A Systematic Review of What Malaysia Can Learn to Improve Orang Asli Students’ Mathematics Learning from Other Countries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
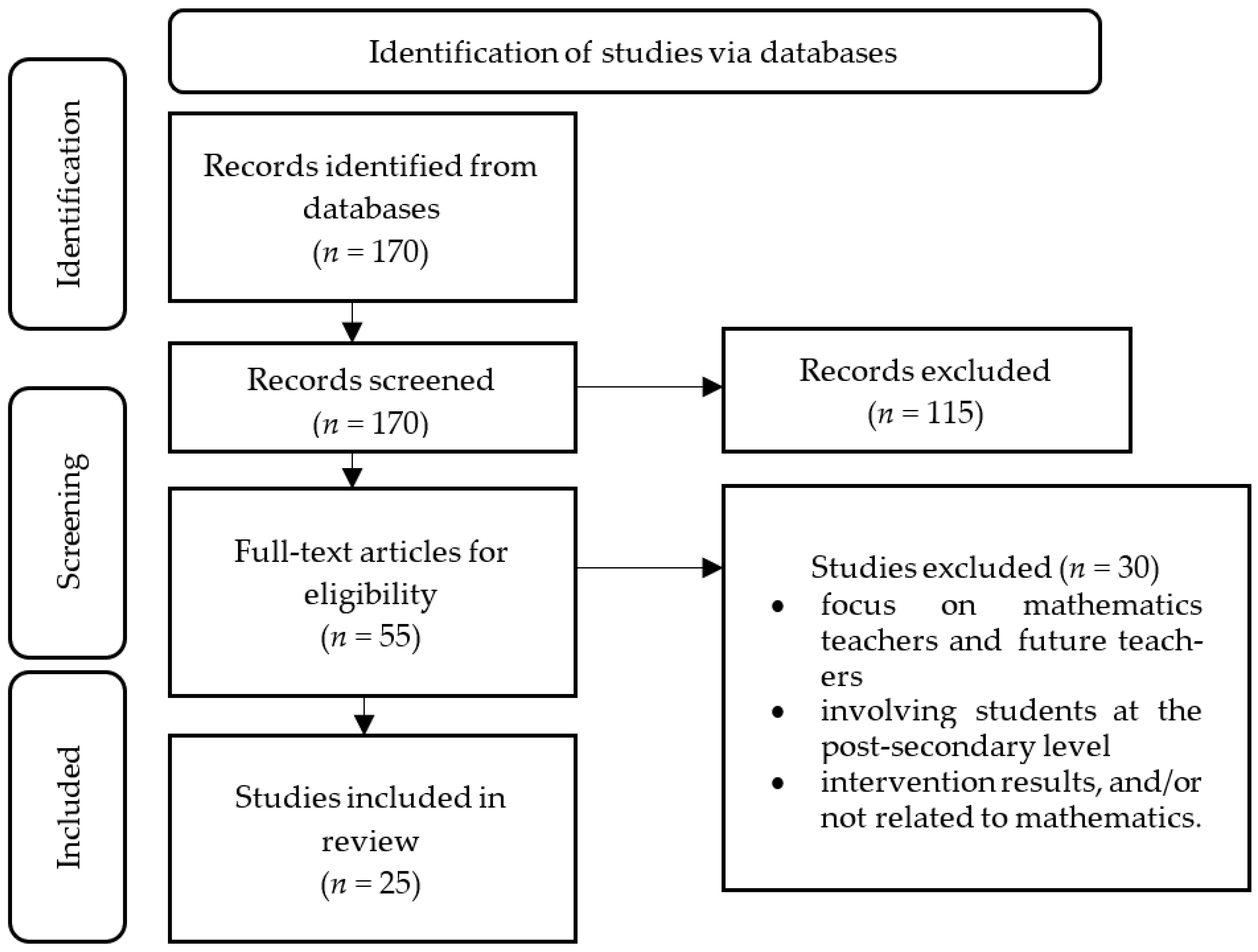
2.1. Systematic Review Design and Search Process
2.2. Screening and Eligibility Studies
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
3.2. Intervention Characteristics
3.3. Features of the Intervention Practice
3.4. Reported Outcomes
3.4.1. Enhancing Indigenous Students’ Mathematics Cognitive-Related Outcomes
3.4.2. Enhancing Indigenous Students’ Mathematics Psychomotor-Related Outcomes
3.4.3. Enhancing Indigenous Students’ Mathematics Affective-Related Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. Many Interventions Were Given to The Elementary School Indigenous Students
4.2. Cultural Relevance and Scientific Inquiry: Main Features of the Interventions
4.3. The Importance of Indigenous Languages in Mathematical Learning
4.4. Less Intervention Designed by Indigenous Teachers and Ongoing Support for Non-Indigenous Teachers
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Department of Orang Asli Development (JAKOA). Available online: https://www.jakoa.gov.my/orang-asli (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- United Nations. The 2030 Agenda and the Sustainable Development Goals: An opportunity for Latin America and the Caribbean (LC/G. 2681-P/Rev). 2018. Available online: https://repositorio.cepal.org/handle/11362/40156 (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Sani, N.; Idris, A.R. Identifying the challenges encountered by teachers in dealing with indigenous students. MOJEM Malays. Online J. Educ. Manag. 2017, 1, 48–63. Available online: https://sare.um.edu.my/index.php/MOJEM/article/view/6173/3877 (accessed on 18 October 2017).
- Azlina, M.K.; Ma’rof, R. Atribusi kemiskinan dalam kalangan pelajar orang asli di Malaysia. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Social Science Research ICSSR 2013, Penang, Malaysia, 4–5 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Education. Malaysia Education Blueprint: 2013–2025; Ministry of Education, Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas, C. The Orang Asli and the Contest for Resources: Indigenous Politic, Development and Identity in Peninsular Malaysia; International Work Group for Indigenous Affairs: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Orang Asli Development (JAKOA). Pelan Strategik Kemajuan Orang Asli (2011–2015); Jabatan Kemajuan Orang Asli Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2011.
- Tanius, E.; Siregar, S.; Mohd Kasim, C.M.; Abdul Jalil, S.Z.S. Indigenous (orang asli) primary school mathematics performance in Selangor, Malaysia. Int. J. Innov. Res. Eng. Multidiscip. Phys. Sci. 2020, 8, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, Z.; Ching, T.Y.; Muda, N.A. Numeracy competency of year 5 aboriginal students using written and oral tests. Math. Enthus. 2020, 17, 32–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md-Ali, R.; Veloo, A.; Shanmugam, S.; Yusoff, Y.J.; Hashim, R.A. The issues and challenges of mathematics teaching and learning in Malaysia orang Asli primary schools from teachers’ perspectives. Malays. J. Learn. Instr. 2021, 18, 129–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Education. Pelaporan Pentaksiran Sekolah Rendah 2017; Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Arshad, M. Prinsip dan Amalan Dalam Pengajaran Literasi Bahasa Melayu; Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sani, N.; Idris, A.R. Implementation of Linus programme based on the model of Van Meter and Van Horn. MOJES Malays. Online J. Educ. Sci. 2013, 1, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, N.A.; Mustapha, R. Reflections on Pedagogical and Curriculum Implementation at Orang Asli Schools in Pahang. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 172, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloo, A.; Shanmugam, S.K.S.; Md-Ali, R.; Yusoff, Y.J.; Awang-Hashim, R. Grade five Indigenous (Orang Asli) pupil’s achievement in bilingual versions of mathematics test. J. Lang. Linguist. Stud. 2021, 17, 1863–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafi, W.A.W.; Ahmad, S.; Ali, N. Faktor budaya dan persekitaran dalam prestasi pendidikan anak Orang Asli Malaysia: Kajian kes di Kelantan. Geogr. Malays. J. Soc. Space 2014, 10, 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, N.A.; Mustapha, R.; Talib, J.A. Developing the Orang Asli human capital: A case study on the roles and determination of educational goals among Orang Asli parents in Kuantan, Pahang. Geogr. Malays. J. Soc. Space 2016, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Md Nor, S.; Roslan, S.; Mohamed, A.; Hassan, K.; Mat Ali, M.A.; Manaf, J.A. Dropout prevention initiatives for Malaysian indigenous orang asli children. Int. J. Sch. Disaffect. 2011, 8, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloo, A.; Shanmugam, S.K.S.; Md-Ali, R.; Yusoff, Y.J.; Awang-Hashim, R. Examining indigenous (Orang Asli) pupils’ achievement in mathematics computation and word problem items. J. Lang. Linguist. Stud. 2021, 17, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, S.K.S.; Veloo, A.; Md-Ali, R. Culturally responsive assessment: Assessing mathematics performance of Indigenous pupils in Malaysia using trilingual test. Diaspora Indig. Minor. Educ. 2020, 15, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardoin, N.M.; Bowers, A.W. Early childhood environmental education: A systematic review of the research literature. Educ. Res. Rev. 2020, 31, 100353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbin, J.; Strauss, A. Basics of Qualitative Research: Techniques and Procedures for Developing Grounded Theory, 4th ed.; Sage Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, E.; Young, J.; DeVries, E. The impact of early numeracy engagement on four-year-old Indigenous students. Australas. J. Early Child. 2008, 33, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Olp, M.; Nelson, C.; Saiz, L. Conceptualizing a mathematics curriculum: Indigenous knowledge has always been mathematics education. Educ. Stud. 2019, 55, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q. Supporting indigenous students in science and STEM education: A systematic review. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, C.; Cooper, T.; Baturo, A. Creating your own symbols: Beginning algebraic thinking with Indigenous students. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference of the International Group for the Psychology of Mathematics Education, Seoul, Korea, 8–13 July 2007; Woo, J., Lew, H., Seo, D., Park, K., Eds.; The Korea Society of Educational Studies in Mathematics: Seoul, Korea, 2007; pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Moloi, T.J. The use of Morabara game to concretise the teaching of the mathematical content. Mediterr. J. Soc. Sci. 2014, 5, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nkopodi, N.; Mosimege, M. Incorporating the indigenous game of morabaraba in the learning of mathematics. S. Afr. J. Educ. 2009, 29, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloi, T.J.; Mosia, M.S.; Matabane, M.E.; Sibaya, K.T. The use of indigenous games to enhance the learning of word problems in grade 4 mathematics: A case of Kgati. Int. J. Learn. Teach. Educ. Res. 2021, 20, 240–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.M.; Lin, C.L.; Kao, H.L. Exploring teaching performance and students’ learning effects by two elementary indigenous teachers implementing culture-based mathematics instruction. Creat. Educ. 2013, 4, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tai, C.H.; Leou, S.; Hung, J.F. The effectiveness of teaching indigenous students mathematics using example-based cognitive methods. J. Interdiscip. Math. 2015, 18, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigney, L.; Garrett, R.; Curry, M.; MacGill, B. Culturally responsive pedagogy and mathematics through creative and body-based learning: Urban Aboriginal schooling. Educ. Urban Soc. 2020, 52, 1159–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, E.; DeVries, E. Young Australian Indigenous students’ engagement with numeracy: Actions that assist to bridge the gap. Aust. J. Educ. 2009, 53, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, R.; Mushin, I. Language for learning in Indigenous classrooms: Foundations for literacy and numeracy. In Pedagogies to Enhance Learning for Indigenous Students; Jorgensen, R., Sullivan, P., Grootenboer, P., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2013; pp. 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, E.; Miller, J. Young Australian Indigenous students’ effective engagement in mathematics: The role of language, patterns, and structure. Math. Educ. Res. J. 2013, 25, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Warren, E.; Armour, D. Examining changes in young Aboriginal and Torres Strait Island students and their beginning primary school teachers’ engagement in the teaching and learning of mathematics. ZDM Math. Educ. 2020, 52, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, R.; Lowrie, T. Both ways strong: Using digital games to engage Aboriginal learners. Int. J. Incl. Educ. 2011, 17, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegg, J.; Graham, L. A three-level intervention pedagogy to enhance the academic achievement of Indigenous students: Evidence from QuickSmart. In Pedagogies to Enhance Learning for Indigenous Students; Springer: Singapore, 2013; pp. 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, B. Bloom’s taxonomy. Teach. Educ. Spec. Educ. 1956, 10, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, E.J. The Classification of Educational Objectives in the Psychomotor Domain, 3rd ed.; Gryphon House: Washington, DC, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Krathwohl, D.R.; Bloom, B.S.; Masia, B.B. (Eds.) Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, the Classification of Educational Goals. Handbook II: Affective Domain; David McKay Co., Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, P.; van Riel, N. Building confidence and fostering engagement in Aboriginal learners. In Pedagogies to Enhance Learning for Indigenous Students; Jorgensen, R., Sullivan, P., Grootenboer, P., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2013; pp. 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demitra, D.; Sarjoko, S. Effects of Handep cooperative learning based on indigenous knowledge on mathematical problem solving skill. Int. J. Instr. 2018, 11, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisker, E.E.; Lipka, J.; Adams, B.L.; Rickard, A.; Andrew-Ihrke, D.; Yanez, E.E.; Millard, A. The potential of a culturally based supplemental mathematics curriculum to improve the mathematics performance of Alaska Native and other students. J. Res. Math. Educ. 2012, 43, 75–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewah, C.; Van Wyk, M.M. The place of indigenous cultural games by educators in the teaching and learning of mathematics. J. Hum. Ecol. 2014, 48, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, K. Changing the teaching of mathematics for improved Indigenous education in a rural Australian city. J. Math. Teach. Educ. 2015, 18, 53–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessens, A.; Engel, M. How important is where you start? Early mathematics knowledge and later school success. Teach. Coll. Rec. 2013, 115, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, F.H. Pendidikan masyarakat orang Asli. In Orang Asli: Isu, Transformasi dan Cabaran; Redzuan, M., Gill, S.S., Eds.; Penerbit Universiti Putra Malaysia: Serdang, Malaysia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Orang Asli Development (JAKOA). Bilangan dan Peratus Keciciran Pelajar Orang Asli, 1994–2008; Jabatan Hal Ehwal Orang Asli: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2008.
- Ministry of Education. Laporan Awal Pelan Pembangunan Pendidikan Malaysia 2013–2025; Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2012.
- Nordin, R.; Yahya, M.S.; Danjuma, I. Orang Asli student icons: An innovative teaching method for orang Asli students. Pertanika J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2018, 26, 219–238. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaratnam, D.P.; Jaafar, A.H.; Salleh, N.; Othman, R.; Idris, S.H. Transformasi modal insan melalui peningkatan pendidikan: Kajian kes komuniti Orang Asli di Cameron Highlands, Pahang. Pros. Persidang. Kebangs. Ekon. Malaysia ke 7 2012, 7, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, Z.A. Peranan Jabatan Hal Ehwal Orang Asli (JHEOA) dalam pembangunan masyarakat Orang Asli. In Orang Asli: Isu, Transformasi dan Cabaran; Redzuan, M., Gill, S.S., Eds.; Universiti Putra Malaysia: Serdang, Malaysia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Redzuan, M. Pembangunan dan kemunduran komuniti peribumi: Kes kemiskinan dalam komuniti orang Asli. In Kemiskinan Di Malaysia: Isu Fundamental & Paparan Realiti; Paim, L., Haron, S.A., Eds.; Penerbit Universiti Putra Malaysia: Serdang, Malaysia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sterenberg, G. Considering Indigenous knowledges and mathematics curriculum. Can. J. Sci. Math. Technol. Educ. 2013, 13, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.F.A.; Taha, N.M. Teaching and learning approaches that intriguing orang Asli students’ interests in school. Asian J. Soc. Sci. Res. 2018, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, E.; Young, J.; De Vries, E. Australian Indigenous students: The role of oral language and representations in the negotiation of mathematical understanding. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual Conference of the Mathematics Education Research Group of Australasia; Watson, J., Beswick, K., Eds.; MERGA Inc.: Adelaide, Australia, 2007; pp. 775–784. [Google Scholar]
- Matang, R.A.S.; Owens, K. The role of indigenous traditional counting systems in children’s development of numerical cognition: Results from a study in Papua New Guinea. Math. Educ. Res. J. 2014, 26, 531–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma’alip, S.; Teo, K.S. Language use of orang Asli Che Wong in Kuala Gandah. Geogr. Malays. J. Soc. Space 2016, 12, 62–78. [Google Scholar]
- Simons, G.F.; Fennig, C.D. Ethnologue: Languages of the World, 21st ed.; SIL International: Dallas, TX, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard, D.M.; Simons, G.F.; Fennig, C.D. (Eds.) Ethnologue: Languages of Asia; SIL International: Dallas, TX, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bahagian Teknologi Pendidikan Negeri Pahang Majlis pelancaran pelan transformasi pendidikan Orang Asli kebangsaan. Available online: http://buletinkpm.blogspot.com/2012/07/majlis-pelancaran-pelan-transformasi.html (accessed on 22 July 2020).
- Sabzalian, L.; Tuck, E.; Yang, K.W. Indigenous Children’s Survivance in Public Schools; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, N.; Moll, L.C.; Amanti, C. (Eds.) Funds of Knowledge: Theorizing Practices in Households, Communities, and Classrooms; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shaharuddin, A.M. Quality teachers for quality education. In Proceedings of the 17th Conference of Commonwealth, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 15–18 June 2009; Ministers of Education: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2009. [Google Scholar]






| Coding Category | Sub-Category | Example of the Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Study characteristics | Publication outlet | South African Journal of Education, Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, Australian Journal of Education, Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences |
| Publication year | 2009, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2021 | |
| Country | Australia, South Africa, Indonesia, Taiwan | |
| Intervention characteristics | Research design | Case study, participatory action research, quasi-experiment |
| Research method | Quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods | |
| Intervention implementer (s) | Kindergarten teachers, mathematics teachers, indigenous teachers | |
| Length of the intervention | 1 year, 3 years | |
| Number of students | Grade two, 125 students (students were aged 4 years, 11 months on average), a team of grade 10 learners | |
| Learning topics | Algebra, Numbers, Geometry | |
| Features of the intervention | Patterns and The numeracy intervention Early Algebra, Pre-school (PEAP) mathematical language embedded within learning activities, professional development (PD) program, morabaraba as an indigenous game, three projects; Stronger Smarter Learning Community, Make It Count, 8-ways Aboriginal approach to teaching | |
| Outcomes of the intervention | Overall outcomes | Positive, negative, null |
| Outcomes reported | Improve young children’s ability to solve mathematics and reasoning mathematically, as well as their grasp of and participation in Western mathematics and the mathematical language. In addition, perform high cognitive skills of synthesis and analysing skills, understanding of mathematical concepts, self-esteem in mathematics, and ownership of their mathematics learning. |
| Domain | Explanations |
|---|---|
| I—Cognitive-related outcomes | Involves learning and intellectual skill improvement. This involves the ability to recognise or recall particular facts, procedural patterns, and ideas that support intellectual capacities growth and competencies [39]. |
| II—Psychomotor-related outcomes | Includes using motor skills, moving around, and being coordinated [40]. |
| III—Affective-related outcomes | Includes how we handle emotional issues, including our feelings, values, appreciation, zeal, attitudes, and motivations [41]. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdullah, A.H. A Systematic Review of What Malaysia Can Learn to Improve Orang Asli Students’ Mathematics Learning from Other Countries. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13201. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013201
Abdullah AH. A Systematic Review of What Malaysia Can Learn to Improve Orang Asli Students’ Mathematics Learning from Other Countries. Sustainability. 2022; 14(20):13201. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013201
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdullah, Abdul Halim. 2022. "A Systematic Review of What Malaysia Can Learn to Improve Orang Asli Students’ Mathematics Learning from Other Countries" Sustainability 14, no. 20: 13201. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013201
APA StyleAbdullah, A. H. (2022). A Systematic Review of What Malaysia Can Learn to Improve Orang Asli Students’ Mathematics Learning from Other Countries. Sustainability, 14(20), 13201. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013201





