Prediction of Groundwater Quality Index Using Classification Techniques in Arid Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
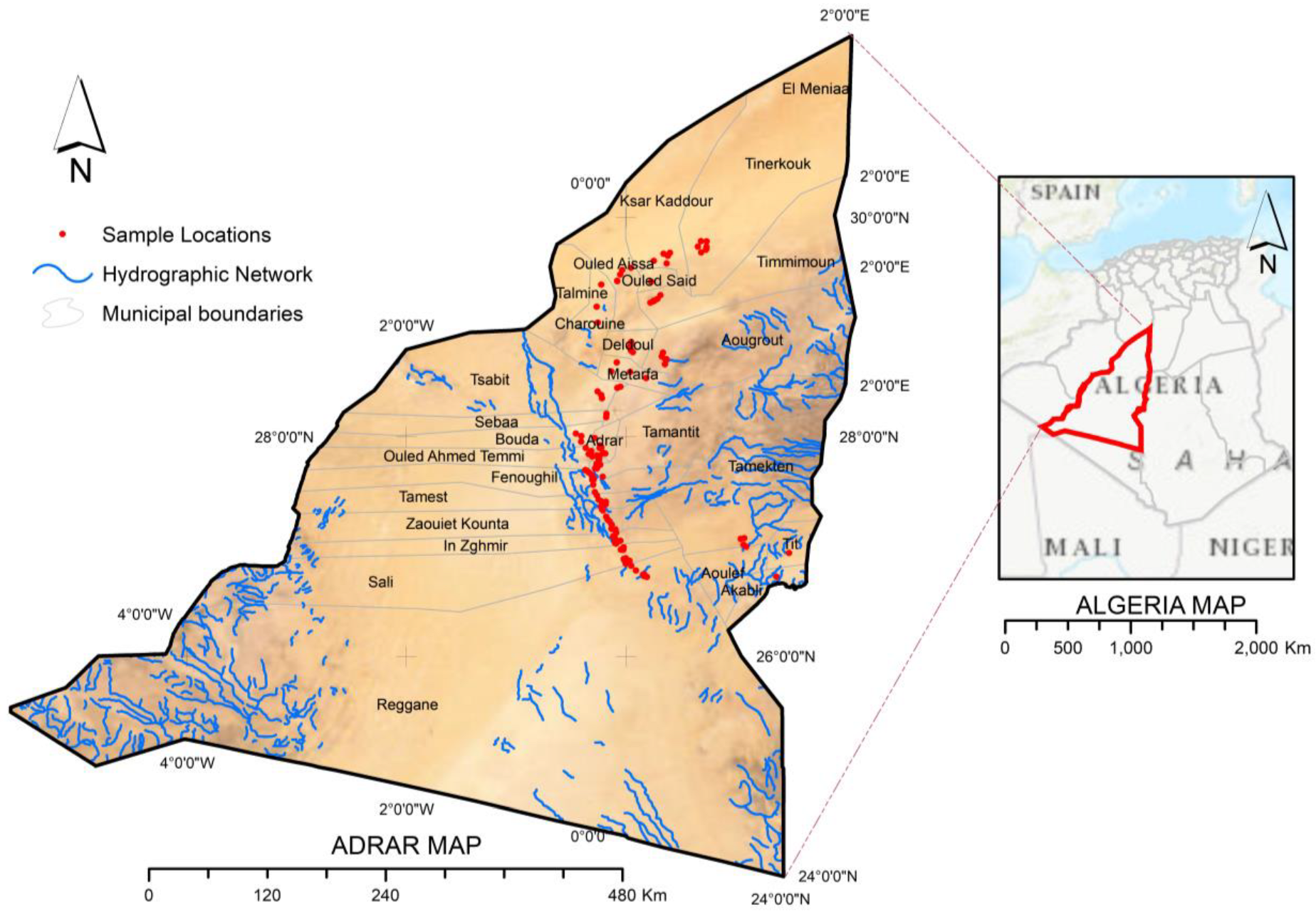
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Irrigation Water Quality Criteria
2.3.1. Suitability Indices for Irrigation
2.3.2. Irrigation Water Quality Index (IWQI)
2.4. Classification Learner
2.4.1. Support Vector Machine (SVM) Classifier
2.4.2. Weighted K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) Classifier
- The value of the variable k, which expresses the number of neighbors, is determined.
- The distances between a new point and those in the dataset are calculated.
- After arranging the points according to the minimum distance calculated in the previous step, the number of adjacent ones is calculated.
- The class for the neighbors is defined.
- Finally, the class with the most neighbors is the expected class for this point.
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Composition of the Study Area
3.2. Irrigation Water Quality Results
3.3. Artificial Intelligence
3.3.1. SVM Results for Standardized Data
3.3.2. SVM Results for Normalized Data
3.3.3. SVM Results for Raw Data
3.3.4. KNN Results for Normalized Data
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rao, N.S.; Dinakar, A.; Sravanthi, M.; Kumari, B.K. Geochemical characteristics and quality of groundwater evaluation for drinking, irrigation, and industrial purposes from a part of hard rock aquifer of South India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 31941–31961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrudey, S.E.; Hrudey, E.J.; Pollard, S.J. Risk management for assuring safe drinking water. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmunds, W.M. Renewable and non-renewable groundwater in semi-arid and arid regions. In Developments in Water Sciece; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 50, pp. 265–280. [Google Scholar]
- Mays, L.W. Groundwater resources sustainability: Past, present, and future. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 4409–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oweis, T.; Hachum, A. Water harvesting and supplemental irrigation for improved water productivity of dry farming systems in West Asia and North Africa. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S.S.; Li, G.; Andersen, M.N.; Liu, F. Biochar enhances yield and quality of tomato under reduced irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 138, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besser, H.; Mokadem, N.; Redhouania, B.; Rhimi, N.; Khlifi, F.; Ayadi, Y.; Omar, Z.; Bouajila, A.; Hamed, Y. GIS-based evaluation of groundwater quality and estimation of soil salinization and land degradation risks in an arid Mediterranean site (SW Tunisia). Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Groves, C.; Yuan, D.; Kambesis, P. Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the groundwater quality in the Nandong karst underground river system in Yunan, China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2009, 109, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerselvam, B.; Ravichandran, N.; Kaliyappan, S.P.; Karuppannan, S.; Bidorn, B. Quality and Health Risk Assessment of Groundwater for Drinking and Irrigation Purpose in Semi-Arid Region of India Using Entropy Water Quality and Statistical Techniques. Water 2023, 15, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, T.M.; Yaseen, Z.M. A survey on river water quality modelling using artificial intelligence models: 2000–2020. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124670. [Google Scholar]
- Babiker, I.S.; Mohamed, M.A.; Hiyama, T. Assessing groundwater quality using GIS. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 699–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrinley, J.R.; Berkowitz, S.T.; Zakria, D.; Totten, D.J.; Kurtulus, M.; Drolet, B.C. Lessons from operations management to combat the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Med. Syst. 2020, 44, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Li, Q.; Khan, S.; Khalaf, O.I. Urban water resource management for sustainable environment planning using artificial intelligence techniques. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 86, 106515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, K.; Doshi, A.; Patel, P. Intelligent irrigation system using artificial intelligence and machine learning: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 6, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Scholz, M.; Ali, M.; Gad, M.; Elsayed, S.; Khadr, M.; Hussein, H.; Ibrahim, H.H.; Eid, M.H. Evaluation and prediction of groundwater quality for irrigation using an integrated water quality indices, machine learning models and GIS approaches: A representative case study. Water 2023, 15, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, M.; Qin, R.; Mao, X. A review on machine learning, artificial intelligence, and smart technology in water treatment and monitoring. Water 2022, 14, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Sihag, P.; Singh, K. Modelling of impact of water quality on infiltration rate of soil by random forest regression. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2017, 3, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, W.C.; Bahadori, A.; Zhang, J.; Ahmad, Z. Prediction of water quality index (WQI) using support vector machine (SVM) and least square-support vector machine (LS-SVM). Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2021, 19, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Yan, J.; Gao, C.; Yang, S. Prediction of water quality time series data based on least squares support vector machine. Procedia Eng. 2012, 31, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Dandy, G.C.; Maier, H.R. Protocol for developing ANN models and its application to the assessment of the quality of the ANN model development process in drinking water quality modelling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 54, 108–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdour, A.; Jodar-Abellan, A.; Pardo, M.Á.; Ghoneim, S.S.; Hussein, E.E. Designing Efficient and Sustainable Predictions of Water Quality Indexes at the Regional Scale Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Water 2022, 14, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaagai, A.; Aouissi, H.A.; Bencedira, S.; Hinge, G.; Athamena, A.; Haddam, S.; Gad, M.; Elsherbiny, O.; Elsayed, S.; Eid, M.H. Application of Water Quality Indices, Machine Learning Approaches, and GIS to Identify Groundwater Quality for Irrigation Purposes: A Case Study of Sahara Aquifer, Doucen Plain, Algeria. Water 2023, 15, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samtio, M.S.; Rajper, K.H.; Mastoi, A.S.; Sadaf, R.; Rajper, R.H.; Hakro, A.A.; Agheem, M.H.; Lanjwani, M.F. Hydrochemical assessment of groundwater from taluka Dahili, Thar Desert, Pakistan, for irrigation purpose using water quality indices. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 103, 2368–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.; Rahman, M.M.; Nguyen, N.C.; Le Vo, P.; Le Van, T.; Ngo, H. Assessment of surface water quality using the water quality index and multivariate statistical techniques—A case study: The upper part of Dong Nai river basin, Vietnam. J. Water Sustain. 2017, 7, 225–245. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.K.; Mokhtar, A.; Abdo, A.I. Application of neural network and time series modeling to study the suitability of drain water quality for irrigation: A case study from Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 898–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, A.; Elbeltagi, A.; Gyasi-Agyei, Y.; Al-Ansari, N.; Abdel-Fattah, M.K. Prediction of irrigation water quality indices based on machine learning and regression models. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.T.; Hasan, M.Y.; Monir, M.U.; Biswas, B.K.; Quamruzzaman, C.; Junaid, M.; Samad, M.A.; Rahman, M.M. Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability by applying the geospatial and IWQI techniques for irrigation purposes in the southwestern coastal plain of Bangladesh. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’nassri, S.; El Amri, A.; Nasri, N.; Majdoub, R. Estimation of irrigation water quality index in a semi-arid environment using data-driven approach. Water Supply 2022, 22, 5161–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, H.; Al-Salamah, I.S.; Ghumman, A.R. Development of groundwater quality index using fuzzy-based multicriteria analysis for Buraydah, Qassim, Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 42, 4033–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Rong, S.; Wang, R.; Yu, S. Recent advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning for nonlinear relationship analysis and process control in drinking water treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoui, M.A.; Bentouba, S.; Bourouis, M. The Potential of Solar Thermoelectric Generator STEG for Implantation in the Adrar Region. Alger. J. Renew. Energy Sustain. Dev 2020, 2, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassoud, A.; Khelafi, H.; Mokhtari, A.M.; Bada, A. Evaluation of summer thermal comfort in arid desert areas. Case study: Old adobe building in Adrar (South of Algeria). Build. Environ. 2021, 205, 108140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, A.; Saba, D.; Benmedjahed, M.; Blal, M. An overview on the development of the irrigation system in the province of Adrar (Algeria). Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djamai, M.; Merzouk, N.K. Wind farm feasibility study and site selection in Adrar, Algeria. Energy Procedia 2011, 6, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasri, B.; Kalloum, S.; Benhamza, M.; Taha, A.; Benatiallah, D. Water quality study of the foggaras in the Adrar region (southwest Algeria) using WQI and GIS. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, Y.; Orban, P.; Deschamps, P.; Brouyere, S. Hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics of groundwater in the Continental Intercalaire aquifer system: Insights from Mzab Ridge and surrounding regions, North of the Algerian Sahara. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 34, 100791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gamal, S.A. An assessment of recharge possibility to North-Western Sahara Aquifer System (NWSAS) using environmental isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2011, 398, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boualem, R.; Bachir, A.; Rabah, K. The foggara: A traditional system of irrigation in arid regions. GeoScience Eng. 2014, 60, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyen, Z.; Moore, G.A.; Wrigley, R.J. Soil salinity and sodicity effects of wastewater irrigation in South East Australia. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 99, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdour, A.; Guerine, L.; Allali, M. Assessment of drinking and irrigation water quality using WQI and SAR method in Maâder sub-basin, Ksour Mountains, Algeria. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, L. Classification and Use of Irrigation Waters; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1955.
- Musa, A.I.; Tsubo, M.; Ali-Babiker, I.-E.A.; Iizumi, T.; Kurosaki, Y.; Ibaraki, Y.; El-Hag, F.; Tahir, I.S.; Tsujimoto, H. Relationship of irrigated wheat yield with temperature in hot environments of Sudan. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 145, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şener, Ş.; Varol, S.; Şener, E. Evaluation of sustainable groundwater utilization using index methods (WQI and IWQI), multivariate analysis, and GIS: The case of Akşehir District (Konya/Turkey). J. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 47991–48010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meireles, A.C.M.; Andrade, E.M.d.; Chaves, L.C.G.; Frischkorn, H.; Crisostomo, L.A. A new proposal of the classification of irrigation water. Rev. Ciência Agronômica 2010, 41, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.; Westcot, D. Food, agriculture organization of the United Nations (FAO), water quality for agriculture. Irrig. Drain. Rome Pap. 1994, 29, 77044-2. [Google Scholar]
- El Bilali, A.; Taleb, A. Prediction of irrigation water quality parameters using machine learning models in a semi-arid environment. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2020, 19, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouadri, S.; Elbeltagi, A.; Islam, A.R.M.; Kateb, S. Performance of machine learning methods in predicting water quality index based on irregular data set: Application on Illizi region (Algerian southeast). Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmahamed, Y.; Kherif, O.; Teguar, M.; Boubakeur, A.; Ghoneim, S.S. Accuracy improvement of transformer faults diagnostic based on DGA data using SVM-BA classifier. Energies 2021, 14, 2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. Moisture prediction of transformer oil-immersed polymer insulation by applying a support vector machine combined with a genetic algorithm. Polymers 2020, 12, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, E.; Isazadeh, M.; Samadianfard, S.; Ramli, M.F.; Mosavi, A.; Nabipour, N.; Shamshirband, S.; Hajnal, E.; Chau, K.-W. Groundwater quality assessment for sustainable drinking and irrigation. Sustainability 2019, 12, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, L.; Defaflia, N.; Merghadi, A.; Fehdi, C.; Yunus, A.P.; Dou, J.; Pham, Q.B.; Abdo, H.G.; Almohamad, H.; Al-Mutiry, M. Ground Surface Deformation Analysis Integrating InSAR and GPS Data in the Karstic Terrain of Cheria Basin, Algeria. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.M.; Saravanan, S.; Almohamad, H.; Al Dughairi, A.A.; Abdo, H.G. Effects of Climate Change on Streamflow in the Godavari Basin Simulated Using a Conceptual Model including CMIP6 Dataset. Water 2023, 15, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Parameter | Unit | Min | Max | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mEq/L | 1.07 | 15.10 | 4.90 | 2.11 | |
| mEq/L | 0.65 | 14.63 | 5.52 | 2.56 | |
| mEq/L | 1.52 | 38.70 | 13.03 | 5.93 | |
| mEq/L | 0.15 | 5.26 | 0.65 | 0.47 | |
| mEq/L | 1.97 | 35.21 | 12.37 | 6.06 | |
| mEq/L | 2.08 | 20.83 | 8.35 | 3.59 | |
| mEq/L | 0.75 | 4.35 | 2.60 | 0.49 | |
| mEq/L | 0.12 | 3.02 | 0.74 | 0.41 | |
| EC | µδ/cm | 620.00 | 5920.00 | 2475.75 | 927.00 |
| pH | -- | 7.35 | 8.19 | 7.71 | 0.19 |
| T | °C | 21.3 | 24.8 | 23.4 | 2.62 |
| Parameters | Limiting Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–35 | 35–60 | 60–85 | 85–100 | |
| ) | ||||
| Parameters | SAR | EC | Cl | Na | HCO3 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.189 | 0.211 | 0.194 | 0.204 | 0.202 | 1 |
| Range of IWQI | Irrigation Water State |
|---|---|
| 70–100 | Very good |
| 55–70 | Good |
| 40–55 | Satisfactory |
| 0–40 | Unsuitable |
| Irrigation Water State | Very Good | Good | Satisfactory | Unsuitable | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | 14 | 18 | 32 | 92 | 156 |
| Testing | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 10 |
| EC | Na | HCO3 | Cl | SAR | IWQI | IWQI State |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 83.33 | 122.25 | 75.90 | 92.61 | 94.96 | 93.77 | Very Good |
| 88.55 | 119.71 | 70.00 | 92.61 | 94.58 | 93.08 | Very Good |
| 63.33 | 71.59 | 47.50 | 80.54 | 88.02 | 69.82 | Good |
| 69.67 | 72.68 | 43.61 | 71.39 | 87.97 | 68.81 | Good |
| 51.17 | 40.43 | 50.33 | 39.58 | 75.45 | 51.15 | Satisfactory |
| 43.67 | 30.29 | 58.00 | 27.84 | 77.02 | 47.07 | Satisfactory |
| 40.17 | 12.17 | 37.05 | 27.84 | 73.36 | 37.71 | Unsuitable |
| 36.67 | 1.30 | 62.62 | 27.84 | 60.99 | 37.58 | Unsuitable |
| Name | IWQI | Type | Name | IWQI | Type | Name | IWQI | Type | Name | IWQI | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAA | 93.77 | VG | SAID | 52.25 | St | RH | 38.32 | Us | SALI | 30.78 | Us |
| TAZ | 93.08 | VG | KDR | 52.00 | St | BKR | 38.12 | Us | TAAT | 29.92 | Us |
| TAB | 84.95 | VG | TAMT | 51.15 | St | HMM | 38.00 | Us | ALF2 | 29.67 | Us |
| TIN | 84.15 | VG | MNSR | 47.07 | St | BHH | 37.90 | Us | ISSA2 | 29.42 | Us |
| ASDI | 83.41 | VG | RSL | 46.32 | St | FNL2 | 37.81 | Us | RGN | 28.82 | Us |
| TIL | 81.16 | VG | AMR | 46.18 | St | TILL | 37.71 | Us | CHM | 28.59 | Us |
| TIM | 80.21 | VG | TITAF | 45.60 | St | RBT | 37.58 | Us | FAT | 28.49 | Us |
| KSRH | 73.22 | VG | KBL | 45.52 | St | GHRT | 37.10 | Us | ABR2 | 27.80 | Us |
| TIL | 73.05 | VG | TMT2 | 45.36 | St | KSN | 36.98 | Us | CHRW | 27.55 | Us |
| ABD | 72.27 | VG | KNN | 44.99 | St | HDJD | 36.82 | Us | DRA | 27.55 | Us |
| TIL2 | 72.13 | VG | YCF | 44.74 | St | BAAM | 36.61 | Us | AITM | 27.12 | Us |
| TIB | 71.86 | VG | ABN | 44.35 | St | TEBN | 36.51 | Us | IGOS | 27.01 | Us |
| OUF | 71.04 | VG | FNGL | 43.75 | St | SHL | 36.44 | Us | TIMA | 26.66 | Us |
| SNLGZ | 70.95 | VG | RTB | 43.63 | St | BOR | 36.40 | Us | LAGH | 26.61 | Us |
| AERO | 70.51 | VG | RCHD | 43.28 | St | WHB | 36.12 | Us | AJIR | 26.53 | Us |
| BGM | 70.25 | VG | MHD | 42.96 | St | GBR | 35.81 | Us | GDM | 25.43 | Us |
| TIL3 | 69.82 | Gd | TIMI2 | 42.82 | St | ZGL | 35.57 | Us | NOM | 24.77 | Us |
| TAA | 68.81 | Gd | TID | 42.27 | St | SYCF | 35.44 | Us | BKRI | 24.36 | Us |
| GUR | 68.42 | Gd | AZO | 41.75 | St | SHL | 35.34 | Us | SML | 23.76 | Us |
| MHD | 66.80 | Gd | TIMO | 41.68 | St | ABBO | 35.13 | Us | TKK | 23.40 | Us |
| AKBR | 65.87 | Gd | BSL | 41.48 | St | YHIA | 34.91 | Us | HJMH | 21.67 | Us |
| TZA | 65.72 | Gd | BHH | 41.19 | St | CHTB | 34.90 | Us | BRL | 21.23 | Us |
| ATAR | 65.70 | Gd | AIAN | 41.18 | St | FNFL | 34.69 | Us | TWT | 21.11 | Us |
| BARB | 65.66 | Gd | ADM | 41.09 | St | FTH | 34.61 | Us | AWM | 20.96 | Us |
| MAIZ | 65.36 | Gd | CHRF | 40.57 | St | LHMR | 34.37 | Us | TSFT | 20.39 | Us |
| SBAA | 65.35 | Gd | BNZT | 40.56 | St | TGH | 34.35 | Us | NEFS | 19.06 | Us |
| SLM | 65.06 | Gd | CHKH | 40.53 | St | ZKNT | 34.23 | Us | ZKKR | 18.28 | Us |
| TIL4 | 64.75 | Gd | TNRT | 40.25 | St | MSS | 34.05 | Us | AZRF | 16.21 | Us |
| TIL5 | 64.53 | Gd | TIMI3 | 40.10 | St | TLB | 34.04 | Us | AMS | 15.77 | Us |
| LAA | 64.23 | Gd | MNC | 39.90 | Us | HFR | 33.79 | Us | CHRW | 14.88 | Us |
| TMR | 63.96 | Gd | ZGH | 39.84 | Us | TMR | 33.60 | Us | AWLF | 14.65 | Us |
| TYB | 60.48 | Gd | IKKIS | 39.84 | Us | NZA | 33.54 | Us | DGHA | 14.65 | Us |
| YAK | 57.47 | Gd | MHD | 39.77 | Us | KID | 33.50 | Us | TLAL | 13.26 | Us |
| KORT | 57.13 | Gd | AKR | 39.67 | Us | SMD | 33.43 | Us | ARR | 11.94 | Us |
| ISSA | 56.55 | Gd | TKN | 39.60 | Us | TIAF | 33.29 | Us | TSAM | 10.34 | Us |
| TIMI | 55.89 | Gd | AWLF | 39.59 | Us | ABB2 | 32.60 | Us | HBL | 9.68 | Us |
| KABR | 54.93 | St | MSTR | 39.47 | Us | ABLI | 32.54 | Us | TLH | 9.68 | Us |
| MRG | 54.43 | St | ALM | 39.14 | Us | MCN | 32.36 | Us | MLK | 8.73 | Us |
| ARPT2 | 53.66 | St | RKIA | 38.91 | Us | ZGLF | 32.33 | Us | LAAR | 7.48 | Us |
| BLKB | 52.83 | St | TRR | 38.83 | Us | SALI | 32.04 | Us | TRR | 3.64 | Us |
| BALI | 52.78 | St | MLD | 38.63 | Us | AGHIL | 31.19 | Us | |||
| TIT | 52.76 | St | TDM | 38.46 | Us | BGL | 30.90 | Us |
| Training Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Classifier | Raw Data | Standardized | Normalized |
| Cubic KNN | 84.6 | 85.9 | 85.3 |
| Fine KNN | 89.1 | 89.1 | 91 |
| Medium KNN | 86.5 | 85.9 | 87.2 |
| Cosine KNN | 82.7 | 84 | 83.3 |
| Corase KNN | 59 | 59 | 59 |
| Weighted KNN | 92.3 | 92.3 | 92.9 |
| Corase tree | 89.1 | 86.5 | 89.1 |
| Medium tree | 86.5 | 84 | 87.2 |
| Quadratic discriminant | 88.5 | 85.3 | 88.5 |
| Linear discriminant | 88.5 | 88.5 | 89.7 |
| Ensemble bagged trees | 87.8 | 89.7 | 90.4 |
| Ensemble boosted trees | 59 | 59 | 59 |
| Ensemble subspace KNN | 86.5 | 85.3 | 88.5 |
| Ensemble subspace discriminant | 87.8 | 87.2 | 87.2 |
| Linear SVM | 92.9 | 91 | 92.3 |
| Ensemble RUSBoosted trees | 88.5 | 87.8 | 89.7 |
| Fine Gaussian SVM | 76.3 | 75.6 | 75.6 |
| Cubic SVM | 92.3 | 92.9 | 94.2 |
| Medium Gaussian SVM | 92.3 | 90.4 | 92.9 |
| Quadratic SVM | 92.3 | 89.1 | 91.7 |
| Coarse Gaussian SVM | 83.3 | 82.1 | 82.1 |
| EC | Na | HCO3 | Cl | SAR | IWQI | Actual Water Type | 1* | 2* | 3* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 69.33 | 67.61 | 61.15 | 78.43 | 85.43 | 72.13 | Very Good | Very Good | Very Good | Very Good |
| 72.33 | 59.28 | 65.50 | 86.80 | 76.37 | 71.86 | Very Good | Very Good | Very Good | Very Good |
| 60.67 | 57.46 | 49.00 | 80.31 | 81.21 | 65.35 | Good | Good | Good | Good |
| 70.00 | 52.03 | 48.85 | 83.12 | 72.39 | 65.06 | Good | Good | Good | Good |
| 53.00 | 26.67 | 64.00 | 51.31 | 70.52 | 52.83 | Satisfactory | Satisfactory | Satisfactory | Satisfactory |
| 56.33 | 28.48 | 89.67 | 27.84 | 61.23 | 52.78 | Satisfactory | Satisfactory | Satisfactory | Satisfactory |
| 52.67 | 41.16 | 58.69 | 33.71 | 78.58 | 52.76 | Satisfactory | Satisfactory | Satisfactory | Satisfactory |
| 48.33 | 19.42 | 34.10 | 27.84 | 67.16 | 39.14 | Unsuitable | Unsuitable | Unsuitable | Unsuitable |
| 40.00 | −13.19 | 70.00 | 27.84 | 72.07 | 38.91 | Unsuitable | Unsuitable | Unsuitable | satisfactory |
| 44.67 | 12.17 | 42.95 | 27.84 | 67.98 | 38.83 | Unsuitable | Unsuitable | Unsuitable | Unsuitable |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Derdour, A.; Abdo, H.G.; Almohamad, H.; Alodah, A.; Al Dughairi, A.A.; Ghoneim, S.S.M.; Ali, E. Prediction of Groundwater Quality Index Using Classification Techniques in Arid Environments. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9687. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129687
Derdour A, Abdo HG, Almohamad H, Alodah A, Al Dughairi AA, Ghoneim SSM, Ali E. Prediction of Groundwater Quality Index Using Classification Techniques in Arid Environments. Sustainability. 2023; 15(12):9687. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129687
Chicago/Turabian StyleDerdour, Abdessamed, Hazem Ghassan Abdo, Hussein Almohamad, Abdullah Alodah, Ahmed Abdullah Al Dughairi, Sherif S. M. Ghoneim, and Enas Ali. 2023. "Prediction of Groundwater Quality Index Using Classification Techniques in Arid Environments" Sustainability 15, no. 12: 9687. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129687
APA StyleDerdour, A., Abdo, H. G., Almohamad, H., Alodah, A., Al Dughairi, A. A., Ghoneim, S. S. M., & Ali, E. (2023). Prediction of Groundwater Quality Index Using Classification Techniques in Arid Environments. Sustainability, 15(12), 9687. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129687









