Assessment of Water-Induced Soil Erosion as a Threat to Natura 2000 Protected Areas in Crete Island, Greece
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
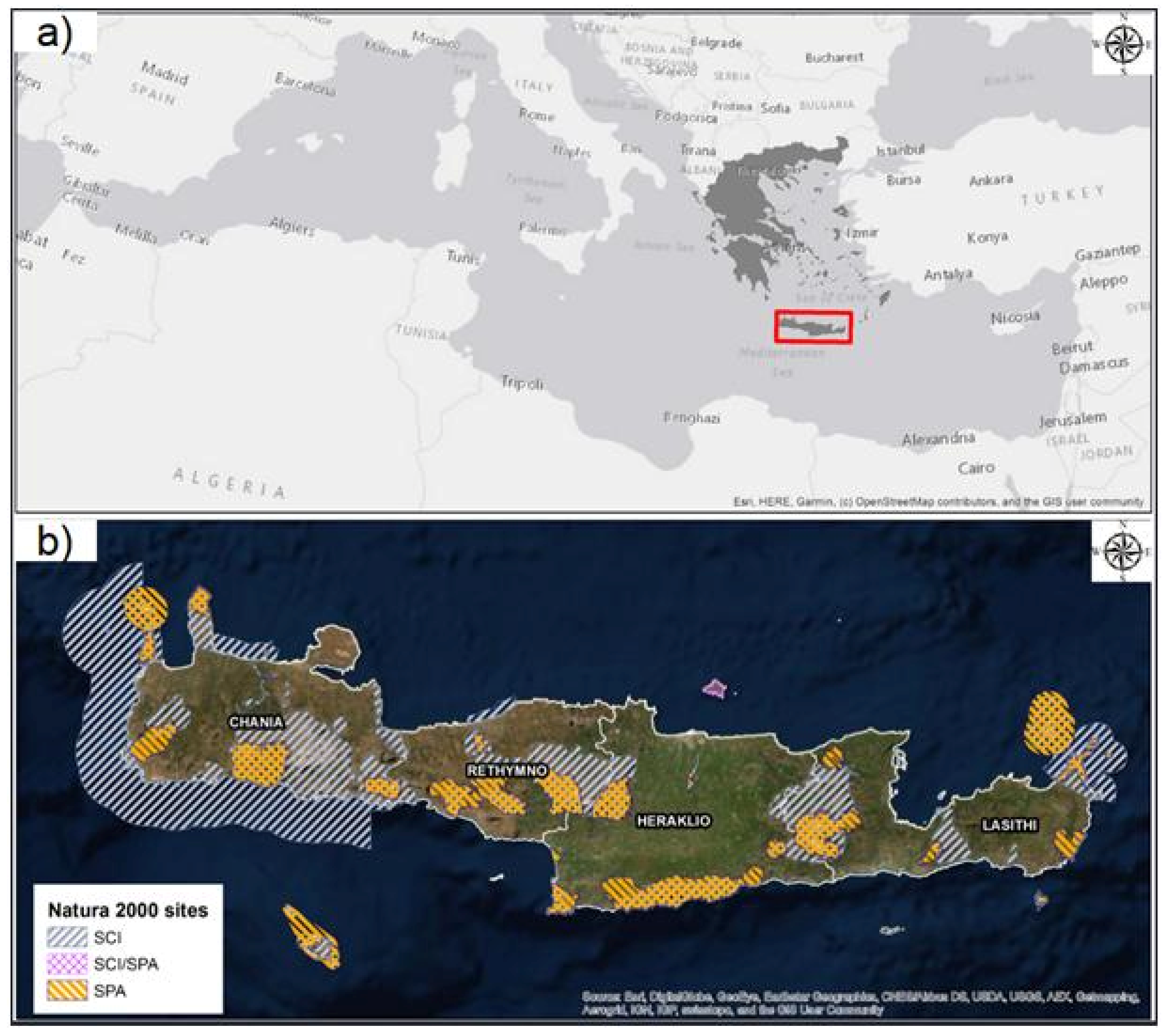
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. RUSLE Model Description
2.4. Methodology Outline
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alewell, C.; Egli, M.; Meusburger, K. An attempt to estimate tolerable soil erosion rates by matching soil formation with denudation in Alpine grasslands. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 1383–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giuliani, G.; Chatenoux, B.; Benvenuti, A.; Lacroix, P.; Santoro, M.; Mazzetti, P. Monitoring land degradation at national level using satellite Earth Observation time-series data to support SDG15–exploring the potential of data cube. Big Earth Data 2020, 4, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arshad, M.A.; Martin, S. Identifying critical limits for soil quality indicators in agro-ecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 88, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, C.A.; Maes, J.; Geijzendorffer, I.; Metzger, M.J. An assessment of soil erosion prevention by vegetation in Mediterranean Europe: Current trends of ecosystem service provision. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, K.R.; Al-Kaisi, M.; Lal, R.; Cihacek, L. Impact of soil erosion on soil organic carbon stocks. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 71, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panagos, P.; Standardi, G.; Borrelli, P.; Lugato, E.; Montanarella, L.; Bosello, F. Cost of agricultural productivity loss due to soil erosion in the European Union: From direct cost evaluation approaches to the use of macroeconomic models. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgiazzi, A.; Panagos, P. Soil biodiversity and soil erosion: It is time to get married: Adding an earthworm factor to soil erosion modelling. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2018, 27, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polykretis, C.; Alexakis, D.D.; Grillakis, M.G.; Agapiou, A.; Cuca, B.; Papadopoulos, N.; Sarris, A. Assessment of water-induced soil erosion as a threat to cultural heritage sites: The case of Chania prefecture, Crete Island, Greece. Big Earth Data 2021, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselberger, S.; Ohler, L.M.; Junker, R.R.; Otto, J.C.; Glade, T.; Kraushaar, S. Quantification of biogeomorphic interactions between small-scale sediment transport and primary vegetation succession on proglacial slopes of the Gepatschferner, Austria. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2021, 46, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezak, N.; Borrelli, P.; Panagos, P. A first assessment of rainfall erosivity synchrony scale at pan-European scale. Catena 2021, 198, 105060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, S.; Alexandridis, V.; Chatzichristaki, C.; Stefanidis, P. Assessing soil loss by water erosion in a typical Mediterranean ecosystem of northern Greece under current and future rainfall erosivity. Water 2021, 13, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Spinoni, J.; Meusburger, K.; Michaelides, S.; Begueria, S.; Klik, A.; Petan, S.; Janecek, M.; Olsen, P.; et al. Mapping monthly rainfall erosivity in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1298–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. A New European Slope Length and Steepness Factor (LS-Factor) for Modeling Soil Erosion by Water. Geosciences 2015, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DiBiase, R.A.; Whipple, K.X. The influence of erosion thresholds and runoff variability on the relationships among topography, climate, and erosion rate. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panagos, P.; Meusburger, K.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Alewell, C. Soil erodibility in Europe: A high-resolution dataset based on LUCAS. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 479, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efthimiou, N. The new assessment of soil erodibility in Greece. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 204, 104720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moges, D.M.; Bhat, H.G. Integration of geospatial technologies with RUSLE for analysis of land use/cover change impact on soil erosion: Case study in Rib watershed, north-western highland Ethiopia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, N.; Psomiadis, E. The significance of land cover delineation on soil erosion assessment. Environ. Manag. 2018, 62, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao; Yang; Guo, B.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, D.; Zhen, X.; Chen, S.; Wu, H.; Wei, C.; et al. Spatial–temporal evolution patterns of soil erosion in the Yellow River Basin from 1990 to 2015: Impacts of natural factors and land use change. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2021, 12, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A.; Concepcion Ramos, M. Soil alteration due to erosion, ploughing and levelling of vineyards in northeast Spain. Soil Use Manag. 2009, 25, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Orenes, F.; Roldán, A.; Mataix-Solera, J.; Cerdà, A.; Campoy, M.; Arcenegui, V.; Caravaca, F. Soil structural stability and erosion rates influenced by agricultural management practices in a semi-arid Mediterranean agro-ecosystem. Soil Use Manag. 2012, 28, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairis, O.; Karavitis, C.; Salvati, L.; Kounalaki, A.; Kosmas, K. Exploring the impact of overgrazing on soil erosion and land degradation in a dry Mediterranean agro-forest landscape (Crete, Greece). Arid Land Res. Manag. 2015, 29, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, Y.; Dimitriou, E.; Skoulikidis, N. Vulnerability of a Northeast Mediterranean Island to Soil Loss. Can Grazing Management Mitigate Erosion? Water 2019, 11, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borrelli, P.; Panagos, P.; Langhammer, J.; Apostol, B.; Schütt, B. Assessment of the cover changes and the soil loss potential in European forestland: First approach to derive indicators to capture the ecological impacts on soil-related forest ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myronidis, D.I.; Emmanouloudis, D.A.; Mitsopoulos, I.A.; Riggos, E.E. Soil erosion potential after fire and rehabilitation treatments in Greece. Environ. Modeling Assess. 2010, 15, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallinis, G.; Gitas, I.Z.; Tasionas, G.; Maris, F. Multitemporal monitoring of land degradation risk due to soil loss in a fire-prone Mediterranean landscape using multi-decadal Landsat imagery. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 1255–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamesouti, M.; Petropoulos, G.P.; Papanikolaou, I.D.; Kairis, O.; Kosmas, K. Erosion rate predictions from PESERA and RUSLE at a Mediterranean site before and after a wildfire: Comparison & implications. Geoderma 2016, 261, 44–58. [Google Scholar]
- Efthimiou, N.; Psomiadis, E.; Panagos, P. Fire severity and soil erosion susceptibility mapping using multi-temporal Earth Observation data: The case of Mati fatal wildfire in Eastern Attica, Greece. Catena 2020, 187, 104320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Nunes, J.P.; Baartman, J.E.; Urbina, C.F. Testing the impacts of wildfire on hydrological and sediment response using the OpenLISEM model. Calibration and evaluation for a burned Mediterranean forest catchment. Catena 2021, 207, 105658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; ITPS. Status of the World’s Soil Resources (SWSR)–Main Report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and Intergovernmental Technical Panel on Soils: Rome, Italy, 2015; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i5199e.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Montanarella, L.; Pennock, D.J.; McKenzie, N.; Badraoui, M.; Chude, V.; Baptista, I.; Mamo, T.; Yemefack, M.; Singh Aulakh, M.; Yagi, K.; et al. Soil conservation in Europe: Wish or reality? Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Imeson, A.; Meusburger, K.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Alewell, C. Soil conservation in Europe: Wish or reality? Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keesstra, S.D.; Bouma, J.; Wallinga, J.; Tittonell, P.; Smith, P.; Cerdà, A.; Montanarella, L.; Quinton, J.N.; Pachepsky, Y.; van der Putten, W.H. The significance of soils and soil science towards realization of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Soil 2016, 2, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EC. Proposal for a Establishing a Framework for the Protection of Soil and Amending. Directive 2004/35/EC COM, 232. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uricelex:52006PC0232 (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Robinson, N. The European union’s environmental agenda. Environ. Politics 1999, 8, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; Da Fonseca, G.A.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffenbaugh, N.S.; Giorgi, F. Climate change hotspots in the CMIP5 global climate model ensemble. Clim. Change 2012, 114, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velázquez, J.; Tejera, R.; Hernando, A.; Núñez, M.V. Environmental diagnosis: Integrating biodiversity conservation in management of Natura 2000 forest spaces. J. Nat. Conserv. 2010, 18, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Alewell, C.; Alvarez, P.; Anache, J.A.A.; Baartman, J.; Ballabio, C.; Bezak, N.; Biddoccu, M.; Cerdà, A.; Chalise, D.; et al. Soil erosion modelling: A global review and statistical analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 780, 146494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Katsoyiannis, A. Soil erosion modelling: The new challenges as the result of policy developments in Europe. Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. A review of the design and operation of runoff and soil loss plots. Catena 2016, 145, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, P.; Sapountzis, M.; Stathis, D. Sheet erosion after fire at the urban forest of Thessaloniki (Northern Greece). Silva Balc. 2002, 2, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Boix-Fayos, C.; Martínez-Mena, M.; Arnau-Rosalén, E.; Calvo-Cases, A.; Castillo, V.; Albaladejo, J. Measuring soil erosion by field plots: Understanding the sources of variation. Earth Sci. Rev. 2006, 78, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanmaercke, M.; Poesen, J.; Radoane, M.; Govers, G.; Ocakoglu, F.; Arabkhedri, M. How long should we measure? An exploration of factors controlling the inter-annual variation of catchment sediment yield. J. Soils Sediments 2012, 12, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kosmadakis, I.; Tsardaklis, P.; Ioannou, K.; Zaimes, G.N. A Novel Fully Automated Soil Erosion Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies in Agriculture, Food and Environment (HAICTA 2015), Kavala, Greece, 17–20 September 2015; pp. 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Myronidis, D.; Arabatzis, G. Evaluation of Greek post-fire erosion mitigation policy through spatial analysis. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2009, 18, 865–872. [Google Scholar]
- Myronidis, D.; Ioannou, K.; Sapountzis, M.; Fotakis, D. Development of a sustainable plan to combat erosion for an island of the Mediterranean region. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2010, 19, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Meusburger, K.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, S.K.; Reddy, G.P.; Mishra, V.N.; Bajpai, R.K. Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System in Water Erosion Assessment. Agric. Rev. 2020, 41, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polykretis, C.; Alexakis, D.D.; Grillakis, M.G.; Manoudakis, S. Assessment of intra-annual and inter-annual variabilities of soil erosion in Crete Island (Greece) by incorporating the Dynamic “Nature” of R and C-Factors in RUSLE modeling. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, H. Dynamic Changes of Soil Erosion in the Taohe River Basin Using the RUSLE Model and Google Earth Engine. Water 2020, 12, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouadja, A.; Benfetta, H.; Porto, P.; Flanagan, D.C.; Mihoubi, M.K.; Omeir, M.R.; Graia, M.; Ghosal, K.; Talchabhadel, R. Mapping potential soil erosion using RUSLE, Remote Sensing, and GIS: A case study in the watershed of Oued El Ardjem, Northwest Algeria. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavidez, R.; Jackson, B.; Maxwell, D.; Norton, K. A review of the (Revised) Universal Soil Loss Equation ((R) USLE): With a view to increasing its global applicability and improving soil loss estimates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6059–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batista, P.; Laceby, J.; Davies, J.; Carvalho, T.; Tassinari, D.; Silva, M.; Curi, N.; Quinton, J. A framework for testing large-scale distributed soil erosion and sediment delivery models: Dealing with uncertainty in models and the observational data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 137, 104961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karydas, C.G.; Panagos, P.; Gitas, I.Z. A classification of water erosion models according to their geospatial characteristics. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014, 7, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Bhattacharya, S.D. Identification of the relationship between temporally varying land surface temperature of winter season with the cover management factor of revised universal soil loss equation: A case study from upper Bakreshwar river basin. In Geoinformatics in Research & Development; Banerjee, T., Ed.; South Asian Institute for Advanced Research and Development (SAIARD): Kolkata, India, 2021; pp. 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- Aksoy, H.; Kavvas, M.L. A review of hillslope and watershed scale erosion and sediment transport models. Catena 2005, 64, 247–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Lane, L.J.; Lopes, V.L. Modeling soil erosion. In Soil Erosion Research Methods, 2nd ed.; Lal, R., Ed.; Taylor and Francis: Routledge, UK, 2017; pp. 127–158. [Google Scholar]
- Igwe, P.U.; Onuigbo, A.A.; Chinedu, O.C.; Ezeaku, I.I.; Muoneke, M.M. Soil erosion: A review of models and applications. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2017, 4, 237341. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses, a Guide to Conservation Planning; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; Volume 537, p. 62.
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; Porter, J.P. RUSLE: Revised universal soil loss equation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1991, 46, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Alewell, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Panagos, P. Using the USLE: Chances, challenges and limitations of soil erosion modelling. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Bhattacharya, S.D. A review of RUSLE model. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2020, 48, 689–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, M.; Cecchi, S.; Orlandini, S.; Mugnai, G.; Zanchi, C.A. Simulation of field-measured soil loss in Mediterranean hilly areas (Chianti, Italy) with RUSLE. Catena 2016, 145, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, N.; Lykoudi, E.; Karavitis, C. Comparative analysis of sediment yield estimations using different empirical soil erosion models. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 2674–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianinetto, M.; Aiello, M.; Polinelli, F.; Frassy, F.; Ravazzani, M.R.G.; Bocchiola, D.; Chiarelli, D.; Soncini, A.; Vezzoli, R. D-Rusle: A dynamic model to estimate potential soil erosion with satellite time series in the Italian alps. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 52, 34–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaimes, G.N.; Emmanouloudis, D.; Iakovoglou, V. Estimating soil erosion in Natura 2000 areas located on three semi-arid Mediterranean islands. J. Environ. Biol. 2012, 33, 277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Médail, F. The specific vulnerability of plant biodiversity and vegetation on Mediterranean islands in the face of global change. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2017, 17, 1775–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kougioumoutzis, K.; Kokkoris, I.P.; Panitsa, M.; Trigas, P.; Strid, A.; Dimopoulos, P. Plant diversity patterns and conservation implications under climate-change scenarios in the mediterranean: The case of Crete (Aegean, Greece). Diversity 2020, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapoglou, E.; Vozinaki, A.E.; Tsanis, I. Climate Change Impact on the Frequency of Hydrometeorological Extremes in the Island of Crete. Water 2019, 11, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tzoraki, O.; Kritsotakis, M.; Baltas, E. Spatial Water Use Efficiency Index towards resource sustainability: Application in the island of Crete, Greece. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2015, 31, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanis, I.K.; Koutroulis, A.G.; Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Jacob, D. Severe climate-induced water shortage and extremes in Crete. Clim. Change 2011, 106, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutroulis, A.G.; Tsanis, I.K.; Daliakopoulos, I.N. Seasonality of floods and their hydrometeorologic characteristics in the island of Crete. J. Hydrol. 2010, 394, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourgialas, N.N.; Karatzas, G.P. A flood risk decision making approach for Mediterranean tree crops using GIS; climate change effects and flood-tolerant species. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 63, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morianou, G.G.; Kourgialas, N.N.; Psarras, G.; Koubouris, G.C. Mapping sensitivity to desertification in Crete (Greece), the risk for agricultural areas. J. Water Clim. Change 2018, 9, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corine Land Cover (CLC). Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover/clc2018 (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; van der Zanden, E.H.; Poesen, J.; Alewell, C. Modelling the effect of support practices (P-factor) on the reduction of soil erosion by water at European scale. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 51, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Van Liedekerke, M.; Jones, A.; Montanarella, L. European Soil Data Centre: Response to European policy support and public data requirements. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brini, I.; Alexakis, D.D.; Kalaitzidis, C. Linking Soil Erosion Modeling to Landscape Patterns and Geomorphometry: An Application in Crete, Greece. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezak, N.; Borrelli, P.; Panagos, P. Exploring the possible role of satellite-based rainfall data to estimate inter-and intra-annual global rainfall erosivity. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2021, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padulano, R.; Rianna, G.; Santini, M. Datasets and approaches for the estimation of rainfall erosivity over Italy: A comprehensive comparison study and a new method. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 34, 100788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, N.; Lykoudi, E.; Psomiadis, E. Inherent relationship of the USLE, RUSLE topographic factor algorithms and its impact on soil erosion modelling. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 1879–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinzi, K.; Ngetar, N.S. The assessment of water-borne erosion at catchment level using GIS-based RUSLE and remote sensing: A review. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santos Loureiro, N.; de Azevedo Coutinho, M. A new procedure to estimate the RUSLE EI30 index, based on monthly rainfall data and applied to the Algarve region, Portugal. J. Hydrol. 2001, 250, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillakis, M.G.; Polykretis, C.; Alexakis, D.D. Past and projected climate change impacts on rainfall erosivity: Advancing our knowledge for the eastern Mediterranean island of Crete. Catena 2020, 193, 104625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karydas, C.G.; Petriolis, M.; Manakos, I. Evaluating alternative methods of soil erodibility mapping in the Mediterranean Island of Crete. Agriculture 2013, 3, 362–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozos, D.; Skilodimou, H.D.; Loupasakis, C.; Bathrellos, G.D. Application of the revised universal soil loss equation model on landslide prevention. An example from N. Euboea (Evia) Island, Greece. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 3255–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, N. The importance of soil data availability on erosion modeling. Catena 2018, 165, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liampas, S.-A.G.; Stamatiou, C.C.; Drosos, V.C. Comparison of three DEM sources: A case study from Greek forests. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of Environment, Paphos, Cyprus, 26–29 March 2018; Volume 10773. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolakopoulos, K.G. Accuracy assessment of ALOS AW3D30 DSM and comparison to ALOS PRISM DSM create with classical photogrammetric techniques. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 53, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florinsky, I.V.; Skrypitsyna, T.N.; Trevisani, S.; Romaikin, S.V. Statistical and visual quality assessment of nearly-global and continental digital elevation models of Trentino, Italy. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, A.; Brocca, L. Determining the best remotely sensed DEM for flood inundation mapping in data sparse regions. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 1884–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, D.K.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised Slope Length Factor for the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Trans. ASAE 1989, 30, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, P.J.J.; Govers, G. A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE LS factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Pilesjö, P.; Hasan, A. A Triangular Form-based Multiple Flow Algorithm to Estimate Overland Flow Distribution and Accumulation on a Digital Elevation Model. Trans. GIS 2014, 18, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polykretis, C.; Grillakis, M.G.; Alexakis, D.D. Exploring the impact of various spectral indices on land cover change detection using change vector analysis: A case study of Crete Island, Greece. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Knijff, J.M.; Jones, R.J.A.; Montanarella, L. Soil Erosion Risk Assessment in Europe; European Soil Bureau and European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandridis, T.K.; Sotiropoulou, A.M.; Bilas, G.; Karapetsas, N.; Silleos, N.G. The effects of seasonality in estimating the C-factor of soil erosion studies. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkoris, I.; Dimopoulos, P.; Xystrakis, F.; Tsiripidis, I. National scale ecosystem condition assessment with emphasis on forest types in Greece. One Ecosyst. 2018, 3, e25434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kokkoris, I.; Mallinis, G.; Bekri, E.; Vlami, V.; Zogaris, S.; Chrysafis, I.; Mitsopoulos, I.; Dimopoulos, P. National Set of MAES Indicators in Greece: Ecosystem Services and Management Implications. Forests 2020, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA Linkages of Species and Habitat Types to MAES Ecosystems. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/linkages-of-species-and-habitat (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Amani, M.; Ghorbanian, A.; Ahmadi, S.A.; Kakooei, M.; Moghimi, A.; Mirmazloumi, S.M.; Moghaddam, S.H.A.; Mahdavi, S.; Ghahremanloo, M.; Parsian, S.; et al. Google earth engine cloud computing platform for remote sensing big data applications: A comprehensive review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5326–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Karydas, C.; Ballabio, C.; Gitas, I. Seasonal monitoring of soil erosion at regional scale: An application of the G2 model in Crete focusing on agricultural land uses. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 27, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karydas, C.G.; Sekuloska, T.; Silleos, G.N. Quantification and site-specification of the support practice factor when mapping soil erosion risk associated with olive plantations in the Mediterranean island of Crete. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 149, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouli, M.; Soupios, P.; Vallianatos, F. Soil erosion prediction using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) in a GIS framework, Chania, Northwestern Crete, Greece. Environ. Geol. 2009, 57, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazamias, A.P.; Sapountzis, M. Spatial and temporal assessment of potential soil erosion over Greece. Water 2017, 59, 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. Spatio-temporal analysis of rainfall erosivity and erosivity density in Greece. Catena 2016, 137, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.C.; Cardinale, B.J.; Wynn-Thompson, T. Plant biodiversity effects in reducing fluvial erosion are limited to low species richness. Ecology 2016, 97, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, D.; Gaglioppa, P.; Schirpke, U.; Guadagno, R.; Marucci, A.; Palmieri, M.; Pellegrino, D.; Gusmerotti, N. Assessment and governance of Ecosystem Services for improving management effectiveness of Natura 2000 sites. Bio-Based Appl. Econ. 2014, 3, 229–247. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino, D.; Schirpke, U.; Marino, D. How to support the effective management of Natura 2000 sites? J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2017, 60, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanastasis, V.P.; Bautista, S.; Chouvardas, D.; Mantzanas, K.; Papadimitriou, M.; Mayor, A.G.; Koukioumi, P.; Papaioannou, A.; Vallejo, R.V. Comparative assessment of goods and services provided by grazing regulation and reforestation in degraded Mediterranean rangelands. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 28, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaltsas, D.; Panayiotou, E.; Kougioumoutzis, K.; Chatzaki, M. Overgrazed shrublands support high taxonomic, functional and temporal diversity of Mediterranean ground spider assemblages. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 103, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostadinov, S.; Stanojevic, G. Design of Technical Erosion Control Measures for the Reconstruction of Degraded Steep Lands. In Reclaimed Land: Erosion Control, Soils and Ecology; Haigh, M., Balkema, A., Eds.; Brookfield: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 111–136. [Google Scholar]
- Andreu, V.; Khuder, H.; Mickovski, S.; Spanos, I.; Norris, J.; Dorren, L.; Nicoll, B.; Achim, A.; Rubio, J.; Luc, J.; et al. Ecotechnological solutions for unstable slopes: Ground bio- and eco-engineering techniques and strategies. In Slope Stability and Erosion Control: Ecotechnological Solutions; Norris, J.E., Stokes, A., Mickovski, S.B., Cammeraat, E., van Beek, R., Nicoll, B.C., Achim, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 211–275. [Google Scholar]
- Lasanta, T.; Arnáez, J.; Oserín, M.; Ortigosa, L.M. Marginal lands and erosion in terraced fields in the Mediterranean mountains. Mt. Res. Dev. 2001, 21, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| Dataset | Data Source | Data Accessibility | Spatial Resolution | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-2 Level 2A imagery | European Space Agency (ESA) via GEE | ee.ImageCollection (“COPERNICUS/S2_SR”) | 10 m | raster |
| ALOS DEM | Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) | https://www.eorc.jaxa.jp/ALOS/en/url_change_info_e.htm (accessed on 10 October 2021) | 30 m | raster |
| Daily Rainfall | ERA5-Land European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) via GEE | ee.ImageCollection (“ECMWF/ERA5/DAILY”) | ~9 km | raster |
| Soil Map of Greece | Greek Ministry of the Environment & Energy | http://mapsportal.ypen.gr/maps/289 (accessed on 10 October 2021) | - | vector |
| Support practices | European Soil Data Center (ESDAC) | https://esdac.jrc.ec.europa.eu/content/support-practices-factor-p-factor-eu (accessed on 10 October 2021) | 1 km | raster |
| Species Diversity | Art 17 Directive 92/43/EEC (EIONET) | http://cdr.eionet.europa.eu/gr/eu/art17/envxrm90g/GR_Art17_species_distribution.zip/manage_document (accessed on 10 October 2021) | 10 km | Vector (grid) |
| N2K Terrestrial Habitat type | Greek Ministry of the Environment & Energy | http://mapsportal.ypen.gr/layers/geonode:habitats_egsa87 (accessed on 10 October 2021) | - | vector |
| Parent Material | K Value |
|---|---|
| Alluvial Deposits | 0.015 |
| Hard Limestone | 0.0008 |
| Flysch | 0.017 |
| Colluvial Limestone | 0.1 |
| Dolomite Limestone | 0.0008 |
| Colluvial Peridotite | 0.1 |
| Granite | 0.2 |
| Peridotite | 0.05 |
| Tertiary deposits | 0.015 |
| Schist | 0.07 |
| Corine Land Cover Level 2 | Area (km2) | C-Factor Value |
|---|---|---|
| Scrub and/or herbaceous vegetation associations | 3794.5 | 0.42 |
| Permanent crops | 2366.4 | 0.26 |
| Heterogeneous agricultural areas | 1102.3 | 0.34 |
| Open spaces with little or no vegetation | 410.4 | 0.68 |
| Forests | 299.7 | 0.16 |
| Arable land | 88.15 | 0.50 |
| Pastures | 59.2 | 0.49 |
| MAES Ecosystem Category (Level 1) | MAES Ecosystem Category (Level 2) | MAES Ecosystem Category (Level 3) | Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial | Woodland and Forests | Floodplain forests (Riparian forest/Fluvial forest) | 10.5 |
| Mediterranean coniferous forests | 311.7 | ||
| Mediterranean deciduous forests | 4.0 | ||
| Mediterranean sclerophyllous forests | 334.9 | ||
| Grasslands | Grasslands | 4.9 | |
| Heathland and shrub | Moors and heathland | 1292.6 | |
| Sclerophyllous vegetation | 40.2 | ||
| Sparsely vegetated | Beaches, dunes, sands | 12.9 | |
| Sparsely vegetated areas | 36.5 | ||
| Wetlands | Inland freshwater and saline marshes | 1.3 | |
| Freshwater | Rivers and lakes | Rivers and lakes | 0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stefanidis, S.; Alexandridis, V.; Ghosal, K. Assessment of Water-Induced Soil Erosion as a Threat to Natura 2000 Protected Areas in Crete Island, Greece. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2738. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052738
Stefanidis S, Alexandridis V, Ghosal K. Assessment of Water-Induced Soil Erosion as a Threat to Natura 2000 Protected Areas in Crete Island, Greece. Sustainability. 2022; 14(5):2738. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052738
Chicago/Turabian StyleStefanidis, Stefanos, Vasileios Alexandridis, and Kaushik Ghosal. 2022. "Assessment of Water-Induced Soil Erosion as a Threat to Natura 2000 Protected Areas in Crete Island, Greece" Sustainability 14, no. 5: 2738. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052738
APA StyleStefanidis, S., Alexandridis, V., & Ghosal, K. (2022). Assessment of Water-Induced Soil Erosion as a Threat to Natura 2000 Protected Areas in Crete Island, Greece. Sustainability, 14(5), 2738. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052738








