Road Safety Policies for Saudi Females: A Fuzzy Logic Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Travel Behavior and Road Safety
1.2. Fuzzy Control System
2. Methodology
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Safety Policies
- Engineering programs
- Enforcement programs
- Education programs
- Legislation programs
3. Analysis
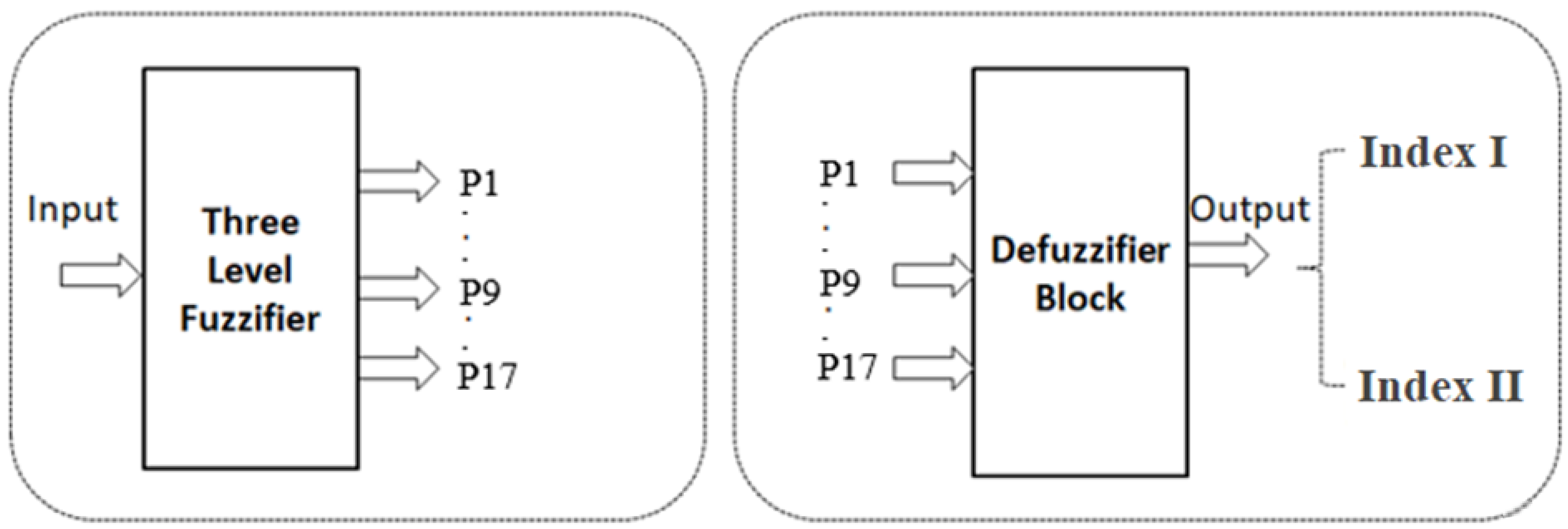
3.1. Fuzzy Logic-Based Model
3.2. Fuzzy System for the Engineering Safety Program
4. Fuzzy System Evaluation
5. Comparative Analysis of the Results and Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ledesma, R.D.; Tosi, J.D.; Díaz-Lázaro, C.M.; Poó, F.M. Predicting road safety behavior with implicit attitudes and the Theory of Planned Behavior. J. Saf. Res. 2018, 66, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, W.; Malibari, A. Saudi Women and Vision 2030: Bridging the Gap? Behav. Sci. 2021, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axhausen, K.W. Chapter 11 Concepts of Travel Behavior Research, 360. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237262766_Concepts_of_Travel_Behavior_Research (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- WHO. WHO Global Status Report on Road Safety 2013: Supporting a Decade of Action; World Health Organisation: Luxembourg, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation Development (OECD). Road Accidents (Indicator). 2016. Available online: http://data.oecd.org/transport/road-accidents.htm (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Grayson, G.B.; Maycock, G. From proneness to liability. In Road User Behaviour. Theory and Research; Rothengatter, J.A., De Bruin, R., Eds.; Van Gorcum: Assen, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 234–242. [Google Scholar]
- Lajunen, T.; Summala, H. Can we trust self-reports of driving? Effects of impression management on driver behaviour questionnaire responses. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2003, 6, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourens, P.F.; Vissers, J.A.; Jessurun, M. Annual mileage, driving violations, and accident involvement in relation to drivers’ sex, age, and level of education. Accid. Anal. Prev. 1999, 31, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulleberg, P.; Rundmo, T. Personality, attitudes and risk perception as predictors of risky driving behaviour among young drivers. Saf. Sci. 2003, 41, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teese, R.; Bradley, G. Predicting Recklessness in Emerging Adults: A Test of a Psychosocial Model. J. Soc. Psychol. 2008, 148, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whissell, R.W.; Bigelow, B.J. The Speeding Attitude Scale and the Role of Sensation Seeking in Profiling Young Drivers at Risk. Risk Anal. 2003, 23, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltedal, S.; Rundmo, T. The effects of personality and gender on risky driving behaviour and accident involvement. Saf. Sci. 2006, 44, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagil, D. Gender and age-related differences in attitudes toward traffic laws and traffic violations. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 1998, 1, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L. Traffic Safety and the Driver, 1st ed.; Van-Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Rukaibi, F.; Ali, M.A.; Aljassar, A.H. Traffic safety attitudes and driving behavior of university students: Case study in Kuwait. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2006, 1969, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bener, A.; Ozkan, T.; Lajunen, T. The driver behaviour questionnaire in Arab Gulf countries: Qatar and United Arab Emirates. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2008, 40, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.; Bromfield, N.F. Attitudes, driving behavior, and accident involvement among young male drivers in Saudi Arabia. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2017, 47, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y. A Two-Stage Fuzzy Logic Control Method of Traffic Signal Based on Traffic Urgency Degree. Model. Simul. Eng. 2014, 2014, 694185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koukol, M.; Zajíčková, L.; Marek, L.; Tuček, P. Fuzzy Logic in Traffic Engineering: A Review on Signal Control. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 979160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Pham, T.T.; Boustany, N. Introduction to Fuzzy Sets, Fuzzy Logic, and Fuzzy Control Systems. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2001, 54, B102–B103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jäkel, J.; Mikut, R.; Bretthauer, G. Fuzzy Control Systems. Control. Syst. Robot. Autom. 2004, XVII, 1–11. Available online: http://www.eolss.net/sample-chapters/c18/e6-43-23.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Jha, M.; Shukla, S. Design Of Fuzzy Logic Traffic Controller For Isolated Intersections with Emergency Vehicle Priority System Using MATLAB Simulation, computer Science Bibliography. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1405.0936. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2014arXiv1405.0936J/abstract (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Passino, K.M.; Yurkovich, S. Fuzzy Control, Copyright 1998, Addison Wesley Longman, Inc. Available online: https://www2.ece.ohio-state.edu/~passino/FCbook.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Urrea, C.; Kern, J.; Alvarado, J. Design and Evaluation of a New Fuzzy Control Algorithm Applied to a Manipulator Robot. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C. Fuzzy logic in control systems: Fuzzy logic controller. I. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1990, 20, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Disha, S. Designing and Modeling Fuzzy Control Systems. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2011, 16, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Mendel, J.M. Fuzzy logic systems for engineering: A tutorial. Proc. IEEE. 1995, 83, 345–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tatari, O.; Onat, N.; Abdel-Aty, M.; Alirezaei, M. Dynamic Simulation Models for Road Safety and Its Sustainability Implications. 2015. Available online: http://safersim.nads-sc.uiowa.edu/final_reports/UCF-2-Y1_FinalReport.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Heydari, S.; Hickford, A.; McIlroy, R.; Turner, J.; Bachani, A.M. Road safety in low-income countries: State of knowledge and future directions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- May, T.; Crass, M. Sustainability in transport: Implications for policy makers. Transp. Res. Rec. J. 2007, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arowolo, M.O.; Rohani, J.; Rani, M.R.A. Development of Road Safety Sustainability Model for Malaysian Road. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 606, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Group (Class) | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Driving/non driving | Car driver | 18 |
| Non-car driving | 82 | |
| Age of respondents (years) | 18–25 | 33 |
| 26–35 | 23 | |
| 36–45 | 21 | |
| 46–55 | 14 | |
| Over 55 | 9 | |
| Education Level of respondents | Less than high school | 4 |
| High school | 25 | |
| Diploma | 31 | |
| University Graduate | 36 | |
| Post-graduate | 4 | |
| Work status of respondents | Full-time workers | 15 |
| Part-time workers | 27 | |
| Students | 23 | |
| Non-working | 35 | |
| Income of respondents | Highest category | 28 |
| Medium category | 48 | |
| Lowest category | 24 |
| Groups of Safety Programs | Example Policies |
|---|---|
| Engineering safety programs | P1: Engineering speed reduction policies P2: Monitor drivers’ speed P3: Improve Road network alignment P4: Use of road signs and marking P5: Pedestrian crossing facilities |
| Enforcement safety programs | P6: Enforce speed limits P7: Enforce penalties P8: Physical presence of traffic police |
| Education and raising awareness safety programs | P9: Continuous courses after obtaining driving license P10: Theory driving tests P11: Media awareness campaigns P12: School awareness campaign |
| Legislation safety programs | P13: Speed limits P14: Speeding penalties P15: Seat belt P16: Age of driving P17: Licensing system, especially for foreign drivers |
| Road Safety Programs | Index-I | Index-II | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engineering | P1: Engineering speed-reduction policies | 2.658 | 1.654 |
| P2: Monitor drivers’ speed | 2.431 | 1.112 | |
| P3: Improve Road network alignment | 3.732 | 1.727 | |
| P4: Use of road signs and marking | 4.154 | 1.875 | |
| P5: Pedestrian crossing facilities | 2.126 | 1.267 | |
| Enforcement | P6: Enforce speed limits | 3.572 | 1.392 |
| P7: Enforce penalties | 1.812 | 1.303 | |
| P8: Physical presence of traffic police | 4.291 | 1.283 | |
| Education and raising awareness | P9: Continuous courses after obtaining driving license | 2.715 | 1.231 |
| P10: Theory driving tests | 1.875 | 1.332 | |
| P11: Media awareness campaigns | 3.931 | 1.909 | |
| P12: School awareness campaign | 4.179 | 1.894 | |
| Legislation | P13: Speed limits | 3.830 | 1.733 |
| P14: Speeding penalties | 2.329 | 1.329 | |
| P15: Seat belt | 1.987 | 1.386 | |
| P16: Age of driving | 2.241 | 1.721 | |
| P17: Licensing system, especially for foreign drivers | 4.156 | 1.925 |
| Calibrated Indices | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Index-I | Index-II | ||
| Engineering policy | P5 | 0.4252 | 0.6335 |
| P2 | 0.4862 | 0.556 | |
| P1 | 0.5316 | 0.827 | |
| P3 | 0.7464 | 0.8635 | |
| P4 | 0.8308 | 0.9375 | |
| Enforcement policy | P7 | 0.3624 | 0.6515 |
| P6 | 0.7144 | 0.696 | |
| P8 | 0.8582 | 0.6415 | |
| Education and raising awareness policy | P10 | 0.375 | 0.666 |
| P9 | 0.543 | 0.6155 | |
| P11 | 0.7862 | 0.9545 | |
| P12 | 0.8358 | 0.947 | |
| Legislation policy | P15 | 0.3974 | 0.693 |
| P14 | 0.4658 | 0.6645 | |
| P16 | 0.4482 | 0.8605 | |
| P13 | 0.766 | 0.8665 | |
| P17 | 0.8312 | 0.9625 | |
| Input Variables | P5 | P2 | P1 | P3 | P4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engineering policy | 0–0.49 | 0.49–0.52 | 0.52–0.65 | 0.65–0. 8 | 0.8–1 |
| Input Variables | P7 | P6 | P8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enforcement policy | 0–0.5 | 0.5–0.75 | 0.75–1 |
| Input Variables | P10 | P9 | P11 | P12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Education and raising awareness policy | 0–0.50 | 0.50–0.69 | 0.69–0.84 | 0.84–1 |
| Input Variables | P15 | P14 | P16 | P13 | P17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Legislation policy | 0–0.49 | 0.49–0.55 | 0.55–0.65 | 0.65–0.80 | 0.80–1 |
| If-Then Rules Joining Inputs and Output |
|---|
| If (Engineering-safety program is P5) then (Index I is Low) (Index II is Medium) |
| If (Engineering-P safety program is P1) then (Index I is Medium) (Index II is High) |
| If (Engineering-safety program is P4) then (Index I is High) (Index II is High) |
| If (Enforcement-safety program is P7) then (Index I is Low) (Index II is Medium) |
| If (Enforcement-safety program is P6) then (Index I is High) (Index II is Medium) |
| If (Enforcement-safety program is P8) then (Index I is High) (Index II is Medium) |
| If (Education-raising-awareness-safety program is P10) then (Index I is Low) (Index II is Medium) |
| If (Education-raising-awareness-safety program is P9) then (Index I is Medium) (Index II is Medium) |
| If (Education-raising-awareness-safety program is P11) then (Index I is High) (Index II is High) |
| If (Education-raising-awareness-safety program is P12) then (Index I is High) (Index II is High) |
| If (Legislation-safety program is P15) then (Index I is Low) (Index II is Medium) |
| If (Legislation-safety program is P14) then (Index I is Low) (Index II is Medium) |
| If (Legislation-safety program is P16) then (Index I is Low) (Index II is High) |
| If (Legislation-safety program is P13) then (Index I is High) (Index II is High) |
| If (Legislation-safety program is P17) then (Index I is High) (Index II is High) |
| Variables | Engineering Safety Program | Output Indices | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P5 | P2 | P1 | P3 | P4 | Index I (Fuzzy) | Index II (Fuzzy) | |
| 0.478 | --- | --- | --- | --- | 0.175 | 0.549 | |
| --- | 0.507 | --- | --- | --- | 0.531 | 0.547 | |
| --- | --- | 0.617 | --- | --- | 0.532 | 0.86 | |
| --- | --- | --- | 0.77 | --- | 0.85 | 0.86 | |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.86 | |
| Variables | Engineering Safety Program | Output Indices | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P7 | P6 | P8 | Index I (Fuzzy) | Index II (Fuzzy) | |
| 0.442 | --- | --- | 0.173 | 0.501 | |
| --- | 0.704 | --- | 0.841 | 0.501 | |
| --- | --- | 0.807 | 0.841 | 0.501 | |
| Variables | Education–Raising Awareness Safety Program | Output Indices | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P10 | P9 | P11 | P12 | Index I (Fuzzy) | Index II (Fuzzy) | |
| 0.478 | --- | --- | --- | 0.166 | 0.493 | |
| --- | 0.566 | --- | --- | 0.492 | 0.493 | |
| --- | --- | 0.828 | --- | 0.825 | 0.822 | |
| --- | --- | --- | 0.865 | 0.825 | 0.822 | |
| Variables | Legislation Safety Program | Output Indices | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P15 | P14 | P16 | P13 | P17 | Index I (Fuzzy) | Index II (Fuzzy) | |
| 0.478 | --- | --- | --- | --- | 0.175 | 0.507 | |
| --- | 0.529 | --- | --- | --- | 0.174 | 0.507 | |
| --- | --- | 0.566 | --- | --- | 0.175 | 0.839 | |
| --- | --- | --- | 0.7712 | --- | 0.831 | 0.839 | |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | 0.880 | 0.831 | 0.839 | |
| Inputs | Outputs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Road safety Policies | Index I | Index II | ||
| Engineering safety program | Analytical results | Fuzzy system results | Analytical results | Fuzzy system results |
| P5 | 0.4252 | 0.175 | 0.6335 | 0.549 |
| P2 | 0.4862 | 0.531 ** | 0.556 | 0.547 ** |
| P1 | 0.5316 | 0.532 ** | 0.827 | 0.86 ** |
| P3 | 0.7464 | 0.85 ** | 0.8635 | 0.86 ** |
| P4 | 0.8308 | 0.85 ** | 0.9375 | 0.86 ** |
| Enforcement safety program | ||||
| P7 | 0.3624 | 0.173 * | 0.6515 | 0.501 * |
| P6 | 0.7144 | 0.841 * | 0.696 | 0.501 * |
| P8 | 0.8582 | 0.841 * | 0.6415 | 0.501 * |
| Education and raising awareness safety program | Index I (Fuzzy) | Index II (Fuzzy) | ||
| P10 | 0.375 | 0.166 | 0.666 | 0.493 * |
| P9 | 0.543 | 0.492 * | 0.6155 | 0.493 * |
| P11 | 0.7862 | 0.825 * | 0.9545 | 0.822 * |
| P12 | 0.8358 | 0.825 * | 0.947 | 0.822 * |
| Legislation safety program | ||||
| P15 | 0.3974 | 0.175 | 0.693 | 0.507 * |
| P14 | 0.4658 | 0.174 | 0.6645 | 0.507 * |
| P16 | 0.4482 | 0.175 | 0.8605 | 0.839 ** |
| P13 | 0.766 | 0.831 * | 0.8665 | 0.839 ** |
| P17 | 0.8312 | 0.831 * | 0.9625 | 0.839 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lashin, M.M.A.; Saleh, W.S.E.S. Road Safety Policies for Saudi Females: A Fuzzy Logic Analysis. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14074154
Lashin MMA, Saleh WSES. Road Safety Policies for Saudi Females: A Fuzzy Logic Analysis. Sustainability. 2022; 14(7):4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14074154
Chicago/Turabian StyleLashin, Maha M. A., and Wafaa Salah Eldin Shoukry Saleh. 2022. "Road Safety Policies for Saudi Females: A Fuzzy Logic Analysis" Sustainability 14, no. 7: 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14074154
APA StyleLashin, M. M. A., & Saleh, W. S. E. S. (2022). Road Safety Policies for Saudi Females: A Fuzzy Logic Analysis. Sustainability, 14(7), 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14074154





