1. Introduction
Business success in business is the final measure for economic actors, generally starting with micro or small businesses that require various determining factors. Scientific attention also appears in several perspectives, such as the competitive advantage approach in the article [
1,
2] in collaboration with the circular economy and Ref. [
3] analysis with information technology capabilities and organizational intelligence. This condition reflects that startups can contribute to technological growth and have a multiplier effect on many businesses. A startup is an organization designed to find the right business model which has become an important issue from a scientific perspective, such as [
4] an agile culture combining clan with adhocracy; the ability to nurture their absorptive, innovative, and adaptive capabilities effectively; and a human capital with adequate entrepreneurial skills, emotional attachment to and fitness with the start-up [
5]. This indicates that the components of entrepreneurial intention including knowledge sharing, reputation, social relations, and identity have a positive effect on the performance of digital startups mediated by social media [
6]. Meanwhile, adding the word ‘digital’ is intended for startup companies that integrate digitalization into their products and processes. The word ‘startup’ has also become very familiar in the entrepreneurial world, but only few know the meaning of the word ‘startup’ itself. Currently, a startup is defined as a business that is just beginning and it applies technological innovation to run its core business and solve a problem in society. Therefore, it has a ‘disruptive’ nature in an existing market/industry or even creates a new industry.
The success of the Business Incubator is a business support process that can accelerate the successful development of startup companies so that they can motivate the millennial generation to have new companies ranging from technology, and retail, to media. Although other aspects have appeared in some scientific literacy, sustainable supply chain management [
7], strategic improvisation and organizational memory [
8], human resources management strategies [
9], sustainable supply chain management [
10], and smart contracts improve procurement efficiency through cost, time, and quality [
11]. Some of the startups are growing and successful, but some of them have had to close their business due to one or two factors that the company did not do well. Previous research related to the determinants of the success of a startup business is as follows: According to [
12], acceptable factors to reflect success in a startup business in Surabaya are work ethic, motivation, work discipline, integrity, work involvement, communication, business ethics, and adaptation. An unacceptable factor to reflect on the success of a startup business in Surabaya is the marketing strategy. Ref. [
13] stated that the determinants of business success for startup businesses at Tyfons, Tlab, and Icube startups, were good human resources/teams, right timing, as well as sufficient ideas and funding. An agile culture combining clan with adhocracy; the ability to nurture their absorptive, innovative, and adaptive capabilities effectively; and human capital with adequate entrepreneurial skills, emotional attachment to, and fitness with the startup [
4]. It harmonizes with their agile culture, effectively enabling innovation programs enabled startups to remain focused on their innovation initiatives and not worry about scalability since the solutions collaborations between employees internally and with external actors enable rapidness to the market [
5]. The research gap in research tries to solve the issue of, in Indonesia today, there are thousands of startups that have spread throughout the region. Competition always haunts startup businessmen. This will be difficult for new startups, if they do not have strong business knowledge. Many new startups fail in their development, due to poor business planning, and are unable to compete with other market competitors and lack of investor funds. Therefore, new startups need an incubator program in building a business to be more focused and ready to be launched into the community, from developing a business to getting investors. Successful companies are constantly creating and distributing new knowledge and rapidly applying it to new technologies and products [
6]. From these several literacies, this study explores the factors needed in incubators and startups, according to certain conditions, and analyzes them into critical success factors.
3. Methods
A descriptive method with a quantitative approach is used in this study, with a time starting from February to September 2021. The scope of the study is in the work area of the Center for Human Resources Development and Research in Communication and Information Technology, Surabaya, East Java, Indonesia. This data collection is based on a government program in recording business data in each region in the province of East Java so that this data is taken collectively and simultaneously [
51]. Primary data were obtained from 100 people consisting of managers of 41 incubators and managers of 59 digital startups spread across the cities of Banyuwangi, Jember, Madiun, Malang, and Surabaya as respondents in this study. Characteristics of the selection of respondents are based on the demographic criteria of domicile location, type, and business turnover. The data collection instrument used interviews, observations, and questionnaire guidelines. The questionnaire was answered quantitatively with a Likert scale whose value was limited from one to five [
52]. A value of one means very uncertain; a value of two means undefined; the value of three means quite decisive; the value of four means determining; a value of five means very decisive [
14]. Data collection methods include (1) participation, direct involvement with incubator managers and digital startup managers; (2) Focus Group Discussion, to filter problems according to the focus of the study. The analysis is based on the success factors, in this study, among others: (1) synergy; (2) product; (3) process; (4) innovation management; (5) communication; (6) culture; (7) experience; (8) information technology; (9) innovation skills; (10) functional skills; and (11) implementation skills. To measure the adequacy of the sample and its significance value, we used KMO Measure, MSA, and Bartlett’s test. The critical point used for the KMO value is between 0.5 and 1, while for Bartlett’s test it is less than the significance level (α = 0.05) [
51]. The test results at this point are described as follows:
These results (
Table 1) indicate that factor analysis is appropriate to use to simplify the eleven startup success factors and formulate strategic recommendations to accelerate startup success. To determine the accuracy and reliability of the questionnaire in measuring respondents’ perceptions, the study instrument was tested [
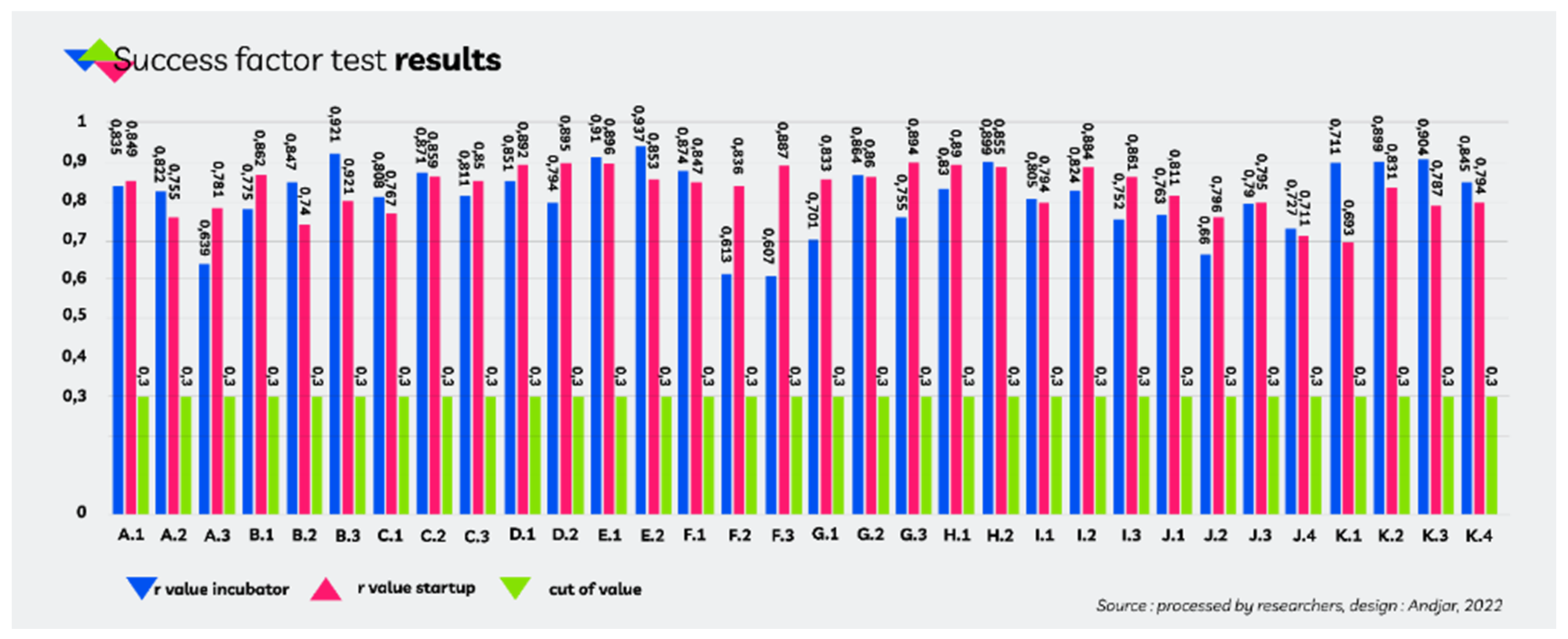
53]. Tests using the provisions of items and indicators of a research instrument that can be declared valid are having a positive correlation value greater than 0.30 (r > 0.30). The provision of a research instrument is declared reliable if it has a Cronbach Alpha value exceeding 0.60 (α cronbach ≥ 0.60). The description of the indicators of each success factor along with the results of instrument testing is presented in
Figure 1.
Referring to the test results of the instrument as shown in the table above, the overall value of r and Cronbach’s Alpha meets the critical value as the limit for determining an instrument to be valid and reliable. This shows that the instrument is declared valid and reliable; in other words, respondents understand part by part the statement of startup success factors, and there is a match between respondents’ perceptions with the purpose of this study.
4. Results
As defined by the National Business Incubator Association (NBIA), a Business Incubator is a business support process that can accelerate the successful development of startups and startups by providing entrepreneurs with the necessary resources and services. These services are typically developed or managed by incubator management and are offered both within the Business Incubator itself and through a network owned by the Business Incubator. Business incubators usually provide programs for early stage entrepreneurs or startups, which are designed to foster and accelerate the success of business development through a series of capital programs followed by partnership support or through coaching other business elements to turn the business into a profitable company, and have management over proper organization and finance, as well as being a sustainable company, so that it has a positive impact on society.
4.1. Respondent Character
A total of 100 people consisting of 41 incubators and 59 startups in the cities of Banyuwangi regency, Jember regency, Madiun regency, Malang regency, and Surabaya city as respondents in this research study have characteristics based on the demographic criteria of domicile location, type and business turnover. As many as 24% of incubators are domiciled in Banyuwangi regency and Malang regency, 22% in Madiun regency, 15% in Jember regency, and 12% in Surabaya city, and the rest did not answer. The majority of incubators domiciled in Jember are representatives of the UPT Kewirausahaan dan Inkubator Bisnis Teknologi (KIBT) Banyuwangi State Polytechnic and Poliwangi. The Jember incubator came from the Politeknik Negeri Jember and Primadhani. Madiun came from the Politeknik Negeri Madiun c, Malang came from the Politeknik Negeri Malang, and Surabaya came from the Inkubator Bisnis Politeknik Elektronika Negeri Surabaya. Startups as research subjects other than the incubator in this research study are also domiciled in these five cities with the majority domiciled in Banyuwangi (27%), Malang, and Jember (20% each), and the rest are domiciled in Madiun (14%) and Surabaya (12%). The types of businesses that are currently being carried out are also diverse, including the fields of food, beverage, handicrafts, services, and information and technology fields, one of which is the development of community security applications in Madiun City, property services, aquaculture and agriculture, convection, construction, even in the field of education. The variety in types of business also, of course, accompanies the variety in turnover in for each type of business. Detected based on the domicile area, Madiun and Surabaya excel with an estimated total business turnover from less than IDR 300 million (IDR ≤ 300 million) to IDR 4.5 billion. In more detail, Madiun includes services in the creative industry, application creation services, and property services. Surabaya with the types of business services, manufacturing, IT, aquaculture, and agriculture, where Surabaya is the second biggest city on the island of Java, which has the highest turnover range compared to startups domiciled in the other three regions (Banyuwangi, Jember, Malang). Jember with its startups, covering the types of food, beverage, manufacturing, and handicraft businesses, has a turnover ranging from IDR 300 million to IDR 500 million.
Meanwhile, Banyuwangi and Malang each have a type of business with a turnover of less than IDR 300 million with the types of business in food, beverage, convection, creative industry, software house, fertilizer, animal feed, and construction (
Figure 2).
4.2. Determinants of Incubator and Startup Success based on Respondent Priority Scale
Incubator and Startup respondent groups who are domiciled in five cities in this research study both agree that the eleven determinants of startup success need to be implemented in entrepreneurship. However, in practice, both incubators and startups have their priorities.
Regarding the priority scale according to the incubator, product is the main priority scale because it is a vocational-based institution. As product is the main thing, innovative and valuable products have a selling value in the market, and as the main factor in startup development, success is measured by the level of sales; the second priority is innovation skills because innovation makes a product survive in the market, is used in the context of product development, its application is carried out after careful planning, and innovation is what makes a product unique. The third priority is process and communication because the process supports the success, development, and marketing of products and determines production. Meanwhile, communication is the main means of conveying ideas and actions, and with clearer direction and communication, we can find solutions to problems that have the potential to hinder startups, as well as being a medium for creating teamwork. The three priority scales are compiled based on facts that have been known by the incubator as a companion for startup actors in entrepreneurship (see
Figure 3). Thus, product, innovation skills, process, and communication are four of the eleven determinants of startup success which, according to the incubator’s observations, have proven to be the determinants of success and have been implemented by startup actors.
Regarding the priority scale according to startup, synergy and communication are the main priority scales because they can improve the performance of each line, provide a benchmark for business stability and sustainability, and be the basis for implementing the vision and mission to reach targets, accelerate startup development progress and build individual trust in the team. Terms of communication are an important component because it is a means of initial interaction in forming a solid team and supporting the smooth production process. The second priority is the product because it is an important component, as well as business support and startup icon, while the third priority is innovation skills that make startups superior and competitive. Thus, synergy, communication, product, and innovation skills are four of the eleven critical success factors that have been implemented by startup actors (see
Figure 4).
4.3. Factor Analysis
The factor analysis in this research study is used to identify and evaluate the influencing factors and strategies for accelerating the success of digital startups. Furthermore, it is needed to find out whether the eleven business success factors used in this study are adequate for further analysis. The test uses the MSA with the limit of the anti-image correlation matrix value with a critical point of 0.5 which must be passed by the eleven factors.
These results indicate (
Figure 4) that the anti-image correlation matrix value of the eleven factors for both incubator and startup respondents has exceeded the critical point of 0.500. In other words, eleven factors measured from the incubator’s and startup’s point of view were deemed adequate for further analysis.
4.4. Simplification of Startup Success Factors from the Incubator and Startup Perspective
There are three simplification groups of the eleven success factors of digital startups based on the incubator’s point of view, whereas from the startup’s point of view, only one factor is formed. Further identified, the three factors formed based on the results of the 41 incubator’s perception measurement, it can be stated that factor 1 to factor 3 determines the urgency or priority factor chosen as a strategy in accelerating the success of digital startups. Factor 1 is declared as the top priority, factor 2 is the second priority, and factor 3 is the third priority. Meanwhile, from the startup point of view, the eleven success factors for startups are inseparable units in the implementation of entrepreneurship. These eleven factors are considered very important and, in the process, must be implemented together or simultaneously.
It can be seen that the incubator divides the eleven determinants of startup success into three priorities (
Figure 5), while startups do not divide the eleven factors into several priority levels. This shows that from the point of view of the incubator as a guide in the implementation of entrepreneurship, it provides three levels of urgency that can be used as a reference by startups in entrepreneurship and proceed step by step toward the point of success.
Meanwhile, the startup does not break down the eleven factors into several levels of urgency like the incubator, meaning that the startup views the eleven factors as an integral part that cannot be separated from its implementation from the initial process to finalization in one rotation of startup business activities. Although in the process, there are several of the eleven factors that cannot be carried out simultaneously, and in concept, they are interrelated and influence each other.
5. Discussion
So far, the determinants of startup success are determined based on the priority of the interests of the main components and supporting processes, development, and marketing. According to the Incubator Product point of view, innovation skills, process, and communication are four of the eleven determinants of startup success according to observations. The incubator has proven to be a determinant of success and has been implemented by startup actors. Meanwhile, according to digital startup business actors, synergy, communication, product, and innovation skills are four of the eleven critical success factors that have been implemented so far.
The difference in priority scale between the incubator and startup perspectives is a natural thing because startup business actors know the details from the planning, process, to the production marketing stages [
29]. This makes business actors have preferences ranging from the main factors to alternative factors that are used as a reference in the entrepreneurship process, in addition to getting guidance from the incubators. Examining in more detail with factor analysis, the eleven factors that support the success of digital startups are simplified into three parts, which are then identified as a scale of urgency in further implementation according to the incubator’s point of view. Meanwhile, according to startup, it is not simplified and instead includes eleven factors into one main priority [
30]. These conditions are described in detail to form a strategy to accelerate the success of startups that is compiled from the point of view of the incubator as an evaluator and the startup as a business actor (see
Table 2).
From the previous description, the strategies that need to be implemented to accelerate the success of digital startup businesses are divided into stages according to development priorities. The top priority, the most important and main strategy to be taken immediately in accelerating the success of a startup, is related to two things: synergy and product. Synergy—building synergies is related to how each member of the company can help each other and share to improve the quality of knowledge and skills, which is done by sharing knowledge through cross-technology, cross-hierarchical and cross-functional exchanges [
54]. Regarding synergies, the strategies that need to be implemented are: providing an understanding of startups, that to build a business, good cooperation is needed with a common vision and mission of the company so that knowledge and skills are needed in developing a business through the creation of products and services, both those that are general or by the field and position handled. Product—product development needs to be carried out by startups to produce products that are easily accessible, easy to use, and are consistent with the aesthetics of a digital product service, so that product users will feel the ease and comfort of using the product. Regarding products, the strategies that need to be implemented are: increasing understanding of product knowledge, especially related to design, features, brand names, product variations, quality, services, packaging, and returns, as well as providing ease of access and use, thus providing convenience and convenience for users [
55].
The second priority, in accelerating startup success is related to five variables, including process, management of innovation, information technology, innovation skills, and functional skills, so the strategies implemented are also related to these variables. Process—how startups run the product development process from concept to customer to provide solutions needed by customers, which involves: (a) bundling, combining components of digital product and service portfolios to provide clear boundaries and relationships between products and services; (b) devices, information about hardware and software used in the development phase; and (c) channels, related to the use of digital information channels, which include: software platforms, operating systems, and web services. Regarding the process, the strategies that need to be implemented are: building a good understanding for startups in product development from concept to product to customer that provides solutions according to customer needs, which include: (a) merging digital product and service components; (b) use of software and hardware in development; and (c) the use of software, operating systems, and web services. Management of innovation— how startups can manage innovation so that they can run the product development process quickly while reducing the uncertainty that will occur which includes: management style, consistent stages of innovation management, problem-solving and good planning. Regarding the management of innovation, the strategies that need to be implemented are: building knowledge and skills in managing innovation development, through a productive management style, good planning, consistent innovation, and emphasis on problem-solving. Information Technology—related to information technology is how startups can use information technology to support their business success, either as the main product or as a support. Regarding information technology, the strategies that need to be implemented are: increasing the understanding and skills of startups in utilizing information technology to support business success. Innovation skills—innovation skills involve skills that should be possessed by a good startup: basic skills, academic skills, technical skills, generic skills, soft skills, managerial skills, and entrepreneurial skills that contribute to innovation. Regarding innovation skills, the strategies that need to be implemented are: developing skills, that can be basic, academic, technical, or generic, soft skills, management, and entrepreneurship that supports innovation. Functional skills are related to how startups can use the information and digital technology, in the form of (a) the ability to use software and hardware; (b) understanding of internet technology; (c) understanding of hardware/system architecture; and (d) ability to troubleshoot software and hardware problems. In terms of functional skills, the strategies that need to be implemented are: developing startup skills in using information and digital technology which includes: (a) software and hardware; (b) internet technology; (c) system architecture; (d) solving software and hardware problems [
56].
The third priority, or final priority in accelerating startup success, is related to four variables, namely: communication, culture, experience, and implementation skills. Communication is about how startups inform the value of products and industry service standards so that they can be quickly accepted by the industry, market, and potential consumers, where this communication can use online or offline channels [
57]. Concerning communication, the strategies that need to be implemented are increasing understanding and skills in understanding the value of products and service standards accepted by the industry, market, and consumers to be delivered online and offline. Culture is related to how startups create a comfortable and conducive working atmosphere to support company members to interact and communicate to make startups have a solid team [
58], which includes: (1) structured, flexible, and balanced work rhythms; (2) the availability of a special time for improvisation and innovation by each employee; and (3) the existence of a coordination mechanism in the process of improvisation and innovation. Concerning culture, the strategies that need to be implemented are: increasing the understanding of startups in building a comfortable and conducive work atmosphere through interaction and communication between members of the startup team related to (a) work rhythm and (b) improvisation and innovation. Experience in previous projects allows the company to develop the ability to improve subsequent innovations so that they can develop skills in technology, production, and marketing, which enable the use of learning by acquiring advantages and maximizing the experience in managing the organization or producing better products. Regarding the experience, the strategies that need to be implemented are increasing understanding of the use of experience to support the learning by completing the process of managing the business. Implementation skills—this is the startup’s ability to anticipate and prepare policies related to product implementation used by users, including (a) knowledge of company practices and organizational protocols; (b) understanding and effective use of industrial terminology in product implementation; (c) knowledge of and compliance with the requirements of industry norms; and (d) knowledge of and compliance with company and product standards. Regarding implementation skills, the strategies that need to be implemented are: improving startup capabilities related to (a) company practices and organizational protocols; (b) use of industrial terminology in product implementation; (c) knowledge of and compliance with the requirements of industry norms, as well as company and product standards.
One of the Indonesian government’s programs for business incubators and startups is to provide training to nurture the talents of digital startup founders. The full activity is completed online. Preparing for mentoring and becoming a school for founders (startup founders) can be accessed anywhere in tier 1, tier 2, or tier 3 cities. In the startup incubator, there are many activities that are usually carried out, starting from introducing startups in front of investors, to introducing products and even introducing the startup business model itself. Then, the startup gets a direction and guidance to be able to perfect the concept, product, marketing and various things that can accelerate the growth of the business. Usually, the startup incubator program will take approximately six months. This is because not only startups that already have businesses that will be incubated, but startups whose products are still in the form of concepts or ideas will also be incubated. Through this program, the Ministry believes there will be more accelerated start-ups that can contribute to increasing the number of unicorns and even decacorns in Indonesia, which accelerates the national digital transformation process. With the programs that have been presented, it is hoped that more people in Indonesia, especially the younger generation, are interested and actively participate in creating businesses by utilizing advanced technology and digitalization.
6. Conclusions
According to Inkubar’s point of view, the factors that influence the success of digital startups are eleven success factors with three different priorities. The priority levels are as follows: the top priority consists of two factors, namely: synergy and product; the second priority consists of five factors, namely: process, management of innovation, information technology, innovation skills, and functional skills; the third priority consists of four factors, namely: communication, culture, experience, and implementation skills. Meanwhile, in the view of the incubator, all factors have the same priority in supporting the success of digital startups, which include the following factors: synergy, product, process, management of innovation, communication, culture, experience, information technology, innovation skills, functional skills, and implementation skills.
Strategies that need to be implemented to accelerate the success of digital startup businesses are divided into stages according to development priorities that are the incubator’s concern. Top priority, the most important and main strategy to be taken immediately in accelerating the success of a startup, is related to two things: synergy and product. Synergy factor strategy to build a business requires good cooperation with the same vision and mission of the company so that knowledge and skills are needed in developing business through the creation of products and services, both generals in nature and by the fields and positions handled. Product factor strategy increases understanding of product knowledge, especially related to design, features, brand name, product variety, quality, service, packaging, and returns, as well as providing ease of access and use, thus providing convenience and comfort for users.
Second priority, the second priority in accelerating startup success is related to five variables, including process, management of innovation, information technology, innovation skills, and functional skills. Building a good understanding for startups in product development from concept to product to customer that provides solutions according to customer needs, which include: (a) combining components of digital products and services; (b) use of software and hardware in development; and (c) the use of software, operating systems, and web services. Building knowledge and skills in managing innovation development, through productive management style, good planning, consistent innovation, and emphasis on problem-solving. Improving the understanding and skills of startups in utilizing information technology to support business success. Develop skills: basic, academic, technical, generic, soft skills, management, and entrepreneurship that support innovation. Develop startup skills in using information and digital technology which includes: (a) software and hardware; (b) internet technology; (c) system architecture; (d) solving software and hardware problems.
The third or final priority in accelerating startup success is related to four variables, namely: communication, culture, experience, and implementation skills. Improving understanding and skills in understanding the value of products and service standards that are accepted by the industry, markets, and consumers to deliver online and offline. Improving the understanding of startups in building a comfortable and conducive working atmosphere through interaction and communication between members of the startup team related to (a) work rhythm, and (b) improvisation and innovation. Increasing understanding of the use of experience to support the learning by doing the process of managing a business. Improve startup capabilities related to (a) enterprise practices and organizational protocols; (b) use of industrial terminology in product implementation; (c) knowledge of and compliance with the requirements of industry norms, as well as company and product standards.
The recommendation from this research is the need for educational and training activities for startups carried out by the Business Incubator or Techno Park. The activities are carried out to take into account the priority scale so that the success of startups can be achieved gradually, according to the level of importance and the availability of the education and training implementation budget.