Landscape Pattern Changes Affect Runoff and Sediment Yield in the Nandong Underground River System in Southwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
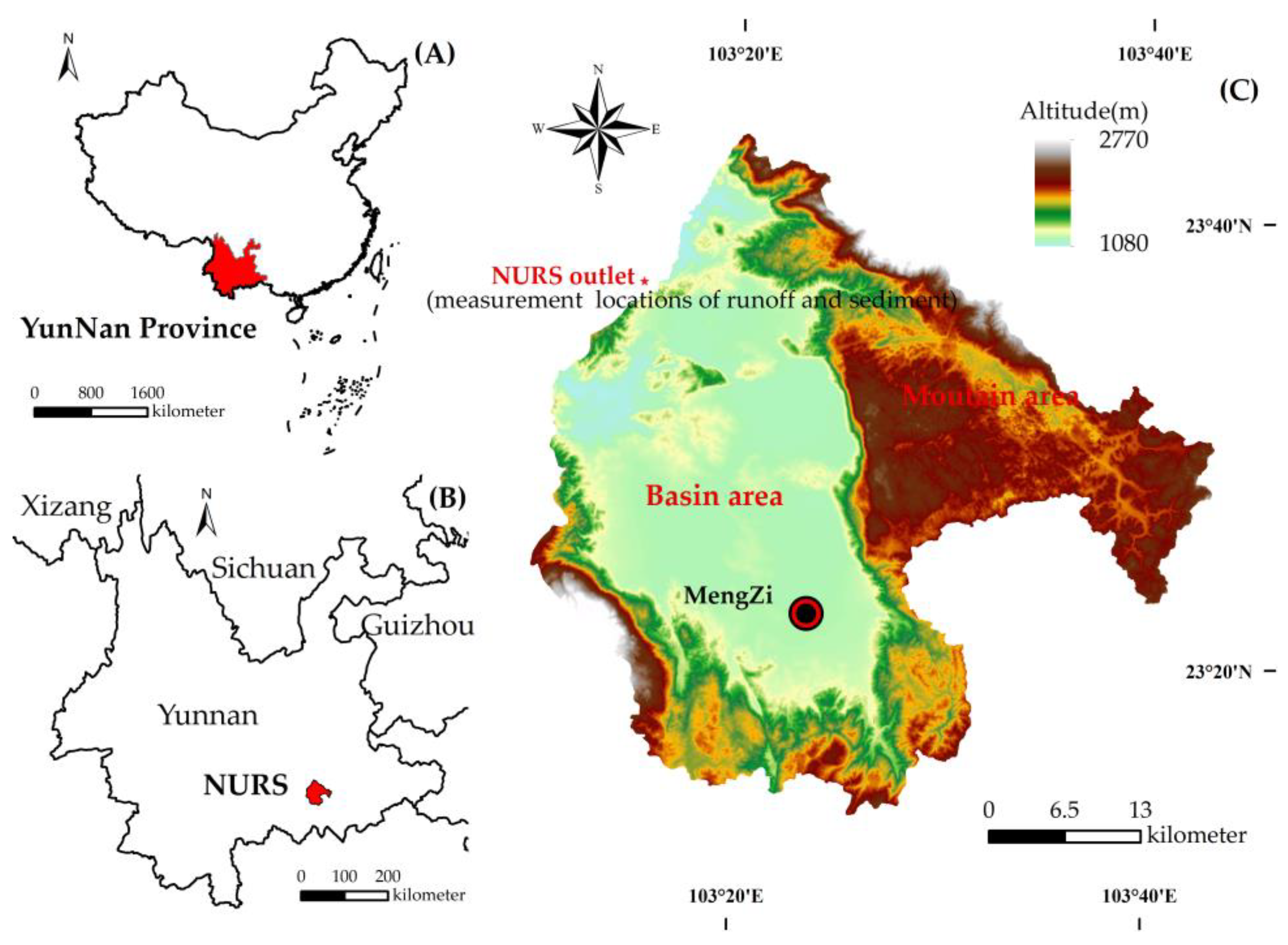
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Data
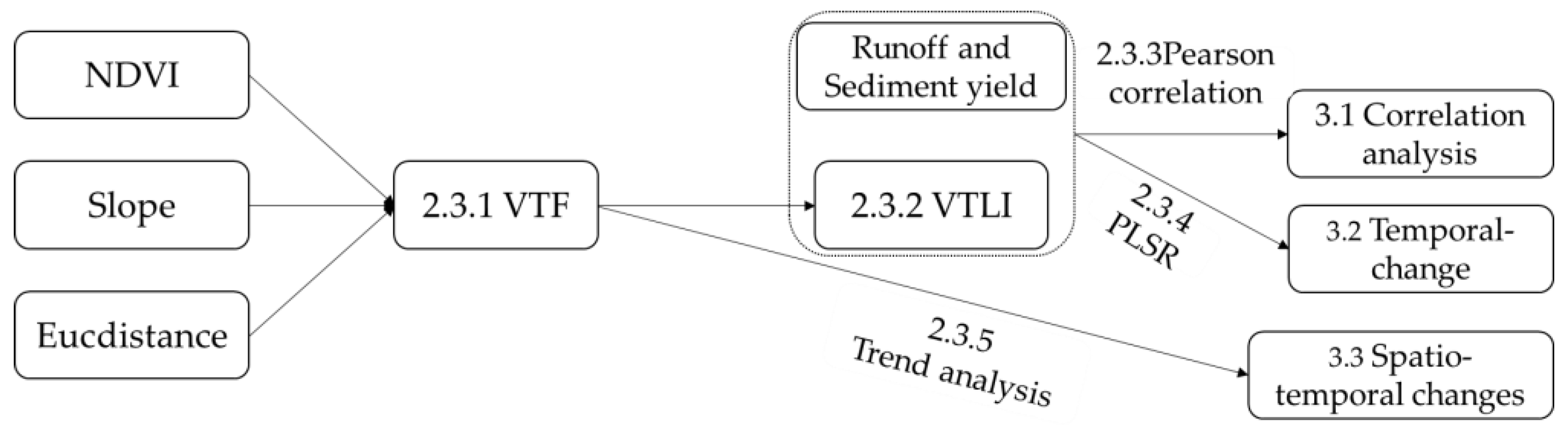
2.3. Method
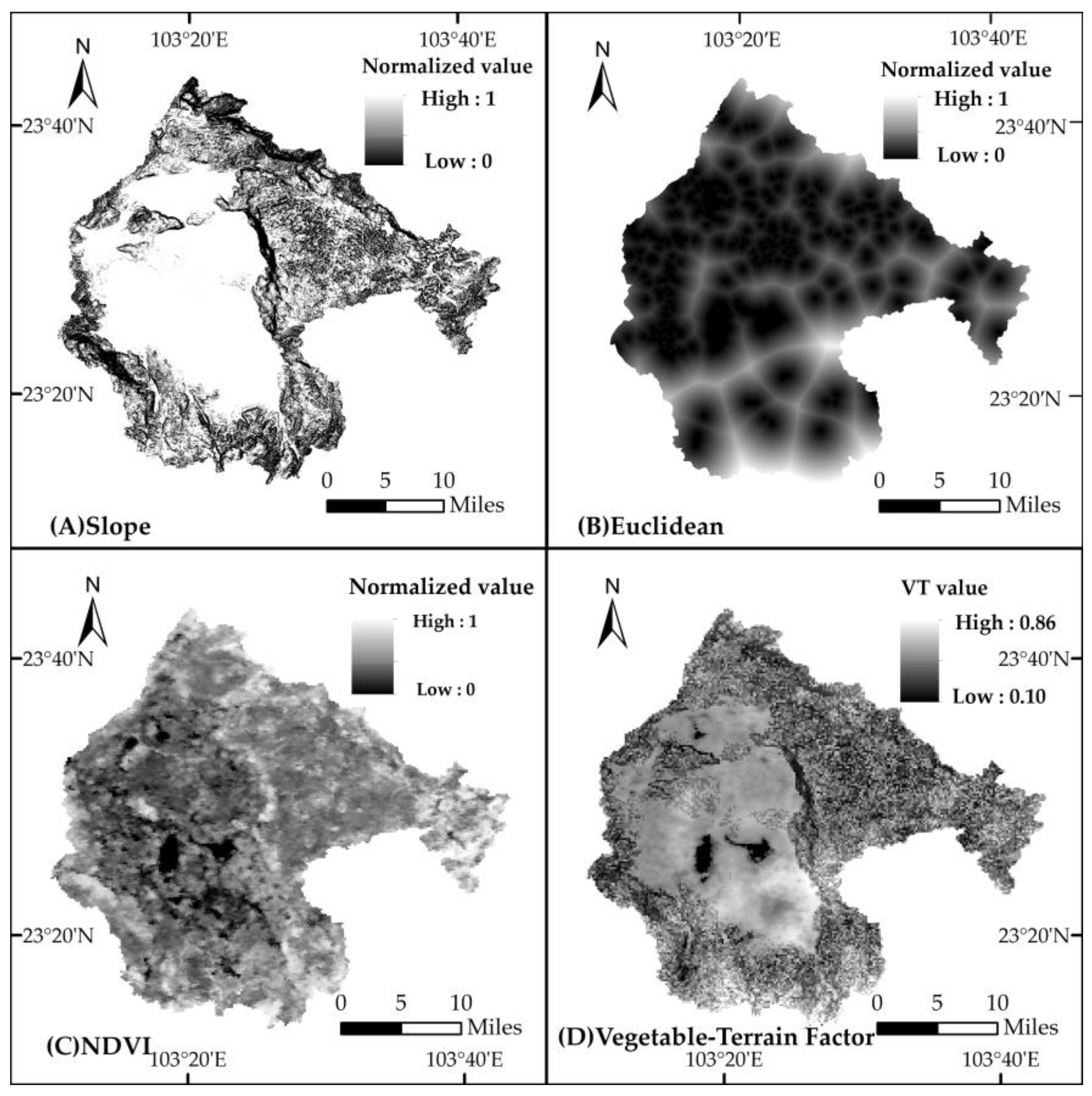
2.3.1. Vegetation-Terrain Factor (VTF)
2.3.2. Vegetation Terrain Landscape Index (VTLI)
2.3.3. Pearson Correlation
2.3.4. PLSR
2.3.5. Trend Analysis
3. Results
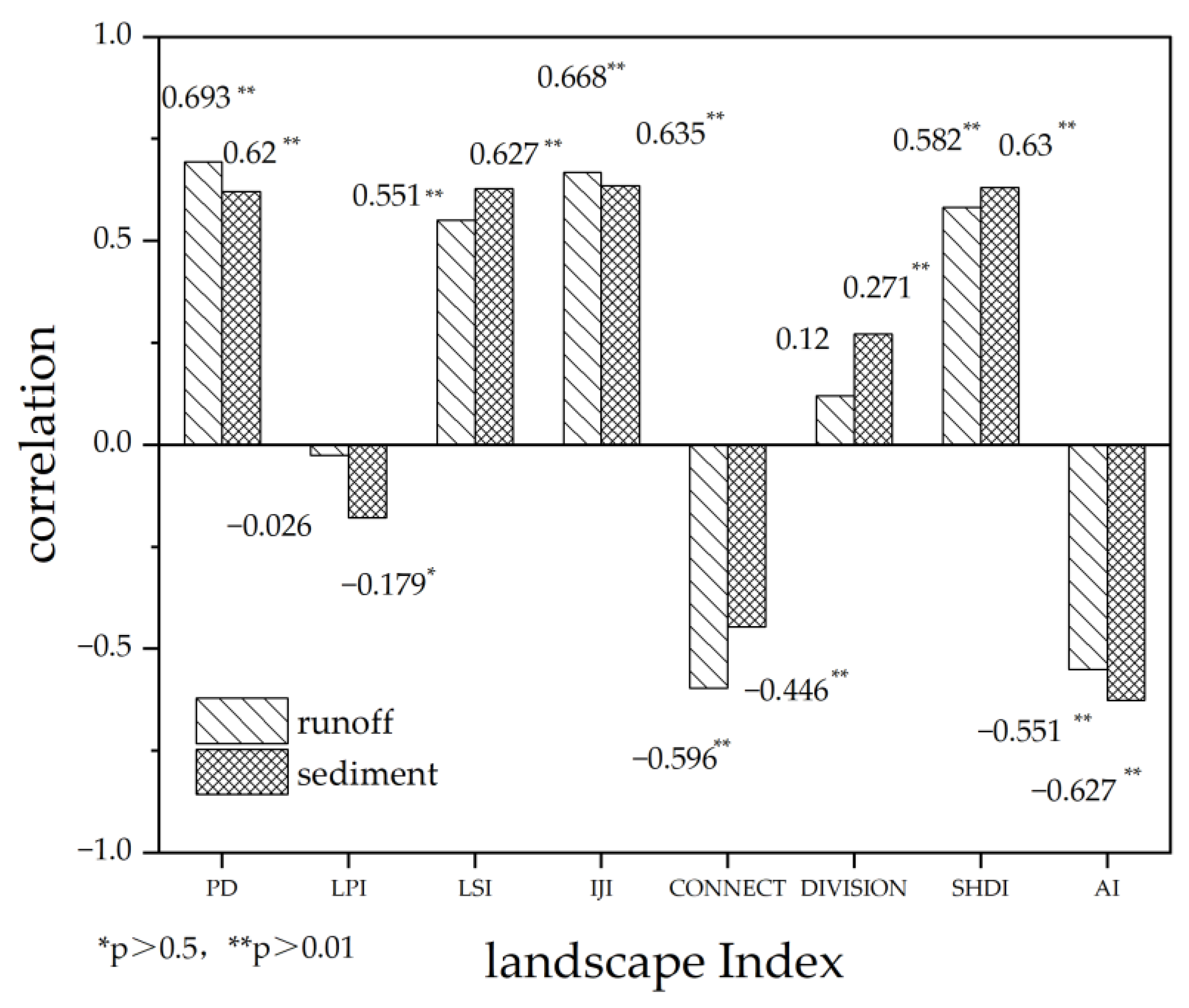
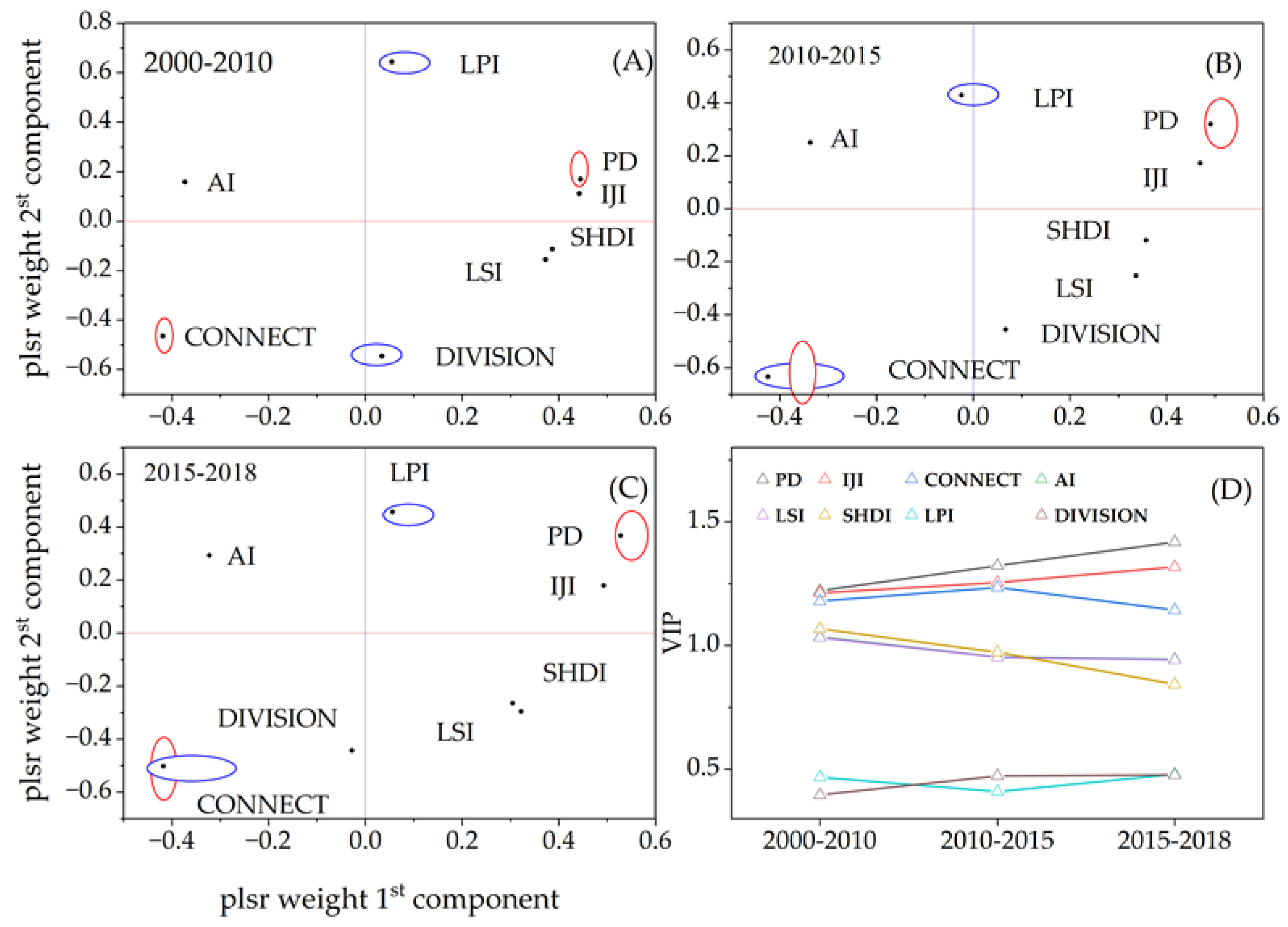
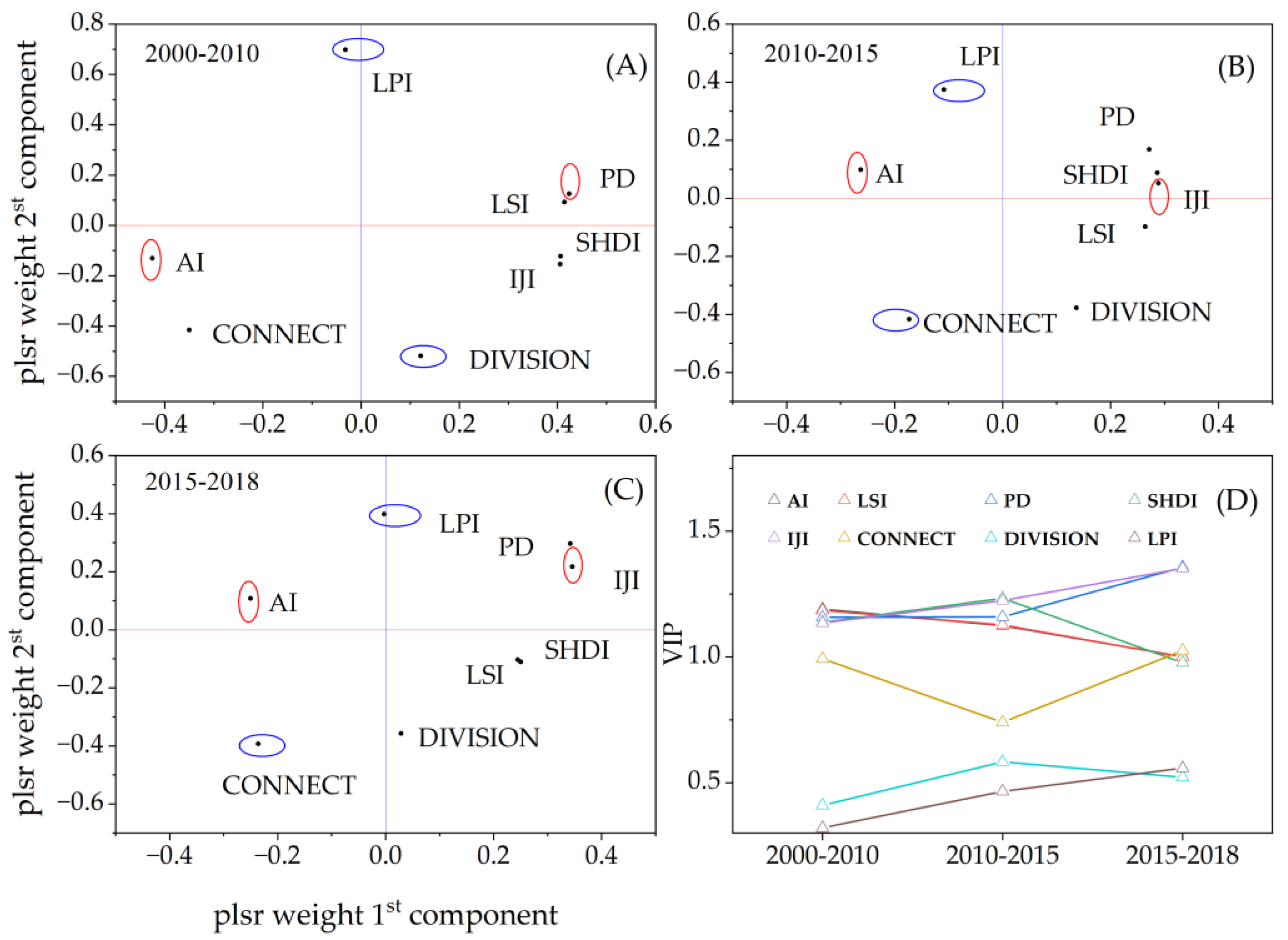
3.1. VTLI Correlation Analysis
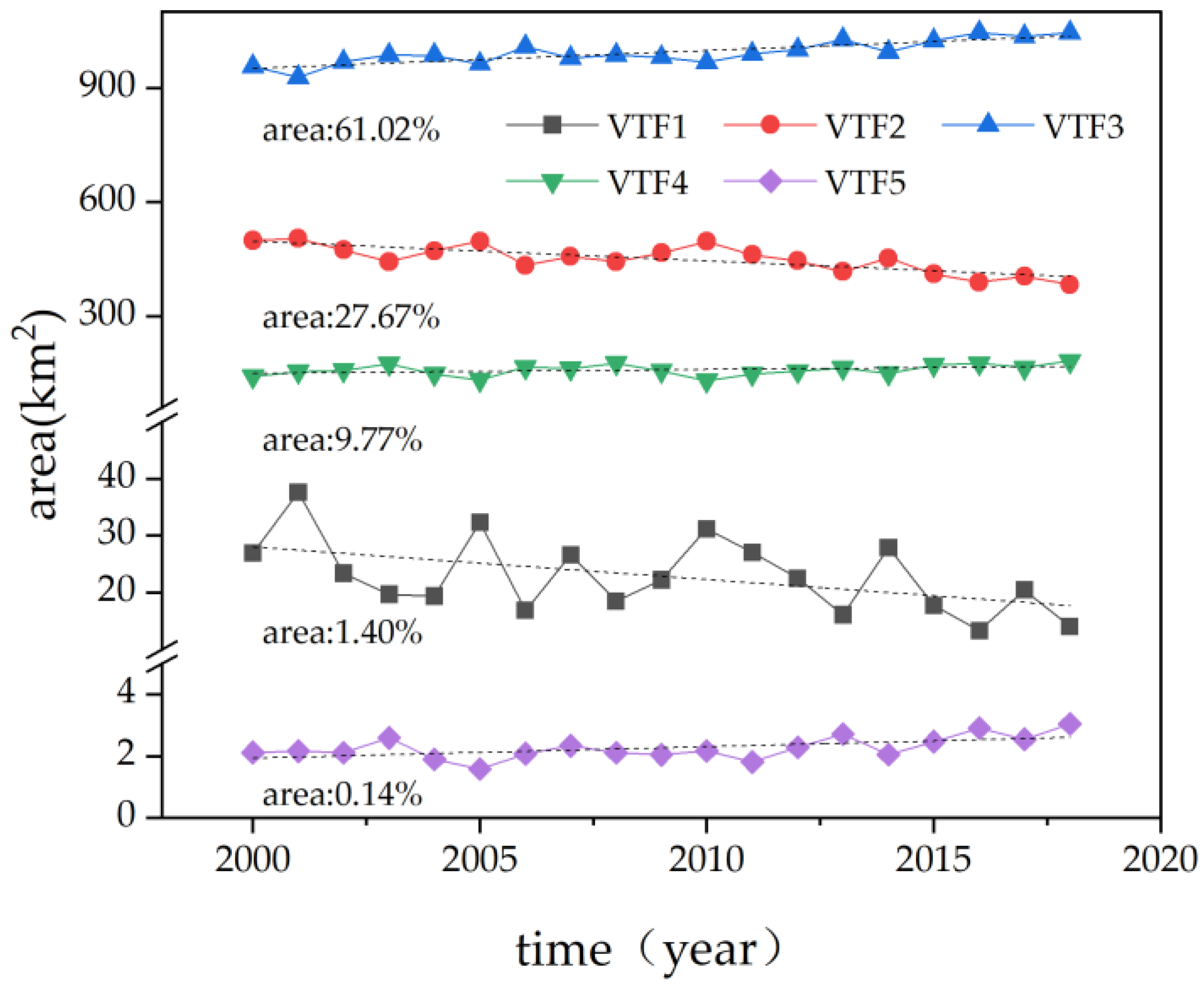
3.2. VTLI Changes
3.3. Spatio-Temporal Changes in VTF
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison to Traditional Landscape Indices
4.2. VTLI with Runoff and Sediment
4.2.1. VTLI Correlation
4.2.2. VTLI Changes
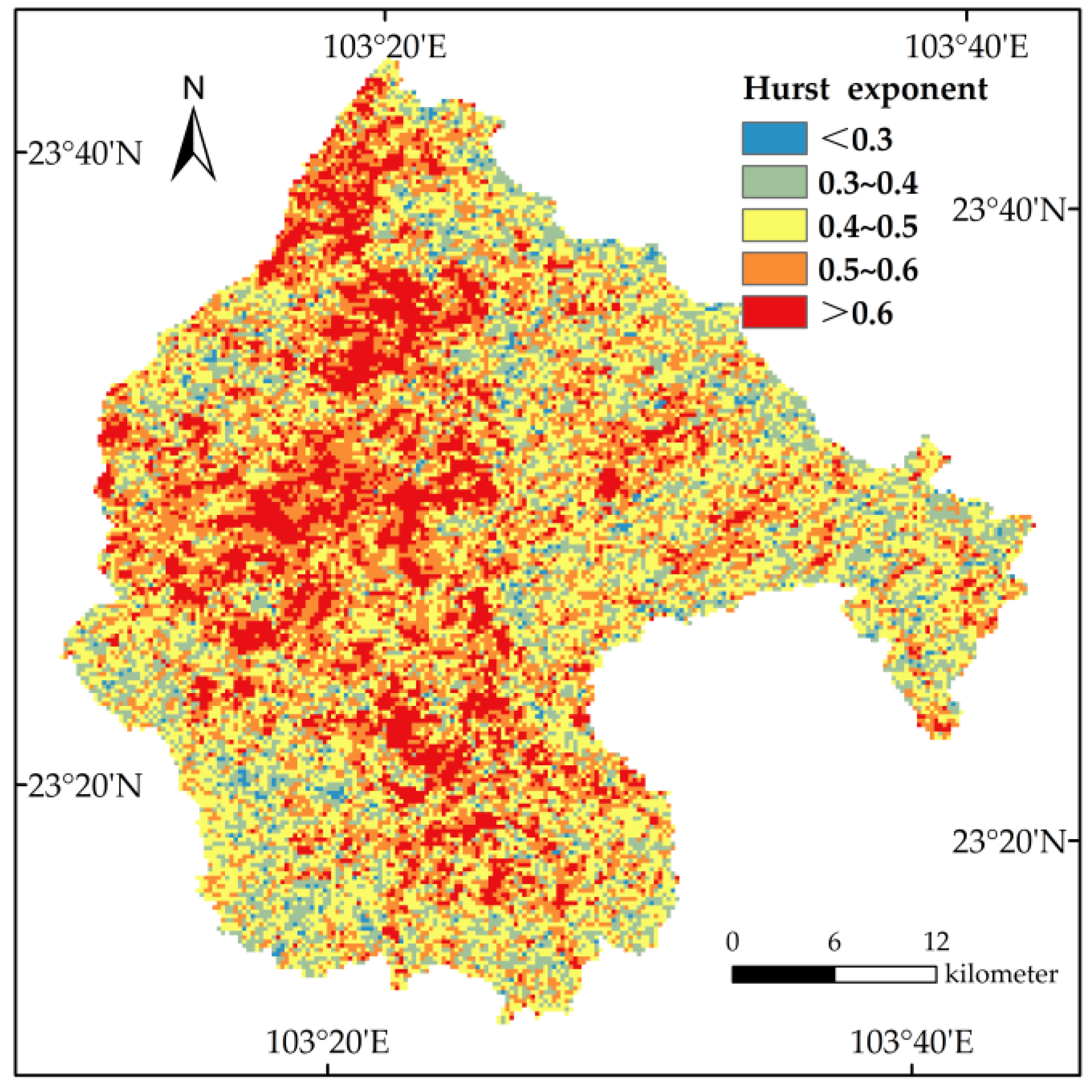
4.3. VTF Change and Sustainability
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Chen, L.D.; Liu, Y.; Lv, Y.H.; Feng, X.M.; Fu, B.J. Landscape pattern analysis in landscape ecology: Current, challenges and future. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 5521–5531. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.J.; Xu, Y.D.; Lv, Y.H. Scale Characteristics and Coupled Research of Landscape Pattern and Soil and Water Loss. Adv. Earth Sci. 2010, 25, 673–681. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.Y.A.; Daityari, S.; Chakrapani, G.J. Factors responsible for temporal and spatial variations in water and sediment discharge in Ramganga River, Ganga Basin, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Han, L.; Ao, Y.; Yin, S.; Li, R. Landscape ecological risk assessment in Qinling Mountain. Geol. J. 2018, 53, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, S.; Khan, M.Y.A.; Chakrapani, G.J. Grain size characteristics and provenance determination of sediment and dissolved load of Alaknanda River, Garhwal Himalaya, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Jiang, Z.C.; Li, Y.Q.; Lan, F.N.; Yu, Y.; Huang, Y.X. A Study of Soil Anti-erodibility of Different Slope Positions on Plateau Depression in Karst Gabin Basin. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2021, 42, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, J.A.; Wilcox, B.P.; Breshears, D.D.; Imeson, A.C. Vegetation patches and runoff–erosion as interacting ecohydrological processes in semiarid landscapes. Ecology 2005, 86, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krause, S.; Lewandowski, J.; Grimm, N.B.; Hannah, D.M.; Pinay, G.; McDonald, K.; Martí, E.; Argerich, A.; Pfister, L.; Klaus, J.; et al. Ecohydrological interfaces as hot spots of ecosystem processes. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 6359–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.G. Landscape Ecology-Concepts and Theories. Chin. J. Ecol. 2000, 19, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, H.Y.; Mark, C. Quantifying landscape structure: A review of landscape indices and their application to forested landscapes. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2016, 20, 418–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.A. Spatial Variation in the Grain Size Characteristics of Sediments in Ramganga River, Ganga Basin, India. In Handbook of Environmental Materials Management; Hussain, C.M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Martinez-Murillo, J.F.; Pereira, P. Loess Plateau: From degradation to restoration. Sci. Total Env. 2020, 738, 140206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, K.D.; Wilcox, B.P.; Breshears, D.D.; MacDonold, L. Runoff and Erosion in a Piiion-Juniper Woodland: Influence of Vegetation Patches. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 1869–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boix-Fayos, C.; Barberá, G.G.; López-Bermúdez, F.; Castillo, V.M. Effects of check dams, reforestation and land-use changes on river channel morphology: Case study of the Rogativa catchment (Murcia, Spain). Geomorphology 2007, 91, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Fang, N.F.; Zhang, P.C.; Shi, Z.H. Impacts of land use change on watershed streamflow and sediment yield: An assessment using hydrologic modelling and partial least squares regression. J. Hydrol. 2013, 484, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Sofia, G. Human topographic signatures and derived geomorphic processes across landscapes. Geomorphology 2016, 255, 140–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Ma, D.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Yin, M.; Bandala, E.R.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Multiple surface runoff and soil loss responses by sandstone morphologies to land-use and precipitation regimes changes in the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2022, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, S.P.; Noone, D.; Bowen, G. Water Resources. Hydrologic connectivity constrains partitioning of global terrestrial water fluxes. Science 2015, 349, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rui, X.F.; Jiang, C.Y. Review of research of hydro-geomorphological processes interaction. Adv. Water Sci. 2010, 21, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Loiskandl, W.; Kaul, H.-P.; Himmelbauer, M.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Bodner, G. Estimation of runoff mitigation by morphologically different cover crop root systems. J. Hydrol. 2016, 538, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gan, G.; Liu, Y.; Sun, G. Understanding interactions among climate, water, and vegetation with the Budyko framework. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 212, 103451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.B.; Gage, S.H. Landscape approaches to the analysis of aquatic ecosystems. Freshw. Biol. 1997, 37, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.Y.; Walcott, S.; Kaplan, B.; Cao, J.; Lin, W.; Chen, M.J.; Liu, D.S.; Ning, Y.M. An analysis of the relationship between spatial patterns of water quality and urban development in Shanghai, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2005, 29, 197–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Jiang, Z.C.; Yu, Y.; Shan, Z.J.; Lan, F.N.; Yue, X.F.; Liu, P.; Gyasi-Agyei, Y.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Evaluation of soil erosion and sediment deposition rates by the (137)Cs fingerprinting technique at different hillslope positions on a catchment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.Y.; Wu, X.Q.; Zhou, J.X.; Xiao, G.Y. Comprehensive Benefit Evaluation of Rocky Desertification Control in the Typical County of Karst Fault Basin: A Case Study of Jianshui County, Yunnan Province. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2021, 42, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.T.; Wu, X.Q. Research on the Spatial-temporal Variation of NPP in Yunnan Fault-depression Basins Based on CASA Model in 2005–2019. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2021, 42, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.W.; Wang, K.L.; Brandt, M.; Yue, Y.M.; Liao, C.J.; Fensholt, R. Assessing Future Vegetation Trends and Restoration Prospects in the Karst Regions of Southwest China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, B.; Peng, S.H.; He, R.S.; Zhou, C.Q. Zoning of Environmental Geology and Function in Karst Fault-Depression Basins. Carsologica Sin. 2017, 36, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.F.; Satterfield, E.A. Cover: Southern Africa, 2 February 2002 to 16 May 2002, Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) 500 m land surface reflectance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 26, 4137–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Evaluation of Earth Observation based global long term vegetation trends—Comparing GIMMS and MODIS global NDVI time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N. Characteristics of maximum-value composite images from temporal AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 7, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Bu, R.C.; Chang, Y.; Hu, Y.M.; Wen, Q.C.; Wang, X.G.; Xu, C.G.; Li, Y.H.; He, H.S. The response of landscape metrics against pattern scenarios. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2004, 24, 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- He, P.; Zhang, H.R. Study on Factor Analysis and Selection of Common Landscape Metrics. For. Res. 2009, 22, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, L.; Xu, K.; Xu, X.; Lian, J.; Ma, C. Development of a landscape indicator to evaluate the effect of landscape pattern on surface runoff in the Haihe River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.N. Effects of landscape pattern on runoff and sediment in the Loess Plateau: A multi-scale study. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Yang, X.N.; Chen, P.Y.; Sun, W.Y.; Ming, M.X.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G.J. Effects of shrub patch pattern on runoff and sediment yield. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Li, Z.W.; Xu, C.H.; Liu, M.X.; Wang, K.L.; Yu, B.F. Annual Runoff is Highly Linked to Precipitation Extremes in Karst Catchments of Southwest China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 2745–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fu, B.J.; He, C.S.; Sun, G.; Gao, G.Y. A comparative analysis of forest cover and catchment water yield relationships in northern China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 262, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Z.X. Landscape pattern and hydrological processes in Yanhe River basin of China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2014, 69, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.H.; Huang, X.D.; Ai, L.; Fang, N.F.; Wu, G.L. Quantitative analysis of factors controlling sediment yield in mountainous watersheds. Geomorphology 2014, 226, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Caballero-Calvo, A.; Senciales González, J.M.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Exploring long-term datasets of land use, economy, and demography variations in karst wetland areas to detect possible microclimate changes. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 2743–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Jiang, Z.C.; Chen, Z.H.; Yu, Y.; Lan, F.N.; Shan, Z.J.; Sun, Y.J.; Liu, P.; Tang, X.B.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Anthropogenic Disturbances and Precipitation Affect Karst Sediment Discharge in the Nandong Underground River System in Yunnan, Southwest China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, X.; Wang, K.L.; Yue, Y.M.; Brandt, M.; Liu, B.; Zhang, C.H.; Liao, C.J.; Fensholt, R. Quantifying the effectiveness of ecological restoration projects on long-term vegetation dynamics in the karst regions of Southwest China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 54, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Data | Use | Revolution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEM | Slope map | 10 m | CAS (http://www.cnic.cas.cn/ accessed on 25 April 2020) |
| NDVI | NDVI map | 250 m/month | MOD13Q1 (http://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov accessed on 6 June 2020) |
| Water system map | Eucdistance map | 10 m | Project Team |
| Runoff and sediment | Correlation/change analysis | per month | Hydrology and Water Resources Bureau |
| Indicators | NDVI | Slope | Eucdistance | VTF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Character | bare~high coverage | flat~steep slope | short~long | (water and soil conservation capacity) weak~strong |
| Original value | 0~0.89 | 0~67° | 0~0.39 | - |
| Normalized value | 0~1 | 0~1 | 0~1 | - |
| Proportion | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | - |
| VTF value | - | - | - | 0.10~0.86 |
| Landscape Index | Description |
|---|---|
| PD (Patch Density) | An important indicator of landscape fragmentation |
| LPI (Largest Patch Index) | Reflect the richness and dominant species in the landscape |
| LSI (Landscape Shape Index) | Complexity of the shape of a landscape type |
| IJI (Interspersion Juxtaposition Index) | Overall dispersion and juxtaposition of various patch types |
| CONNECT (Landscape Connectivity) | Degree of connection between patches |
| DIVISON (Division of Landscape) | Degree of separation of landscape types |
| SHDI (Diversity Index) | Reflect landscape heterogeneity |
| AI (Aggregation Index) | Degree of aggregation of landscape types |
| Component | 2000–2010 | 2010–2015 | 2015–2018 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Sediment | Water | Sediment | Water | Sediment | |
| 1 | 0.567 | 0.648 | 0.462 | 0.388 | 0.672 | 0.489 |
| 2 | 0.619 | 0.762 | 0.541 | 0.417 | 0.720 | 0.553 |
| 3 | 0.625 | 0.793 | 0.562 | 0.459 | 0.756 | 0.578 |
| 4 | 0.639 | 0.809 | 0.578 | 0.514 | 0.778 | 0.613 |
| Indicators | Degrade | Stable | Recover |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainable (Hurst > 0.5) | 2.48% | 21.58% | 31.05% |
| Unsustainable (Hurst < 0.5) | 5.09% | 19.96% | 19.84% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Lan, F.; Sun, Y. Landscape Pattern Changes Affect Runoff and Sediment Yield in the Nandong Underground River System in Southwest China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010835
Liu P, Jiang Z, Li Y, Lan F, Sun Y. Landscape Pattern Changes Affect Runoff and Sediment Yield in the Nandong Underground River System in Southwest China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(1):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010835
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Peng, Zhongcheng Jiang, Yanqing Li, Funing Lan, and Yingjie Sun. 2023. "Landscape Pattern Changes Affect Runoff and Sediment Yield in the Nandong Underground River System in Southwest China" Sustainability 15, no. 1: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010835
APA StyleLiu, P., Jiang, Z., Li, Y., Lan, F., & Sun, Y. (2023). Landscape Pattern Changes Affect Runoff and Sediment Yield in the Nandong Underground River System in Southwest China. Sustainability, 15(1), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010835





