Improvement of the Crude Glycerol Purification Process Derived from Biodiesel Production Waste Sources through Computational Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
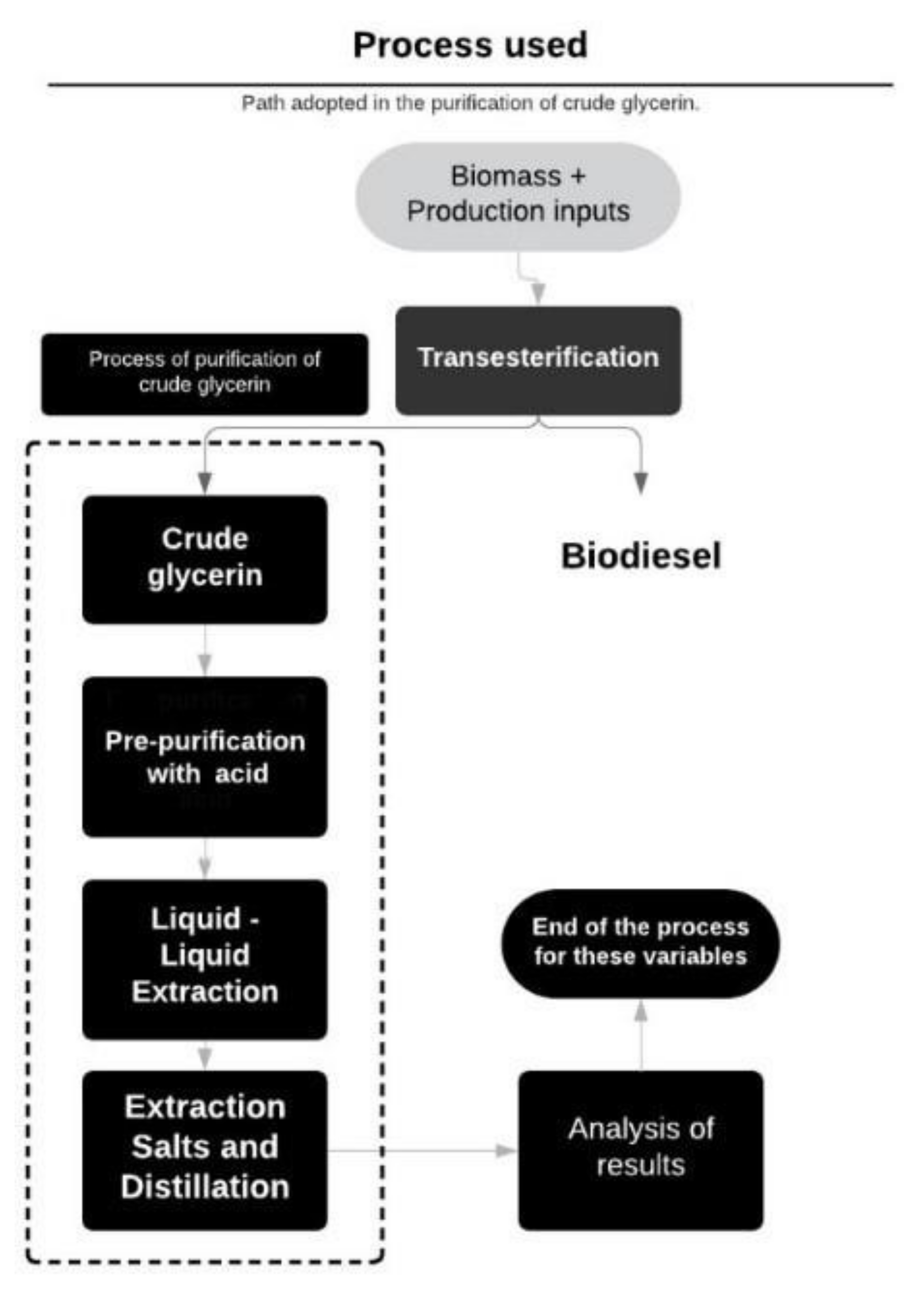
2. Materials and Methods
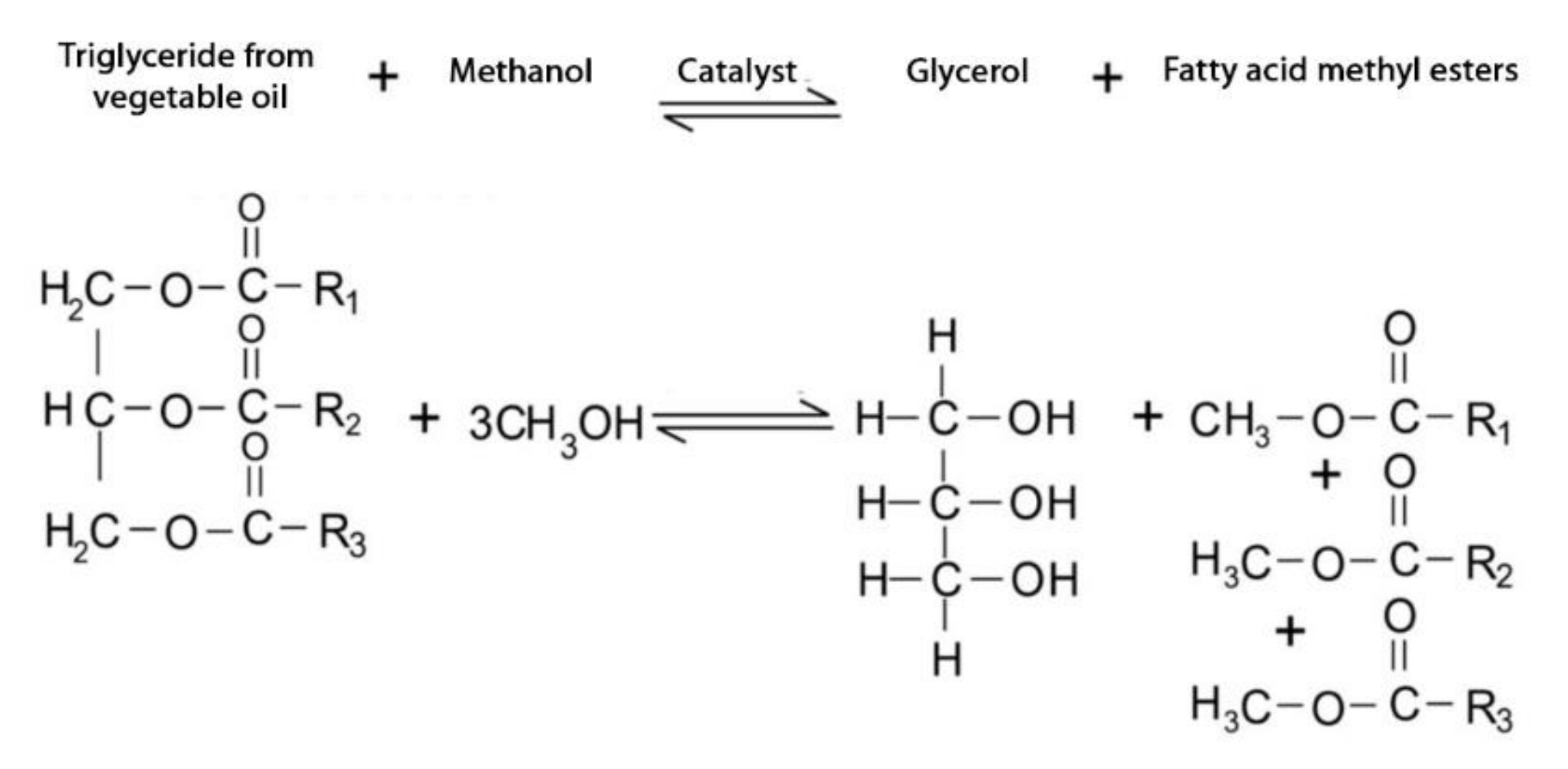
2.1. Glycerol Transesterification
2.2. Aspen Plus Model
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding

Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pereira Gabriel, C.K. Produção de Biodiesel a Partir de Óleo de Palma. Master’s Thesis, Instituto Superior Técnico, Lisbon, Portugal, 2015; pp. 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Malek, L. Simulation of Propionaldehyde Production from Glycerol. Master’s Thesis, Department of Chemical Engineering, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, B.H.H.; Chong, C.T.; Ge, Y.; Ong, H.C.; Ng, J.-H.; Tian, B.; Ashokkumar, V.; Lim, S.; Seljak, T.; Józsa, V. Progress in utilisation of waste cooking oil for sustainable biodiesel and biojet fuel production. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 223, 113296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A. and A. Rouboa. Renewable energy from solid waste: Life cycle analysis and social welfare. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2020, 85, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miscenco, D. Recuperação e Valorização de Glicerol Bruto da Produção de Biodiesel a Partir de Óleos Alimentares Usados; Faculdade de Ciências e Tecnologia da Universidade de Coimbra: Coimbra, Portugal, 2016; pp. 1–140. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, A.D.P.; Rodrigues Filho, G.M.; Mendes, M.F. Avaliação técnica de diferentes processos de separação para purificação do glicerol como subproduto—Revisão. Rev. Bras. Energ. Renov. 2017, 6, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.R.; Kugelmeier, C.L.; Pinheiro, R.S.; Batalha, M.O.; da Silva César, A. Glycerol from biodiesel production: Technological paths for sustainability. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 88, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardi, M.; Aroua, M.; Hashim, N.A. Progress, prospect and challenges in glycerol purification process: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatriz, A.; Araújo, Y.J.K.; De Lima, D.P. Glicerol: Um breve histórico e aplicação em sínteses estereosseletivas. Quim. Nova 2011, 34, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peiter, G.C.; Alves, H.J.; Sequinel, R.; Bautitz, I.R. Alternativas para o uso do glicerol produzido a partir do biodiesel. Rev. Bras. Energ. Renov. 2016, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, I.R.; Mahler, C.F.; Oliveira, L.B.; Reis, M.M.; Bassin, J.P. Assessing the use of crude glycerol from biodiesel production as an alternative to boost methane generation by anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 143, 105831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrpooya, M.; Ghorbani, B.; Abedi, H. Biodiesel production integrated with glycerol steam reforming process, solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) power plant. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 206, 112467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milessi, T.S.S.; Tabuchi, S.C.T.; Antunes, F.A.F.; da Silva, S. Variação da temperatura no tratamento do glicerol residual de biodiesel visando sua aplicação como fonte de carbono em processos fermentativos. In Proceedings of the 5º BIOCOM, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil, 21–23 March 2012; pp. 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, A.; Ashok, B.; Alagumalai, A.; Chyuan, O.H.; Le, P.T.K. Critical review on third generation micro algae biodiesel production and its feasibility as future bioenergy for IC engine applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 228, 113655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, H.C.; Tiong, Y.W.; Goh, B.H.H.; Gan, Y.Y.; Mofijur, M.; Fattah, I.R.; Chong, C.T.; Alam, M.A.; Lee, H.V.; Silitonga, A. Recent advances in biodiesel production from agricultural products and microalgae using ionic liquids: Opportunities and challenges. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 228, 113647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingos, A.M.; Pitt, F.D.; Chivanga Barros, A. Purification of residual glycerol recovered from biodiesel production. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 29, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- do Corgo e Silva, S. Breve Enciclopédia do Biodiesel; Vida Económica: Porto, Portugal, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Palomino-Romero, J.A.; Leite, O.M.; Barrios Eguiluz, K.I.; Salazar-Banda, G.R.; Silva, D.P.; Cavalcanti, E.B. Tratamentos dos efluentes gerados na produção de biodiesel. Quimica Nova 2012, 35, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pott, R.W.; Howe, C.J.; Dennis, J.S. The purification of crude glycerol derived from biodiesel manufacture and its use as a substrate by Rhodopseudomonas palustris to produce hydrogen. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, E.A.M. Avaliação de Metodologia de Purificação da Glicerina Gerada Como Coproduto na Produção de Biodiesel; Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná: Curitiba, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Stojković, I.J.; Stamenković, O.S.; Povrenović, D.S.; Veljković, V.B. Purification technologies for crude biodiesel obtained by alkali-catalyzed transesterification. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Andrade, I.; Avella-Moreno, E.; Sierra-Cantor, J.F.; Guerrero-Fajardo, C.A.; Sodre, J.R. Purification of glycerol from biodiesel production by sequential extraction monitored by 1H NMR. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 132, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Freitas, E.S. Produção de Biodiesel a Partir do Sebo Bovino: Proposta de um Sistema de Logística Reversa; Universidade Federal da Bahia: Salvador, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rivaldi, J.D.; Sarrouh, B.F.; Fiorilo, R.; Silva, S. Glicerol de biodiesel: Estratégias biotecnológicas para o aproveitamento do glicerol gerado da produção de biodiesel. Biotecnol. Ciênc. Desenvolv. 2016, 37, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Candeias, D. Valorization of crude glycerin from biodiesel production by acetalization. Téc. Lisboa 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, A.; Monteiro, E.; Rouboa, A. Numerical approaches and comprehensive models for gasification process: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 110, 188–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.B.; Rouboa, A. Optimizing the DMFC operating conditions using a response surface method. Appl. Math. Comput. 2012, 218, 6733–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchal, M.A.S.; Birchal, V.S. Automação De Uma Planta De Produção De Biodiesel. E-Xacta 2013, 6, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dos Santos, J.S.; de Araújo, A.C.B. Modelagem matemática do processo reativo e de. In Proceedings of the XXI Congresso Brasileiro de Engenharia Química, Fortaleza, Brazil, 25–29 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bastos, R.R.C.; da Luz Corrêa, A.P.; da Luz, P.T.S.; da Rocha Filho, G.N.; Zamian, J.R.; da Conceição, L.R.V. Optimization of biodiesel production using sulfonated carbon-based catalyst from an amazon agro-industrial waste. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 205, 112457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, J.; Errazu, A. Esterification of free fatty acids using sulfuric acid as catalyst in the presence of triglycerides. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 892–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.K.; Lee, K.T.; Mohamed, A.R. Homogeneous, heterogeneous and enzymatic catalysis for transesterification of high free fatty acid oil (waste cooking oil) to biodiesel: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 500–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakpong, P.; Wootthikanokkhan, S. High free fatty acid coconut oil as a potential feedstock for biodiesel production in Thailand. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 1682–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.H.; Lai, L.; Chin, L. Production of biodiesel from palm oil (Elaeis guineensis) using heterogeneous catalyst: An optimized process. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Medina, J.; Olivares-Carrillo, P. Evidence of thermal decomposition of fatty acid methyl esters during the synthesis of biodiesel with supercritical methanol. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2011, 56, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Hanna, M.A. Biodiesel production: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 70, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudha, M.I.; Laksmana, D.I. Glycerin purification of biodiesel production side products by distillation method. In Proceedings of the Seminar Nasional Kimia-National Seminar on Chemistry (SNK 2018), State University of Surabaya, Jawa Timur, Indonesia, 7–12 August 2018; pp. 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, P.; Baroi, C.; Dalai, A.K. Feasibility study of crude glycerol purification processes. J. Basic Appl. Eng. Res. 2015, 2, 60–63. [Google Scholar]






| Degree | Degree I | Degree II | Degree III |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purity | ~99.5% (Technical degree) | 96-99.5% (USP * degree) | 99.5-99.7% (Kosher or USP/FCC **) |
| Manufacturing and Use | Prepared by synthetic process and used in chemical industry, but not applicable to food or drug formulation. | Prepared from sources of animal fat or vegetable oil, suitable for food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic products. | Prepared from vegetable oil sources, suitable for use in kosher food and beverages. |
| Component | Wt. (%) |
|---|---|
| Glycerol | 50 |
| Methanol | 35 |
| Potassium hydroxide | 10 |
| Methyl oleate | 5 |
| Sulfuric acid | 0 |
| Water | 0 |
| Property | Crude Glycerol | Sulfuric Acid |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 25 | 25 |
| Pressure (kPa) | 101.325 | 101.325 |
| Molar flow (kmol/h) | 24.10 | 10.99 |
| Mass flow (kg/h) | 1200 | 283.78 |
| Component Mass Fraction (%) | ||
| Glycerol | 50.0 | 0.0 |
| Methanol | 35.0 | 0.0 |
| Potassium hydroxide | 10.0 | 0.0 |
| Methyl oleate | 5.0 | 0.0 |
| Sulfuric acid | 0.0 | 37.0 |
| Water | 0.0 | 63.0 |
| Component | Mass Fraction (%) |
|---|---|
| Glycerol | 2.22 |
| Methanol | 41.39 |
| Potassium hydroxide | 0.0 |
| Methyl oleate | 4.34 × 10−6 |
| Sulfuric acid | 9.88 × 10−4 |
| Water | 56.38 |
| Property | Glycerol | Residual | Wat + Meth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molar flow (kmol/h) | 6.69 | 2.70 | 3.30 |
| Mass flow (kg/h) | 616.53 | 867.25 | 84.20 |
| Component Mass Fraction (%) | |||
| Glycerol | 99.768 | 20.64 | 2.22 |
| Methanol | 2.47 × 10−3 | 1.56 × 10−3 | 41.39 |
| Potassium hydroxide | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Methyl oleate | 5.17 × 10 −3 | 23.82 | 23.82 × 10−10 |
| Sulfuric acid | 0.206 | 55.53 | 4.33 × 10−10 |
| Water | 0.018 | 8.23 × 10−5 | 56.38 |
| Stage | Glycerol (%) | Sulfuric Acid (%) | Methyl Oleate (%) | Methanol (%) | Potassium Hydroxide (%) | Water (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13.19 | 37.79 | 49.01 | 3.46 × 10−6 | 4.83 × 10−6 | 1.03 × 10−5 |
| 2 | 53.95 | 26.19 | 19.86 | 6.43 × 10−6 | 3.65 × 10−18 | 2.01 × 10−5 |
| 3 | 89.80 | 7.44 | 2.75 | 8.43 × 10−6 | 0.0 | 2.69 × 10−5 |
| 4 | 98.37 | 1.39 | 0.24 | 9.44 × 10−6 | 0.0 | 3.04 × 10−5 |
| 5 | 99.77 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 8.59 × 10−4 | 0.0 | 3.46 × 10−3 |
| Property | Arora et al. [38] | This Work |
|---|---|---|
| Glycerol (%) | 99 | 99.77 |
| Methanol (%) | 0.047 | 2.47 × 10−3 |
| Potassium hydroxide (%) | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Methyl oleate (%) | 3.61 × 10−6 | 5.17 × 10−3 |
| Sulfuric acid (%) | 3.60 × 10−6 | 0.206 |
| Water (%) | 0.072 | 0.018 |
| Mass flow (kg/h) | 436.90 | 616.53 |
| Molar flow (kmol/h) | 4.76 | 6.69 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, M.; Ramos, A.; Monteiro, E.; Rouboa, A. Improvement of the Crude Glycerol Purification Process Derived from Biodiesel Production Waste Sources through Computational Modeling. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031747
Oliveira M, Ramos A, Monteiro E, Rouboa A. Improvement of the Crude Glycerol Purification Process Derived from Biodiesel Production Waste Sources through Computational Modeling. Sustainability. 2022; 14(3):1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031747
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Matheus, Ana Ramos, Eliseu Monteiro, and Abel Rouboa. 2022. "Improvement of the Crude Glycerol Purification Process Derived from Biodiesel Production Waste Sources through Computational Modeling" Sustainability 14, no. 3: 1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031747
APA StyleOliveira, M., Ramos, A., Monteiro, E., & Rouboa, A. (2022). Improvement of the Crude Glycerol Purification Process Derived from Biodiesel Production Waste Sources through Computational Modeling. Sustainability, 14(3), 1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031747









