Investigating the Steady-State Rheological Properties of Activated Sewage Sludge for Effective Post-Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Sludge Samples
2.2. Determination of Sludge Particle Size and Shape
2.3. Steady-State Rheological Test
2.4. Rheological Model Simulation
- τ—shear stress (mPa);
- τ0—the yield stress (mPa);
- ηp—the plastic viscosity (mPa·s);
- —the shear rate (s−1);
- —the rheological index.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Typical Rheological Properties of Sludge
3.2. The Effect of Concentration on the Rheological Properties of Sludge
3.3. The Effects of Temperature on the Rheological Properties of Sludge
3.4. Sludge Rheological Model
3.5. Case Study for Effective Post-Treatment
- (1)
- Calculate the Reynolds number of the flow using the limiting viscosity obtained in the experiment with Equation (2):where:
- Re—Reynolds number;
- —velocity of flow (m/s);
- —pipe diameter (m);
- —kinematic viscosity coefficient, that is, the ratio of limiting viscosity to sludge density.
- (2)
- Use the Muddy diagram to obtain the friction coefficient combined with the relative roughness coefficient () of the pipe and Re:where:
- —friction coefficient;
- —relative roughness coefficient.
- (3)
- Calculate the frictional head loss using the Darcy–Weisbach formula:where:
- —frictional head loss, m;
- —pipeline length, m;
- —acceleration of gravity, m/s2.
- (4)
- Determine the pump power N:where:
- N—power of delivery pump, kW;
- H—pump lift, m;
- ρ—density of sludge, kg/m3;
- η—efficiency of delivery pump, %;
- HST—static lift of delivery pump, m.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hämäläinen, A.; Kokko, M.; Chatterjee, P.; Kinnunen, V.; Rintala, J. The effects of digestate pyrolysis liquid on the thermophilic anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge—Perspective for a centralized biogas plant using thermal hydrolysis pretreatment. Waste Manag. 2022, 147, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, T.T.; Zhang, L.J.; Chen, S.S.; Dai, X.H.; Dong, B. A novel application of dissolved ozone flotation on sewage sludge thickening: Performance and mechanism investigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Q.; Xu, S.Q.; Zhao, K.; Song, G.; Zhao, S.N.; Liu, R.P. Risk control of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) and antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB) during sewage sludge treatment and disposal: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogwueleka, T.C.; Ofeoshi, C.I.; Ubah, J.I. Application of bio-drying technique for effect-ive moisture reduction and disposal of sewage sludge in the framework of water-energy nexus. Energy Nexus 2021, 4, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farno, E.; Lester, D.R.; Eshtiaghi, N. Constitutive modelling and pipeline flow of thixo-tropic viscoplastic wastewater sludge. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marufuzzaman, M.; Ekşioğlu, S.D.; Hernandez, R. Truck versus pipeline transportation cost analysis of wastewater sludge. Transport. Res. A-Pol. 2015, 74, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Duan, Y.F.; Li, H.F. Wall slip and rheological behavior of petroleum-coke sludge slurries flowing in pipelines. Powder Technol. 2012, 230, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.W. Pipeline transportation for sludge in city’s waste water treatment plant. Metal Mine Des. Const. 2000, 32, 32–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guibaud, G.; Dollet, P.; Tixier, N.; Dagot, C.; Baudu, M. Characterisation of the evo-lution of activated sludges using rheological measurements. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 1803–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, Z.C.; Ao, H.J. Experimental deduction of the relationship between sludge viscidity, concentration and temperature. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2006, 7, 72–73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.X. Study on Rheological Properties of Anaerobic Digestion Sludge of Food Wastes. Ph.D. Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2014. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.Q. Study of rheological properties of sludge in oxidation ponds. China N. Technol. Prod. 2010, 4, 18–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, G.M.; Zhuang, D.Y.; Ma, X.M.; Wu, M. Rheological characteristics experiment of paper sludge. Environ. Eng. 2008, 26, 245–248. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.H. Research and Analysis on Physical and Chemical Properties of Oily Sludge. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2014. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Wang, Y.L.; Dong, Y.D. Effect of solid contents on the controlled shear stress rheological properties of different types of sludge. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1917–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.K.; Wu, J.; Poncin, S.; Li, H.Z. Rheological characteristics of highly concentrated anaerobic digested sludge. Biochem. Eng. J. 2014, 86, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippa, L. Modeling the effect of sediment concentration on the flow-like behavior of natural debris flow. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2020, 35, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippa, L. Yield Stress Model for Natural Debris Flows in Presence of Fine and Coarse–Grained Sediments. Water 2021, 13, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippa, L.; Doghieri, F.; Pellegrino, A.M.; Pavesi, E. Thixotropic Behavior of Reconstituted Debris-Flow Mixture. Water 2021, 13, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Xu, J.R. Investigation on Rheological Properties of Flocculated Sludge Suspension. Fluid Mach. 2007, 35, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.D.; Li, X.G.; Jin, D.L.; Yang, Y.; Fang, Y.R.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Ye, Y.G. A new pressure gradient model of slurry shield pipeline system coupling with rheological properties and wall slip behaviour under sandy stratum. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 134, 105024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Li, Y.L.; Yang, R.S.; Xu, B.; Lu, B. Rheological behavior with time dependence and fresh slurry liquidity of cemented aeolian sand backfill based on response surface method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 371, 130768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.R.; Ding, W.T.; Zhu, Z.J.; Liu, R.T.; Wang, C.Z.; Yu, W.D.; Wang, Z.C. Experimental study on rheological behaviors of Na-bentonite slurries under seawater intrusion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 357, 129369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Yin, D.S.; Gao, Y.F.; Ren, J.T. Concentration dependence of yield stress, thixotropy, and viscoelasticity rheological behavior of lithium-ion battery slurry. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 19073–19080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.J.; Wang, Y.L. Steady rheological characteristics of the concentrated water treatment residuals (CWTR). Acta Sci. Circum. 2012, 32, 678–682. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, M.; Nakamura, H. Influence of molecular weight and concentration of carboxymethyl cellulose on rheological properties of concentrated anode slurries for lithium-ion batteries. JCIS Open 2022, 6, 100048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Mohapatra, R.K.; Belbsir, H.; Routray, A.; Parhi, P.K.; El-Hami, K. Combined effect of natural dispersant and a stabilizer in formulation of high concentration coal water slurry: Experimental and rheological modeling. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 320, 114441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.F.; Zhu, M.M.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Leong, Y.K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.K. Rheological behaviour and stability characteristics of biochar-water slurry fuels: Effect of biochar particle size and size distribution. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 156, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, D.R.; Sato, K.; Toyota, T.; Funatsu, K.; Tomita, Y. Effect of particle size distribution on pressure drop and concentration profile in pipeline flow of highly concentrated slurry. Int. J. Multiphas. Flow. 2005, 31, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.J.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Wei, C.F.; Li, P.C. Ionic strength and temperature dependence of rheological behavior of deep-water sedimental slurries. Ocean Eng. 2022, 265, 112655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudez, J.C.; Slatter, P.; Eshtiaghi, N. The impact of temperature on the rheological behaviour of anaerobic digested sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroutian, S.; Eshtiaghi, N.; Gapes, D.J. Rheology of a primary and secondary sewage sludge mixture: Dependency on temperature and solid concentration. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 140, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Luo, M.; Lu, H.X.; Hu, X.G.; Zhu, Q. Rheological modeling and simulation of semi-solid slurry based on experimental study. Scripta Mater. 2022, 220, 114932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





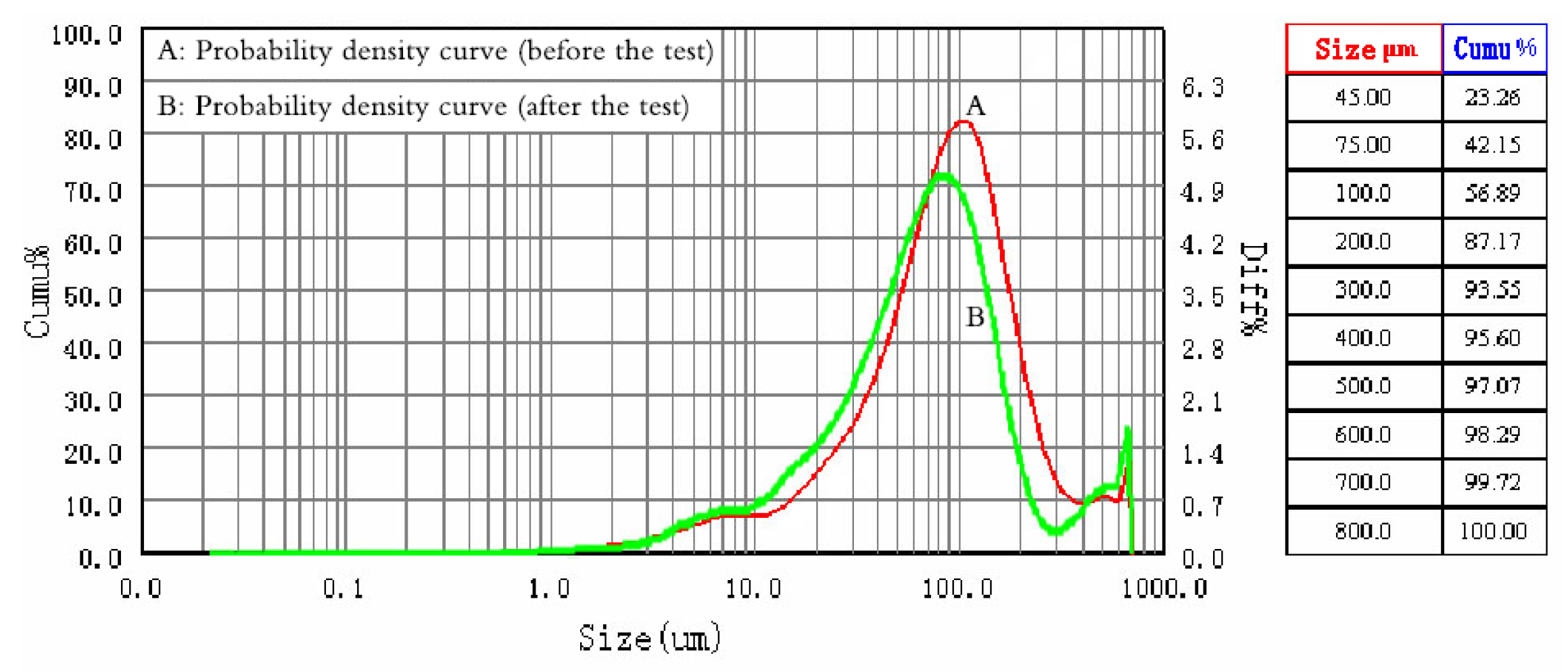
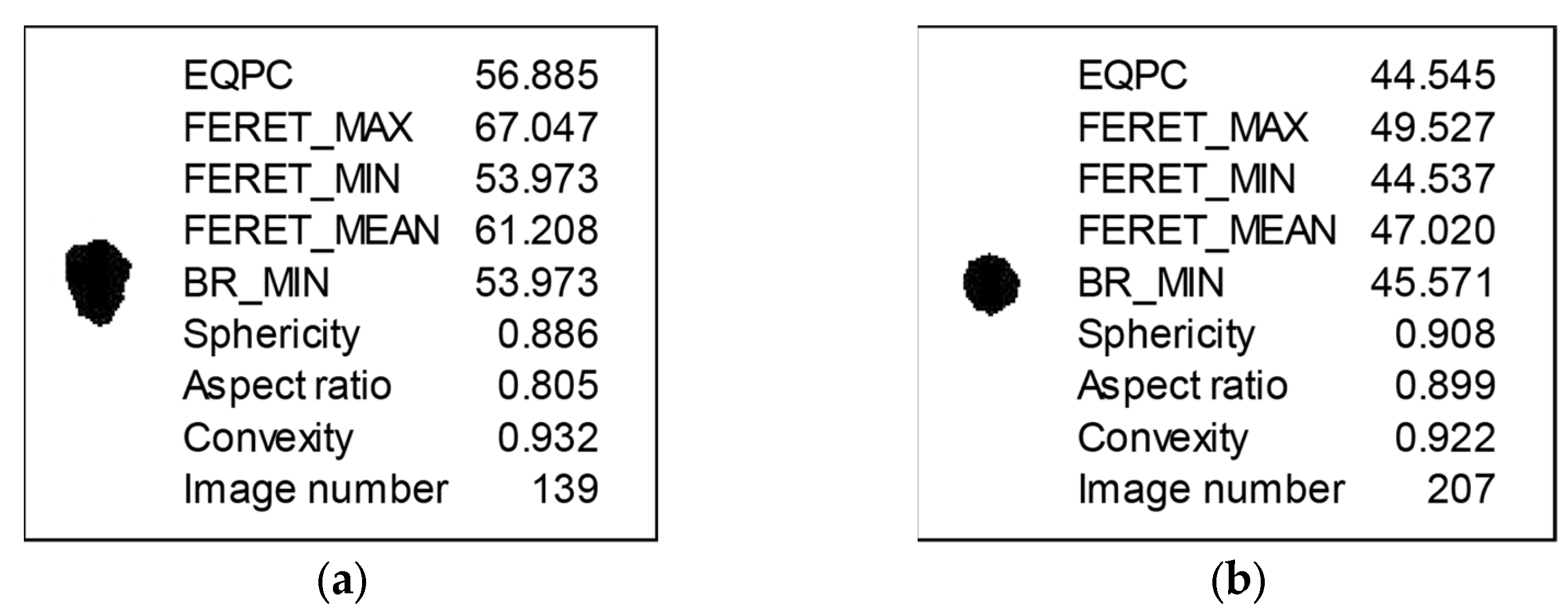

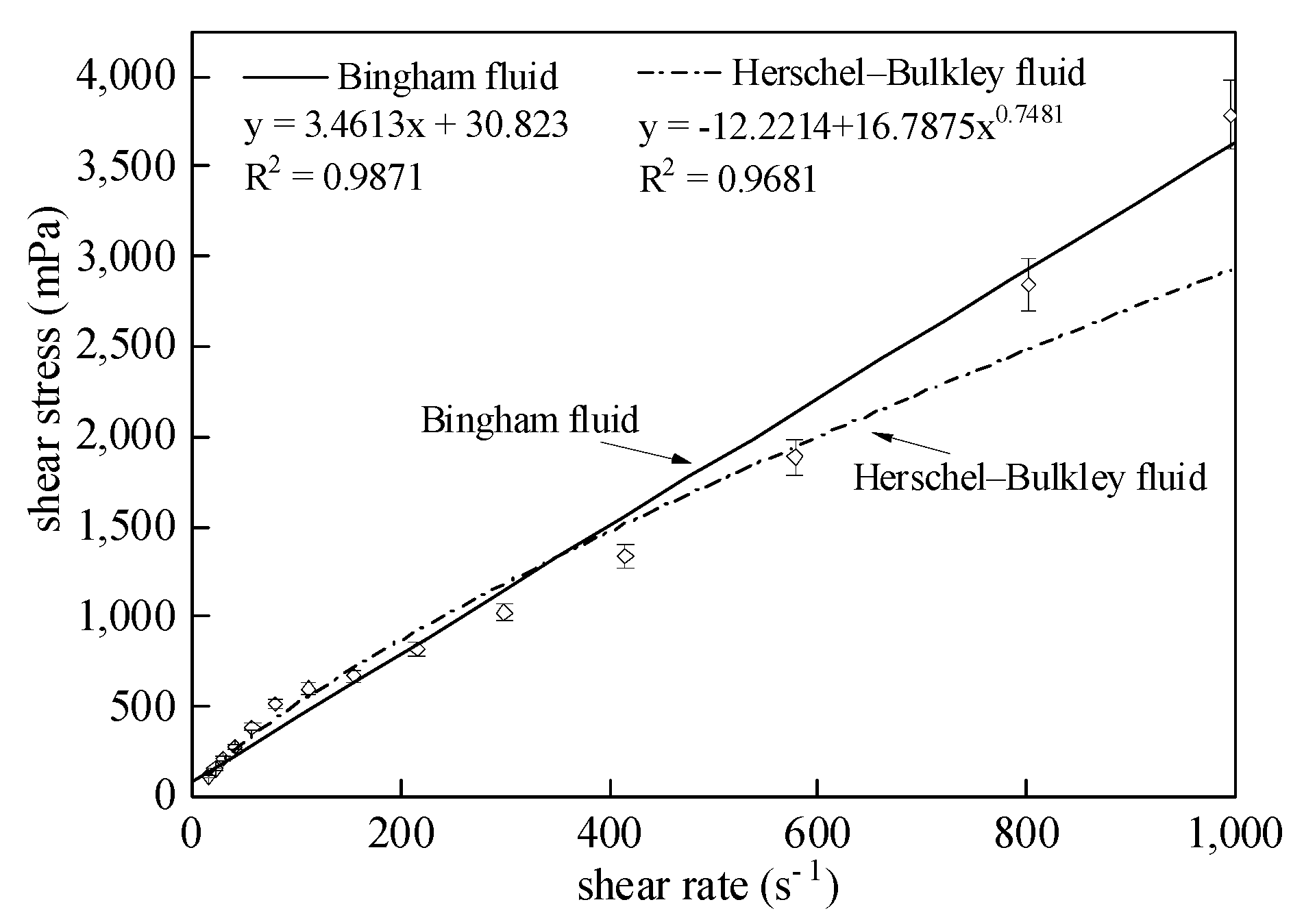
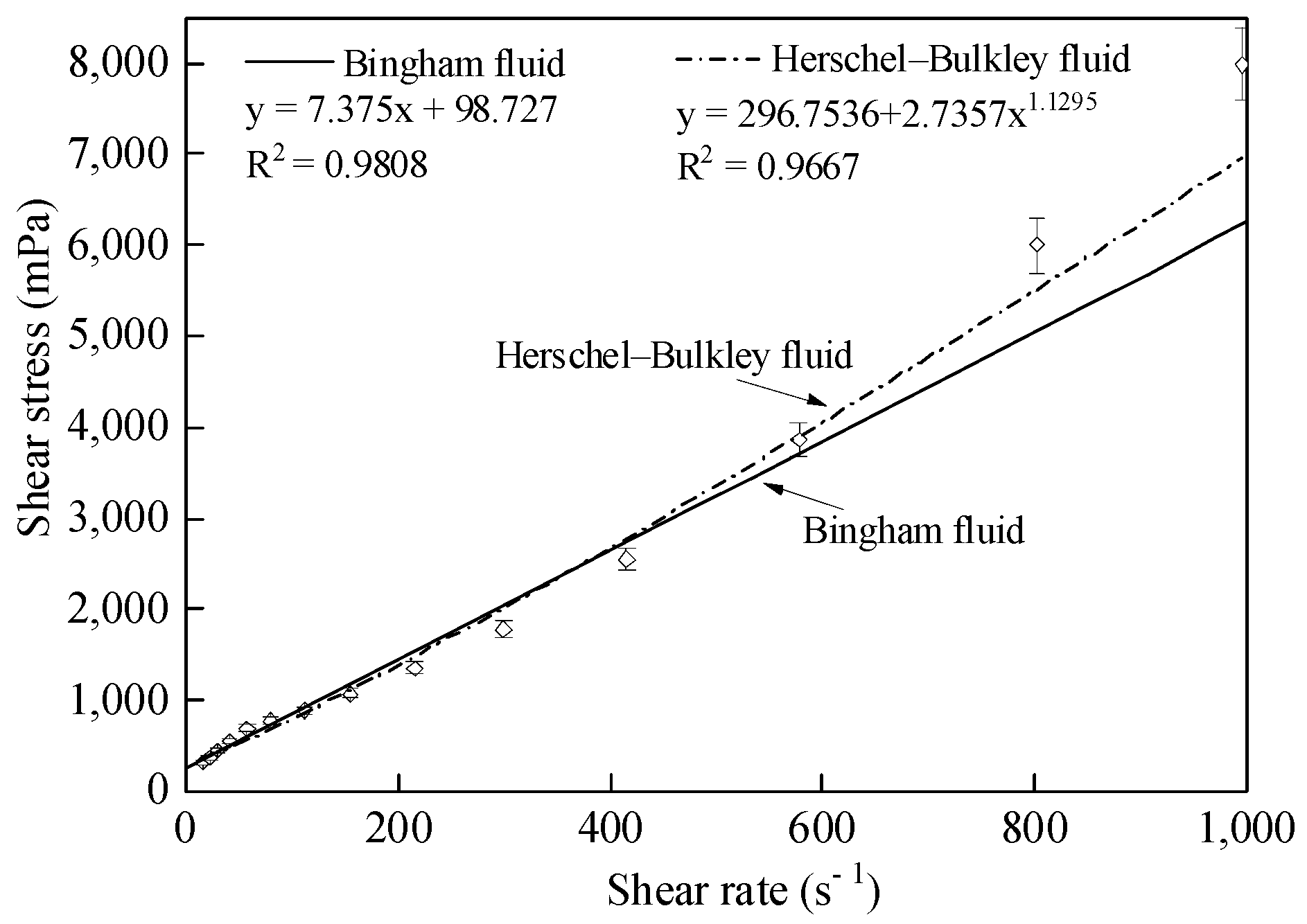
| Serial Number | Moisture Content (%) | CW (%) | Density (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 97.62 | 2.38 | 1005.26 |
| 2 | 96.06 | 3.94 | 1009.05 |
| 3 | 94.61 | 5.39 | 1014.96 |
| Shear Rate (s−1) | Temperature | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 293 K | 298 K | 303 K | ||||
| Shear Stress (Pa) | Viscosity (Pa·s) | Shear Stress (Pa) | Viscosity (Pa·s) | Shear Stress (Pa) | Viscosity (Pa·s) | |
| 15.5009 | 0.14362 | 0.00926 | 0.1356 | 0.00875 | 0.09587 | 0.00618 |
| 19.2330 | 0.16653 | 0.00866 | 0.1608 | 0.00836 | 0.12303 | 0.0064 |
| 26.7254 | 0.21378 | 0.008 | 0.19496 | 0.00729 | 0.1705 | 0.00638 |
| 37.1364 | 0.26573 | 0.00716 | 0.24001 | 0.00646 | 0.22361 | 0.00602 |
| 51.6009 | 0.3278 | 0.00635 | 0.29581 | 0.00573 | 0.27112 | 0.00525 |
| 71.6997 | 0.38507 | 0.00537 | 0.36755 | 0.00513 | 0.30855 | 0.0043 |
| 99.6266 | 0.45399 | 0.00456 | 0.43603 | 0.00438 | 0.34095 | 0.00342 |
| 138.426 | 0.53565 | 0.00387 | 0.49387 | 0.00357 | 0.39709 | 0.00287 |
| 192.333 | 0.62979 | 0.00327 | 0.5623 | 0.00292 | 0.49716 | 0.00258 |
| 267.233 | 0.75763 | 0.00283 | 0.68807 | 0.00257 | 0.66374 | 0.00248 |
| 371.334 | 0.9528 | 0.00257 | 0.94998 | 0.00256 | 0.89543 | 0.00241 |
| 516.003 | 1.4622 | 0.00283 | 1.25161 | 0.00243 | 1.23022 | 0.00238 |
| 716.984 | 2.33272 | 0.00325 | 1.87687 | 0.00262 | 1.73887 | 0.00243 |
| 996.296 | 3.76797 | 0.00378 | 2.95372 | 0.00296 | 2.46221 | 0.00247 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Deng, H.; Yan, B. Investigating the Steady-State Rheological Properties of Activated Sewage Sludge for Effective Post-Treatment. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9948. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15139948
Lu H, Li Q, Chen X, Deng H, Yan B. Investigating the Steady-State Rheological Properties of Activated Sewage Sludge for Effective Post-Treatment. Sustainability. 2023; 15(13):9948. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15139948
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Hai, Qingpo Li, Xinglin Chen, Huan Deng, and Bojiao Yan. 2023. "Investigating the Steady-State Rheological Properties of Activated Sewage Sludge for Effective Post-Treatment" Sustainability 15, no. 13: 9948. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15139948
APA StyleLu, H., Li, Q., Chen, X., Deng, H., & Yan, B. (2023). Investigating the Steady-State Rheological Properties of Activated Sewage Sludge for Effective Post-Treatment. Sustainability, 15(13), 9948. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15139948








