Operational Data-Driven Intelligent Modelling and Visualization System for Real-World, On-Road Vehicle Emissions—A Case Study in Hangzhou City, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. System Framework
2.2. Real-World Data Collection
2.3. Real-Time Data Fusion
2.4. Model Framework for On-Road Vehicle Emissions
2.5. “Distance–Decay” Relationship of Hotspot Region
2.6. Traffic Control Strategies
3. System Application
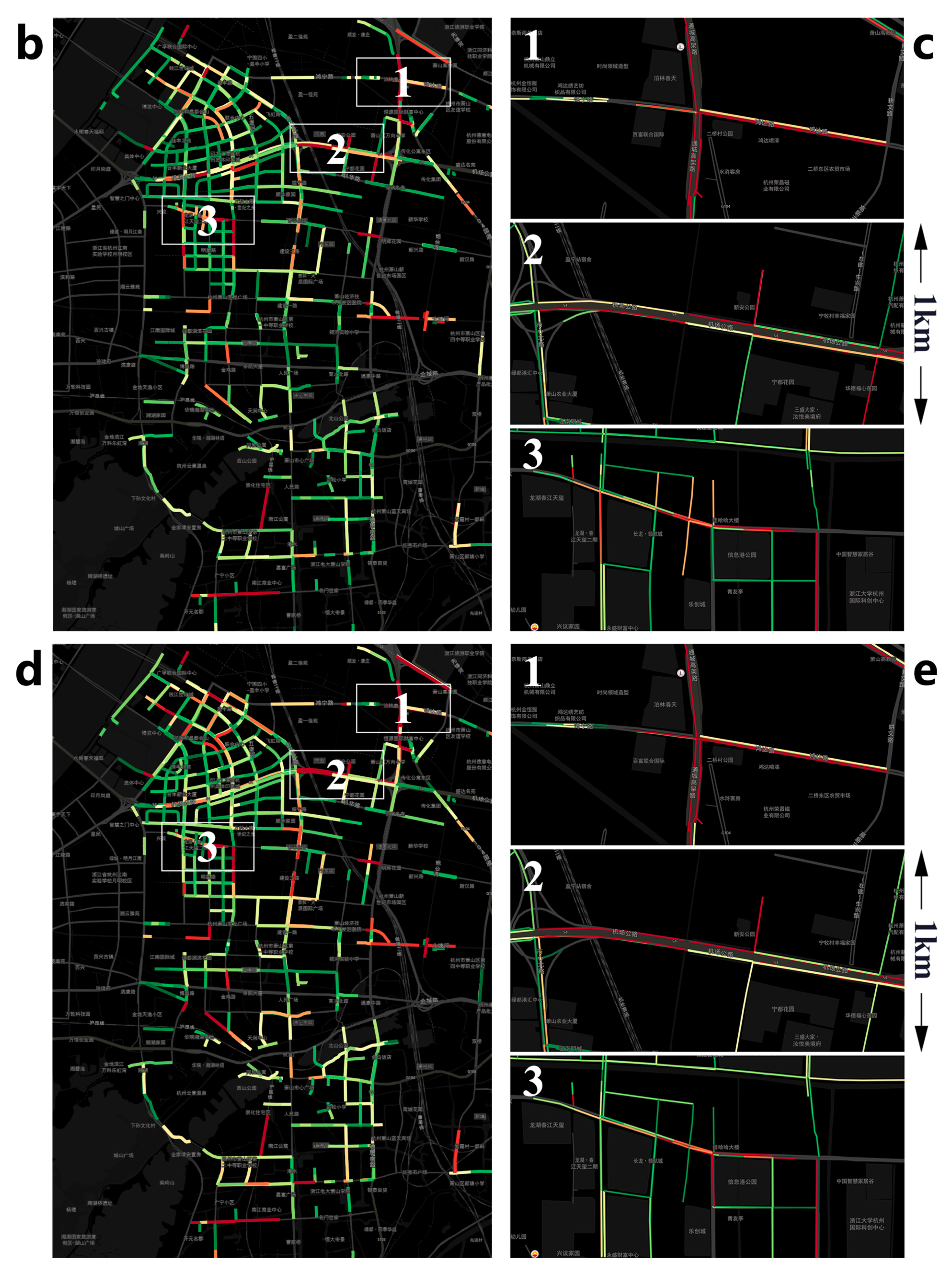
3.1. Map of Traffic Characteristics and Hotspots
3.2. Real-Time, On-Road Vehicle Emissions
3.3. Map of Emission Hotpots and Drivers
3.4. Impacts of Traffic Control Scenarios
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Xing, J.; He, X.; Zhang, K.M.; Wang, S.; Hao, J. Air quality and health benefits from fleet electrification in China. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, P.; Jiang, L.; Xia, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Switching to electric vehicles can lead to significant reductions of PM2.5 and NO2 across China. One Earth 2021, 4, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Tong, D.; Shao, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; He, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Drivers of Improved PM2.5 Air Quality in China from 2013 to 2017; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Volume 116, pp. 24463–24469. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Cao, X.; Ai, Y.; Xu, K.; Zhang, Y. Primary Air Pollutants Emissions Variation Characteristics and Future Control Strategies for Transportation Sector in Beijing, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhu, C.; Hao, J.; Liu, H.; Hua, S.; Tian, H. Temporal-spatial characteristics and source apportionment of PM2.5 as well as its associated chemical species in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecology, M.O.; China, E.O.T.P. China Vehicle Environmental Management Annual Report; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Song, C.; Wu, L.; Xie, Y.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Lin, Y.; Jin, T.; Wang, A.; Liu, Y.; et al. Air pollution in China: Status and spatiotemporal variations. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anenberg, S.C.; Miller, J.; Minjares, R.; Du, L.; Henze, D.K.; Lacey, F.; Malley, C.S.; Emberson, L.; Franco, V.; Klimont, Z.; et al. Impacts and mitigation of excess diesel-related NOx emissions in 11 major vehicle markets. Nature 2017, 545, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunkunle, O.; Ahmed, N.A. Overview of Biodiesel Combustion in Mitigating the Adverse Impacts of Engine Emissions on the Sustainable Human–Environment Scenario. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Huang, R.; Wang, J.; Yan, H.; Zheng, Y.; Hao, J. High-resolution simulation of link-level vehicle emissions andconcentrations for air pollutants in a traffic-populated eastern Asian city. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 9965–9981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyu, P.; Wang, P.S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Review of the studies on emission evaluation approaches for operating vehicles. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2021, 8, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangones, S.C.; Jaramillo, P.; Fischbeck, P.; Rojas, N.Y. Development of a high-resolution traffic emission model: Lessons and key insights from the case of Bogotá, Colombia. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Jiang, S.; Liang, B. A study on the model of traffic flow and vehicle exhaust emission. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 736285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, A.K.; Mustafi, N.N. Real-world automotive emissions: Monitoring methodologies, and control measures. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Dentener, F.; Muntean, M.; Pouliot, G.; Keating, T.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.; Wankmüller, R.; et al. HTAP_v2.2: A mosaic of regional and global emission grid maps for 2008 and 2010 to study hemispheric transport of air pollution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 11411–11432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.; Woo, J.; He, K.; Lu, Z.; Ohara, T.; Song, Y.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; et al. MIX: A mosaic Asian anthropogenic emission inventory under the international collaboration framework of the MICS-Asia and HTAP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 935–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, Z.; Fu, L.; He, K.; Hao, J. Historical evaluation of vehicle emission control in Guangzhou based on a multi-year emission inventory. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 76, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, E.; Liu, H.; Pan, H.; Ji, S.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Ahmad, B. Evaluation of vehicle emission in Yunnan province from 2003 to 2015. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gately, C.K.; Hutyra, L.R.; Peterson, S.; Sue Wing, I. Urban emissions hotspots: Quantifying vehicle congestion and air pollution using mobile phone GPS data. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gately, C.K.; Hutyra, L.R. Large Uncertainties in Urban-Scale Carbon Emissions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 242–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Xia, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Ye, J.; Hou, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; et al. Hyperfine-resolution mapping of on-road vehicle emissions with comprehensive traffic monitoring and an intelligent transportation system. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 16985–17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, B.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.; Gong, S.; He, J.; Zou, C.; Song, G.; Li, X.; Wu, Z. Development of a vehicle emission inventory with high temporal–spatial resolution based on NRT traffic data and its impact on air pollution in Beijing–Part 1: Development and evaluation of vehicle emission inventory. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 3161–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, L.; Lin, X.; Xu, W.; Ding, H. A high temporal-spatial vehicle emission inventory based on detailed hourly traffic data in a medium-sized city of China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Bao, S.; Wu, X.; Yang, D.; Wu, Y. Mapping dynamic road emissions for a megacity by using open-access traffic congestion index data. Appl. Energy 2020, 260, 114357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chang, M.; Wang, X.; Hang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Shao, M. Development of the Real-time On-road Emission (ROE v1.0) model for street-scale air quality modeling based on dynamic traffic big data. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2020, 13, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, S.; Niu, T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, K.M.; Wu, Y. High-resolution mapping of vehicle emissions of atmospheric pollutants based on large-scale, real-world traffic datasets. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8831–8843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.; Yu, C.; Yuan, W.; Wu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X. High-resolution vehicle emission inventory and emission control policy scenario analysis, a case in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Han, K.; Chen, X.M.; Ong, G.P. Spatial-temporal inference of urban traffic emissions based on taxi trajectories and multi-source urban data. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2019, 106, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, X.; Guo, R.; Xia, T.; Guo, Z.; Long, Y.; Zhang, H.; Song, X.; Ryosuke, S. Mining urban sustainable performance: Millions of GPS data reveal high-emission travel attraction in Tokyo. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Xiang, M.; Fang, K.; Li, Y.; Ye, Y.; Shi, Z.; Liu, J. Spatial-temporal distribution of carbon emissions by daily travel and its response to urban form: A case study of Hangzhou, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Lv, Z.; Qi, L.; Wang, X.; Shi, M.; Liu, H. A big data approach to improving the vehicle emission inventory in China. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaton, S.P.; Bishop, G.A.; Zhang, Y.; Stedman, D.H.; Ashbaugh, L.L.; Lawson, D.R. On-Road Vehicle Emissions: Regulations, Costs, and Benefits. Science 1995, 268, 991–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgaughey, G.R.; Desai, N.R.; Allen, D.T.; Seila, R.L.; Lonneman, W.A.; Fraser, M.P.; Harley, R.A.; Pollack, A.K.; Ivy, J.M.; Price, J.H. Analysis of motor vehicle emissions in a Houston tunnel during the Texas Air Quality Study 2000. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3363–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Malhotra, B.; Dale, S.; Qiang, M. RFID based vehicular networks for smart cities. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 29th International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops (ICDEW), Brisbane, Australia, 8–12 April 2013; pp. 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Zhao, C.; Lin, T.; Li, X.; Prishchepov, A.V. Spatio-temporal patterns of traffic-related air pollutant emissions in different urban functional zones estimated by real-time video and deep learning technique. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Frey, H.C. Variability in Light-Duty Gasoline Vehicle Emission Factors from Trip-Based Real-World Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12525–12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Song, G.; Yu, L. Sensitive analysis of emission rates in MOVES for developing site-specific emission database. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2014, 32, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Peng, J.; Wu, L.; Ma, C.; Zou, C.; Wei, N.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Andre, M.; Li, D.; et al. Speed-guided intelligent transportation system helps achieve low-carbon and green traffic: Evidence from real-world measurements. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, J.S.; Messier, K.P.; Gani, S.; Brauer, M.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Lunden, M.M.; Marshall, J.D.; Portier, C.J.; Vermeulen, R.C.H.; Hamburg, S.P. High-Resolution Air Pollution Mapping with Google Street View Cars: Exploiting Big Data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6999–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Dong, M.; Ota, K.; Li, Q.; Ye, T.; Wu, J.; Li, J. A Secure Mechanism for Big Data Collection in Large Scale Internet of Vehicle. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louhghalam, A.; Akbarian, M.; Ulm, F. Carbon management of infrastructure performance: Integrated big data analytics and pavement-vehicle-interactions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gately, C.K.; Hutyra, L.R.; Wing, I.S.; Brondfield, M.N. A Bottom up Approach to on-road CO2 Emissions Estimates: Improved Spatial Accuracy and Applications for Regional Planning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2423–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, A.M.; Mezić, I. Data-driven analysis and forecasting of highway traffic dynamics. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Niu, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, K.M.; Wallington, T.J.; Xie, Q.; Wu, X.; Xu, H. Fine-grained vehicle emission management using intelligent transportation system data. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Cai, M.; Lin, X.; Chen, T.; Li, L.; Liu, Y. RTVEMVS: Real-time modeling and visualization system for vehicle emissions on an urban road network. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 309, 127166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Huang, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Yan, R.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Jing, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Emission inventory of air pollutants and chemical speciation for specific anthropogenic sources based on local measurements in the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 2003–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X. The City Brain: Towards Real-Time Search for the Real-World. In Proceedings of the 41st International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 8–12 July 2018; pp. 1343–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, H.; He, J. An Inconsistency Free Formalization of B/S Architecture. In Proceedings of the 31st IEEE Software Engineering Workshop (SEW 2007), Columbia, MD, USA, 6–8 March 2007; pp. 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, H.E.; Lane, D. Web Database Applications with PHP and MySQL: Building Effective Database-Driven Web Sites; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sevastopol, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Carazo, J.M.; Stelzer, E.H.K. The BioImage Database Project: Organizing Multidimensional Biological Images in an Object-Relational Database. J. Struct. Biol. 1999, 125, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balduzzi, M.; Zaddach, J.; Balzarotti, D.; Kirda, E.; Loureiro, S. A Security Analysis of Amazon’s Elastic Compute Cloud Service. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, Trento, Italy, 26–30 March 2012; pp. 1427–1434. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, E.J. Ajax: Asynchronous JavaScript and XML. Dr. Dobb’s J. 2006, 31, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Waldman, C.G.; Hagel-Sorensen, C. Dynamic Generation of Cascading Style Sheets. U.S. Patent 20,070,220,480, 20 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Zhuge, C.; Ma, W. Towards a Very Large Scale Traffic Simulator for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Testbeds. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.13907. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, B.; Fu, L.; He, K.; Hao, J. On-Road Vehicle Emission Control in Beijing: Past, Present, and Future. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Qin, X.; Wang, B.; Xu, J.; Shen, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, K.; Deng, C.; Yan, R.; Xu, K.; et al. Counteractive effects of regional transport and emission control on the formation of fine particles: A case study during the Hangzhou G20 summit. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 13581–13600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Yu, S.; Li, P.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Mehmood, K.; Liu, W.; Chai, T.; et al. Significant wintertime PM2.5 mitigation in the Yangtze River Delta, China, from 2016 to 2019: Observational constraints on anthropogenic emission controls. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 14787–14800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Xue, L.; He, J.; Xu, W.; Qi, B.; Du, R.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; et al. Exploring the inconsistent variations in atmospheric primary and secondary pollutants during the 2016 G20 summit in Hangzhou, China: Implications from observations and models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 5391–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Park, J.; Park, J.; Park, S. Emission factor development for light-duty vehicles based on real-world emissions using emission map-based simulation. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, L.; Yang, Y. Development of a high-resolution emission inventory and its evaluation and application through air quality modeling for Jiangsu Province, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| Scenario | Strategy | Vehicle Category | Spatiotemporal Scale |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Vehicles with particular tail numbers of license plates are forbidden. Specifically, the prohibited tail numbers were 1 and 9 on Monday, 2 and 8 on Tuesday, 3 and 7 on Wednesday, 4 and 6 on Thursday, and 5 and 0 on Friday. | All | Over residential and arterial roads during morning and evening rush hours from Monday to Friday |
| S2 | Vehicles with even and odd tail numbers of license plates are alternately prohibited. | All | Over residential and arterial roads during morning and evening rush hours from Monday to Friday |
| S3 | HDVs and HDTs are forbidden | HDVs and HDTs | Over highways all day long |
| S4 | All vehicles follow the even–odd rule. | All | Over all roads all day long |
| Road Type | Road Length | Vehicle Category | Emission (g)/Emission Intensity (g/km) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO | HC | NOx | PM2.5 | |||
| Highways | 11.1 km | HDVs and HDTs | 113.5/10.2 | 83.3/7.5 | 1300.2/116.8 | 61.1/5.5 |
| Total | 2381.1/213.9 | 247.4/22.2 | 1872.2/168.2 | 77.0/6.9 | ||
| Arterial roads | 63.5 km | HDVs and HDTs | 348.7/5.5 | 257.6/4.1 | 3988.2/62.8 | 187.3/3.0 |
| Total | 16,398.9/258.4 | 1419.1/22.4 | 8039.3/126.7 | 299.9/4.7 | ||
| Residential streets | 232.0 km | HDVs and HDTs | 1308.0/5.6 | 978.5/4.2 | 14,891.9/64.2 | 698.5/3.0 |
| Total | 36,085.2/155.5 | 3501.2/15.1 | 23,703.0/102.2 | 944.4/4.1 | ||
| Scenario | Traffic Fluxes Reduction | On-Road Vehicle Emissions Reduction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO | NO | HC | PM2.5 | ||
| S1 | 3.3% | 3.4% | 2.7% | 3.1% | 2.3% |
| S2 | 8.3% | 8.5% | 6.8% | 7.7% | 5.6% |
| S3 | 3.7% | 4.8% | 69.4% | 33.7% | 79.3% |
| S4 | 53.3% | 53.3% | 54.1% | 53.6% | 54.3% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, L.; Ye, J.; Hou, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; et al. Operational Data-Driven Intelligent Modelling and Visualization System for Real-World, On-Road Vehicle Emissions—A Case Study in Hangzhou City, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5434. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095434
Wang L, Chen X, Xia Y, Jiang L, Ye J, Hou T, Wang L, Zhang Y, Li M, Li Z, et al. Operational Data-Driven Intelligent Modelling and Visualization System for Real-World, On-Road Vehicle Emissions—A Case Study in Hangzhou City, China. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5434. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095434
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lu, Xue Chen, Yan Xia, Linhui Jiang, Jianjie Ye, Tangyan Hou, Liqiang Wang, Yibo Zhang, Mengying Li, Zhen Li, and et al. 2022. "Operational Data-Driven Intelligent Modelling and Visualization System for Real-World, On-Road Vehicle Emissions—A Case Study in Hangzhou City, China" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5434. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095434
APA StyleWang, L., Chen, X., Xia, Y., Jiang, L., Ye, J., Hou, T., Wang, L., Zhang, Y., Li, M., Li, Z., Song, Z., Jiang, Y., Liu, W., Li, P., Zhang, X., & Yu, S. (2022). Operational Data-Driven Intelligent Modelling and Visualization System for Real-World, On-Road Vehicle Emissions—A Case Study in Hangzhou City, China. Sustainability, 14(9), 5434. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095434







