Symbiotic Relationships in Business Ecosystem: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- RQ 1. What types of symbiotic relationships exist between participants in a business ecosystem?
- RQ 2. How do symbiotic relationships evolve, and how are they developed in a business ecosystem?
- RQ 3. How can participants in a business ecosystem benefit from symbiotic relationships?
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. The Emergence of the Concept of Business Ecosystem
2.2. Participants of the Business Ecosystem
2.3. The Role of Business Platform in Business Ecosystem
2.4. Research Gap in the Field of Business Ecosystem
3. Data and Research Method
4. Systematic Review of Symbiotic Relationships in the Business Ecosystem
4.1. Descriptive Analysis
4.2. Typology of Symbiotic Relationships in a Business Ecosystem
4.3. Symbiosis in a Business Ecosystem
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clarysse, B.; Wright, M.; Bruneel, J.; Mahajan, A. Creating value in ecosystems: Crossing the chasm between knowledge and business ecosystems. Res. Policy 2014, 43, 1164–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-R. The technological roadmap of Cisco’s business ecosystem. Technovation 2009, 29, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Mejia, C.; Kajikawa, Y. Business, innovation and digital ecosystems landscape survey and knowledge cross sharing. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 147, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Leyer, M.; Tate, M. The transformational impact of blockchain technology on business models and ecosystems: A symbiosis of human and technology agents. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 67, 1184–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senyo, P.K.; Liu, K.; Effah, J. Digital business ecosystem: Literature review and a framework for future research. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 47, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basole, R.C. Visualization of interfirm relations in a converging mobile ecosystem. J. Inf. Technol. 2009, 24, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltoniemi, M. Preliminary theoretical framework for the study of business ecosystems. Emerg. Complex. Organ. 2006, 8, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Basole, R.C.; Karla, J. On the evolution of mobile platform ecosystem structure and strategy. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2011, 3, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awano, H.; Tsujimoto, M. The Mechanisms for Business Ecosystem Members to Capture Part of a Business Ecosystem’s Joint Created Value. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarakas, W.P. Two-sided markets and the utility of the future: How services and transactions can shape the utility platform. Electr. J. 2017, 30, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.H.; Costello, F.J.; Kim, C. Assisting sustainable entrepreneurial activities through the analysis of mobile IT services’ success and failure factors. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, M.L.; Hine, M.J. Who Inhabits a Business Ecosystem? The Technospecies as a Unifying Concept. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2015, 5, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltoniemi, M.; Vuori, E. Business ecosystem as the new approach to complex adaptive business environments. Proc. Ebus. Res. Forum 2004, 2, 267–281. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.F. Predators and prey: A new ecology of competition. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1993, 71, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Vasconcelos Gomes, L.A.; Facin, A.L.F.; Salerno, M.S.; Ikenami, R.K. Unpacking the innovation ecosystem construct: Evolution, gaps and trends. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karhiniemi, M. Creating and Sustaining Successful Business Ecosystems. Master’s Thesis, Aalto University School of Business, Espoo, Finland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto, M.; Kajikawa, Y.; Tomita, J.; Matsumoto, Y. A review of the ecosystem concept—Towards coherent ecosystem design. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iansiti, M.; Levien, R. Keystones and dominators: Framing operating and technology strategy in a business ecosystem. Harvard Bus. Sch. Work. Pap. 2004, 03-061, 1–82. [Google Scholar]
- Dedehayir, O.; Mäkinen, S.J.; Roland Ortt, J. Roles during innovation ecosystem genesis: A literature review. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walton, N. Ecosystems Thinking and Modern Platform-Based Ecosystem Theory. In The Internet as a Technology-Based Ecosystem; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 85–117. [Google Scholar]
- Galateanu-Avram, E.; Avasilcai, S. Business Ecosystems Arhitecture. Ann. ORADEA Univ. Fascicle Manag. Technol. Eng. 2013, XXII, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verna, A. Mapping Business Ecosystems. Partneringresources 2016, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bocken, N.; Boons, F.; Baldassarre, B. Sustainable business model experimentation by understanding ecologies of business models. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 1498–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarikka-Stenroos, L.; Ritala, P. Network management in the era of ecosystems: Systematic review and management framework. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2017, 67, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. The Platform Business Model and Strategy: A Dynamic Analysis of the Value Chain and Platform Business; The University of Manchester (United Kingdom): Manchester, UK, 2016; ISBN 1073914879. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenhard, M.; Kijl, B.; Nieuwenhuis, L. Market adoption barriers of multi-stakeholder technology: Smart homes for the aging population. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2014, 89, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikas, K.; Hansen, K.M. Software ecosystems—A systematic literature review. J. Syst. Softw. 2013, 86, 1294–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachira, F.; Dini, P.; Nicolai, A. A network of digital business ecosystems for Europe: Roots, processes and perspectives. Eur. Comm. Bruxelles Introd. Pap. 2007, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Nambisan, S.; Baron, R.A. Entrepreneurship in innovation ecosystems: Entrepreneurs’ self-regulatory processes and their implications for new venture success. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2013, 37, 1071–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.F. The Death of Competition; Harper Business: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 1–297. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.-K.; Wu, C.-M.; Chen, L.-S.; Huang, Y.-P. The Influential Factors of Taiwan SMEs’ Clustering Keystone Business Strategy—The Perspective of Business Ecosystem Using FAHP. Sustainability 2021, 13, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch-Sijtsema, P.M.; Bosch, J. Plays nice with others? Multiple ecosystems, various roles and divergent engagement models. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2015, 27, 960–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veugelers, R. Eco-systems for young digital innovators. J. Technol. Transf. 2018, 43, 1449–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhou, H. The dynamic equilibrium and simulation of mobile internet platform innovation ecosystem: A symbiotic evolution model. Kybernetes 2016, 45, 1406–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, K.; Lin, Y.; Li, B.; Burström, T.; Butel, L.; Yu, J. Business ecosystem research agenda: More dynamic, more embedded, and more internationalized. Asian Bus. Manag. 2018, 17, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volberda, H.W.; Lewin, A.Y. Co-evolutionary dynamics within and between firms: From evolution to co-evolution. J. Manag. Stud. 2003, 40, 2111–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Feng, N.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Q. A conceptual framework of two-stage partner selection in platform-based innovation ecosystems for servitization. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.; Sun, S.L. The Genesis of Fabless Business Model: Institutional Entrepreneurs in an Adaptive Ecosystem. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 2017, 34, 587–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuis, L.J.M.M.; Ehrenhard, M.L.; Prause, L. The shift to Cloud Computing: The impact of disruptive technology on the enterprise software business ecosystem. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 129, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zuo, L.; Tang, J. Dominant platform capability, symbiotic strategy and the construction of “Internet + WEEE collection” business ecosystem: A comparative study of two typical cases in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltoniemi, M. Business Ecosystem: A Conceptual Model of an Organisation Population from the Perspectives of Complexity and Evolution; Tampere University of Technology: Tampere, Finland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Iansiti, M.; Levien, R. The Keystone Advantage: What the New dynamics of Business Ecosystems Mean for Strategy, Innovation, and Sustainability; Harvard Business Press: Brighton, MA, USA, 2004; ISBN 1591393078. [Google Scholar]
- Iansiti, M.; Levien, R. The New Operational Dynamics of Business Ecosystems: Implications for Policy, Operations and Technology Strategy; Citeseer: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hyeyoung, K.I.M.; Jae-Nam, L.E.E.; Jaemin, H.A.N. The Role of IT in Business Ecosystems 2010. Commun. ACM 2010, 53, 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.H.; Burgess, N.D.; Rahbek, C. Flagship species, ecological complementarity and conserving the diversity of mammals and birds in sub-Saharan Africa. Anim. Conserv. 2000, 3, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M. A Study on Platform’s New Strategy in Media 2.0 Era-Based on “Keystone” Concept & Google Case. In Proceedings of the 21st European Regional Conference of the International Telecommunications Society (ITS), Copenhagen, Denmark, 13–15 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pagano, U. The Origin of Organizational Species; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 1315011077. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, J.D.; Crawford, S.E.S. Organizational ecology and the movement of nonprofit organizations. State Local Gov. Rev. 2008, 40, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, P.C.; Gawer, A. The Rise of the Platform Enterprise A Global Survey; The Center for Global Enterprise: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Lee, D.; Hwang, J. Platform openness and the productivity of content providers: A meta-frontier analysis. Telecomm. Policy 2015, 39, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y. Winner-takes-all or co-evolution among platform ecosystems: A look at the competitive and symbiotic actions of complementors. Sustainability 2019, 11, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobson, P.W. Competing, countervailing, and coalescing forces: The economics of intra-and inter-business system competition. Antitrust Bull. 2006, 51, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Lee, H. The Primary Actors of Technology Standardization in the Manufacturing Industry. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 101886–101901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, D.; Lorusso, L.N. How to write a systematic review of the literature. HERD Health Environ. Res. Des. J. 2018, 11, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis-Beck, M.; Bryman, A.E.; Liao, T.F. The Sage Encyclopedia of Social Science Research Methods; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2003; ISBN 1452261458. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Hongqi, L.; Khan, S.U.; Zhongguo, Y.; Liping, Z. Success factors for software outsourcing partnership management: An exploratory study using systematic literature review. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 23589–23612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, N.; Grottke, M.; Mishra, S.; Brem, A. A systematic literature review of constraint-based innovations: State of the art and future perspectives. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2016, 64, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Given, L.M. The Sage Encyclopedia of Qualitative Research Methods; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2008; ISBN 1452265895. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, S.; Lee, H. Shaping a Circular Economy in the Digital TV Industry: Focusing on Ecopreneurship through the Lens of Dynamic Capability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.F. Coding, sorting and sifting of qualitative data analysis: Debates and discussion. Qual. Quant. 2015, 49, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, T. Manual or electronic? The role of coding in qualitative data analysis. Educ. Res. 2003, 45, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldaña, J. The Coding Manual for Qualitative Researchers; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2021; ISBN 1529755999. [Google Scholar]
- Garza-Reyes, J.A. Lean and green-a systematic review of the state of the art literature. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 102, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benitez, G.B.; Ayala, N.F.; Frank, A.G. Industry 4.0 innovation ecosystems: An evolutionary perspective on value co-creation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 228, 107735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatautis, R. The rise of the platforms: Business model innovation perspectives. Eng. Econ. 2017, 28, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peppard, J.; Rylander, A. From value chain to value network:: Insights for mobile operators. Eur. Manag. J. 2006, 24, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saunders, S.R.; Carlaw, S.; Giustina, A.; Bhat, R.R.; Rao, V.S.; Siegberg, R. Femtocells: Opportunities and Challenges for Business and Technology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, K.; Lin, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yu, J. Linking business ecosystem lifecycle with platform strategy: A triple view of technology, application and organisation. Int. J. Technol. Manag. 2013, 62, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owyang, B.J. Collaborative Economy. Encycl. Creat. Invent. Innov. Entrep. 2020, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Koh, B.; Raghunathan, S. Value appropriation between the platform provider and app developers in mobile platform mediated networks. J. Inf. Technol. 2015, 30, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnahan, S.; Agarwal, R.; Campbell, B. The Effect of Firm Compensation Structures on the Mobility and Entrepreneurship of Extreme Performers. Business 2010, 1154, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lsckia, T. Amazon’s evolving ecosystem: A cyber-bookstore and application service provider. Can. J. Adm. Sci. 2009, 26, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritala, P.; Golnam, A.; Wegmann, A. Coopetition-based business models: The case of Amazon.com. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2014, 43, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isckia, T.; Lescop, D. Open Innovation within Business Ecosystems: A Tale from Amazon.com: Open innovation. Commun. Strateg. 2009, 1, 37–54. [Google Scholar]
- Boons, F.; Bocken, N. Towards a sharing economy—Innovating ecologies of business models. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 137, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, D.; Ming, X.; Zhang, X. Sustainable and smart product innovation ecosystem: An integrative status review and future perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 123005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.Y.; Zhao, S.; Elesh, D.; Davies, A.; Simon, J.; Deiglmeier, K.; Miller, D.T.D.; Phills, J.; Deiglmeier, K.; Miller, D.T.D.; et al. Platform Strategy & Open Business Models. Int. J. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Khanagha, S.; Ansari, S.; Paroutis, S.; Oviedo, L. Mutualism and the dynamics of new platform creation: A study of cisco and fog computing. Strateg. Manag. J. 2022, 43, 476–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rai, B.; Freedman, H.I.; Addicott, J.F. Analysis of three species models of mutualism in predator-prey and competitive systems. Math. Biosci. 1983, 65, 13–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wang, H. How to bridge the gap between innovation niches and exploratory and exploitative innovations in open innovation ecosystems. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 124, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roma, P.; Perrone, G. Cooperation among competitors: A comparison of cost-sharing mechanisms. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 180, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majava, J.; Isoherranen, V.; Kess, P. Business Collaboration Concepts and Implications for Companies. Int. J. Synerg. Res. 2013, 2, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, T.L.F.; Poulin, R. Parasitism, commensalism, mutualism, exploring the many shades of symbioses. Vie Et Milieu/Life Environ. 2008, 58, 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Crawley, S. Free Ride: How Digital Parasites are Destroying the Culture Business, and How the Culture Business Can Fight Back. Intellect. Prop. J. 2012, 24, 315. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Ye, R.M.; Wu, J. Platform strategies for innovation ecosystem: Double-case study of Chinese automobile manufactures. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 1564–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gakkhar, S.; Gupta, K. A three species dynamical system involving prey–predation, competition and commensalism. Appl. Math. Comput. 2016, 273, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulme-Beaman, A.; Dobney, K.; Cucchi, T.; Searle, J.B. An ecological and evolutionary framework for commensalism in anthropogenic environments. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galvão, G.D.A.; Homrich, A.S.; Geissdoerfer, M.; Evans, S.; Scoleze Ferrer, P.S.; Carvalho, M.M. Towards a value stream perspective of circular business models. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 162, 105060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccia, M.; Watts, J. A theory of the evolution of technology: Technological parasitism and the implications for innovation magement. J. Eng. Technol. Manag.—JET-M 2020, 55, 101552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaringella, L.; Radziwon, A. Innovation, entrepreneurial, knowledge, and business ecosystems: Old wine in new bottles? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 59–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellinen, A.; Ritala, P.; Järvi, K.; Sainio, L.M. Taking initiative in market creation—A business ecosystem actor perspective. Int. J. Bus. Environ. 2012, 5, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwana, A. Platform Ecosystems: Aligning Architecture, Governance, and Strategy; Newnes: Oxford, UK, 2013; ISBN 0124080545. [Google Scholar]
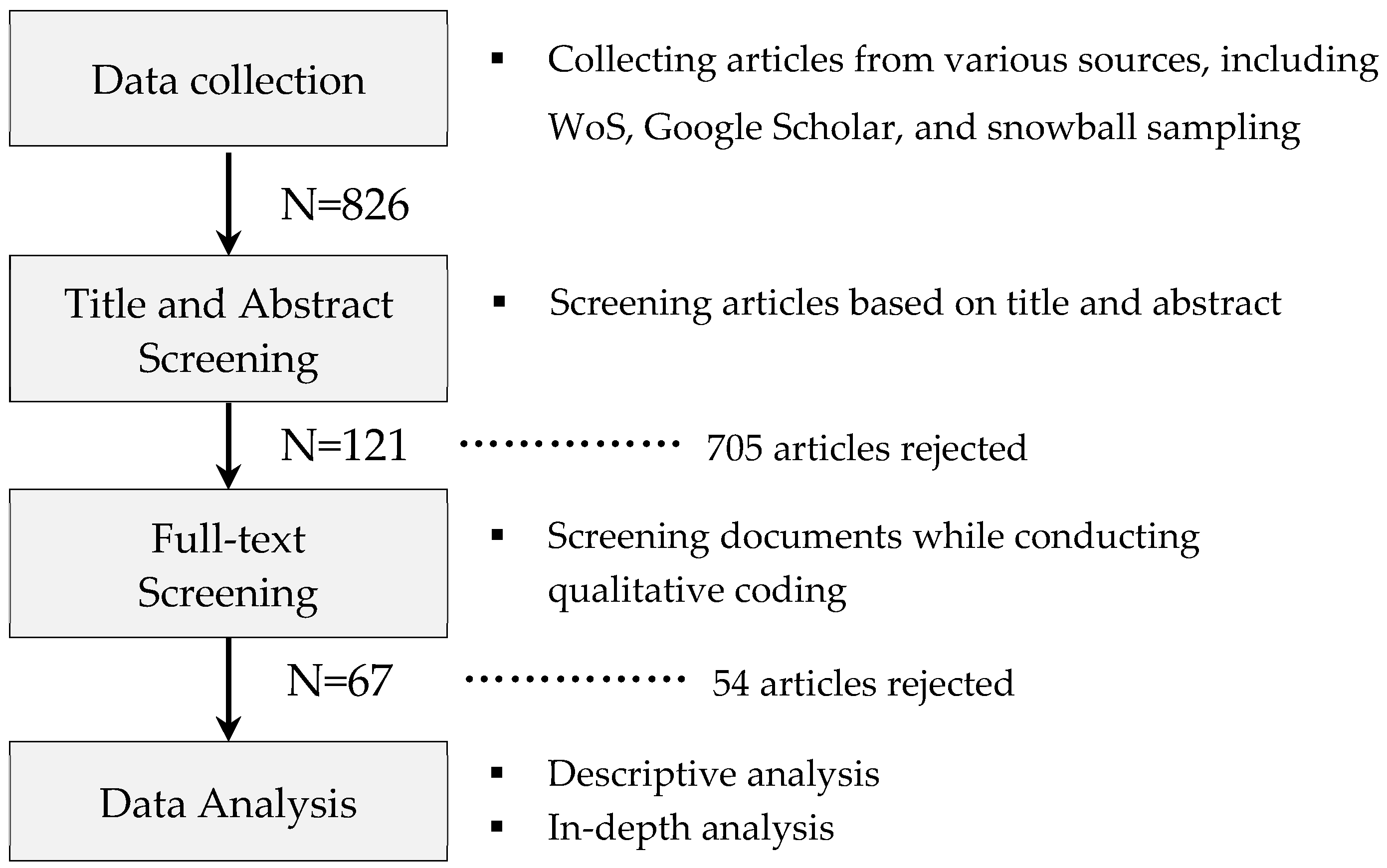

| Data Source | Description | Number of Documents |
|---|---|---|
| ScienceDirect | A database for academic journals with scientific and medical publications published by Elsevier. | 499 |
| Springer | Online subscription-based academic journal publisher provides scientific indexing services. | 246 |
| Web of Science | Provides comprehensive citation data from multiple databases by Clarivate. | 10 |
| Scopus | Database of abstracts and citations from book series and journals launched by Elsevier in 2004. | 9 |
| Snowball sampling | Snowball sampling is a purposive sampling method used to collect data using the initial data set as a lead. | 62 |
| Sum | 826 | |
| Data Type | Source | Sum | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Science Direct | Scopus | Springer | WoS | Snowball Sampling | ||
| Article | 26 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 14 | 50 |
| Book | - | - | 2 | - | 1 | 3 |
| Conference proceeding | - | - | 1 | - | 2 | 3 |
| Dissertation | - | - | - | - | 3 | 3 |
| Editorial perspective | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 2 |
| Magazine | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| Report | - | - | - | - | 3 | 3 |
| Working paper | - | - | - | - | 2 | 2 |
| Sum | 27 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 27 | 67 |
| Journal | Number of Articles |
|---|---|
| Technology Forecasting and Social Change | 9 |
| Journal of Cleaner Production | 5 |
| Technovation | 2 |
| Technology Innovation Management Review | 2 |
| Industrial Marketing Management | 2 |
| Asian Business and Management | 2 |
| Journal of Systems and Software | 2 |
| Others | 43 |
| Research Methods | A Proportion of Each Method | |
|---|---|---|
| Qualitative/Quantitative/Mixed | Detailed Methods | |
| Qualitative (84%) | Case study | 34% |
| SLR | 26% | |
| Narrative review | 20% | |
| Content analysis | 2% | |
| Integrative review | 2% | |
| Quantitative (14%) | Survey | 2% |
| Logistic model | 2% | |
| Network analysis | 2% | |
| Regression | 2% | |
| Others | 6% | |
| Mixed (2%) | Comparative historical Analysis + regression | 2% |
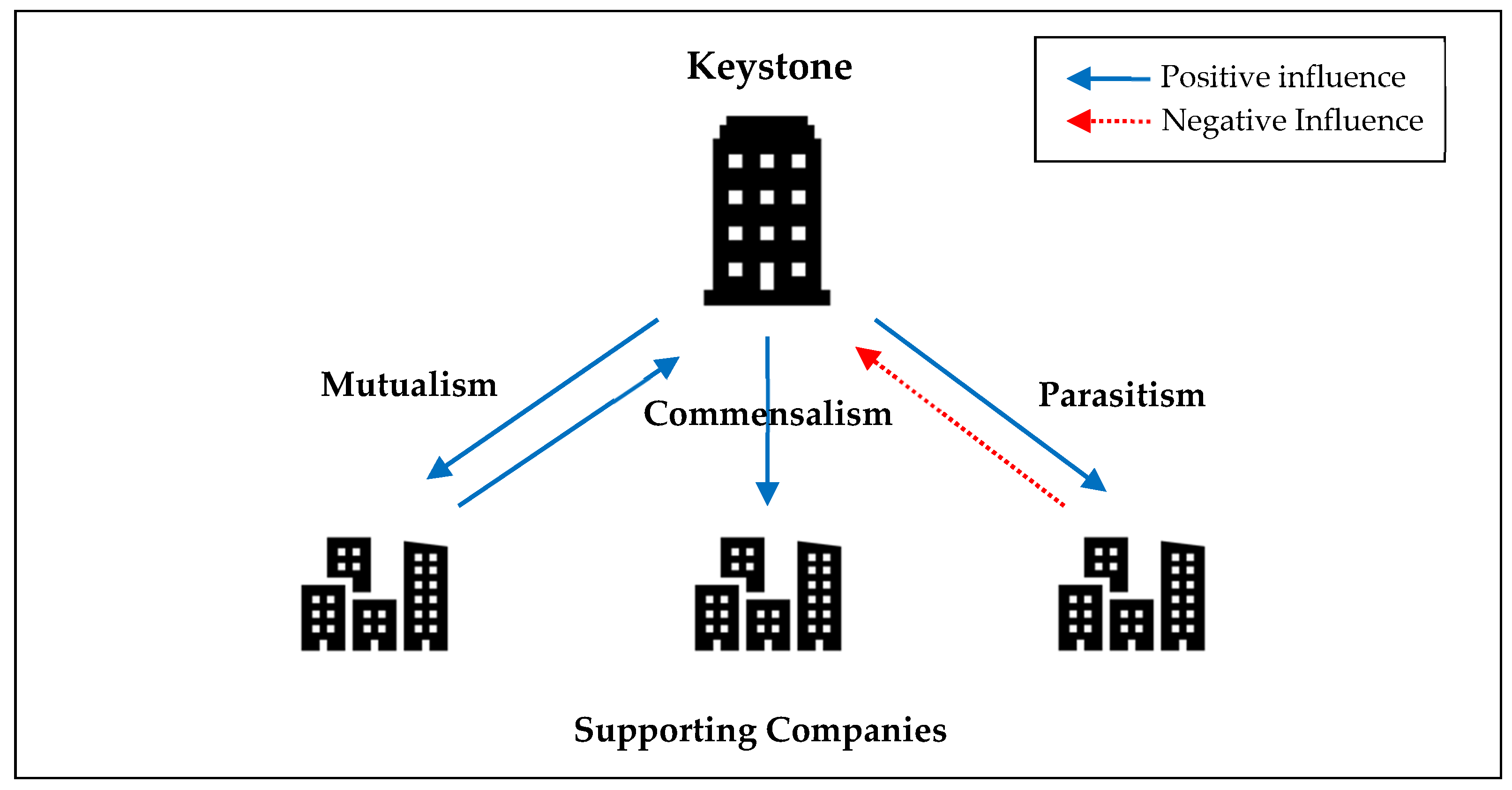
| Category | Mutualism | Commensalism | Parasitism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition |
|
| |
| Relationship |
|
|
|
| Features |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, C.; Moon, S.; Lee, H. Symbiotic Relationships in Business Ecosystem: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042252
Yoon C, Moon S, Lee H. Symbiotic Relationships in Business Ecosystem: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability. 2022; 14(4):2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042252
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Changhee, Seungyeon Moon, and Heesang Lee. 2022. "Symbiotic Relationships in Business Ecosystem: A Systematic Literature Review" Sustainability 14, no. 4: 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042252
APA StyleYoon, C., Moon, S., & Lee, H. (2022). Symbiotic Relationships in Business Ecosystem: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability, 14(4), 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042252








