Abstract
Given the semi-private nature of the mode, the conversion of taxi vehicles to electric requires a feasibility analysis, as it can impact their operations and revenues. In this research, we assess the feasibility of taxi companies in Santiago de Chile operating with battery electric vehicles (BEVs), considering the current electric mobility infrastructure of the city. We used a large database of GPS pulses provided by a taxi app to obtain a complete picture of typical taxi trips and operations in the city. Then, we performed an assessment of the feasibility of the fleet conversion by considering battery capacity, driving range, proximity to recharging stations, and charging power. The results are promising, as the number of completed trips ranges from 87.35% to 94.34%, depending on the BEV driving range. The analysis shows the importance of installing fast charging points in the locations or BEV driving ranges.
1. Introduction
The continuous growth of population and industries has resulted in an increase in global CO2 levels. One of the major industries contributing to this increase is the transportation industry. In Chile, the transportation sector is the second-largest sector responsible for CO2 emissions [1], which represented more than a third of the total emissions in 2019 [2]. This increase is mainly due to the rapid growth of the country’s automotive industry. According to [3], between 2010 and 2021, the number of vehicles continuously increased at an average rate of 6.1% per year.
This increase is observed in both private transportation and public transportation sectors. Between 2018 and 2020, there was an approximate average of 210,000 vehicles, including taxis, buses, and minibuses, with taxis accounting for approximately 50% of the total public transportation vehicles [4]. For this reason, in 2017, the Chilean government, with the aim of curtailing greenhouse gas emissions and CO2 emissions, adopted an electromobility strategy that seeks to attain 100% electric vehicles for urban public transportation by 2050 [5].
The goal is challenging as there are multiple factors influencing the adoption of electric vehicles in public transportation, especially taxis. According to a survey conducted in Shenzhen and Guangzhou, involving over 725 taxi drivers, Reference [6] found that the main adoption factors in taxi drivers are similar to those expressed by private car owners. For private car owners, References [7,8,9,10] showed that while drivers are becoming more confident with electric vehicles, the most relevant characteristics in their purchasing decisions are the purchase prices, fuel economy, and the battery’s driving range (maximum distance that an electric vehicle can travel with one charge).
For taxi drivers, there are other important factors that influence their decisions to replace their conventional gasoline vehicles (CGV) with battery electric vehicles (BEVs), which are even more difficult than for private car owners. These aspects include the locations of recharging stations [11,12,13], the number of recharging points compared to available gas stations [11], the possibility of parking, fast-charge stations [11], and the cost of the vehicle [7,8,9,14]. In addition, another key factor for taxi drivers is performance expectancy [6]. Reference [15] defined performance expectancy as “the degree to which an individual believes that using new technology can improve his/her job performance”. For taxis, this generates the question of whether a fleet of BEV taxis would have the capacity to meet the demands, considering the current battery ranges and recharging times. For the former, this is important, as CGVs do not have problems completing day-trip distances of 200–400 km (typical values for a taxi in a day), but for a BEV, this distance poses a challenge due to the limitations of their current driving ranges, as shown in [6]. The latter is relevant, considering that charging times for an electric vehicle with a 30 kW battery can vary between 8 min and 14 h, depending on the type of recharge [5].
In this paper, we evaluate the feasibility of replacing CGVs with BEVs for taxis from an operational perspective. That is, we evaluate the feasibility of taxis operating with BEVs in the same fashion as conventional CGVs. Moreover, our evaluation aims to determine the feasibility of taxis operating with electric batteries in a major urban area such as Santiago, Chile (a city of 7 million people), and to determine certain conditions that need to be considered by policymakers in order to reach the established goal. To perform this study, we used a large dataset of GPS taxi data from Fantaxico, a taxi app (https://flotas.fantaxico.com (accessed on 1 February 2023)) that has been operating in Santiago, Chile, since 2013. The data were obtained from 634 taxis, which stored 15 s GPS pulses, as well as pick-ups/drop-offs, tariffs, and other information. The availability of a significant volume of GPS data from a fleet of taxis and the possibility of analyzing the data at the level of each journey provide opportunities to study the feasibility that these vehicles can make their trips using batteries (under the assumption that taxis will attempt to operate in a manner similar to how they operate with gasoline vehicles). In addition, different scenarios that mix factors, such as the battery driving range, charging times, and distances to charging stations, were also included in the analysis.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents an overview of related studies that focus on fleet conversion feasibility. Section 3 presents a description of the data utilized in this study. Section 4 describes the methodology followed to assess the feasibility of the battery conversion of taxis in Santiago. In Section 5, we present the results, including an assessment of the current scenario, as well as other possible scenarios that can improve the feasibility of battery conversion. Finally, we present our conclusions in Section 6.
2. Literature Review
The feasibility of electric taxis has been examined from multiple facets. One facet involves the benefit-to-cost ratio, which was explored in [16]; the authors used data from a pilot study of three taxis in Daejeon, South Korea. Other studies focused mainly on environmental benefits [17,18], or energy consumption [19], as well as influencing factors for the acceptability of electric vehicles by taxi drivers [6].
In this section, we revise the literature related to the feasibility of battery electric vehicles (BEVs) for taxi trips, which includes the analysis of the feasibility of BEVs for private use. As [20] points out, this is usually made by analyzing travel patterns for a period of time, where survey questionnaires or GPS data are used to determine such patterns.
2.1. Feasibility of BEVs for Private Use
For private-use vehicles, Reference [21] computed the daily vehicle miles traveled (DVMT) to infer the suitability of replacing gasoline vehicles with electric vehicles in Atlanta, USA. To perform this evaluation, Reference [21] assumed that drivers would not change their driving patterns, which implies that they would charge once a day, typically overnight while at home. With that, they computed the market by identifying the proportion of the 484 vehicles analyzed that could meet their daily range of travel needs. They found that a small proportion of vehicles exceeded a range of 100 miles ( km) per day, thus pointing out that the market for electric vehicles, at least for private use, is feasible. Similarly, for private-use vehicles, Reference [22] used GPS data to assess the feasibility of electric vehicles in households in Seattle, USA. They found that a typical household in this city drives 23 miles (≈37 km) per day, meaning that electric vehicles with 100-mile battery ranges satisfy the trip-distance needs. Reference [23] also used five weeks of GPS data to analyze home-to-home tour distances in Australia, aiming to assess the feasibility of making these trips using electric vehicles. Their results align with previous studies showing that a large percentage (90%) of day-to-day driving can be accommodated because they involve short-range distance trips; while trips over 170 km would require a recharge. Notice that all of these studies are focused on privately owned vehicles used for home-based trips, and it is assumed that the recharging process occurs at night or while they are parked.
A more recent study conducted by [24] collected data (GPS travel survey data) from November 2004 to April 2006 in the Seattle metropolitan area. The study aimed to estimate the feasibility of electric vehicles based on the reliability of the battery range estimation. A driver is presented with two options for his daily trip: a CGV and a BEV. The feasibility is then calculated as the number of days that the driver replaces a CGV with a BEV, considering that for the BEV, a battery range is estimated. Their numerical results also show that to increment the feasibility of the usage of the BEV, an increase in the mean and a reduction in the standard deviation of the BEV range distribution is required.
Moreover, related to the driving range, Reference [25] conducted a daily driving usage study from a dataset comprising information on more than 1000 vehicles in Europe. An analysis on the distances and trip durations of the journeys, as well as the energy consumed and idle time analysis, were performed. Their analysis showed that, in terms of driving range, a hybrid electric vehicle can cover the daily needs of the sample as the majority of the urban trips comprise less than 50 km trips. However, they found that longer trips cannot recover energy due to short idle times and that autonomy (driving range) would need to increase, up to 400 km.
2.2. Feasibility of BEVs for Taxis
As can be observed from the recollection of studies in the previous section, the battery range (or battery autonomy) is an important aspect in the decision for the adoption of BEVs for private use. However, current surveys on taxi drivers show that the battery range is just one of many important factors. For instance, Reference [6] conducted a survey in Shenzhen and Guangzhou (both in China), comprising 725 respondents, to identify the factors driving the acceptance of electric vehicles by taxi drivers in these cities.
They found that the factors influencing the adoption are performance expectancy, effort expectancy, facilitating conditions, hedonic motivation, vehicle price value, habit, and satisfaction with incentive policies. These findings are similar to those found for private car users by [8,10,14,26]. Reference [26] studied the effects of the battery range as well as battery depletion using household questionnaire data gathered in Nagoya, Japan. From the data, they developed a probabilistic distribution (Weibull and log-normal) of daily travel distances. They found that anxiety is reduced when drivers have charging stations available in places where they tend to park for long periods (large-scale retail facilities, workplaces, expressway rest areas); this reduces the range desire for electric vehicles. They also modeled the response to the probability of battery depletion and found that the respondents had low expectations that the battery would be depleted based on their travel distance expectations. Thus, according to the authors, battery depletion will not play a significant role in the purchasing decisions of BEVs.
Reference [10] conducted a stated preference survey consisting of 996 respondents in Italy and 938 respondents in Slovenia; the authors found that the vehicle price, driving range, and environmental awareness are key in consumers’ decisions to adopt BEVs in both countries. Reference [9] conducted a survey in 30 provinces in China, involving 1021 respondents, to determine the impact of purchasing subsidies on the decision to adopt electric vehicles. Their results indicate that cost concerns of BEVs in China can be compensated by subsidies. However, respondents were more concerned with the operational aspects of the BEVs, such as cruising power or the availability of charging facilities.
Reference [8] conducted a stated preference survey in Italy, confirming that vehicle attributes, such as purchase price, fuel economy, and driving range, play very relevant roles. These results show new factors in comparison to a previous study conducted in Italy, where fast-charging networks, driving ranges, and financial incentives were identified as the primary factors influencing the purchasing decisions of electric vehicles [14].
Another recent behavioral study was conducted in Hong Kong by [27]; the authors collected 250 surveys from taxi drivers. They found similar factors affecting the adoption of BEVs, such as daily driving distance, driving range per full charge, and charging time. They also pointed out the importance of a network of charging stations and power infrastructure.
Reference [18] conducted a feasibility analysis on the conversion of current vehicles used as“taxi colectivos” (shared taxis with fixed routes and no timetables) in Santiago de Chile. The study explored the installation of batteries that could be charged using the current electric grid or through a solar recharging station at the beginning of the taxi routes. They found that the most beneficial effect was obtained when the batteries were charged with a solar grid; however, this solution is still unreliable due to solar intermittence. The study assumed that a “taxi colectivo” trip in Santiago could be completed with a fully charged battery, which might be an acceptable assumption only if the route “taxi colectivo” is short. In another study, Reference [28] addressed the feasibility of replacing taxis with BEVs in Seoul, South Korea, using a cost–benefit analysis. Their study included the cost assessment of vehicles and infrastructure while the benefits were computed by means of a traffic assignment. Reference [29] assessed the feasibility of replacing taxis by using real-world driving data and battery simulations in Canada. A life battery simulation appears reasonable in this context, considering that cold weather affects the duration of the battery. They considered two scenarios, one with one shift that charged overnight, and the other with two shifts, with two charges at the beginning of each shift. In both cases, the losses due to lost trips were small, showing that the losses for taxis would be minimal if replaced by BEVs.
In a similar fashion to [20], which used GPS data from the NYC yellow cabs to conduct the assessment, in this study, we assessed electric taxi feasibility based on GPS traces. However, as opposed to New York, Santiago de Chile’s taxi drivers do not work in shifts, as each driver is usually the owner and driver of their taxi. This makes the operation different in terms of use due to the long operational times, driving distances, and long dwell patterns. In addition, to make our results accurate and very close to reality, we used the locations of all current charging stations available in Santiago.
3. Data Description
The study used GPS data collected from the taxi app Fantaxico (Fermanti Servicios de Ingeniería S.A.), which has operated in Santiago, Chile, since 2013. During the time the data were collected, a total of 634 taxis used the application. For reference, different from certain countries, the taxis used in Santiago are owned or driven by a single driver.
3.1. Data Processing
The original data included 300 GB of information, corresponding to 8 specific months of data between 2014 and 2016 (updated data are currently unavailable for legal reasons), and included 15 s pulses of GPS data per vehicle. Among the data information, we obtained the latitude and longitude, time, and status of the trip (passenger on board, trip completed, tariffs), among other information.
A cleaning data process was performed to detect erroneous information as well as incomplete information. As a result, we obtained a total of 352,555 taxi trips. The next subsection presents the characteristics found in taxi trips. Part of the information from this dataset was used in [30] for clustering O-D to infer trip patterns. However, in [30], only the drop-off and pick-up locations were used, whereas in this paper, we used complete GPS traces.
3.2. Data Summary
The data show that the majority of taxis drive less than 200 km per day, as shown in Figure 1 (notice that the distribution of kilometers driven per day is skewed, with the majority of daily trips being less than 200 km per day). We also found that an average taxi drives km per trip. The longest trip recorded was 65.85 km.
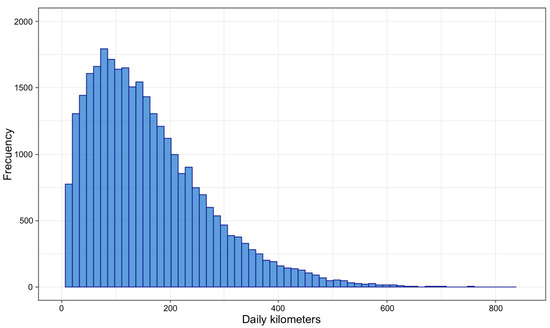
Figure 1.
Daily kilometers traveled by taxi trips.
As shown in Figure 2a, we can observe two different groups: weekdays (87.61%) and weekends (12.39%). Weekdays are distributed almost uniformly, with 18% of trips per day, except for Mondays (15%). In contrast, the trip percentages for the weekends were only 7.21% and 5.18% for Saturday and Sunday, respectively. With respect to Figure 2b, we can observe that most trips were between 9:00 and 20:00, corresponding to labor day hours, while a second peak occurred between 1:00 and 2:00 at night.
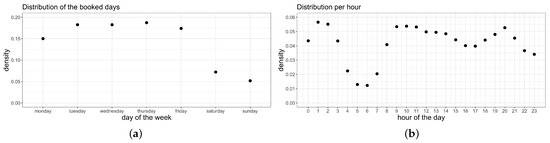
Figure 2.
Distribution of taxi trips. (a) Distribution per day. (b) Distribution per hour.
In terms of the pick-up and drop-off locations, Figure 3a shows the probability density distribution for passenger pick-ups. Similarly, Figure 3b shows the density distribution for drop-offs. As can be observed, both distributions are similar, meaning that the passengers take the same trip in both directions. It is also important to note the places with the highest densities correspond to important attractors and/or generators. Specifically, in both figures, we can observe three different locations: the airport in the top-left, the downtown location in the center of the figure, and the financial district in the middle-right of the figure. Note that the x points from Figure 3 mark the charging stations in the city.
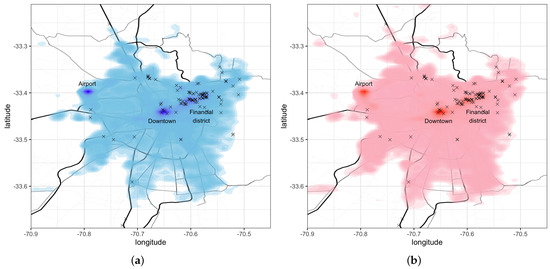
Figure 3.
Distribution of passengers. (a) Pick-up distribution. (b) Drop-off distribution. The x points mark the locations of the charging stations based on EnelX https://www.enelx.com/cl/es/mapa-puntos-de-carga (accessed on 1 March 2023) and Plataforma de Electromovilidad, the Ministry of Energy of the Government of Chile https://energia.gob.cl/electromovilidad/ecocarga (accessed on 1 March 2023).
4. Methodology
This study aimed to calculate the percentage of occupied taxi trips that could be completed in a day if BEVs were used instead of CGVs as the means to evaluate the feasibility of such a replacement. In doing so, we coded a program in Python that determined the portion of daily trips that were feasible, considering the battery capacity as well as the battery driving range (battery autonomy) of the electric vehicle and the time required for a taxi to recharge the battery. For the analysis, we assumed that the complete fleet of taxis used BEVs. Then, we simulated taxi trips based on the actual routes, pick-ups, and drop-offs obtained from the GPS data. For that, the code reconstructed the route of each taxi trip per day. In doing so, a total of 352,555 taxi routes were reconstructed for 634 taxis. Thus, for each taxi, we have the actual routes, travel times, and locations/times of the pick-ups and drop-offs. We followed a methodology similar to [20], which seeks to replicate whether a taxi should take a passenger or not if it has enough battery to complete the trip. If not, the taxi can recharge based on the availability of recharging facilities and the ability to pick up the next passenger. Otherwise, the taxi will skip the trip to the electric station and wait or drive to the next passenger. Details of this procedure follow, starting with the parameters used in this procedure.
4.1. Parameters
One of the parameters required for the assessment is the autonomy of the BEV. Equation (1) shows the full battery driving range (the full autonomy) of vehicle i, which can be computed as the efficiency of the battery in km/kWh times the capacity of the battery in KWh.
The data obtained from the Ministry of Energy of the Government of Chile (www.consumovehicular.cl (accessed on 1 February 2023) show that the autonomy of electric vehicles currently available in Chile varies between 130 and 250 km. For this study, we included four values of full autonomy, i.e., 150, 175, 210, and 245 km. These values were calculated by considering two battery capacities: 30 and 35 kWh, which match the capacities of batteries available in the Chilean market. Similarly, for each of these values, efficiencies of 5 and 7 km/kWh were included in the analysis. The combination of these values generated the four full autonomies (from 30 kWh ∗ 5 km/kWh = 150 km to 35 kWh ∗ 7 km/kWh = 245 km).
Other parameters were related to the charging stations, as the decision of recharging a battery of a BEV depends on the distance to the closest station, the power of the station, and the percentage of the remaining charge in the battery. Regarding the latter, Reference [19] pointed out that about 75% of taxi drivers would not recharge unless the battery had less than 50% of its charge. Thus, we considered that the driver would not recharge if the battery had 50% or more charge in the battery. To compute the recharging times, we considered two additional parameters: the distance to the closest charging station () and the charging power available in the station (). To determine the closest charging station, we considered the locations of current charging stations in Santiago de Chile, which consisted of a total of 124 stations (see the x in Figure 3). Finally, for the charging power, we found that the majority of charging stations had a charging power of 22 kW, while several of them were close to 7.4 kW or 50 kW. These values will also be included in the analysis.
4.2. Daily Trip Taxi Feasibility Procedure
The proposed procedure seeks to compute the percentage of trips that can be completed from the data we obtained. In other words, as we reconstruct the routes and the whole-day information for each taxi from the GPS data (routes, as well as locations of pick-ups and drop-offs), we can simply apply this procedure to obtain the number of trips in a day that a taxi could complete if the CGV is replaced by a BEV.
To determine the proportion of feasible taxi trips, another program was coded, considering the values of the parameters discussed in Section 4.1. The procedure is similar to the procedure proposed by [20]. That is, it analyzes whether a trip can be completed with a battery charge at the beginning of the day by evaluating the alternatives of recharging and/or picking up a passenger. However, the main difference is that in [20], the drivers worked in shifts. That is, they needed to recharge before their shifts were completed, while in our case, this restriction did not apply, as the drivers were the sole owners of their vehicles.
The developed procedure registers the number of trips k for each vehicle i. The distance traveled from the initial taxi location to the passenger of trip k is stored at , the distance of the trip is stored in the variable , while the distance between the taxi location and the closest electric station is recorded at variable . The available time associated with is , which represents the minutes available between trips k and . Similarly, denotes the driving time to the closest electric station. Depending on the values of these variables, the taxi can have time—or not—to recharge the battery. Table 1 shows a summary with the description of the variables, and Figure 4 shows a flowchart with the general steps included.

Table 1.
Variables and definitions.
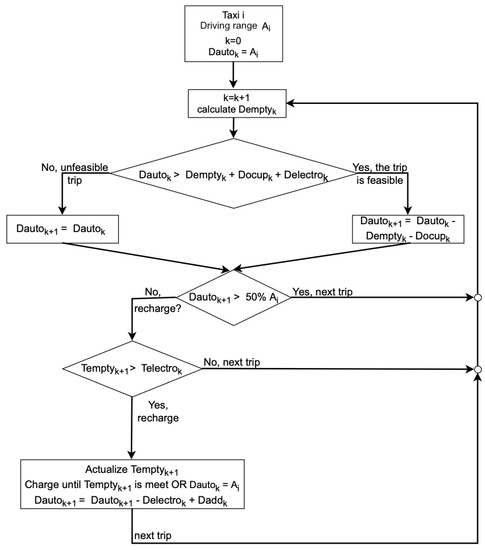
Figure 4.
Flow chart of the procedure to analyze the feasibility of replacing fuel taxis with an electric taxi fleet.
As shown in the figure, the procedure starts with for each vehicle, assuming that the battery is charged at full, at the beginning of the day. This is a valid assumption, considering that, different from [20], the taxis in Chile are owned by the drivers, who start working at the beginning of the day. The next step is to calculate the distance to the next passenger (). Then, we compare the total distance of trip k () plus the distance to the closest electric station , with the current driving range of vehicle . We included to avoid the situation where the BEV runs out of battery power. If the total distance exceeds the current taxi battery driving range , the trip is considered infeasible because it will require the driver to interrupt the trip to recharge, and the driving range of the next trip is updated with the current driving range (). If the trip is feasible, the current driving range is updated by subtracting the distance to the pick-up location and the distance traveled with the passenger ().
Once the current driving range is updated, we check whether to proceed with the next trip or attempt to charge the car. Regarding the latter, we check if the driving range of the vehicle is greater than 50% of its original charge (), as recommended by [19]. In this case, the taxi moves to the next trip. Otherwise, we check if there is enough time to charge (). If the taxi does not have enough time, then it moves to the next trip. If there is enough time, then the taxi goes to the closest electric station and charges the battery until we are ready for the next passenger or the battery is full. In the case that we do not know the next passenger, we could assume , forcing the taxi to go to the charging station. In the flow chart, the increment in the driving range is given by , where is the driving distance from the last passenger drop-off to the electric station and is the driving range added by the current charging station. Either way, after the charging process, the taxi moves to the next trip.
In the case that the taxi does not have enough time to be fully charged, we estimate using Equation (2), which is based on [20]. In this equation, we first calculate the actual time in hours that the taxi will be charging its battery (). This time is multiplied by the actual power of the electric station () and the driving range efficiency of the vehicle () in km/kWh.
The next section provides more details on the feasibility assessment of using the taxi data we obtained with the procedure described in this section.
5. Operational Analysis
In this section, we perform an operational analysis to assess the feasibility of the fleet conversion, considering two scenarios. The first scenario considers the actual locations and power of the charging stations operating in Santiago, Chile. This scenario works as the base case for comparison, while the second analysis is a sensitivity that includes fictitious charge stations with different power capacities.
5.1. Base Case Scenario: Actual Locations of Charging Stations in Santiago, Chile
The first analysis was performed by considering the actual locations and charging power of the 124 electric stations in Santiago, Chile. The electric power of these stations ranged from 3.5 to 55.0 kW, with 53 of them between 3.5 and 14 kW (40 were close to 7.5 kW), while 41 electric stations had a charging power of 22.0 kW, and 30 had a charging power between 44 and 55 kW (16 of them with 50 kW). For battery capacity and efficiency, we considered the values described in Section 4.1. This generated the four battery driving range values (150, 175, 210, and 245 km) as described in Section 4.1. In the case of time, as we considered the actual locations of the stations, we were able to compute the travel times from the location’s last drop-off passenger to the closest station using the shortest path.
The results can be observed in Table 2. The table shows the percentage of feasible trips (trips completed) and the four different vehicle driving range values. As can be observed, even with the lowest value of the driving range, most of the trips are feasible, ranging between 87.33% and 94.34%, with the result of the lowest driving range being the most probable because it aligns with the driving range of the available BEVs in the Chilean market.

Table 2.
Feasible trips (for all driving ranges and real charging stations in Santiago).
5.2. Sensitivity Analysis
To analyze the feasibility of electric vehicles, we considered 48 fictitious scenarios, corresponding with the combination of 4 different variables (battery driving range, battery efficiency, charging power, and driving time to the charge station). The values of the first three parameters are those described in Section 4.1. This means that we considered the 4 values of the driving range (150, 175, 210, and 245 km), the 2 values of efficiency (5 and 7 km/kWh), and the 3 charging powers (7.4, 22.0, and 50.0 kW).
The driving time parameter is included to assess the importance of the locations of charging stations. That is, instead of using the actual locations of the stations as in Section 5.1, we assume fictitious charging stations located at 5, 15, 30, and 40 min driving times from the last passenger drop-off location of the taxi. With these combinations of scenarios, we can evaluate the importance of having several powerful charging stations (50 kW and 5 min of driving) versus the worst-case scenario (7.4 kW and 40 min driving). The results are summarized in Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6, which report the percentages of feasible trips, similar to the base case in Section 5.1.

Table 3.
Feasible trips (battery capacity 30 kW, efficiency 5 km/kWh).

Table 4.
Feasible trips (battery capacity 35 kW, efficiency 5 km/kWh).

Table 5.
Feasible trips (battery capacity 30 kW, efficiency 7 km/kWh).

Table 6.
Feasible trips (battery capacity 35 kW, efficiency 7 km/kWh).
Table 3 shows the first set of results for the 150 km driving range and 5 km/kWh of efficiency. As can be observed in the table, the percentage of feasible trips diminishes when the driving time increases. In contrast, it increases considerably with respect to the charging power. Even though both results are expected (and the same pattern will be observed in the other tables), note the importance of the station’s charging power, as it makes the most difference rather than the driving time. For example, increasing the station’s charging power from 7.4 to 50.0 kW increases the percentage of feasible trips from 73.53% to 86.02% (for 40 min) and from 75.87% to 89.36% (5 min). This means an increase of 12.50% (40 min) to 13.49% (5 min), respectively. In contrast, when we reduce the time from 40 to 5 min, the maximum increase of feasibility is just 3.41% (station charging power 22 kW, from 81.16% to 84.57%). Similarly, it is important to note that the increment in the percentage of feasible trips is higher when we change the charging power from 7.4 to 22 kW, rather than 22 to 50 kW. When we change from 7.4 to 22 kW in the worst-case scenario (40 min), the percentage of feasible trips increases from 73.52% to 81.16% (a difference of 7.64%). In contrast, from 22 to 50 kW, in the best case scenario (5 min), it only increases from 84.57% to 89.36% (a difference of 4.79%).
Table 4 shows the second set of results for the 175 km driving range and an efficiency of 5 km/kWh. Similar to Table 3, we can conclude that the percentage of feasible trips diminishes when the driving time increases, and it increases with respect to an increase in charging power. Again, the station charging powers seem more important. In addition to the observations made for the 150 km driving range, the number of feasible trips also increases with the largest driving range of the car. This increment ranges from 2.37 % (50.0 kW, 5 min, from 89.36% in Table 3 to 91.73% in Table 4) to 4.76% (7.4 kW, 40 min, from 73.52% in Table 3, and 78.28% in Table 4).
Finally, Table 5 and Table 6 show the results for the autonomies of 210 km and 245 km, respectively, and an efficiency of 7 km/kWh. As expected, we observe the same patterns. That is, the percentage of feasible trips diminishes when the driving times to charge stations increase. On the contrary, the percentage of feasible trips increases with respect to the charging power and the driving range of the vehicle. However, for the latter, this increment is not proportional to the driving range of the vehicle. Increasing the driving range from 150 to 175 km and from 175 to 210 km results in average increments of 3.53% and 4.60% in terms of feasibility; the feasibility reduces to only 2.64% when it changes from 210 to 245 km, which is significantly lower than previous increments.
Notice the significant change in the importance of the charging power compared to the driving time (location of the stations). For example, instead of having charging stations every 5 min (or multiple charging stations that required 5 min of driving plus waiting time) with a capacity of 7.5 kWh (75.87% of feasible trips), it was considerably better to have 50 kWh stations, even if it required 40 min of driving (or few charging stations that required 40 min of driving plus waiting time), as they would result in a feasibility percentage of 86.02%, a difference of 10.15%. In contrast with vehicles with higher driving ranges (210 km or 245 km), the same comparison had difference percentages of 5.02% (87.05% to 92.07%) and 3.82% (90.37% to 94.19%), respectively. In fact, this difference, in terms of feasibility, is minimal if we compare the 22 kW with the 50 kW for vehicles with high driving ranges (210 km or 245 km) and different driving times. Specifically, when considering a 5-minute driving time and a 22 kW charging station, the feasibility percentages are 91.81% and 94.08% for vehicles with driving ranges of 210 km and 245 km, respectively. Instead, when compared to 40 min driving times and 50 kW, we obtained feasibility percentages of 92.07% and 94.19%, respectively.
5.3. Comparison with Other Studies
As the results show, the feasible trips (completed trips) range approximately from 73% to 95%, depending on the driving range, power efficiency, and battery capacity. These values are in line with those obtained by [29]. Reference [29] found values between 87% and 98% for efficiencies between 4.66 to 5.08 km/Kwh, which are comparable to the results shown in Table 3 and Table 4, which present values between 73.5% and 89.36% for the most pessimistic driving range values, and between 78.28% and 91.73% in the most optimistic driving range. For [20], the authors’ results are less optimistic because they argue that only 8% of the yellow taxis in NYC can complete 99% of their occupied trips. This might have been influenced by the charging network in NYC, which they claimed needed to be expanded.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we evaluated the feasibility of the conversion of taxis from CGVs to BEVs from an operational perspective in the city of Santiago de Chile. That is, we performed a simulation based on real GPS taxi data to determine the percentage of taxi trips that can be completed with BEVs. GPS taxi data were used to determine the actual patterns and passenger pick-up and drop-off locations. We also used the actual locations and electric power of the currently available charging stations in Santiago de Chile. Our results show that the current infrastructure and technology will not allow for the completion of 100% of the trips as the percentage of completed trips varies between 87.35% (the most likely scenario, given the battery driving range of BEVs available in the Chilean market) and 94.34%, depending on the driving range. This implies that if taxi drivers replace their CGVs with BEVs, they would reduce their income to a certain amount, even with a high-value battery driving range However, we consider that the loss is not high and the scenario is promising. Moreover, the loss can be compensated with subsidies or any other public policy intervention to compensate taxi drivers.
We also performed a sensitivity analysis to evaluate the impact of the driving range efficiency, as well as the power and locations of the charging stations. From this analysis, one important conclusion is the importance of charging power in the stations over their locations (evaluated as the driving time to the closest station) and even the vehicle driving range. Thus, in order to reach the goal of 100% vehicle conversion in taxis, improvements in the charging power are recommended. One limitation in the analysis is the assumption that driving to the electric station will actually be beneficial to the taxi, as the driving distance and charging time could reduce the driving range of the vehicle, instead of increasing it. For example, if the time to the next passenger is a little higher than the time to drive to the station, the charging time will be minimal, thus reducing the driving range of the taxi. Since addressing this issue will significantly increase the complexity of the procedure, future work should consider these specific cases in a computationally efficient way. In addition, two recent works (see [31,32]) have applied data-oriented techniques to locate charging stations. Thus, another line for future work will involve the development of optimization models with data-oriented models to localize the minimum number of charging stations and the type of charging power at each station, to optimize the number of feasible trips. In addition, future work will improve the simulator, for instance, when considering the effect of weather. The weather in Santiago de Chile can be considered mild, but as shown in [33], cold weather (below −15 °C) affects the battery performance and the driving range of the vehicle, which needs to be accounted for in certain cities.
Finally, another aspect not considered in this analysis is the cost of the electric vehicle. The costs of BEVs are significantly higher than fuel-based vehicles. There is consensus in the literature that the adoption of BEVs requires the use of subsidies. In that regard, currently, the Chilean Government has implemented subsidies for taxi conversions in three regions of Chile [34]. Future work can also focus on assessing the effectiveness of such programs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.F.Y.; Methodology, W.F.Y. and S.M.; Software, S.M. and D.M.; Validation, S.M.; Formal analysis, W.F.Y., S.M. and D.M.; Resources, W.F.Y.; Data curation, S.M. and D.M.; Writing—original draft, W.F.Y., S.M. and D.M.; Writing—review & editing, W.F.Y. and S.M.; Supervision, S.M.; Project administration, W.F.Y.; Funding acquisition, W.F.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The APC was partially funded by Universidad Adolfo Ibáñez: Programa de Apoyo a la Investigación UAI 2023.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is unavailable due to privacy or ethical re-strictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- IEA. Energy Policies Beyond IEA Countries: Chile 2018 Review; IEA: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- CNE. Anuario Estadístico de Energía. 2020. Available online: https://www.cne.cl/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/AnuarioCNE2020.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- CEIC. Chile Motor Vehicles Sales Growth, 2010–2021. 2022. Available online: https://www.ceicdata.com/en/indicator/chile/motor-vehicles-sales-growth (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- INE. Base de Datos de Permisos de Circulación. 2021. Available online: https://www.ine.gob.cl/docs/default-source/parque-de-vehiculos/bbdd/2021/base-de-datos-permisos-de-circulación.accdb?sfvrsn=dba78113_5&download=true (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Ministerio de Energía. Estrategia Nacional de Electro-Movilidad. 2020. Available online: https://energia.gob.cl/sites/default/files/estrategia-nacional-electromovilidad_ministerio-de-energia.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Zhou, M.; Long, P.; Kong, N.; Zhao, L.; Jia, F.; Campy, K.S. Characterizing the motivational mechanism behind taxi driver’s adoption of electric vehicles for living: Insights from China. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2021, 144, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsekoglu, Ö. Socio-demographic characteristics, psychological factors and knowledge related to electric car use: A comparison between electric and conventional car drivers. Transp. Policy 2018, 72, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielis, R.; Rotaris, L.; Giansoldati, M.; Scorrano, M. Drivers’ preferences for electric cars in Italy. Evidence from a country with limited but growing electric car uptake. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2020, 137, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z. Urban households’ purchase intentions for pure electric vehicles under subsidy contexts in China: Do cost factors matter? Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2020, 135, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotaris, L.; Giansoldati, M.; Scorrano, M. The slow uptake of electric cars in Italy and Slovenia. Evidence from a stated-preference survey and the role of knowledge and environmental awareness. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2021, 144, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Globisch, J.; Plötz, P.; Dütschke, E.; Wietschel, M. Consumer preferences for public charging infrastructure for electric vehicles. Transp. Policy 2019, 81, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canepa, K.; Hardman, S.; Tal, G. An early look at plug-in electric vehicle adoption in disadvantaged communities in California. Transp. Policy 2019, 78, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Gao, W.; Li, B.; Wang, L. Locating charging stations for electric vehicles. Transp. Policy 2020, 98, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giansoldati, M.; Danielis, R.; Rotaris, L.; Scorrano, M. The role of driving range in consumers’ purchasing decision for electric cars in Italy. Energy 2018, 165, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.; Kim, H.; Chang, H.J. A Feasibility Test on Adopting Electric Vehicles to Serve as Taxis in Daejeon Metropolitan City of South Korea. Sustainability 2016, 8, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dong, J.; Lin, Z.; Hu, L. Predicting market potential and environmental benefits of deploying electric taxis in Nanjing, China. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2016, 49, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, A.; Roberts, C.; Simon, F.; Ordoñez, J. Solar electricity production and taxi electrical vehicle conversion in Chile. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wei, S.; Sun, F.; Hu, X.; Shiao, Y. Large-scale deployment of electric taxis in Beijing: A real-world analysis. Energy 2016, 100, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Dong, J.; Lin, Z.; Yang, J. Analyzing battery electric vehicle feasibility from taxi travel patterns: The case study of New York City, USA. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 87, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearre, N.S.; Kempton, W.; Guensler, R.L.; Elango, V.V. Electric vehicles: How much range is required for a day’s driving? Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2011, 19, 1171–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Kockelman, K.M. Predicting the market potential of plug-in electric vehicles using multiday GPS data. Energy Policy 2012, 46, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, S.; Backman, H.; Ellison, A.B. An empirical assessment of the feasibility of battery electric vehicles for day-to-day driving. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2014, 66, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wu, X.; Liu, C.; Lin, Z.; Hu, L. The impact of reliable range estimation on battery electric vehicle feasibility. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2020, 14, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Chiara, B.; Deflorio, F.; Eid, M. Analysis of real driving data to explore travelling needs in relation to hybrid–electric vehicle solutions. Transp. Policy 2019, 80, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, T.; Sato, H.; Morikawa, T. Range and Battery Depletion Concerns with Electric Vehicles. J. Adv. Transp. 2017, 2017, 7491234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.A.; Lau, Y.Y.; Wong, L.M.; Wu, J. A Preliminary Feasibility Study of Electric Taxi Promotion in Hong Kongâ Behavior Modelling of Driving Patterns and Preferences. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.C.; Lee, H. Economic appraisal of implementing electric vehicle taxis in Seoul. Res. Transp. Econ. 2019, 73, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darcovich, K.; Ribberink, H.; Michelet, C.; Lombardi, K.; Ghorab, M. The Feasibility of Electric Vehicles as Taxis in a Canadian Context. In Proceedings of the 2019 Electric Vehicles International Conference (EV), Bucharest, Romania, 3–4 October 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, C.; Moreno, S.; Yushimito, W.F. Characterization of Mobility Patterns with a Hierarchical Clustering of Origin-Destination GPS Taxi Data. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 12700–12710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keawthong, P.; Muangsin, V.; Gowanit, C. Location Selection of Charging Stations for Electric Taxis: A Bangkok Case. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Qi, Y. Application of Clustering Algorithms in the Location of Electric Taxi Charging Stations. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delos Reyes, J.R.M.; Parsons, R.V.; Hoemsen, R. Winter Happens: The Effect of Ambient Temperature on the Travel Range of Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 4016–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Programa Mi Taxi Eléctrico. Available online: https://mitaxielectrico.cl (accessed on 9 May 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).