Abstract
Three industrial solid wastes including red mud, carbide slag, and phosphogypsum combined with ordinary Portland cement were used as curing agents to solidify/stabilize loess polluted by a high concentration of copper ions. The unconfined compressive strength, resistivity, permeability coefficient, copper ion leaching concentration, pH value, and other engineering application evaluation indexes were analyzed to preliminarily assess the applicability of the curing agent in the remediation of soil contaminated with a high concentration of copper ions. The mineral phases and functional groups of solidified soil were detected using XRD and FTIR, showing that the strength, electrical resistivity, and pH value of solidified soil decrease following the addition of copper ions. Moreover, the strength and resistivity of solidified soil increase with the curing age, and the pH value decreases with age. For solidified contaminated soil, when the total content of curing agent increases from 10 to 20%, the maximum 28 d strength increases from 1.35 to 5.43 MPa, and in this study, its permeability coefficient, copper ion leaching concentration, and pH value were found to be within the limits set by relevant national standards. In conclusion, red mud-carbide slag-phosphogypsum combined with cement has a good stabilizing effect on sites polluted with a high concentration of copper ions.
1. Introduction
In recent years, copper production and consumption in China has ranked first in the world [1]. Waste gas, water, and residue discharged from copper-zinc-ore-smelting areas and wastewater discharged from electroplating and metal processing inevitably cause serious copper pollution to the original site of the factory [2]. Soil polluted with heavy metals does not only seriously deteriorate its engineering properties [3] but the heavy metals in soil will also cause contamination to surrounding soil with rainwater scouring and groundwater circulation and may affect food safety and human health [4]. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop effective technologies for the remediation of soil polluted with heavy metal ions to reduce environmental pollution.
In recent years, environmental geotechnical workers have conducted much research regarding potential remediation technologies of heavy-metal-contaminated soil. Various remediation schemes have been developed. Among them, physical remediation methods such as the soil exchange method, thermal desorption method [5], and glass solidification [6] method have had a significant effect on the remediation of heavy-metal-contaminated sites, but their shortcomings in energy consumption make them unconducive to the treatment of large amounts of contaminated soil. The chemical leaching [7] method has the potential risk of leaching the solution to the environment, while the electric remediation method, as an advanced remediation method without secondary pollution, presents the problem of the high cost of power consumption, and bioremediation [8] and phytoremediation technology [9] has the defect of a long remediation cycle, which is not conducive to the treatment of projects with a tight construction period. This study is based on the treatment of large-scale and high-concentration heavy-metal-contaminated sites, and S/S technology has the following characteristics: strong economic applicability, convenient operation, a short construction period, and a friendly environment.
Cement [10], lime [11], and other traditional building cementitious materials are used to solidify inorganic wastes, such as heavy-metal-contaminated soil, showing excellent engineering characteristics and a strong solidification efficiency of harmful substances. However, the strength of cement slurry is seriously reduced by heavy metals, and the high concentration of heavy metals exceeds the curing capacity of cement, resulting in an increased leaching concentration [12]. The energy consumption of the cement-manufacturing industry accounts for about 8% of the total energy consumption in China and releases a large amount of greenhouse gases that pollute the environment [13]. Red mud is a powdery solid waste produced during alumina production from bauxite ore [14]. The annual output of red mud is as high as 175.5 million tons, the global red mud reserve is close to 4 billion tons and its methods for its application in all aspects have gradually enriched [15]. Many scholars [16,17] have found that red mud has certain pozzolanic activity and can be used as a source of solidified body strength through the micro analysis of geopolymers produced by red mud as raw materials and some building materials. Many experimental studies prove the favorable performance of solidifying poor foundations and repairing heavy metal-polluted soil. Mukiza et al. [18] used red mud instead of any cement to test the strength of road-base material, showing that red-mud-solidified soil meets the strength requirements of China’s first-class highways. Zhang et al. [19] used red mud, carbide slag, and electrolytic manganese slag as subgrade materials, which exhibited strong compressive strengths and durability. Suo et al. [20] used red mud and cement to solidify soil with a high concentration of copper ions, and the engineering characteristics and leaching toxicity of the solidified soil fully met the requirements.
Carbide slag is a by-product of acetylene production by calcium carbide hydrolysis. Taking advantage of its high Ca(OH)2 content, carbide slag can be used to replace lime or cement in the remediation of urban industrially polluted site soil, as it better meets the requirements of site remediation regarding the strength and solidification efficiency of toxic pollutants [21]. Kou et al. [22] used carbide slag combined with cement and slag as cementitious material which shows strong mechanical properties and is conducive to the formation of hydration products. Zhang et al. [23] used the carbide slag treated by wet grinding as the alkali activator for blast furnace slag, which improved the compressive strength of cementitious materials well and increased the hydrate content. Suo et al. [24] studied the solidification stability of 1% copper ion-contaminated soil solidified by carbide slag and various industrial waste residues. The results showed that the addition of carbide slag can improve the solidification efficiency of Cu2+ and ensure a low leaching concentration. Sun et al. [25] solidified soil contaminated with 2% copper with 20% carbide slag, achieving a higher strength than the strength of 0.5 MPa required by the Ministry of Environmental Protection of China for general solidified bodies. Phosphogypsum is a by-product of the process of extracting phosphoric acid from phosphate rock. Wang et al. [26] showed experimentally that the strength characteristics and heavy metal stabilization ability of phosphogypsum combined with red mud in curing soil contaminated with a high concentration of copper lead and zinc ions are better than those of fly ash and red mud. Jin et al. [27] developed a ternary cementitious system composed of ground blast furnace slag, calcium carbide slag and phosphogypsum. It was found that the excitation of calcium carbide slag and phosphogypsum led to a sufficient hydration reaction of the cementitious system, and the compressive strength was able to reach 45.6 MPa. In this paper, carbide slag and phosphogypsum are applied to the activator of red mud as the curing agents of heavy metal-contaminated sites.
In this work, we developed a high-efficiency curing agent for stabilizing/solidifying soil polluted with a high concentration of copper ions. The unconfined compressive strength, permeability coefficient, copper ion leaching concentration, and pH value of solidified soil test specimens of red mud, carbide slag, and phosphogypsum with different ratios and dosages were obtained through indoor tests such as the evaluation indexes to evaluate the curing performance of the curing agent. The results were compared with the performance index requirements of solidified soil mechanics and national and international environmental safety standards to prove the applicability of the curing agent and provide data support for landfill disposal and resource utilization of solidified soil.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
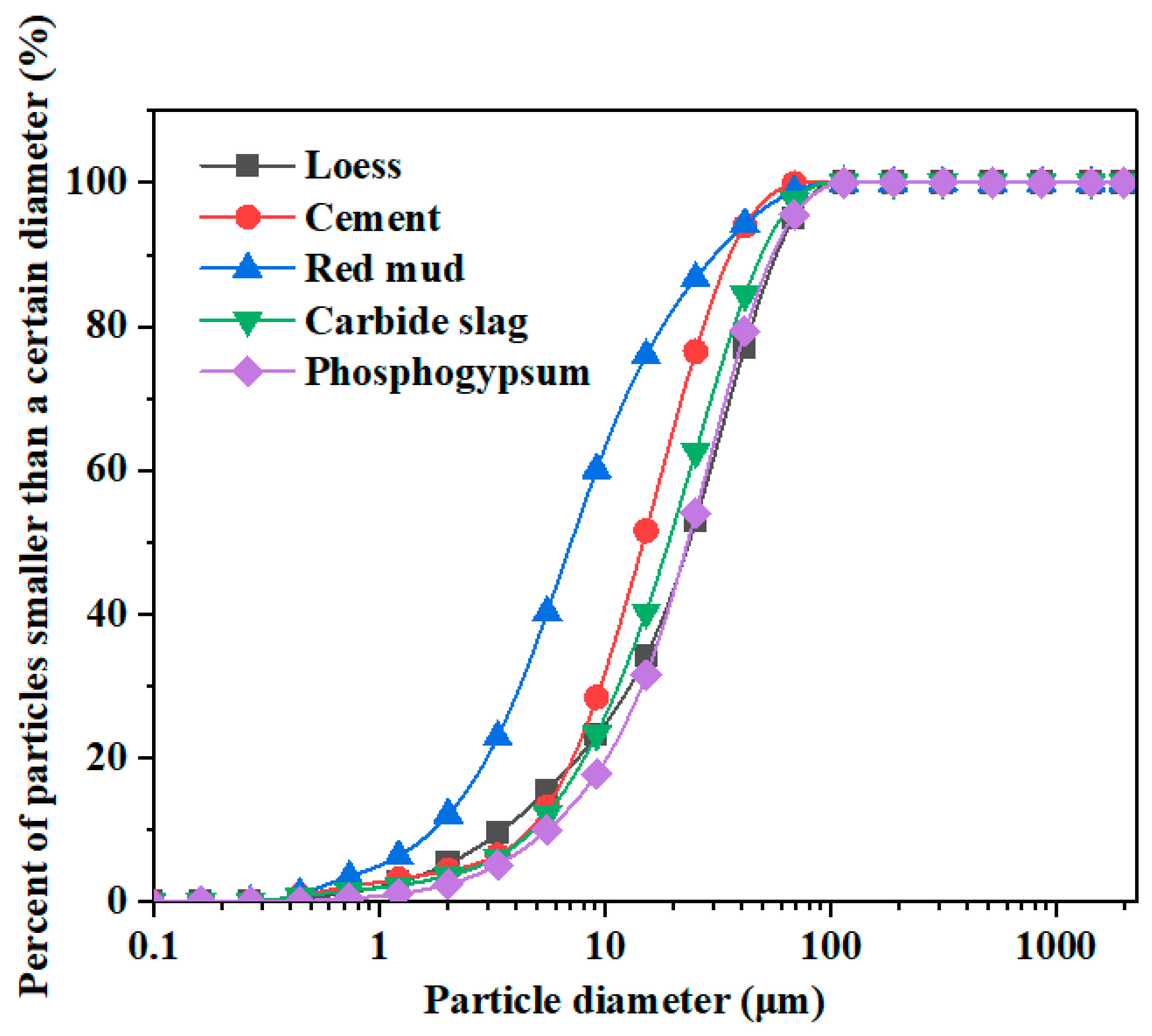
As the material for soil samples, loess of Taiyuan City, Shanxi Province, China, was used in this study with a plastic limit of 10.8%, liquid limit of 28.2%, plasticity index of 10.8, and pH value of 7.3. The test results for soil with different ion concentrations are shown in Table 1. Red mud (pH 9.89) was produced using the Bayer process by Aluminum Co., Ltd. (Xiaoyi, China). Carbide slag (pH 12) was taken from the calcium carbide slag yard of Chemical Co., Ltd. (Yushe, China). Phosphogypsum (pH 4.61) was obtained from a chemical enterprise (Shandong, China). Ordinary Portland cement (42.5R/N) was purchased from the Lion Cement Company in Taiyuan. Heavy metal pollution ions were derived from a Copper nitrate trihydrate (Cu(NO3)2·3H2O) reagent (Aladdin Industry Corporation, Shanghai, China), and distilled water (pH 7) was used for the tests. Particle size distribution curves, the main chemical compositions, and the content of raw materials are shown in Figure 1 and Table 2.

Table 1.
Ion concentrations in loess particles (mg·kg−1).
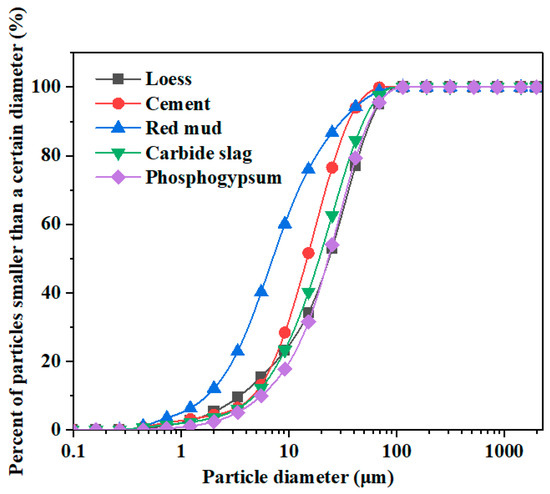
Figure 1.
Particle size distribution curves of raw materials.

Table 2.
Main chemical composition and content of raw materials (%).
2.2. Test Scheme Design
The National Soil Pollution Survey Bulletin (2014) shows that copper pollution sites account for 0.05% of all contaminated sites, according to the Chinese soil environmental quality standard (GB15618-2018), the risk screening value for soil contamination of copper is 200 mg/kg when the soil pH > 7.5. However, copper pollution sites with more than 10 g/kg have been reported [28]. Therefore, the solidification and remediation effect of soil heavily polluted with copper ions are studied in this article, and soil uniformly polluted at a high concentration of 10 g/kg copper was manually configured as the soil sample to be solidified.
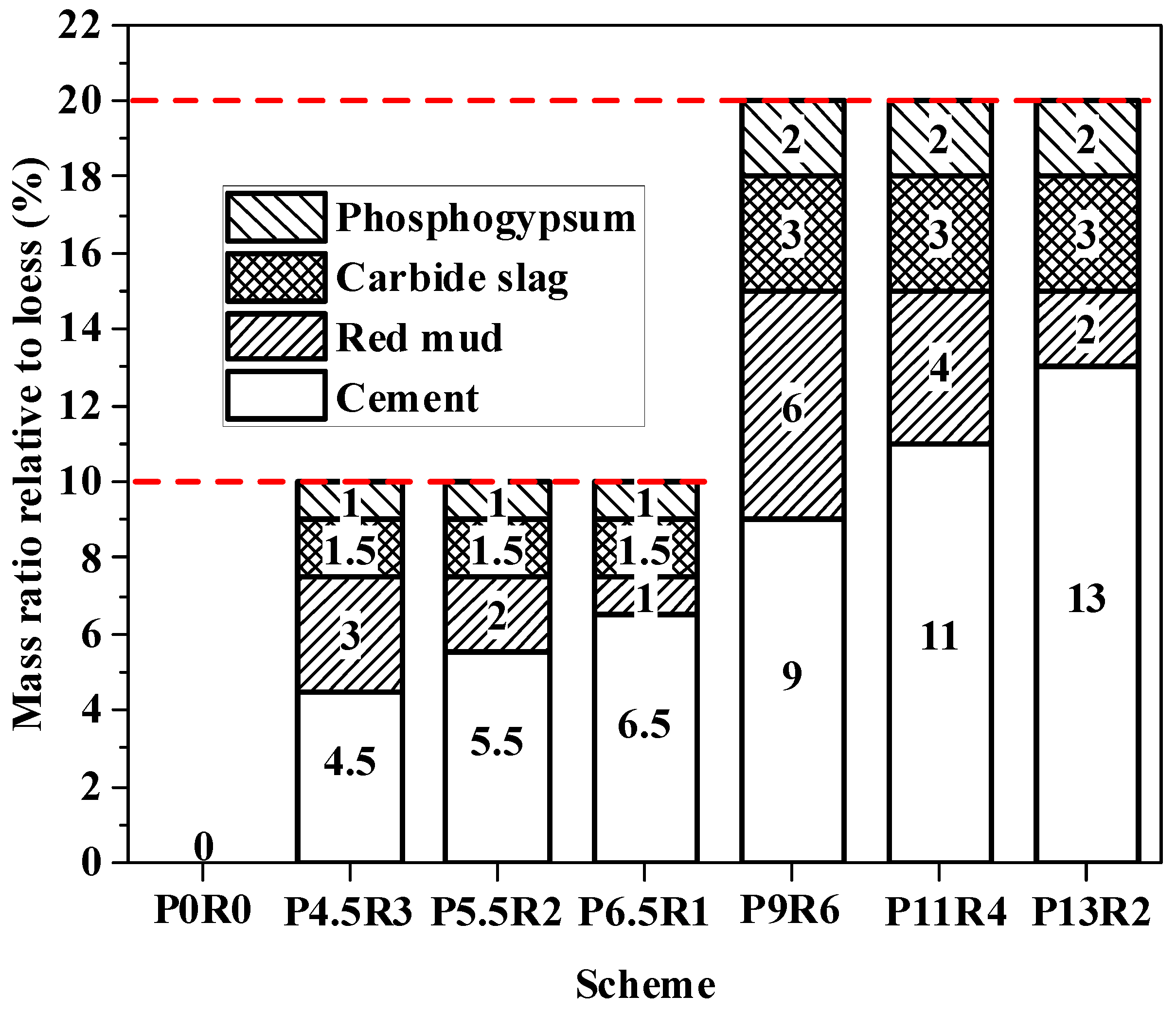
When hazardous waste is treated by solidification/stabilization technology, first the engineering characteristics and environmental safety required by the landfill and resource utilization of the solidified body should be met, and the compatibilization ratio should be reduced as much as possible (i.e., ratio of the volume of the solidified body to the volume of hazardous waste before the solidification agent is added), to avoid incurring an additional burden to the final disposal of the solidified body. In this study, a low total content of inorganic binder of 10% (mass ratio relative to the dry weight of polluted loess) and a medium content of curing agent of 20% were preliminarily set, and cement proportions of 0.45, 0.55, and 0.65 (i.e., proportion of cement in the curing agent) were chosen. The specific mixing schemes are shown in Figure 2. Scheme “P0R0” acted as the control group, and no curing agent was added. For each mixing ratio scheme, 1% copper ion-polluted loess and uncontaminated loess were simultaneously solidified, and subsequent tests were carried out. For simplicity, solidified 1% copper ion-contaminated soil was denoted as “RCP1%”, and solidified uncontaminated soil was denoted as “RCP0%”.
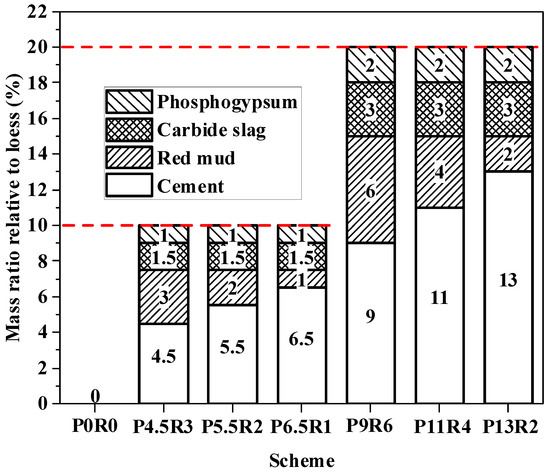
Figure 2.
Curing agent mixing schemes.
2.3. Specimen Praparation
All materials were air dried and crushed, passed through a 2-mm geotechnical sieve, weighed, mixed with loess, cement, red mud, calcium carbide slag, and phosphogypsum according to the mixing amount of each component shown in Figure 2, and the obtained mixtures were thoroughly mixed. Then, according to the optimal moisture content determined by a compaction test, 12% of distilled water (relative to the total mass of solidified soil) was weighed. Moreover, copper nitrate trihydrate (Cu(NO3)2·3H2O) powder was weighed (Cu2+ concentration: 10 g/kg, relative to the mass of loess) and dissolved in distilled water. The copper nitrate solution was evenly sprayed into the solidified soil sample, which was thoroughly mixed by continuously stirring for 10 min and then poured into an airtight bag and equilibrated for 24 h to fully integrate water and Cu2+ with the particles in the mixture. Then, 200 g of this mixture (according to the maximum dry density) was weighed and poured into a Φ×H = 50 × 50 mm cylindrical column mold for static pressure forming, and six parallel samples were prepared for each scheme. Then, the compacted test specimens were removed using a demoulding machine and wrapped in cling film. Finally, they were cured in a curing container with a constant temperature and humidity (temperature 20 °C, humidity 95%) for standard curing. After 7, 14, and 28 days of curing, the specimens were removed from this container for subsequent tests.
2.4. Test Contents and Methods
Strength is an important property of soil or geomaterials [29]. The unconfined compressive strength was measured using the microcomputer-controlled electronic universal testing machine WDW-100 according to the test code for highway materials stabilized with inorganic binder (JTG E51–2009) [30]. The resistivity reference for the test method can be found in [31]. The permeability coefficient was tested using a flexible wall permeameter (PN3230M). The leaching toxicity test refers to the method mentioned in the solid waste-extraction procedure for leaching toxicity—the sulphuric acid and nitric acid method (HJ/T299–2007) [32], and the pH was determined according to the standard test method for the identification of the corrosivity of hazardous wastes (GB5085.1–2007) [33].
A phase analysis with XRD was performed using a Bruker D8 ADVANCE X-ray diffractometer with CuKa radiation, 40 kV voltage, a 200 mA current, and a scan range of 2 = 10°–90°. FTIR measurements of the raw materials were performed before and after the hydration reaction using a Nicolet NEXUS-670 FTIR spectrometer in the wave number range of 4000–500 cm−1 at a resolution of 1 cm−1. The general Tessier progressive extraction method [34] was used to analyze five categories of heavy metal components, namely exchangeables, carbonates, iron oxides, manganese oxides, organic, and residue forms.
3. Results
3.1. Basic Engineering Indexes
3.1.1. Unconfined Compressive Strength
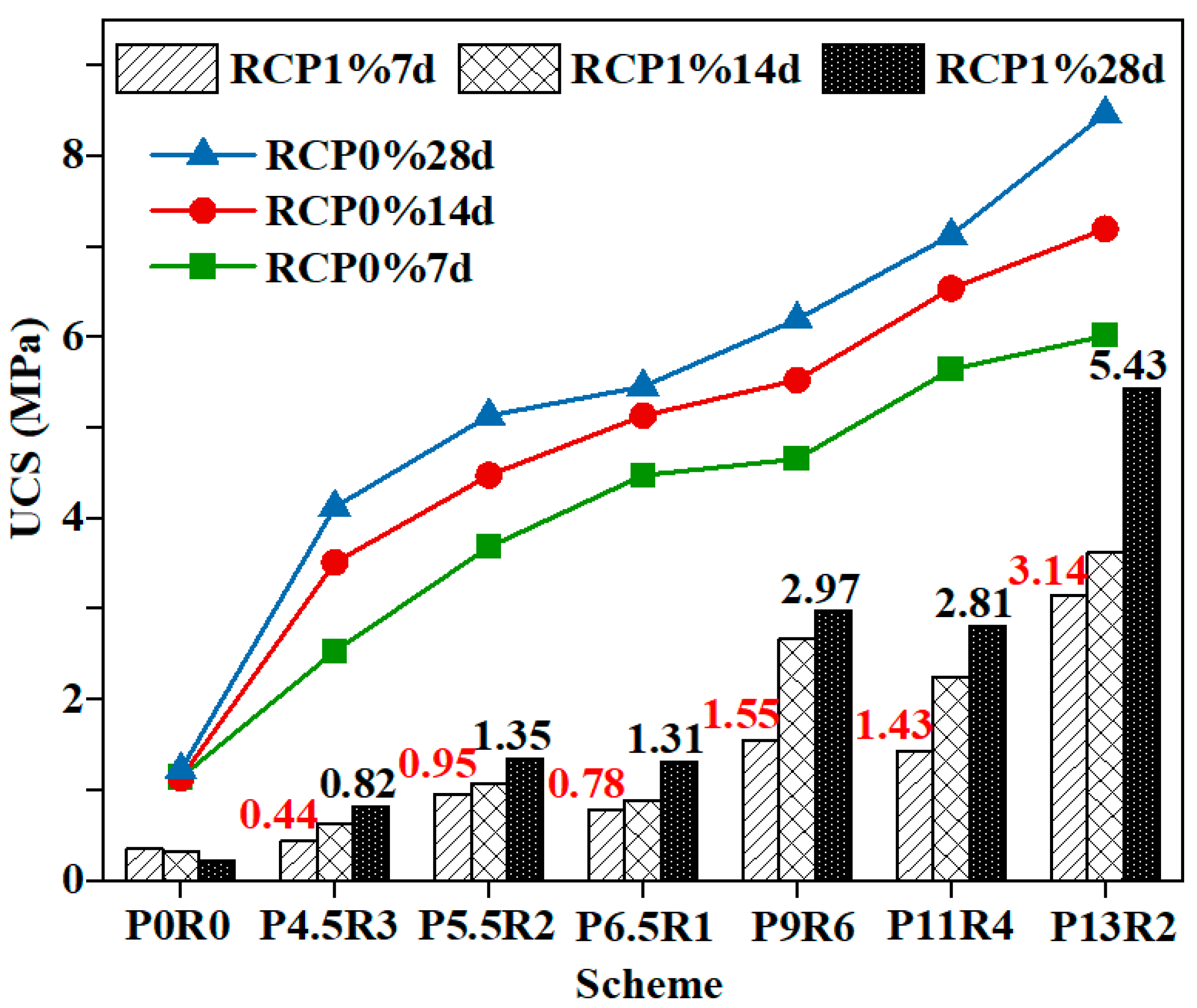
Figure 3 shows the variation of the unconfined compressive strength (UCS) of contaminated and uncontaminated solidified soil test specimens and the age for schemes with different curing agent proportions, revealing that the strength of RCP1% was less than that of RCP0% at the same curing age. Moreover, it shows that the presence of Cu2+ hinders the extent of the reinforcing effect of the curing agent. A large number of studies on curing heavy-metal-contaminated soil with inorganic binder [34,35,36] show that the strength of the solidified soil contaminated with heavy metals, such as copper, lead, and zinc, is lower than that of solidified soil without heavy metals at the same ratio, and the greater the heavy metal concentration is, the stronger the deterioration of strength. Table 3 summarizes the strength ratios of RCP1% to RCP0% at 7, 14, and 28 days for all curing schemes, showing only slight differences between the ratios of schemes “P4.5R3”, “P5.5R2”, and “P6.5R1” with a total content of 10%, which all exhibited strength ratios of about 0.2. When the cement proportion increased from 0.45 (scheme “P4.5R3”) to 0.65 (scheme “P6.5R1”), the strength values of RCP0% and RCP1% increased by 1.77 times at 7 d of age. When the total content of the curing agent increased to 20%, the ratio of RCP1% to RCP0% increased slightly with age. When the proportion of cement increased from 0.45 (scheme “P9R6”) to 0.65 (scheme “P13R2”), the strength values of RCP0% and RCP1% increased by 1.29 and 2.03 times at 7 d of age, respectively.
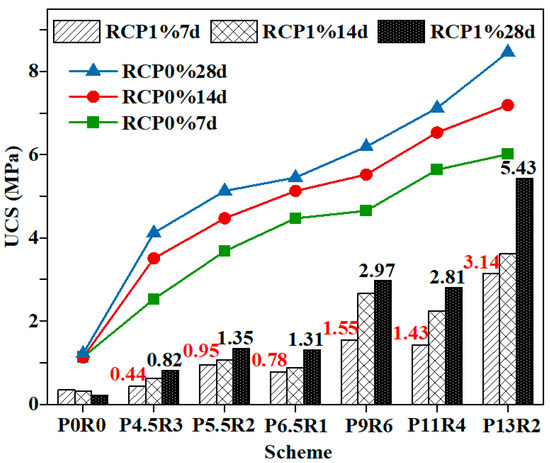
Figure 3.
Change of the strengths of RCP1% and RCP0% with the curing age.

Table 3.
Ratios of unconfined compressive strength of RCP1% and RCP0%.
Figure 3 shows that the strength of the RCP solidified soil test block increased gradually with age, whether copper ions had been added or not. The gradual increase in strength indicates that the hydration of active components in the curing agent occurred step by step, and that it was not a short-term physical and chemical reaction. The formed hydration products will continue to participate in the reaction with newly dissolved active components, which is a dynamic reaction process [37]. However, the strength of scheme “P0R0” without the curing agent decreased gradually with age, indicating that the contaminated soil as such had no good adhesion properties. Without admixture, the invasion of pollutants leads to soil softening [38], resulting in soft and weak soil and serious secondary disasters. Therefore, such sites should be repaired in time.
Figure 3 and Table 3 show that RCP1%, RCP0%, and their strength ratio of scheme “P13R2” reached a high level, which may be due to the high cement proportion of 0.65, which greatly improved the production of cement hydration products and provided a sufficient alkalinity and Ca(OH)2 content for the pozzolanic reaction, which is conducive to the dissolution of active components in RCP. The strength (3.14 MPa) of RCP1%7d in scheme “P13R2” meets the Chinese standard for road bases with a medium and low traffic volume and the strength requirements of 3–5 MPa for base fillers in the Netherlands. The strength of RCP1% at 28 d of age (5.43 MPa) meets the requirements in the UK for the strength of the base course filler of 4.5 MPa and the Chinese standard for super heavy roads of 5–7 MPa. Therefore, 20% solidified soil can meet the strength requirements of the resource utilization of solidified soil. The strength of RCP1% with a content of 10% meets the strength requirements of the United States and Great Britain of 0.35 and 0.7 MPa, respectively, for contaminated soil treated and stabilized using the landfill method.
3.1.2. Permeability Coefficient
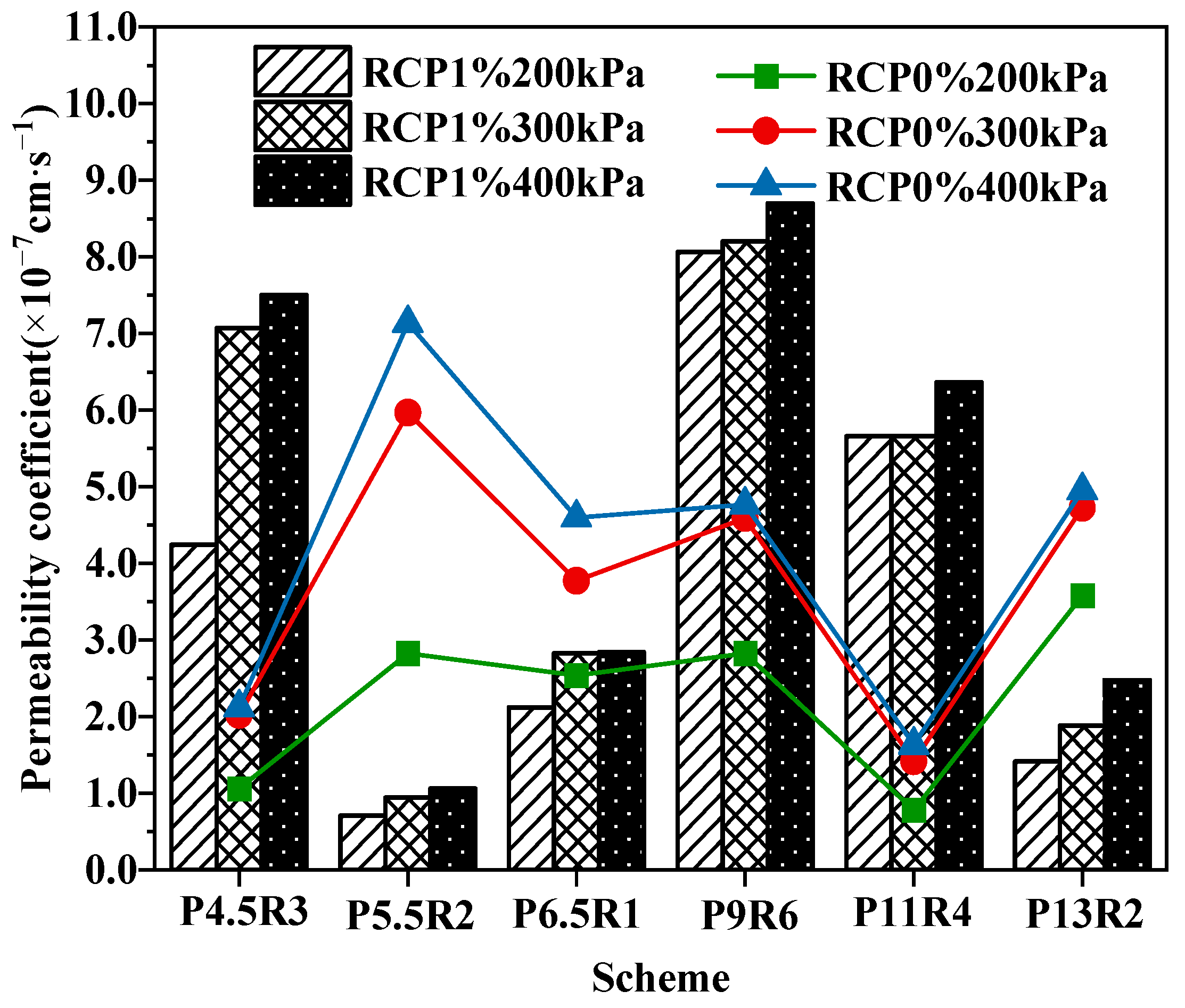
The permeability coefficient is an important factor that controls the migration rate of heavy metal ions and the dissolution of pollutants in the solidified body. Figure 4 shows the permeability coefficients of solidified soil under the osmotic pressure of 200, 300, and 400 kPa for the different schemes. All the test blocks had small permeability coefficients in the range of (1–10) × 10−7 cm·s−1, and the different mixing schemes did not exhibit any significant differences. Moreover, the permeability coefficient increased only slightly with the increase in osmotic pressure, indicating a strong adhesion of the hydration products to solid particles, which can resist the scouring of high-pressure leachate. Many studies [38,39] have found that the greater the concentration of heavy metal ions, the greater the permeability coefficient. However, different mixing schemes in this study showed different tendencies, probably because many curing agents were used in this study, and various reactions were complex. Aggregate filling, hydration product cementation, particle agglomeration, particle compaction under confining pressure, and osmotic pressure jointly affect the structure of seepage channels in solidified soil [40].
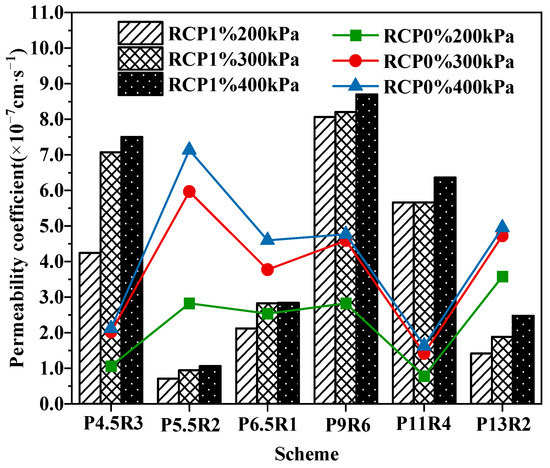
Figure 4.
Change in the permeability coefficients of RCP1% and RCP0% with osmotic pressure.
3.1.3. Electrical Resistivity
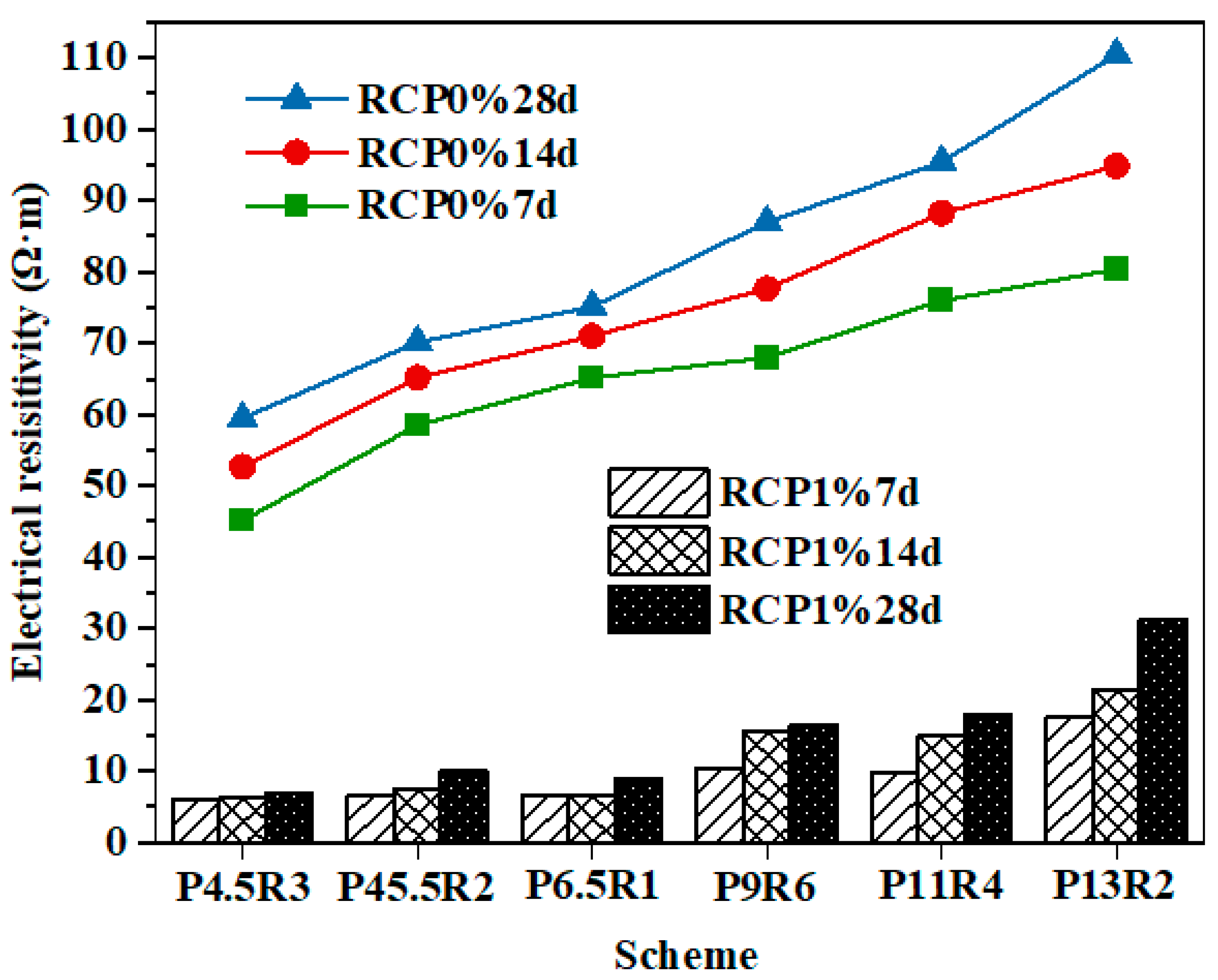
In a large number of studies in China, electrical resistivity test technology has been applied as a nondestructive and convenient test method to the typical complex three-phase system of soil [41], and a good correlation between the resistivity value of solidified soil test specimens, UCS, and pollutant concentration has been established. Many studies [42] found that the addition of heavy metal ions greatly improves the conductivity of soil and greatly reduces its resistivity. The higher the ion concentration, the more intense the decline in resistivity. Figure 5 shows the change in resistivity with the age of contaminated and uncontaminated solidified soil test specimens, revealing that the resistivity of RCP1% was much lower than that of the RCP0% test specimens due to the addition of 1% copper ions. The presence of heavy metals hindered cement hydration, resulting in poor particle adhesion and a loose structure, but also led to a greater pore solution through pores and a smooth conductive path. In addition, the high concentration of the heavy metal pore solution increased the conductivity of the pore water, which greatly reduced the resistivity of the solidified soil.
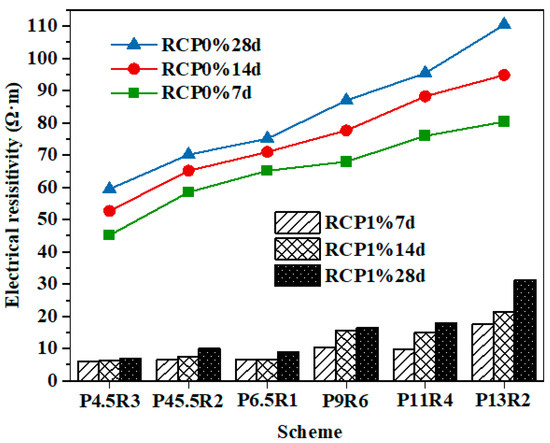
Figure 5.
Change of the electrical resistivity of RCP1% and RCP0% with the curing age.
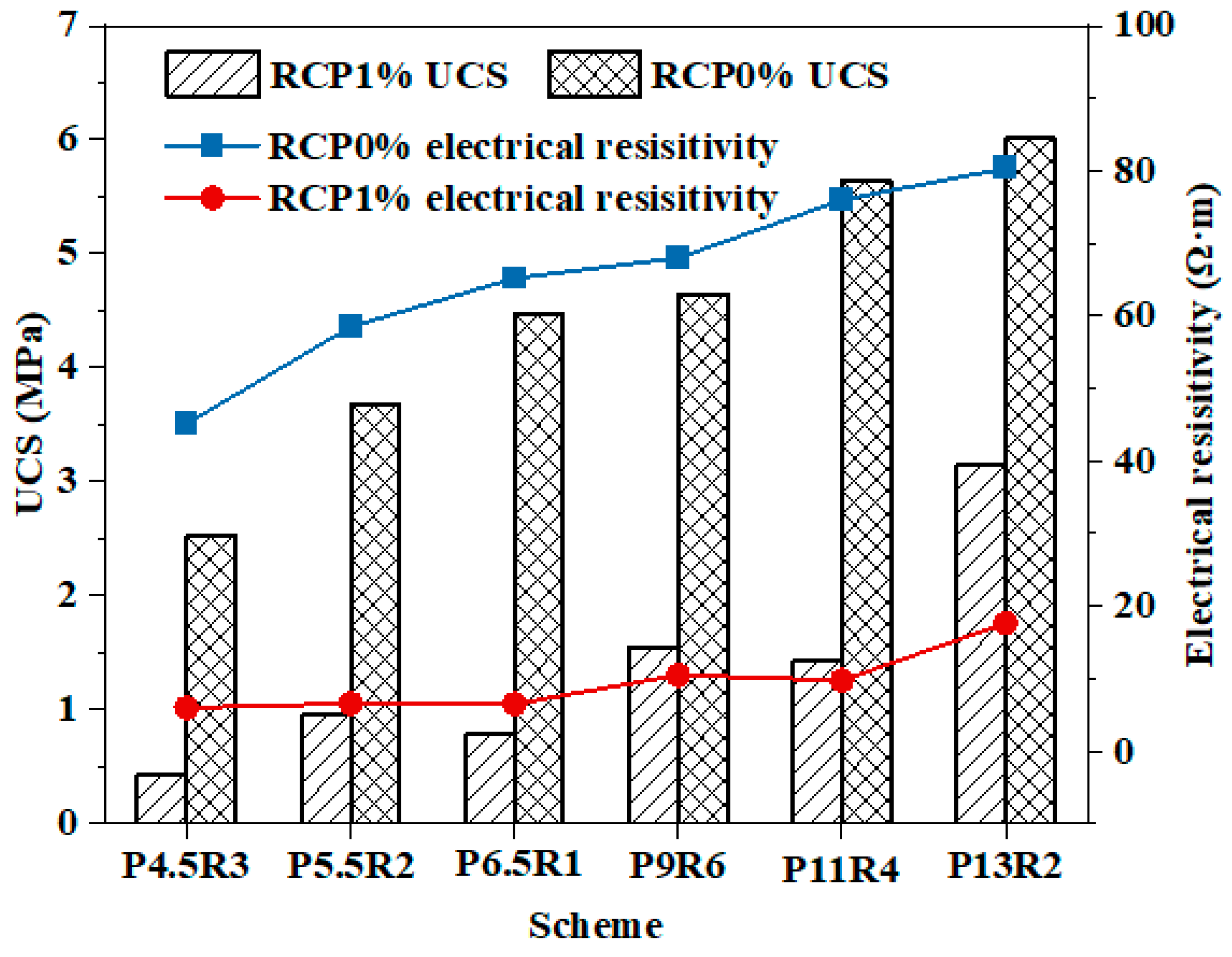
Figure 5 shows that the resistivity of the RCP solidified soil test specimens increased gradually with age whether copper ions were added or not, revealing that with an increase in the curing time, the amount of hydration products of the curing agent gradually increased, the degree of cementation increased, and the porosity and saturation decreased, resulting in a denser soil structure and a stronger blocking effect on the alternating current [43]. It has been proved that resistivity test technology can be used in nondestructive evaluation methods to estimate the hydration degree of a curing agent in solidified/stabilized soil. A comparison of Figure 3 and Figure 5 in combination with the proportion scheme of the curing agent in Figure 2 shows that with the increase in the cement proportion in the curing agent, the strength and resistivity maintained the same growth trend, and both increased with the increase in age. Moreover, 1% copper ions also reduce the strength and resistivity of solidified soil. The plot of the strength and resistivity of solidified and unsolidified soil test specimens at the age of seven days shown in Figure 6 reveals that both change trends were in good agreement, which proves that the resistivity test technology can be used as an accurate test method to characterize the strength characteristics of solidified soil.
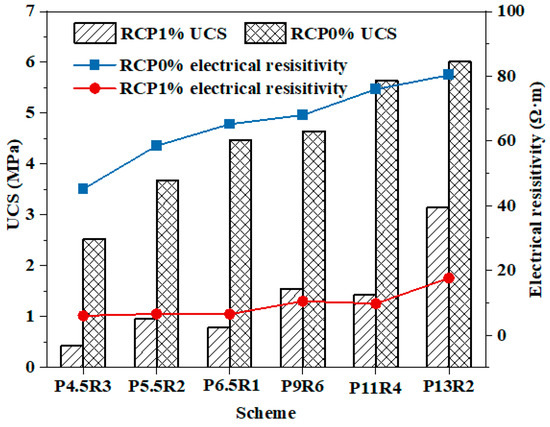
Figure 6.
Strengths and electrical resistivity of RCP1% and RCP0% at 7 d of age.
3.2. Environmental Safety Evaluation Index
3.2.1. PH of Solidified Soil
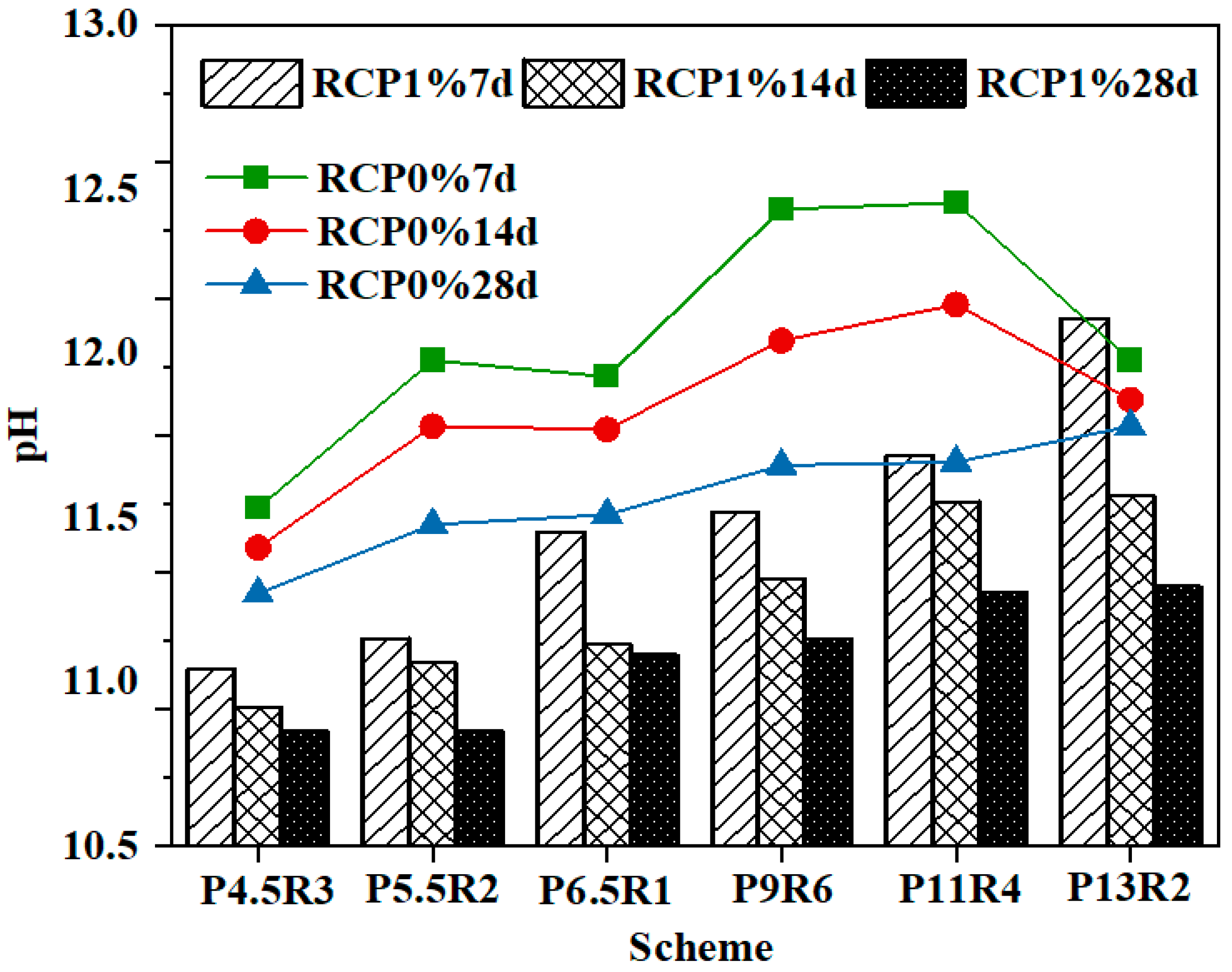
Figure 7 shows the change of the pH values of RCP1% and RCP0% with age, clearly revealing that the pH value of RCP1% was lower than that of RCP0% at the same age. This can be explained by the high concentrations of Cu2+ that reacted with OH− in pore solutions to form the [Cu(OH)4]2− complex, which consumes a large number of basic anions. In addition, the reaction of Cu2+ with carboxyl (-OH) and hydrated groups (-OH2) to release H+ also reduces the pH value of solidified soil [41]. Moreover, the inhibitory effect of Cu2+ on cement hydration reduced the generation of Ca(OH)2. Cu2+ not only reduced the pH of solidified soil but also led to the unstable decomposition of hydration products. The low pH value has a weak effect on the excitation and dissolution of active minerals in solid waste, which is not conducive to the pozzolanic reaction and greatly affects the improvement of its strength.
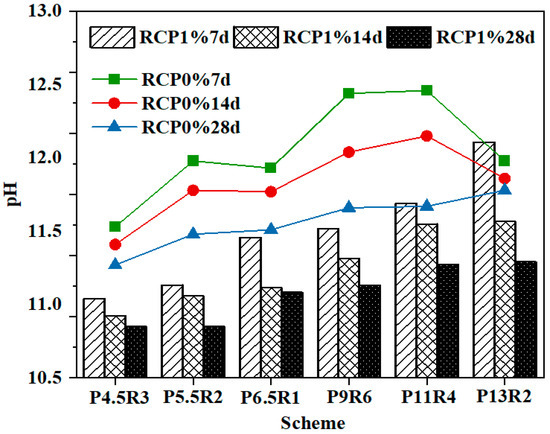
Figure 7.
PH changes of RCP1% and RCP0% with the curing age.
Moreover, Figure 7 shows that whether the solidified soil contained heavy metal ions or not, the change in the pH value was different from that of strength and resistivity, as the pH decreased gradually with an increase in age, which is consistent with the pH change law of red mud, calcium carbide slag, and lime, which are reported as curing agents in other studies [26,43]. The decrease in the pH value with the curing age is due to the pozzolanic reaction of siliceous and aluminum compounds in raw materials in an alkaline environment, which consumes Ca(OH)2 to convert it into secondary cementitious products such as C–S–H and C–A–S–H with low alkalinity, resulting in a decrease in the pH value of the soil. However, Figure 7 shows that the pH at the age of 28 days remained above 10.5, revealing that the pH value is still able to ensure the thermodynamic stability of cementitious products and the important role of pozzolanic products in soil-pore filling, particle adhesion, and soil-strength development.
Alongside the mixing ratios of the curing agents presented in Figure 2, it is found that the pH values of schemes “P9R6”, “P11R4”, and “P13R2” with a total content of 20% were higher than those of schemes “P4.5R3”, “P5.5R2”, and “P6.5R1” with a total content of 10%, but the pH values of all these schemes were lower than the pH limit defined in the standard for the corrosive identification of hazardous wastes (GB 5085.1-2007). This shows that the higher the amount of the curing agent, the more alkaline the solidified soil. The higher alkaline environment is conducive to the dissolution of reactive SiO2/Al2O3 in RCP and accelerates the pozzolanic reaction rate [42]. A higher pH value can ensure the stability of C–S–H [44] and leads to a higher mechanical strength. At the same time, the alkaline environment has a better stabilization effect on heavy metal ions and strong acid resistance [42]. Therefore, the positive effect of an increased amount of curing agent on strength and impermeability should not be considered unilaterally, and the risk of corrosion that the pH of the cured body may cause to the surrounding environment should also be evaluated.
3.2.2. Leaching Toxicity
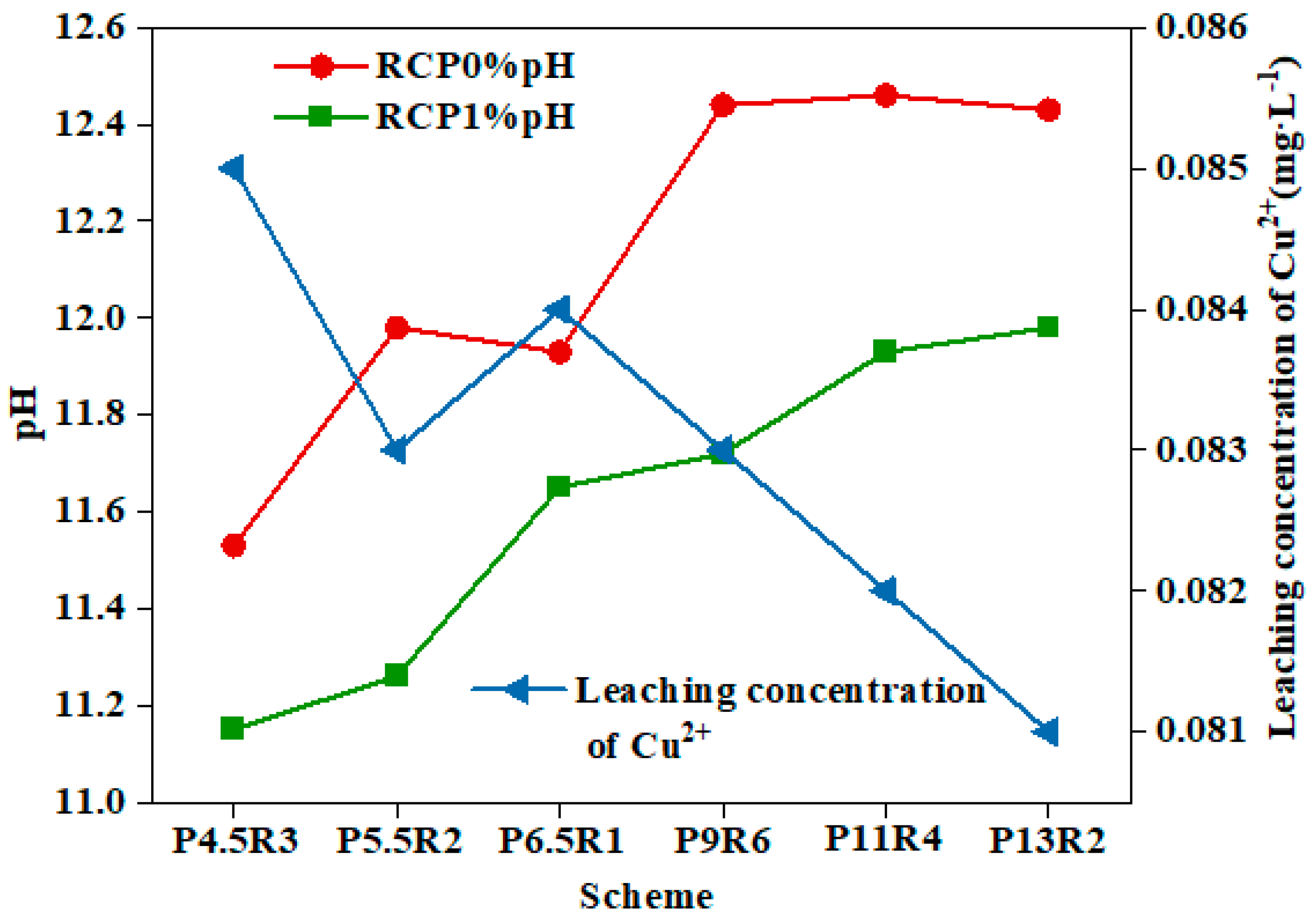
Figure 8 shows the pH values of RCP1% and RCP0% and the copper ion leaching concentration of RCP1%. The leaching toxicity of scheme “P4.5R3” with a lower amount of curing agent was 0.085 mg/L, and the proportion of cement was only 0.45, which is far less than the copper ion leaching limit (100 mg/L) of the identification standard for the leaching toxicity of hazardous wastes (GB5085.3-2007) [45]. The solidification efficiency reached up to 99.99%, and it was also found that with an increase in the proportion of cement and the total content, the leaching toxicity decreased, indicating that the curing agent had a high solidification stability for copper ions and is able to meet the requirements of environmental safety. It has been reported that the solidification effect of Cu2+ in polluted soil is significantly affected by the pH, and the ion mobility in a weak alkaline environment is the lowest [46]. The addition of cement and carbide slag increased the pH of the contaminated soil. Cu2+ was better bound to the surface of the gel, and Cu(OH)2 precipitates under alkaline conditions, thereby reducing the leaching toxicity of copper ions.
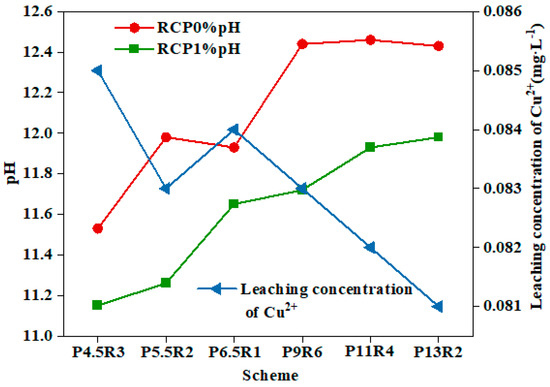
Figure 8.
PH and copper ion leaching concentrations of RCP1% and RCP0% at 7 d of age.
3.2.3. Heavy Metal Speciation
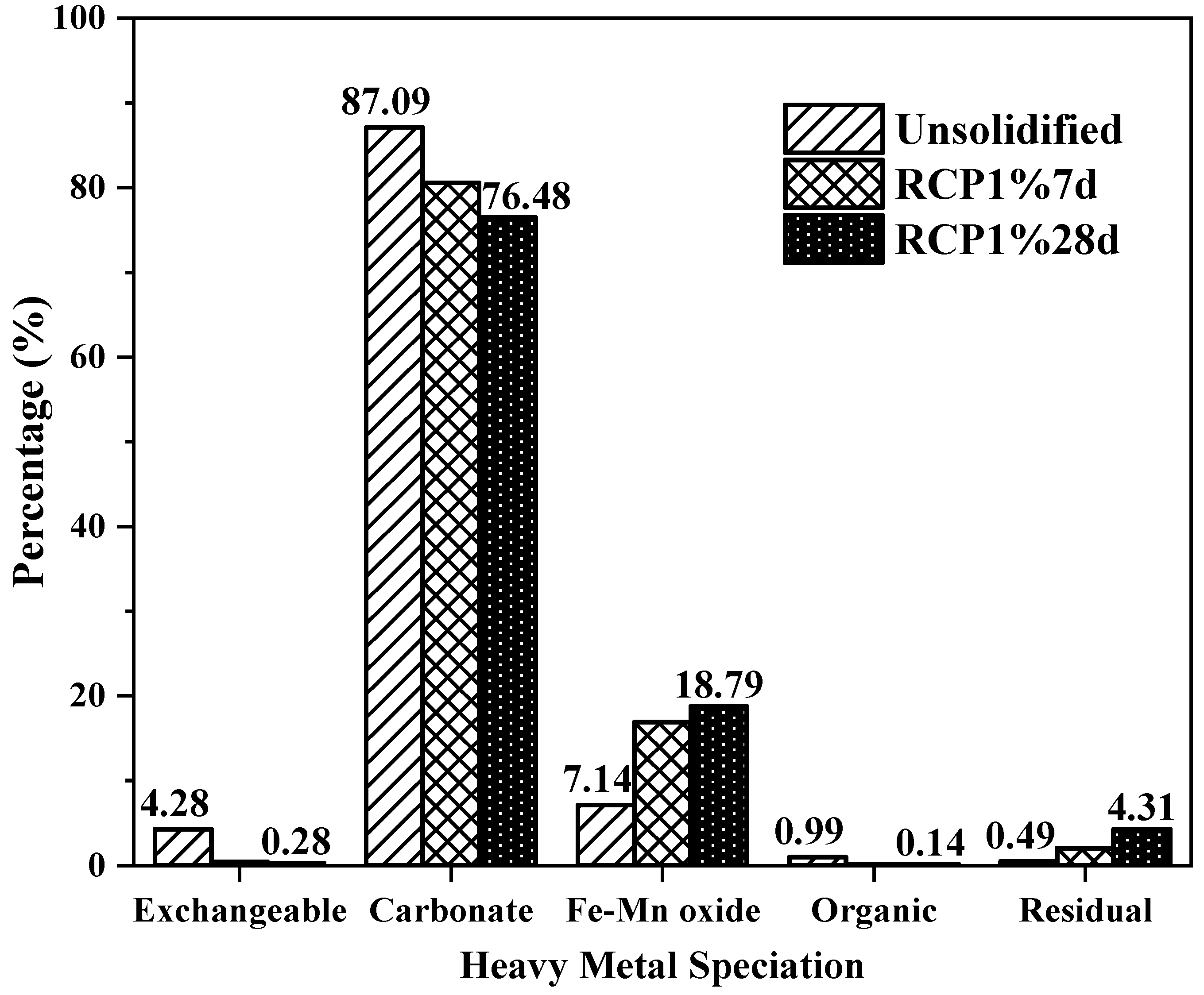
A comprehensive quantitative analysis of heavy metals is commonly used to assess the impact of heavy metals on the environment, but it cannot perfectly reflect its potential ecological harm. Heavy metals exist in different forms in soil, and each form has a different impact on the ecosystem [47]. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze each heavy metal form after curing to better understand the curing process and improve its effectiveness. The Tessier test program considers the possible effects of various environmental conditions on trace elements in soil. The exchangeable form refers to the exchange of heavy metals adsorbed onto clay minerals and other components of soil. This form has the greatest level of activity and can be used to evaluate the bioavailability of heavy metals in soil. The carbonate form refers to heavy metals combined with carbonate precipitation, which is sensitive to the acidity and alkalinity of soil. When the soil pH decreases, carbonate-bound heavy metals dissolve, thus increasing their mobility and bioavailability. In the bound state of iron and manganese oxides, heavy metals are adsorbed onto the iron or manganese oxides in the soil by strong ionic bonding. The change in the soil environment can release some heavy metals, which is potentially harmful to crops, and this bound state is relatively stable compared with the first two states. The organic form refers to the complexation and chelation between heavy metals and organic matter in the soil. This form is relatively stable and in general is not easily absorbed and utilized by organisms. The residual form refers to heavy metals in silicate, primary and secondary minerals, and other soil lattices and can be stably combined in sediments for a long period in a normal environment, with little mobility and bioavailability and minimal toxicity [34].
The speciation distributions of Cu in unsolidified contaminated soil and the RCP1% specimens of scheme “P13R2” at 7 and 28 days of curing age are shown in Table 4. This clearly shows that after adding the curing agent the content of the first two unstable forms in the RCP1%7d test specimens was lower than that of unsolidified soil, while the content of the more stable iron and manganese oxidation fraction and residue fraction were greatly increased, indicating that the RCP curing agent can reduce the sensitivity of heavy metals to environmental changes such as acidity and alkalinity. However, the proportion of each form to the total metal content in Figure 9 revealed that the proportion of the carbonate-bound form was the highest, regardless of whether it was solidified or not. Therefore, in the resource utilization of solidified contaminated soil, environmental safety in the highly acidic soil environment and groundwater environment needs to be considered. Regarding the influence of age on the form and content of heavy metals in RCP solidified soil, the decrease in the exchangeable form and carbonate form and the increase in the more stable form of the latter three in the solidified soil after 28 d of age were very small. The transformation of the ion morphology is a long-term and slow process, which also changes with the transformation of the morphology of the hydration product of the curing agent.

Table 4.
Speciation distribution of Cu in specimens (mg·kg−1).
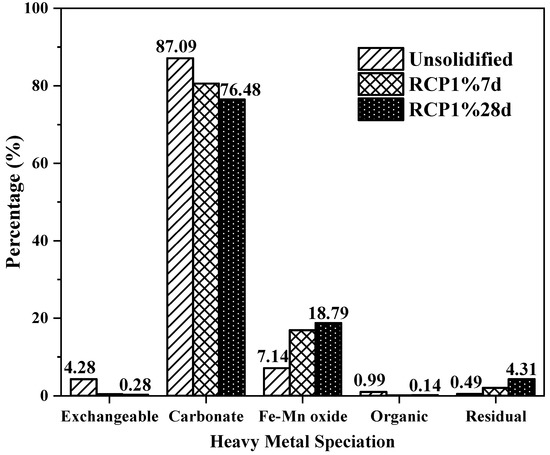
Figure 9.
Percentage of each Cu fraction in unsolidified and solidified soils.
3.3. Material Characterization
3.3.1. XRD
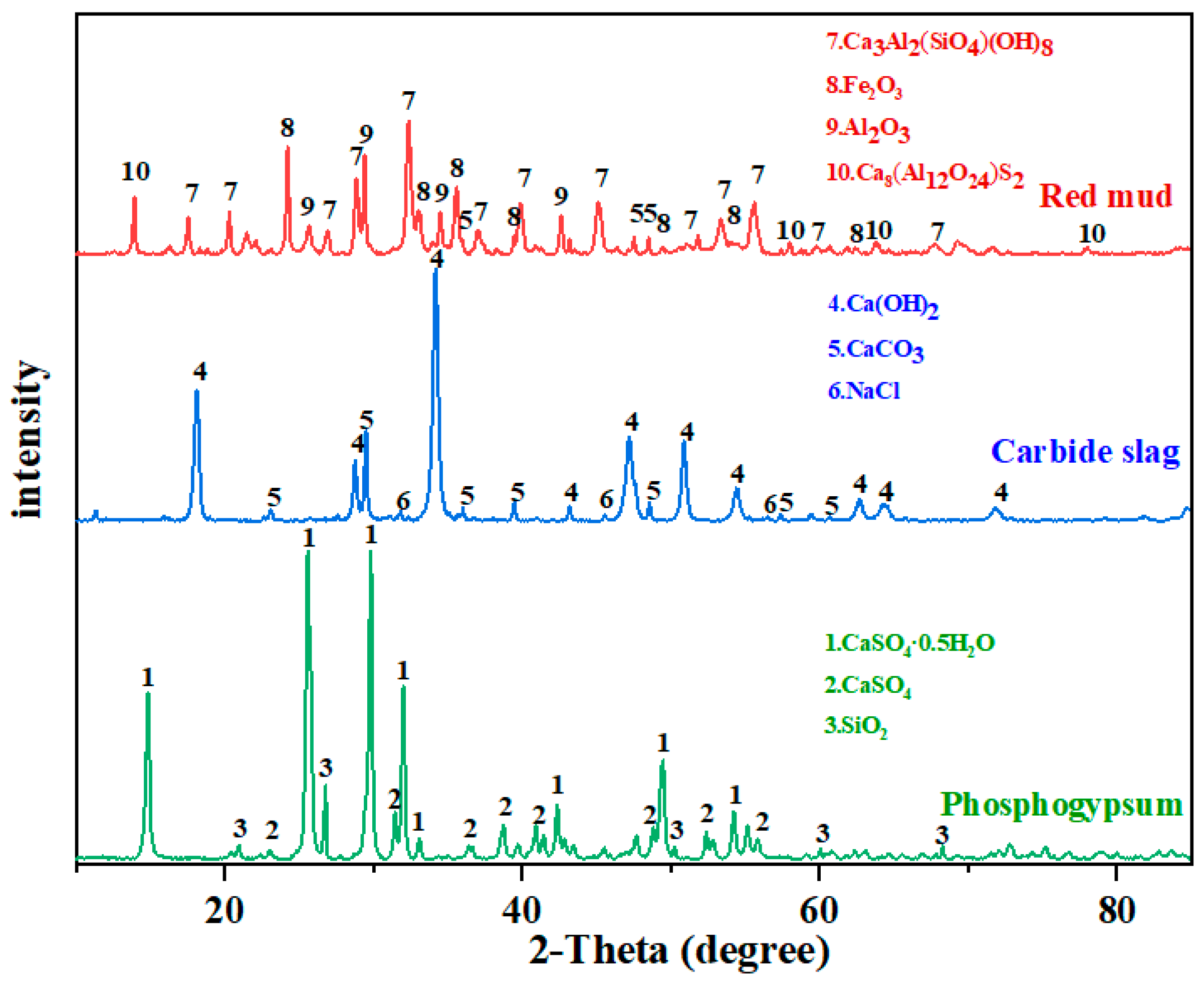
To elucidate the internal mechanism by which the curing agent improves the engineering characteristics of contaminated soil, the mineral components of the raw materials before and after hydration were analyzed with XRD. The XRD spectrum of the raw materials in Figure 10 shows that the mineral phases of red mud are minerals such as Ca3Al2(SiO4)(OH)8, Fe2O3, and Al(OH)3. Red-mud minerals contain a large number of active Al–O and Si–O chemical bonds, which can be broken and released in an alkaline environment [48] due to the high pozzolanic activity [49] The high OH− content of calcium minerals, such as Ca(OH)2 and CaCO3, in carbide slag is used as an activator for the release of active substances from red mud [50]. In phosphogypsum, many gypsum phases were detected, and sulfate is known to be a crucial element of ettringite, the hydration product of common inorganic materials. Phosphogypsum makes up for the vacancy of sulfate in other curing agents.
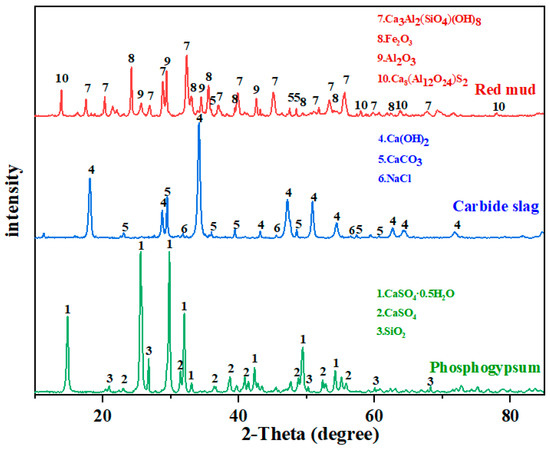
Figure 10.
Mineralogical phases of granulated raw materials.
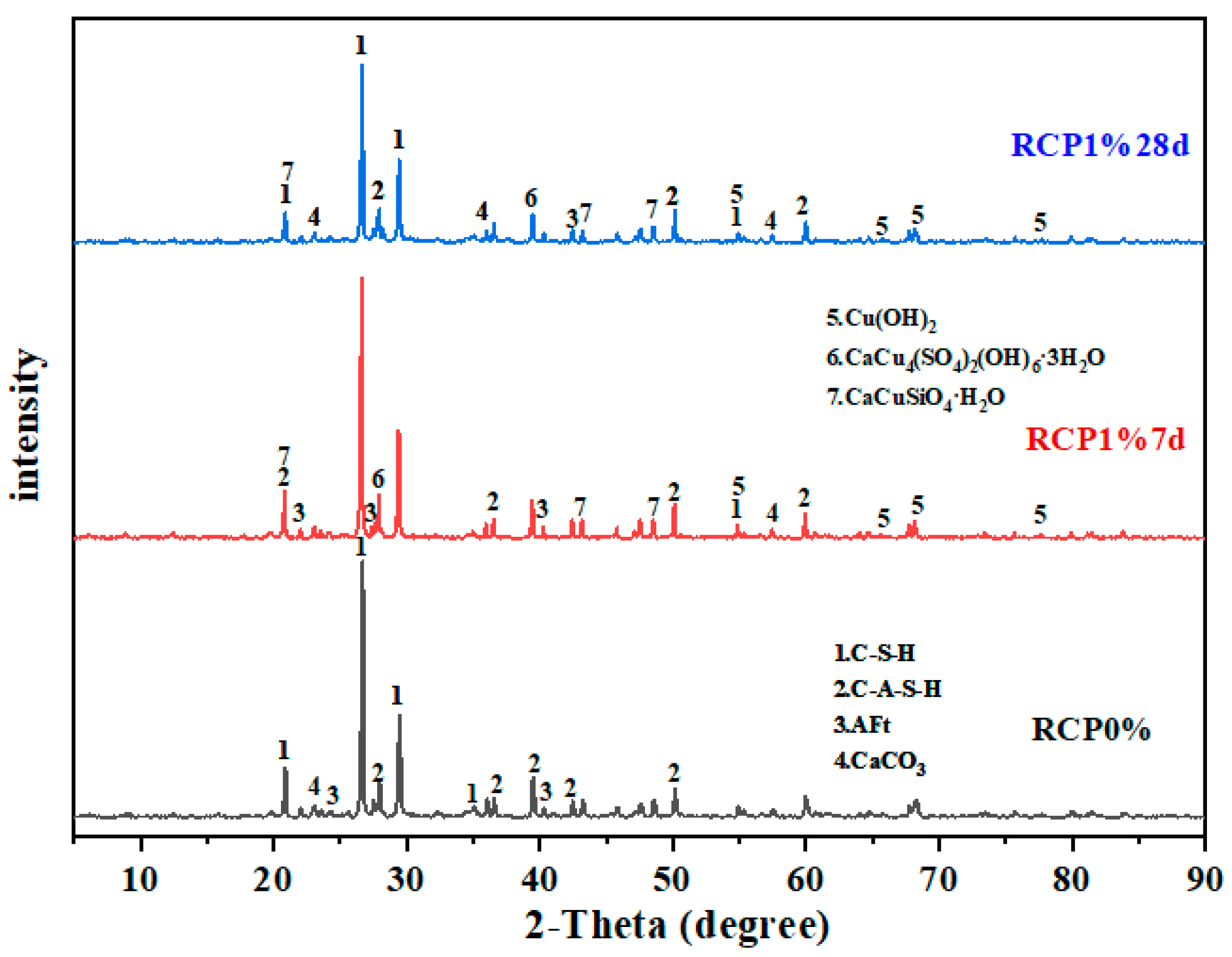
Figure 11 shows the XRD spectra of RCP0% and RCP1% soil prepared according to scheme “P13R2” after curing and hydration in which the hydration products C–S–H, C–A–H, and AFt were identified. The formed hydration products have good adhesion properties and can bind the soil particles in the bulk state into blocks with a high overall strength, which is helpful to meet the strength requirements of solidified soil in engineering applications. In addition, copper-containing phases, such as Cu(OH)2, CaCu4 (SO4)2(OH)6·3H2O, CaCuSiO4·H2O, and CaCuAl(Si2O6)(OH)3, were detected in RCP1% at 7 d and 28 d, indicating that Cu2+ underwent a series of chemical reactions in the solidified soil to combine with the compound. Copper ions combined with minerals have a higher leaching stability than can be achieved with simple physical surface adsorption, which is conducive to the solidification and stabilization of copper ions and reduces its leaching concentration.
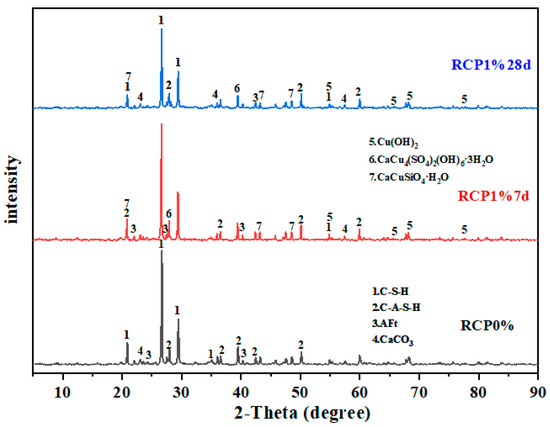
Figure 11.
XRD patterns of RCP0% and RCP1% solidified soil.
3.3.2. FTIR
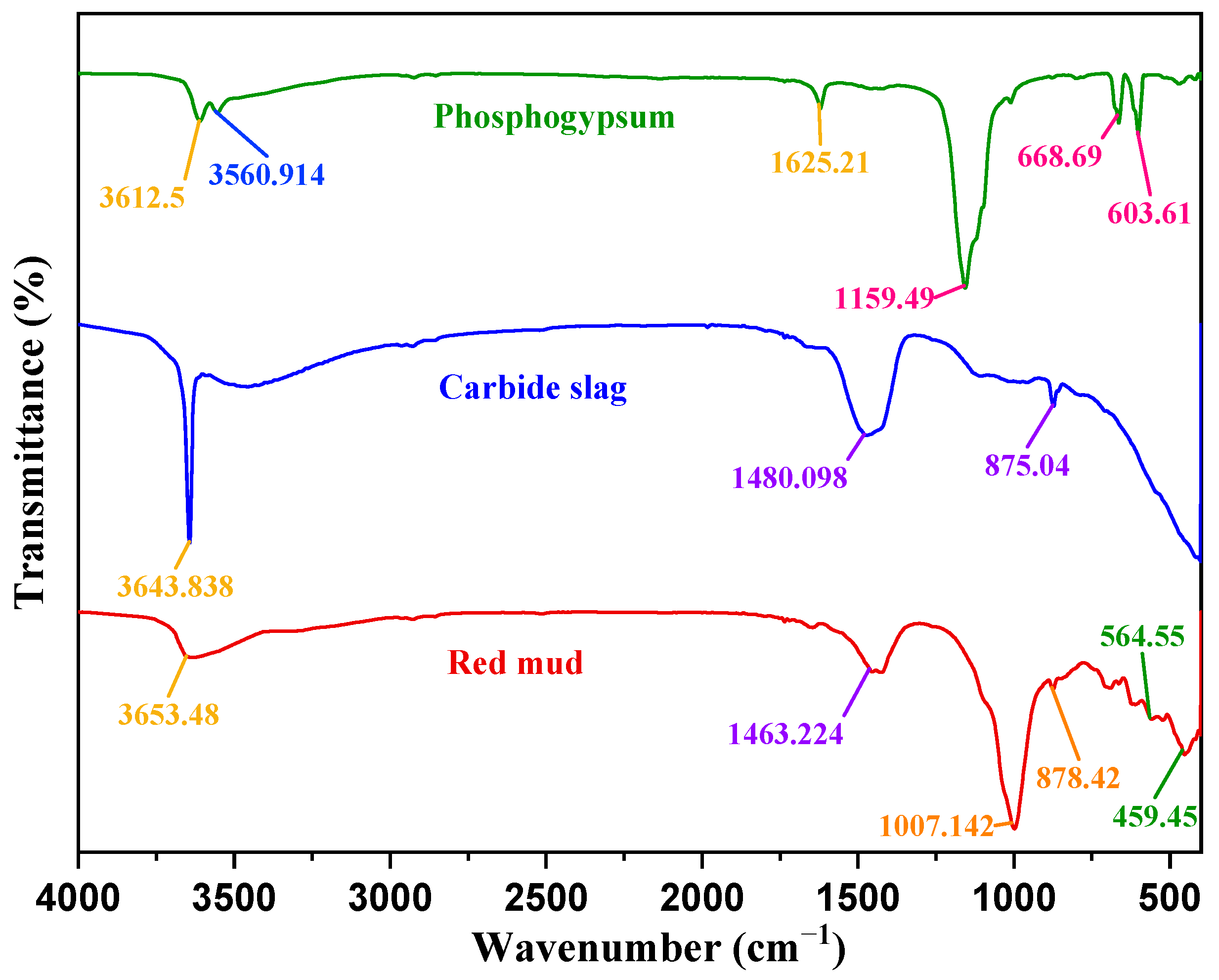
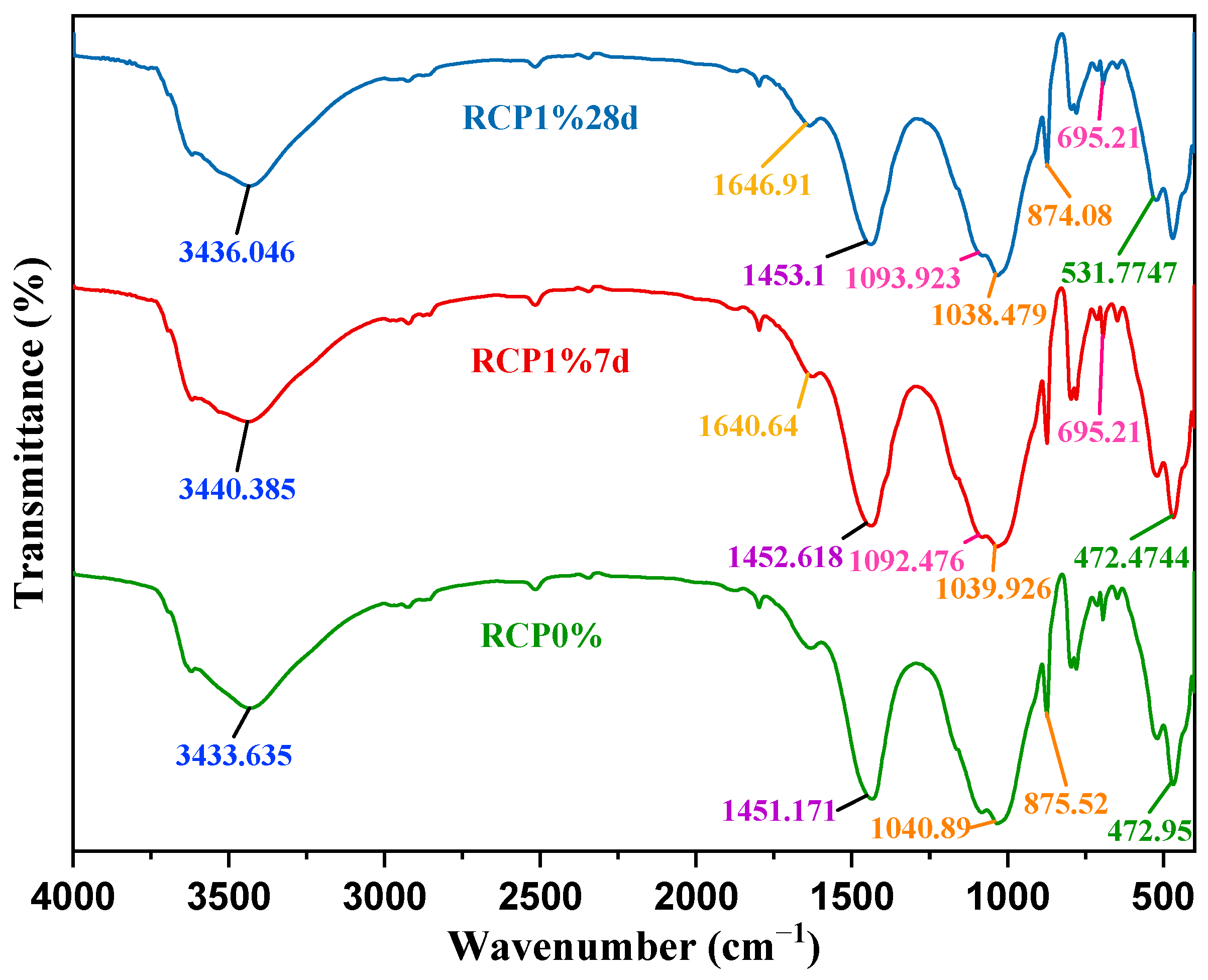
Figure 12 shows the FTIR spectra of the raw materials of RCP curing agents, revealing an obvious absorption peak in the range of 4000–1330 cm−1. The stretching vibration of the O–H group appeared near 3600 cm−1, indicating the existence of the OH− anion group [51]. At the absorption peak near 3600 cm−1 of the RCP curing agents, the peak strength of carbide slag was the largest. The high intensity of this peak in calcium carbide slag is mainly related to its chemical composition of Ca(OH)2. The intensities of the peak near 3600 cm−1 in phosphogypsum and red mud were low, which was probably due to the presence of O–H in water. In phosphogypsum, the absorption peak at 3560 cm−1 was related to Si–OH absorption [49], and the peak near 1600 cm−1 was a result of the H–O–H bending vibration of the interlayer water [52]. SO42− absorption peaks were detected in the ranges of 1210–1040 and 680–570 cm−1. In red mud, the SiO44− absorption was detected in the range of 1175–860 cm−1, and the absorption bands at 549–400 cm−1 correspond to the vibrations of Si–O and Al–O. Red mud and carbide slag, but not phosphogypsum, exhibited strong absorption peaks at 1530–1320 and 890–800 cm−1 due to the antisymmetric stretching vibration of the CO32− bond, probably resulting from CaCO3 or other carbonate substances.
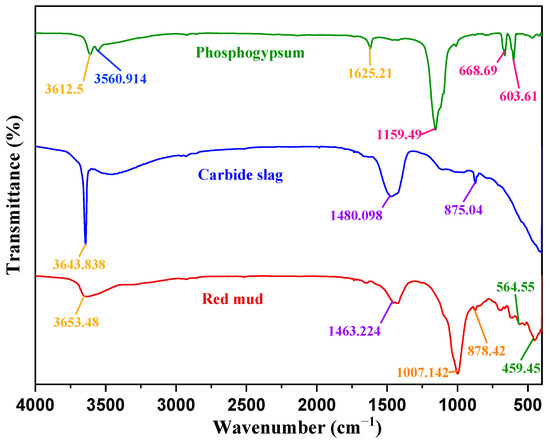
Figure 12.
FTIR spectra of the raw materials of the RCP curing agents.
Figure 13 reveals that the positions of the absorption peaks in the FTIR spectra of RCP0% and RCP1% at 7 and 14 d were roughly the same. The broad absorption band near 3440 cm−1 was related to the Al–OH stretching vibration in the octahedral structure of ettringite (AFt) [35]. The absorption peak of the carbonate bending vibration near 1450 cm−1 in RCP solidified soil was enhanced compared with those of the raw materials of the curing agent, which may be due to the large proportion of loess materials rich in calcium carbonate and the formation of new carbonate minerals. The SO42− absorption peaks near 1100 and 695 cm−1 decreased with an increase in the curing age, indicating that SO42− was consumed in the formation of AFt. The strong absorption peaks near 1000 and 874 cm−1 corresponded to the anti-symmetric Si–O–T (T = Si, Al) stretching vibration of [TO4], indicating the formation of C–S–H and C–A–S–H gels [52]. Moreover, the generated [AlO4]− was negatively charged and interacted with positively charged Ca2+ and Na+ in the pore solution to form cementitious hydration products [21,51]. Heavy metal cations in contaminated soil also interact with alumina tetrahedrons or replace other cations to form a stable mineral structure [52,53,54], which is also an important mechanistic explanation for the stabilization of contaminating ions. The absorption bands near 530 and 472 cm−1 corresponded to vibrations of Si–O and also decreased with an increase in the hydration time, implying that more active silicate minerals in red mud dissolve and participate in the formation of hydration products, such as C–S–H and C–A–S–H [55]. Red mud, carbide slag, and phosphogypsum provide essential elements for the formation of hydration products. The selection of the curing agent is reasonable as a mutual supplement of components and elements.
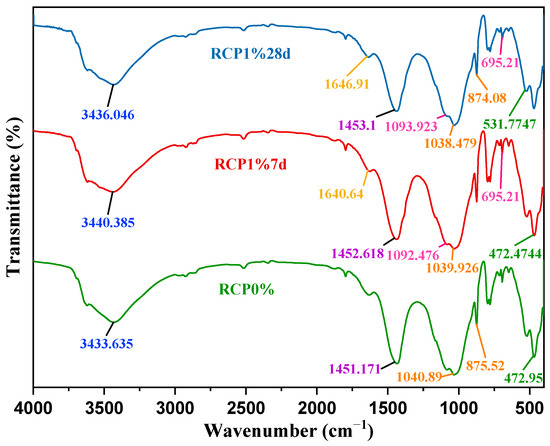
Figure 13.
FTIR spectra of RCP0% and RCP1% solidified soil.
4. Discussion
The increase in strength and the mechanism of action of the curing agent in curing heavy metals of RCP combined with cement-solidified soil is the result of the interaction of cement, red mud, carbide slag, and phosphogypsum and can be explained by the following factors [56]: ① The initial strength of the stabilized soil increased mainly due to the high content of tricalcium silicate (C3S) and dicalcium silicate (C2S) in the cement, and active minerals were actively incorporated into the hydration reaction to form C–S–H, C–A–H, and C–A–S–H gels, which could encapsulate contaminated soil particles and have been proven to have a strong adsorption capacity for heavy metals [57]; ② The cation exchange between Ca2+ generated by the cement hydration reaction, Ca2+ generated by carbide slag hydrolysis, Cu2+ in heavy metal solution and easily exchangeable cations such as Na+ and K+ initially adsorbed on clay particles leads to a reduction in the thickness of the clay particle diffusion double layer. As a result, soil particles flocculate and coagulate [44] to increase the structure density and the strength. Meanwhile, Cu2+ is also preserved on the soil surface; ③ Some cementitious substances hardened to form the skeleton, enhance strength and can wrap and bond heavy metal ions to form pellets so that the heavy metals are sealed and form a relatively stable spatial structure; ④ A large number of Ca(OH)2 generated in pore solutions react with active substances such as SiO2 and Al2O3 dissolved in soil and red mud to produce secondary gel products, such as C–S–H, C–A–H, and C–A–S–H. As a result, a space network structure forms, the adhesion and stability between particles improve, and the volcano ash reaction occurs, which are the main factors promoting the strength of the solidified body in the later stage; ⑤ CaSO4 dissolved in phosphogypsum can combine with Al2O3 in an alkaline environment to form ettringite. This expansive acicular crystal cannot only fill the pores but can also increase the intercalation capacity of the hydration products and make the spatial structure of soil more compact [58], and heavy metal ions enter C–S–H or C–A–S–H and AFt crystals through replacement, which is the main mechanism of solidification; ⑥ In a strong alkaline pore solution saturated with Ca(OH)2, Cu2+ is easily precipitated due to its low solubility and may form insoluble salts such as silicate, carbonate, and sulfate, which will reduce the migration ability of Cu2+ and fix heavy metals. Ca(OH)2 also crystallizes and precipitates to form Ca(OH)2 crystals. Ca(OH)2 crystals have good cohesion and water stability, which increases the structure density and the strength of the mixture; ⑦ In addition, Ca(OH)2 carbonizes with air or CO2 dissolved in water to produce CaCO3 crystals. CaCO3 crystals also have high strength and water stability and fill the pores of the structure to make the structure more compact. However, since it is difficult for CO2 in the air to enter the structure, this process is a long-term and slow process.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, solid wastes (red mud, carbide slag and phosphogypsum) instead of cement were used as curing agents to solidify/stabilize copper-contaminated soil. The basic engineering indexes and the environmental safety evaluation index of the tested specimens with different contents of curing agent were tested. Meanwhile, the hydration products of solidified soil were characterized with XRD and FTIR. The major conclusions drawn from this study are as follows:
(1) When the total content of curing agent is 10%, due to the deterioration of copper ions at a concentration of 1%, the strength ratio of RCP1% to RCP0% is only about 0.2 at 7, 14, and 28 d curing age. For a curing agent with a total content of 20%, the ratio of RCP1% to RCP0% increases from 0.48 to 0.64 when the proportion of cement increases from 0.45 to 0.65. The resistivity and strength values show the same variation trend.
(2) When the contents of cement, red mud, carbide slag, and phosphogypsum are 13%, 2%, 3%, and 2%, respectively, the maximum strength of RCP1% is 5.43 MPa, and the permeability coefficients are in the range of (1–10) 10−7 cm/s. The resistivity and strength increase with an increase in the total content of curing agent, cement content, and curing age.
(3) The maximum pH and copper ion leaching concentration value in all schemes are 12.46 and 0.085 mg/L, which are within the environmental safety limit of hazardous wastes in China. When the total content of curing agent increases, the pH increases and the leaching concentration decreases, reaching a solidification efficiency of 99.99%.
(4) The microcharacterization results of solidified soil show that C–S–H, C–A–H, AFt, and copper-containing compounds, such as Cu(OH)2 and CaCu4(SO4)2(OH)6·3H2O, are produced by the hydration reaction between soil, the curing agent, and heavy metal ions, and the speciation of copper ions changes from the exchangeable and the carbonate form to the iron manganese oxidation and residue form.
In this paper, the applicability of RCP as a Cu2+ curing agent was initially explored. In future research, it is necessary to continue to study the curing effect and mechanism of the curing agent on different heavy metal ions in complex contaminated sites, as well as the long-term stability of solidified soil in a complex natural environment and to carry out research on the on-site solidification technology of the actual polluted site, to provide theoretical support for the application of RCP in engineering.
Author Contributions
Methodology, C.S. and L.L.; investigation, P.F.; resources, L.L. and P.F.; data curation, J.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, J.Z.; writing—review and editing, L.L.; supervision, L.L.; project administration, C.S. and L.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received external funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51978438).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51978438).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yin, S.; Wei, C.; Fan, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, L. Review and Prospects of Bioleaching in the Chinese Mining Industry. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2021, 28, 1397–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Fang, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, S.; Jiao, B.; Li, D. The Utilization of Alkali-Activated Lead–Zinc Smelting Slag for Chromite Ore Processing Residue Solidification/Stabilization. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Wu, X.; Cai, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z. Strength and Leaching Characteristics of Magnesium Phosphate Cement-Solidified Zinc- Contaminated Soil under the Effect of Acid Rain. Soil Sediment Contam. 2018, 27, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piri, M.; Sepehr, E.; Samadi, A.; Farhadi, K.H.; Alizadeh, M. Contaminated Soil Amendment by Diatomite: Chemical Fractions of Zinc, Lead, Copper and Cadmium. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Lee, S.; Jho, E.H. Removal of TPH, UCM, PAHs, and Alk-PAHs in Oil-Contaminated Soil by Thermal Desorption. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Shu, X.; Huang, W.; Miao, Y.; Shi, M.; Chen, S.; Li, B.; Luo, F.; Xie, Y.; Shao, D.; et al. Rapid Solidification of Sr-Contaminated Soil by Consecutive Microwave Sintering: Mechanism and Stability Evaluation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, S.; Chen, M.; Lu, H.; Chen, Y.; Shi, L. Recycling of Chemical Eluent and Soil Improvement after Leaching. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 104, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Chen, L.; Guo, K.; Xie, J.; Shu, Y.; He, S.; Xiao, F. Progress of Uranium-Contaminated Soil Bioremediation Technology. J. Environ. Radioact. 2022, 241, 106773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazaryan, K.A.; Movsesyan, H.S.; Minkina, T.M.; Nevidomskaya, D.G.; Rajput, V.D. Phytoremediation of Copper-Contaminated Soil by Artemisia Absinthium: Comparative Effect of Chelating Agents. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contessi, S.; Dalconi, M.C.; Pollastri, S.; Calgaro, L.; Meneghini, C.; Ferrari, G.; Marcomini, A.; Artioli, G. Cement-Stabilized Contaminated Soil: Understanding Pb Retention with XANES and Raman Spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Pu, S.; Zhang, J.; Wan, Y.; Song, W.; Wang, H. Water Resistance and Compressibility of Silt Solidified with Lime and Fly-Ash Mixtures. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contessi, S.; Calgaro, L.; Dalconi, M.C.; Bonetto, A.; Bellotto, M.P.; Ferrari, G.; Marcomini, A.; Artioli, G. Stabilization of Lead Contaminated Soil with Traditional and Alternative Binders. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 120990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, Y.; Mazumdar, B.; Ghosh, P. Dataset on the Electrical Energy Consumption and Its Conservation in the Cement Manufacturing Industry. Data Br. 2020, 28, 104967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, B.; Akcil, A.; Lee, J.-c. Red Mud Valorization an Industrial Waste Circular Economy Challenge; Review over Processes and Their Chemistry. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 520–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archambo, M.; Kawatra, S.K. Red Mud: Fundamentals and New Avenues for Utilization. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2021, 42, 427–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, W.; Zhu, Y. Steel Slag–Red Mud-Based Multi-Solid Waste Pavement Base Material: Preparation, Properties and Microstructure Study. JOM 2022, 74, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaidi, S.M.A.; Tayeh, B.A.; Isleem, H.F.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; Ahmed, H.U.; Emad, W. Sustainable Utilization of Red Mud Waste (Bauxite Residue) and Slag for the Production of Geopolymer Composites: A Review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukiza, E.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, N. Preparation and Characterization of a Red Mud-Based Road Base Material: Strength Formation Mechanism and Leaching Characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 220, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Tang, B.; Wang, Y.; Mukiza, E. Synergic Effects of Electrolytic Manganese Residue-Red Mud-Carbide Slag on the Road Base Strength and Durability Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 220, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, C.; Yao, X.; Song, Z.; Dong, X. Mechanical and Leaching Characteristics of Red Mud Residue Solidified/Stabilized High Cu(II)-Contaminated Soil. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, K.; He, X. Characteristics and Mechanism of Adsorption of Tartaric Acid by Carbide Slag Ascertained and Applied to Prepare a Binder. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 337, 130477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, R.; Guo, M.Z.; Han, L.; Li, J.S.; Li, B.; Chu, H.; Jiang, L.; Wang, L.; Jin, W.; Sun Poon, C. Recycling Sediment, Calcium Carbide Slag and Ground Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag into Novel and Sustainable Cementitious Binder for Production of Eco-Friendly Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 305, 124772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tan, H.; He, X.; Yang, W.; Deng, X. Utilization of Carbide Slag-Granulated Blast Furnace Slag System by Wet Grinding as Low Carbon Cementitious Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 249, 118763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, C.; Fang, P.; Cao, H.; Cao, J.; Liu, K.; Dong, X. Influence and Microscopic Mechanism of the Solid Waste-Mixture on Solidification of Cu2+-Contaminated Soil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 305, 124651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.J.; Ma, J.; Chen, Y.G.; Tan, B.H.; Cheng, W.J. Mechanical Behavior of Copper-Contaminated Soil Solidified/Stabilized with Carbide Slag and Metakaolin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Pan, H.; Xu, J. Evaluation of red mud based binder for the immobilization of copper, lead and zinc. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zeng, J.; He, X.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Tan, H. Sustainable Clinker-Free Solid Waste Binder Produced from Wet-Ground Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag, Phosphogypsum and Carbide Slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 330, 127218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, S. An overview of current status of copper pollution in soil and remediation efforts in China. Earth Sci. Front. 2018, 25, 305–313. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, W.; Congress, S.S.C.; Cai, G.; Liu, S.; Dong, X.; Chen, R.; Liu, X. A Hybrid GMDH Neural Network and Logistic Regression Framework for State Parameter–Based Liquefaction Evaluation. Can. Geotech. J. 2021, 58, 1801–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E51-2009; Test Methods of Materials Stabilized with Inorganic Binders of Highway Engineering. China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Zhang, S.; LI, Y.; Kou, X.; Dong, X. Study of electrical resistivity and strength characteristics of zinc contaminated soil solidified by cement. Rock Soil Mech. 2015, 36, 2899–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ/T299-2007; Solid Waste-Extraction Procedure for Leaching Toxicity-Sulphuric Acid & Nitric Acid Method. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- GB5085.1-2007; Identification Standards for Hazardous Wastes-Identification for Corrosivity. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, Z.; Bai, J.; Memon, S.; Dong, B.; Fang, Y.; Xu, W.; Xing, F. Properties of Chemically Combusted Calcium Carbide Residue and Its Influence on Cement Properties. Materials 2015, 8, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navarro-Blasco, I.; Duran, A.; Sirera, R.; Fernández, J.M.; Alvarez, J.I. Solidification/stabilization of toxic metals in calcium aluminate cement matrices. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duran, A.; Sirera, R.; Pérez-Nicolás, M.; Navarro-Blasco, I.; Fernández, J.M.; Alvarez, J.I. Study of the early hydration of calcium aluminates in the presence of different metallic salts. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 81, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, M.; Du, Y.; Reddy, K.R.; Wu, H. Effects of Freeze-Thaw on Characteristics of New KMP Binder Stabilized Zn- and Pb-Contaminated Soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 19473–19484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Yang, J.; Cui, J.; Zhou, W.; Guo, X. Study on mechanical and permeability characteristics of nickel-copper-contaminated soil solidified by CFG. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18577–18591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Liu, X. Influence of Freeze–Thaw Cycles and Binder Dosage on the Engineering Properties of Compound Solidified/Stabilized Lead-Contaminated Soils. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zha, F.; Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Deng, Y.; Yang, C.; Chu, C. Electrical resistivity of heavy metal contaminated soils solidified/stabilized with cement-fly ash. Rock Soil Mech. 2019, 40, 4573–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zha, F.; Deng, Y.; Cui, K.; Zhang, X. Effect of an alkaline environment on the engineering behavior of cement-stabilized/solidified Zn-contaminated soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 28248–28257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Cai, G.; Bian, H. Estimation of heavy metal-contaminated soils’ mechanical characteristics using electrical resistivity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 13561–13575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Du, Y.; Liu, S.; Wei, M.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Arulrajah, A. Multi-scale laboratory evaluation of the physical, mechanical, and microstructural properties of soft highway subgrade soil stabilized with calcium carbide residue. Can. Geotech. J. 2016, 53, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GB5085.3-2007; Identification Standards for Hazardous Wastes-Identification for Extraction Toxicity. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Bauer, T.V.; Pinskii, D.L.; Minkina, T.M.; Shuvaeva, V.A.; Soldatov, A.V.; Mandzhieva, S.S.; Tsitsuashvili, V.S.; Nevidomskaya, D.G.; Semenkov, I.N. Application of XAFS and XRD methods for describing the copper and zinc adsorption characteristics in hydromorphic soils. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Muhammad, F.; Yu, L.; Xia, M.; Huang, X.; Jiao, B.; Shiau, Y.; Li, D. The solidification of lead-zinc smelting slag through bentonite supported alkali-activated slag cementitious material. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W. Preparation, characterization and application of red mud, fly ash and desulfurized gypsum based eco-friendly road base materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Tang, B.; Wang, Y.; Mukiza, E. Preparation and characterization of cement treated road base material utilizing electrolytic manganese residue. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Guo, W.; Wang, X.; Pan, H.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, D. Utilization of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash with Red Mud-Carbide Slag for Eco-Friendly Geopolymer Preparation. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heah, C.Y.; Kamarudin, H.; Mustafa Al Bakri, A.M.; Bnhussain, M.; Luqman, M.; Khairul Nizar, I.; Ruzaidi, C.M.; Liew, Y.M. Study on solids-to-liquid and alkaline activator ratios on kaolin-based geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 35, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Li, L. Evaluation of blends bauxite-calcination-method red mud with other industrial wastes as a cementitious material: Properties and hydration characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Eswed, B.I.; Aldagag, O.M.; Khalili, F.I. Efficiency and mechanism of stabilization/solidification of Pb(II), Cd(II), Cu(II), Th(IV) and U(VI) in metakaolin based geopolymers. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 140, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, F.; Mu, J. Solidification/stabilization mechanism of Pb(II), Cd(II), Mn(II) and Cr(III) in fly ash based geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Muhammad, F.; Zeng, L.; Li, S.; Huang, X.; Jiao, B.; Shiau, Y.C.; Li, D. Solidification/stabilization of lead-zinc smelting slag in composite based geopolymer. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpiene, J.; Lagerkvist, A.; Maurice, C. Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments—A review. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derakhshan Nejad, Z.; Jung, M.C.; Kim, K.H. Remediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals with an emphasis on immobilization technology. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 927–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chang, C.W.; Namdar, A.; She, Y.; Lin, C.H.; Yuan, X.; Yang, Q. Stabilization of expansive soil using cementing material from rice husk ash and calcium carbide residue. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 221, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).