Spatial-Temporal Changes in Water Supply and Demand in the Citarum Watershed, West Java, Indonesia Using a Geospatial Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
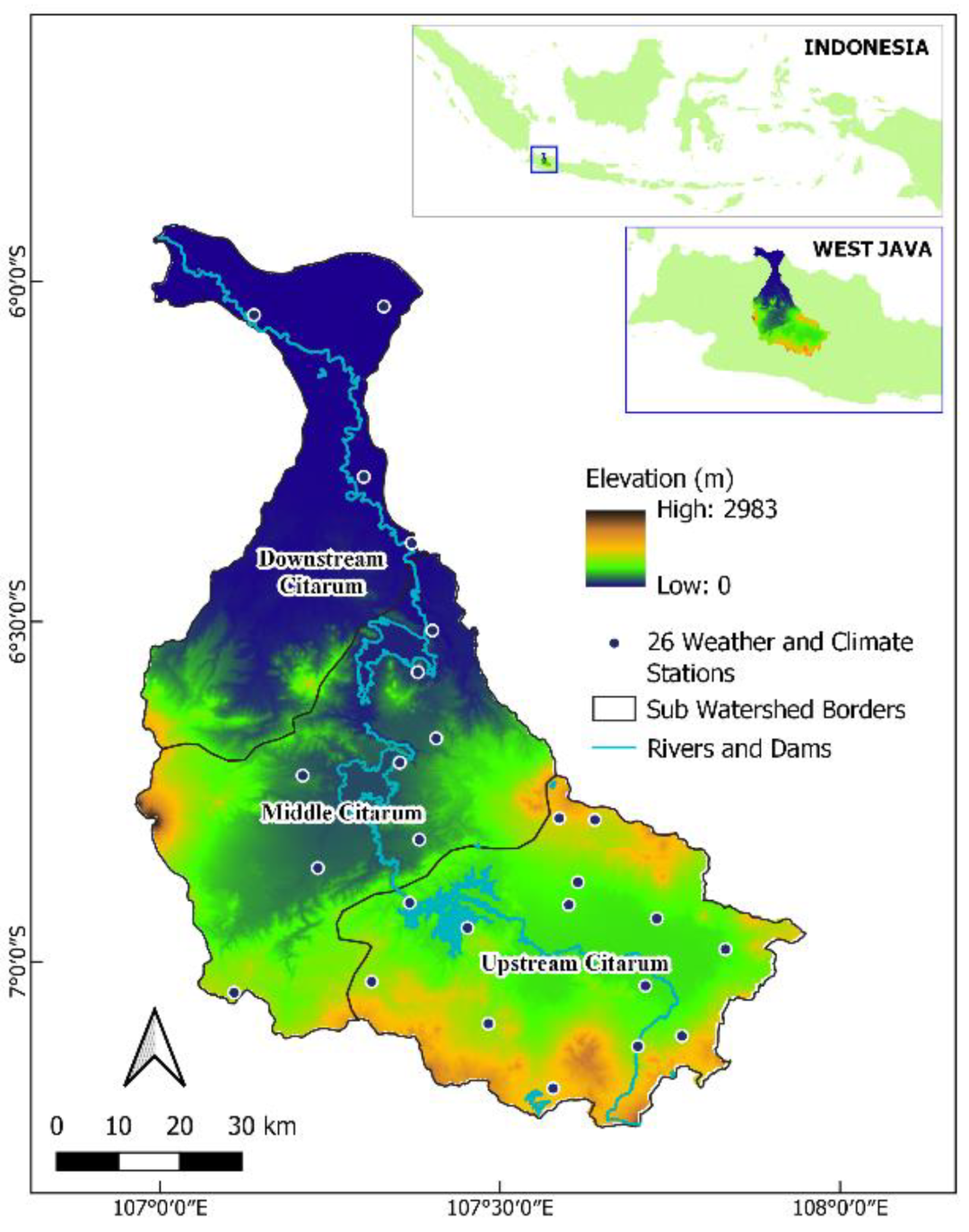
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
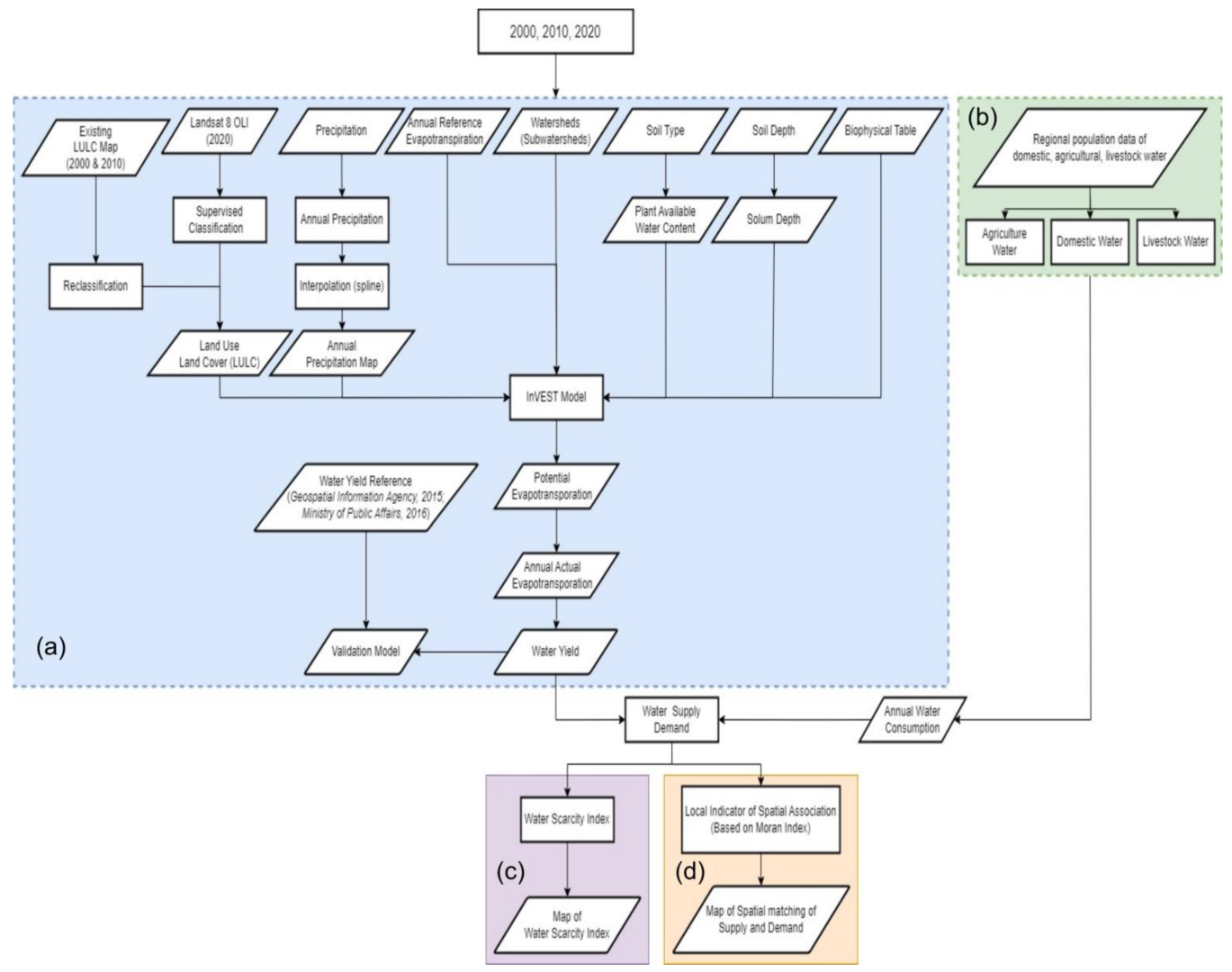
2.3. Research Framework
- With the prepared primary spatial data and the WY module from the InVEST model, the WY service from the Citarum is calculated and evaluated quantitatively (i.e., supply quantity). The results of model calculations are validated with water results from Badan Informasi Geospasial (BIG) and the Ministry of Public Works or previous research (Figure 3a). Furthermore, the WS map and WD map (grid data) are summarized by type of LULC using the zonal statistical tool in GIS software.
- Water consumption (total WD) in the study area is calculated based on the standard of domestic WD, livestock and agriculture water use data from Badan Pusat Statistik (BPS) or Ministry of Public Works and the results of previous studies. In the study of WD for industry, no calculations were carried out. The calculation results present a demand model, exploring the spatial and temporal variations in WD in the Citarum (Figure 3b).
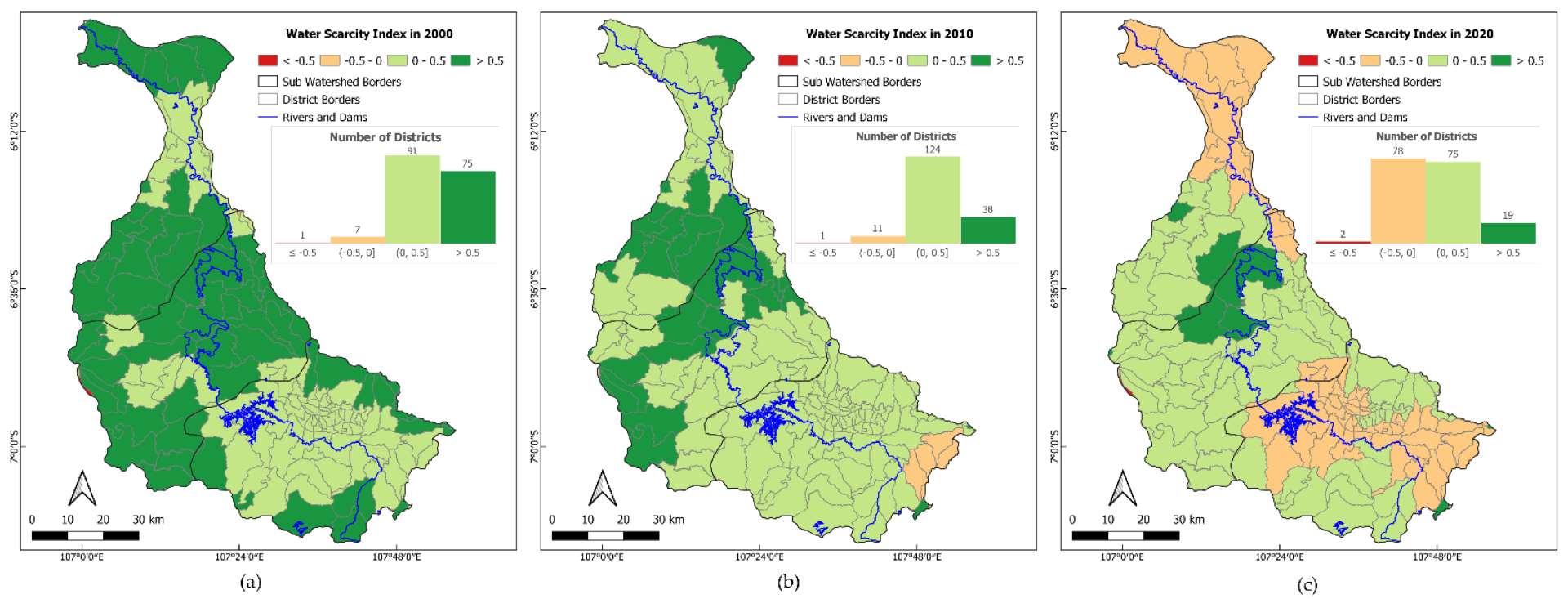
- Water Scarcity Index (WSI). Based on activities 1 and 2, modelling the supply–demand balance, calculating the WSI and exploring the water security situation in the CW (Figure 3c).
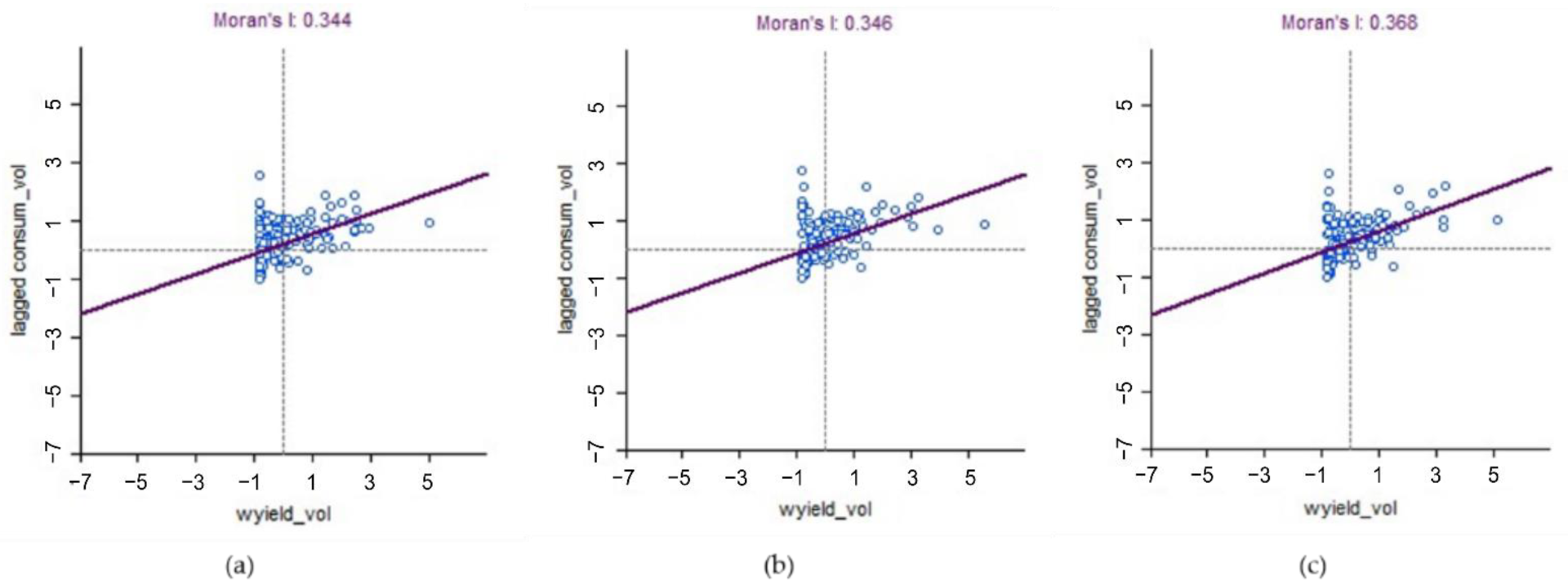
- Analysis of Supply and Demand Characteristics of WY.The relationship between supply and demand for water services in the area and their spatial distribution characteristics are obtained through the calculation of the supply–demand ratio and local Moran’s I, respectively (Figure 3d).
2.3.1. Spatial Patterns of WS
2.3.2. Spatial Patterns of WD
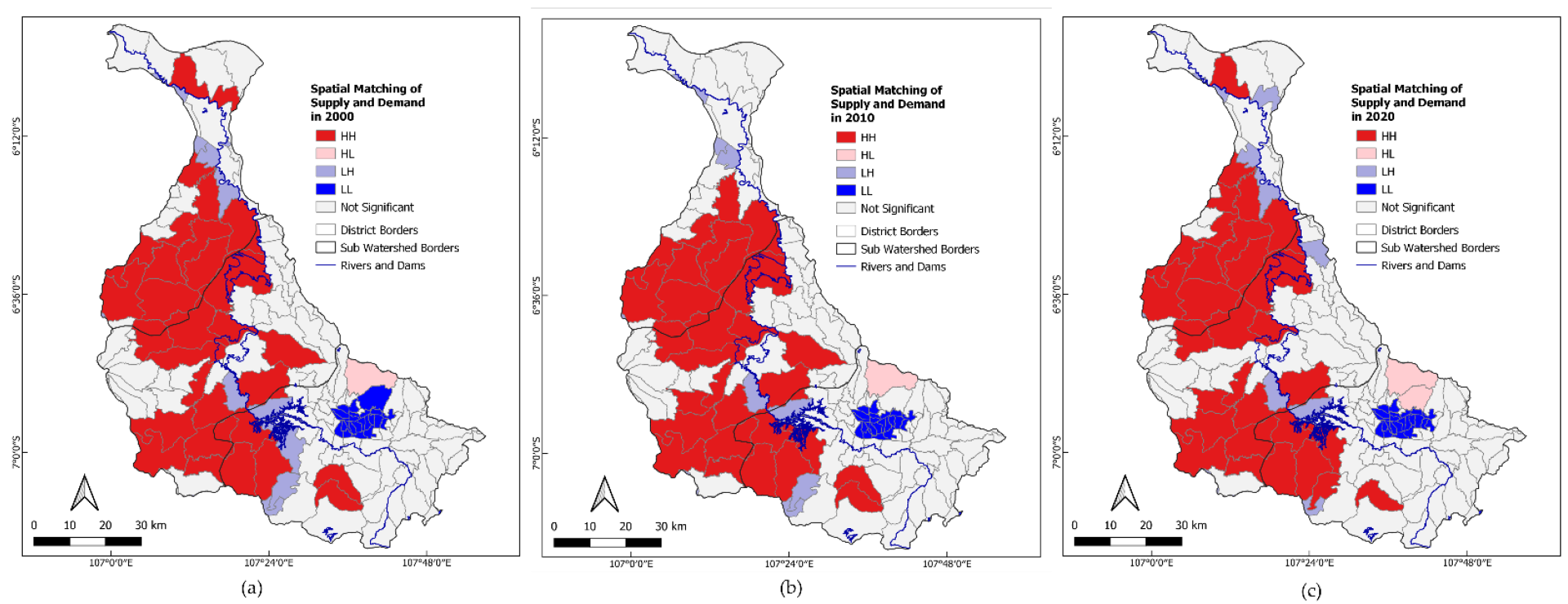
2.3.3. The Imbalance between WS and WD
2.3.4. Spatial Characteristics of Supply and Demand of WY Service
- Iixy > 0 represents a positive spatial connection between the two variables; a higher value suggests a stronger spatial correlation.
- Iixy < 0 shows the negative spatial correlation, emphasizing the latter as the value decreases.
- Iixy = 0 reflects a randomly distributed pattern over space.
3. Results
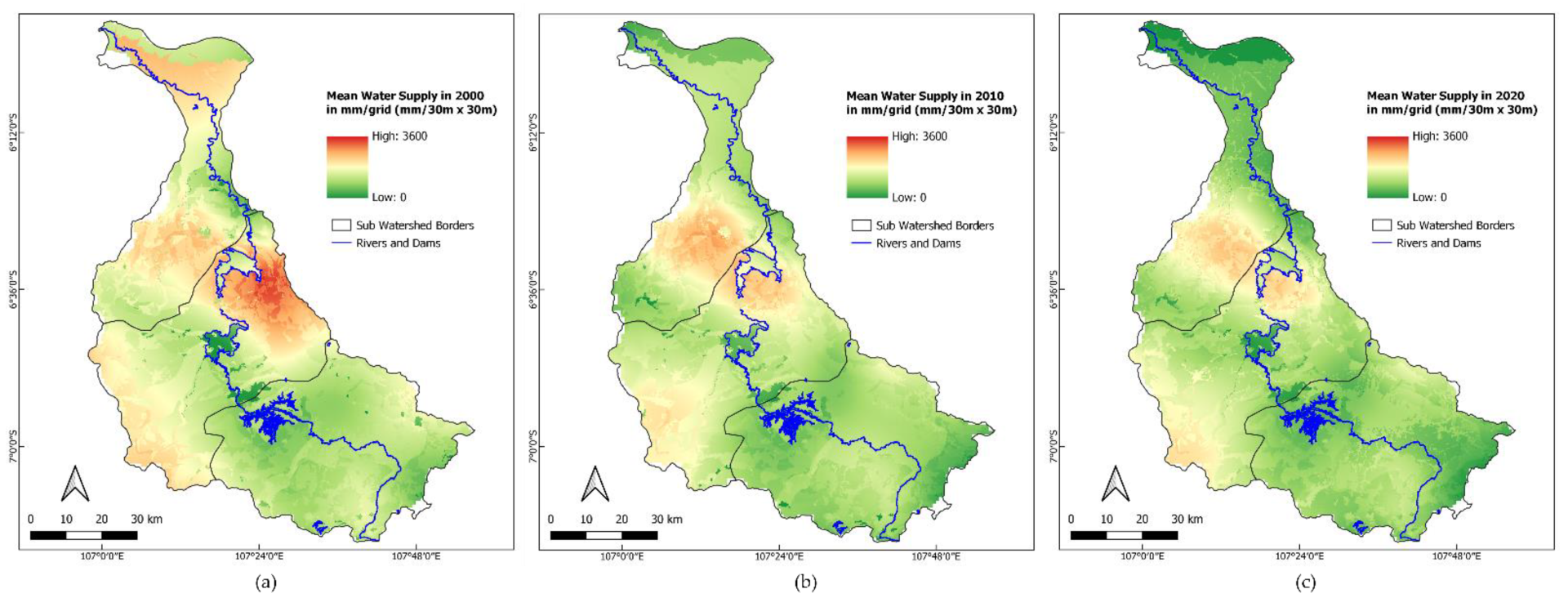
3.1. Spatial Patterns of WS
3.2. Spatial Patterns of WD
3.3. The Imbalance between WS and WD
3.4. Spatial Characteristics of Supply and Demand of WY Service
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Patterns of WS and WD
4.2. The Imbalance between WS and WD
4.3. Spatial Characteristic of Supply and Demand of WY Service
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koopman, J.F.L.; Kuik, O.; Tol, R.S.J.; van der Vat, M.P.; Hunink, J.C.; Brouwer, R. Distributing Water Between Competing Users in the Netherlands. In Economy-Wide Modeling of Water at Regional and Global Scales; Wittwer, G., Ed.; Advances in Applied General Equilibrium Modeling; Springer: Singapore, Singapore, 2019; pp. 159–192. ISBN 9789811361005. [Google Scholar]
- Sathre, R.; Antharam, S.M.; Catena, M. Water Security in South Asian Cities: A Review of Challenges and Opportunities. CivilEng 2022, 3, 873–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, A.J.; Smilovic, M. Groundwater Irrigation and Implication in the Nile River Basin. In Global Groundwater; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Suroso, D.; Setiawan, B.; Abdurahman, O. Impact of Climate Change on the Sustainability of Water Supply in Indonesia. In Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on Water Supply Management System and Social Capital, Surabaya, Indonesia, 15–16 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Y.; Avraamidou, S.; Xiao, X.; Pistikopoulos, E.N.; Li, J.; Zeng, Y.; Song, F.; Yu, J.; Zhu, M. A Food-Energy-Water Nexus Approach for Land Use Optimization. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 659, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yao, S.; Deng, Y.; Jia, L.; Hou, M.; Gong, Z. Spatio-Temporal Study on Supply and Demand Matching of Ecosystem Water Yield Service—A Case Study of Wei River Basin. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 1677–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Meyfroidt, P. Global Land Use Change, Economic Globalization, and the Looming Land Scarcity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3465–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Wei, H. Assessment of Ecosystem Services Supply and Demand (Mis)Matches for Urban Ecological Management: A Case Study in the Zhengzhou–Kaifeng–Luoyang Cities. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boithias, L.; Acuña, V.; Vergoñós, L.; Ziv, G.; Marcé, R.; Sabater, S. Assessment of the Water Supply: Demand Ratios in a Mediterranean Basin under Different Global Change Scenarios and Mitigation Alternatives. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirdashtvan, M.; Najafinejad, A.; Malekian, A.; Sa’doddin, A. Sustainable Water Supply and Demand Management in Semi-Arid Regions: Optimizing Water Resources Allocation Based on RCPs Scenarios. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 5307–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulianto, F.; Khomarudin, M.R.; Hermawan, E.; Budhiman, S.; Sofan, P.; Chulafak, G.A.; Nugroho, N.P.; Brahmantara, R.P.; Nugroho, G.; Priyanto, E.; et al. Flood Inundation Modelling Using an RProFIM Approach Based on the Scenarios of Landuse/Landcover Change and Return Periods Differences in the Upstream Citarum Watershed, West Java, Indonesia; In Review; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ambarwulan, W.; Nahib, I.; Widiatmaka, W.; Suryanta, J.; Munajati, S.L.; Suwarno, Y.; Turmudi, T.; Darmawan, M.; Sutrisno, D. Using Geographic Information Systems and the Analytical Hierarchy Process for Delineating Erosion-Induced Land Degradation in the Middle Citarum Sub-Watershed, Indonesia. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 710570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujarwo, M.W.; Indarto, I.; Mandala, M. The Impact of Land Use and Land Cover Change on Hydrological Processes in Brantas Watershed, East Java, Indonesia. Kuwait J. Sci. 2021, 49, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, R.; Dasanto, B.D.; Perdinan; Marthinus, D. Hydrologic Balance of Citarum Watershed under Current and Future Climate. In Climate Change Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sampurna, A.T. Analisis Kebutuhan Dan Ketersediaan Air Wilayah Sungai Citarum. Master’s Thesis, Brawijaya University, Malang, Indonesia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, T.; Boccelli, D.L. Estimating Distribution System Water Demands Using Markov Chain Monte Carlo. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2019, 145, 04019023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, R.; Meadows, M.E.; Ji, G.; Xu, J. Modelling Water Yield with the InVEST Model in a Data Scarce Region of Northwest China. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2020, 20, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Sridharan, S.; Gholston, S. Using Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis to Leverage Social Indicator Databases: The Discovery of Interesting Patterns. Soc. Indic. Res. 2007, 82, 287–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, J.; Ertur, C. Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis of the Distribution of Regional per Capita GDP in Europe, 1980–1995. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2000, 82, 175–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.C.M.; Fonseca, B.M. ESDA (Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis) of Vegetation Cover in Urban Areas-Recognition of Vulnerabilities for the Management of Resources in Urban Green Infrastructure. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, F. Research on the Regional Spatial Effects of Green Development and Environmental Governance in China Based on a Spatial Autocorrelation Model. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2020, 55, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Xue, Y.; Lan, Y.; Fu, Y. Agricultural Water Utilization Efficiency in China: Evaluation, Spatial Differences, and Related Factors. Water 2022, 14, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.; Liu, M.; Shen, Y.; Xu, K.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Luo, J. Quantifying Impacts of Climate Dynamics and Land-Use Changes on Water Yield Service in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahib, I.; Ambarwulan, W.; Rahadiati, A.; Munajati, S.L.; Prihanto, Y.; Suryanta, J.; Turmudi, T.; Nuswantoro, A.C. Assessment of the Impacts of Climate and LULC Changes on the Water Yield in the Citarum River Basin, West Java Province, Indonesia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siswanto, S.Y.; Francés, F. How Land Use/Land Cover Changes Can Affect Water, Flooding and Sedimentation in a Tropical Watershed: A Case Study Using Distributed Modeling in the Upper Citarum Watershed, Indonesia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusratmoko, E.; Semedi, J.M. Water Availability in Patuha Mountain Region Using InVEST Model “Hydropower Water Yield”. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 125, 01015. [Google Scholar]
- Sholeh, M.; Pranoto, P.; Budiastuti, S.; Sutarno, S. Analysis of Citarum River Pollution Indicator Using Chemical, Physical, and Bacteriological Methods. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 2049, 020068. [Google Scholar]
- Citarum, P.B.C. Profile of B. Balai Besar Wilayah Sungai Citarum-Ciliwung (BBWS Citarum Ciliwung). Profil BBWS Citarum. Available online: https://sda.pu.go.id/balai/bbwscitarum/profil-bbws-citarum/ (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Sharp, R.; Tallis, H.; Ricketts, T.; Guerry, A.D.; Wood, S.A.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Nelson, E.; Ennaanay, D.; Wolny, S.; Olwero, N. InVEST+ VERSION+ User’s Guide; The Natural Capital Project: Stanford, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Team, R.D.C. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2009. Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 14 March 2022).
- Anselin, L. GeoDa (Spatial Statistical Program). Encycl. Res. Methods Criminol. Crim. Justice 2021, 2, 839–841. [Google Scholar]
- Ermida, S.L.; Soares, P.; Mantas, V.; Göttsche, F.M.; Trigo, I.F. Google Earth Engine Open-Source Code for Land Surface Temperature Estimation from the Landsat Series. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, G.; Markham, B.L.; Helder, D.L.; Chander, G.; Markham, B.L.; Helder, D.L. Summary of Current Radiometric Calibration Coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+, and EO-1 ALI Sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, K.E. Soil Water Characteristics: Hydraulic Properties Calculator. 2009. Available online: https://hrsl.ba.ars.usda.gov/soilwater/Index.htm (accessed on 13 March 2022).
- Amhar, F. The Problematics of Indonesian Geoportal and Its Future Strategies. In Proceedings of the 39th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 15–19 October 2018; Volume 3, pp. 1868–1877. [Google Scholar]
- Amhar, F. Quality Test Various Existing Dem in Indonesia toward 10 Meter National Dem. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.-ISPRS Arch. 2016, 41, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BPS-Statistics of Jawa Barat Province. BPS Jawa Barat Dalam Angka 2000; BPS-Statistics of Jawa Barat Province: Bandung, Indonesia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- BPS-Statistics of Jawa Barat Province. BPS Jawa Barat Dalam Angka 2010; BPS-Statistics of Jawa Barat Province: Bandung, Indonesia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- BPS-Statistics of Jawa Barat Province. BPS Jawa Barat Dalam Angka 2020; BPS-Statistics of Jawa Barat Province: Bandung, Indonesia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- BSN. SNI 19-6728.1-2002 Penyusunan Neraca Sumber Daya-Bagian 1: Sumber Daya Air Spasial; Badan Standardisasi Nasional: Jakarta Pusat, Indonesia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Budyko, M. Climate and Life; Miller, D., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Canqiang, Z.; Wenhua, L.; Biao, Z.; Moucheng, L. Water Yield of Xitiaoxi River Basin Based on InVEST Modeling. J. Resour. Ecol. 2012, 3, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hickel, K.; Dawes, W.R.; Chiew, F.H.S.; Western, A.W.; Briggs, P.R. A Rational Function Approach for Estimating Mean Annual Evapotranspiration. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baw-puh, F. On the Calculation of the Evaporation from Land Surface. Sci. Atmospherica Sin. 1981, 5, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Donohue, R.J.; Roderick, M.L.; McVicar, T.R. Roots, Storms and Soil Pores: Incorporating Key Ecohydrological Processes into Budyko’s Hydrological Model. J. Hydrol. 2012, 436–437, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badan Informasi Geospasial. Pemetaan Dinamika Sumberdaya Alam Terpadu Wilayah Sungai Citarum; Mapping of the Dynamics of Integrated Natural Resources of the Citarum River Basin; Badan Informasi Geospasial: Cibinong, Indonesia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shiksha, B.; Seong, Y.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Jung, Y. Water Yield Estimation of the Bagmati Basin of Nepal Using GIS Based InVEST Model. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2019, 52, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Guan, Y.; Khan, F.; Khan, Z. A Comprehensive Index for Measuringwater Security in an UrbanizingWorld: The Case of Pakistan’s Capital. Water 2020, 12, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Mao, D.H. Analysis of Water Yield Service of Lianshui River Basin in China Based on Ecosystem Services Flow Model. Water Supply 2022, 22, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Assessing Urban Atmospheric Environmental Efficiency and Factors Influencing It in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.N.; Tang, L.; Zhang, H. Spatial Effects of Environmental Regulation and Ecological Welfare Performance in Yangtze River Economic Belt. Reform Econ. Syst. 2021, 3, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Mediawan, Y.; Montarcih, L.; Soetopoi, W.; Prayogo, T.B. Water Balance Supporting the Irrigation Water Demand in Java Island, Indonesia. Indones. J. Geogr. 2021, 53, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmad, R.; Wirda, M.A. Long-Term Spatiotemporal Trend Analysis of Precipitation and Temperature in Citarum Watershed, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 930, 012038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kementerian Pekerjaan Umum dan Perumahan Rakyat. Rencana Pengelolaan Sumber Daya Air Wilayah Sungai Citarum Tahun. Management Plan of Citarum River Basin. 2016. Available online: https://www.coursehero.com/file/60545948/Rencana-Pengelolaan-Sumber-Daya-Air-WS-Citarumpdf/ (accessed on 23 March 2022). (In Indonesian).
- Niu, P.; Zhang, E.; Feng, Y.; Peng, P. Spatial-Temporal Pattern Analysis of Land Use and Water Yield in Water Source Region of Middle Route of South-to-North Water Transfer Project Based on Google Earth Engine. Water 2022, 14, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Long, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, D.; Wu, H.; Li, S. Identifying the Drivers of Water Yield Ecosystem Service: A Case Study in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chu, B.; Feng, X.; Li, Y.; Fu, B.; Liu, S.; Jin, J. Spatiotemporal Variation and Driving Factors of Water Yield Services on the Qingzang Plateau. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, M.K. Runoff Coefficient. In Encyclopedia of Snow, Ice and Glaciers; Singh, V.P., Singh, P., Haritashya, U.K., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; p. 952. ISBN 978-90-481-2641-5. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, X.H.; Qi, Y.; Wang, H.W.; Zhang, J.L.; Yang, R. Assessing Changes of Water Yield in Qinghai Lake Watershed of China. Water 2020, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFries, R.; Eshleman, K.N. Land-Use Change and Hydrologic Processes: A Major Focus for the Future. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 2183–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harka, A.E.; Roba, N.T.; Kassa, A.K. Modelling Rainfall Runoff for Identification of Suitable Water Harvesting Sites in Dawe River Watershed, Wabe Shebelle River Basin, Ethiopia. J. Water Land Dev. 2020, 47, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarigan, S.; Tukayo, R. Impact of Land Use Change and Land Management on Irrigation Water Supply in Northern Java Coast. J. Trop. Soils 2013, 18, 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Astuti, I.S.; Sahoo, K.; Milewski, A.; Mishra, D.R. Impact of Land Use Land Cover (LULC) Change on Surface Runoff in an Increasingly Urbanized Tropical Watershed. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 4087–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Chen, S.; Wu, M.; Deng, Y.; Xu, H.; Jia, Y.; Liu, F. Using the InVEST Model to Assess the Impacts of Climate and Land Use Changes on Water Yield in the Upstream Regions of the Shule River Basin. Water 2021, 13, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, C.; Jang, C. Assessing the Impacts of Land Use Changes on Watershed Hydrology Using MIKE SHE. Environ. Geol. 2009, 57, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldesenbet, T.A.; Elagib, N.A.; Ribbe, L.; Heinrich, J. Hydrological Responses to Land Use/Cover Changes in the Source Region of the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 724–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, H.H.; Mustafa, A.M.; Kolerski, T. Hydrological Responses to Large-Scale Changes in Land Cover of River Watershed: Review. J. Water Land Dev. 2021, 50, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M.; Ab, W. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements—FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56. Irrig. Drain. 1998, 300, D05109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardhianie, N.; Daniel, D.; Purwanto, P.; Kismartini, K. Jakarta Water Supply Provision Strategy Based on Supply and Demand Analysis. H2Open J. 2022, 5, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarigan, N.; Dasanto, B.D. Bogor Water Adequacy Status for 2009–2019. Agromet 2022, 36, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citarum Kondisi Fisik Dan Spasial—Citarum. Physical and Spatial Conditions. Available online: http://citarum.org/tentang-kami/sekilas-citarum/kondisi-fisik-dan-spasial.html (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Lin, D.; Lin, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xiang, A.; Xiao, S. Water Yield Service Influence by Climate and Land Use Change Based on InVEST Model in the Monsoon Hilly Watershed in South China. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2022, 13, 2024–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; An, S. Quantifying Water Provision Service Supply, Demand, and Spatial Flow in the Yellow River Basin. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningrum, W.S.; Widyaningsih, Y.; Indra, T.L. Spatial Modeling on the Upperstream of the Citarum Watershed: An Application of Geoinformatics. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1827, 20017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntoro, A.A.; Cahyono, M.; Soentoro, E.A. Land Cover and Climate Change Impact on River Discharge: Case Study of Upper Citarum River Basin. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2018, 50, 364–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Xu, C.; Wu, P. Assessing Socioeconomic Drought Based on a Standardized Supply and Demand Water Index. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 1937–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OhIsson, L. Water Conflicts and Social Resource Scarcity. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Ocean. Atmos. 2000, 25, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Liu, J.; Savenije, H.H.G. A Simple Approach to Assess Water Scarcity Integrating Water Quantity and Quality. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanjra, M.A.; Ejaz Qureshi, M. Global Water Crisis and Future Food Security in an Era of Climate Change. Food Policy 2010, 35, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatmoko, W.; Firmansyah, R.; Fathony, A. Water Security of River Basins in West Java. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Changsha, China, 18–20 September 2020; Volume 419. [Google Scholar]
- Juwana, I.; Muttil, N.; Perera, B.J.C. Application of West Java Water Sustainability Index to Three Water Catchments in West Java, Indonesia. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 70, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasbiah, A.W.; Kurniasih, D. Analysis of Water Supply and Demand Management in Bandung City Indonesia. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Moscow, Russia, 27 May–6 June 2019; Volume 245. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales, P.; Ajami, N.K. Urban Water Sustainability: An Integrative Framework for Regional Water Management. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2015, 12, 11291–11329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartiwa, B.; Murniati, E.; Bormudoi, A. Application of Hydrological Model, RS and GIS for Flood Mapping of Citarum Watershed, West Java Province, Indonesia. J. Remote Sens. Technol. 2013, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type of Dataset | Data Sources | Processing | Data Format |
|---|---|---|---|
| LULC maps (2000, 2010) | Ministry of Environment and Forestry | Converting polygon to raster | Raster data with a spatial resolution of 30 m |
| LULC maps 2020 | US Geological Survey, http://www.usgs.govUSGSpath/row122-121/64 (accessed on 17 March 2022) | Supervised Classification | Raster data with a spatial resolution of 30 m |
| Rainfall and temperature | The National Bureau of Meteorology, Climatology, and Geophysics; Citarum Ciliwung River Basin Center; PT. Jasa Tirta II | Numerical/Table Data, with location coordinates; a spline interpolation technique | Raster data with a spatial resolution of 30 m |
| Evapotranspiration map | WorldClim https://worldclim.org/data/index.html (accessed on 17 March 2022) | a spline interpolation technique | Raster data with a spatial resolution of 30 m |
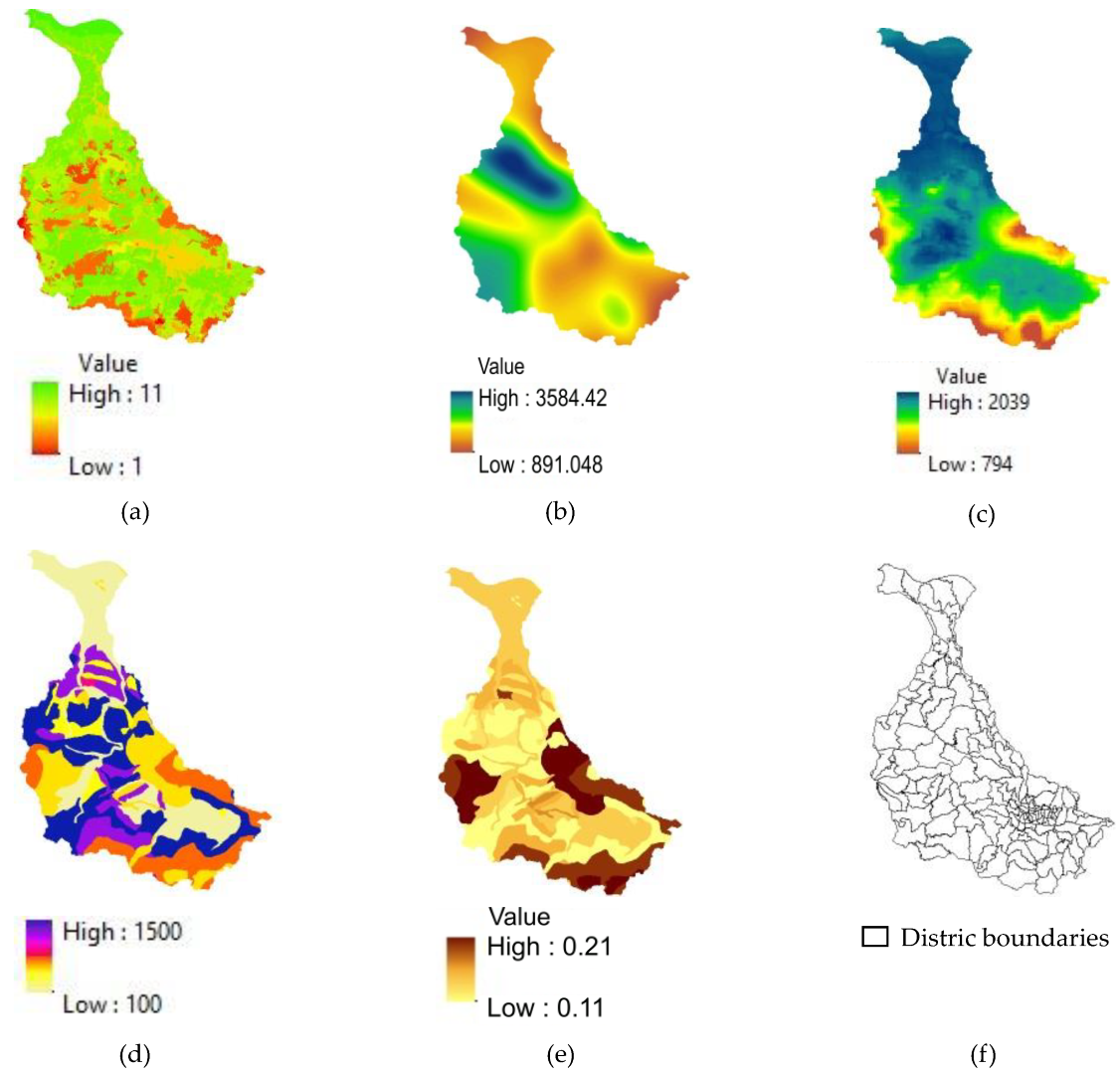
| Soil type data: soil texture, organic matter content, and effective rooting depth | Citarum Ciliwung River Basin Center | Extraction and resampling, conversion from polygon to raster | Raster data with a spatial resolution of 30 m |
| Watershed boundaries | Citarum Ciliwung River Basin Center | Digital watershed: extraction from DEM | Vector, CSV |
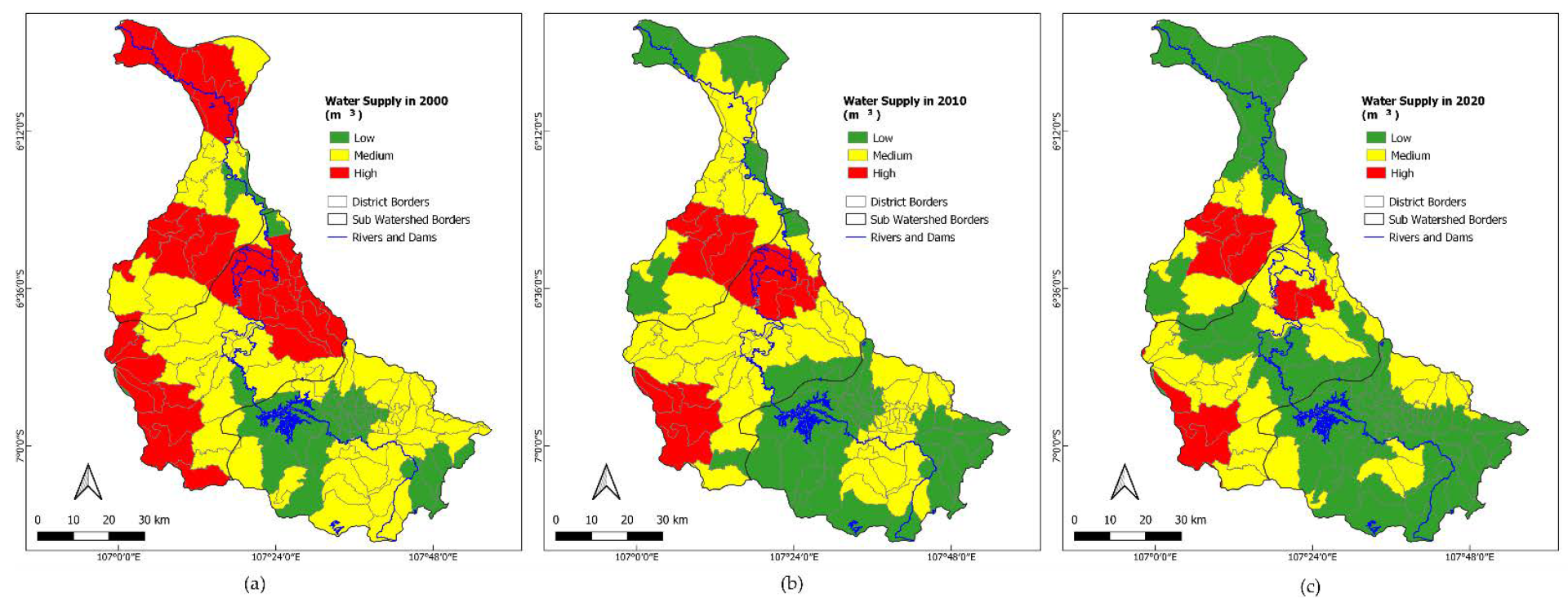
| Watershed | Area | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ha) | 108 m3 | % | 108 m3 | % | 108 m3 | % | |
| Upstream CW | 245,413 | 26.18 | 25.18 | 22.14 | 26.06 | 19.91 | 27.65 |
| Middle CW | 251,373 | 44.20 | 42.51 | 36.50 | 42.96 | 32.24 | 44.78 |
| Downstream CW | 194,130 | 33.60 | 32.31 | 26.33 | 30.99 | 19.85 | 27.57 |
| Total | 690,916 | 103.98 | 100.00 | 84.97 | 100.00 | 72.00 | 100.00 |
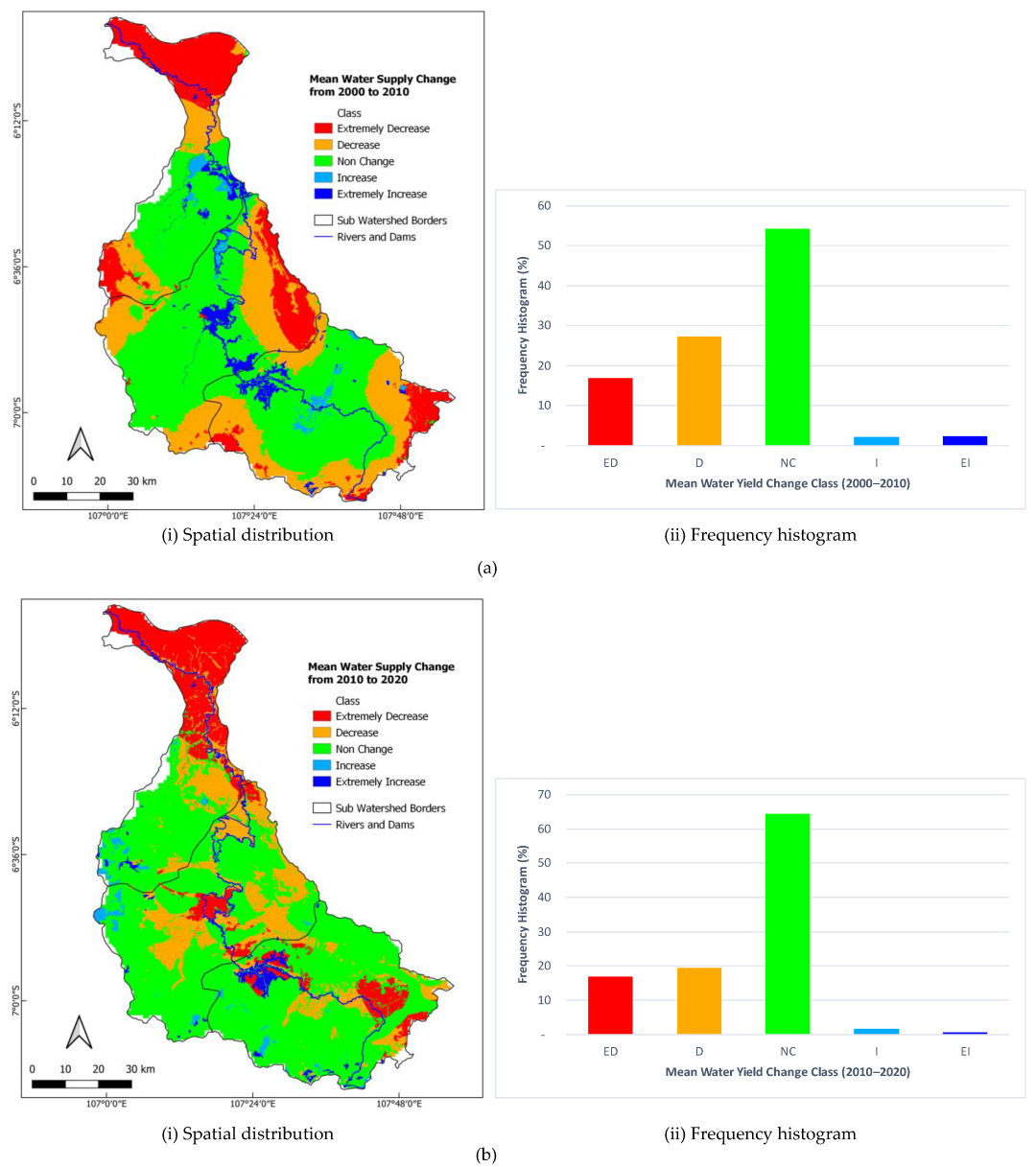
| Watershed | 2000–2010 | 2010–2020 | 2000–2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 108 m3 | % | Predicate | 108 m3 | % | Predicate | 108 m3 | % | Predicate | |
| Upstream CW | −4.04 | −15.44 | NC | −2.24 | −10.09 | NC | −6.28 | −3.97 | NC |
| Middle CW | −7.70 | −17.42 | NC | −4.26 | −11.66 | NC | −11.96 | −27.05 | D |
| Downstream CW | −7.27 | −21.63 | NC | −6.48 | −24.61 | D | −13.75 | −40.92 | ED |
| Total | −19.01 | −18.28 | NC | −12.97 | −15.27 | NC | −31.98 | −30.76 | D |
| LULC Type | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | Average WSC * | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS | R * | WSC * | WS | R * | WSC * | WS | R * | WSC * | ||
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | |||||
| Shrubs | 1838 | 2382 | 0.77 | 1779 | 2197 | 0.81 | 1511 | 2382 | 0.63 | 0.74 |
| Dry Agriculture | 1581 | 2280 | 0.69 | 1254 | 1855 | 0.68 | 1205 | 2280 | 0.53 | 0.63 |
| Virgin Forest | 1594 | 2450 | 0.65 | 1358 | 2231 | 0.61 | 1306 | 2450 | 0.53 | 0.60 |
| Estate Crops Plantation | 1609 | 2512 | 0.64 | 1359 | 2149 | 0.63 | 1099 | 2512 | 0.44 | 0.57 |
| Paddy Field | 1570 | 2426 | 0.65 | 1283 | 1999 | 0.64 | 965 | 2426 | 0.40 | 0.56 |
| Plantation Forest | 1414 | 2311 | 0.61 | 1160 | 2011 | 0.58 | 1045 | 2311 | 0.45 | 0.55 |
| Settlement Area | 1335 | 2011 | 0.66 | 1177 | 1688 | 0.70 | 1095 | 2011 | 0.54 | 0.64 |
| Airport | 824 | 1496 | 0.55 | 930 | 1466 | 0.63 | 895 | 1496 | 0.60 | 0.59 |
| Fishpond | 1254 | 3330 | 0.38 | 561 | 1294 | 0.43 | 845 | 3330 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
| Lake | 736 | 2660 | 0.28 | 893 | 2254 | 0.40 | 696 | 2660 | 0.26 | 0.31 |
| Bare land | 501 | 2187 | 0.23 | 512 | 1916 | 0.27 | 410 | 2187 | 0.19 | 0.23 |
| LULC Type | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | Change 2010–2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area | WS | Area | WS | Area | WS | Area | WS | |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| Paddy Field | 35.36 | 36.95 | 27.57 | 28.77 | 30.36 | 29.57 | 2.79 | 0.8 |
| Dry Agriculture | 24.56 | 25.84 | 30.95 | 31.57 | 28.56 | 35.05 | −2.39 | 3.48 |
| Plantation Forest | 10.74 | 10.11 | 10.87 | 10.27 | 12.05 | 11.20 | 1.18 | 0.93 |
| Settlement Area | 9.18 | 8.15 | 11.57 | 11.08 | 12.65 | 11.27 | 1.08 | 0.19 |
| Estate Crops Plantation | 6.51 | 6.97 | 6.41 | 7.09 | 4.52 | 5.62 | −1.89 | −1.47 |
| Virgin Forest | 4.62 | 4.9 | 3.59 | 3.97 | 2.36 | 4.38 | −1.23 | 0.41 |
| Shrubs | 2.6 | 3.18 | 2.57 | 3.72 | 3.63 | 1.19 | 1.06 | −2.53 |
| Fishpond | 2.79 | 2.33 | 2.83 | 1.29 | 2.88 | 0 | 0.05 | −1.29 |
| Lake | 2.26 | 1.11 | 2.26 | 1.64 | 2.26 | 1.29 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Bare land | 1.33 | 0.44 | 1.34 | 0.56 | 0.69 | 0.42 | −0.65 | −0.14 |
| Airport | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
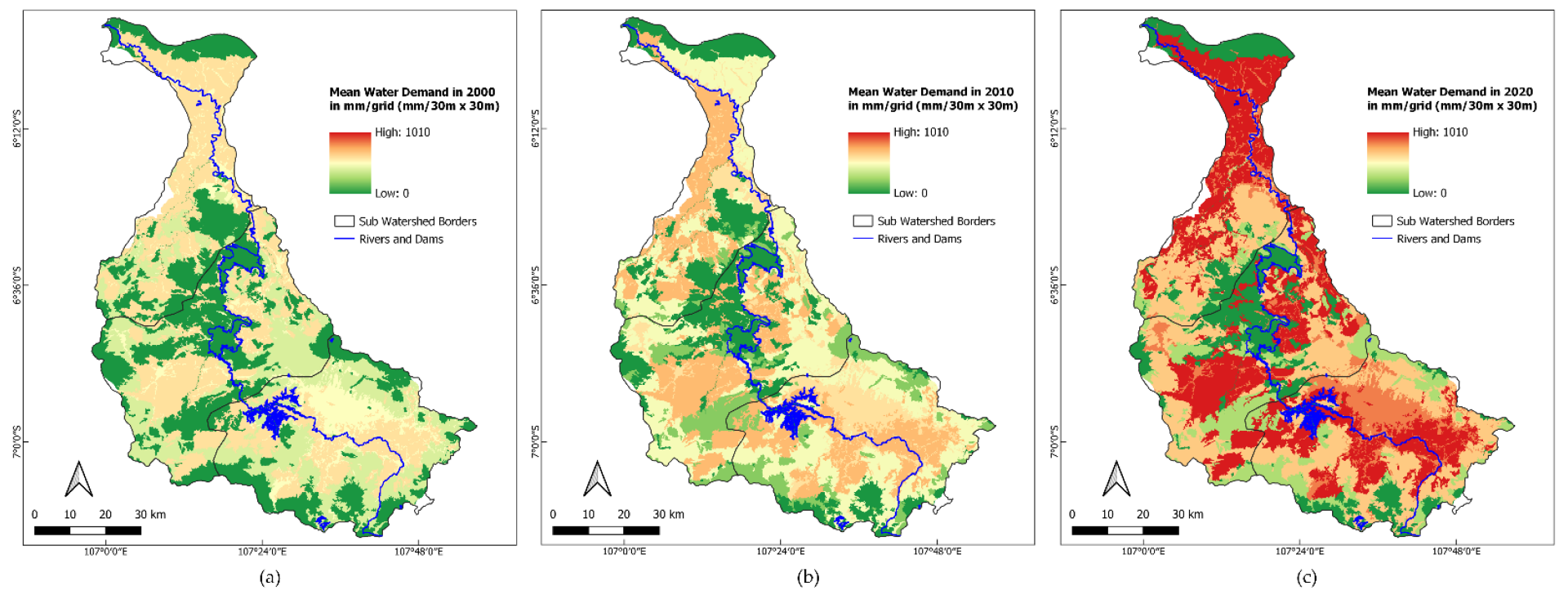
| Watershed | Area | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ha) | 108 m3 | % | 108 m3 | % | 108 m3 | % | |
| Upstream CW | 245,413 | 10.16 | 37.87 | 13.04 | 39.50 | 18.27 | 37.48 |
| Middle CW | 251,373 | 8.81 | 32.84 | 11.17 | 33.84 | 16.41 | 33.67 |
| Downstream CW | 194,130 | 7.86 | 29.30 | 8.79 | 26.63 | 14.06 | 28.85 |
| Total | 690,916 | 26.83 | 100.00 | 33.00 | 100.00 | 48.74 | 100.00 |
| Watershed | 2000–2010 | 2010–2020 | 2000–2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 108 m3 | % | Predicate | 108 m3 | % | Predicate | 108 m3 | % | Predicate | |
| Upstream CW | 2.88 | 28.35 | I | 5.23 | 40.11 | EI | 8.11 | 79.82 | EI |
| Middle CW | 2.36 | 26.79 | I | 5.24 | 46.91 | EI | 7.60 | 86.27 | EI |
| Downstream CW | 0.93 | 11.83 | NC | 5.27 | 59.95 | EI | 6.20 | 78.88 | EI |
| Total | 6.17 | 23.00 | I | 15.74 | 47.70 | EI | 21.91 | 81.66 | EI |
| LULC Type | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | Average | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area | WD | Area | WD | Area | WD | Area | WD | |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| Paddy Filed | 35.36 | 59.22 | 27.57 | 45.03 | 30.36 | 49.50 | 2.79 | 4.47 |
| Dry Agriculture | 24.56 | 27.60 | 30.95 | 33.88 | 28.56 | 31.44 | −2.38 | −2.44 |
| Plantation Forest | 10.74 | 2.09 | 10.87 | 5.11 | 12.05 | 4.96 | 1.18 | −0.15 |
| Settlement Area | 9.18 | 12.81 | 11.57 | 15.71 | 12.65 | 13.86 | 1.08 | −1.85 |
| Estate Crops Plantation | 6.51 | 0.08 | 6.41 | 0.07 | 4.52 | 0.06 | −1.89 | −0.02 |
| Virgin Forest | 4.62 | 0.02 | 3.59 | 0.02 | 2.36 | 0.02 | −1.23 | 0.00 |
| Shrubs | 2.60 | 0.02 | 2.57 | 0.02 | 3.63 | 0.01 | 1.06 | −0.01 |
| Fishpond | 2.79 | 0.01 | 2.83 | 0.01 | 2.88 | 0.01 | 0.05 | −0.00 |
| Lake | 2.26 | 0.09 | 2.26 | 0.09 | 2.26 | 0.09 | 0.00 | −0.00 |
| Bare land | 1.33 | 0.02 | 1.34 | 0.02 | 0.69 | 0.01 | −0.65 | −0.00 |
| Airport | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.04 | −0.00 | −0.00 |
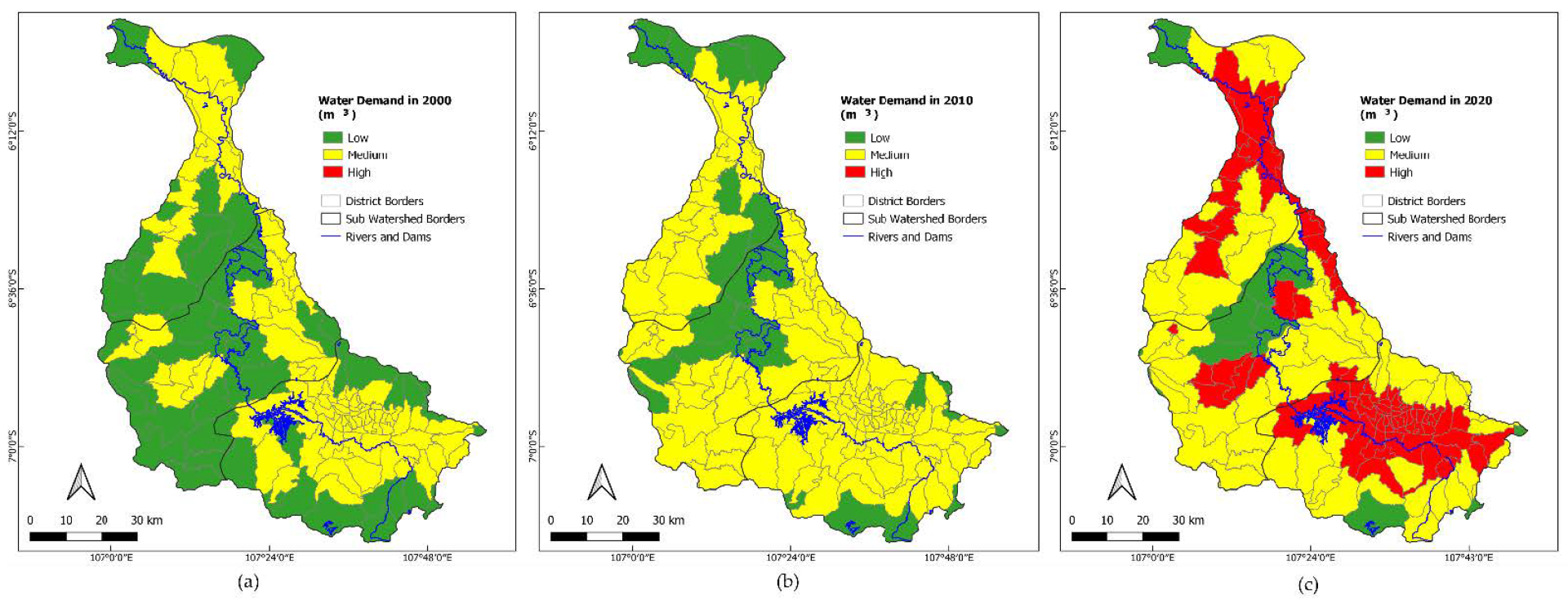
| Sub-Watershed | Area | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ha) | WC * 108 m3 | SDR | WSI | WC * 108 m3 | SDR | WSI | WC * 108 m3 | SDR | WSI | |
| Upstream CW | 245,413 | 10.16 | 2.58 | 0.41 | 13.04 | 1.70 | 0.23 | 18.27 | 1.09 | 0.04 |
| Middle CW | 251,373 | 8.81 | 5.02 | 0.70 | 11.17 | 3.27 | 0.51 | 16.41 | 1.96 | 0.29 |
| Downstream CW | 194,130 | 7.86 | 4.27 | 0.63 | 8.79 | 3.00 | 0.48 | 14.06 | 1.41 | 0.15 |
| Total | 690,916 | 26.83 | 3.88 | 0.59 | 33.01 | 2.57 | 0.41 | 48.74 | 1.48 | 0.17 |
| Year | Moran’s I | Z Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 0.344 | 10.2678 | 0.001 |
| 2010 | 0.346 | 11.9778 | 0.001 |
| 2020 | 0.368 | 12.4305 | 0.001 |
| Supply–Demand Matching Type | Supply–Demand Matching Type | Zone Management | Regency and Sub-District | Planning Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surplus | High supply-low demand | Conservation area | Upstream CW: Bandung Regency (1 sub-district) and West Bandung Regency (1 sub-district) | Strict ecological protection policy, efforts to maintain the supply capacity of water production services in the area, and maintain the ecological quality do not decline. |
| Deficit | High supply-high demand | Upstream CW: Bandung Regency (2 sub-districts), West Bandung Regency (6 sub-districts) Downstream CW: Bekasi Regency (2 sub-districts), Bogor Regency (4 sub-districts), Cianjur Regency (7 sub-districts), Karawang Regency Middle CW: Purwakarta (2 sub-districts) | ||
| Deficit | Low supply-high demand | Restoration area | Upstream CW: Bandung Regency (1 sub-district) and West Bandung (1 sub-district) Downstream CW: Bekasi Regency (3 sub-districts), Bogor Regency (1 sub-district), Karawang Regency (3 sub-districts) Middle CW: Cianjur Regency (3 sub-districts), Purwakarta Regency (1 sub-district) | Socialization and community empowerment in strict water-saving efforts throughout the community; planting and reforestation of open areas; and control of watertight areas of newly added construction sites. |
| Deficit | Low supply-low demand | Improvement area | Downstream CW: Bandung City (23 sub-districts) | Establish ecological control guidelines that focus on protecting water resources based on a socio-ecological approach, strengthening ecological protection and restoration strategies; utilization of engineering technology for ecological management of the main water system (Citarum and Ciliwung river). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nahib, I.; Amhar, F.; Wahyudin, Y.; Ambarwulan, W.; Suwarno, Y.; Suwedi, N.; Turmudi, T.; Cahyana, D.; Nugroho, N.P.; Ramadhani, F.; et al. Spatial-Temporal Changes in Water Supply and Demand in the Citarum Watershed, West Java, Indonesia Using a Geospatial Approach. Sustainability 2023, 15, 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010562
Nahib I, Amhar F, Wahyudin Y, Ambarwulan W, Suwarno Y, Suwedi N, Turmudi T, Cahyana D, Nugroho NP, Ramadhani F, et al. Spatial-Temporal Changes in Water Supply and Demand in the Citarum Watershed, West Java, Indonesia Using a Geospatial Approach. Sustainability. 2023; 15(1):562. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010562
Chicago/Turabian StyleNahib, Irmadi, Fahmi Amhar, Yudi Wahyudin, Wiwin Ambarwulan, Yatin Suwarno, Nawa Suwedi, Turmudi Turmudi, Destika Cahyana, Nunung Puji Nugroho, Fadhlullah Ramadhani, and et al. 2023. "Spatial-Temporal Changes in Water Supply and Demand in the Citarum Watershed, West Java, Indonesia Using a Geospatial Approach" Sustainability 15, no. 1: 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010562
APA StyleNahib, I., Amhar, F., Wahyudin, Y., Ambarwulan, W., Suwarno, Y., Suwedi, N., Turmudi, T., Cahyana, D., Nugroho, N. P., Ramadhani, F., Siagian, D. R., Suryanta, J., Rudiastuti, A. W., Lumban-Gaol, Y., Karolinoerita, V., Rifaie, F., & Munawaroh, M. (2023). Spatial-Temporal Changes in Water Supply and Demand in the Citarum Watershed, West Java, Indonesia Using a Geospatial Approach. Sustainability, 15(1), 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010562










