Prevalence of Enterovirus in Water Consumed in Rural Areas in a State in the Midwest Region of Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
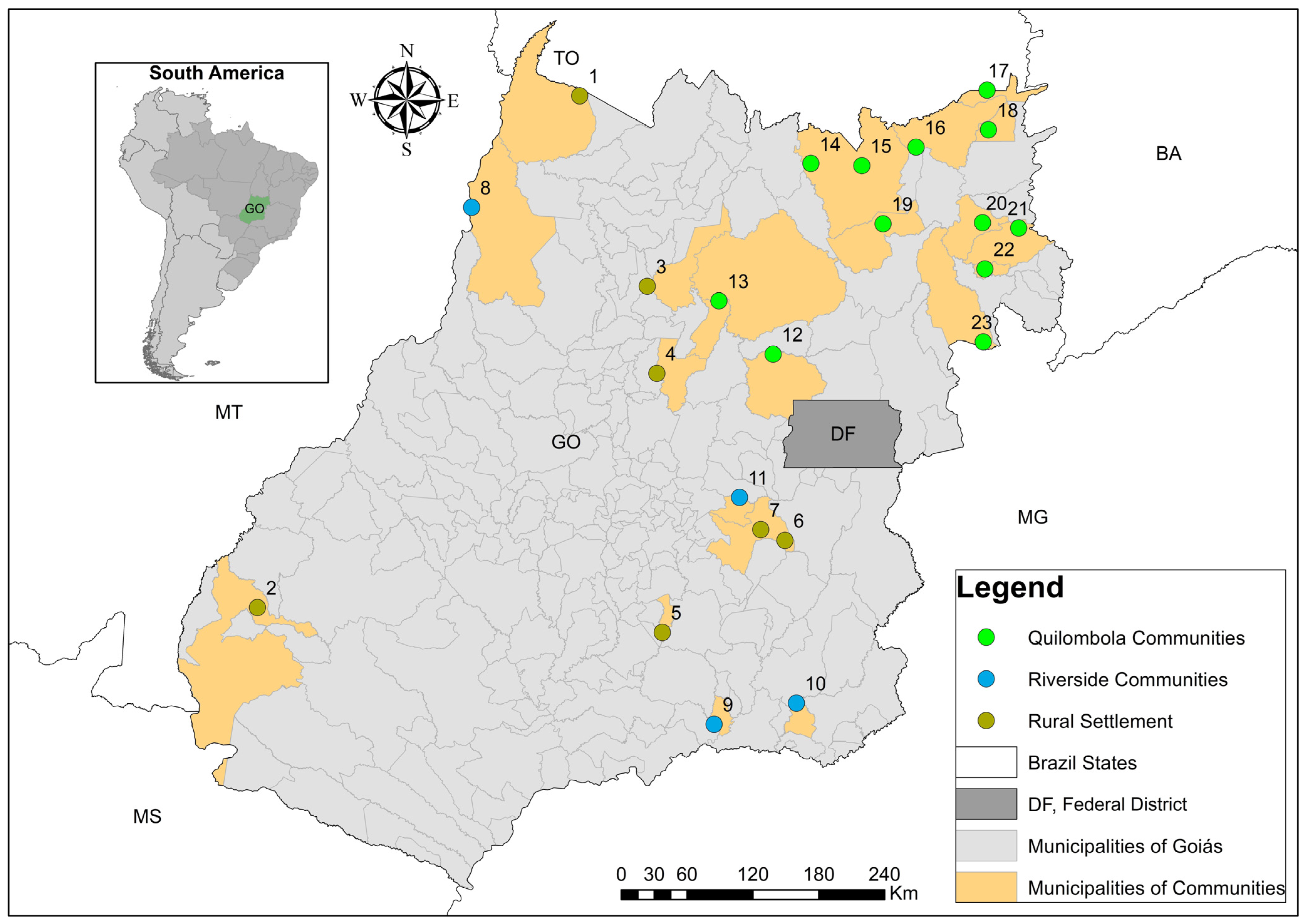
2.1. Sampling Methodology and Site Description
2.2. Viral Concentration and Molecular Analysis
2.2.1. Extraction of Viral Nucleic Acids—Sybr Green®
2.2.2. Extraction of Viral Nucleic Acids—Taqman®
2.2.3. Viral Controls
2.2.4. Detection and Quantification of Enterovirus Using the Sybr Green® System
RT-qPCR
2.2.5. Detection and Quantification of Enteric Viruses Using the TaqMan® System
cDNA Synthesis for the TaqMan® System
2.2.6. qPCR
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Sanitation Conditions
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- BRASIL. Good Practices in Water Supply: Procedures for Minimizing Health Risks, 1st ed.; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2006; pp. 1–251. ISBN 85-334-1243-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, R.; Suhogusoff, A.; Marcellini, S.S.; Villar, P.C.; Marcellini, L. Groundwater and Its Environmental and Socioeconomic Importance for Brazil, 1st ed.; Instituto de Geociências/USP: São Paulo, Brasil, 2019; pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRASIL. Basic Course on Surveillance of the Quality of Water for Human Consumption: Module II: Water Supply, 1st ed.; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2020; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Fortes, A.C.C.; Barrocas, P.R.G.; Kligerman, D.C. Water quality surveillance and the role of information to ensure access. Saúde Debate 2019, 43, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANA. Situation of Water Resources in Brazil: Annual Report, 1st ed.; Agência Nacional de Águas: Brasilia, Brasil, 2018; pp. 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Mendonça, F.C.; Almeida, R.S.; de Oliveira, D.F.; Santos, A.G. Evaluation of the quality of water for human consumption in an groundwater source in the Recôncavo region of Bahia. Rev. Águas Subterrâneas 2019, 33, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, L.N.; de Araújo, S.M.S. Water quality in rural areas: Bacteriological and physical-chemical analysis of the waters of the stone tanks of the communities KM 21 (Campina Grande) and Pedra Redonda (Pocinhos). Rev. Bras. Geogr. Fís 2016, 9, 1737–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 1 in 3 People Globally Do Not Have Access to Safe Drinking Water—UNICEF, WHO. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/18-06-2019-1-in-3-people-globally-do-not-have-access-to-safe-drinking-water-unicef-who (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Calgaro, H.F.; Filho, J.B. Domestic Sewage in Rural. Areas: Treatment and Implications for Human Health, 253rd ed.; Coordenadoria de Desenvolvimento rural Sustentável: São Paulo, Brazil, 2020; pp. 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Global WASH (Water, Sanitation & Hygiene) Fast Facts. US. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/healthywater/global/wash_statistics.html#:~:text=3.6%20billion%20people%2C%20nearly%20half,million%20people%20practice%20open%20defecation (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Gibson, K.E.; Opryszko, M.C.; Schissler, J.T.; Guo, Y.; Schwab, K.J. Evaluation of Human Enteric Viruses in Surface Water and Drinking Water Resources in Southern Ghana. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 84, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, A.L.; Brasil, A.L.; Madrid, F.J.P.L.; Figueiredo, I.C.S.; Schneider, J.; Cruz, L.M.O.; Duarte, N.C.; Fernandes, P.M.; Coasaca, R.L.; Garcia, R.S.; et al. Treatment of Domestic Sewage in Isolated Communities: Reference for Choosing Solutions, 1st ed.; Biblioteca da Área de Engenharia e Arquitetura: Campinas, Brazil, 2018; pp. 1–153. ISBN 978-85-85783-94-5. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.N. Microbiota and enteric viruses infection. Med. Microecol. 2020, 3, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouseettine, R.; Hassou, N.; Bessi, H.; Ennaji, M.M. Waterborne Transmission of Enteric Viruses and Their Impact on Public Health. In Emerging and Reemerging Viral Pathogens—Volume 1: Fundamental and Basic Virology Aspects of Human, Animal and Plant Pathogens, 1st ed.; Ennaji, M.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 907–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, T.T.; Lipp, E.K. Enteric Viruses of Humans and Animals in Aquatic Environments: Health Risks, Detection, and Potential Water Quality Assessment Tools. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Ver. 2005, 69, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiulia, N.M.; Gonzalez, R.; Thompson, H.; Aw, T.G.; Rose, J.B. Quantifcation and Trends of Rotavirus and Enterovirus in Untreated Sewage Using Reverse Transcription Droplet Digital PCR. Food Environ. Virol. 2021, 13, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioffi, B.; Monini, M.; Salamone, M.; Pellicanò, R.; Di Bartolo, I.; Guida, M.; La Rosa, G.; Fusco, G. Environmental surveillance of human enteric viruses in wastewaters, groundwater, surface water and sediments of Campania Region. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 38, 101368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upfold, N.S.; Luke, G.A.; Knox, C. Occurrence of Human Enteric Viruses in Water Sources and Shellfish: A Focus on Africa. Food Environ. Virol. 2021, 13, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Emerging Issues in Water and Infectious Disease; WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- Marcheggiani, S.; D’Ugo, E.; Puccinelli, C.; Giuseppetti, R.; D’Angelo, A.M.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Spurio, R.; Medlin, L.K.; Guillebault, D.; Weigel, W.; et al. Detection of Emerging and Re-Emerging Pathogens in Surface Waters Close to an Urban Area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 5505–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, A. Human enteric viruses in the water environment: A minireview. Int. Microbiol. 1998, 1, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Tavares, M.T.; Cardoso, D.d.D.d.P.; Brito, W.M.E.D. Waterborne enteric viruses: Microbiological and water quality control aspects. Rev. Patol. Trop. 2005, 34, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Canada. Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality: Guideline Technical Document—Enteric Viruses, 2nd ed.; Health Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2019; pp. 1–123.
- Faccin-Galhardi, L.C.; Lopes, N.; Espada, S.F.; Linhares, R.E.C.; Pelayo, J.S.; Nozawa, C. Waterborne Viral Pathogens: Detection, Control and Monitoring of Water Quality for Human Consumption. Virus Rev. Res. 2013, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, P. Enteroviruses. Medicine 2017, 45, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ganesh, A. Water quality indicators: Bacteria, coliphages, enteric viruses. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2013, 23, 484–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staggemeier, R.; Bortoluzzi, M.; Heck, T.M.S.; da Luz, R.B.; Fabres, R.B.; Soliman, M.C.; Rigotto, C.; Baldasso, N.A.; Spilki, F.R.; Almeida, S.E.M. Animal and human enteric viruses in water and sediment samples from dairy farms. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 152, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajtar, B.; Majek, M.; Polánski, L.; Polz-Dacewicz, M. Enteroviruses in water environment—A potential threat to public health. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2008, 15, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Lugo, D.; Krogstad, P. Enteroviruses in the Early 21st Century: New Manifestations and Challenges. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2016, 28, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comerlato, J.; Oliveira, L.K.; Spilki, F.R. Enteroviruses as indicators of water quality. Rev. Bras. Biociênc. 2011, 9, 114–125. [Google Scholar]
- Pachepsky, Y.; Shelton, D.; Dorner, S.; Whelan, G. Can E. coli or thermotolerant coliform concentrations predict pathogen presence or prevalence in irrigation waters? Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haramoto, E.; Katayama, H.; Oguma, K.; Ohgaki, S. Application of cation-coated filter method to detection of noroviruses, enteroviruses, adenoviruses, and torqueteno viruses in the Tamagawa River in Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2403–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, H.D.; Anunciação, C.E.; Santos, S.F.O.; García-Zapata, M.T.A. Virological analysis of water quality: A review of viral concentration and detection methodologies. Rev. Bras. Biociênc. 2011, 9, 405–415. [Google Scholar]
- Haramoto, E.; Kitajima, M.; Hata, A.; Torrey, J.R.; Masago, Y.; Sano, D.; Katayama, H. A review on recent progress in the detection methods and prevalence of human enteric viruses in water. Water Res. 2018, 135, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; Serrano-Heras, G.; Castaño, M.J.; Solera, J. Real-time PCR detection chemistry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 439, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, S.; Suarez, E.R.; Pinhal, M.A.S. Real-time PCR and RT-PCR technology and its applications in the medical field. Rev. Bras. Med. 2010, 67, 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- TaqMan vs. SYBR Chemistry for Real-Time PCR. Thermo Fisher Scientific. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/br/en/home/life-science/pcr/real-time-pcr/real-time-pcr-learning-center/real-time-pcr-basics/taqman-vs-sybr-chemistry-real-time-pcr.html (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Tajadini, M.; Panjehpour, M.; Javanmard, S.H. Comparison of SYBR Green and TaqMan methods in quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of four adenosine receptor subtypes. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2014, 3, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, F.R. Application of Viral concentration Methodology for Astrovirus Detection in Environmental Waters. Master’s Thesis, Instituto Nacional de Controle de Qualidade em Saúde (INCQS/Fiocruz), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, L.R.; de Almeida, P.F.; Matos, J.B.T.L. Prospection of molecular techniques (REal-Time PCR and FISH) to be used in environmental samples for research in the area of biotechnology. Cad. Prospec 2016, 9, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fongaro, G.; Silva, H.D.; Elmahdy, E.M.; Magri, M.E.; Schissi, C.D.; Moreira, M.; Lanna, M.C.S.; Silveira-Lacerda, E.P.; Barardi, C.R.M. Enteric viruses as contaminants and bioindicators in environmental samples. Virus Rev. Res. 2015, 20, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, H.; Shimasaki, A.; Ohgaki, S. Development of a virus concentration method and its application to detection of enterovirus and Norwalk virus from coastal seawater. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchia, A.D.; Fleck, J.D.; Comerlato, J.; Kluge, M.; Bergamaschi, B.; da Silva, J.V.S.; da Luz, R.B.; Teixeira, T.F.; Garbinatto, G.N.; Oliveira, D.V.; et al. First description of Adenovirus, Enterovirus, Rotavirus and Torqueteno virus in water samples collected from the Arroio Dilúvio, Porto Alegre, Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2012, 72, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.L.; Sobsey, M.D.; Sangermano, L.R.; Palmer, C.J. Simple method of concentrating enteroviruses and hepatitis A virus from sewage and ocean water for rapid detection by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 3488–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalize, P.S. Participatory Technical Diagnosis of the Vazante Community: Divinópolis de Goiás, 1st ed.; Cegraf UFG: Goiânia, Brazil, 2020; pp. 1–225. [Google Scholar]
- Apostol, L.N.G.; Imagawa, T.; Suzuki, A.; Masago, Y.; Lupisan, S.; Olveda, R.; Oshitani, H. Genetic diversity and molecular characterization of enteroviruses from sewage-polluted urban and rural rivers in the Philippines. Virus Genes 2012, 45, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Dhole, T.N. Assessment of enteroviruses from sewage water and clinical samples during eradication phase of polio in North India. Virol. J. 2018, 157, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilki, F.R.; Luz, R.B.D.; Fabres, R.B.; Soliman, M.C.; Kluge, M.; Fleck, J.D.; Rodrigues, M.T.; Comerlato, J.; Cenci, A.; Cerva, A.; et al. Detection of human adenovirus, rotavirus and enterovirus in water samples collected on dairy farms from Tenente Portela, Northwest of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, F.S.; Scalize, O.S.; Gabriel, E.F.M.; Gomes, R.P.; Gama, A.R.; Demoliner, M.; Spilki, F.R.; Vieira, J.D.G.; Carneiro, L.C. Escherichia coli, Species C Human Adenovirus, and Enterovirus in Water Samples Consumed in Rural Areas of Goiás, Brazil. Food Environ. Virol. 2021, 14, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giglio, O.; Caggiano, G.; Bagordo, F.; Barbuti, G.; Brigida, S.; Lugoli, F.; Grassi, T.; La Rosa, G.; Lucentini, L.; Uricchio, V.F.; et al. Enteric Viruses and Fecal Bacteria Indicators to Assess Groundwater Quality and Suitability for Irrigation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradbury, K.R.; Borchardt, M.A.; Gotkowitz, M.; Spencer, S.K.; Zhu, J.; Hunt, R.J. Source and Transport of Human Enteric Viruses in Deep Municipal Water Supply Wells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4096–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.J. Enterically infecting viruses: Pathogenicity, transmission and significance for food and waterborne infection. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 98, 1354–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FUNASA. Funasa’s Manual of Good Practices in Sanitation Management in Rural Areas, 1st ed.; Ministério da Saúde: Brasilia, Brazil, 2019; pp. 1–77. [Google Scholar]
- John, D.E.; Rose, J.B. Review of Factors Affecting Microbial Survival in Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7345–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, L.A.; Filho, A.N.; Junior, O.D.R.; Ferreira, F.L.A.; Barros, L.S.S. Drinking water as a health risk factor in rural properties. Rev. Saude Publica 2003, 37, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piranha, J.M.; Pacheco, A. Viruses in groundwater used to supply rural communities in the municipality of São José do Rio Preto (SP). Águas Subterrâneas 2004, 1–15. Available online: https://repositorio.usp.br/item/002131611 (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- da Luz, R.B.; Staggemeier, R.; Fratta, L.X.S.; Longo, L.; Schutz, R.; Soliman, M.C.; Kluge, M.; Fabres, R.B.; Schenkel, G.C.; Bruni, F.P.; et al. Viral and bacterial contamination in groundwater in the outcropping portion of the Guaraní Aquifer, municipality of Ivoti, RS. Rev. Ambient. Agua 2017, 12, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- One Health Office Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/onehealth/who-we-are/one-health-office-fact-sheet.html?CDC_AA_refVal=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.cdc.gov%2Fonehealth%2Fmultimedia%2Ffactsheet.html (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- IBGE. 2017 Agricultural Census—Preliminary Results, 1st ed.; Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2017; pp. 1–108. [Google Scholar]
- Vale, G.B.d.; Junior, H.C.R.; Scalize, P.S. Service and precariousness of sanitary sewage in rural communities in the state of Goiás, Brazil. Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2022, 27, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizzolo, M.; Gea, M.; Carraro, E.; Gilli, G.; Bonetta, S.; Pignata, C. Occurrence of human pathogenic viruses in drinking water and in its sources: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 132, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, S.; Griebler, C. Pathogenic Microrganims and Viruses in Groundwater, 1st ed.; Acatech: Munich, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Borchardt, M.A.; Bradbury, K.R.; Gotkowitz, M.B.; Cherry, J.A.; Parker, B.L. Human enteric viruses in groundwater from a confined bedrock aquifer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6606–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, J.P.R.; Aldous, P.; Bunting, S.Y.; McNally, S.; Townsend, B.R.; Barnett, M.J.; Harding, T.; Ragione, R.M.L.; Stuart, M.E.; Tipper, H.J.; et al. Seasonality of enteric viruses in groundwater-derived public water sources. Water Res. 2021, 207, 117813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, E.; Glennerster, R.; Hussam, R. Throwing the Baby out with the Drinking Water: Unintended Consequences of Arsenic Mitigation Efforts in Bangladesh; Working Paper; Department of Economics, Harvard University: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, V.; Islam, M.S.; Yunus, M.; Ali, M.T.; Khan, A.F.; Alam, N.; Faruque, A.S.G.; Bell, G.; Sobsey, M.; Emch, M. Deep tubewell microbial water quality and access in arsenic mitigation programs in rural Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verheyen, J.; Timmen-Wego, M.; Laudien, R.; Boussaad, I.; Sen, S.; Koc, A.; Uesbeck, A.; Mazou, F.; Pfister, H. Detection of adenoviruses and rotaviruses in drinking water sources used in rural areas of Benin, West Africa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 2798–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotkowitz, M.B.; Bradbury, K.R.; Borchardt, M.A.; Zhu, J.; Spencer, S.K. Effects of Climate and Sewer Condition on Virus Transport to Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8497–8504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, H.M.; McGinnis, S.; Blunt, R.; Stokdyk, J.; Wu, J.W.; Cagle, A.; Denno, D.M.; Spencer, S.; Firnstahl, A.; Borchardt, M.A. Septic Systems and Rainfall Influence Human Fecal Marker and Indicator Organism Occurrence in Private Wells in Southeastern Pennsylvania. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3159–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddle, E.S.; Mager, S.M.; Nel, E.L. The suitability of shallow hand dug wells for safe water provision in sub-Saharan Africa: Lessons from Ndola, Zambia. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 57, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, H.T.L.; Baumann, L.R.F.; Scalize, P.S. A Contamination Predictive Model for Escherichia coli in Rural Communities Dug Shallow Wells. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.; Borchardt, M.A.; Kieke, J.B.A.; Dunfield, K.; Parker, B.L. Virus occurrence in private and public wells in a fractured dolostone aquifer in Canada. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 1117–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRASIL. Annex XX of Consolidation Ordinance No. 5 of October 3, 2017: Control and Surveillance of the Quality of Water for Human Consumption and Its Potability Standard; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- National Sanitation Information System (SNIS). Thematic Diagnosis: Water and Sewage Services, 1st ed.; Ministério do Desenvolvimento Regional: Brasília, Brazil, 2021; pp. 1–91. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos, W.B.; Bernardino, F.G.; Silva, L.L.S.; Ferreira, W.B. Alternative collective water supply systems in Brazil. In CONAPESC, 5th ed.; Realize Editora: Campina Grande, Brazil, 2021; pp. 1047–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Scalize, P.S.; Bezerra, N.R. Rural basic sanitation. In Specialization Course in Sanitation and Environmental Health: Rural Basic Sanitation, 1st ed.; CEGRAF UFG: Goiânia, Brazil, 2020; pp. 1–254. [Google Scholar]
- BRASIL. GM/MS Ordinance No. 888, of May 4, 2021: Amends Annex XX of Consolidation Ordinance GM/MS No. 5, of September 28, 2017, to Provide for Water Quality Control and Surveillance Procedures for Human Consumption and Its Potability Standard; Diário Oficial da União, Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wurtzer, S.; Prevost, B.; Lucas, F.S.; Moulin, L. Detection of enterovirus in environmental waters: A new optimized method compared to commercial real-time RT-qPCR kits. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 209, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Zheng, H.; Yuan, F.; Zhu, H.; Kuang, D.; Shen, Z.; Lu, Y.; Yuan, Z. Comparative Study of Two Methods of Enteric Virus Detection and Enteric Virus Relationship with Bacterial Indicator in Poyang Lake, Jiangxi, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, B.M.; Chen, C.H.; Wan, M.T.; Chang, P.J.; Fan, C.W. Detection and identification of enteroviruses from various drinking water sources in Taiwan. J. Hydrol. 2009, 365, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller-Wegener, U. Interaction of humic substances with biota. In Humic Substances and Their Role in the Environment; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1988; pp. 179–192. [Google Scholar]
- Radstrom, P.; Lofstrom, C.; Lovenklev, M.; Knutsson, R.; Wolffs, P. Strategies for overcoming PCR inhibition. CSH Protoc. 2008, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, M.; Lobos, S.; Lorca, M.; Navarrete, E. Enterovirus in natural waters of Valparaíso: A methodological proposal for its analysis. Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanogr. 2009, 44, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipper, H.; Buta, C.; LaÈmmle, K.; Brunner, H.; Bernhagen, J.; Vitzthum, F. Mechanisms underlying the impact of humic acids on DNA quantification by SYBR Green I and consequences for the analysis of soils and aquatic sediments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Y.; Ouda Kadadou, D.; Banat, F.; Naddeo, V.; Alsafar, H.; Yousef, A.F.; Barceló, D.; Hasan, S.W. Detection and removal of waterborne enteric viruses from wastewater: A comprehensive review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, I.A.; Jurzik, L.; Stango, A.; Sure, K.; Uberla, K.; Wilhelm, M. Detection of human viruses in rivers of a densily populated area in Germany using a virus adsorption elution method optimized for PCR analyses. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2657–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Virus | Target Gene | Name | Sequence | Polarity | Position | Ta * (°C) | Amplicon (pb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EV | 5’UTR | ENT-F1 | 5′-GATGAACCGCAGCGTCAA-3′ | Sense | 443–459 a | 62 | 116 |
| ENT-F2 | 5′-ACACGGACACCCAAAGTAG-3′ | Reverse | 541–559 b |
| Source Type | Source Subtype | Quantity of Samples | Enterovirus | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sybr Green® | TaqMan® | |||||||||
| WSS | IAS | Total | WSS | IAS | Total | WSS | IAS | Total | ||
| Groundwater | Shallow tubular wells | 1 | 30 | 31 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Deep tubular wells | 11 | 16 | 27 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Shallow dug wells | 0 | 47 | 47 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Spring | 3 | 14 | 17 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 15 | 107 | 122 | 1 | 6 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Surface water | Rivers, streams | 0 | 17 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Water truck (river) (1) | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 2 | 17 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Cistern | Rainwater | 0 | 19 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 17 | 143 | 160 | 1 | 6 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Community Name | ID | Water Supply Source | Domestic Sewage Disposal Site | Distance from the Source of Contamination to the Source of Water Supply | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domestic Sewage | Barn | Pigsty | Chicken Coop | ||||
| João de Deus | 9 | Shallow tubular well | Rudimentary cesspool | 100 | 132 | 77 | 128 |
| Olhos D’Água | 4 | Shallow tubular well | Rudimentary cesspool | LD | NA | NA | NA |
| Olhos D’Água | 7 | Shallow tubular well | Rudimentary cesspool | 30 | NA | NA | 24 |
| Itajá 2 | 15 | Shallow dug well | Septic tank | 24 | 43 | 28 | 39 |
| Lageado | 4 | Shallow dug well | Rudimentary cesspool | 18 | 7 | 28 | 8 |
| Canabrava | 21 | Spring | Rudimentary cesspool | LD | NA | NA | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bordoni, G.P.; Barbosa, L.C.G.; Oliveira, T.R.; Lima, F.S.; Goes, V.M.; Estrela, M.C.; de Souza, P.Z.; de Oliveira Santos, M.; de Souza, G.R.L.; Vieira, J.D.G.; et al. Prevalence of Enterovirus in Water Consumed in Rural Areas in a State in the Midwest Region of Brazil. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9886. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15139886
Bordoni GP, Barbosa LCG, Oliveira TR, Lima FS, Goes VM, Estrela MC, de Souza PZ, de Oliveira Santos M, de Souza GRL, Vieira JDG, et al. Prevalence of Enterovirus in Water Consumed in Rural Areas in a State in the Midwest Region of Brazil. Sustainability. 2023; 15(13):9886. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15139886
Chicago/Turabian StyleBordoni, Graziela Picciola, Lucas Candido Gonçalves Barbosa, Thais Reis Oliveira, Fernando Santos Lima, Viviane Monteiro Goes, Mariely Cordeiro Estrela, Priscila Zanette de Souza, Mônica de Oliveira Santos, Guilherme Rocha Lino de Souza, José Daniel Gonçalves Vieira, and et al. 2023. "Prevalence of Enterovirus in Water Consumed in Rural Areas in a State in the Midwest Region of Brazil" Sustainability 15, no. 13: 9886. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15139886
APA StyleBordoni, G. P., Barbosa, L. C. G., Oliveira, T. R., Lima, F. S., Goes, V. M., Estrela, M. C., de Souza, P. Z., de Oliveira Santos, M., de Souza, G. R. L., Vieira, J. D. G., Scalize, P. S., & Carneiro, L. C. (2023). Prevalence of Enterovirus in Water Consumed in Rural Areas in a State in the Midwest Region of Brazil. Sustainability, 15(13), 9886. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15139886








