Former Foodstuff Products (FFPs) as Circular Feed: Types of Packaging Remnants and Methods for Their Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Main Types of Packaging Remnants Found in Former Foods
2.1. Plastic Materials
2.2. Aluminum Materials
2.3. Paper and Board Materials
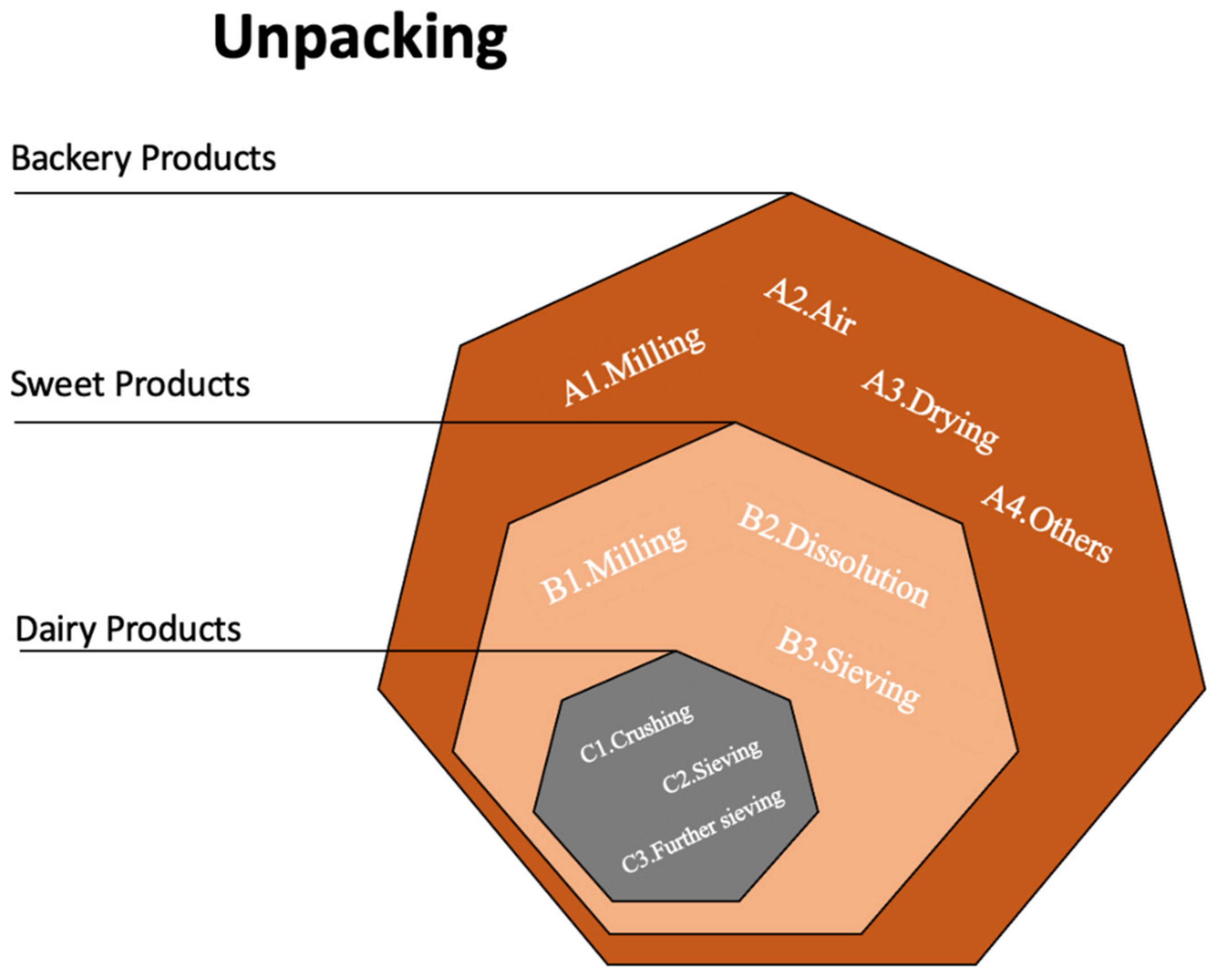
3. Methods for Detecting Packaging Remnants
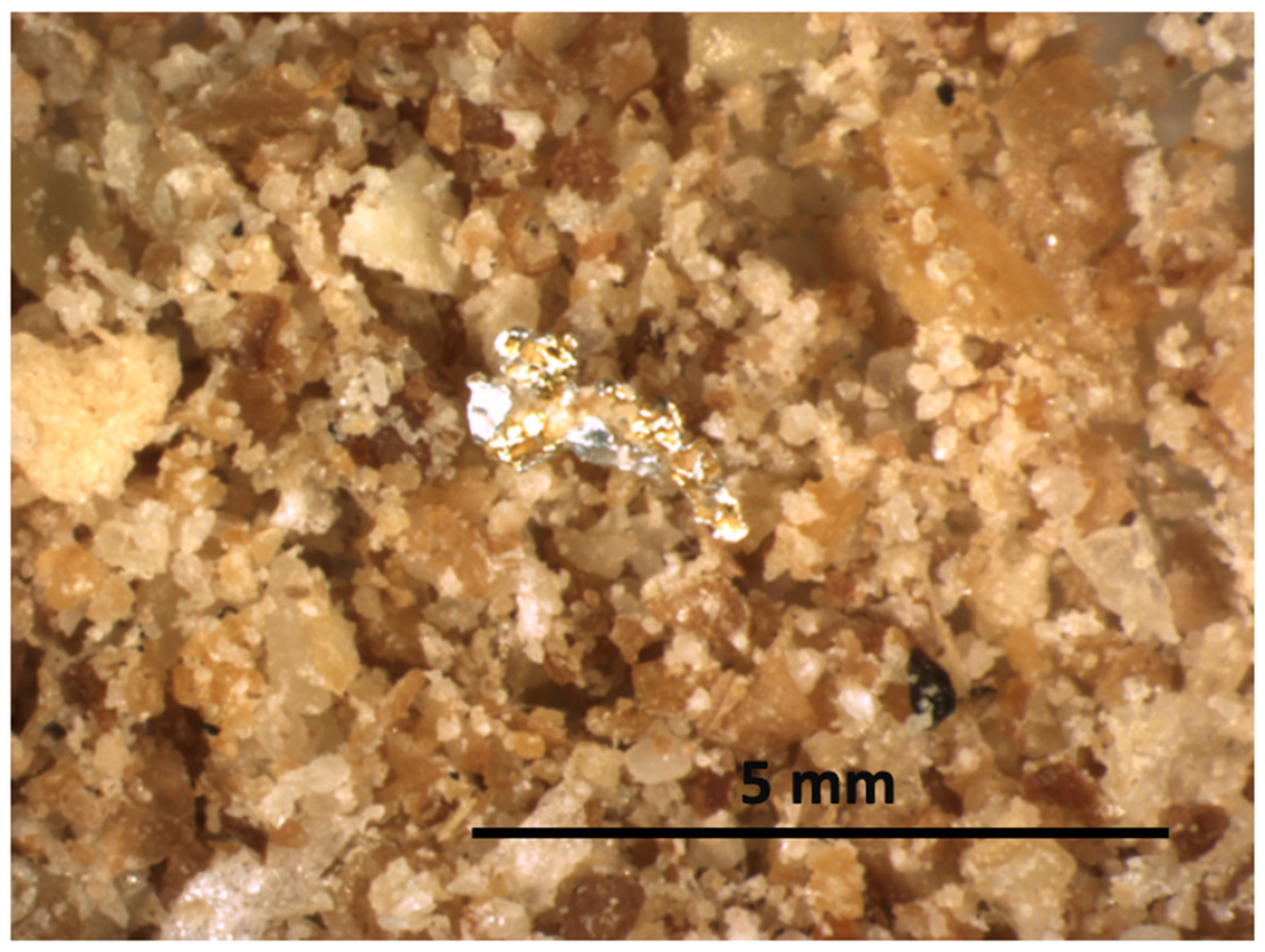
3.1. Visual Inspection
3.2. Computer Vision and Multivariate Image Analysis
3.3. Electronic Nose (e-Nose)
4. Pros and Cons of the Methods Presented
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wohner, B.; Pauer, E.; Heinrich, V.; Tacker, M. Packaging-Related Food Losses and Waste: An Overview of Drivers and Issues. Sustainability 2018, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manalili, N.M.; Dorado, M.A.; van Otterdijk, R. Appropriate Food Packaging Solutions for Developing Countries; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2011; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i3684e/i3684e.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Tretola, M.; Ottoboni, M.; Di Rosa, A.R.; Giromini, C.; Fusi, E.; Rebucci, R.; Leone, F.; Dell’Orto, V.; Chiofalo, V.; Pinotti, L. Former Food Products Safety Evaluation: Computer Vision as an Innovative Approach for the Packaging Remnants Detection. J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017, 1064580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretola, M.; Ottoboni, M.; Luciano, A.; Dell’Orto, V.; Cheli, F.; Pinotti, L. Tracing food packaging contamination: An electronic nose applied to leftover food. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 1748–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smárason, B.; Alriksson, B.; Jóhannsson, R. Safe and sustainable protein sources from the forest industry—The case of fish feed. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 84, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) No.2017/1017 of 15 June 2017 amending Regulation (EU) No 68/2013 on the Catalogue of feed materials. Off. J. Eur. Union 2017, L 159, 48–119. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); James, K.; Millington, A.; Randall, N. Food and feed safety vulnerabilities in the circular economy. EFSA Support. Publ. 2022, 19, 7226E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano, A.; Tretola, M.; Ottoboni, M.; Baldi, A.; Cattaneo, D.; Pinotti, L. Potentials and Challenges of Former Food Products (Food Leftover) as Alternative Feed Ingredients. Animals 2020, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinotti, L.; Luciano, A.; Ottoboni, M.; Manoni, M.; Ferrari, L.; Marchis, D.; Tretola, M. Recycling food leftovers in feed as opportunity to increase the sustainability of livestock production. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano, A.; Espinosa, C.D.; Pinotti, L.; Stein, H.H. Standardized total tract digestibility of phosphorus in bakery meal fed to pigs and effects of bakery meal on growth performance of weanling pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 284, 115148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano, A.; Tretola, M.; Mazzoleni, S.; Rovere, N.; Fumagalli, F.; Ferrari, L.; Comi, M.; Ottoboni, M.; Pinotti, L. Sweet vs. Salty Former Food Products in Post-Weaning Piglets: Effects on Growth, Apparent Total Tract Digestibility and Blood Metabolites. Animals 2021, 11, 3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretola, M.; Di Rosa, A.R.; Tirloni, E.; Ottoboni, M.; Giromini, C.; Leone, F.; Bernardi, C.E.M.; Dell’Orto, V.; Chiofalo, V.; Pinotti, L. Former food products safety: Microbiological quality and computer vision evaluation of packaging remnants contamination. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, K.; Bugusu, B. Food Packaging? Roles, Materials, and Environmental Issues. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, R39–R55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, G.; Desiato, R.; Giovannini, T.; Pinotti, L.; Tretola, M.; Gili, M.; Marchis, D. Gravimetric quantitative determination of packaging residues in feed from former food. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 1446–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, M.; Escher, F. Aluminium Foil as a Food Packaging Material in Comparison with Other Materials. Food Rev. Int. 2007, 23, 407–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinotti, L.; Giromini, C.; Ottoboni, M.; Tretola, M.; Marchis, D. Review: Insects and former foodstuffs for upgrading food waste biomasses/streams to feed ingredients for farm animals. Animal 2019, 13, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Y.R.; Nagel, J.R.; Rajamani, R.K. Eddy current separation for recovery of non-ferrous metallic particles: A comprehensive review. Miner. Eng. 2019, 133, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Raamsdonk, L.W.D.; Pinckaers, V.G.Z.; Vliege, J.J.M.; van Egmond, H.J. Examination of Packaging Materials in Bakery Products: A Validated Method for Detection and Quantification; RIKILT-Institute of Food Safety: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Calvini, R.; Luciano, A.; Ottoboni, M.; Ulrici, A.; Tretola, M.; Pinotti, L. Multivariate image analysis for the rapid detection of residues from packaging remnants in former foodstuff products (FFPs)-a feasibility study. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2020, 37, 1399–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) No.767/2009 of the European Parliament and of the council of 13 July 2009 on the placing on the market and use of feed, amending European Parliament and Council Regulation (EC) No 1831/2003 and repealing Council Directive 79/373/EEC, Commission Directive 80/511/EEC. Off. J. Eur. Union 2009, L 229/1, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Commision Regulation (EU) no. 1935/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 October 2004 on Materials and Articles Intended to Come into Contact with Food and Repealing Directives 80/590/EEC and 89/109/EEC. Off J. Eur. Union 2004, L 338, 4–17. [Google Scholar]
- Van Raamsdonk, L.W.D.; Rijk, R.; Schouten, G.P.J.; Mennes, W.; Meijer, G.A.L.; van der Poel, A.F.B.; de Jong, J. A Risk Evaluation of Traces of Packaging Materials in Former Food Intended as Feed Materials; Report 2011.002; RIKILT-Institute of Food Safety: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2011; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/241885675_A_risk_evaluation_of_traces_of_packaging_materials_in_former_food_products_intended_as_feed_materials (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Wang, J.; Zheng, L.; Li, J. A critical review on the sources and instruments of marine microplastics and prospects on the relevant management in China. Waste Manag. Res. 2018, 36, 898–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at Sea: Where Is All the Plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cincinelli, A.; Scopetani, C.; Chelazzi, D.; Lombardini, E.; Martellini, T.; Katsoyiannis, A.; Fossi, M.C.; Corsolini, S. Microplastic in the surface waters of the Ross Sea (Antarctica): Occurrence, distribution and characterization by FTIR. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, J.; Gago, J.; Otero, V.; Sobral, P. Microplastics in coastal sediments from Southern Portuguese shelf waters. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 114, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanhai, L.D.K.; Officer, R.; Lyashevska, O.; Thompson, R.C.; O’Connor, I. Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition along a latitudinal gradient in the Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GESAMP, Sources, Fate and Effects of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Global Assessment. 2015. Available online: http://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=XF2017002714 (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Law, K.L.; Thompson, R.C. Microplastics in the seas. Science 2014, 345, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Galloway, T.S. Ingestion of Nanoplastics and Microplastics by Pacific Oyster Larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14625–14632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, A.; Romano, N.; Galloway, T.; Hamzah, H. Virgin microplastics cause toxicity and modulate the impacts of phenanthrene on biomarker responses in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, A.; Golieskardi, A.; Bin Ho, Y.; Larat, V.; Salamatinia, B. Microplastics in eviscerated flesh and excised organs of dried fish. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, H.; Sigl, R.; Brauer, E.; Feyl, S.; Giesemann, P.; Klink, S.; Leupolz, K.; Löder, M.G.; Löschel, L.A.; Missun, J.; et al. Spatial and temporal variation of macro-, meso- and microplastic abundance on a remote coral island of the Maldives, Indian Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 116, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.-J.; Huang, X.-P.; Xiang, L.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Li, Y.-W.; Li, H.; Cai, Q.-Y.; Mo, C.-H.; Wong, M.-H. Source, migration and toxicology of microplastics in soil. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, M.C.; Ziersch, L.; Hempel, S. Microplastic transport in soil by earthworms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, G.O.; Ferrante, M.; Banni, M.; Favara, C.; Nicolosi, I.; Cristaldi, A.; Fiore, M.; Zuccarello, P. Micro- and nano-plastics in edible fruit and vegetables. The first diet risks assessment for the general population. Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainieri, S.; Barranco, A. Microplastics, a food safety issue? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 84, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, R.; Harris, R.; Mitchell, S. Plastic contamination of the food chain: A threat to human health? Maturitas 2018, 115, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.; Nash, R. Microplastics: Finding a consensus on the definition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (Contam). Presence of microplastics and nanoplastics in food, with particular focus on seafood. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e04501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medana, C. Analysis of Chemical Contaminants in Food. Toxics 2020, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermo, P.; Soddu, G.; Miani, A.; Comite, V. Quantification of the Aluminum Content Leached into Foods Baked Using Aluminum Foil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertl, K.; Goessler, W. Aluminium in foodstuff and the influence of aluminium foil used for food preparation or short time storage. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2018, 11, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severus, H. The Use of aluminium—Especially as Packaging Material—in the Food Industry. In Aluminium in Food and the Environment; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 1989; Volume 73, pp. 88–101. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, T.; Falk, S.; Rohrbeck, A.; Georgii, S.; Herzog, C.; Wiegand, A.; Hotz, S.; Boschek, B.; Zorn, H.; Brunn, H. Migration of aluminum from food contact materials to food—A health risk for consumers? Part I of III: Exposure to aluminum, release of aluminum, tolerable weekly intake (TWI), toxicological effects of aluminum, study design, and methods. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2017, 29, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshwal, G.K.; Panjagari, N.R. Review on metal packaging: Materials, forms, food applications, safety and recyclability. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 57, 2377–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, M.G.; White, S.M.; Flamm, W.; Burdock, G.A. Safety Evaluation of Dietary Aluminum. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 33, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO); World Health Organization. Evaluation of certain food additives. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 2005, 928, 1–156. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, B.; Taylor, S. The high throughput assessment of aluminium alloy corrosion using fluorometric methods. Part I-Development of a fluorometric method to quantify aluminium ion concentration. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, S. Aluminium Release from Food Packaging. European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). 2016. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/sites/default/files/event/160524a/160524a-p22.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- CITPA (International Confederation of Paper and Board Converters in Europe). Food Contact Guidelines for the Compliance of Paper & Board Materials and Articles. 2018. Available online: https://www.citpa-europe.org/sites/default/files/Food%20Contact%20Guidelines_2019_final.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Geueke, B. Food Packaging & Health: Paper and Board Food Packaging. Food packaging forum. 2016. Available online: https://www.foodpackagingforum.org/food-packaging-health/food-packaging-materials/paper-and-board (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Ozaki, A.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Fujita, T.; Kuroda, K.; Endo, G. Safety assessment of paper and board food packaging: Chemical analysis and genotoxicity of possible contaminants in packaging. Food Addit. Contam. 2007, 22, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottenio, D.; Escabasse, J.Y.; Podd, B. Packaging Materials 6: Paper and Board for Food Packaging Applications. ILSI Europe Packaging Material Task Force. 2004. Available online: https://www.pac.gr/bcm/uploads/6-paper-and-board-for-food-packaging-applications.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Binderup, M.-L.; Pedersen, G.A.; Vinggaard, A.M.; Rasmussen, E.S.; Rosenquist, H.; Cederberg, T.L. Toxicity testing and chemical analyses of recycled fibre-based paper for food contact. Food Addit. Contam. 2002, 19, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, M.; Grob, K. Is recycled newspaper suitable for food contact materials? Technical grade mineral oils from printing inks. Eu. Food Res. Tech. 2010, 230, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.P.; Batchelor, B.G.; Harris, I.P.; Perry, S.J. Intelligent visual inspection of food products. SPIE 1991, 1386, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Raamsdonk, L.W.D.; van der Zande, M.; Koelmans, A.A.; Hoogenboom, R.L.A.P.; Peters, R.J.B.; Groot, M.J.; Peijnenburg, A.A.C.M.; Weesepoel, Y.J.A. Current Insights into Monitoring, Bioaccumulation, and Potential Health Effects of Microplastics Present in the Food Chain. Foods 2020, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Lopes, I.; Andrady, A.L.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. A One Health perspective of the impacts of microplastics on animal, human and environmental health. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendran, R. Application of Computer Vision Technique on Sorting and Grading of Fruits and Vegetables. J. Food Process. Technol. 2011, 10, 146094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rosa, A.R.; Leone, F.; Cheli, F.; Chiofalo, V. Fusion of electronic nose, electronic tongue and computer vision for animal source food authentication and quality assessment—A review. J. Food Eng. 2017, 210, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geladi, P.; Grahn, H.F. Multivariate Image Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats-Montalbán, J.M.; de Juan, A.; Ferrer, A. Multivariate image analysis: A review with applications. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2011, 107, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvini, R.; Orlandi, G.; Foca, G.; Ulrici, A. Colourgrams GUI: A graphical user-friendly interface for the analysis of large datasets of RGB images. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2019, 196, 103915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, K.; Dodd, G. Analysis of discrimination mechanisms in the mammalian olfactory system using a model nose. Nature 1982, 299, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Methods | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Visual inspection (Stereomicroscopy) |
|
|
| Computer vision and multivariate image analysis |
|
|
| Electronic nose |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luciano, A.; Mazzoleni, S.; Ottoboni, M.; Tretola, M.; Calvini, R.; Ulrici, A.; Manoni, M.; Bernardi, C.E.M.; Pinotti, L. Former Foodstuff Products (FFPs) as Circular Feed: Types of Packaging Remnants and Methods for Their Detection. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13911. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142113911
Luciano A, Mazzoleni S, Ottoboni M, Tretola M, Calvini R, Ulrici A, Manoni M, Bernardi CEM, Pinotti L. Former Foodstuff Products (FFPs) as Circular Feed: Types of Packaging Remnants and Methods for Their Detection. Sustainability. 2022; 14(21):13911. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142113911
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuciano, Alice, Sharon Mazzoleni, Matteo Ottoboni, Marco Tretola, Rosalba Calvini, Alessandro Ulrici, Michele Manoni, Cristian E. M. Bernardi, and Luciano Pinotti. 2022. "Former Foodstuff Products (FFPs) as Circular Feed: Types of Packaging Remnants and Methods for Their Detection" Sustainability 14, no. 21: 13911. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142113911
APA StyleLuciano, A., Mazzoleni, S., Ottoboni, M., Tretola, M., Calvini, R., Ulrici, A., Manoni, M., Bernardi, C. E. M., & Pinotti, L. (2022). Former Foodstuff Products (FFPs) as Circular Feed: Types of Packaging Remnants and Methods for Their Detection. Sustainability, 14(21), 13911. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142113911








