An Optimal Layout Model of Curved Panels for Using 3D Printing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
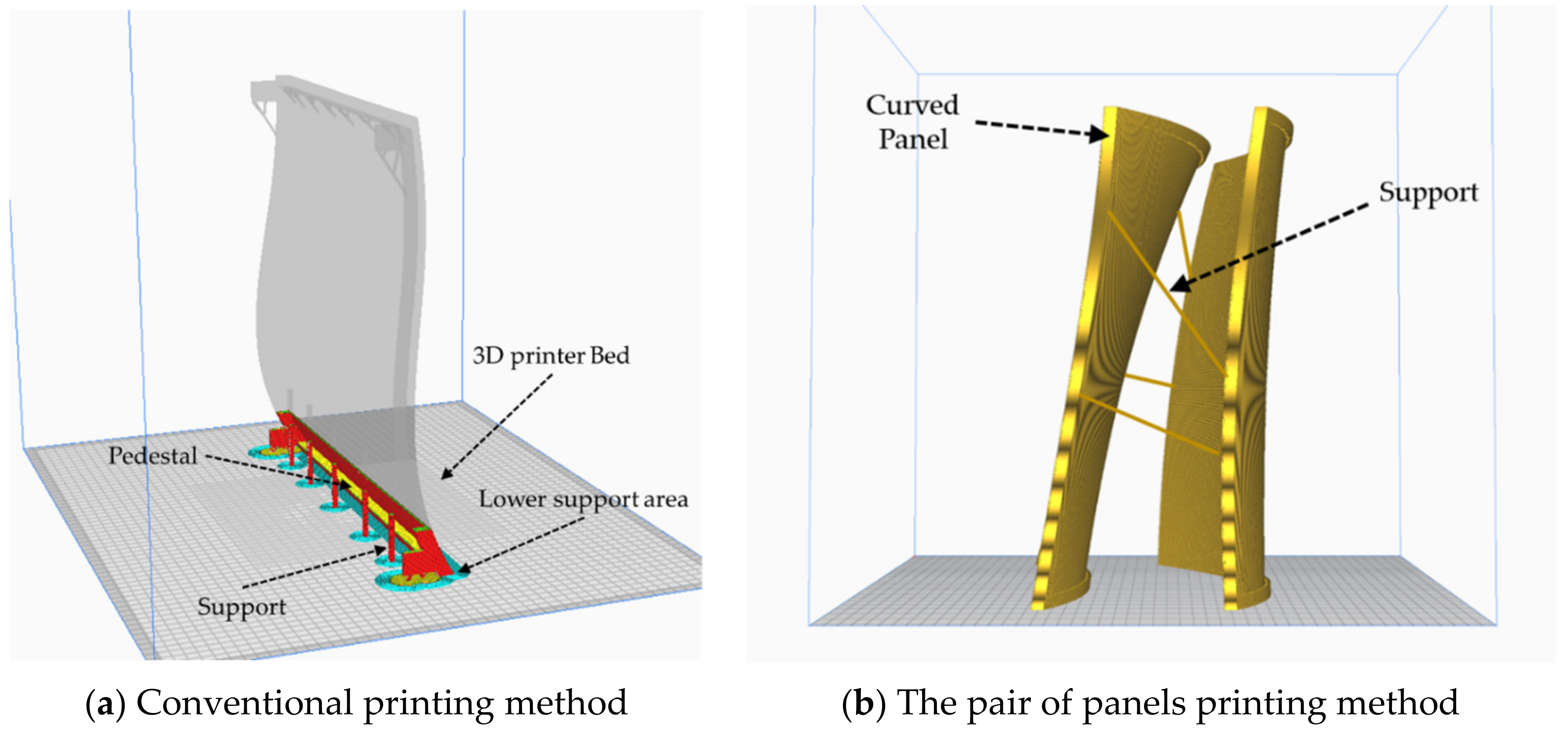
2. 3D Printing Method for Curved Panel
3. Previous Research on 3D Print Planning
3.1. Overhang
3.2. Optimal Path Plan of 3D Printing
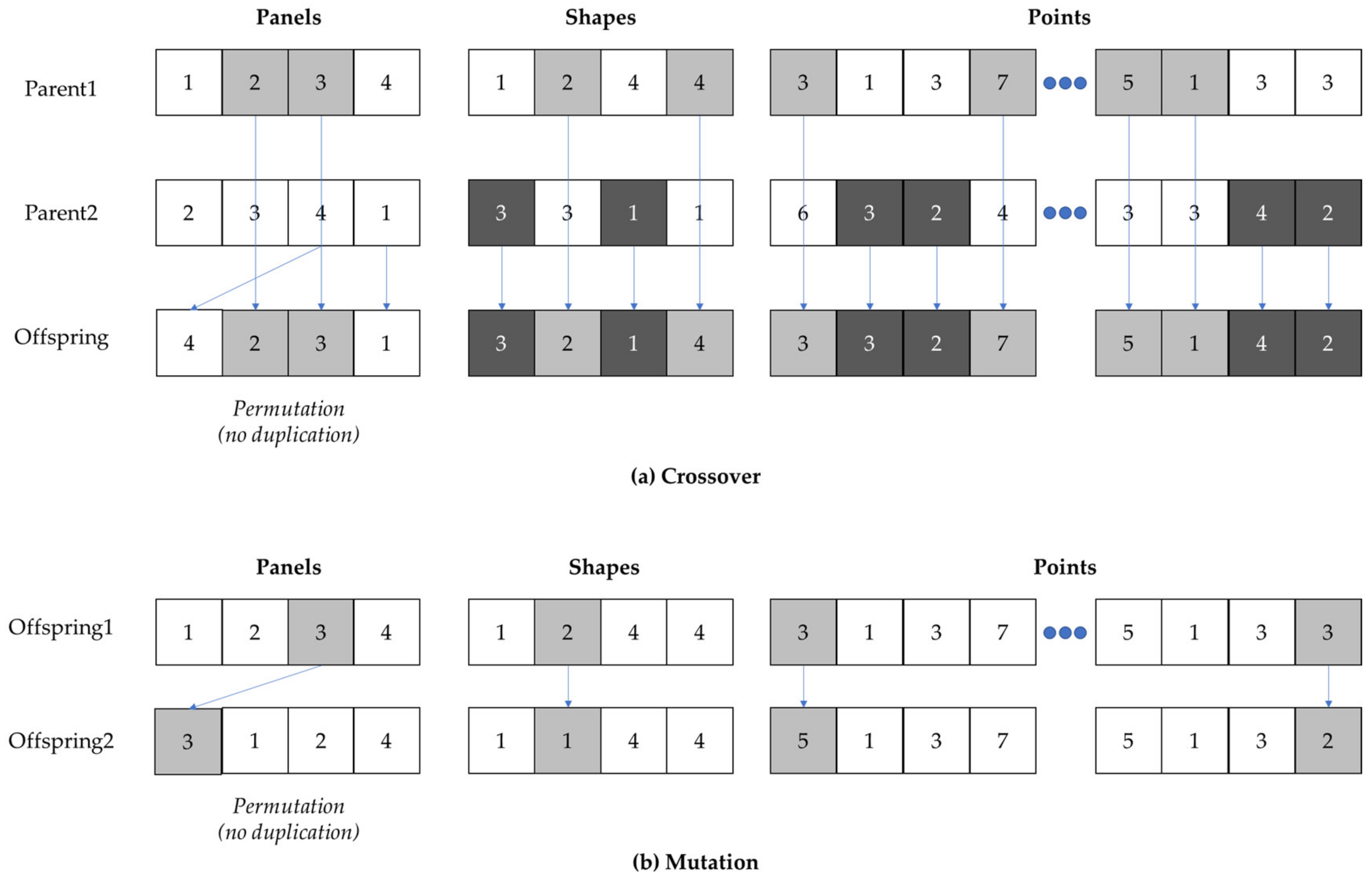
4. Optimizing Curved Panel Printing Layout
4.1. Panel Printing Method in Pairs
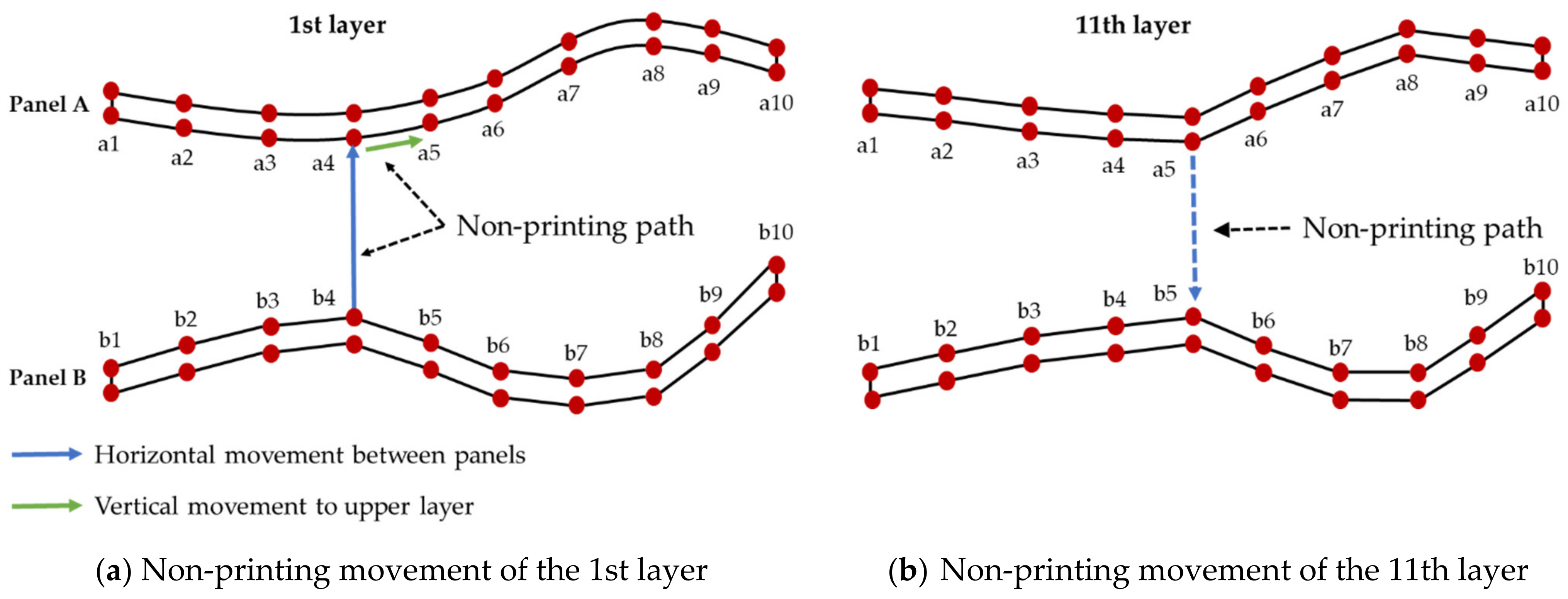
4.2. Calculation of Non-Printing Paths
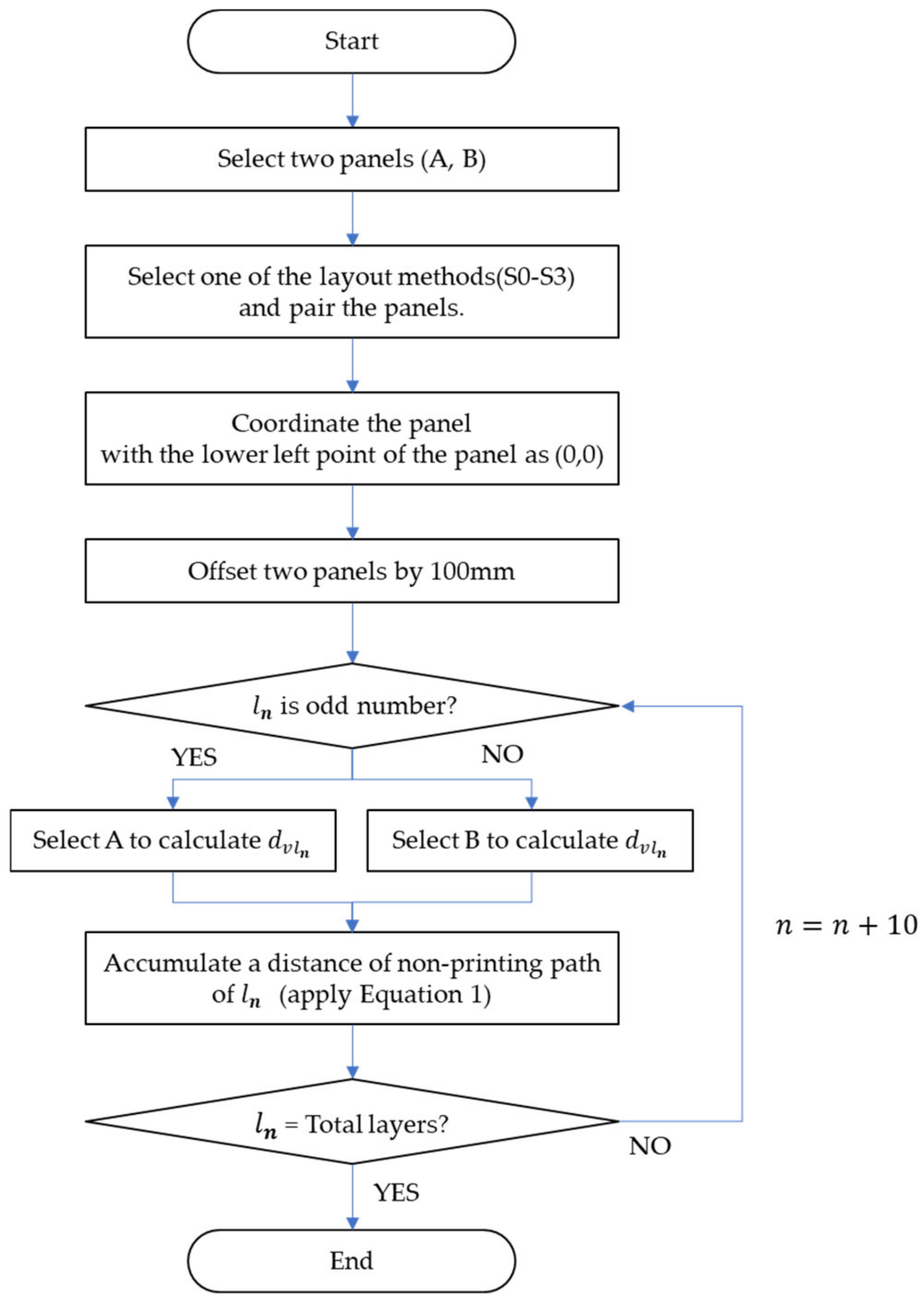
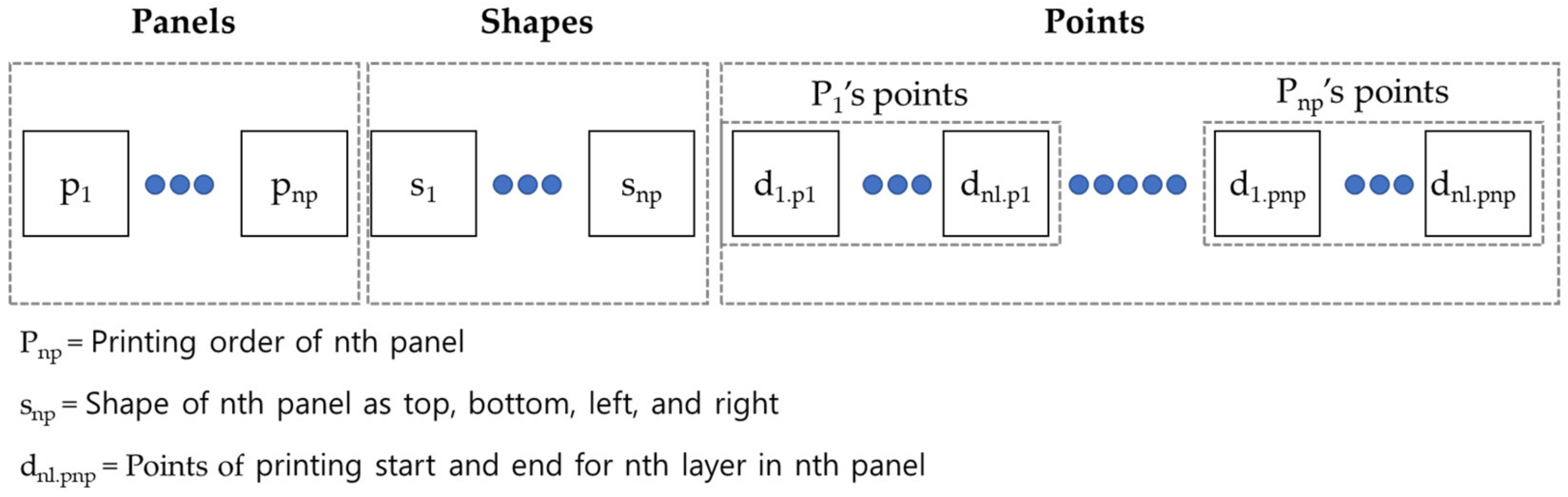
4.3. Printing Layout Optimization Model
5. Case Study
5.1. Case Overview
5.2. Result and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kavuma, A.; Ock, J.; Jang, H. Factors influencing time and cost overruns on freeform construction projects. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 23, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosoarca, M.; Anastasiadis, A.; Apostolos, K. Are freeform architectures ecological buildings? J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2014, 15, 366–373. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.; Buswell, R.A.; Valentine, P.J.; Piker, D.; Austin, S.A.; De Kestelier, X. Modeling curved-layered printing paths for fabricating large-scale construction components. Addit. Manuf. 2016, 12, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hague, R.J.M.; Campbell, I.; Dickens, P. Implications on design of rapid manufacturing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2003, 217, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jovanović, M.; Raković, M.; Tepavčević, B.; Borovac, B.; Nikolić, M. Robotic fabrication of freeform foam structures with quadrilateral and puzzle shaped panels. Autom. Constr. 2017, 74, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, Y.; Park, J. Review of Freeform Buildings using CNC T-BAR System. In Proceedings of the Korean Society of Architecture and Construction Engineering Conference, Gyeongju, Korea, 17–19 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khoshnevis, B.; Hwang, D.; Yao, K.T.; Yeh, Z. Mega-scale fabrication by contour crafting. Int. J. Ind. Syst. Eng. 2006, 1, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.; Buswell, R.A.; Le, T.T.; Austin, S.A.; Gibb, A.G.F.; Thorpe, A. Developments in construction-scale additive manufacturing processes. Autom. Constr. 2012, 21, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muflikhun, M.A.; Sentanu, D.A. Characteristics and performance of carabiner remodeling using 3D printing with graded filler and different orientation methods. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 130, 105795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, A.D.; Ruli; Supriyanto, E.; Rasgianti; Prawara, B.; Martides, E.; Junianto, E.; Wibowo, A.; Sentanuhady, J.; Muflikhun, M.A. First-rate manufacturing process of primary air fan (PAF) coal power plant in Indonesia using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) technology. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 4075–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papacharalampopoulos, A.; Bikas, H.; Stavropoulos, P. Path planning for the infill of 3D printed parts utilizing Hilbert curves. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 21, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkinson, N.; Gao, Y.; McAfee, D.J. Design for environment analysis applied to rapid manufacturing. Proc. IMechE Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2006, 10, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buswell, R.A.; Soar, R.C.; Gibb, A.G.F.; Thorpe, A. Freeform Construction: Mega-scale rapid manufacturing for construction. Autom. Constr. 2007, 16, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ezair, B.; Fuhrmann, S.; Elber, G. Volumetric covering print-paths for additive manufacturing of 3D models. Comput. Aided Des. 2018, 100, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacace, S.; Cristiani, E.; Rocchi, L. A level set based method for fixing overhangs in 3D printing. Appl. Math. Model. 2017, 44, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mumtaz, K.; Vora, P.; Hopkinson, N. A method to eliminate anchors/supports from directly laser melted metal powder bed processes. In Proceedings of the International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 8–10 August 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Ven, E.; Maas, R.; Ayas, C.; Langelaar, M.; van Keulen, F. Overhang control based on front propagation in 3D topology optimization for additive manufacturing. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 369, 113169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaynor, A.T.; Meisel, N.A.; Williams, C.B.; Guest, J.K. Topology optimization for additive manufacturing: Considering maximum overhang constraint. In Proceedings of the 15th AIAA/ISSMO Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 16–20 June 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloots, M.; Spierings, A.B.; Wegener, K. Assessing new support minimizing strategies for the additive manufacturing technology SLM. In Proceedings of the International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 12–14 August 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, M.; Merli, L.; Torti, F.; Mazur, M.; Brandt, M. Optimal topology for additive manufacture: A method for enabling additive manufacture of support-free optimal structures. Mater. Des. 2014, 63, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Jin, S.; Wang, C.C. Support slimming for single material based additive manufacturing. Comput. Aided Des. 2015, 65, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Kim, T.K.; Lee, T.; Hwang, B. Minimization model for 3D printing non-productive pathto improve the productivity of curved finishing panel. In Proceedings of the Conference of the Korean Society of Ecological and Environmental Architecture, Seoul, Korea, 3–4 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ezair, B.; Massarwi, F.; Elber, G. Orientation analysis of 3D objects toward minimal support volume in 3D-printing. Comput. Graph. 2015, 51, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Kang, Z. Level set-based topology optimization with overhang constraint: Towards support-free additive manufacturing. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2018, 339, 591–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, A.N.; Schmidt, R.; Bærentzen, J.A. Automatic balancing of 3D models. Comput. Aided Des. 2015, 58, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wah, P.K.; Murty, K.G.; Joneja, A.; Chiu, L.C. Tool path optimization in layered manufacturing. IIE Transl. 2002, 34, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechowicz, P.; Koszalka, L.; Pozniak-Koszalka, I.; Kasprzak, A. Path Optimization in 3D Printer: Algorithms and experimentation system. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Computational and Business Intelligence, Wroclaw, Poland, 5–7 September 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Tian, L.; Xue, X.; Jia, Q. An Intelligent 3D Printing Path Planning Algorithm 3D Printing Path Planning Algorithm: An Intelligent Sub-Path Planning Algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovation in Artificial Intelligence, Xiamen, China, 5–8 March 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, M.; Koszalka, L.; Pozniak-Koszalka, I.; Kasprzak, A. MZZ-GA Algorithm for Solving Path Optimization in 3D Printing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 28–31 July 2015. [Google Scholar]


| Existing | Optimal | |
|---|---|---|
| Print order of the panels | 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99 | 6, 25, 3, 17, 97, 23, 59, 39, 68, 20, 40, 62, 74, 14, 46, 87, 44, 75, 96, 41, 92, 98, 67, 37, 36, 34, 60, 43, 61, 27, 0, 70, 69, 28, 90, 54, 93, 86, 76, 56, 11, 2, 80, 84, 8, 83, 73, 18, 30, 10, 99, 38, 16, 82, 33, 94, 13, 48, 72, 77, 19, 50, 64, 35, 71, 58, 24, 42, 21, 49, 95, 31, 88, 5, 15, 78, 57, 85, 32, 52, 29, 65, 66, 63, 4, 89, 1, 9, 12, 22, 55, 47, 79, 81, 7, 91, 45, 53, 51, 26 |
| Shape | 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 | 0, 2, 0, 3, 0, 2, 1, 2, 0, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 2, 3, 2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 3, 2, 1, 1, 2, 0, 3, 2, 3, 0, 2, 1, 0, 2, 3, 1, 0, 2, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 0, 3, 3, 1, 0, 1, 3, 0, 3, 1, 2, 1, 3, 2, 2, 3, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 0, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 0, 3, 0, 1, 3, 2, 3, 1, 3, 1, 3, 2, 3, 1, 2, 0, 2 |
| Existing (A) | Optimal (B) | Increase/Decrease (A − B) | Variance ((A − B)/B) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance of non-printing path, [mm] | 23,380,538 | 19,044,898 | 4,335,640 mm reduction | 18.54% reduction |
| Non-printing time, [h] | 185.56 | 151.15 | 34.41 h reduction | |
| Printing time, [h] | 700 | 700 | - | - |
| Total printing time, [h] | 885.56 | 851.15 | 34.41 h reduction | 3.89% reduction |
| Non-printing ratio, [%] | 26.51 | 21.59 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cha, M.; Kim, C.-W.; Lee, T.; Kim, B.-J.; Cho, H.; Kim, T.; Lim, H. An Optimal Layout Model of Curved Panels for Using 3D Printing. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13896. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142113896
Cha M, Kim C-W, Lee T, Kim B-J, Cho H, Kim T, Lim H. An Optimal Layout Model of Curved Panels for Using 3D Printing. Sustainability. 2022; 14(21):13896. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142113896
Chicago/Turabian StyleCha, Minsu, Chang-Won Kim, Taehee Lee, Baek-Joong Kim, Hunhee Cho, Taehoon Kim, and Hyunsu Lim. 2022. "An Optimal Layout Model of Curved Panels for Using 3D Printing" Sustainability 14, no. 21: 13896. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142113896
APA StyleCha, M., Kim, C.-W., Lee, T., Kim, B.-J., Cho, H., Kim, T., & Lim, H. (2022). An Optimal Layout Model of Curved Panels for Using 3D Printing. Sustainability, 14(21), 13896. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142113896





