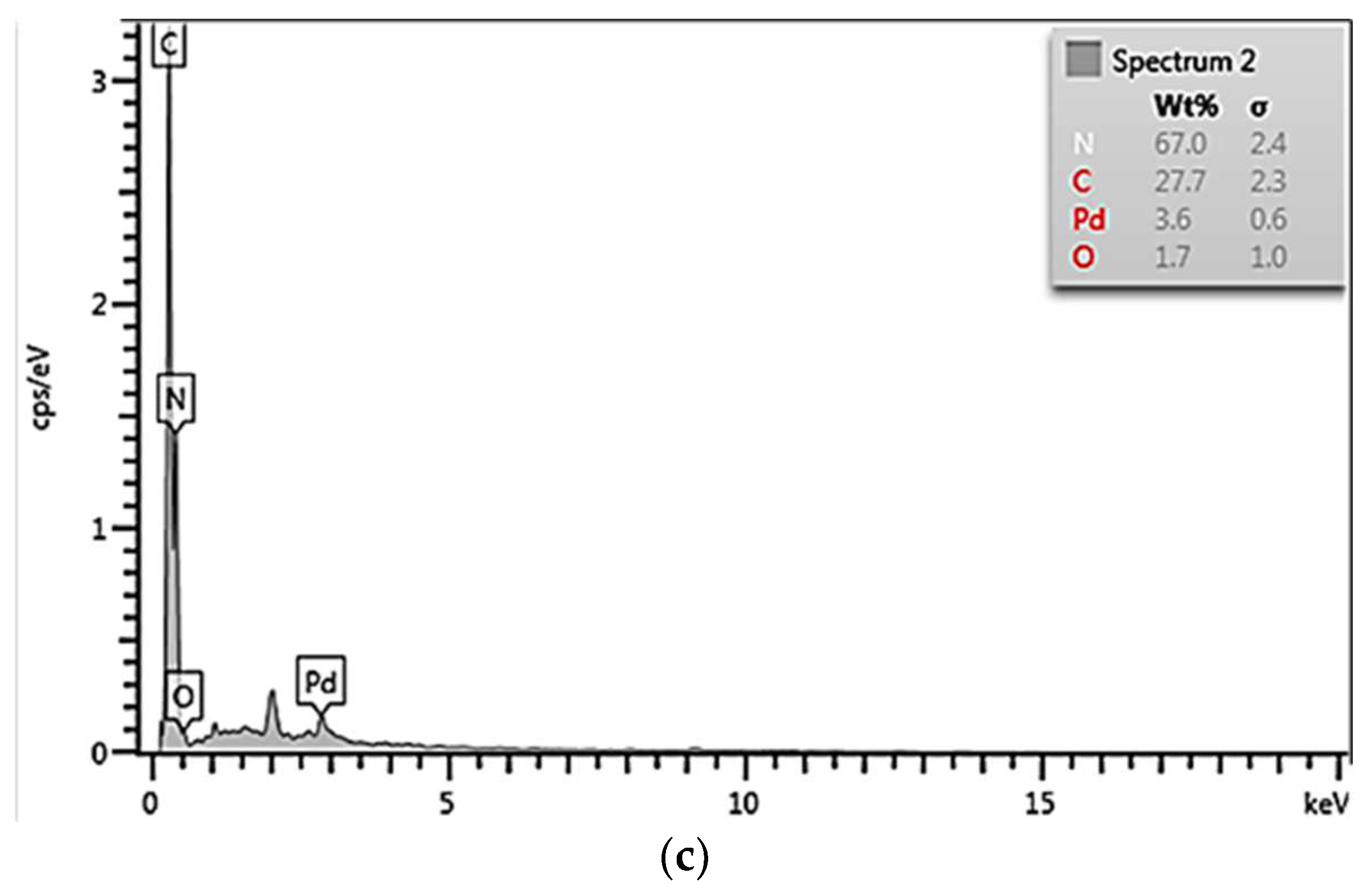
3.1. Catalysts Properties and Features
3.2. Catalytic Performance over Formic Acid, Acetic Acid and their Mixture Decomposition Reaction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, K.N.; Wan Isahak, W.N.R.; Rosli, M.I.; Yusop, M.R.; Kassim, M.B.; Yarmo, M.A. Rare earth metal doped nickel catalysts supported on exfoliated graphitic carbon nitride for highly selective CO and CO2 methanation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 571, 151321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.A.H.; Dzakaria, N.; Isahak, W.N.R.W.; Yarmo, M.A. Effect of nickel on bimetallic nanoalloy catalyst for hydrogen generation. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2017, 21, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahari, N.A.; Isahak, W.N.R.W.; Masdar, M.S.; Ba-Abbad, M.M. Optimization of the controllable crystal size of iron/zeolite nanocomposites using a Box–Behnken design and their catalytic activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2018, 9, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Ma, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q.; Qiu, H. An effective low Pd-loading catalyst for hydrogen generation from formic acid. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 18375–18382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakiryilmaz, N.; Arbag, H.; Oktar, N.; Dogu, G.; Dogu, T. Catalytic performances of Ni and Cu impregnated MCM-41 and Zr-MCM-41 for hydrogen production through steam reforming of acetic acid. Catal. Today 2019, 323, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homlamai, K.; Maihom, T.; Choomwattana, S.; Sawangphruk, M.; Limtrakul, J. Single-atoms supported (Fe, Co, Ni, Cu) on graphitic carbon nitride for CO2 adsorption and hydrogenation to formic acid: First-principles insights. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 499, 143928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Sang, R.; Sponholz, P.; Junge, H.; Beller, M. Reversible hydrogenation of carbon dioxide to formic acid using a Mn-pincer complex in the presence of lysine. Nat. Energy 2022, 7, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xiao, P.; Li, H.; Carabineiro, S.A.C. Graphitic carbon nitride: Synthesis, properties, and applications in catalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16449–16465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.Z.; Ahmad, K.N.; Isahak, W.N.R.W.; Pudukudy, M.; Masdar, M.S.; Jahim, J.M. Synthesis, Characterisation and Catalytic Activity of NiO supported Al2O3 for CO2 Hydrogenation to Carboxylic Acids: Influence of Catalyst Structure. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 268, 12079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, Z.A.C.; Shaari, N.; Saharuddin, T.S.T. Progress and major BARRIERS of nanocatalyst development in direct methanol fuel cell: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 22114–22146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, N.A.M.; Shaari, N.; Ramli, Z.A.C. Progress of g-C3N4 and carbon-based material composite in fuel cell application. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 12, 16281–16315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaran, M.; Dhanusuraman, R.; Tsai, P.C.; Ponnusamy, V.K. One-step preparation of graphitic carbon nitride/Polyaniline/Palladium nanoparticles based nanohybrid composite modified electrode for efficient methanol electro-oxidation. Fuel 2019, 251, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zi, G.; Zhou, C.; Liu, B.; Liu, G.; Wang, L.; Huang, W. One-step supramolecular preorganization constructed crinkly graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets with enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 104, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Xiao, X.; Wang, S.; Huang, W. Boron dopant simultaneously achieving nanostructure control and electronic structure tuning of graphitic carbon nitride with enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 14876–14884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Du, P.; Zhao, D.; Li, S.; Sun, F.; Duin, E.C.; Liu, W. 2D/1D graphitic carbon nitride/titanate nanotubes heterostructure for efficient photocatalysis of sulfamethazine under solar light: Catalytic “hot spots” at the rutile–anatase–titanate interfaces. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 263, 118357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Xiao, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, W. Boosting the photocatalytic hydrogen production performance of graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets by tailoring the cyano groups. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 610, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Wang, S.; Zuo, J.; Zhang, B. Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction Coupled with Alcohol Oxidation over Porous Carbon Nitride. Catalysts 2022, 12, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Zhou, L.; Xu, S.; Jin, B.; Ge, X.; Qian, X.; Xu, L.; Chen, F.; Zhan, X.; Yang, Y.; et al. Defect engineered mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride modified with AgPd nanoparticles for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from formic acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Dai, P.; Zhu, L.; Yan, L.; Chen, R.; Liu, D.; Gu, X.; Li, L.; Xue, Q.; Zhao, X. Graphitic carbon nitride catalyzes selective oxidative dehydrogenation of propane. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 262, 118277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Torres-Pinto, A.; LaGrow, A.P.; Diaconescu, V.M.; Simonelli, L.; Sampaio, M.J.; Bondarchuk, O.; Amorim, I.; Araujo, A.; et al. Single-atom Ir and Ru anchored on graphitic carbon nitride for efficient and stable electrocatalytic/photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 310, 121318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyessa, G.W.; dela Cruz, J.B.; Rameez, M.; Hung, C.-H. Nanocomposite catalyst of graphitic carbon nitride and Cu/Fe mixed metal oxide for electrochemical CO2 reduction to CO. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 291, 120052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navlani-García, M.; Salinas-Torres, D.; Mori, K.; Kuwahara, Y.; Yamashita, H. Enhanced formic acid dehydrogenation by the synergistic alloying effect of PdCo catalysts supported on graphitic carbon nitride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 28483–28493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Lu, T. Carbon-supported Pd–Ir catalyst as anodic catalyst in direct formic acid fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2008, 175, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Li, H.; Su, D.; Antonietti, M. Highly Selective Hydrogenation of Phenol and Derivatives over a Pd@Carbon Nitride Catalyst in Aqueous Media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2362–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; He, Y.; Peng, R. Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) as a metal-free catalyst for thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24507–24512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihet, M.; Dan, M.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Lazar, M.D.; Blanita, G. Controllable H2 Generation by Formic Acid Decomposition on a Novel Pd/Templated Carbon Catalyst. Hydrogen 2020, 1, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, F.; Motta, D.; Roldan, A.; Hammond, C.; Villa, A.; Dimitratos, N. Hydrogen Generation from Additive-Free Formic Acid Decomposition Under Mild Conditions by Pd/C: Experimental and DFT Studies. Top. Catal. 2018, 61, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Kolpin, A.; Chi, S.; Tsang, E.; Jones, S.; Kolpin, A.; Chi, S.; Tsang, E. Modification of Pd for formic acid decomposition by support grafted functional groups Modification of Pd for formic acid decomposition by support grafted functional groups. Catal. Struct. React. 2015, 1, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Li, Z.H. Palladium-atom catalyzed formic acid decomposition and the switch of reaction mechanism with temperature. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 10005–10017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nayili, A.; Majdi, H.S.; Albayati, T.M.; Saady, N.M.C. Formic Acid Dehydrogenation Using Noble-Metal Nanoheterogeneous Catalysts: Towards Sustainable Hydrogen-Based Energy. Catalysts 2022, 12, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiti, M.; Padovan, D.; Hammond, C. Continuous Production of Hydrogen from Formic Acid Decomposition Over Heterogeneous Nanoparticle Catalysts: From Batch to Continuous Flow. ACS Catal. 2019, 10, 9188–9198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.-L.; Tsumori, N.; Xu, Q. Immobilizing Extremely Catalytically Active Palladium Nanoparticles to Carbon Nanospheres: A Weakly-Capping Growth Approach. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11743–11748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Shen, Y.-B.; Zhan, Y.-L.; Ning, F.-D.; Yan, L.-M.; Zhou, X.-C. Highly active iridium catalyst for hydrogen production from formic acid. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 1746–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







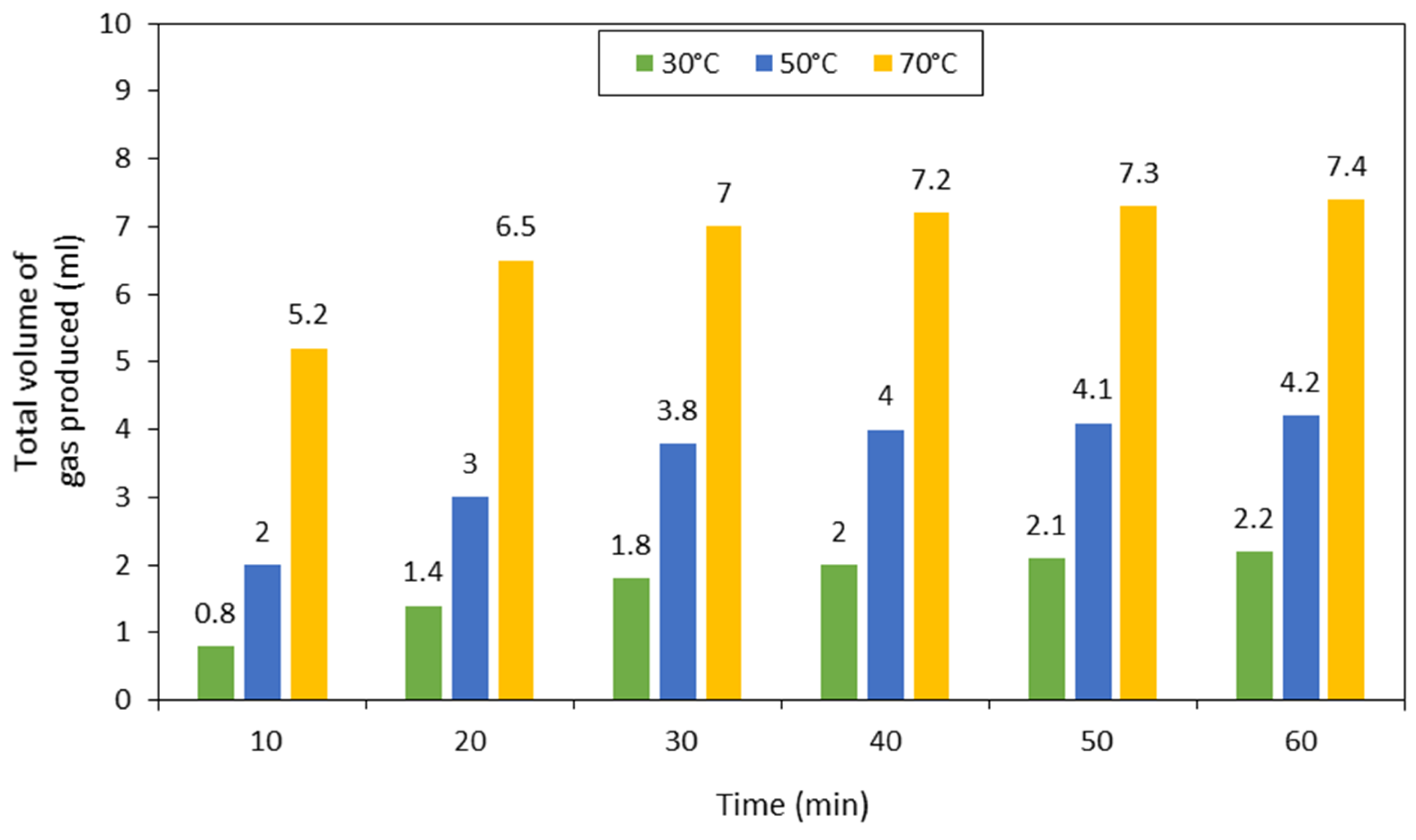

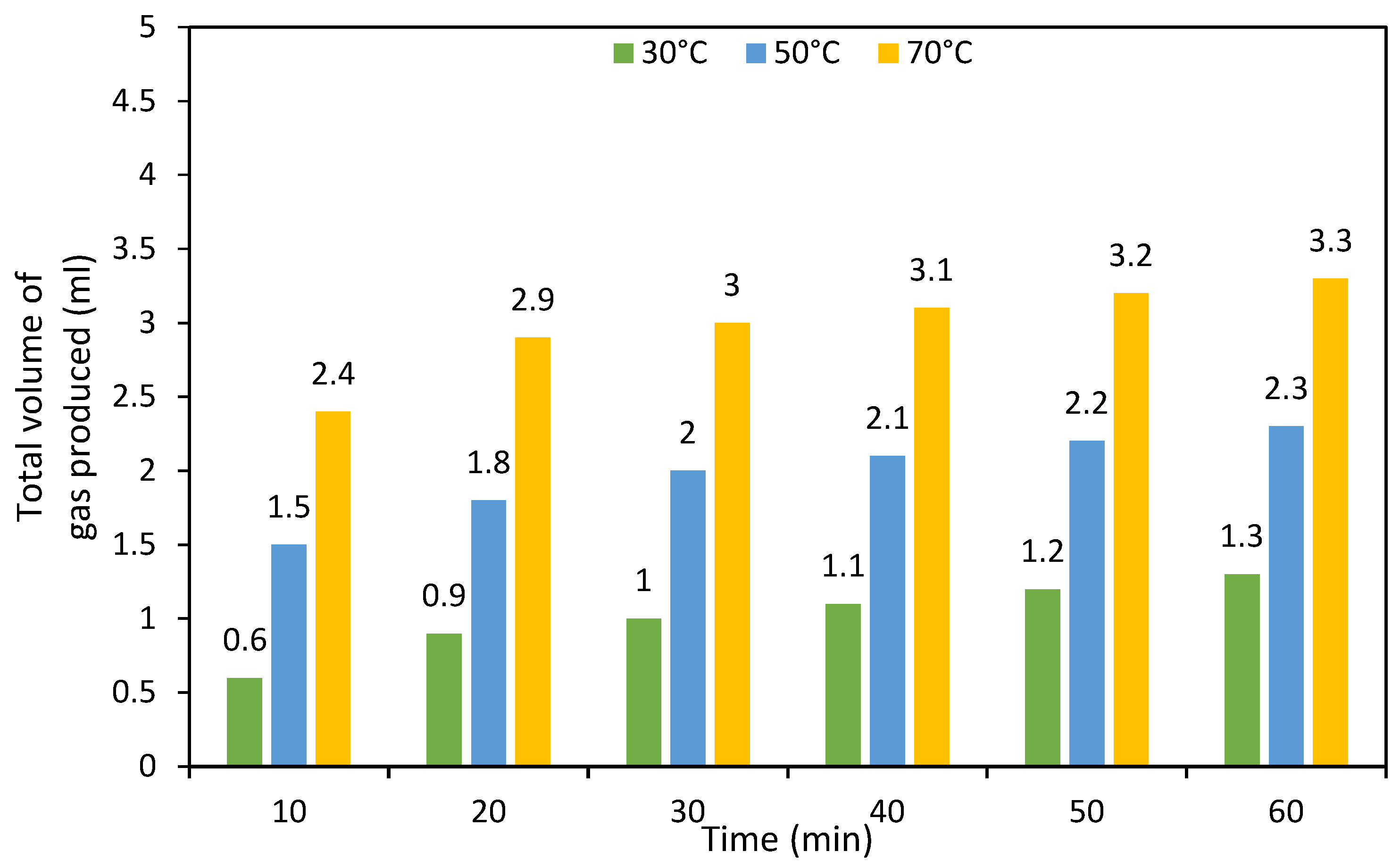

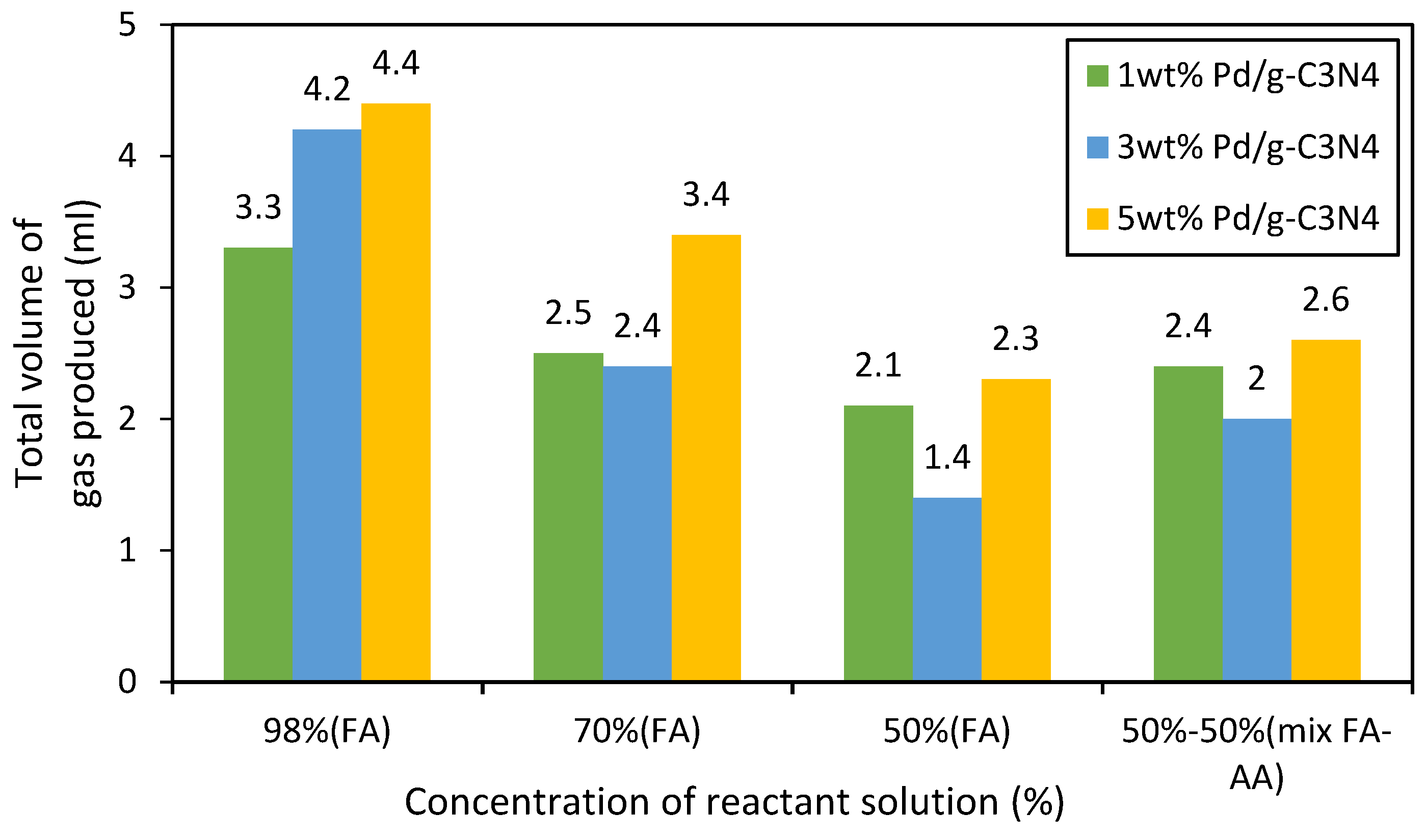

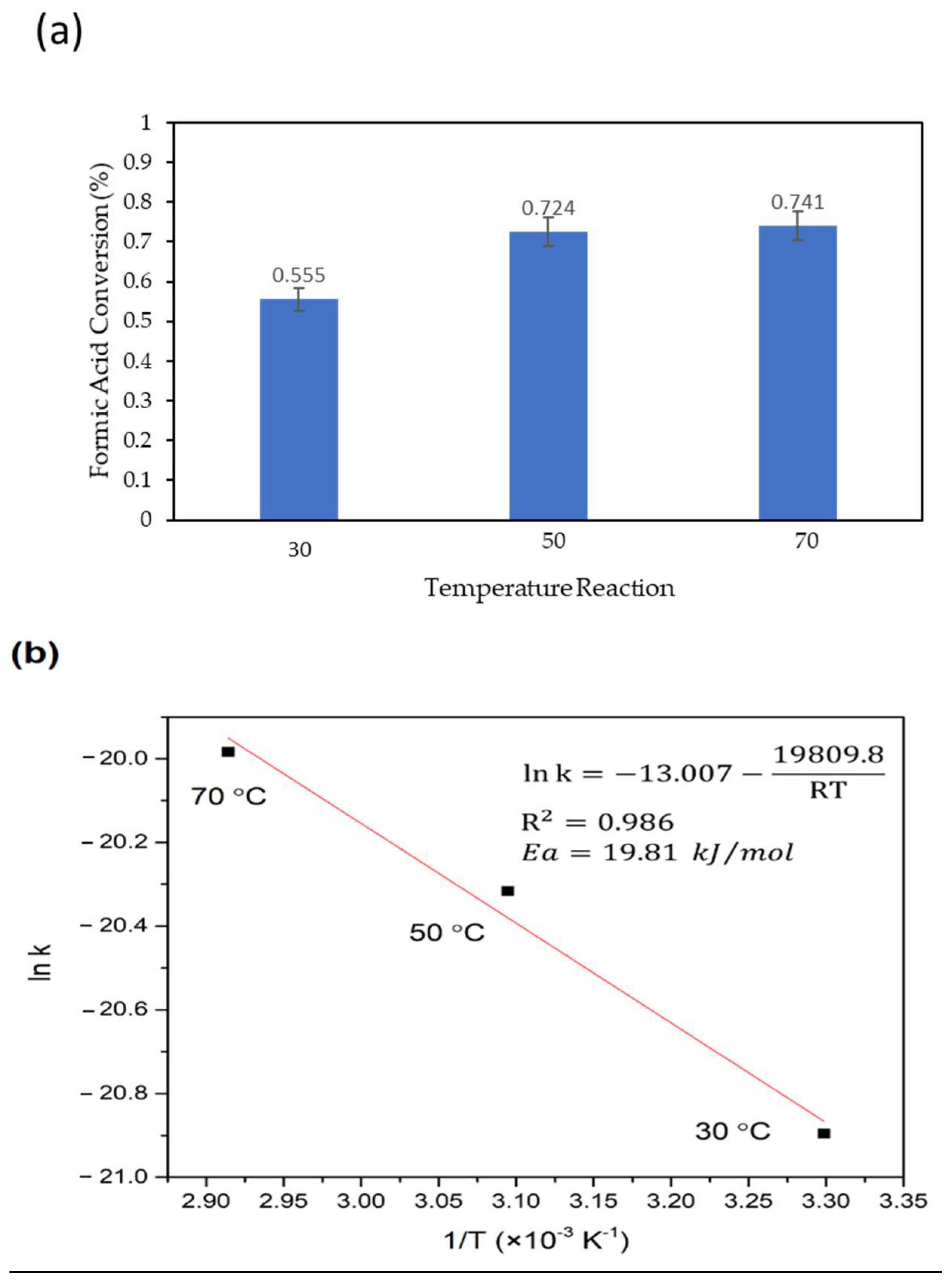

| Type of Catalyst | Crystallinity Percentage (%) | Amorphous Percentage (%) | Average Crystal Size of Metal/Metal Oxide (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 wt% Pd/g-C3N4 | 47.4 | 52.6 | 8.14 |
| 3 wt% Pd/g-C3N4 | 49.2 | 50.8 | 11.14 |
| 5 wt% Pd/g-C3N4 | 56.8 | 43.2 | 17.63 |
| 5 wt% Cu/g-C3N4 | 48.5 | 51.5 | 20.39 |
| 5 wt% Zn/g-C3N4 | 50.7 | 49.3 | 25.24 |
| Catalysts | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Micropore Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCN | 8.56 | 1.189 | 0.0196 | 9.14 |
| 1% Pd/GCN | 7.55 | 1.76 | 0.0172 | 9.12 |
| 3% Pd/GCN | 7.32 | 1.62 | 0.0173 | 9.45 |
| 5% Pd/GCN | 7.18 | 1.35 | 0.0193 | 9.45 |
| 5% Cu/GCN | 10.27 | 1.77 | 0.0226 | 8.82 |
| 5% Zn/GCN | 10.25 | 1.54 | 0.0215 | 8.41 |
| Elements | Catalysts with Different Pd Loadings (wt%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 wt% of Pd | 3 wt% of Pd | 5 wt% of Pd | |
| Nitrogen | 64.9 | 63.2 | 67.0 |
| Carbon | 30.9 | 29.1 | 27.7 |
| Oxygen | 3.3 | 5.4 | 1.7 |
| Palladium | 0.9 | 2.3 | 3.6 |
| Catalysts | FA Conversion (%) | TON | TOF (h−1) | Total Gas Produced (mL) (1st Cycle) | Total Gas Produced (mL) (2nd Cycle) | Total Gas Produced (mL) (3rd Cycle) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 wt% Pd/g-C3N4 | 0.555 | 1449.3 | 1449.3 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 2.7 |
| 5 wt% Cu/g-C3N4 | 0.051 | 57.2 | 57.2 | 0.3 | n.d | n.d |
| 5 wt% Zn/g-C3N4 | 0.020 | 23.2 | 23.2 | 0.12 | n.d | n.d |
| Pd/rGO [30] | n.d | n.d | 911.0 (10 mL of FA used) | 80 | n.d | n.d |
| Pd/C [31] | 9.5 | n.d | 1500 (at 50 °C, 5 bar) | n.d | n.d | n.d |
| IrCp * Cl2bpym [33] | n.d | n.d | 2490 (at 40 °C, 300 mL of FA) | 350 | n.d | n.d |
| Catalysts | Hydrogen (%) | Carbon Dioxide (%) | Other Gas (N2) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 wt% Pd/g-C3N4 | 95.3 | 4.7 | n.d |
| 5 wt% Cu/g-C3N4 | 92.0 | 6.7 | 1.3 |
| 5 wt% Zn/g-C3N4 | 87.5 | 10.5 | 2.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Isahak, W.N.R.W.; Kamaruddin, M.N.; Ramli, Z.A.C.; Ahmad, K.N.; Al-Azzawi, W.K.; Al-Amiery, A. Decomposition of Formic Acid and Acetic Acid into Hydrogen Using Graphitic Carbon Nitride Supported Single Metal Catalyst. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13156. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013156
Isahak WNRW, Kamaruddin MN, Ramli ZAC, Ahmad KN, Al-Azzawi WK, Al-Amiery A. Decomposition of Formic Acid and Acetic Acid into Hydrogen Using Graphitic Carbon Nitride Supported Single Metal Catalyst. Sustainability. 2022; 14(20):13156. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013156
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsahak, Wan Nor Roslam Wan, Muhammad Nizam Kamaruddin, Zatil Amali Che Ramli, Khairul Naim Ahmad, Waleed Khalid Al-Azzawi, and Ahmed Al-Amiery. 2022. "Decomposition of Formic Acid and Acetic Acid into Hydrogen Using Graphitic Carbon Nitride Supported Single Metal Catalyst" Sustainability 14, no. 20: 13156. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013156
APA StyleIsahak, W. N. R. W., Kamaruddin, M. N., Ramli, Z. A. C., Ahmad, K. N., Al-Azzawi, W. K., & Al-Amiery, A. (2022). Decomposition of Formic Acid and Acetic Acid into Hydrogen Using Graphitic Carbon Nitride Supported Single Metal Catalyst. Sustainability, 14(20), 13156. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013156









