Abstract
The emerging blockchain technology is believed to be a disruptive innovation in the fields of both supply chain management and financial management. Yet, little is known on the interaction of the two domains. In this paper, we conducted a thematic literature review in the novel field of blockchain and supply chain finance (SCF), which is based on 52 papers published from 2017 to 2021 in academic journals, proceedings and books. Based on thematic analysis, the current status of this field is concluded and presented in this research, including the challenges in traditional SCF, factors influencing blockchain adoption in SCF, blockchain-based SCF solutions, and the blockchain adoption mechanism and system design in SCF. Furthermore, a conceptual framework of blockchain adoption in SCF is developed, which combines the emerged themes. Finally, three future research directions are proposed for further research, including cost optimization of blockchain adoption in SCF, risk management of blockchain operations in SCF, and blockchain and sustainable SCF. This research presents a timely and useful summary on existing research and points out the future research directions on blockchain and SCF.
1. Introduction
The past 20 years have witnessed an increasing development in the field of supply chain finance (SCF), which can be seen in the growth of academic research and in the expansion of the SCF market, especially since the financial crisis of 2008 [1,2,3,4]. SCF aims at integrating financial flows with physical flows and information flows [5]. By implementing SCF solutions, working capitals of supply chain enterprises can be optimized, and the problem of liquidity shortage can be improved [3,6]. Taking China as an example, companies in need of financial services from SCF businesses are mainly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), and the market demand of SCF for accounts receivable financing is increasing rapidly [7]. However, the actual loaning of funds is only about one trillion CNY, because financial institutions are unwilling to provide financial services for SMEs for risk management concerns [8]. Although the potential market of SCF is huge, how to leverage the full potential of SCF remains a challenge both in academia and industry.
In this digital age, the whole world has been through the fast development of information technology. Blockchain, a disruptive innovation technology proposed by Nakamoto [9], was first used for Bitcoin transaction as a distributed ledger. Its peer-to-peer network structure, combined with encryption algorithms and consensus mechanisms, allows for several outstanding characteristics, including decentralization, traceability, immutability, transparency, and smart contracts [10,11,12], which have led to widespread interest in many areas. As argued by Babich and Hilary [13], blockchain enables adding credits to enterprises and building trust among stakeholders, which facilitates leveraging SCF potential and creating shared value [14]. Some researchers have conducted an initial exploration in this newly emerging field of blockchain and SCF. Hofmann et al. [15] proposed novel conceptual frameworks to extend SCF practices into a new domain with the support of blockchain technology. The similar contributions to develop conceptual models can also be found in other papers [16,17,18,19]. In addition to conceptual frameworks, analytical approaches and case studies have also been employed to explore this field [20,21,22,23,24]. Although this novel field has been explored to some extent, the relevant research is still limited and scattered. On the one hand, this field is still lacking awareness and attention in academics; on the other hand, the boundaries of this research field have not been outlined for shedding light on future directions [25]. Therefore, we propose two research questions as follows:
- (1)
- What is the existing research on blockchain and SCF?
- (2)
- What are the future research directions for the novel field of blockchain and SCF?
To fill the research gap and better understand the impact of blockchain technology on the development of SCF, we conducted a thematic analysis to investigate this under-researched area [26,27,28]. Papers were selected using keyword-based search, and 52 papers were identified as datasets on blockchain and SCF. Furthermore, four emerging themes from the current research of this novel field are uncovered, which represent a patterned response within the dataset. Subtle features relevant to these themes are further developed and analyzed to depict the selected papers in detail [29]. Finally, three topics are determined for future directions, including cost optimization, risk management, and sustainable SCF. To the best of our knowledge, this paper is among the first in the research to provide a literature review using thematic analysis and to determine areas for future research on blockchain and SCF.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. The methodology employed to carry out the literature review is presented in Section 2, and descriptive results are given in Section 3. Based on collected papers, we provide the findings from thematic analysis in Section 4. This is followed by future directions for this novel field of blockchain and SCF in Section 5. The final section presents the conclusion of this paper.
2. Methodology
In order to outline the current research and provide some meaningful insights for future research, we first located the relevant articles and then conducted a thematic literature review for a deeper analysis [29]. The methodology of this work is organized as follows.
2.1. Determining Search Terms and Databases
The existing literatures about SCF mainly focus on both supply chain side and financial side [4]. In order to fully cover the current research about SCF and blockchain, we used the keywords and strings, listed in Figure 1, according to Gelsomino et al. [3] and Alkhudary et al. [30], which are related to SCF and blockchain, respectively. Aiming to locate as much relevant literature as possible, the keywords and strings are searched in three databases, including Web of Science (WoS), Scopus, and EBSCO, which have a comprehensive coverage on academic research and have been widely adopted in literature review studies [31].
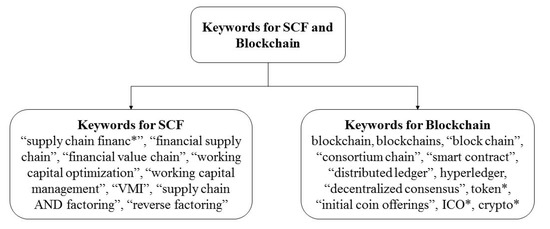
Figure 1.
Keywords for SCF and blockchain. (* at the end of a word will find all terms that use that stem). (Source: Gelsomino et al. [3], Alkhudary et al. [30]).
2.2. Selection and Assessment Procedure
In the data selection and assessment procedure, we followed two steps: data collection, abstract and content assessment. To include the relevant research sufficiently and exclude unimportant results, we selected the inclusion and exclusion criteria listed in Table 1. All the papers that are related to both blockchain and SCF were picked out, with December 2021 as the searching cut off time. We found 174 papers in WoS, 131 papers in Scopus, and 63 papers in EBSCO. After removing all duplicate data, 192 papers remained. Considering the exclusion criteria, only articles published in English were kept for the accuracy of understanding. Papers were abandoned if they are not closely related to blockchain and SCF, or only emphasize one of the two aspects. This step was conducted by scanning the abstracts first, and if 10 items in a row deviated from topics, the paper was excluded [29]. Then, the whole texts were read to further update the data list. Following this method, our dataset includes major journals on operations management and information science. In addition to academic journals, conferences and books are also included in this research, owing to the scarcity of this newly emerging research field [31]. In total, 52 papers were finally retained for the thematic literature review. The full list of the reviewed papers can be found in Supplementary Materials (Table S1).

Table 1.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria.
2.3. Data Analysis
All the selected publications were analyzed using a combination of deductive and inductive data analysis methods. Initially, each paper was analyzed deductively from descriptive method, focusing on the categorization of papers by year, journal, author, research methods, and theory. Furthermore, thematic analysis was applied to the analysis of each paper inductively. Thematic analysis is an effective method to investigate the selected data comprehensively while requiring researchers to be well organized [26]. Thus, it was employed to organize the literature and produce themes that emerged in the dataset, which can be useful for constructing awareness of this novel field in academics [32]. Following the guidance of Hastig and Sodhi [29], we carried out thematic analysis in six steps: first, familiarizing ourselves with the entire dataset; second, generating initial codes; third, searching for themes; fourth, reviewing the identified themes; fifth, defining and amending themes; and sixth, producing the report. Specifically, steps 2, 3, and 4 were conducted iteratively until all the themes could finally be used to categorize and outline the papers precisely.
3. Descriptive Analysis
The 52 papers located through the thematic literature review were analyzed to identify the type of publication, publication year, research methodology, and authors. The aim of this descriptive analysis is to understand the trends and distribution of this novel research field. In terms of publication type, this research found that 50% of the papers collected are from academic journals. Conference papers accounted for 46%, and books 4%. This result suggests that the research on blockchain and SCF has generated academic interest, but it is immature and emerging at this stage.
Figure 2 presents the number of published papers by year. Although the result is up to December 2021, we can still clearly recognize a growing trend in the research field.

Figure 2.
Papers published by year.
The distribution of methodologies employed in these papers is illustrated in Table 2. As this emerging field is still in the early stage of research, conceptual framework construction is the most frequent used methodology among these papers. Mathematical analysis, modeling, and simulation are in the second place. The sum of these methodology categories is more than 52 because some of papers adopt mixed research methods in their research.

Table 2.
Methodology employed in the research.
To figure out the leading research in this field, we listed the top journals and authors in Table 3. The table suggests that 10 papers are published in the above ABS 2 rated journals, which indicate the hot trend of the research topic. As for the theories employed in these papers, we only found Nash bargaining theory [19,21] and mean–risk theory [21,33], which shows that existing theories are focusing on decision making, such as revenue sharing and risk taking. The thin theoretical foundation demonstrates that this novel research field is still immature and should be enhanced with theory support.

Table 3.
Top journals and authors. (4 * is the highest rank according to ABS ranking list).
4. Thematic Results: Understanding the Key Themes
In order to categorize and reorganize the literature, thematic analysis of the selected literature was conducted [29]. The thematic analysis allowed us to identify themes and develop subthemes. These themes and subthemes are used as coding categories, with proof quotes and relevant references to support the codes. All of selected literature was systematically reviewed by the authors, and reasonable deduction to the themes were made by analyzing the contents of these papers.
After fully reviewing the whole contents of these papers, we broke data down into four themes, including challenges in the traditional SCF, factors influencing blockchain adoption in SCF, blockchain-based SCF solutions, and blockchain adoption mechanism and system design in SCF, which outline the context of blockchain technology for improving SCF practices. Themes and subthemes are depicted in Figure 3. The following is the detailed discussion about these themes.
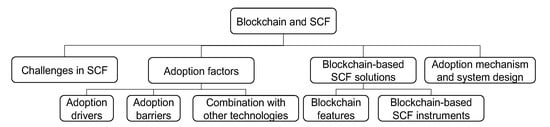
Figure 3.
Themes and subthemes of blockchain and SCF.
4.1. Challenges in the Traditional SCF
The first theme that emerges from the thematic analysis is about challenges in the traditional SCF. Although SCF has experienced its development over 20 years, there are still many challenges in the traditional SCF that impede its implementation in supply chains (listed in Supplementary Materials Table S2). The huge potential value of SCF cannot be fully discovered unless these challenges are identified and dealt with properly.
Stakeholders in SCF have independent objectives of profit maximization regarding different organizational structures, costs, and risks, which increases the difficulty of coordination and gives rise to the poor performance of the entire supply chain. Moreover, SCF involves several partners and complicated business processes, but the previous technologies are not capable of providing transparency to eliminate information asymmetry problems, leading to failure in the effective integration of information flow, physical flow, and financial flow [10,38].
Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) have been a main driver to the economic development. However, SMEs are always faced with the problem of liquidity shortage and have little access to financial services although they are in need of financial support [15], owing to their limited size and working capital. On the one hand, financial institutions hold a conservative financing attitude toward SMEs because of difficulties in risk control [39]. On the other hand, SCF instruments can only radiate throughout a small number of SMEs. For instance, in reverse factoring, first-tier SME suppliers may obtain loans from banks and other types of lenders through the endorsement of focal enterprises. However, lower-tier SME suppliers normally cannot utilize focal enterprises’ credits to apply for loans because they do not have direct contracts with focal enterprises.
Due to a large number of manual inspections and paper-based transactions, Liu et al. [40] presented a case of the tobacco industry, which indicates that it difficult to avoid credit problems caused by human intervention. Manual processes and paper-based documents in SCF activities remain unobservable to the counterparty side, and therefore, non-transparency raises the probability of fraudulent risks, including invoice fraud and data tampering. A well-known financial fraud is double financing, where the enterprise sells the same invoice to two or more financial institutions [41]. These fraudulent behaviors damage the mutual trust among stakeholders in SCF, which impedes integrated management and warehouse supervision [42].
In conventional transactions, the indirect interaction between two principal entities leads to inefficient operation in SCF businesses and represents a single point of failure in terms of centralized systems [43]. In addition, paper-based transactions and a lack of automation increase the total transaction costs for supply chain partners.
In a nutshell, the challenges mentioned above impede the development of SCF; therefore, business processes, roles of different stakeholders, and supervision approach may need to be adjusted to fully activate the potential of SCF.
4.2. Factors Influencing Blockchain Adoption in SCF
The factors influencing blockchain adoption in SCF come from three perspectives. On the one hand, benefits brought by blockchain drive supply chain partners to adopt blockchain technology in SCF practices. On the other hand, there are also some barriers that impede blockchain adoption, owing to the immaturity of this newly emerged technology. Moreover, to fully leverage SCF potential, the adoption of blockchain technology in SCF needs to be combined with other technologies. Therefore, this theme was divided into three subthemes, drivers, barriers, and combination with other technologies to adopt blockchain in SCF.
4.2.1. Drivers of Blockchain Adoption
The drivers of the adoption of blockchain technology originates from several attractive benefits. This theme presents the drivers of blockchain adoption in SCF (with details in Supplementary Materials Table S3), including cost reduction, business efficiency, trust building, and easy access to financing.
Blockchain-based SCF solutions contribute to digitizing business processes and reducing manual intervention, which enables the elimination of paper-based documents. The cumbersome onboarding processes, such as Know-your-customer (KYC) checks, which involve the duplication of work among financial institutions, can be eliminated because the distributed network structure can break information silos [15,16]. The blockchain platform also enables operation cost reduction based on the analysis of the operational data [20]. These advantages can be leveraged to reduce financing cost in SCF.
Supported by blockchain technology, related entities can accumulate credit data and construct a multi-trusted supply chain financial network. In such a network, it is possible for financial institutions to have access to all the resource flows in SCF businesses, which facilitates the risk control on financing SMEs [15,39]. In addition, lower-tier suppliers, which have indirect connection with focal enterprises, can also be endorsed by focal enterprises because the digital invoices issued on chain can be split and transferred to lower-tier suppliers [19]. Therefore, SMEs, even at the lower tiers, will have easy access to financial services in blockchain-based solutions.
Every material and product may possess a digital tag to represent the relevant information, including location, status, and type [11]. Information flows can be easily acquired and checked in real time efficiently, and each entity is supervised by all the other stakeholders. Owing to asymmetric encryption algorithms and hash functions, blockchain ensures that information recorded on the chain is immutable. This feature can prevent some fraudulent behaviors, which facilitates trust building among stakeholders and enables leveraging the highest potential of SCF [44]. Among the various functions of blockchain technology, the convenient information sharing, automatic transaction execution, and simplification of manual processes also improves business efficiency in SCF.
4.2.2. Barriers of Blockchain Adoption
Although blockchain technology has many characteristics that are highly suitable for improving the performance of SCF, there are indeed some barriers which impede organizations from adopting this disruptive technology. The detailed major barriers of blockchain adoption are presented in Supplementary Materials Table S4.
Privacy disclosure is one of the core barriers in the adoption of blockchain technology, as information sharing among the blockchain network gives rise to worries about the disclosure of trade secrets [45]. In SCF, manufacturers’ financing quotas, order quantities, prices, etc., are all business secrets [42]. Enterprises are worried that transparency without effective data privacy protection mechanism may harm their business advantages [46,47].
Another core barrier that arouses concerns from individuals and organizations is the fraudulent source data. Although blockchain technology can guarantee that data recorded on the blockchain cannot be tampered with, how to ensure the authenticity and validity of source data is still a difficult problem. The 51% attack, data malleability issue, and cryptography problems result in organizations’ concerns about the cybersecurity of using blockchain [20,46]. Lack of knowledge and hesitation for new technology impede collaboration and coordination from intra-organization and inter-organization [48]. Other barriers exist in the high cost of deploying blockchain technology, the lack of sophisticated policy system, legal and regulation institutions [15,48]. All of these barriers need to be coped with properly for further implementation of blockchain technology.
4.2.3. Combination with Other Technologies
Leveraging the full potential of implementing blockchain in SCF cannot be realized without the combination with other technologies. These technologies can be divided into two categories, information technology and business system, which play an important role in intra- and inter-company information sharing [49,50]. Supplementary Materials Table S5 illustrates the details of these technologies.
Blockchain, in essence, is a distributed database, the characteristics of which can only be used for data stored on the blockchain [42]. Thus, the acquisition of data, especially the information flow, physical flow, and financial flow, needs the assistance of other technologies. Combined with IoT, global position system (GPS), and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, the blockchain-based platform can automatically monitor the position, temperature, quality, and quantity of products and materials [45,47]. In addition, AI can be used to analyze and record data on chain in real time. In this way, the blockchain-based platform improves data reliability while reducing costs [15].
Moreover, the existing information systems in SCF play an important role in supply chain activities and financing services, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) system and electronic data interchange (EDI), which provide the foundation for blockchain adoption in SCF. The value creation from exploiting blockchain in SCF comes from integrating it with existing systems rather than replacing or disrupting them entirely, which also helps to minimize the adoption resistance [51,52,53]. Therefore, the interfaces between blockchain and the current systems may need further study in the future [15,54].
4.3. Blockchain-Based SCF Solutions
To improve SCF practices, the challenges inherent in the traditional SCF solutions need to be dealt with properly, which can be achieved by blockchain technology owing to its special features. Furthermore, with the support of blockchain technology, the stakeholders and the related interactions of improved SCF practices have changed compared to the traditional solutions. Therefore, this theme was divided into two subthemes, blockchain features and blockchain-based SCF instruments.
4.3.1. Blockchain Features for Dealing with Challenges
This theme focuses on blockchain features and explains why blockchain technology is suitable for dealing with challenges in traditional SCF. Blockchain is featured with decentralization, transparency, traceability, immutability, and smart contracts, which can be applied to address the traditional SCF challenges, details are listed in Table 4.

Table 4.
Blockchain features for dealing with challenges.
Owing to the traceability and immutability characteristics of blockchain technology, all of the data recorded on the blockchain are immutable and able to be traced, including physical flow, information flow, and financial flow. Moreover, paper-based documents, such as invoices and warehouse receipts, can also be digitized and recorded on the blockchain. Thus, these features can deal with fraudulent behaviors in SCF, including invoice fraud, data tampering, and double financing.
The decentralization feature of blockchain originates from a peer-to-peer distributed network, and all of involved entities with permission will be able to share and monitor the information related to invoice, auction, shipping, and payment in a transparent manner [41]. Transparency and decentralization can be leveraged to deal with the lack of trust among stakeholders, and trusted intermediaries can be eliminated under this structure.
Smart contracts can be used to identify, match, and execute transactions automatically, which is suitable for simplifying time-consuming and high-cost manual processes in the complicated SCF businesses.
All of these features in blockchain can be utilized in blockchain-based SCF solutions to facilitate the integration of resource flows and the coordination of stakeholders in SCF businesses, further mitigating the challenges in the traditional SCF.
4.3.2. Blockchain-Based SCF Instruments
SCF partners utilize SCF instruments to provide financial services for capital shortage parties in supply chain, by resource coordination, such as exchanging purchasing orders, invoices, letter of credit, and relevant information [58]. Many researchers refine the business model of SCF instruments by transforming partners and interactions among them, which enables leveraging the highest potential of SCF through blockchain technology. Table 5 illustrates the list of blockchain-based SCF instruments presented in the literature.

Table 5.
Blockchain-based SCF instruments.
The most frequently studied SCF instruments under the environment of blockchain are factoring and reverse factoring. On the one hand, financing businesses can be identified and executed automatically without time-consuming and costly manual processes. On the other hand, digital invoices issued on chain can be split and transferred to lower-tier suppliers; meanwhile, financial institutions can acquire information flow, physical flow, financial flow, and business flow easily, which facilitates risk management on lower-tier suppliers [15,19].
In inventory financing, the management of product warehousing, stocking, and delivering, provided by logistics service providers (LSPs) not only demands a large amount of human and material resources, but also suffers from moral hazard and fraud risk [36]. To overcome these problems, LSPs can cooperate with technology service providers to combine blockchain platform with other technologies, such as internet of things (IoT), video streaming media, and machine vision, which enables all the trade information to be acquired and recorded on chain in real time [15,20]. With the support of blockchain technology, the inventory financing platform can store related data safely and immutably.
Therefore, in the blockchain-based SCF solutions, banks have access to all the needed information acquired by LSPs and credit history of SMEs recorded on chain. Thus, banks and other financial service providers are more willing to finance SMEs [19,21,34]. Additionally, the automatic supervision on physical flows can be achieved by a blockchain-based SCF platform, which is more reliable and cost effective.
Some other instruments, which have been refined by blockchain, are also involved in the literature, including letter of credit, purchasing order financing, warehouse receipt pledge financing, pre-shipment financing, and vendor managed inventory (VMI). However, there are still many SCF instruments that have not been explored based on blockchain, including fixed asset-based financing, leasing, raw material financing, dynamic discounting, invoice discounting, etc. [1,2].
4.4. Blockchain Adoption Mechanism and System Design in SCF
This theme focuses on the mechanisms and systems proposed in the context of blockchain and SCF, which are listed in Table 6. As an innovation, blockchain technology needs further development in the mechanisms and relevant systems, which enables it to be more suitable for applications in practice. To be specific, these mechanisms and systems benefit SCF from three aspects: cost reduction, efficiency improvement and trust building, and risk management.

Table 6.
Mechanism and system design.
In order to verify the effectiveness of blockchain technology in improving SCF performances, Chod et al. [10] designed an novel software system, called b_verify, to leverage the infrastructure advantages of public blockchain. The blockchain verification system can provide the integrated data flows at low cost, which enables it more efficiently than traditional monitoring mechanisms. In addition, Li et al. [45] designed a multi-agent system to build a trusted business environment with the consideration of real-life constrains from multiple parties. The proposed conceptual framework is able to organize key system components and microservices, which could simplify and facilitate the development of similar systems to SCF and cross-border logistics settlement enabled by blockchain. A hybrid finite state machine-based smart contract (HFSM-SC) was designed and incorporated into coordinate diversified resources, business processes, and business decisions, which allowed for autonomous life-cycle management in logistics finance. Moreover, Chen and Wang [62] focused on the application of fractional calculus system in the blockchain-based supply chain financial system. By establishing a three-dimensional SCF fractional calculus game model, this research explored the characteristics and chaos behaviors and verified the feasibility of the system.
To make better use of blockchain benefits, researchers have designed systems that allow stakeholders to share information more effectively by building trust among them. The traditional invoice financing suffers from risks of willful default and fraudulent behavior by buyers. Additionally, risk insurance is economically unfeasible, owing to the lack of significant countermeasures aiming at reducing the fraud opportunity. The proposed blockchain-based InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) by Guerar et al. [41] allows for mitigating these risks by adding transporter entity and reputation profile. The former provides shipping information while the latter presents invoice status, paid or unpaid by buyers on the due date without disclosing confidential data. This mechanism enables trust building among stakeholders by allowing investors selecting trustworthy counterparts. Similarly, Guggenberger et al. [57] developed a blockchain-based information hub to support VMI. The prototype is based on Hyperledger Fabric, providing the integrated use of private data, encrypted data transmission, while fulfilling the stated IT security requirements. The system benefits VMI from information sharing and mitigation of the bullwhip effect.
Considering the risk management in SCF, Chakraborty et al. [63] developed a credit analysis mechanism, which integrates multiple stakeholders in the blockchain platform, including banks, insurance companies, card agencies, retailers, and manufacturers. Artificial intelligence (AI) was deployed into the framework to facilitate credit scoring of individuals by analyzing financial details of customer and transaction statements, which improved the efficiency and reliability of predicting the eligibility of individuals [63]. A dynamic adaption and automated evaluation about credit ratings would take place if buyers default intently or suppliers do not deliver goods in time. In addition, in order to detect the fraudulent behaviors in SCF businesses, Zhou et al. [64] proposed a financial fraud detection system, which combined the big data mining with a convolutional neural network. The proposed system enhances financial fraud detection with high precision and reduces losses from fraudulent behaviors in SCF. Additionally, the information disclosure problem resulted from blockchain itself needs to be overcome for the involvement of more enterprises. Therefore, privacy protection mechanisms are developed to protect trade secrets without affecting information sharing [42,46].
The analysis of this theme also reflects that the development of blockchain and SCF needs the collaboration of multiple disciplines, such as business/management, accounting and finance, computer science, and big data analysis. However, there is a shortage on such talents and these talents need cross discipline training, which requires adjustments in current higher education.
5. The Conceptual Framework of Blockchain Adoption in SCF
The analysis about the literature in the field of blockchain and SCF indicates that the current research in this field can be divided into four themes and seven sub-themes. These themes reflect researchers’ main focuses on this field, including (1) What benefits can blockchain bring to SCF? (2) What are the barriers when adopting blockchain? (3) Which solutions in the traditional SCF can be benefited from blockchain technology? (4) Why can blockchain technology disrupt the traditional SCF solutions? (5) How can blockchain technology benefit traditional SCF solutions? (6) Who are willing to participate in blockchain-based SCF solutions? These research focuses can also reflect a topic that both academics and the industry are concerned about, the adoption of blockchain in SCF.
To provide a holistic view of blockchain adoption in SCF, we developed a conceptual framework, as shown in Figure 4. The conceptual framework consists of five dimensions: blockchain features, adoption drivers of blockchain in SCF, adoption barriers of blockchain in SCF, application areas in SCF, and major stakeholders involved in blockchain-based SCF solutions. The framework refers to the framework of blockchain applications in the maritime industry developed by Pu and Lam [66] and Moon and Ngai [67], but there are several differences. The traditional SCF is faced with many challenges which hinders its development, such as deployment cost operation cost [68], and sustainability issues [69]. The special features of blockchain enables challenges in SCF to be overcome, which drives the adoption of blockchain in SCF. However, adoption drivers are also accompanied by adoption barriers. Therefore, we employ adoption drivers and adoption barriers to substitute commercial benefits and allocation challenges from the original framework, respectively. In order to explain blockchain applications in SCF more clearly, we incorporate three aspects into application areas, adoption mechanisms and systems, blockchain-based instruments, and combination with other technologies, which are three sub-themes that emerged from the previous analysis. Specifically, mechanisms and systems are designed to overcome adoption barriers of blockchain. Other technologies not only help SCF to overcome adoption barriers of blockchain, but also are beneficial to improve blockchain-based SCF instruments. With the five dimensions, the conceptual framework answers the fundamental questions of what, why, how, and who in terms of blockchain adoption in SCF. Based on this framework, we further propose three future directions from ample future research opportunities in the next section.

Figure 4.
The conceptual framework of blockchain adoption in SCF.
6. Future Directions
Three main gaps are uncovered from this novel research field. Thus, recommendations for future research are provided based on these gaps.
6.1. Cost Optimization of Blockchain Adoption in SCF
The characteristics of blockchain are suitable for coping with the pain points in the traditional SCF, and a list of benefits have been identified from the current literature. However, the topic of cost optimization about deploying blockchain in SCF mainly exists in the analysis of the conceptual framework, explaining why blockchain benefits the cost reduction in SCF [16,20,38,40,59]. A deeper exploration of this topic for theoretical and practical insights is limited in these papers. Therefore, much more research could be conducted to further investigate the topic of cost optimization related to blockchain-enabled SCF, and the research gap is illustrated using information processing theory (IPT) [4,70].
Based on the IPT, organizations are regarded as information processing systems, which possess capabilities of collecting, processing, and acting on information [48], to deal with uncertainties from the environment [71]. The information processing capability should be fitted with information processing requirements; otherwise, any direction of mismatch will lead to inefficiencies [72]. For instance, if information processing requirements cannot be handled by the capacity sufficiently, it will be difficult to integrate information flows, physical flows, and financial flows and to coordinate organizations in SCF [72]. In contrast, too much information processing capacity gives rise to redundancy and unnecessary costs [71].
In SCF, task characteristics, task environment, and task interdependence related uncertainties increase stakeholders’ information processing requirements [4]. Accordingly, the information processing capacity of stakeholders in SCF needs to be improved. As a disruptive innovation technology derived by the combination of Internet and computer science, blockchain technology supports a peer-to-peer network which enables a closer connection among involved entities in SCF. In addition, blockchain-based SCF solutions cannot be achieved without combination with other technologies, for the reason that blockchain can only be used for recording and storing data safely rather than generating data [73]. For example, in blockchain-based inventory financing, all the business processes occur among involved parties, including planning, purchasing, shipment, and payment, which need to be recorded on the blockchain platform [74]. In terms of warehouse supervision, IoT technologies, GPS, video streaming media, and other technologies need to be deployed to obtain the real-time data of mortgages. Owing to the more highly connected organizational structure and a wider use of information technologies in blockchain-based inventory financing, compared to the traditional inventory financing, the information processing capacity of stakeholders increases accordingly [4]. However, the transformation in SCF based on blockchain technology leads to several cost-related problems, which deserve to be explored.
First, we have little knowledge about whether the improved information processing capability fits the information processing requirements of stakeholders in blockchain-enabled SCF businesses. Excess information processing capability needs to be optimized because it leads to redundancy and unnecessary costs, which is a waste of resources. Second, although blockchain-based SCF solutions enable reduction in human costs, transaction costs, and supervision costs [15,16], it needs additional deployment and operation costs compared to traditional SCF solutions [48]. The performance advancement in SCF and additional costs brought by blockchain should be weighed against each other by decision makers to achieve an optimal solution. Choi [21,33] performed an initial attempt to analyze the cost of using blockchain technology in SCF, and the research assumed that using blockchain only needs a unit operational cost in every transaction. Further research can be conducted with a more specific analysis, considering deployment costs, operational costs, and even service fees from technology service providers. Third, not only the business process of SCF is transformed by blockchain technology, but also shareholders and stakeholders are different in blockchain-based SCF solutions. The inclusion of additional partners in the blockchain network, such as insurance companies, needs resource orchestration from both the intra-organization and inter-organization [75]. The balance between costs and profits of resource orchestration requires further exploration to support decision making by organizations. Fourth, the transparency feature of blockchain mitigates the cost of information sharing in the supply chain [16], while giving rise to the increase in the difficulty of maintaining secure supply chain information networks [48]. Xu et al. [53] proved that blockchain features can preserve security and increase transparency at the same time based on the findings from text mining of Twitter data and multiple cases analysis of blockchain applications. The proposition needs further demonstration by analytical models, and further explorations could be conducted on how these benefits impact supply chain pricing, ordering, and financing strategies. Last, blockchain-based SCF solutions with different stakeholders may lead to novel pricing strategies in contract management, and therefore, the design of an automated pricing mechanism among stakeholders in SCF will be a promising topic for future research by utilizing the inherent characteristic of blockchain and smart contracts [19,21,22].
6.2. Risk Management of Blockchain Operations in SCF
Financial activities are usually accompanied by risks, and risk management is a fundamental method in coping with risk issues in SCF [55]. As the foundation of SCF is supply chain, supply chain financial risks have a close relationship with supply chain risks. Supply chain risks can be divided into two types: disruption risk and operational risk [76]. Among them, disruption risk refers to the risks resulted from bankruptcies, disasters, and terrorist attacks. In 2020, as the COVID-19 pandemic posed serious threats to more than 200 countries, many governments had to pause their economies, leading to a wide range of supply chain disruptions. Obviously, SCF providers also suffered from huge losses. However, black swan events such as the COVID-19 pandemic cannot be predicted precisely by humans, and supply chain disruptions also cannot be avoided totally. Therefore, researchers suggested that supply chain management should focus on the improvement of supply chain resilience [77]. The concept refers to the adaptive ability of the supply chain to respond to disruptions and recover to continuous operation levels by maintaining control over the structure and functions of the supply chain [78].
Theoretically, blockchain technology can facilitate financial institutions, such as banks, to manage risks of financing with small scale, limited working capital, and low credits. On the one hand, credits can be delivered to SMEs from focal enterprises along the supply chain [15,16]. On the other hand, the authenticity of transactions can be verified, and fraudulent financing behaviors, such as double financing, can be avoided through a blockchain-based SCF platform [15,16,38,44]. Therefore, a large number of lower-tier suppliers and retailers can be financed by SCF providers. However, most of the current research about risk management of SCF providers by blockchain is mainly at the stage of conceptual framework construction, which lacks correspondence to reality. Future research can conduct specific case analyses or relevant empirical studies to verify the efficacy of the suggested framework and derive additional practical implications and guidelines [19]. Moreover, analytics, modeling, and simulation approaches may be suitable for measuring the reliability of the proposed conceptual framework from both qualitative and quantitative perspectives [16].
In terms of blockchain technology, not only the benefits, but also the negative impacts of adopting blockchain technology in SCF should be investigated to avoid possible problems in practice [19]. For instance, the use of cryptocurrency increases the security of transactions. However, the government regulations and rules about the use of cryptocurrency are still imperfect, which leads to many legal and regulatory matters. Some countries forbid the transactions using cryptocurrency because it is used for money laundering and may also pose a threat to domestic currency. These practical factors need to be considered and improved in the future. In addition, Bitcoin is not the only type of cryptocurrency, and therefore, it may be interesting to explore whether a portfolio of cryptocurrencies can be employed to mitigate transaction risk [33].
Another advantage of blockchain technology is information sharing because the peer-to-peer network of blockchain enables connecting individual organizations as information silos. However, this feature may also impede organizations from adopting blockchain technology due to concern about privacy disclosure. Some works in the literature have proposed privacy protection mechanisms to maintain the confidentiality of business secrets, which still need further research [39,46,54]. Business secrets and data privacy need to be analyzed specifically under different supply chain financial business scenarios, which enables the performance improvement of privacy protection mechanism [46]. Privacy protection from the knowledge discovery perspective can be explored in the configurations of blockchain-based SCF solutions. By incorporating internet of things and AI, smart contracts can become smarter in privacy protection [54].
6.3. Blockchain and Sustainable SCF
With the development of economy, more and more countries and people are beginning to pay attention to sustainability, focusing not only on the economy, but also on the environment and society. As the impacts of greenhouse gases and climate change are among the main challenges of sustainable development faced by the whole society, sustainability dimensions have been considered in other fields of academics and industry. A novel concept closely related to SCF was proposed by Bancilhon et al. [79], which is sustainable supply chain finance (SSCF). SSCF is defined as SCF activities that support transactions in supply chain, in a manner that minimizes negative influences and creates environmental, social, and economic benefits for all stakeholders involved in bringing products and services to the market [79].
The reasons for exploring SSCF comes from two aspects: on the one hand, enterprises in supply chain are in high demand for sustainable development to seize potential opportunities in the future [69]; on the other hand, the mature conditions in digital SCF enable suppliers’ capability of engaging in sustainability by removing financial barriers [79,80]. However, previous research mainly focused on the impact of SCF on the economic effects of supply chain, ignoring its influence on environmental improvements and social responsibility [81]. Supply chain traceability is an essential element both in improving SCF performance and in achieving sustainability, which refers to the ability to identify and trace product information, including history, distribution, location, and application. The characteristics of blockchain are suitable for enterprises to meet these requirements, and many problems in this new area deserve further exploration.
In SCF, the physical flows in supply chain may be disrupted if the financial flows are not managed suitably. For instance, enterprises are not able to sustain the operational performance of the whole supply chain if they only focus on reducing the cash conversion cycle by extending payment terms for suppliers, as this strategy will exacerbate suppliers’ liquidity shortage [82]. Zhan et al. [83] demonstrated that reverse factoring is more efficient in promoting sustainability performance, compared to the advanced payment strategy. With the support of blockchain, the integration of physical flows, information flows, and financial flows will be enhanced owing to blockchain characteristics, which enable improving the performance of the whole supply chain and further achieving the sustainability objectives. The business models of blockchain-based SCF have been explored in the current literature [15,19,20,38,41]. However, we still have little knowledge about the business models of blockchain-based SCF when considering the requirements of sustainability.
Zhou et al. [84] conducted a cased-based research study of Alibaba Group’s implementation in agriculture SCF and found that SCF was no longer limited in optimizing working capitals of capital constrained partners by integrating financial flows with information and physical flows, but also could be utilized to facilitate supply chain enterprises to improve sustainable development. In the Alibaba Group’s innovative SSCF project, the funded enterprises contributed to the improvement in the environmental and food-safety problems, owing to the use of standardized fertilizers and pesticides [85]. The success of this project is inseparable from the supervision for fertilizers and pesticides and the traceability of agricultural products, which can be further improved by blockchain technology.
Another case of SSCF can be found in Nestle, which selected the “creating shared value” principle as its sustainability strategy. Dairy farmers supply fresh milk for Nestle, but they are generally lacking in capital. To deal with this problem, Nestle collaborated with governmental and financial institutions to provide farmers with funds [75]. However, few papers have explored the relationship between sustainability and SCF, specifically, the employment of sustainability requirements in SCF and how SCF improves sustainability performance [81]. Yadav and Singh [85] figured out six major causes, which promote the integration of blockchain with supply chain to achieve sustainability goals. However, the drivers for promoting the integration of blockchain technology with SSCF are still uninvestigated. In addition, many organizations are willing to employ blockchain to facilitate product life-cycle transparency and to trace the carbon footprint of supply chains accurately [29], whereas the adoption of blockchain in facilitating sustainable supply chain management is impeded by four categories of barriers, including inter-organizational, intra-organizational, technical, and external barriers [48]. To overcome adoption barriers and facilitate sustainable management, synergistic mechanisms may need to be explored in the coordination and collaboration of supply chain partners and their stakeholders for different business purposes and overall sustainability goals [86].
Moreover, the inherent smart contracts in blockchain technology can be used to design social contracts for sustainability, which benefits the sustainable development in SCF [25]. Blockchain technology allows for transactions in SCF without centralized institutions and intermediaries, eliminating paper-based documents. The improvement exists in efficiency increase and cost saving, which will attract a large number of people to use. However, this gives rise to another problem in sustainability, as the consensus mechanism of blockchain is an important cause for huge waste of resources, particularly electricity [86]. While blockchain technology is introduced to leverage sustainability practices, the operation in blockchain also leads to serious environmental burdens. Therefore, more efficient protocols in blockchain need to be developed to mitigate energy consumption [87].
7. Conclusions
In this paper, 52 research papers on the topic of blockchain and SCF, published between 2017 and December 2021, were examined. The stream of literature was analyzed by two methods, descriptive analysis and thematic analysis.
The current status of this field emerged from the descriptive results. The year 2017 saw the initial research contribution to this area, indicating that this research field is still in its infancy. The majority of the identified literature are the proceeding papers. With 10 papers in ABS 2 above journals, the existing research suggest that the research on SCF have attracted high quality journals. However, only two theories about revenue sharing and risk taking were used in this novel field, indicating the demand yet immaturity of this field.
Using thematic analysis, we categorized the identified papers into four themes, including challenges in the traditional SCF, factors of blockchain adoption in SCF, blockchain-based SCF solutions, and adoption mechanism and system design. The research field on blockchain and SCF is an emerging area, and therefore, it has huge potential for further study. First, as the deployment of blockchain technology is combined with other technologies, and the business processes of SCF are changed, cost optimization problems in blockchain-based SCF solutions need further exploration. Second, research on the risk management of blockchain-based SCF solutions is weak, such as the use of cryptocurrency and privacy disclosure. Third, considering the sustainability objectives of economy, social, and environment, blockchain technology can be further explored to improve the performance of the SSCF.
In terms of the research methods, both qualitative and quantitative research methodologies need to be applied to form the rigorous knowledge of this emergent research stream [32]. The case study and other field-based research can help us understand the detailed and complex mechanisms and business models, whilst quantitative methods, such as analytical modeling and simulation experiment, can shed theoretic lights on counter-intuitive findings related to the interactions of multiple parties. The current theoretical application in blockchain and SCF are weak; more theories such as innovation adoption/diffusion [88], network theory [89], and information processing theory [4] can be applied.
This research also provides practical implications. We propose a conceptual framework on the implementation of blockchain technology in SCF. The framework could provide practitioners with a tool to support the decision-making process. In particular, our framework answers the fundamental questions of what, why, how, and who in terms of block-chain adoption in SCF. In addition, the content analysis on existing research could provide practitioners with a screenshot of the existing research on SCF. The proposed three research directions could provoke practitioners’ attentions during the implementation process.
While considerable effort was invested to ensure the full coverage of papers in this novel field, it is possible that some relevant literature may have been omitted unintentionally. However, we believe that this study represents the current status of this novel field during the specific time frame, and we hope that the pointed future research directions can provide a useful reference to the research community.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su142013450/s1, References [90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114] are cited in the supplementary materials Table S1: Selected review papers; Table S2: Challenges in the traditional SCF; Table S3: Drivers of blockchain adoption; Table S4: Barriers of blockchain adoption; Table S5: Other technologies in blockchain adoption in SCF
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.G.; methodology, Y.G.; validation, Y.Z. and M.A.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.G.; writing—review and editing, Y.Z. and M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
The study did not involve human participants.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the editor and reviewers for taking the time to review our manuscript and providing constructive feedback to improve our manuscript. Special thanks to Tianyu Zhang from Beijing Institute of Technology for supporting the initial data collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bals, C. Toward a supply chain finance (SCF) ecosystem–Proposing a framework and agenda for future research. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2019, 25, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakuu, S.; Masi, D.; Godsell, J. Exploring the relationship between mechanisms, actors and instruments in supply chain finance: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 216, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelsomino, L.M.; Mangiaracina, R.; Perego, A.; Tumino, A. Supply chain finance: A literature review. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2016, 46, 348–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Blome, C.; Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhi, B. Towards an integrated conceptual framework of supply chain finance: An information processing perspective. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 219, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuttke, D.A.; Blome, C.; Foerstl, K.; Henke, M. Managing the innovation adoption of supply chain finance—Empirical evidence from six European case studies. J. Bus. Logist. 2013, 34, 148–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, E. Supply chain finance: Some conceptual insights. Beiträge Beschaff. Logist. 2005, 16, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, H.K.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Lyons, A. The effect of supply chain finance initiatives on the market value of service providers. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 216, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Yang, X.; Yu, K. How do supply chain network and SMEs’ operational capabilities enhance working capital financing? An integrative signaling view. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 220, 107447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, S. Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system. Decent. Bus. Rev. 2008, 21260. [Google Scholar]
- Chod, J.; Trichakis, N.; Tsoukalas, G.; Aspegren, H.; Weber, M. On the financing benefits of supply chain transparency and blockchain adoption. Manag. Sci. 2020, 66, 4378–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshetri, N. 1 Blockchain’s roles in meeting key supply chain management objectives. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018, 39, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pournader, M.; Shi, Y.; Seuring, S.; Koh, S.L. Blockchain applications in supply chains, transport and logistics: A systematic review of the literature. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 2063–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, V.; Hilary, G. OM Forum—Distributed ledgers and operations: What operations management researchers should know about blockchain technology. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2020, 22, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menghwar, P.S.; Daood, A. Creating shared value: A systematic review, synthesis and integrative perspective. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2021, 23, 466–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, E.; Strewe, U.M.; Bosia, N. Supply Chain Finance and Blockchain Technology: The Case of Reverse Securitization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Omran, Y.; Henke, M.; Heines, R.; Hofmann, E. Blockchain-driven supply chain finance: Towards a conceptual framework from a buyer perspective. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference of the International Purchasing and Supply Education and Research Associatio, Balatonfured, Hungary, 9–12 April 2017; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Zheng, L. Construction of VMI Mode Supply Chain Management System Based on Block Chain. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Algorithms and Architectures for Parallel Processing, New York, NY, USA, 2–4 October 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 611–616. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Lyu, T.; Li, R. A study on SMIE credit evaluation model based on blockchain technology. Procedia CIRP 2019, 83, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Zhang, Z.; Gauthier, J. Blockchain-based intelligent contract for factoring business in supply chains. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 308, 777–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cai, T.; He, W.; Chen, L.; Zhao, G.; Zou, W.; Guo, L. A blockchain-driven supply chain finance application for auto retail industry. Entropy 2020, 22, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.-M. Supply chain financing using blockchain: Impacts on supply chains selling fashionable products. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.-M. Financing product development projects in the blockchain era: Initial coin offerings versus traditional bank loans. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Wang, H. Case Study of How to Help Manufacturing Enterprises Obtain Loan through Supply Chain Documents on Blockchain Platform. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Application (ICCEA), Guangzhou, China, 18–20 March 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 192–195. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Huang, G.; Guo, X. Financing strategy analysis for a multi-sided platform with blockchain technology. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 4513–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, O.; Ally, M.; Dwivedi, Y. The state of play of blockchain technology in the financial services sector: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 54, 102199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.F.; Quezada, L.E.; Tan, K.H.; da Costa, S.E.G. Systemic approach to the new production research challenges. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 222, 107495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinis, S.; Bamford, D.; Papalexi, M.; Vafadarnikjoo, A. Services procurement: A systematic literature review of practices and challenges. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2021, 24, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastig, G.M.; Sodhi, M. Blockchain for supply chain traceability: Business requirements and critical success factors. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2020, 29, 935–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudary, R.; Brusset, X.; Fenies, P. Blockchain in general management and economics: A systematic literature review. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2020, 32, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seuring, S.; Yawar, S.A.; Land, A.; Khalid, R.U.; Sauer, P.C. The application of theory in literature reviews–illustrated with examples from supply chain management. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2020, 41, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, M.S.; Tang, C.S. Guiding the next generation of doctoral students in operations management. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 150, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.-M. Creating all-win by blockchain technology in supply chains: Impacts of agents’ risk attitudes towards cryptocurrency. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2021, 72, 2580–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.-M.; Guo, S.; Liu, N.; Shi, X. Optimal pricing in on-demand-service-platform-operations with hired agents and risk-sensitive customers in the blockchain era. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 284, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Chen, C.; Shi, X.; Ng, C.T. Operations strategy for supply chain finance with asset-backed securitization: Centralization and blockchain adoption. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 241, 108261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Jiang, T. Optimal strategies for financing a three-level supply chain through blockchain platform finance. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 41, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Luo, X.R.; Lee, F.; Benitez, J. Value creation in blockchain-driven supply chain finance. Inf. Manag. 2021, 59, 103510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogucharskov, A.; Pokamestov, I.; Adamova, K.; Tropina, Z.N. Adoption of blockchain technology in trade finance process. J. Rev. Glob. Econ. 2018, 7, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wei, C.; Guo, X.; Lu, X.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, C.; Song, X.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, H. Confidentiality support over financial grade consortium blockchain. In Proceedings of the 2020 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Portland, OR, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 2227–2240. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Cao, N. Framework Design of Financial Service Platform for Tobacco Supply Chain Based on Blockchain. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Algorithms and Architectures for Parallel Processing, New York, NY, USA, 2–4 October 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Guerar, M.; Verderame, L.; Merlo, A.; Migliardi, M. Blockchain-based risk mitigation for invoice financing. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Database Applications & Engineering Symposium, Athens, Greece, 10–12 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Du, M.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, J.; Yang, H.; Ma, X. Supply chain finance innovation using blockchain. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 67, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L. Research on Sustainability of Supply Chain Financial Model in Fujian Free Trade Zone; IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; p. 032029. [Google Scholar]
- Lycklama à Nijeholt, H.; Oudejans, J.; Erkin, Z. DecReg: A Framework for Preventing Double-Financing Using Blockchain Technology. In Proceedings of the ACM Workshop on Blockchain, Cryptocurrencies and Contracts, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2 April 2017; pp. 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Shao, S.; Ye, Q.; Xu, G.; Huang, G.Q. Blockchain-enabled logistics finance execution platform for capital-constrained E-commerce retail. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2020, 65, 101962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Kong, X.; Lan, Q.; Zhou, Z. The privacy protection mechanism of Hyperledger Fabric and its application in supply chain finance. Cybersecurity 2019, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahkani, M.J.; Wang, S.; Urbański, M.; Egorova, M. Sustainable B2B E-commerce and blockchain-based supply chain finance. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, S.; Kouhizadeh, M.; Sarkis, J.; Shen, L. Blockchain technology and its relationships to sustainable supply chain management. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 2117–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, I.D.; Holland, C.P.; Westcott, T. Motorola’s global financial supply chain strategy. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2013, 18, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandfluh, M.; Hofmann, E.; Schoensleben, P. Financing buyer–supplier dyads: An empirical analysis on financial collaboration in the supply chain. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2016, 19, 200–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoek, R. Exploring blockchain implementation in the supply chain: Learning from pioneers and RFID research. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2019, 39, 829–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.D.; Tee, R. Generativity: A systematic review and conceptual framework. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2022, 24, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Lee, J.; Barth, J.R.; Richey, R.G. Blockchain as supply chain technology: Considering transparency and security. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2021, 51, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, D.E. Configuring blockchain architectures for transaction information in blockchain consortiums: The case of accounting and supply chain systems. Intell. Syst. Account. Financ. Manag. 2017, 24, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.-L. A Simple Survey for SUPPLY Chain Finance Risk Management with Applications of Blockchain; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 116–133. [Google Scholar]
- Safiullin, M.; Elshin, L.; Abdukaeva, A.; Savushkin, M. Assessing the impact of supply chain financing using blockchain technology on credit risks in the banking sector of the Russian Federation. Int. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2020, 9, 703–708. [Google Scholar]
- Guggenberger, T.; Schweizer, A.; Urbach, N. Improving interorganizational information sharing for vendor managed inventory: Toward a decentralized information hub using blockchain technology. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 67, 1074–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, E.; Belin, O. Supply Chain Finance Solutions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yaksick, R. Overcoming supply chain finance challenges via blockchain technology. In Disruptive Innovation in Business and Finance in the Digital World; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Casino, F.; Dasaklis, T.K.; Patsakis, C. Enhanced vendor-managed inventory through blockchain. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th South-East Europe Design Automation, Computer Engineering, Computer Networks and Social Media Conference (SEEDA-CECNSM), Piraeus, Greece, 20–22 September 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dasaklis, T.; Casino, F. Improving vendor-managed inventory strategy based on Internet of Things (IoT) applications and blockchain technology. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain and Cryptocurrency (ICBC), Seoul, Korea, 14–17 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Wang, D. Combined application of blockchain technology in fractional calculus model of supply chain financial system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 131, 109461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Aich, S.; Seong, S.J.; Kim, H.-C. A blockchain based credit analysis framework for efficient financial systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 21st International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), PyeongChang, Korea, 17–20 February 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Sun, G.; Fu, S.; Fan, X.; Jiang, W.; Hu, S.; Li, L. A distributed approach of big data mining for financial fraud detection in a supply chain. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 64, 1091–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerar, M.; Merlo, A.; Migliardi, M.; Palmieri, F.; Verderame, L. A fraud-resilient blockchain-based solution for invoice financing. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 67, 1086–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.; Lam, J.S.L. Blockchain adoptions in the maritime industry: A conceptual framework. Marit. Policy Manag. 2021, 48, 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.; Ngai, E. The adoption of RFID in fashion retailing: A business value-added framework. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2008, 108, 596–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.-P.; Wu, X.-Y.; Cao, B.-B. Considering the traceability awareness of consumers: Should the supply chain adopt the blockchain technology? Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 309, 837–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L. Sustainable supply chain Finance: Towards a research agenda. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegielski, C.G.; Jones-Farmer, L.A.; Wu, Y.; Hazen, B.T. Adoption of cloud computing technologies in supply chains: An organizational information processing theory approach. Int. J. Logist. Manage. 2012, 23, 184–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tushman, M.L.; Nadler, D.A. Information processing as an integrating concept in organizational design. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1978, 3, 613–624. [Google Scholar]
- Trautmann, G.; Turkulainen, V.; Hartmann, E.; Bals, L. Integration in the global sourcing organization—An information processing perspective. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2009, 45, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeyratne, S.A.; Monfared, R.P. Blockchain ready manufacturing supply chain using distributed ledger. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2016, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bensaou, M.; Venkatraman, N. Configurations of interorganizational relationships: A comparison between US and Japanese automakers. Manag. Sci. 1995, 41, 1471–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Jia, F.; Brown, S.; Koh, L. Supply chain learning of sustainability in multi-tier supply chains: A resource orchestration perspective. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2018, 38, 1061–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.S. Perspectives in supply chain risk management. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2006, 103, 451–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüttner, U.; Maklan, S. Supply chain resilience in the global financial crisis: An empirical study. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2011, 16, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, K.; Scott, P.S.; Fynes, B. Mitigation processes–antecedents for building supply chain resilience. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2014, 19, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancilhon, C.; Karge, C.; Norton, T. Win-Win-Win: The Sustainable Supply Chain Finance Opportunity; Report BSR: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Glover, J.L.; Champion, D.; Daniels, K.J.; Dainty, A.J. An Institutional Theory perspective on sustainable practices across the dairy supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 152, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Jia, F.; Brown, S.; Gong, Y.; Xu, Y. Supply chain finance: A systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 204, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Lai, Y.; Liang, C. Drivers and outcomes of supply chain finance adoption: An empirical investigation in China. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 220, 107453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Li, S.; Chen, X. The impact of financing mechanism on supply chain sustainability and efficiency. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 205, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, S. Innovative financial approach for agricultural sustainability: A case study of Alibaba. Sustainability 2018, 10, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Singh, S.P. Blockchain critical success factors for sustainable supply chain. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 152, 104505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhizadeh, M.; Zhu, Q.; Sarkis, J. Blockchain and the circular economy: Potential tensions and critical reflections from practice. Prod. Plan. Control 2020, 31, 950–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.M.; Fosso Wamba, S.; De Bourmont, M.; Telles, R. Blockchain adoption in operations and supply chain management: Empirical evidence from an emerging economy. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 6087–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E.M.; Singhal, A.; Quinlan, M.M. Diffusion of innovations. In An Integrated Approach to Communication Theory and Research; Routledge: London, UK, 2014; pp. 432–448. [Google Scholar]
- Sytch, M.; Tatarynowicz, A.; Gulati, R. Toward a theory of extended contact: The incentives and opportunities for bridging across network communities. Organ. Sci. 2012, 23, 1658–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Wang, F.; Hao, Z.; Li, H. Credit evaluation system based on blockchain for multiple stakeholders in the food supply chain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Zhou, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, X. December. A real time stare in market strategy for supply chain financing pledge risk management. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM), Bangkok, Thailand, 16–19 December 2018; pp. 1116–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Dong, A. The coordination mechanism of supply chain finance based on block chain. IOP Publ. 2018, 189, 062019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, D. April. Research on blockchain application for E-commerce, finance and energy. IOP Publ. 2019, 252, 042126. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, L.; Jia, S.; Lan, Q.; Zhou, Z. Research on Blockchain-Based Commercial Paper Financing in Supply Chain. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent and Interactive Systems and Applications, Shanghai, China, 28–30 June 2019; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Zhuang, X. Financing a capital-constrained supply chain: Factoring accounts receivable vs a BCT-SCF receivable chain. Kybernetes 2021, 50, 2209–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kim, D.K.; Jeong, D. A survey of the application of blockchain in multiple fields of financial services. J. Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 16, 935–958. [Google Scholar]
- Su, L.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Tian, W. Research of innovative business classification in bulk commodity digital supply chain finance. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Application (ICCEA), Guangzhou, China, 18–20 March 2020; pp. 170–173. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Ru, C. Application of blockchain technology in supply chain finance. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Mechanical, Control and Computer Engineering (ICMCCE), Harbin, China, 25–27 December 2020; pp. 1342–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T. Application and Challenge of Blockchain in Supply Chain Finance. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Analytics for Cyber-Physical-Systems, Shanghai, China, 28–29 December 2020; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1372–1377. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, J.Z.; He, W.; Li, W. Mitigating information asymmetry in inventory pledge financing through the Internet of things and blockchain. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2021, 34, 1429–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Yuan, Y. How blockchain impacts the supply chain finance platform business model reconfiguration. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2021, 25, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijanto, A. Blockchain technology adoption in supply chain finance. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2021, 16, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, Q.; Shen, M.I. Applying blockchain technology to reshape the service models of supply chain finance for SMEs in China. Singap. Econ. Rev. 2021, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.R.; Islam, M.A. Application of blockchain for supply chain financing: Explaining the drivers using SEM. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2021, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; He, D.; Su, H. Evolutionary game analysis of blockchain technology preventing supply chain financial risks. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2021, 16, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Research on supply chain financial risk assessment based on blockchain and fuzzy neural networks. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yang, Y.; Chu, X. Research on the Influence Mechanism of Block Chain on the Credit of Transportation Capacity Supply Chain Finance. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Du, C. Zheshang Bank’s “Blockchain+ Supply Chain Finance” Accounts Receivable Financing Model of Research. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 275, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. Application of blockchain technology in supply chain finance in beibu gulf region. In Proceedings of the International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (IWCMC), Qingdao, China, 28–30 May 2021; pp. 1860–1864. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Xiao, P.; Chai, H.; Tu, X.; Sun, Q.; Cai, H.; Wang, F.Y. Research on Construction of Supply Chain Financial Platform Based on Blockchain Technology. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 1st International Conference on Digital Twins and Parallel Intelligence (DTPI), Beijing, China, 22 September 2021; pp. 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Li, Y. Risk analysis of supply chain finance under blockchain technology-based on AHP-FCM model. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Economic Innovation and Low-Carbon Development (EILCD 2021), E3S Web of Conferences, Qingdao, China, 28–30 May 2021; Volume 275, p. 01025. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, F.; Qin, Z. Block chain based supply chain financial risk management research. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1744, 022027.
- Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Jiang, X. Analysis of supply chain finance based on blockchain. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 187, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Jiang, X. Supply chain finance based on smart contract. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 187, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).