Geopolymeric Composite Materials Made of Sol-Gel Silica and Agroindustrial Wastes of Rice, Barley, and Coffee Husks with Wood-Like Finishing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
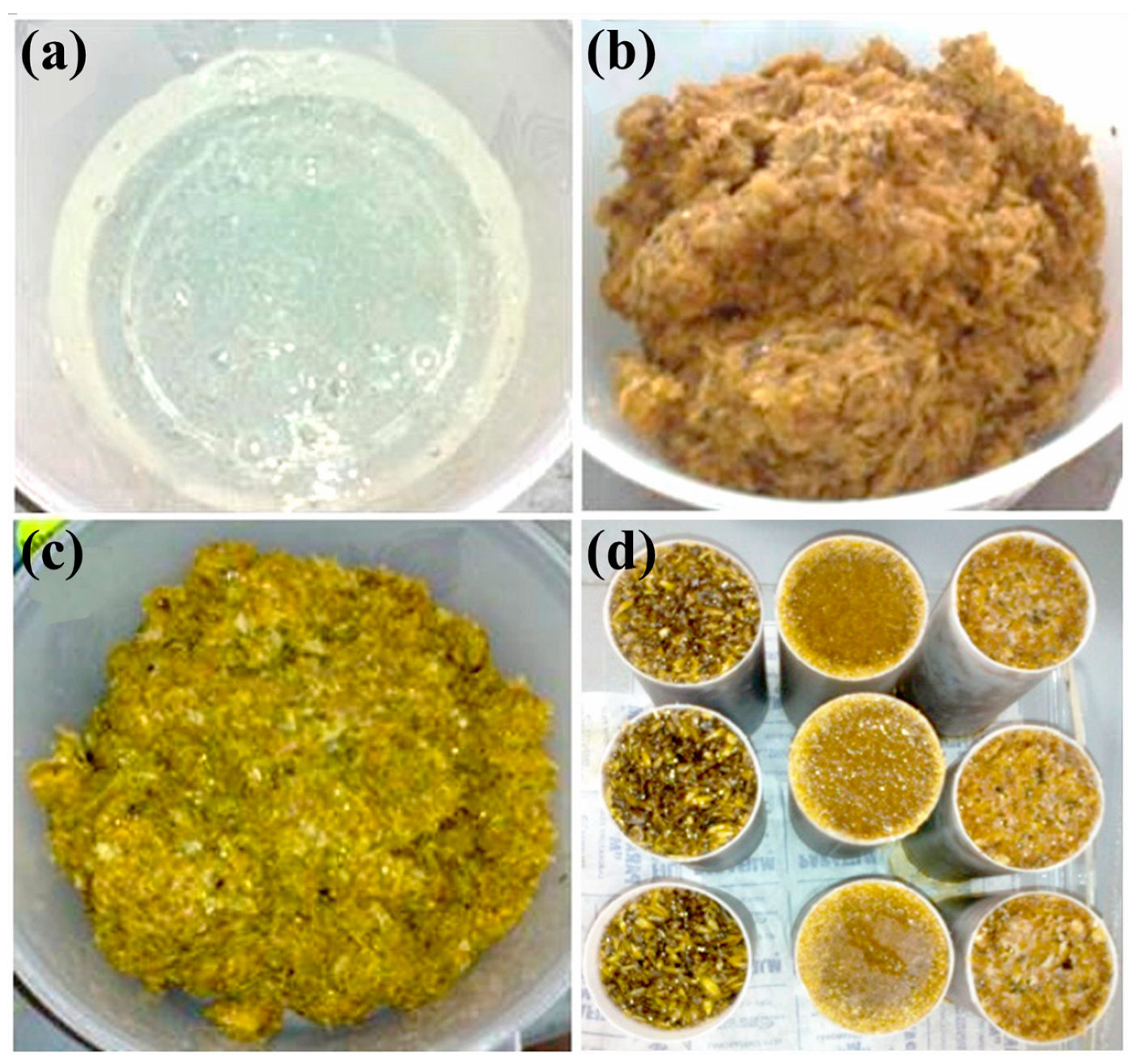
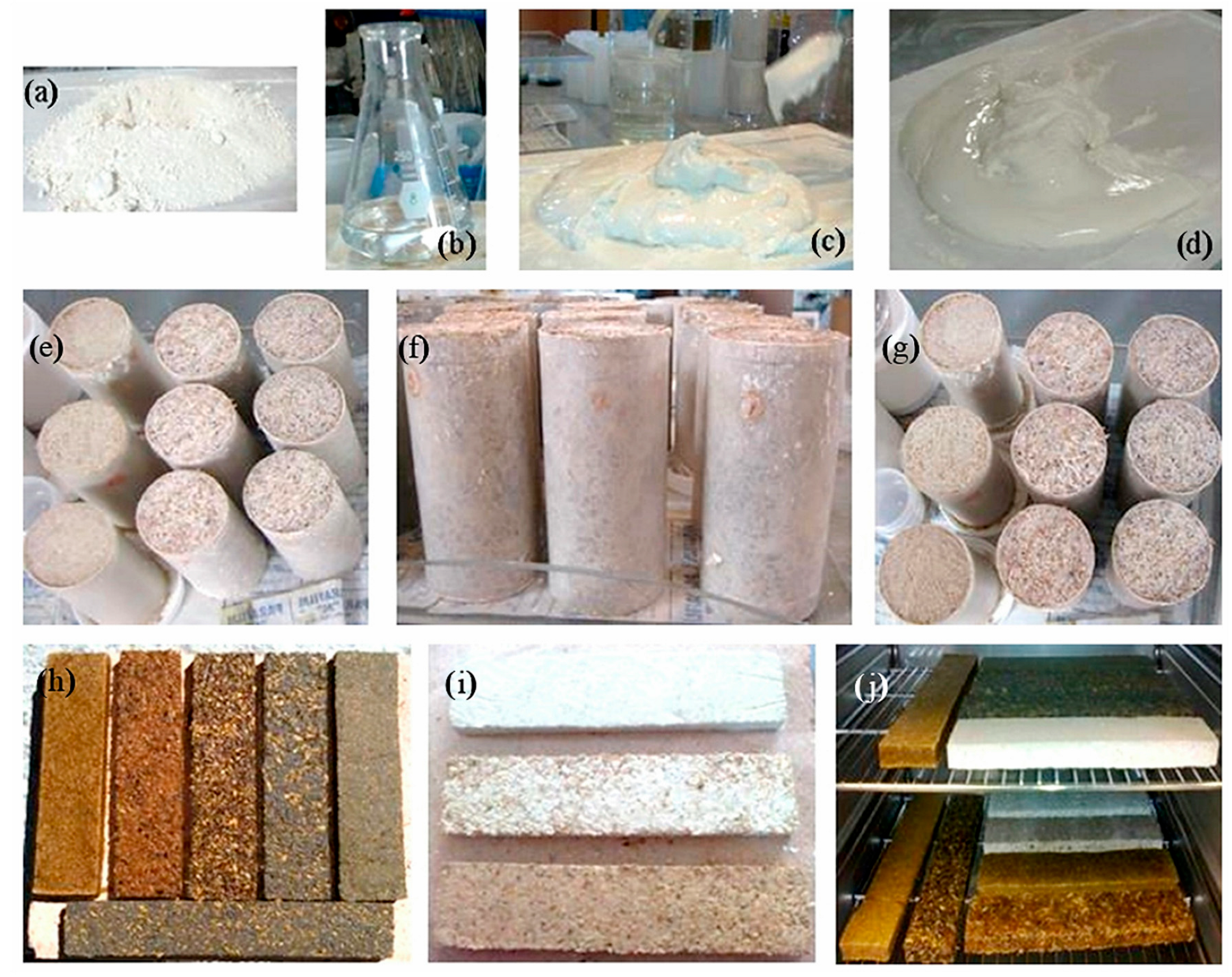
2.2. Preparation of Composite Materials with Geopolymeric Matrix—Husks (Agro-Waste)
2.3. Mechanical Tests
3. Results and Discussion
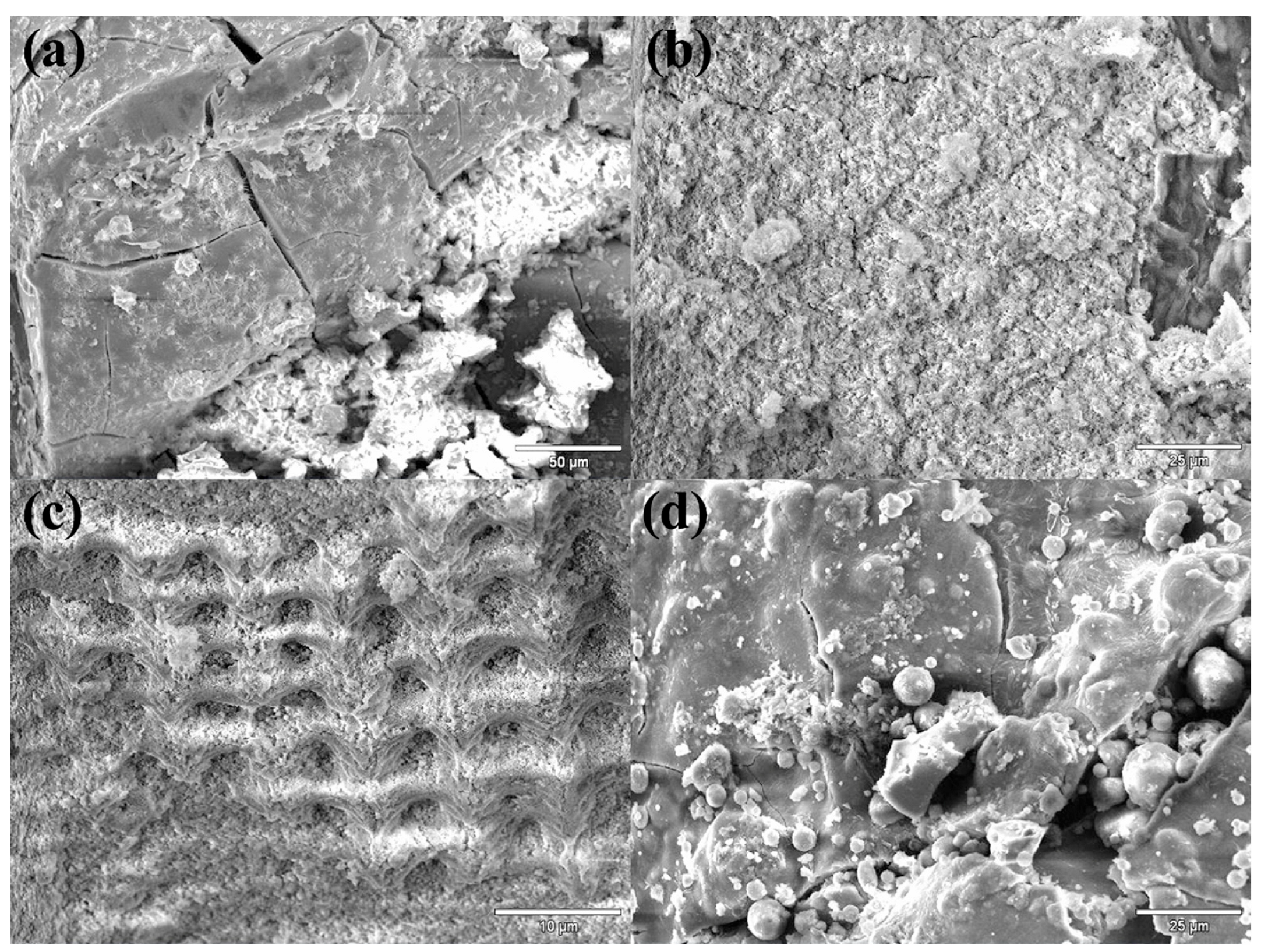
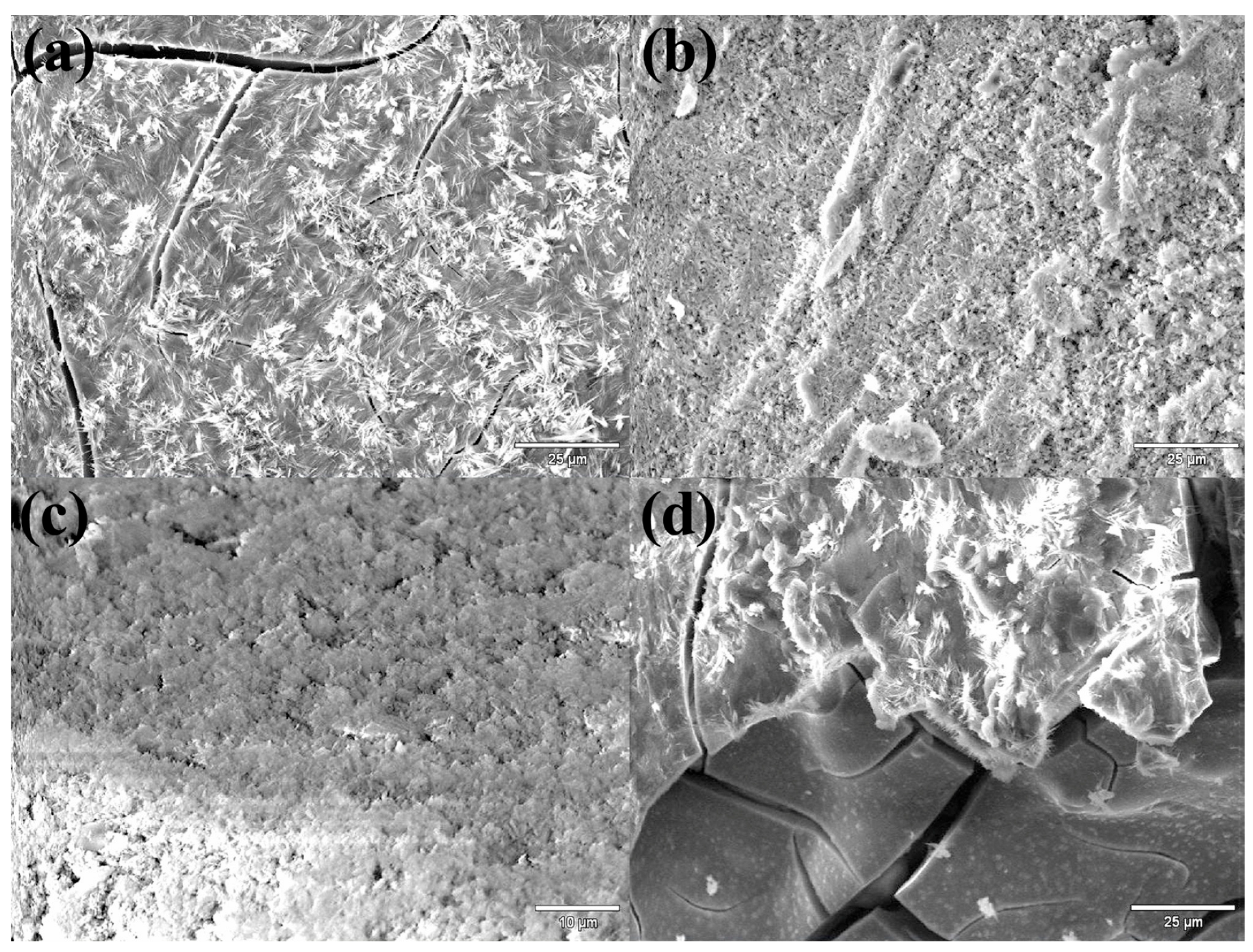
3.1. Structure of Composite Materials with Husks
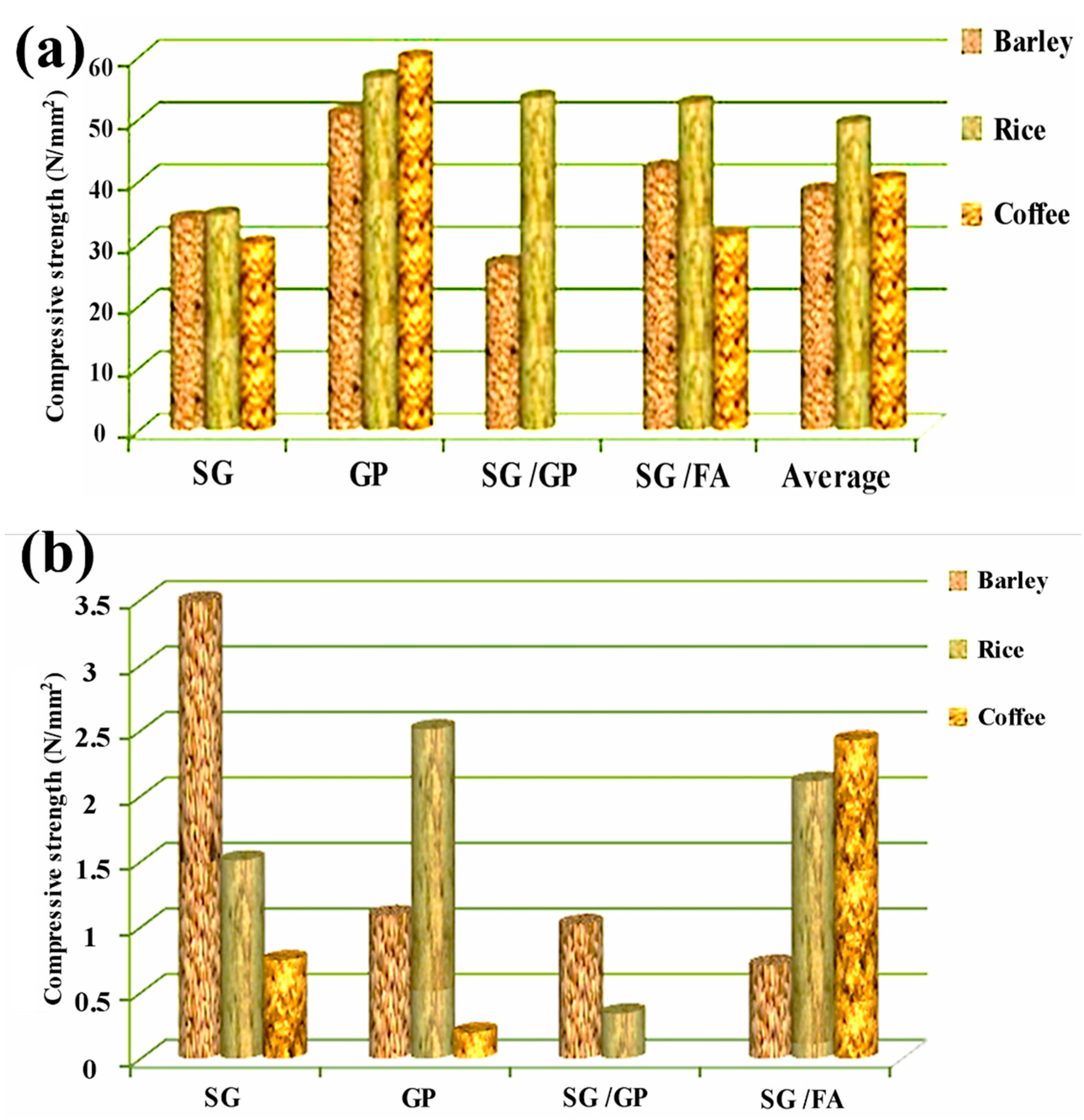
3.2. Hardness and Compression Strength Tests
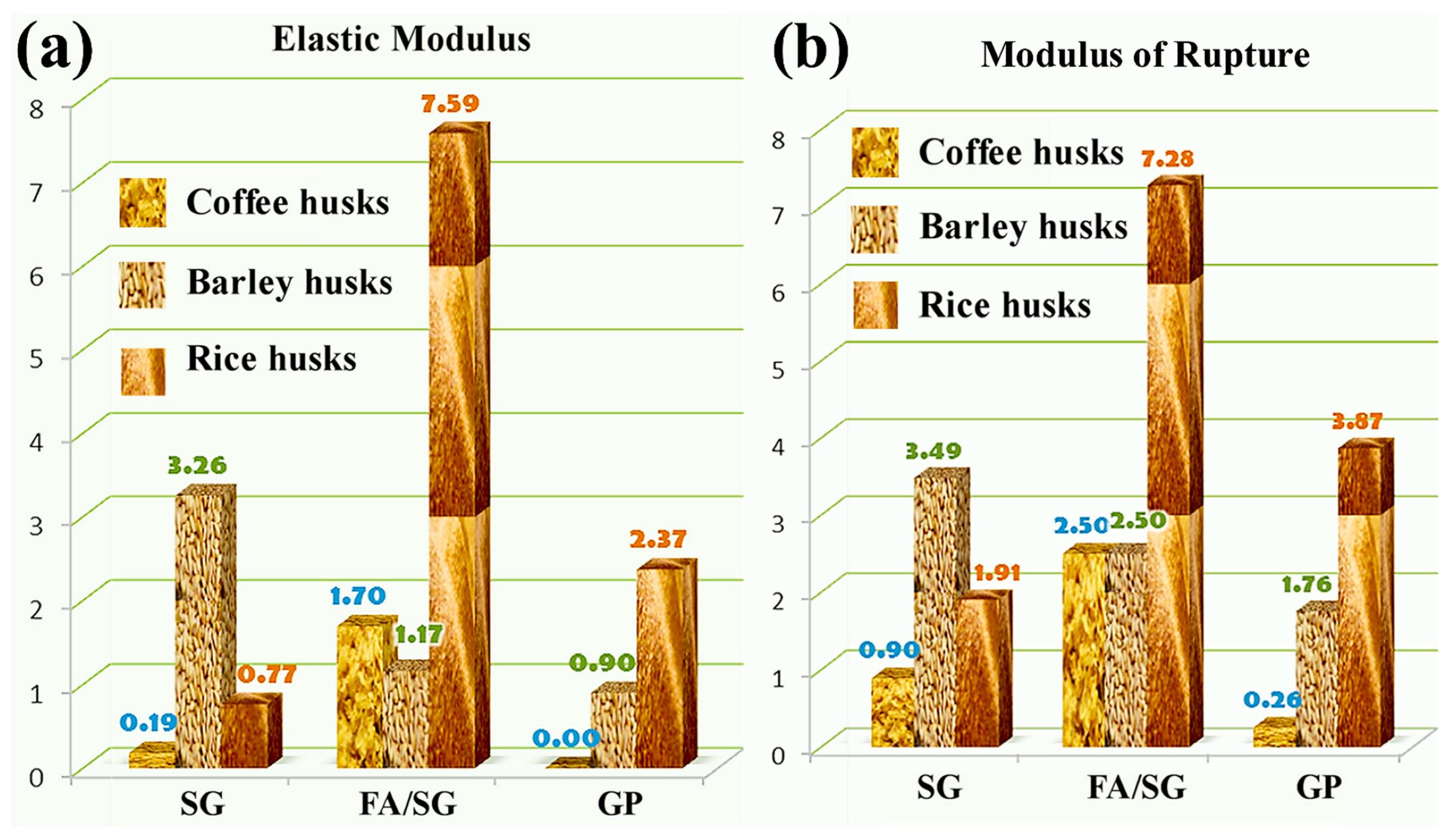
3.3. Flexural Properties
3.4. Adobe-Like Composite Prototypes Made with Husks
3.5. Composite Characteristics Using Sol-Gel Silica Binder
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeyad, A.M.; Magbool, H.M.; Tayeh, B.A.; Garcez de Azevedo, A.R.; Abutaleb, A.; Hussain, Q. Production of Geopolymer Concrete by Utilizing Volcanic Pumice Dust. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Li, W.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Luo, Z. Investigation on Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Fly Ash/Slag-Based Geopolymeric Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 185, 107776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, G.Z.B.; Caldas, L.R.; de Almeida Melo Filho, J.; Monteiro, N.B.R.; Rafael, S.I.M.; da Silva, N.M. Circular Alternatives in the Construction Industry: An Environmental Performance Assessment of Sisal Fiber-Reinforced Composites. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 54, 104603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakravan, H.R.; Jamshidi, M.; Asgharian Jeddi, A.A. Combination of Ground Rice Husk and Polyvinyl Alcohol Fiber in Cementitious Composite. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 215, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayapureddy, Y.; Muniraj, K.; Mutukuru, M.R.G. Sugarcane Bagasse Ash as Supplementary Cementitious Material in Cement Composites: Strength, Durability, and Microstructural Analysis. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2020, 57, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.; Sebaibi, N.; Boutouil, M.; Levacher, D. Determination and Review of Physical and Mechanical Properties of Raw and Treated Coconut Fibers for Their Recycling in Construction Materials. Fibers 2020, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- António, J.; Tadeu, A.; Marques, B.; Almeida, J.A.S.; Pinto, V. Application of Rice Husk in the Development of New Composite Boards. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 176, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdadi, Z.; Asim, N.; Amin, M.; Ambar Yarmo, M.; Maleki, A.; Azizi, M.; Sopian, K. Development of Green Geopolymer Using Agricultural and Industrial Waste Materials with High Water Absorbency. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekalo, S.A.; Reinhardt, H.-W. Fibers of Coffee Husk and Hulls for the Production of Particleboard. Mater. Struct. 2010, 43, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo, I.I.; Rossetto Dinhane, F.C.; de Domenico Valarelli, I.; Pereira Bueno, M.A.; Ferreira, B.S.; de Campos, C.I. Influence of the Addition of Coffee Husk in Physical Properties of Bamboo Particleboard. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1088, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.W.; Scatolino, M.V.; do Prado, N.R.T.; Mendes, R.F.; Mendes, L.M. Addition of Different Proportions of Castor Husk and Pine Wood in Particleboards. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 9, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Mamun, A.A.; Volk, J. Barley Husk and Coconut Shell Reinforced Polypropylene Composites: The Effect of Fibre Physical, Chemical and Surface Properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R.; Mendes, E.; Torrinha, Á.; Morais, S.; Pereira, J.A.; Baptista, P.; Casal, S. Revalorization of Spent Coffee Residues by a Direct Agronomic Approach. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Mu, B.; Yi, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Q. Sustainable Use of Coffee Husks For Reinforcing Polyethylene Composites. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kua, T.-A.; Arulrajah, A.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Du, Y.-J.; Shen, S.-L. Strength Assessment of Spent Coffee Grounds-Geopolymer Cement Utilizing Slag and Fly Ash Precursors. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 115, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-K.; Kuo, T.-M.; Hsu, Y.-S. The Application and Evaluation Research of Coffee Residue Ash into Mortar. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2016, 18, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, P.; Torchia, F.; Belloni, E.; Lascaro, E.; Buratti, C. Environmental Characterisation of Coffee Chaff, a New Recycled Material for Building Applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 147, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Ansumali, S. Global Potential of Rice Husk as a Renewable Feedstock for Ethanol Biofuel Production. BioEnergy Res. 2010, 3, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafigh, P.; Mahmud, H.B.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Zargar, M. Agricultural Wastes as Aggregate in Concrete Mixtures—A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 53, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Rice Production. 2020. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL/visualize (accessed on 26 October 2022).
- Magdaleno-López, C.; Pérez-Bueno, J.d.J.; Flores-Segura, J.C.; Reyes-Araiza, J.L.; Mendoza-López, M.L.; Arés, O.; Manzano-Ramírez, A. A Geopolymeric Composite of Non-Calcined Rice Husks Made of Metakaolin/Sol–Gel Silica. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 53, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximize Market Research Global Rice Husk Ash Market: Industry Analysis and Forecast 2019–2026 by Product, by Application, by Region. Available online: https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/global-rice-husk-ash-market/16297/ (accessed on 26 October 2022).
- Ahmad, M.M.; Ahmad, F.; Azmi, M.; Mohd Zahid, M.Z.A. Properties of Cement Mortar Consisting Raw Rice Husk. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 802, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongdong, W.; Kummerlöwe, C.; Vennemann, N.; Thitithammawong, A.; Nakason, C. A Comparative Investigation of Rice Husk Ash and Siliceous Earth as Reinforcing Fillers in Dynamically Cured Blends of Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) and Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU). J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, C.; Belloni, E.; Lascaro, E.; Merli, F.; Ricciardi, P. Rice Husk Panels for Building Applications: Thermal, Acoustic and Environmental Characterization and Comparison with Other Innovative Recycled Waste Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraj, R.; Lacoste, C.; Lacroix, P.; Bergeret, A. Sustainable Thermal Insulation Biocomposites from Rice Husk, Wheat Husk, Wood Fibers and Textile Waste Fibers: Elaboration and Performances Evaluation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 135, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Provis, J.L.; Dai, J.-G. Role of Soluble Aluminum Species in the Activating Solution for Synthesis of Silico-Aluminophosphate Geopolymers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 93, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, N.; Alghoul, M.; Mohammad, M.; Amin, M.H.; Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Amin, N.; Sopian, K. Emerging Sustainable Solutions for Depollution: Geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 199, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeli, M.; Novais, R.M.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Green Geopolymeric Concrete Using Grits for Applications in Construction. Mater. Lett. 2018, 233, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymers Structures, Processing, Properties and Industrial Applications; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Sawston, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-1-84569-449-4. [Google Scholar]
- Muñiz-Villarreal, M.S.; Manzano-Raḿrez, A.; Sampieri-Bulbarela, S.; Gasca-Tirado, J.R.; Reyes-Araiza, J.L.; Rubio-Á Valos, J.C.; Pérez- Bueno, J.J.; Apatiga, L.M.; Zaldivar-Cadena, A.; Amigó-Borrás, V. The Effect of Temperature on the Geopolymerization Process of a Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdaleno López, C.; Pérez Bueno, J.J.; Mendoza López, M.L.; Reyes Araiza, J.L.; Manzano-Ramírez, A. Fly Ash Lightweight Material of the Cellular Concrete Type Using Sol-Gel and Thermal Treatment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 206, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-López, C.; Reyes Araiza, J.L.L.; Manzano-Ramírez, A.; Rubio Avalos, J.C.C.; Perez-Bueno, J.J.J.; Muñiz-Villareal, M.S.S.; Ventura-Ramos, E.; Vorobiev, Y.; Marín-López, C.; Reyes Araiza, J.L.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of a Concrete Based on Metakaolin Geopolymer. Inorg. Mater. 2009, 45, 1429–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasca-Tirado, J.R.; Rubio-Ávalos, J.C.; Muñiz-Villarreal, M.S.; Manzano-Ramírez, A.; Reyes-Araiza, J.L.; Sampieri-Bulbarela, S.; Villaseñor-Mora, C.; Pérez-Bueno, J.J.; Apatiga, L.M.; Amigó Borrás, V. Effect of Porosity on the Absorbed, Reemitted and Transmitted Light by a Geopolymer Metakaolin Base. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 880–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliseris, J.; Yan, L.; Kasal, B. Numerical Modelling of Flax Short Fibre Reinforced and Flax Fibre Fabric Reinforced Polymer Composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 89, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervaiz, M.; Sain, M.M. Carbon Storage Potential in Natural Fiber Composites. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2003, 39, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Torgal, F.; Jalali, S. Cementitious Building Materials Reinforced with Vegetable Fibres: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, L.; Ma, G.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, X. Preparation and Properties of Bio-Geopolymer Composites with Waste Cotton Stalk Materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsa, A.; Kunthawatwong, R.; Naenudon, S.; Sata, V.; Chindaprasirt, P. Natural Fiber Reinforced High Calcium Fly Ash Geopolymer Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 241, 118143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.; Kim, S.; Bertolotti, B.; Nakamatsu, J.; Aguilar, R. Optimization of a Reinforced Geopolymer Composite Using Natural Fibers and Construction Wastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 258, 119697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers: Ceramic-Like Inorganic Polymers. J. Ceram. Sci. Technol 2017, 8, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers Based on Natural and Synthetic Metakaolin a Critical Review. In Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Advanced Ceramics and Composites: Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings, Hoboken, NJ, USA, 18 January 2018; pp. 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Arreola Estrada, F.; Pérez Bueno, J.d.J.; Meas Vong, Y. MX/a/2013/008232 Composición Cementante de Ceniza Volante 2021. Available online: https://cideteq.repositorioinstitucional.mx/jspui/bitstream/1021/230/1/MX2013008232%28A%29_COMPOSICI%C3%93N%20CEMENTANTE%20DE%20CENIZA%20VOLANTE.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2022).
- Arreola Estrada, F.; Pérez Bueno, J.d.J. MX/a/2013/008234 Material Ligero de Ceniza Volante de Tipo Concreto Celular 2021. Available online: https://cideteq.repositorioinstitucional.mx/jspui/bitstream/1021/229/1/MX2013008234%28A%29_MATERIAL%20LIGERO%20DE%20CENIZA%20VOLANTE%20DE%20TIPO%20CONCRETO%20CELULAR.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2022).
- Perez Bueno, J.d.J.; Roman Zamorano, J.F. MX/a/2016/000437 Bloques de Montmorillonita Para Adsorción de Metales Pesados En Agua Utilizando Bentonita y Cenizas Volantes 2015. Available online: https://cideteq.repositorioinstitucional.mx/jspui/bitstream/1021/274/1/MX2016000437%28A%29_BLOQUES%20DE%20MONTMORILLONITA%20PARA%20ADSORCI%C3%93N%20DE%20METALES%20PESADOS%20EN%20AGUA%20UTILIZANDO%20BENTONITA%20Y%20CENIZAS%20VOLANTES.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2022).
- ASTM International ASTM C947-03(2016); Standard Test Method for Flexural Properties of Thin-Section Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (Using Simple Beam With Third-Point Loading). ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- Mati-Baouche, N.; De Baynast, H.; Lebert, A.; Sun, S.; Lopez-Mingo, C.J.S.; Leclaire, P.; Michaud, P. Mechanical, Thermal and Acoustical Characterizations of an Insulating Bio-Based Composite Made from Sunflower Stalks Particles and Chitosan. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 58, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etuk, S.E.; Agbasi, O.E.; Robert, U.W. Investigation of Heat Transfer and Mechanical Properties of Saccharum Officinarum Leaf Board. Int. J. Energy Water Resour. 2022, 6, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Kasal, B.; Huang, L. A Review of Recent Research on the Use of Cellulosic Fibres, Their Fibre Fabric Reinforced Cementitious, Geo-Polymer and Polymer Composites in Civil Engineering. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 92, 94–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małaszkiewicz, D.; Sztukowska, M. Utilization of Wastes from Medium Density Fiberboards Production as an Aggregate for Lightweight Cement Composite. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 174, 02005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savary, M.; Mehdizadeh Saradj, F.; Shayganmanesh, M.; Tahmasebiboldaji, N.; Kazemi, A.S. Improving the Adobe Material Properties by Laser Material Processing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 249, 118591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkanthi, S.N.; Balthazaar, N.; Perera, A.A.D.A.J. Lime Stabilization for Compressed Stabilized Earth Blocks with Reduced Clay and Silt. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 12, e00326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Oliveira, I.; Silva, V.; Mirão, J.; Faria, P. Vernacular Caramel´s Adobe Masonry Dwellings–Material Characterization. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2022, 16, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Matrix | Compound | Amount (g) |
|---|---|---|
| SG | Colloidal silica | 1176.47 |
| NaOH | 80.00 | |
| Na2SiO3 | 294.12 | |
| H2O | 500.00 | |
| GP | Metakaolin | 1104.50 |
| NaOH | 110.43 | |
| Na2SiO3 | 466.38 | |
| H2O | 1468.62 | |
| SG/GP | Metakaolin | 1104.50 |
| Sol-gel | 466.38 | |
| NaOH | 110.43 | |
| H2O | 1468.62 | |
| SG/FA | Sol-gel | 300.00 |
| Fly ash | 404.00 |
| Equation | Symbol | Parameter | No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| σ | Compressive strength | (1) | |
| F | Maximum applied force [N] | ||
| A | Axial area of the sample [m2] | ||
| r | Deformation of the sample | (2) | |
| D | Displacement of the sample [mm] | ||
| d | Thickness of the test beam [mm] | ||
| L | Length of the test beam [mm] | ||
| Ef | Modulus of elasticity in bending [GPa] | (3) | |
| m | Initial slope of the load-deflection curve [N/mm] | ||
| b | Width of the test beam [mm] | ||
| S | Strain [MPa] | (4) | |
| P | Load applied [N] |
| Matrix | Husks | Yield Strength [MPa] | Yield Deformation [mm/mm] | Ultimate Tensile Strength [MPa] | Ultimate Deformation [mm/mm] | Elastic Modulus [MPa] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sol-gel | Coffee | 0.33 | 0.0018 | 0.661 | 0.0053 | 0.188 |
| Barley | 1.549 | 0.0005 | 2.633 | 0.0012 | 3.259 | |
| Rice | 0.772 | 0.0011 | 1.404 | 0.0039 | 0.773 | |
| Fly ash/Sol-gel | Coffee | 0.929 | 0.0005 | 1.858 | 0.0013 | 1.697 |
| Barley | 0.647 | 0.0005 | 1.812 | 0.0016 | 1.166 | |
| Rice | 0.926 | 0.0001 | 5.250 | 0.0007 | 7.595 | |
| Geopolymer | Coffee | No | No | 0.196 | 0.0023 | No |
| Barley | 0.858 | 0.0009 | 1.288 | 0.0014 | 0.904 | |
| Rice | 1.099 | 0.0005 | 2.857 | 0.0015 | 2.374 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez Espejel, K.; Pérez Bueno, J.d.J.; Magdaleno López, C.; Mendoza López, M.L.; Algara Siller, M.; Reyes Araiza, J.L.; Manzano-Ramírez, A.; Morales Hernández, J. Geopolymeric Composite Materials Made of Sol-Gel Silica and Agroindustrial Wastes of Rice, Barley, and Coffee Husks with Wood-Like Finishing. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16689. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416689
Rodríguez Espejel K, Pérez Bueno JdJ, Magdaleno López C, Mendoza López ML, Algara Siller M, Reyes Araiza JL, Manzano-Ramírez A, Morales Hernández J. Geopolymeric Composite Materials Made of Sol-Gel Silica and Agroindustrial Wastes of Rice, Barley, and Coffee Husks with Wood-Like Finishing. Sustainability. 2022; 14(24):16689. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416689
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez Espejel, Karina, José de Jesús Pérez Bueno, Coraquetzali Magdaleno López, Maria Luisa Mendoza López, Marcos Algara Siller, José Luis Reyes Araiza, Alejandro Manzano-Ramírez, and Jorge Morales Hernández. 2022. "Geopolymeric Composite Materials Made of Sol-Gel Silica and Agroindustrial Wastes of Rice, Barley, and Coffee Husks with Wood-Like Finishing" Sustainability 14, no. 24: 16689. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416689
APA StyleRodríguez Espejel, K., Pérez Bueno, J. d. J., Magdaleno López, C., Mendoza López, M. L., Algara Siller, M., Reyes Araiza, J. L., Manzano-Ramírez, A., & Morales Hernández, J. (2022). Geopolymeric Composite Materials Made of Sol-Gel Silica and Agroindustrial Wastes of Rice, Barley, and Coffee Husks with Wood-Like Finishing. Sustainability, 14(24), 16689. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416689








