Innovation Systems and Sustainability. Development of a Methodology on Innovation Systems for the Measurement of Sustainability Indicators in Regions Based on a Colombian Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Frameworks
2.1. Sustainable Development-Sustainability
2.2. Innovation System (IS)
2.3. Sustainable Innovation Systems (SIS)
3. Materials and Methods
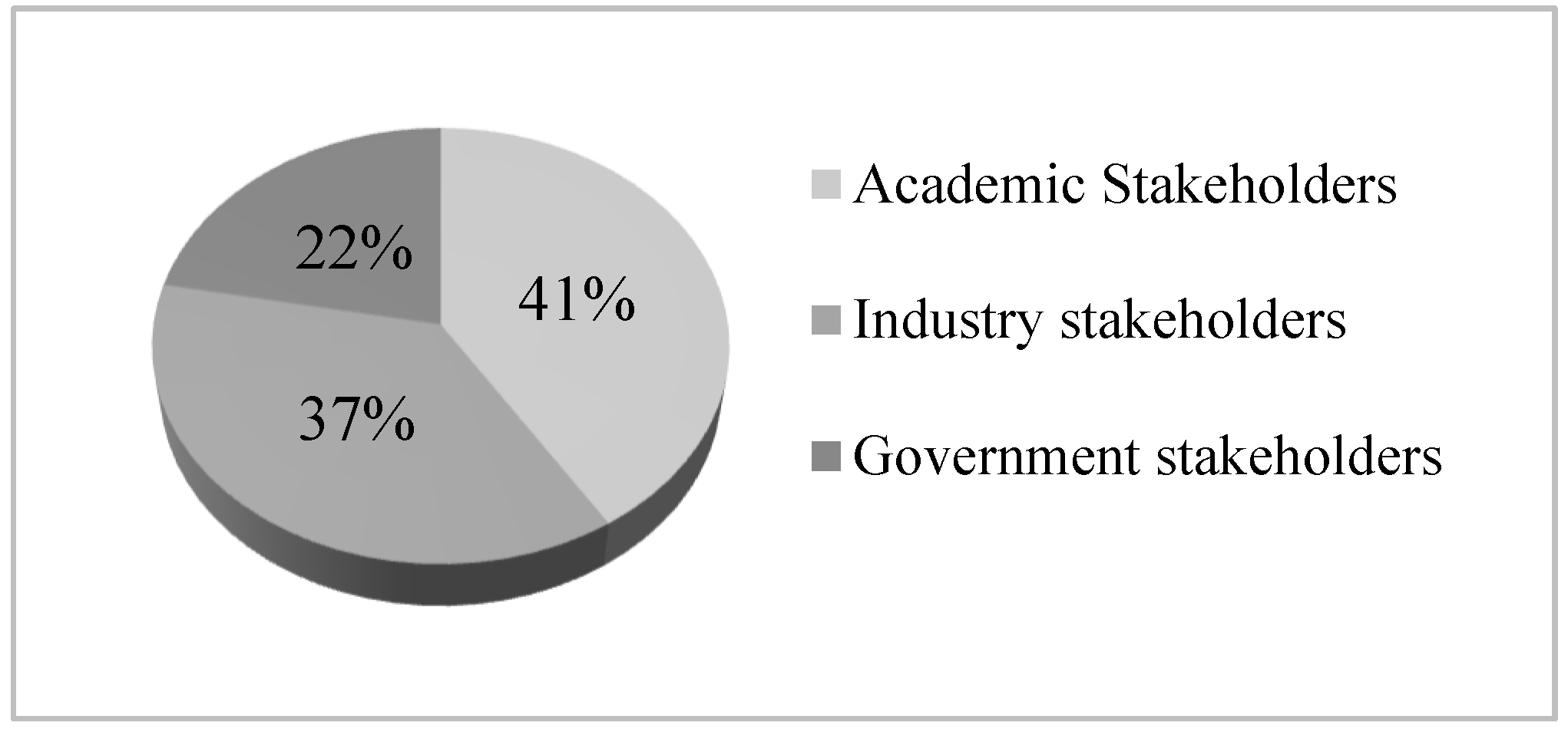
3.1. Stakeholder Selection
- Public and private sectors (companies, associations, and private sector organizations).
- Educational community (human resources (teachers and administrative staff), educational organizations, academic communities, and research groups) [43].
3.2. Literature Review
- Articles were obtained from the SCOPUS database using the search equation, TITLE-ABS-KEY (“innovation system*”) W/3 sustainab*.
- International agreements and consensus that set sustainability goals.
- National regulations related to sustainability [44].
3.3. Questionnaire Construction
3.4. Delphi Methodology (Evaluation of the Relevance and Congruence of the Questions in the Questionnaire)
- Congruence: each expert assesses whether the content of each item included in the questionnaire reflects the specified objectives, “1” if the content is specified, “−1” if he/she believes it does not measure it, and “0” if there are doubts about whether it measures it [11].
- Relevance: each expert assesses whether the content of each item included in the questionnaire reflects the relevance of each item on a Likert scale from 1 to 5, to measure the proposed objective; from “not relevant at all” (1); to “totally relevant” (5) [11].
3.5. Development of the Questionnaire as an Objective Tool
- Academy
- Government
- Industry
- NGOs in the region
3.6. Application of the Tool (Questionnaire) in the Target Group
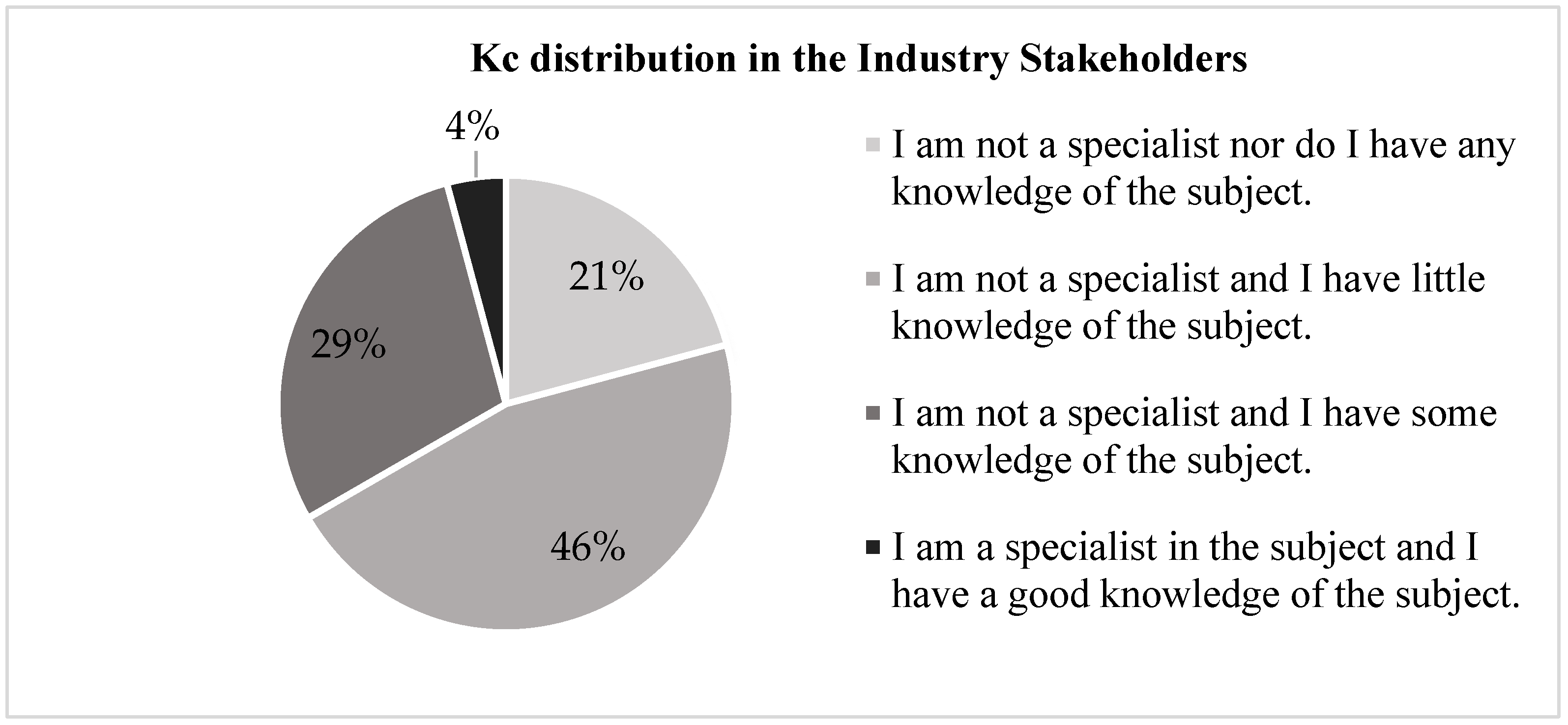
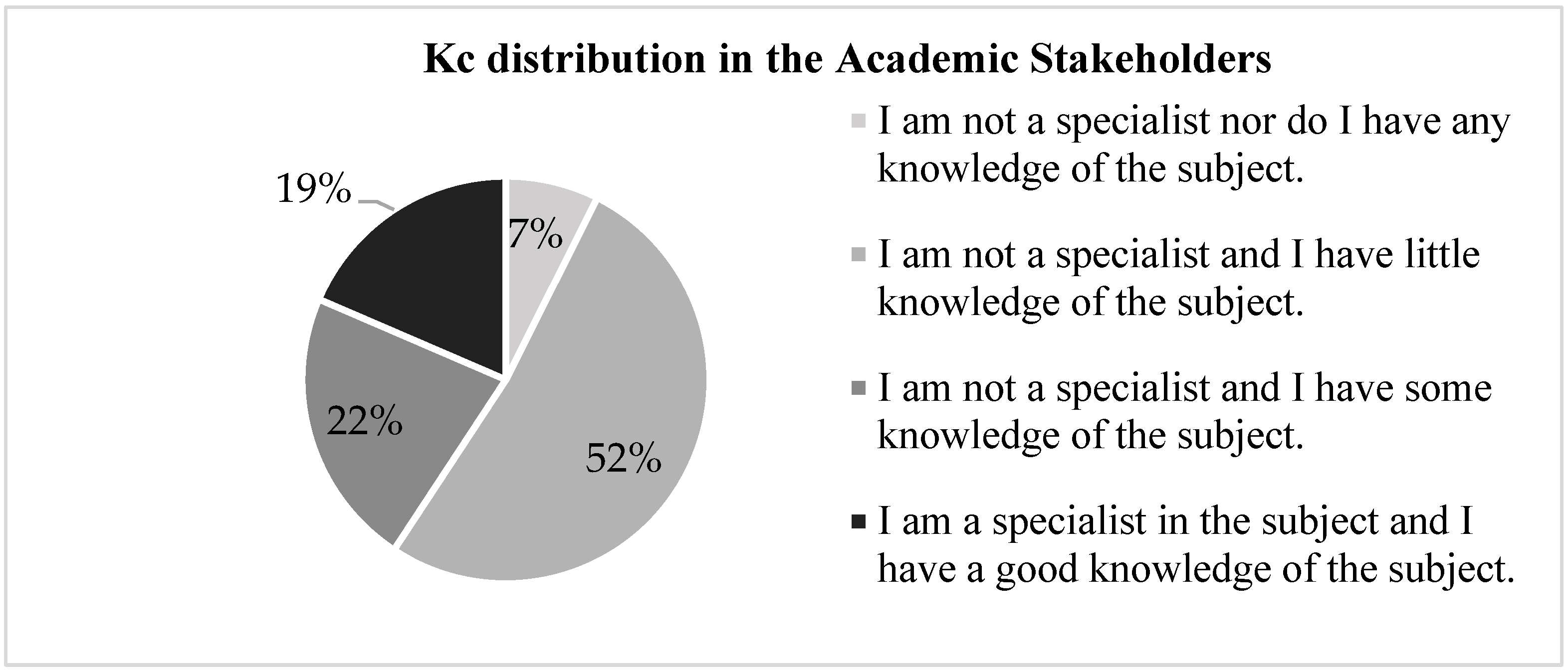
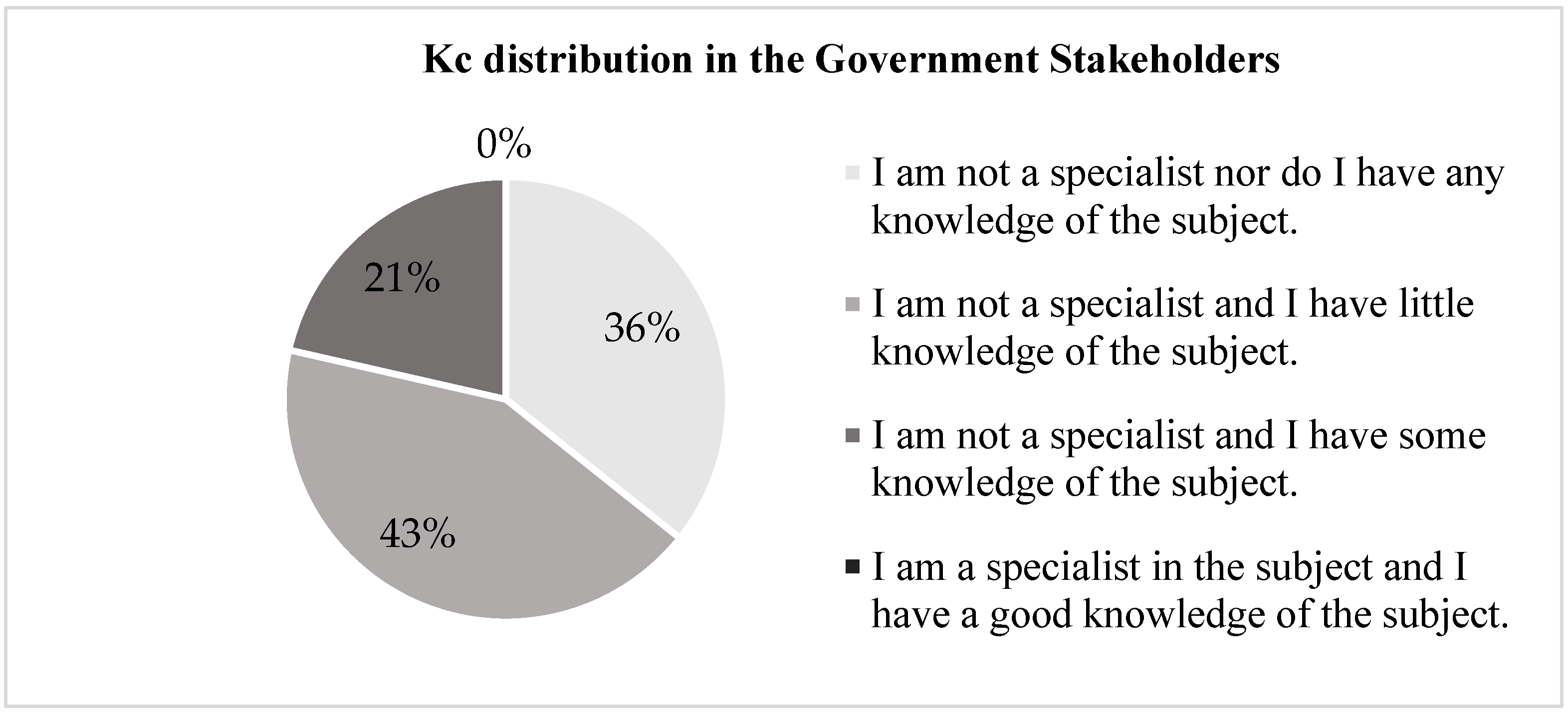
3.7. Analysis of the Application Tools Results and Coefficient of Expert Competence “K”
- Kc= refers to the “coefficient of knowledge” or information that the expert has about the topic or problem posed. It is calculated from the valuation made by the expert himself on a scale of 0 to 10, multiplied by 0.1.
- If K is greater than or equal to 0.8, then there is a high influence from all sources.
- If K is greater than or equal to 0.7, and less than 0.8, then there is a medium influence from all sources.
4. Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Sustainability Variables to Be Considered in Innovation Systems
5.2. Constraints to Sustainability Measurement
5.3. Innovation as a Transverse Axis to Sustainability
5.4. Case Study on the Measurement of a Sustainable Innovation System in the Study Region in Colombia
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López Rodríguez, R. Sustainable Development: A Utopia or an Urgent Need? Complut. Educ. J. 1998, 9, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Gil, C. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): A Critical Review. Eco-Soc. Relat. Glob. Chang. Pap. 2017, 140, 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Canel Bermúdez, M. Why Do We Need a Government Management System Based on Science and Innovation? Ann. Cuba. Acad. Sci. 2021, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Velázquez Álvarez, L.V.; Vargas Hernández, J.G. Sustainability as a Model for Responsible and Competitive Development. Nat. Resour. Environ. Eng. 2012, 11, 97–107. [Google Scholar]
- UNCTAD. A Framework for Science, Technology and Innovation Policy Reviews; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2020; ISBN 9789210039697. [Google Scholar]
- Bernal-Jiménez, M.C.; Rodríguez-Ibarra, D.L. Information and Communication Technologies as a Factor of Business Innovation and Competitiveness. Sci. Tech. 2019, 24, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Sossa, J.W.Z.; López Montoya, O.H.; Acosta Prado, J.C. Determinants of a Sustainable Innovation System. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021, 30, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, T.; Pease, A. RT Delphi: An Efficient, “Round-Less” Almost Real Time Delphi Method. Technol. Soc. Chang. 2006, 73, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, G.; Wright, G. The Delphi Technique as a Forecasting Tool: Issues and Analysis. Int. J. 1999, 15, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zartha Sossa, J.W.; Halal, W.; Hernandez, R. Delphi Method: Analysis of Rounds, Stakeholder and Statistical Indicators. Foresight 2019, 21, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Liaño, B.G.-G.; Pascual-Ezama, D. Delphi Methodology as a Technique for Studying Content Validity. Ann. Psychol. 2012, 28, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, W.J.; Mwebaza, R. The Role of the Climate Technology Centre and Network as a Climate Technology and Innovation Matchmaker for Developing Countries. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayneko, D.; Dayneko, A.; Dayneko, V. Common Problems of the Forest Industry and Institutional Background for Its Innovative Development in Baikal Region. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 574, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez Estrada, A.; Lara Coba, N.R. Proposal for the Design of a Business Innovation System for a Company in the Textile-Apparel Sector; Monografia; Pontificia Javeriana University: Bogota, Colombia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Brundtland, G.H. Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development (Brundtland Commission) Our Common Future; The World Commission on Environment and Development: Geneva, Switzerland, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Pansera, M. Innovation System for Sustainability in Developing Countries: The Renewable Energy Sector in Bolivia. Int. J. Innov. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 7, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grovermann, C.; Wossen, T.; Muller, A.; Nichterlein, K. Eco-Efficiency and Agricultural Innovation Systems in Developing Countries: Evidence from Macro-Level Analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Río, P.; Peñasco, C.; Romero-Jordán, D. What Drives Eco-Innovators? A Critical Review of the Empirical Literature Based on Econometric Methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 2158–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, W.; Hjelm, O.; Clausen, J.; Bienkowska, D. Roles of Intermediaries in Supporting Eco-Innovation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 205, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdá, E.; Khalilova, A. Circular Economy. Ind. Econ. 2016, 401, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen, J.E.; Koskivaara, A.; Makkonen, T.; Yakusheva, N.; Malkamäki, A. Resilient Cross-Border Regional Innovation Systems for Sustainability? A Systematic Review of Drivers and Constraints. Innov. Eur. J. Soc. Sci. Res. 2021, 34, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations; CEPAL. The 2030 Agenda and Its Sustainable Development Goals; United Nations: Santiago, Chile, 2018; ISBN 9789210586436. [Google Scholar]
- Ermilova, M.; Maksimova, T.; Zhdanova, O.; Zohrab, D. Improvement of Innovation Systems in Sustainable Economic Development. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 135, 04027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firsova, A.A.; Makarova, E.L.; Tugusheva, R.R. Institutional Management Elaboration through Cognitive Modeling of the Balanced Sustainable Development of Regional Innovation Systems. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2020, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Alphen, K.; Hekkert, M.P.; Turkenburg, W.C. Accelerating the Deployment of Carbon Capture and Storage Technologies by Strengthening the Innovation System. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2010, 4, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, T.; Dao, V.T. A Longitudinal Exploratory Investigation of Innovation Systems and Sustainability Maturity Using Case Studies in Three Industries. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2019, 32, 668–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Vivanco, A.; Bernardo, M.; Cruz-Cázares, C. Sustainable Innovation through Management Systems Integration. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 1176–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.; Winter, S. In Search of Useful Theory of Innovation. Res. Policy 1977, 6, 36–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, C. Techonology Policy and Economic Performance; Lessons from Japan; Frances Pinter Publishers: London, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Lundvall, B.-Å. Product Innovation and User-Producer Interaction; Aalborg University Press: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1985; ISBN 8773073040. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari, M.; Khodayari, M.; Khaleghi, A.; Danesh, M.; Padash, H. Technological Innovation Research in the Last Six Decades: A Bibliometric Analysis. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2020, 24, 1806–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preobrazhenskiy, Y.V.; Firsova, A.A.; Muzhenskiy, D.A. Spatial Inequality of Innovation Development in Russia. WSEAS Trans. Environ. Dev. 2020, 16, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markard, J.; Hekkert, M.; Jacobsson, S. The Technological Innovation Systems Framework: Response to Six Criticisms. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2015, 16, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundvall, B.-Å. National Systems of Innovation: Towards a Theory of Innovation and Interactive Learning; Anthem Press: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-1-78-308596-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kanda, W.; Kuisma, M.; Kivimaa, P.; Hjelm, O. Conceptualising the Systemic Activities of Intermediaries in Sustainability Transitions. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2020, 36, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satalkina, L.; Steiner, G. Digital Entrepreneurship and Its Role in Innovation Systems: A Systematic Literature Review as a Basis for Future Research Avenues for Sustainable Transitions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Weitz, N.; Carlsen, H.; Nilsson, M.; Skånberg, K. Towards Systemic and Contextual Priority Setting for Implementing the 2030 Agenda. Sustain. Sci. 2018, 13, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urmetzer, S.; Lask, J.; Vargas-Carpintero, R.; Pyka, A. Learning to Change: Transformative Knowledge for Building a Sustainable Bioeconomy. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 167, 106435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaile, M.P.; Urmetzer, S.; Blok, V.; Andersen, A.D.; Timmermans, J.; Mueller, M.; Fagerberg, J.; Pyka, A. Innovation Systems for Transformations towards Sustainability? Taking the Normative Dimension Seriously. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cillo, V.; Petruzzelli, A.M.; Ardito, L.; del Giudice, M. Understanding Sustainable Innovation: A Systematic Literature Review. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019, 26, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, Y.K.; Park, J. The Evolution of N-Helix of the Regional Innovation System: Implications for Sustainability. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 29, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Education Stakeholder. Characterization (Value and Interest Groups); Department of Education Stakeholder: Bogotá, Colombia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Spanish Standard UNE 166006; R&D&I Management: R&D&i Management: Monitoring and Intelligence System. UNE: Madrid, Spain, 2018; p. 30.
- Cabero, J.; Barroso, J. The Use of Expert Judgment for Assessing ICT: The Coefficient of Expert Competence. Bordon 2013, 65, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Sossa, J.W.Z.; Montes Hincapié, J.M.; Toro Jaramillo, I.D.; Villada, H.S. Delphi Method—Proposal to Calculate the Number of Experts in a Delphi Study on Biodegradable Packaging to 2032. Espacios 2014, 35, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environment and Sustainable Development Ministry of Environment and Sustainable Development; Ministry of Commerce, Industry and Tourism. National Circular Economy Strategy: Closing Material Cycles, Technological Innovation, Collaboration and New Business Models. Bogotá, Colombia. 2019. Available online: https://circulareconomy.europa.eu/platform/sites/default/files/national_circular_economy_strategy.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- DNP CONPES 3934—Green Growth Policy; National Planning Department and National Council on Economic and Social Policy: Bogota, Colombia, 2018; pp. 1–114.
- Manyweathers, J.; Hernández-Jover, M.; Lynne, H.; Loechel, B.; Kelly, J.; Felton, S.; El Hassan, M.; Woodgate, R.; Maru, Y. The Australian Science Communicators Conference 2020: Are We Foot and Mouth Disease Ready? J. Ofsci. Commun. 2020, 19, C01. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Fang, H.; Zhang, F.; Fang, S. The Spatial Analysis of Regional Innovation Performance and Industry-University-Research Institution Collaborative Innovation-an Empirical Study of Chinese Provincial Data. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, E.L.; Firsova, A.A. Computer Cognitive Modeling of the Innovative System for the Exploration of the Regional Development Strategy. In Proceedings of the CEUR-WS Second Workshop on Computer Modelling in Decision Making; CMDM: Saratov, Russia, 2017; Volume 2018, pp. 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Purkus, A.; Hagemann, N.; Bedtke, N.; Gawel, E. Towards a Sustainable Innovation System for the German Wood-Based Bioeconomy: Implications for Policy Design. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 3955–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekkert, M.P.; Suurs, R.A.A.; Negro, S.O.; Kuhlmann, S.; Smits, R.E.H.M. Functions of Innovation Systems: A New Approach for Analysing Technological Change. Technol. Soc. Chang. 2007, 74, 413–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergek, A.; Jacobsson, S.; Carlsson, B.; Lindmark, S.; Rickne, A. Analyzing the Functional Dynamics of Technological Innovation Systems: A Scheme of Analysis. Res. Policy 2008, 37, 407–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukkanen, M.; Patala, S. Analysing Barriers to Sustainable Business Model Innovations: Innovation Systems Approach. Int. J. Innov. Manag. 2014, 18, 1440010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkiş, Ş. Sustainability-Oriented Innovation System Analyses of Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, Turkey and Singapore. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 130, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkiş, Ş. Sustainable R & D and Innovation System Comparisons of India, Russia, Mexico and Turkey. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2017, 28, 315–331. [Google Scholar]
- Van Someren, T.C.R.; Van Someren-Wang, S. Strategic Innovation in Russia: Towards a Sustainable and Profitable National Innovation System; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 978-3-31-941081-4. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, T. Development of Innovation Systems for Small Island States: A Functional Analysis of the Barbados Solar Water Heater Industry. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2016, 31, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J. Research on Dynamic Mechanism of Green Coal Mine Construction. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 535, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djeflat, A. Building Systems for Innovation “take off” in African Economies. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 2009, 1, 53–75. [Google Scholar]
- Brent, A.C. Transdisciplinary Approaches to Engineering R&D: Importance of Understanding Values and Culture. In Handbook of Sustainable Engineering; Kauffman, J., Lee, K.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 91–111. ISBN 978-1-40-208939-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rubach, S. Collaborative Regional Innovation Initiatives: A Booster for Local Company Innovation Processes? Syst. Pract. Action Res. 2013, 26, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Li, Q.; Dao-Ping, W.; Zhou, C. Sustainability Evaluation of Regional Innovation System Based on Synthetic Niche-Fitness. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2011, 31, 927–935. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzeretti, L.; Capone, F.; Cinti, T. The Regional Development Platform and “Related Variety”: Some Evidence from Art and Food in Tuscany. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2010, 18, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laster, S. Model-Driven Design: Systematically Building Integrated Blended Learning Experiences. J. Asynchron. Learn. Netw. 2010, 14, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, B. Designing the Conditions for an Innovation System for Sustainable Development in a Knowledge Democracy. In Knowledge Democracy Consequences for Science, Politics, and Media; Veld, R.J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 105–112. ISBN 978-1-11-913053-6. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, F.A.; Sanders, C.B.; Lehoux, P. Imagining Value, Imagining Users: Academic Technology Transfer for Health Innovation. Soc. Sci. Med. 2009, 68, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossink, B.A.G. Nation-Wide Development of Sustainable Production Patterns: The Case of 16 Years of Sustainability in Dutch Residential House Building. Int. J. Glob. Environ. Issues 2009, 9, 356–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floricel, S.; Dougherty, D.J.; Miller, R.; Ibanescu, M. Network Structures and the Reproduction of Resources for Sustainable Innovation. Int. J. Technol. Manag. 2008, 41, 379–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstlberger, W. Regional Innovation Systems and Sustainability-Selected Examples of International Discussion. Technovation 2004, 24, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Báez, C.L. Measuring the Sustainable Development Goals in the European Union through Composite Indicators; Working Papers; Fundación Carolina: Madrid, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasencia Soler, J.A.; Marrero Delgado, F.; Bajo Sanjuán, A.M.; Nicado García, M. Models for Assessing the Sustainability of Organizations. Manag. Stud. 2018, 34, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glac, K. Triple Bottom Line. Wiley Encycl. Manag. 2015, 2, 36–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez Pérez, R.M. Sustainability Indicators: Usefulness and Limitations. Teoría Prax. 2012, 8, 102–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podcameni, M.G.; Cassiolato, J.E.; Lustosa, M.C.; Marcellino, I.; Rocha, P. Exploring the Convergence between Sustainability and Local Innovation Systems from a Southern Perspective: What Brazilian Empirical Evidence Has to Offer. Local Econ. 2019, 34, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljovkina, A.O.; Dusseault, D.L.; Zaharova, O.V.; Klochkov, Y. Managing Innovation Resources in Accordance with Sustainable Development Ethics: Typological Analysis. Resources 2019, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, T.; Mohan, K. Sustainability Innovation Systems (SIS): IT Investments and Stages of Sustainability Maturity. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First Americas Conference on Information Systems, Fajardo, Puerto Rico, 13–15 August 2015; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, M.; Christensen, P.; Johnson, B. Partnerships and Sustainable Regional Innovation Systems: Special Roles for Universities? In Facilitating Sustainable Innovation through Collaboration; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis-Jones, J.; Phiri, A.; Chibwe, T.; Gondwe, T.; Nhamo, N. Taking to Scale Adaptable Climate Smart Technologies; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 978-0-12-810522-1. [Google Scholar]
- DNP CONPES 4021; National Policy for the Control of Deforestation and the Sustainable Management of Forests. Departamento Nacional de Planeación: Bogotá, Colombia, 2020; pp. 1–110.
- Karlsson, R.; Backman, M.; Djupenström, A. Sustainability Considerations and Triple-Helix Collaboration in Regional Innovation Systems; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; ISBN 978-9-04-813158-7. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. 21 Agenda. In Proceedings of the United Nations Conference on Environment & Development, Rio de Janerio, Brazil, 3–14 June 1992. [Google Scholar]
- DNP CONPES 3918; Strategy for the Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) in Colombia. Departamento Nacional de Planeación: Bogotá, Colombia, 2018; p. 267.
- DNP CONPES 3697; Policy for the Commercial Development of Biotechnology from the Sustainable Use of Biodiversity. Departamento Nacional de Planeación: Bogotá, Colombia, 2011.
- DNP CONPES 3510; Policy Guidelines to Promote the Sustainable Production of Biofuels in Colombia. Departamento Nacional de Planeación: Bogotá, Colombia, 2008; p. 44.
- Raina, R.S. Innovation Capability for Agrobiotechnology: Policy Issues. Biotechnol. Dev. Monit. 2003, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- DNP CONPES 3901; Favorable Opinion for the Nation to Contract External Public Credit Operations to Partially Finance the Sustainable Colombia Program. Departamento Nacional de Planeación: Bogotá, Colombia, 2017.
- Jacobsson, S.; Bergek, A. Innovation System Analyses and Sustainability Transitions: Contributions and Suggestions for Research. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2011, 1, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.S.; Nawata, K.; Huang, C.Y. Systemic Functions Evaluation Based Technological Innovation System for the Sustainability of IoT in the Manufacturing Industry. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiullin, M.R.; Chekhlomin, S.V.; Aksyanova, A.V. A System Approach to Assessing the Effectiveness of Regional Innovation Systems in the Concept of Statistical Sustainability. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Rev. 2019, 7, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossink, B.A.G. Interdependent Sustainable Innovation Processes and Systems in Dutch Residential Building. J. Green Build. 2008, 3, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.Y.; Yu, B. Research on Resource Conservation-Oriented Reconfiguration of the Regional Innovation System. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Information Management, Innovation Management and Industrial Engineering, Kunming, China, 26–28 November 2010; Volume 4, pp. 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrgović, P.; Jošanov-Vrgović, I. Open Innovation Systems in Developing Countries: Sustainable Digital Networks and Collaboration in SMEs. Dyn. Relatsh. Manag. J. 2018, 7, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Johannesburg Declaration on Sustainable Development; Division for Sustainable Development: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2002; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, S.W.; Chang, C.L.; Liu, S.M. Innovation System Assessment Model for Sustainability Planning in Taiwan. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiati, R.; Siregar, S.; Marhaendrajana, T.; Wahyuningrum, D. Sustainable Innovation System Using Process of Bagasse Become Sodium Lignosulfonate Surfactant for Enhanced Oil Recovery. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 43, 01026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Gao, P. Industry Sustainability and Innovation System: A Comparative Case Study in China. In Innovation in the Asia Pacific; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T. Radically Resolving User Needs Is Good for Business and Environment. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference, DUXU 2016, Held as Part of HCI International 2016, Toronto, ON, Canada, 17–22 July 2016; pp. 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A. Establishing a System for Innovation in a Professional Services Firm. Bus. Horiz. 2016, 59, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunxiang, L.; Ling, X. Research on the Agricultural Technology Innovation Achievements of China. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Information Management, Innovation Management and Industrial Engineering, Xi’an, China, 23–24 November 2013; Volume 1, pp. 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Marxt, C.; Brunner, C. Analyzing and Improving the National Innovation System of Highly Developed Countries-The Case of Switzerland. Technol. Soc. Chang. 2013, 80, 1035–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, W.L.; Santos, R.; Mirra, E. Innovation Systems and Sustainability: An Approach for Regional Clustering and MNCs Subsidiaries. World Rev. Sci. Technol. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 9, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, W.; Hall, A.; Pehu, E.; Rajalathi, R. Linking Market and Knowledge Based Development: The Why and How of Agricultural Innovation Systems; Van Trijp, H., Ingenbleek, P., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2010; ISBN 978-9-08-686145-3. [Google Scholar]
- Van Mierlo, B.; Arkesteijn, M. Collective Analyses of Barriers to and Opportunities for Sustainable Development Using the Innovation System Framework; Poppe, K.J., Termeer, C., Slingerland, M., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2009; ISBN 978-9-08-686117-0. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Development of Casting Wear Resistant Materials in China. Foundry 2012, 61, 967–984. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, S.K.; Boszczowski, A.K.; Facco, C.A. Greening of Sectoral Innovation System in Brazil Soybean. Agroalimentaria 2011, 17, 71–86. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, J.; Xi, X.; Zhang, Y. Evolution of Regional Low-Carbon Innovation Systems with Sustainable Development: An Empirical Study with Big-Data. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 209, 1545–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DNP CONPES 3343; Sustainable Development Guidelines and Strategies for the Water, Environment and Territorial Development Sectors. Departamento Nacional de Planeación: Bogotá, Colombia, 2005; pp. 1–26.
- DNP CONPES 4007; Strategy for Strengthening Governance in the Land Administration System. Departamento Nacional de Planeación: Bogotá, Colombia, 2020; p. 57.
- DNP CONPES 3990; Colombia Sustainable Bioceanic Potency. Departamento Nacional de Planeación: Bogotá, Colombia, 2020; p. 91.
- Chung, C.-C. Technological Innovation Systems in Multi-Level Governance Frameworks: The Case of Taiwan’s Biodiesel Innovation System (1997–2016). J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anadon, L.D.; Chan, G.; Harley, A.G.; Matus, K.; Moon, S.; Murthy, S.L.; Clark, W.C. Making Technological Innovation Work for Sustainable Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9682–9690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, K.; Nilsson, M.; Rickne, A.; Magnusson, T. Fostering Sustainable Technologies: A Framework for Analysing the Governance of Innovation Systems. Sci. Public Policy 2011, 38, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DNP CONPES 4023; Policy for Reactivation, Revitalization and Sustainable and Inclusive Growth: A New Commitment for the Future of Colombia. Departamento Nacional de Planeación: Bogotá, Colombia, 2021.
- Liu, G.; Gao, P.; Chen, F.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y. Technological Innovation Systems and IT Industry Sustainability in China: A Case Study of Mobile System Innovation. Telemat. Inform. 2018, 35, 1144–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R. Interaction between Innovation Systems, Clustering and Sustainability: Regional Implications. Int. J. Foresight Innov. Policy 2006, 2, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayneko, D.; Dayneko, A.; Peshkov, V.; Matveeva, M. Development of the Regional Innovation System in the Forest Industry of Irkutsk Province Based on Institutional Changes. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 316, 012045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tigabu, A.; Berkhout, F.; van Beukering, P. Development Aid and the Diffusion of Technology: Improved Cookstoves in Kenya and Rwanda. Energy Policy 2017, 102, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, K.S.; Grübler, A.; Kuhl, L.; Nemet, G.; Wilson, C. The Energy Technology Innovation System. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2012, 37, 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potting, J.; Hekkert, M.; Worrell, E.; Hanemaaijer, A. Circular Economy: Measuring Innovation in the Product Chain. Planbur. Voor Leefomgeving 2017, 46, 2544. [Google Scholar]
- DNP CONPES 4004; Circular Economy in the Management of Drinking Water Services and Wastewater Management. Departamento Nacional de Planeación: Bogotá, Colombia, 2020; p. 64.

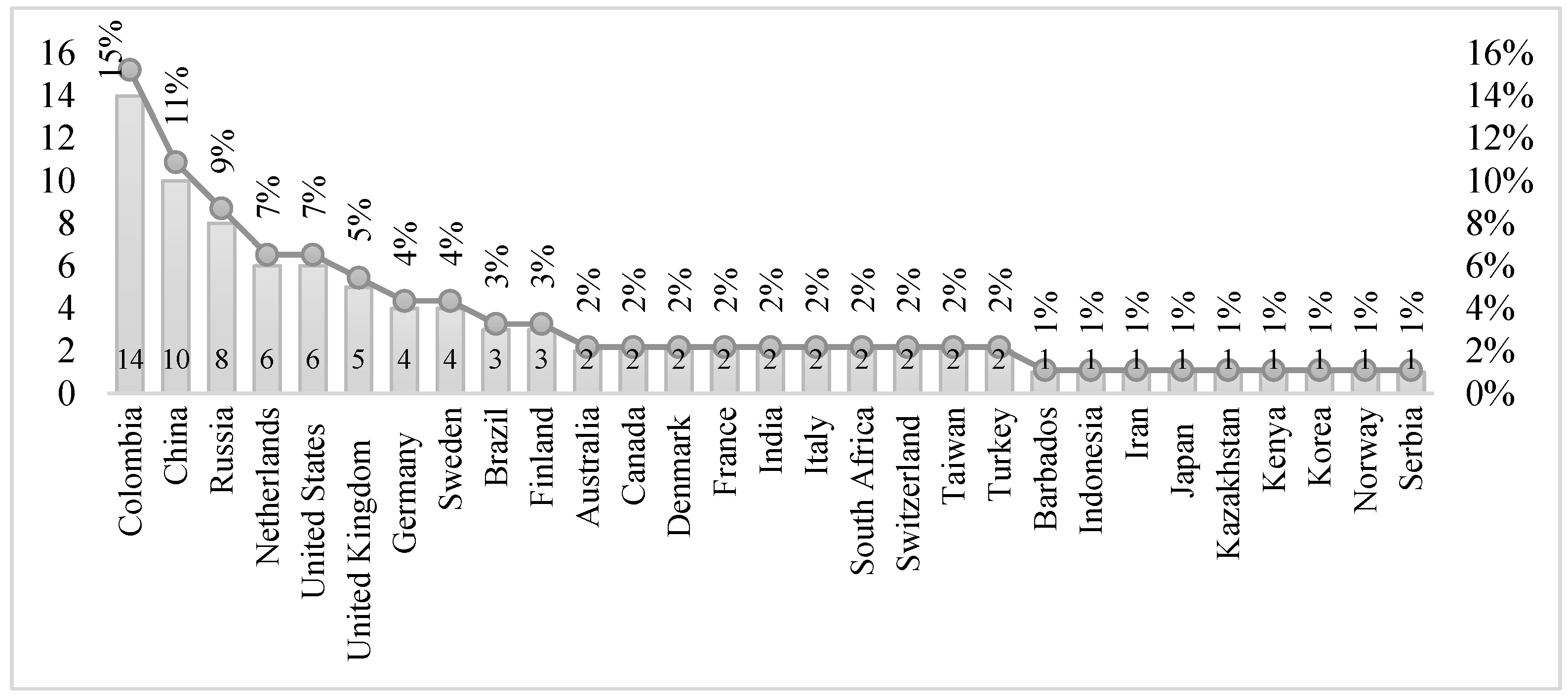
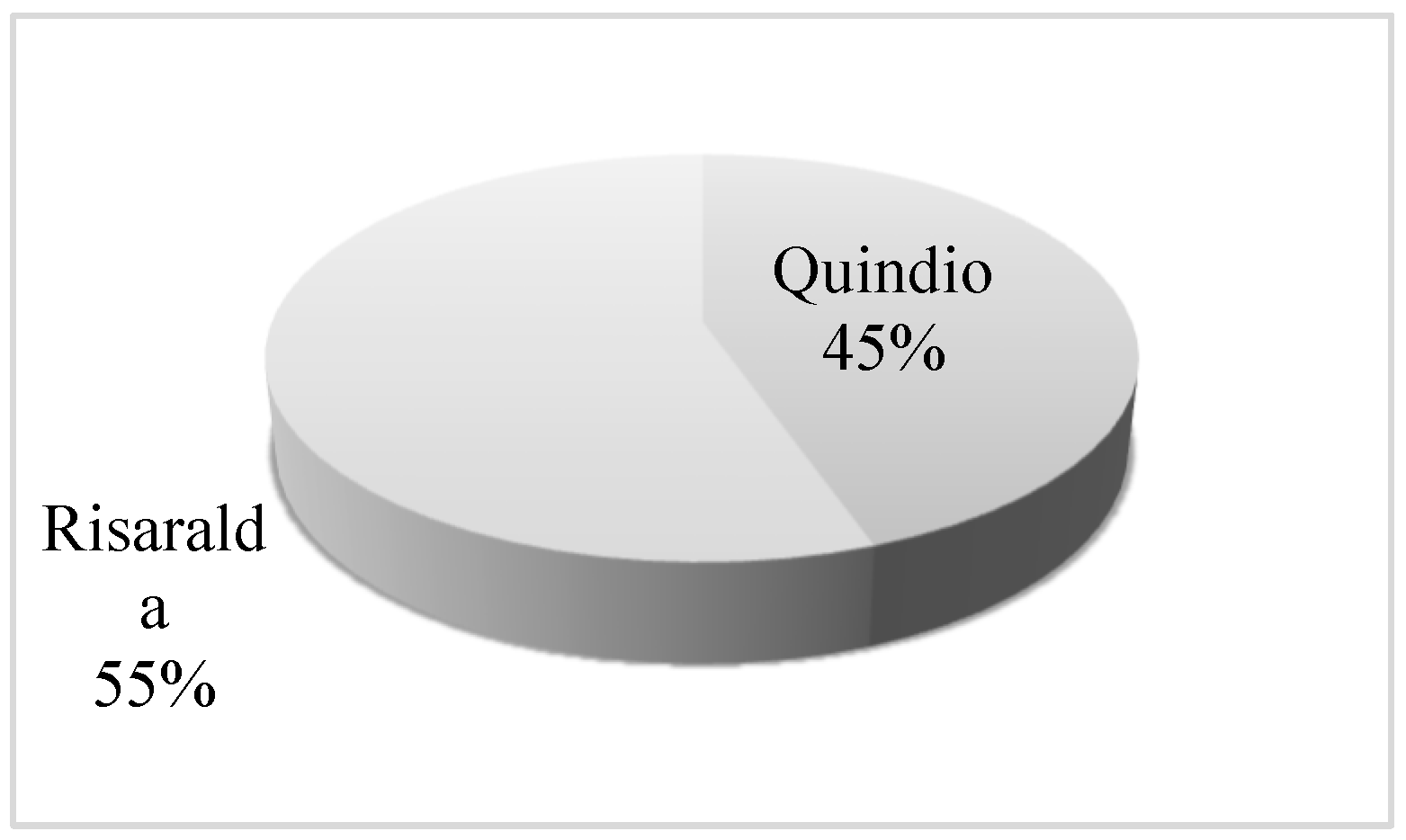
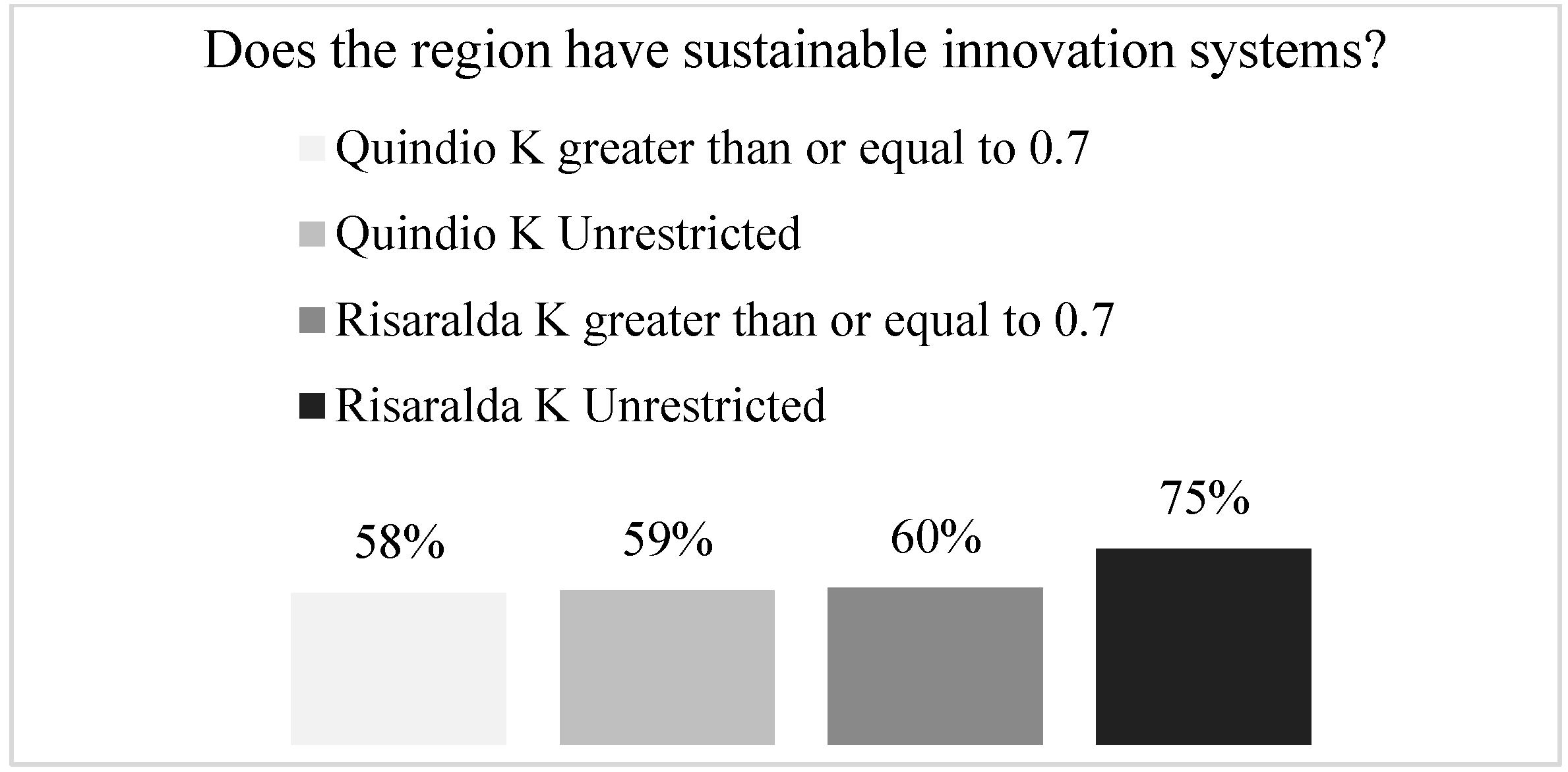
| Ask | Does the Region Have Sustainable Innovation Systems? |
|---|---|
| Quindío K greater than or equal to 0.7 | More than 30% but less than 50% of their processes have sustainable innovation systems. |
| Consensus percentage | 58% |
| Quindío K without restriction | More than 30% but less than 50% of their processes have sustainable innovation systems. |
| Consensus percentage | 59% |
| Risaralda K greater than or equal to 0.7 | More than 30% but less than 50% of their processes have sustainable innovation systems. |
| Consensus percentage | 60% |
| Risaralda K unrestricted | More than 30% but less than 50% of their processes have sustainable innovation systems. |
| Consensus percentage | 75% |
| General K Greater than or equal to 0.7 | More than 30% but less than 50% of their processes have sustainable innovation systems. |
| Consensus percentage | 59% |
| General K Unrestricted | More than 30% but less than 50% of their processes have sustainable innovation systems. |
| Consensus percentage | 68% |
| Analysis | It is found that at a general level more than 30% but less than 50% of the processes in the region surveyed have sustainable innovation systems. |
| Simplified Variable | Reference | Questions |
|---|---|---|
| The proportion of the informal economy. | [5] | What percentage of the region’s economy belongs to informality? |
| When talking about sustainable development, five dimensions must be considered (social, economic, environmental, spatial, and cultural) which must be supported by public-private partnerships for the development of the different sectors. | [5,16,21,32,76,77,78,79] | How many synergies exist between the dimensions of sustainability (social, environmental, economic, spatial, and cultural)? |
| Participation of a wide range of actors from all sectors is a fundamental process to building a sustainable innovation system and increasing the use of the internet and mobile networks provide an opportunity to improve access to knowledge that can accelerate the scaling-up process. | [5,47,80] | At the regional level, are there interconnections between the processes that allow working on the development of systems in an articulated manner? |
| Consolidate sustainable alternatives for production, conservation, and recovery of ecosystem goods and services. | [16,40,42,81,82] | Does the region have sustainable development alternatives that promote the conservation and recovery of ecosystem goods and services? |
| Adopt urgent measures to combat climate change and its effects. | [17,37,83,84,85,86,87] | Does the region have action measures that contribute to reducing climate change and contribute to the sustainability of the processes? |
| Protection and conservation of the set of environmental variables that constitute a good or service. | [16,37,88] | Does the region have regulatory norms for the care and conservation of environmental variables? |
| Continuous improvement is a fundamental variable for the development of new and better sustainable innovation systems. | [78] | Does the region have self-assessment processes in place to determine the status of the different sectors involved? |
| Research and development systems that allow process improvement and the creation of new patentable inventions. | [5,21,24,47,89,90,91] | Does the region have economic resources earmarked for the development of academic research? |
| Regional innovation system based on resource conservation, taking into account the form of resource integration, value orientation, and ecological considerations. | [92,93] | Does the region have sustainable innovation systems? |
| Absorption and adaptation capacity. | [31] | Does the region have technological systems that allow it to adapt to the different changes in the environment? |
| Urban space management, with adequate design and distribution of infrastructure. | [5,16,83,89,94] | Does the region have an adequate distribution of the POT for the development of its economic sectors and the location of its population? |
| Healthy life models. | [83] | Does the region develop plans and models that are disseminated for the knowledge and application of healthy living? |
| Develops programs to improve the working conditions of the organization’s employees. | [95] | Do organizations in the region develop programs to improve the working conditions of the organization’s employees based on sustainable models? |
| There is a correlation between the transition of a country’s economic sectors towards sustainability and their competitiveness, framed in the regulatory and coordination processes adopted by the sectoral innovation system directed towards sustainability. | [42] | Are there economic clusters in the region based on sustainable innovation models? |
| Regional economic activities based on sustainable models. | [26,48,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107] | Are there economic activities based on sustainable innovation models in the region? |
| Explore methodologies for recycling and utilization of carbon emissions, hand in hand with the implementation of low-carbon technologies. | [88,108] | Do technologies that reduce carbon emissions exist in the region? |
| Adaptation of policies to support sustainability. | [21,109] | Are there policies in place in the region to implement sustainable models in the communities? |
| Adoption of strategies for sustainable development based on poverty reduction and increased inclusion and equity. | [16,110] | Is there adoption of strategies for the development of sustainability based on poverty reduction and increased inclusion and equity in the region? |
| Promotes conflict resolution strategies and the search for peace and justice. | [84] | Are there strategies for conflict resolution and the search for peace and justice in the region? |
| Creation of internal support structures to promote sustainability. | [12,13] | Are there any public organizations in the region for the promotion of sustainability? |
| Active participation of stakeholders in the development of the organization’s sustainability innovation. | [12] | Is there active stakeholder participation in the development of innovation-based sustainability of organizations in the region? |
| International management in the conservation and sustainable use of oceans and marine resources for sustainable development. | [37,111] | Is there participation in international conventions for the management of the conservation and sustainable use of oceans and marine resources? |
| Participation in international agreements for the management of innovation in sustainability. | [24] | Is there participation in international agreements for the management of innovation in sustainability in organizations in the region? |
| National and international management in the conservation and sustainable use of oceans and marine resources for sustainable development. | [111] | Is there participation in national or international conventions for the management of the conservation and sustainable use of oceans and marine resources? |
| Promotion of sustainable guidelines in favor of society based on innovation. | [42,77,112,113] | Is there promotion of sustainable pro-society guidelines based on innovation in the region? |
| Establishment of support networks for the promotion of sustainable models in the region. | [35] | Are there communication networks between the different stakeholders involved in sustainability in the region? |
| Search for balanced relations between the state, civil society, and organizations to achieve sustainable institutional development. | [79,110,114] | Are there mechanisms in place in the region to link the state, civil society, and non-profit organizations to achieve sustainable institutional development? |
| Higher education systems allow the flow of knowledge with the support of institutions that contribute to research, development, and dissemination. | [5,7,21,24,47,84,88,89,90,91,95] | Does the region have education systems that contribute to the development of attitudes and cognitive capacities that allow the acquisition of knowledge for decision making, industrial and economic development, based on the collective benefit and the environment? |
| Development of public policy tools that, through regulations, incentives, or mechanisms that motivate actions or behaviors of agents, contribute to environmental protection. | [48,83,85,115] | Does the region have regulatory systems or control mechanisms for environmental protection? |
| Improve the management of information on the status and pressures of forest resources, as a support for the development of actions aimed at the administration and sustainable management of the country’s forests. | [13,81,83] | Does the region know of its forest resource, and do they have tools to protect it? |
| Development of innovative activities, technologies, and infrastructures that contribute to the production of new content. | [12,13,32,91] | Does the region have sufficient activities, technologies, and infrastructure to support the production of new content? |
| Development of innovations in the region. | [12,13] | Does the region have methods that contribute to the production of new developments for the sustainability of the region? |
| Management of the rational use of natural resources, the protection, and conservation of ecosystems, and the reduction of pollution, to protect the environment. | [13,37,79,83,95,109] | Does the region have sustainable guidelines in favor of environmental protection and conservation? |
| The string of value sustainable. | [78,110] | What percentage of the value chain of products and services developed in the region can be considered sustainable? |
| Undertakings in economic projects based on sustainability. | [7,31,78,89] | What percentage of ventures in the region are based on sustainability? |
| Reduction of cultural and linguistic differences in favor of sustainability. | [94] | Are there strategies to reduce the cultural and linguistic gap between the different stakeholders in the region? |
| Compliance with national regulatory standards for sustainability development. | [24,94] | Does the region comply with national regulatory standards for sustainability development? |
| Implements sustainability awareness strategies for the communities in the area of influence. | [47] | Are strategies implemented to sensitize the communities in the area of influence on sustainability in the region? |
| Construction of technological innovations to strengthen sustainability in industry or society. | [5,86,95,110,116,117] | Are there technological innovations for strengthening sustainability in the region’s industries or society? |
| Promotes quality education, research, and dissemination of knowledge in innovation for sustainable purposes. | [5,89] | Are quality education, research, and knowledge dissemination in innovation for sustainable purposes promoted in the region’s educational organizations? |
| State of the region’s economy. | [16,24,84,86] | Based on national standards, how is the economy in the region? |
| Innovation in sustainable regulations. | [5,47,85] | Is the region at the forefront of sustainable development regulations, and is it developing systems for their application and compliance in its processes? |
| Financing of scientific and innovation capacity for the development of new markets. | [81,85,91,108,118] | How is the financing of scientific and innovation capacity for the development of new markets? |
| Availability of resources or tax relief for the development of more sustainable production models. | [47,48,84,89,95] | What is the availability of tax relief in the region for the development of sustainable production models? |
| Framework conditions and favorable environment. | [5] | Is the region’s economic environment conducive to sustainability? |
| Sustainable development planning with the environment, technology, and the different sectors contributing to the process, taking into account multiple planning factors such as training, exploration, dismantling of erroneous knowledge, and organizational development. | [79,92] | Does the region have planning systems in place that allow for a transition between current and sustainable processes? |
| Complementary capabilities and dynamics to the market. | [31] | Are the region’s market dynamics oriented towards a sustainable consumer? |
| Tracking and quantification of resources for SDG compliance. | [84] | Are the region’s resources invested in achieving the SDGs? |
| Application of technological innovation focused on the development of proposals for the implementation of renewable energies as a response to environmental and sustainability challenges. | [23,89,107,115,119,120] | Is the development of proposals for the implementation of renewable energies observed in the region? |
| Mobility and accessibility. | [5,12,21,83,109] | The region has adequate mobility management and planning systems, as well as accessibility, allowing for the adequate development of local sectors. |
| Circularity strategies. | [121,122] | Regarding circularity strategies in your region: have you applied circularity strategies? |
| Sustainability Variables | Associated Questions | Authors Who Relate the Variable | Region | Competition Coefficient K |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| International management in the conservation and sustainable use of oceans and marine resources for sustainable development | Is there participation in national or international conventions for the management of the conservation and sustainable use of oceans and marine resources? | [37,111] | Quindío | K ≥ 0.7 and K < 0.7 |
| Sustainable value chain | What percentage of the value chain of products and services developed in the region can be considered sustainable? | [78,110] | Quindío | K ≥ 0.7 |
| Undertakings in sustainability-based economic projects | What percentage of ventures in the region are based on sustainability? | [7,31,78,89] | Quindío and Risaralda | K < 0.7 |
| Financing of scientific and innovation capacity for the development of new markets | How is the financing of scientific and innovation capacity for the development of new markets? | [81,85,91,108,118] | Quindío and Risaralda | K ≥ 0.7 and K < 0.7 |
| Research and development systems that allow process improvement and the creation of new patentable inventions | Does the region have economic resources earmarked for the development of academic research? | [5,21,24,47,89,90,91] | Quindío | K ≥ 0.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zartha Sossa, J.W.; Gaviria Suárez, J.F.; López Suárez, N.M.; Rebolledo, J.L.S.; Orozco Mendoza, G.L.; Vélez Suárez, V. Innovation Systems and Sustainability. Development of a Methodology on Innovation Systems for the Measurement of Sustainability Indicators in Regions Based on a Colombian Case Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15955. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315955
Zartha Sossa JW, Gaviria Suárez JF, López Suárez NM, Rebolledo JLS, Orozco Mendoza GL, Vélez Suárez V. Innovation Systems and Sustainability. Development of a Methodology on Innovation Systems for the Measurement of Sustainability Indicators in Regions Based on a Colombian Case Study. Sustainability. 2022; 14(23):15955. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315955
Chicago/Turabian StyleZartha Sossa, Jhon Wilder, Juan Fernando Gaviria Suárez, Natalia María López Suárez, José Luis Solleiro Rebolledo, Gina Lía Orozco Mendoza, and Valentina Vélez Suárez. 2022. "Innovation Systems and Sustainability. Development of a Methodology on Innovation Systems for the Measurement of Sustainability Indicators in Regions Based on a Colombian Case Study" Sustainability 14, no. 23: 15955. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315955
APA StyleZartha Sossa, J. W., Gaviria Suárez, J. F., López Suárez, N. M., Rebolledo, J. L. S., Orozco Mendoza, G. L., & Vélez Suárez, V. (2022). Innovation Systems and Sustainability. Development of a Methodology on Innovation Systems for the Measurement of Sustainability Indicators in Regions Based on a Colombian Case Study. Sustainability, 14(23), 15955. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315955







